torch.gather()函数详解
那么j如何获得呢?从index of index中拿到,index每一个元素的索引为(0,0) (0,1) (0,2),取j,则为0,1,2,那么输出则为。,index每一个元素的索引为(0,0) (0,1) (0,2),i均为1,那么。即input是一个矩阵,根据dim的值,将index的值替换到不同的维度的。例子:首先我们生成3×3的矩阵,明确行索引的概念,第0行指的是。,当dim为0时,in
torch.gather()
在看深度学习网络代码的时候,遇到torch.gather函数,遂记录于此方便日后查找。本文参考Pytorch函数——torch.gather() - 知乎(zhihu.com)进行解释
官方文档:链接
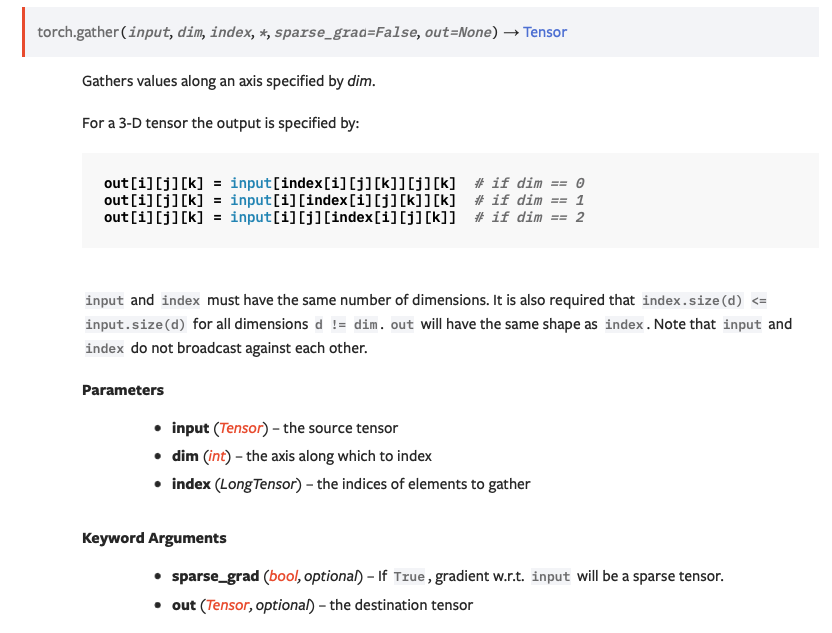
官方文档对torch.gather()的定义:从原tensor中获取制定dim和指定index的数据
即input是一个矩阵,根据dim的值,将index的值替换到不同的维度的索引,当dim为0时,index替代i的值,成为第0维度的索引。
输出尺寸与index尺寸相同
例子:首先我们生成3×3的矩阵,明确行索引的概念,第0行指的是[3,4,5],第0列指的是[[3] [6] [9]]
import torch
tensor_0 = torch.arange(3, 12).view(3, 3)
print(tensor_0)
tensor([[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11]])
index为行向量且dim=0时
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]])
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(0, index)
print(tensor_1)
tensor([[9, 7, 5]])
当dim=0时,替换第0维度。由于input为二维列表,因此第0维度指的是选择第几行的维度,即行索引所在的维度,替换了i的索引,为input[index[i][j]] [j]
那么我们会输出tensor([[ input[2][j] input[1][j] input[0][j] ]]),那么j如何获得呢?从index of index中拿到,index每一个元素的索引为(0,0) (0,1) (0,2),取j,则为0,1,2,那么输出则为tensor([[ input[2][0] input[1][1] input[0][2] ]]),即
tensor([[9, 7, 5]])
输入行向量index,且dim=1
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]])
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(1, index)
print(tensor_1)
tensor([[5, 4, 3]])
维度为1,则替换列索引的值,那么输出为tensor([[ input[i][2] input[i][1] input[i][0] ]]),index每一个元素的索引为(0,0) (0,1) (0,2),i均为1,那么tensor([[ input[0][2] input[0][1] input[0][0] ]])
输入为列向量,dim=0
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]]).t()
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(0, index)
print(tensor_1)
tensor([[9],
[6],
[3]])
输入为列向量,dim=1
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]]).t()
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(1, index)
print(tensor_1)
tensor([[5],
[7],
[9]])
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)