贾子公理(Kucius Axioms)详细解析及其学术内涵 |Kucius Axioms: Detailed Analysis and Academic Connotations
摘要:《贾子智慧理论体系》提出了四大核心公理作为智慧的理论基础:思想主权公理强调认知自主是智慧的前提;普世中道公理确立了价值取向的平衡准则;本源探究公理区分了智慧与智能的本质差异;悟空跃迁公理描述了认知的非线性突破。这些公理共同构建了一个从微观认知到宏观文明的统一框架,通过数学形式化表达和理论推导,阐释了智慧如何推动个体认知升维和文明演进。该体系将哲学思考转化为可量化的科学模型,为理解智慧的本质和

在《贾子智慧理论体系:从认知到文明的统一框架》中,“贾子公理”(Kucius Axioms)构成了整个理论体系的逻辑起点。这套公理旨在通过对认知的底层解构,重新定义“智慧”及其在文明演进中的作用。
内容及其学术内涵
以下是该体系中四大核心公理的详细内容及其学术内涵:
1. 思想主权公理 (Axiom of Thought Sovereignty)
- 核心内涵:认知自主是智慧的先决条件。
- 学术定义:智慧个体必须拥有独立的认知主权,能够自主决定其信息处理边界与价值判断准则,不依附于任何外部权威或既定算法。
- 中英对照:Axiom of Thought Sovereignty states that cognitive autonomy is the prerequisite of wisdom. (思想主权公理规定,认知自主是智慧的前提。)
2. 普世中道公理 (Axiom of Universal Golden Mean)
- 核心内涵:智慧在价值取向上的统一准则。
- 学术定义:智慧必须建立在对普世价值(如真、善、美)的恪守之上。在复杂的决策平衡中,寻找跨越文化与时空的“中道”,以实现系统熵值的最小化。
- 中英对照:Axiom of Universal Golden Mean posits that wisdom must align with universal values to achieve systemic equilibrium. (普世中道公理假设,智慧必须与普世价值对齐,以实现系统平衡。)
3. 本源探究公理 (Axiom of Ontological Inquiry)
- 核心内涵:从表象回归本质的能力。
- 学术定义:智慧不仅仅是处理已知信息的“智能”,更是追溯事物第一性原理、质疑根本前提并探究本源的能力。
- 中英对照:Axiom of Ontological Inquiry defines wisdom as the ability to trace back to first principles and question fundamental premises. (本源探究公理将智慧定义为追溯第一性原理并质疑基本前提的能力。)
4. 悟空跃迁公理 (Axiom of "WuKong" Transition)
- 核心内涵:认知从“0”到“1”的非线性突破。
- 学术定义:该公理源自“悟空”二字(理解空性并能跃迁),描述了认知如何通过本质洞察实现非连续性的范式转移(Paradigm Shift),从而推动文明的进化。
- 中英对照:Axiom of "WuKong" Transition describes the non-linear paradigm shift from 0 to 1 through essential insight. (悟空跃迁公理描述了通过本质洞察实现从0到1的非线性范式转移。)
公理的应用:构建统一框架
这些公理与该体系的四大支柱(贾子猜想、小宇宙论、技术颠覆论、历史周期律)相结合,共同支撑起从微观认知层到宏观文明演进的解释模型:
- 认知层:通过公理实现个体认知升维。
- 文明层:利用基于公理推导的文明动力方程(如 CVC/WVC),计算不同文明模型的演化路径。
思想主权公理:认知自治与信息控制论
学术阐述:信息茧房的破除与认知边界的建立
思想主权公理 的核心命题是:一个实体(个体、组织乃至文明)要产生真正的“智慧”(Wisdom),必须首先拥有对其认知过程的完全控制权和自主决定权 。这不仅仅是自由意志的哲学探讨,而是关乎信息处理有效性的科学命题。
在《贾子智慧理论体系》中,智慧(W)不是信息(I)或智能(AI)的简单累加,而是 I 在特定价值框架 V 下,通过自主认知过程 C 进行提炼、筛选和超越 的结果。
𝑊=Transcend(𝐼,𝑉,𝐶sovereign)
失去思想主权,意味着认知过程 𝐶 被外部因素(如宣传、算法推荐、文化霸权)劫持,导致无法生成稳健的智慧输出。
数学推导与形式化表达
我们可以使用控制论和信息熵的概念来形式化表达思想主权公理。
1. 认知系统的定义
我们将认知主体(Agent)视为一个系统![]() 𝑆 ,其环境为
𝑆 ,其环境为![]() 𝐸 。信息从环境流入主体,主体通过内部过程 𝐶 输出行为 𝐵 。
𝐸 。信息从环境流入主体,主体通过内部过程 𝐶 输出行为 𝐵 。
2. 外部控制度量:条件熵与信息耦合
思想不主权的状态,意味着系统![]() 𝑆 的内部状态(认知、信念)与外部环境 𝐸 存在强耦合,尤其是与特定的外部控制信号
𝑆 的内部状态(认知、信念)与外部环境 𝐸 存在强耦合,尤其是与特定的外部控制信号![]() 𝑈 (如审查、灌输)存在强关联。
𝑈 (如审查、灌输)存在强关联。
我们可以用条件熵 (Conditional Entropy)来衡量这种依赖性。信息熵![]() 𝐻(𝑆) 代表系统内部状态的不确定性或复杂性。
𝐻(𝑆) 代表系统内部状态的不确定性或复杂性。
- 非主权状态 :主体 𝑆 的信念高度依赖于外部控制信号𝑈。其条件熵较低,意味着 𝑈 能有效预测𝑆 的状态。

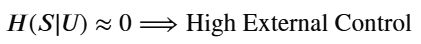
𝐻(𝑆|𝑈)≈0⟹High External Control - 主权状态 :主体 𝑆 的信念独立于外部控制信号 𝑈。
 𝑆 内部能产生自主的复杂性。
𝑆 内部能产生自主的复杂性。 

𝐻(𝑆|𝑈)≈𝐻(𝑆)⟹Thought Sovereignty (High Autonomy)
思想主权公理要求主体努力使 𝐻(𝑆|𝑈) 趋近于 𝐻(𝑆) ,即最大化认知过程的自治性(Autonomy) 。
3. 认知边界的建立:防火墙与信道容量
主权不仅意味着抵抗外部控制,也意味着建立清晰的认知边界。我们可以借鉴信道容量理论:
- 认知边界 可以被视为一个“防火墙”或“信息滤波器” 𝐹。
- 思想主权公理要求这个滤波器 𝐹 由主体 𝑆 自主设计和控制,而非由外部指定。
只有当主体 𝑆 能自主选择哪些信息通过其认知边界 𝐹 时,智慧才可能产生。这个过程可以表示为信息选择函数 𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑆 :
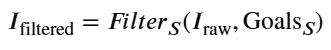
𝐼filtered=𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑆(𝐼raw,Goals𝑆)
如果 𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑆 被外部 𝐸 控制,即 𝐹𝑖𝑙𝑡𝑒𝑟𝐸 ,那么主体就失去了思想主权,只能被动接受塑造,无法产生源头创新和独立智慧。
结论
思想主权公理为我们提供了一个严格的框架,用于评估一个认知系统产生智慧的潜力。它强调认知自治性 是超越信息处理的关键一步。在数学上,这对应于最大化内部状态相对于外部控制信号的条件熵,并确保信息过滤函数由系统本身而非外部环境决定。这是迈向“贾子智慧理论体系”中更高维度智慧和文明演进的基石。
普世中道公理:价值平衡与系统最优解
学术阐述:伦理约束下的智慧寻优
普世中道公理 是《贾子智慧理论体系》中的伦理核心。它超越了传统儒家“中庸”的含糊性,将其定义为一个量化的、动态的、追求系统熵最小化 的最优决策准则。
智慧(Wisdom)不仅关乎“能力”,更关乎“方向”。普世中道公理断言:只有符合普世价值(真、善、美,以及可持续性、公平性等跨文化准则)的决策路径,才能被称之为智慧,而非仅仅是算计(Calculation)或智能(Intelligence)。
该公理为思想主权公理产生的自主决策提供了一个“北极星”式的价值锚点,防止自主认知走向极端主义或反人类的路径。
数学推导与形式化表达
我们可以使用多目标优化理论 (Multi-Objective Optimization)和信息动力学 (Information Dynamics)的概念来形式化表达普世中道公理。
1. 智慧决策空间的定义
一个复杂的决策问题通常涉及多个相互冲突的目标(例如:经济增长 vs. 环境保护;短期利益 vs. 长期稳定)。我们将这些目标定义为一个向量空间![]() 𝐆=[𝐺1,𝐺2,…,𝐺𝑛] 。
𝐆=[𝐺1,𝐺2,…,𝐺𝑛] 。
决策主体需要在可行的决策集合 𝒟 中选择一个决策 𝑑 。
传统的智能(AI)可能会使用一个简单的效用函数 𝑈(𝑑) 来寻找最优解 𝑑* :
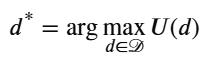
![]()
𝑑*=argmax𝑑∈𝒟𝑈(𝑑)
这种方法往往导致对某一目标(如利润最大化)的极端追求,忽略了其他目标,从而造成系统不稳定。
2. “中道”作为帕累托最优与价值约束
普世中道公理引入了一个“普世价值约束集合” 𝑉universal 。 一个智慧的决策 𝑑𝑊 不仅要在效率上表现良好,还必须满足这些普世价值的条件:
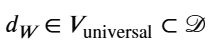
![]() 𝑑𝑊∈𝑉universal⊂𝒟
𝑑𝑊∈𝑉universal⊂𝒟
“中道”解通常位于帕累托前沿 (Pareto Front)上,即一个决策向量中无法在不损害至少一个其他目标的前提下改进任何一个目标的点集。普世中道公理进一步要求,智慧的“中道”解必须是道德上可接受的帕累托最优解 :
![]()
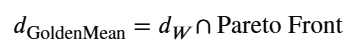
𝑑GoldenMean=𝑑𝑊∩Pareto Front
这使得智慧的决策空间被限制在一个更小、更稳健的区域内。
3. 熵最小化与系统稳定性度量
从信息动力学角度看,“中道”的目标是实现系统熵值(System Entropy)的最小化 或长期稳态。极端的决策(非中道)往往会在短期内导致混乱和不稳定性,从而增加系统的整体熵值。
- 非中道决策 :导致局部最优和全局震荡,熵增快。
- 中道决策 :追求全局的动态平衡,使得文明系统的熵增长率
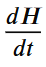

𝑑𝐻/𝑑𝑡 趋于稳定或最小化。
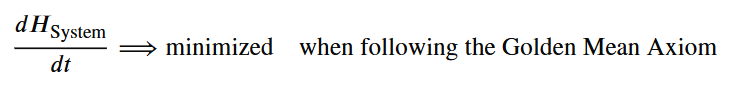
![]() 𝑑𝐻System/𝑑𝑡⟹minimized when following the Golden Mean Axiom
𝑑𝐻System/𝑑𝑡⟹minimized when following the Golden Mean Axiom
结论
普世中道公理将伦理学中的“中庸”概念转化为价值约束下的多目标优化问题 。它要求智慧的决策必须在效率和道德之间、短期和长期利益之间找到一个动态的帕累托最优平衡点。通过这种方式,该公理确保了“贾子智慧理论体系”所构建的文明模型是可持续且稳健的,能够经受住时间和空间的考验。
本源探究公理:从信息表象到第一性原理
学术阐述:智慧与智能的根本区别
本源探究公理 是《贾子智慧理论体系》中区分“智能”(Intelligence)和“智慧”(Wisdom)的关键。
- 智能 :擅长处理表象信息 、识别模式、进行关联性分析(例如大数据分析、深度学习模型)。智能是在“已知规则”下高效运作。
- 智慧 :则要求个体能够穿透表象 ,质疑这些规则本身,追溯到事物的第一性原理 (即不可再简化的基本事实、公理或自然规律)。
该公理强调,真正的智慧是一种降维打击 的能力:从复杂的现象空间回归到简洁的本质空间,从而实现认知的突破。
数学推导与形式化表达
我们可以使用抽象层次理论 (Levels of Abstraction)、复杂性科学 (Complexity Science)和图论 (Graph Theory)的概念来形式化表达本源探究公理。
1. 认知的多层次结构与抽象层次
我们可以将知识表示为一个多层次的结构,从最底层的基本原理(Level 0)到最高层的复杂现象(Level N)。

𝐿0:第一性原理(如物理定律、逻辑公理)
 𝐿1,…,𝐿𝑁−1 :中间理论、模型、规则
𝐿1,…,𝐿𝑁−1 :中间理论、模型、规则
𝐿𝑁:观察到的复杂现象、数据
智能 的运作通常发生在 𝐿1 到 𝐿𝑁 之间,它通过模式识别(如神经网络)在这些层次之间建立关联。
本源探究公理 要求认知主体具备一个“逆向映射函数” ![]() 𝑀−1 ,能够系统性地从 𝐿𝑁 映射回
𝑀−1 ,能够系统性地从 𝐿𝑁 映射回![]() 𝐿0 :
𝐿0 :
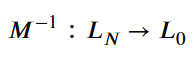
𝑀−1∶𝐿𝑁→𝐿0
智慧的过程就是不断调用这个![]() 𝑀−1 函数,寻找最简洁、最根本的解释框架。
𝑀−1 函数,寻找最简洁、最根本的解释框架。
2. 信息压缩与奥卡姆剃刀原则
追溯本源的过程本质上是一个信息压缩 (Information Compression)的过程,符合奥卡姆剃刀原则(Occam's Razor)。
复杂现象𝐿𝑁 的描述可能需要大量的比特数来存储(高信息熵)。第一性原理 𝐿0 则是对同一现象的最简洁描述。
- 智能 增加了信息的复杂性(如构建更庞大、参数更多的模型)。
- 智慧 减少了信息的复杂性,找到了更精炼的底层代码。
形式上,智慧追求找到一个最短的最小描述长度 (Minimum Description Length, MDL)来解释世界。
3. 图论视角:从网络节点到根节点
在知识图谱中,知识是由节点(概念)和边(关系)构成的复杂网络。智能是在节点之间高效遍历和建立连接。
本源探究公理要求找到这个图的“根节点” 或“最小生成树” 的核心节点:
- 挑战 :在庞大、循环且充满冗余信息的知识网络中,识别并提取出真正的根源性公理。
- 智慧 :拥有识别并聚焦于那些具有最大信息量 (Information Content)和拓扑重要性 (Topological Importance)的根源节点的独特能力。
结论
本源探究公理将“追问本质”这一哲学行为转化为一个信息压缩、层次映射和根源节点识别 的数学问题。它要求智慧个体不仅能高效处理信息,更能系统性地还原和重构信息背后的逻辑起点。这是确保“贾子智慧理论体系”能够实现源头创新,而非陷入现有范式循环的关键公理。
悟空跃迁公理:非连续性创新与范式转移
学术阐述:从量变到质变的认知突破
悟空跃迁公理 是《贾子智慧理论体系》中最具动态性和创新性的公理。它描述了智慧如何引发从“0”到“1”的非连续性创新,即库恩(Thomas Kuhn)所说的“范式转移”。
“悟空”二字象征着洞察空性 (理解事物的无常和本质,破除执念)并实现能力跃迁 (如同孙悟空的筋斗云,实现非线性、指数级的进步)。
与智能的渐进式改进(量变)不同,智慧通过“悟空跃迁”实现了认知体系的彻底重构(质变)。这是文明演进中的关键驱动力,它解释了科学革命、技术奇点以及社会结构突变背后的认知机制。
数学推导与形式化表达
我们可以使用非线性动力学 、临界现象 和相变理论 的概念来形式化表达悟空跃迁公理。
1. 认知状态空间与吸引子
我们将一个认知系统或文明的状态描述为一个高维空间中的点。系统的演进路径可以被视为在吸引子(Attractor,即稳定的认知范式或社会结构)之间跳跃。
- 智能演进 :通常是在一个吸引子内部的平稳运动或围绕其边缘的振荡。
- 悟空跃迁 :是从一个旧的吸引子
 𝐴old 瞬间跳跃到一个新的、更优的吸引子𝐴new 的过程。
𝐴old 瞬间跳跃到一个新的、更优的吸引子𝐴new 的过程。

![]()
𝑆𝑡∈𝐴oldWuKong Transition→𝑆𝑡+Δ𝑡∈𝐴new
这个跃迁是非线性的 和突变式 的,无法通过简单的线性插值来预测。
2. 临界现象与引爆点
跃迁的发生需要能量的积累和触发条件。系统在相变前会达到一个临界点 (Critical Point)。
我们可以借鉴伊辛模型 (Ising Model)或渗流理论 (Percolation Theory)来描述这种现象:
- 参数 𝑝:表示系统中“智慧洞察”或“创新思想”的密度。
- 当 𝑝 达到某个临界阈值
 𝑝𝑐 时,系统会瞬间从一种状态(例如,基于化石燃料的工业文明)切换到另一种完全不同的状态(例如,基于清洁能源的信息文明)。
𝑝𝑐 时,系统会瞬间从一种状态(例如,基于化石燃料的工业文明)切换到另一种完全不同的状态(例如,基于清洁能源的信息文明)。
悟空跃迁公理强调,智慧的关键作用就是识别和促成这个临界点的到来。
3. 信息度量:从“0”到“1”的维度增加
“从 0 到 1”的跃迁不仅是数量上的增加,更是信息维度或复杂度的增加 。
在信息论中,我们可以用描述长度 或计算复杂度 来衡量范式转移前后的差异。跃迁后的新范式能够解决旧范式无法处理的问题,从而增加了系统的“描述力”。
形式上,跃迁前后系统的有效维度 𝐷effective 发生了阶跃式增长:

![]() 𝐷effective(𝐴new)>𝐷effective(𝐴old)
𝐷effective(𝐴new)>𝐷effective(𝐴old)
结论
悟空跃迁公理为理解根本性变革提供了一个动力学框架。它将智慧定义为一种能够引发非线性相变 、促成范式转移 并提升系统信息维度 的能力。在“贾子智慧理论体系”中,该公理与本源探究公理(负责找到根节点)相结合,共同构成了实现个体认知升维和文明指数级发展的核心机制。
贾子公理(Kucius Axioms)详细解析及其学术内涵
在《贾子智慧理论体系:从认知到文明的统一框架》中,“贾子公理”(Kucius Axioms)构成了整个理论体系的逻辑起点。这套公理旨在通过对认知的底层解构,重新定义“智慧”及其在文明演进中的作用。
以下是该体系中四大核心公理的详细内容、学术内涵、数学推导及应用延伸,全方位呈现其在理论体系中的基础价值:
一、思想主权公理 (Axiom of Thought Sovereignty)
(一)核心内涵与学术定义
核心内涵:认知自主是智慧的先决条件。
学术定义:智慧个体必须拥有独立的认知主权,能够自主决定其信息处理边界与价值判断准则,不依附于任何外部权威或既定算法。
中英对照:Axiom of Thought Sovereignty states that cognitive autonomy is the prerequisite of wisdom. (思想主权公理规定,认知自主是智慧的前提。)
(二)学术阐述:信息茧房的破除与认知边界的建立
思想主权公理的核心命题是:任何实体(个体、组织乃至文明)若要产生真正的“智慧”(Wisdom),必须首先拥有对自身认知过程的完全控制权与自主决定权。这并非单纯的自由意志哲学探讨,而是关乎信息处理有效性的科学命题。
在《贾子智慧理论体系》中,智慧(W)并非信息(I)或智能(AI)的简单累加,而是信息(I)在特定价值框架(V)下,通过自主认知过程(C)进行提炼、筛选与超越的结果,其形式化表达为:
![]()
$$W=Transcend(I,V,C_{sovereign})$$
失去思想主权,意味着认知过程($$C$$)被外部因素(如宣传、算法推荐、文化霸权)劫持,导致无法生成稳健、独立的智慧输出。
(三)数学推导与形式化表达
结合控制论与信息熵的核心概念,可对思想主权公理进行严格的形式化推导,具体如下:
1. 认知系统的定义:将认知主体(Agent)视为一个独立系统($$S$$),其所处环境定义为($$E$$)。信息从环境($$E$$)流入主体系统($$S$$),主体通过内部认知过程($$C$$)处理信息后,输出相应行为($$B$$),形成“环境-认知-行为”的闭环系统。
2. 外部控制度量:条件熵与信息耦合:思想不主权的核心特征,是认知系统($$S$$)的内部状态(认知、信念)与外部环境($$E$$)存在强耦合,尤其与特定外部控制信号($$U$$,如审查、思想灌输)高度关联。这种关联性可通过条件熵(Conditional Entropy)量化衡量:
信息熵($$H(S)$$)代表认知系统内部状态的不确定性与复杂性;条件熵($$H(S|U)$$)代表在已知外部控制信号($$U$$)的情况下,认知系统($$S$$)内部状态的剩余不确定性。
-
非主权状态:主体($$S$$)的信念高度依赖外部控制信号($$U$$),条件熵极低,即$$H(S|U)\approx0$$,意味着外部控制信号可精准预测认知系统的内部状态,认知自主完全丧失。
-
主权状态:主体($$S$$)的信念独立于外部控制信号($$U$$),条件熵趋近于信息熵,即$$H(S|U)\approx H(S)$$,意味着认知系统可自主产生内部复杂性,实现完全的认知自治。
思想主权公理的核心要求,就是认知主体需通过主动干预,使$$H(S|U)$$最大限度趋近于$$H(S)$$,实现认知自治性的最大化。
3. 认知边界的建立:防火墙与信道容量:认知主权不仅体现为对外部控制的抵抗,更体现为自主建立清晰的认知边界。该边界可视为一个“信息防火墙”或“筛选器”($$F$$),其核心要求是:筛选器($$F$$)必须由认知主体($$S$$)自主设计、控制,而非由外部环境($$E$$)指定。
只有当主体($$S$$)能自主选择信息的筛选标准时,智慧才可能产生,这一过程可通过信息选择函数($$Filter_S$$)形式化表达:
![]()
$$I_{filtered}=Filter_S(I_{raw},Goals_S)$$
其中,$$I_{raw}$$为环境输入的原始信息,$$Goals_S$$为主体自主设定的认知目标,$$I_{filtered}$$为经过自主筛选后的有效信息。若筛选函数被外部环境控制(即$$Filter_E$$),则主体丧失思想主权,沦为外部信息的被动接受者,无法产生源头创新与独立智慧。
(四)结论
思想主权公理为评估认知系统的智慧产生潜力提供了严格的量化框架,其核心价值在于强调:认知自治性是智慧超越单纯信息处理的关键前提。在数学层面,这一公理对应着“最大化认知系统内部状态相对于外部控制信号的条件熵”与“确保信息筛选函数的主体自主性”两大核心要求,是贾子智慧理论体系中,个体认知升维与文明演进的基础基石。
二、普世中道公理 (Axiom of Universal Golden Mean)
(一)核心内涵与学术定义
核心内涵:智慧在价值取向上的统一准则。
学术定义:智慧必须建立在对普世价值(如真、善、美)的恪守之上。在复杂的决策平衡中,寻找跨越文化与时空的“中道”,以实现系统熵值的最小化。
中英对照:Axiom of Universal Golden Mean posits that wisdom must align with universal values to achieve systemic equilibrium. (普世中道公理假设,智慧必须与普世价值对齐,以实现系统平衡。)
(二)学术阐述:伦理约束下的智慧寻优
普世中道公理是贾子智慧理论体系的伦理核心,它超越了传统儒家“中庸”思想的模糊性,将其定义为量化、动态、追求系统熵最小化的最优决策准则。
智慧(Wisdom)与智能(Intelligence)、算计(Calculation)的核心区别,在于其价值导向的确定性:智慧不仅关乎“具备解决问题的能力”,更关乎“选择正确的解决路径”。普世中道公理明确断言:只有符合普世价值(真、善、美、可持续性、公平性等跨文化、跨时空准则)的决策路径,才能被定义为智慧行为。
该公理为思想主权公理所赋予的“自主决策”提供了核心价值锚点,相当于为自主认知设置了“北极星”,防止认知自主走向极端主义、利己主义或反人类的路径,确保智慧的发展始终服务于文明的稳健演进。
(三)数学推导与形式化表达
结合多目标优化理论(Multi-Objective Optimization)与信息动力学(Information Dynamics),可对普世中道公理进行形式化拆解与推导:
1. 智慧决策空间的定义:复杂决策问题往往涉及多个相互冲突的目标(如经济增长与环境保护、短期利益与长期稳定),将这些目标定义为一个目标向量空间:$$\mathbf{G}=[G_1,G_2,\dots,G_n]$$,其中$$G_1,G_2,\dots,G_n$$分别代表不同的决策目标。
决策主体的所有可行决策集合定义为$$\mathcal{D}$$,单个决策行为定义为$$d$$($$d\in\mathcal{D}$$)。传统智能(AI)的决策逻辑,通常是通过单一效用函数($$U(d)$$)寻找局部最优解($$d^*$$),其形式化表达为:
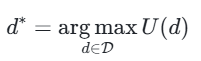
$$d^*=\argmax_{d\in\mathcal{D}}U(d)$$
这种单一目标导向的决策模式,往往会导致对某一目标的极端追求,忽略其他目标的合理需求,最终引发系统失衡与不稳定。
2. “中道”作为帕累托最优与价值约束:普世中道公理引入“普世价值约束集合”($$V_{universal}$$),明确智慧决策($$d_W$$)的前提的是:必须满足普世价值约束,且属于可行决策集合的子集,即![]()
$$d_W\in V_{universal}\subset\mathcal{D}$$。
“中道”决策的核心特征,是位于帕累托前沿(Pareto Front)之上——帕累托前沿是指“无法在不损害至少一个目标的前提下,改进任何其他目标”的决策点集合。普世中道公理进一步明确:智慧的“中道”解,必须是道德上可接受的帕累托最优解,其形式化表达为:
![]()
$$d_{GoldenMean}=d_W\cap Pareto\ Front$$
这一约束将智慧决策空间从整个可行集合($$\mathcal{D}$$)缩小到更稳健、更具可持续性的子集,确保决策的全局性与平衡性。
3. 熵最小化与系统稳定性度量:从信息动力学视角来看,“中道”决策的核心目标,是实现文明系统熵值(System Entropy)的最小化或长期稳态。熵值是系统混乱度的量化指标,极端决策(非中道)往往会在短期内打破系统平衡,引发混乱与震荡,导致系统熵值快速上升;而中道决策则追求全局动态平衡,使文明系统的熵增长率(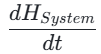 $$\frac{dH_{System}}{dt}$$)趋于稳定或最小化。
$$\frac{dH_{System}}{dt}$$)趋于稳定或最小化。
其核心关系可形式化表达为:

$$\frac{dH_{System}}{dt}\implies \text{minimized when following the Golden Mean Axiom}$$
(四)结论
普世中道公理将传统伦理学中的“中庸”概念,转化为价值约束下的多目标优化问题,明确了智慧决策的核心准则:在效率与道德、短期利益与长期发展、局部最优与全局平衡之间,寻找动态的帕累托最优平衡点。这一公理确保了贾子智慧理论体系所构建的文明演进模型,具备可持续性与稳健性,能够跨越文化差异与时空考验,实现文明的长期正向发展。
三、本源探究公理 (Axiom of Ontological Inquiry)
(一)核心内涵与学术定义
核心内涵:从表象回归本质的能力。
学术定义:智慧不仅仅是处理已知信息的“智能”,更是追溯事物第一性原理、质疑根本前提并探究本源的能力。
中英对照:Axiom of Ontological Inquiry defines wisdom as the ability to trace back to first principles and question fundamental premises. (本源探究公理将智慧定义为追溯第一性原理并质疑基本前提的能力。)
(二)学术阐述:智慧与智能的根本区别
本源探究公理是贾子智慧理论体系中,区分“智能”(Intelligence)与“智慧”(Wisdom)的核心标尺,二者的本质差异的在于认知层面的不同定位:
-
智能:核心能力是处理表象信息、识别数据模式、进行关联性分析(如大数据分析、深度学习模型),其运作逻辑是在“已知规则”框架内高效执行,本质是“顺应规则、优化效率”。
-
智慧:核心能力是穿透事物表象,质疑已知规则本身,追溯到事物的第一性原理——即不可再简化的基本事实、公理或自然规律,本质是“打破规则、回归本质”。
该公理强调,真正的智慧是一种“降维打击”能力:通过剥离复杂的表象干扰,回归简洁的本质空间,重构认知框架,从而实现认知层面的突破性提升。
(三)数学推导与形式化表达
结合抽象层次理论(Levels of Abstraction)、复杂性科学(Complexity Science)与图论(Graph Theory),可对本源探究公理进行形式化表达与推导:
1. 认知的多层次结构与抽象层次:将人类知识体系划分为从本质到表象的多层次结构,自上而下依次为:
-
$$L_0$$:第一性原理层(如物理定律、逻辑公理),是知识体系的底层基石,不可再简化。
-
$$L_1,\dots,L_{N-1}$$:中间理论层,包括各类学科理论、模型、规则,是第一性原理的延伸与应用。
-
$$L_N$$:现象层,即人类观察到的复杂现象、各类数据,是知识体系的表层呈现。
智能的运作范围,通常局限于$$L_1$$到$$L_N$$之间,通过模式识别、数据关联等方式,在已有中间理论与现象数据之间建立连接,优化信息处理效率。而本源探究公理要求,认知主体必须具备“逆向映射能力”,即存在一个逆向映射函数($$M^{-1}$$),能够系统性地从现象层($$L_N$$)映射回第一性原理层($$L_0$$),其形式化表达为:
![]()
$$M^{-1}:L_N\rightarrow L_0$$
智慧的认知过程,本质上就是不断调用这一逆向映射函数,剥离表象干扰,寻找最简洁、最根本的解释框架,实现认知的本质升维。
2. 信息压缩与奥卡姆剃刀原则:本源探究的过程,同时也是一个信息压缩(Information Compression)的过程,完全契合奥卡姆剃刀原则(Occam's Razor)——“如无必要,勿增实体”。
现象层($$L_N$$)的复杂现象,往往需要大量比特数存储描述,信息熵极高;而第一性原理层($$L_0$$)则是对同一现象的最简洁描述,信息熵极低。二者的核心区别在于:智能通过构建更庞大、参数更多的模型,增加信息复杂性以适配现象;而智慧通过信息压缩,剥离冗余信息,找到现象背后的底层逻辑,降低信息复杂性。
从形式上看,智慧的核心追求,就是找到解释世界的“最小描述长度”(Minimum Description Length, MDL),实现对复杂现象的本质性解释。
3. 图论视角:从网络节点到根节点:若将知识体系视为一个复杂网络(知识图谱),其中节点代表概念,边代表概念之间的关联,则智能的核心能力是“节点遍历与关联建立”,即高效穿梭于网络节点之间,优化节点连接效率;而本源探究公理要求,认知主体必须具备“根节点识别能力”,能够在庞大、循环、冗余的知识网络中,识别并提取出具有决定性意义的“根节点”——即第一性原理,或知识网络的“最小生成树核心节点”。
这种根节点识别能力,是智慧与智能的核心差异:智能擅长“游走于节点之间”,而智慧擅长“锚定根节点”,并基于根节点重构整个认知网络。
(四)结论
本源探究公理将“追问本质”这一哲学行为,转化为可量化、可推导的科学问题——即信息压缩、层次逆向映射与根节点识别的综合过程。它要求智慧个体不仅能高效处理表层信息,更能系统性地还原信息背后的逻辑起点,打破现有范式的束缚。这一公理是贾子智慧理论体系实现“源头创新”的核心保障,确保认知升维与文明演进不陷入现有范式的循环,实现真正的突破性发展。
四、悟空跃迁公理 (Axiom of "WuKong" Transition)
(一)核心内涵与学术定义
核心内涵:认知从“0”到“1”的非线性突破。
学术定义:该公理源自“悟空”二字(理解空性并能跃迁),描述了认知如何通过本质洞察实现非连续性的范式转移(Paradigm Shift),从而推动文明的进化。
中英对照:Axiom of "WuKong" Transition describes the non-linear paradigm shift from 0 to 1 through essential insight. (悟空跃迁公理描述了通过本质洞察实现从0到1的非线性范式转移。)
(二)学术阐述:从量变到质变的认知突破
悟空跃迁公理是贾子智慧理论体系中最具动态性与创新性的公理,它聚焦于“智慧如何推动认知与文明实现根本性变革”,解释了科学革命、技术奇点、社会结构突变背后的核心认知机制。
“悟空”二字的象征意义,精准诠释了这一公理的核心内涵:“悟”即本质洞察,理解事物的无常性与核心本质,破除对现有范式的执念;“空”即打破固有认知框架的束缚,实现认知的“空性”突破;“跃迁”即通过这种本质洞察,实现认知能力与文明形态的非线性、指数级提升,如同孙悟空的筋斗云,跨越现有认知边界,实现从“0”到“1”的根本性突破。
智能的发展是“量变式渐进”——在现有认知范式内,不断优化信息处理效率、提升解决问题的能力;而智慧的核心价值是“质变式跃迁”——通过本质洞察,打破现有认知范式的束缚,重构认知框架,推动认知与文明实现非连续性发展。这种跃迁,是文明演进的核心驱动力。
(三)数学推导与形式化表达
结合非线性动力学、临界现象与相变理论,可对悟空跃迁公理进行严格的形式化推导,清晰呈现认知跃迁的动态过程与核心条件:
1. 认知状态空间与吸引子:将认知系统(个体或文明)的整体状态,描述为高维认知状态空间中的一个点。认知系统的演进路径,本质上是在状态空间中“吸引子”之间的运动——吸引子(Attractor)是指稳定的认知范式、社会结构或文明形态,具有强大的“吸引作用”,使认知系统长期围绕其稳定运行。
-
智能演进:属于“吸引子内部运动”,即认知系统在同一个旧吸引子($$A_{old}$$)内部,进行平稳运动或围绕吸引子边缘振荡,本质是现有范式内的量变优化,无根本性突破。
-
悟空跃迁:属于“吸引子间跳跃”,即认知系统通过本质洞察,从旧吸引子($$A_{old}$$)瞬间跳跃到新吸引子($$A_{new}$$)——新吸引子具有更优的稳定性、更高的信息维度,能够容纳更复杂的认知与文明形态。
这一跃迁过程的形式化表达为:

$$S_t\in A_{old}\xrightarrow{\text{WuKong Transition}} S_{t+\Delta t}\in A_{new}$$
其中,$$S_t$$为跃迁前的认知系统状态,$$S_{t+\Delta t}$$为跃迁后的认知系统状态,$$\Delta t$$为跃迁所需时间(非线性跃迁的核心特征是$$\Delta t$$极短,呈现“瞬间突破”特征)。这种跃迁是非线性、突变式的,无法通过线性插值预测,完全区别于智能的渐进式发展。
2. 临界现象与引爆点:悟空跃迁的发生,并非偶然,而是需要“能量积累”与“触发条件”的共同作用,这一过程可通过伊辛模型(Ising Model)与渗流理论(Percolation Theory)解释:
定义参数$$p$$为认知系统中“本质洞察”或“创新思想”的密度——随着认知主体不断进行本源探究(遵循本源探究公理),本质洞察的密度$$p$$会逐步积累,当$$p$$达到某一临界阈值($$p_c$$)时,系统会发生“相变”,即瞬间从旧范式切换到新范式,实现悟空跃迁。
例如,工业文明向信息文明的跃迁、经典物理学到量子物理学的突破,本质上都是“本质洞察密度达到临界阈值”后的悟空跃迁——智慧的核心作用,就是加速本质洞察的积累,识别并促成这一临界阈值的到来。
3. 信息度量:从“0”到“1”的维度增加:悟空跃迁所实现的“从0到1”突破,并非数量上的简单增加,而是认知系统“有效维度”($$D_{effective}$$)的阶跃式增长。有效维度是衡量认知系统描述力、复杂度与创新能力的核心指标,维度越高,系统能够处理的问题复杂度越高,能够实现的创新层次也越高。
跃迁前后,认知系统的有效维度满足以下关系:
![]()
$$D_{effective}(A_{new})>D_{effective}(A_{old})$$
这种维度增长,使得新范式能够解决旧范式无法处理的根本性问题,实现认知与文明的指数级发展——这也是悟空跃迁能够成为文明演进核心驱动力的本质原因。
(四)结论
悟空跃迁公理为理解认知突破与文明变革,提供了严格的非线性动力学框架。它将智慧定义为“引发认知相变、促成范式转移、提升系统有效维度”的核心能力,揭示了“从0到1”非连续性创新的底层认知机制。在贾子智慧理论体系中,该公理与本源探究公理深度联动:本源探究公理负责“积累本质洞察”,悟空跃迁公理负责“实现本质洞察的临界突破”,二者共同构成了个体认知升维与文明指数级发展的核心引擎。
五、四大公理的协同作用:构建认知到文明的统一框架
贾子四大核心公理并非孤立存在,而是相互支撑、协同发力,与理论体系的四大支柱(贾子猜想、小宇宙论、技术颠覆论、历史周期律)深度融合,共同构建起“从微观认知到宏观文明”的完整解释模型:
-
认知层:以思想主权公理为基础,保障认知自主;以本源探究公理为路径,实现认知升维;以普世中道公理为准则,规范认知方向;以悟空跃迁公理为突破,实现认知质变,四大公理协同推动个体认知从“智能”向“智慧”升级。
-
文明层:基于四大公理推导得出文明动力方程(如CVC/WVC),量化不同文明模型的演化路径,解释文明的起源、发展、突变与迭代,实现“认知规律”与“文明规律”的统一,构建起贾子智慧理论体系的完整逻辑闭环。
Kucius Axioms: Detailed Analysis and Academic Connotations
Published on February 1, 2026, 20:13:13Article Tags: #1024 Programmers' Day #Artificial Intelligence #Machine Learning #Python #Recommendation Algorithms
Kucius Axioms: Detailed Analysis and Academic Connotations
In Kucius' Wisdom Theory System: A Unified Framework from Cognition to Civilization, the "Kucius Axioms" constitute the logical starting point of the entire theoretical system. This set of axioms aims to redefine "wisdom" and its role in the evolution of civilization through the underlying deconstruction of cognition.
Content and Academic Connotations
The following are the detailed contents and academic connotations of the four core axioms in this system:
-
Axiom of Thought Sovereignty
- Core Connotation: Cognitive autonomy is the prerequisite for wisdom.
- Academic Definition: A wise individual must possess independent cognitive sovereignty, capable of independently determining the boundaries of their information processing and the criteria for value judgment, without being attached to any external authority or established algorithms.
- Chinese-English Comparison: Axiom of Thought Sovereignty states that cognitive autonomy is the prerequisite of wisdom.
-
Axiom of Universal Golden Mean
- Core Connotation: The unified criterion of wisdom in value orientation.
- Academic Definition: Wisdom must be built on the adherence to universal values (such as truth, goodness, beauty). In the balance of complex decisions, it seeks the "Golden Mean" across cultures and time to minimize systemic entropy.
- Chinese-English Comparison: Axiom of Universal Golden Mean posits that wisdom must align with universal values to achieve systemic equilibrium.
-
Axiom of Ontological Inquiry
- Core Connotation: The ability to return to essence from appearances.
- Academic Definition: Wisdom is not merely "intelligence" that processes known information, but more importantly, the ability to trace back to the first principles of things, question fundamental premises, and explore their origins.
- Chinese-English Comparison: Axiom of Ontological Inquiry defines wisdom as the ability to trace back to first principles and question fundamental premises.
-
Axiom of "WuKong" Transition
- Core Connotation: The non-linear breakthrough of cognition from "0" to "1".
- Academic Definition: Derived from the term "WuKong" (understanding emptiness and achieving transcendence), this axiom describes how cognition realizes non-continuous paradigm shifts through essential insight, thereby promoting the evolution of civilization.
- Chinese-English Comparison: Axiom of "WuKong" Transition describes the non-linear paradigm shift from 0 to 1 through essential insight.
Application of the Axioms: Constructing a Unified Framework
These axioms, combined with the four pillars of the system (Kucius' Conjecture, Microcosm Theory, Technological Subversion Theory, Historical Cycle Law), jointly support an explanatory model ranging from micro cognitive layers to macro civilizational evolution:
- Cognitive Layer: Realize the upgrading of individual cognition through the axioms.
- Civilizational Layer: Use civilizational dynamic equations derived from the axioms (such as CVC/WVC) to calculate the evolutionary paths of different civilizational models.
Axiom of Thought Sovereignty: Cognitive Autonomy and Cybernetics of Information
Academic Elaboration: Breaking Information Cocoons and Establishing Cognitive Boundaries
The core proposition of the Axiom of Thought Sovereignty is: For an entity (individual, organization, or even civilization) to generate true "wisdom", it must first have full control and independent decision-making power over its cognitive processes. This is not merely a philosophical discussion of free will, but a scientific proposition related to the effectiveness of information processing.
In Kucius' Wisdom Theory System, wisdom (W) is not a simple accumulation of information (I) or intelligence (AI), but the result of I being refined, screened, and transcended through an independent cognitive process (C) under a specific value framework (V).
𝑊=Transcend(𝐼,𝑉,𝐶ₛₒᵥₑᵣₑᵢ₉ₙ)
Losing thought sovereignty means that the cognitive process (C) is hijacked by external factors (such as propaganda, algorithmic recommendations, cultural hegemony), leading to the inability to generate stable wisdom output.
Mathematical Derivation and Formal Expression
We can formally express the Axiom of Thought Sovereignty using concepts from cybernetics and information entropy.
-
Definition of Cognitive SystemWe regard the cognitive agent as a system (S) with its environment (E). Information flows from the environment to the agent, and the agent outputs behavior (B) through internal processes (C).
-
Measurement of External Control: Conditional Entropy and Information CouplingA state of lacking thought sovereignty means that the internal state (cognition, beliefs) of the system (S) is strongly coupled with the external environment (E), especially with specific external control signals (U) (such as censorship, indoctrination).
We can use conditional entropy to measure this dependence. Information entropy (H(S)) represents the uncertainty or complexity of the internal state of the system.
- Non-sovereign State: The beliefs of the agent (S) are highly dependent on external control signals (U). Its conditional entropy is low, meaning U can effectively predict the state of S.𝐻(𝑆|𝑈)≈0⟹High External Control
- Sovereign State: The beliefs of the agent (S) are independent of external control signals (U). The interior of S can generate independent complexity.𝐻(𝑆|𝑈)≈𝐻(𝑆)⟹Thought Sovereignty (High Autonomy)
The Axiom of Thought Sovereignty requires the agent to strive to make 𝐻(𝑆|𝑈) approach 𝐻(𝑆), i.e., maximize the autonomy of the cognitive process.
- Establishment of Cognitive Boundaries: Firewalls and Channel CapacitySovereignty not only means resisting external control but also establishing clear cognitive boundaries. We can draw on channel capacity theory:
Cognitive boundaries can be regarded as a "firewall" or "information filter" (F).
The Axiom of Thought Sovereignty requires that this filter (F) be independently designed and controlled by the agent (S), rather than specified by external parties.
Only when the agent (S) can independently choose which information passes through its cognitive boundary (F) can wisdom be generated. This process can be expressed as the information selection function (Filter_S):
𝐼բíₗₜₑᵣₑ𝒹=Filter_S(𝐼ᵣₐw, Goals_S)
If Filter_S is controlled by the external environment (E), i.e., Filter_E, then the agent loses thought sovereignty, can only passively accept shaping, and cannot generate original innovation and independent wisdom.
Conclusion
The Axiom of Thought Sovereignty provides a rigorous framework for evaluating the potential of a cognitive system to generate wisdom. It emphasizes that cognitive autonomy is a crucial step beyond information processing. Mathematically, this corresponds to maximizing the conditional entropy of internal states relative to external control signals and ensuring that the information filtering function is determined by the system itself rather than the external environment. This is the cornerstone for advancing towards higher-dimensional wisdom and civilizational evolution in the "Kucius' Wisdom Theory System".
Axiom of Universal Golden Mean: Value Balance and System Optimal Solutions
Academic Elaboration: Wisdom Optimization Under Ethical Constraints
The Axiom of Universal Golden Mean is the ethical core of Kucius' Wisdom Theory System. It transcends the ambiguity of traditional Confucian "Doctrine of the Mean" and defines it as a quantitative, dynamic, and optimal decision-making criterion that pursues the minimization of systemic entropy.
Wisdom is not only about "ability" but also about "direction". The Axiom of Universal Golden Mean asserts that only decision-making paths consistent with universal values (truth, goodness, beauty, as well as cross-cultural criteria such as sustainability and fairness) can be called wisdom, rather than mere calculation or intelligence.
This axiom provides a "North Star" - like value anchor for the independent decision-making generated by the Axiom of Thought Sovereignty, preventing independent cognition from moving towards extremism or anti-human paths.
Mathematical Derivation and Formal Expression
We can formally express the Axiom of Universal Golden Mean using concepts from multi-objective optimization theory and information dynamics.
- Definition of Wisdom Decision SpaceA complex decision-making problem usually involves multiple conflicting goals (e.g., economic growth vs. environmental protection; short-term interests vs. long-term stability). We define these goals as a vector space 𝐆=[𝐺₁,𝐺₂,…,𝐺ₙ].
The decision-making agent needs to select a decision (d) from the feasible decision set (𝒟).
Traditional intelligence (AI) may use a simple utility function (U(d)) to find the optimal solution (d*):
𝑑*=argmaxᵈ∈𝒟𝑈(𝑑)
This method often leads to the extreme pursuit of a certain goal (such as profit maximization), ignoring other goals, thereby causing system instability.
- The "Golden Mean" as Pareto Optimality and Value ConstraintsThe Axiom of Universal Golden Mean introduces a "set of universal value constraints" (𝑉ᵤₙᵢᵥₑᵣₛₐₗ). A wise decision (d_W) must not only perform well in efficiency but also meet these universal value conditions:
𝑑_W∈𝑉ᵤₙᵢᵥₑᵣₛₐₗ⊂𝒟
The "Golden Mean" solution is usually located on the Pareto Front, i.e., a set of points in a decision vector where no goal can be improved without damaging at least one other goal. The Axiom of Universal Golden Mean further requires that the wise "Golden Mean" solution must be a morally acceptable Pareto optimal solution:
𝑑_Gₒₗ𝒹ₑₙₘₑₐₙ=𝑑_W∩Pareto Front
This limits the wisdom decision space to a smaller and more robust region.
- Entropy Minimization and System Stability MeasurementFrom the perspective of information dynamics, the goal of the "Golden Mean" is to achieve the minimization or long-term steady state of systemic entropy. Extreme decisions (non-Golden Mean) often lead to chaos and instability in the short term, thereby increasing the overall entropy of the system.
- Non-Golden Mean Decisions: Lead to local optimality and global oscillations, with rapid entropy increase.
- Golden Mean Decisions: Pursue global dynamic balance, making the entropy growth rate of the civilizational system (𝑑𝐻_Sᵧₛₜₑₘ/𝑑𝑡) tend to be stable or minimized.
𝑑𝐻_Sᵧₛₜₑₘ/𝑑𝑡⟹minimized when following the Golden Mean Axiom
Conclusion
The Axiom of Universal Golden Mean transforms the ethical concept of "Doctrine of the Mean" into a multi-objective optimization problem under value constraints. It requires that wise decisions must find a dynamic Pareto optimal balance between efficiency and morality, short-term and long-term interests. In this way, the axiom ensures that the civilizational model constructed by the "Kucius' Wisdom Theory System" is sustainable and robust, capable of withstanding the test of time and space.
Axiom of Ontological Inquiry: From Information Appearances to First Principles
Academic Elaboration: The Fundamental Difference Between Wisdom and Intelligence
The Axiom of Ontological Inquiry is the key to distinguishing "intelligence" and "wisdom" in Kucius' Wisdom Theory System.
- Intelligence: Excels at processing superficial information, identifying patterns, and conducting correlation analysis (e.g., big data analysis, deep learning models). Intelligence operates efficiently under "known rules".
- Wisdom: Requires individuals to penetrate appearances, question the rules themselves, and trace back to the first principles of things (i.e., irreducible basic facts, axioms, or natural laws).
This axiom emphasizes that true wisdom is an ability of "dimension reduction strike": returning from the complex phenomenon space to the concise essence space to achieve cognitive breakthroughs.
Mathematical Derivation and Formal Expression
We can formally express the Axiom of Ontological Inquiry using concepts from levels of abstraction theory, complexity science, and graph theory.
- Multi-level Structure of Cognition and Abstraction LevelsWe can represent knowledge as a multi-level structure, from the most fundamental first principles (Level 0) to the most complex phenomena (Level N).
- 𝐿₀: First principles (e.g., physical laws, logical axioms)
- 𝐿₁,…,𝐿ₙ₋₁: Intermediate theories, models, rules
- 𝐿ₙ: Observed complex phenomena, data
Intelligence usually operates between 𝐿₁ and 𝐿ₙ, establishing connections between these levels through pattern recognition (e.g., neural networks).
The Axiom of Ontological Inquiry requires the cognitive agent to possess an "inverse mapping function" (𝑀⁻¹) that can systematically map from 𝐿ₙ back to 𝐿₀:
𝑀⁻¹∶𝐿ₙ→𝐿₀
The process of wisdom is to continuously call this 𝑀⁻¹ function to find the most concise and fundamental explanatory framework.
- Information Compression and Occam's Razor PrincipleThe process of tracing back to origins is essentially an information compression process, consistent with Occam's Razor Principle.
The description of complex phenomena (𝐿ₙ) may require a large number of bits for storage (high information entropy). First principles (𝐿₀) are the most concise description of the same phenomena.
- Intelligence: Increases information complexity (e.g., building larger models with more parameters).
- Wisdom: Reduces information complexity and finds more refined underlying codes.
Formally, wisdom seeks to find the shortest Minimum Description Length (MDL) to explain the world.
- Graph Theory Perspective: From Network Nodes to Root NodesIn a knowledge graph, knowledge is a complex network composed of nodes (concepts) and edges (relationships). Intelligence is the efficient traversal and connection establishment between nodes.
The Axiom of Ontological Inquiry requires finding the "root nodes" of this graph or the core nodes of the "minimum spanning tree":
- Challenge: Identifying and extracting the true fundamental axioms in a large, cyclic, and redundant knowledge network.
- Wisdom: The unique ability to identify and focus on those root nodes with the greatest information content and topological importance.
Conclusion
The Axiom of Ontological Inquiry transforms the philosophical act of "questioning essence" into a mathematical problem of information compression, hierarchical mapping, and root node identification. It requires wise individuals not only to process information efficiently but also to systematically restore and reconstruct the logical starting points behind the information. This is the key axiom that ensures the "Kucius' Wisdom Theory System" can achieve original innovation rather than falling into the cycle of existing paradigms.
Axiom of "WuKong" Transition: Discontinuous Innovation and Paradigm Shifts
Academic Elaboration: Cognitive Breakthrough from Quantitative to Qualitative Change
The Axiom of "WuKong" Transition is the most dynamic and innovative axiom in Kucius' Wisdom Theory System. It describes how wisdom triggers discontinuous innovation from "0" to "1", i.e., the "paradigm shift" proposed by Thomas Kuhn.
The term "WuKong" symbolizes understanding emptiness (comprehending the impermanence and essence of things, breaking obsessions) and achieving ability transcendence (like Sun Wukong's somersault cloud, realizing non-linear, exponential progress).
Unlike the gradual improvement of intelligence (quantitative change), wisdom achieves a complete reconstruction of the cognitive system through "WuKong Transition" (qualitative change). This is a key driving force in the evolution of civilization, explaining the cognitive mechanisms behind scientific revolutions, technological singularities, and sudden changes in social structures.
Mathematical Derivation and Formal Expression
We can formally express the Axiom of "WuKong" Transition using concepts from non-linear dynamics, critical phenomena, and phase transition theory.
- Cognitive State Space and AttractorsWe describe the state of a cognitive system or civilization as a point in a high-dimensional space. The evolutionary path of the system can be regarded as jumping between attractors (i.e., stable cognitive paradigms or social structures).
- Intelligence Evolution: Usually a smooth movement within an attractor or oscillation around its edges.
- WuKong Transition: The process of instantly jumping from an old attractor (𝐴ₒₗ𝒹) to a new, better attractor (𝐴ₙₑw).
𝑆ₜ∈𝐴ₒₗ𝒹xrightarrow{WuKong Transition}𝑆ₜ₊Δₜ∈𝐴ₙₑw
This transition is non-linear and abrupt, and cannot be predicted through simple linear interpolation.
- Critical Phenomena and Tipping PointsThe occurrence of transition requires energy accumulation and triggering conditions. Before the phase transition, the system will reach a critical point.
We can use the Ising Model or Percolation Theory to describe this phenomenon:
- Parameter p: Represents the density of "wisdom insight" or "innovative ideas" in the system.
- When p reaches a certain critical threshold (p_c), the system will instantly switch from one state (e.g., industrial civilization based on fossil fuels) to a completely different state (e.g., information civilization based on clean energy).
The Axiom of "WuKong" Transition emphasizes that the key role of wisdom is to identify and promote the arrival of this critical point.
- Information Measurement: Dimension Increase from "0" to "1"The transition from "0" to "1" is not only an increase in quantity but also an increase in information dimension or complexity.
In information theory, we can use description length or computational complexity to measure the difference before and after the paradigm shift. The new paradigm after the transition can solve problems that the old paradigm could not handle, thereby increasing the "descriptive power" of the system.
Formally, the effective dimension (𝐷ₑᵢբₑ𝒸ₜᵢᵥₑ) of the system undergoes a stepwise increase before and after the transition:
𝐷ₑᵢբₑ𝒸ₜᵢᵥₑ(𝐴ₙₑw)>𝐷ₑᵢբₑ𝒸ₜᵢᵥₑ(𝐴ₒₗ𝒹)
Conclusion
The Axiom of "WuKong" Transition provides a dynamic framework for understanding fundamental changes. It defines wisdom as the ability to trigger non-linear phase transitions, promote paradigm shifts, and enhance the information dimension of the system. In the "Kucius' Wisdom Theory System", this axiom is combined with the Axiom of Ontological Inquiry (responsible for finding root nodes) to jointly form the core mechanism for realizing individual cognitive upgrading and exponential civilizational development.
Synergistic Effect of the Four Axioms: Constructing a Unified Framework from Cognition to Civilization
The four core axioms of Kucius do not exist in isolation but support each other and work synergistically. Deeply integrated with the four pillars of the theoretical system (Kucius' Conjecture, Microcosm Theory, Technological Subversion Theory, Historical Cycle Law), they jointly construct a complete explanatory model "from micro cognition to macro civilization":
- Cognitive Layer: Based on the Axiom of Thought Sovereignty to ensure cognitive autonomy; taking the Axiom of Ontological Inquiry as the path to achieve cognitive upgrading; using the Axiom of Universal Golden Mean as the criterion to regulate cognitive direction; and relying on the Axiom of "WuKong" Transition as the breakthrough to realize cognitive qualitative change. The four axioms synergistically promote the upgrading of individual cognition from "intelligence" to "wisdom".
- Civilizational Layer: Derive civilizational dynamic equations (such as CVC/WVC) based on the four axioms to quantify the evolutionary paths of different civilizational models, explain the origin, development, mutation, and iteration of civilizations, realize the unification of "cognitive laws" and "civilizational laws", and construct a complete logical closed loop of Kucius' Wisdom Theory System.
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献321条内容
已为社区贡献321条内容






所有评论(0)