09.string的模拟实现
本文详细介绍了C++中string类的模拟实现过程。通过自定义命名空间ddd,实现了包括构造函数、拷贝构造、容量管理(size/capacity)、元素访问(operator[])、迭代器、字符串操作(push_back/append/insert/erase)、查找(find/substr)以及流操作(operator<<>>/getline)等核心功能。重点解决了内存管
目录
一、前言
之前我们已经学习了string容器,以及各个接口怎么使用。现在为了更加理解string的底层架构,我们自己模拟实现一下string,这样在以后碰到代码出错或是提高效率的问题的时候能够更好解决。
注:代码实现使用声明定义分离的方式,并且为了不与库中的string,我们将自己定义的string放在一个命名空间ddd中。
二、具体实现
1.私有成员变量
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;2.构造函数string

光是构造函数就有很多细节需要注意:
1.默认构造函数_str不能初始化为空
2.构造时先初始化_size避免重复调用strlen函数
3.初始化列表顺序问题,可以_size用初始化列表初始化,而另外两个在函数体内初始化
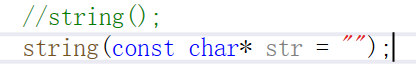
也可以使用全缺省构造函数,这样可以节省代码量,但需将无参构造函数去掉,因为默认构造函数只能有一个
3.拷贝构造
string::string(const string& str) {
_str = new char[str.capacity() + 1];
_size = str.size();
_capacity = str.capacity();
memcpy(_str, str.c_str(), _size + 1);
}4.size和capacity
size_t string::size() const{
return _size;
}
size_t string::capacity() const{
return _capacity;
}返回相应值即可
5.operator[ ]
char& string::operator[](size_t i) {
assert(i < _size);
return _str[i];
}
const char& string::operator[](size_t i) const{
assert(i < _size);
return _str[i];
}两种重载const和非const,然后用assert完成是否超出范围
6.迭代器iterator
// 模拟实现迭代器(但迭代器不是指针,只是用指针模拟)
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin() {
return _str;
}
iterator end() {
return _str + _size;
}const版本加声明定义分离
typedef const char* const_iterator;
const_iterator begin() const;
const_iterator end() const;string::const_iterator string::begin() const {
return _str;
}
string::const_iterator string::end() const {
return _str + _size;
}使用typedef char*模拟迭代器的实现,begin和end返回数组初始指针和末尾指针
测试代码:
测试使用以上的几个接口可实现的功能
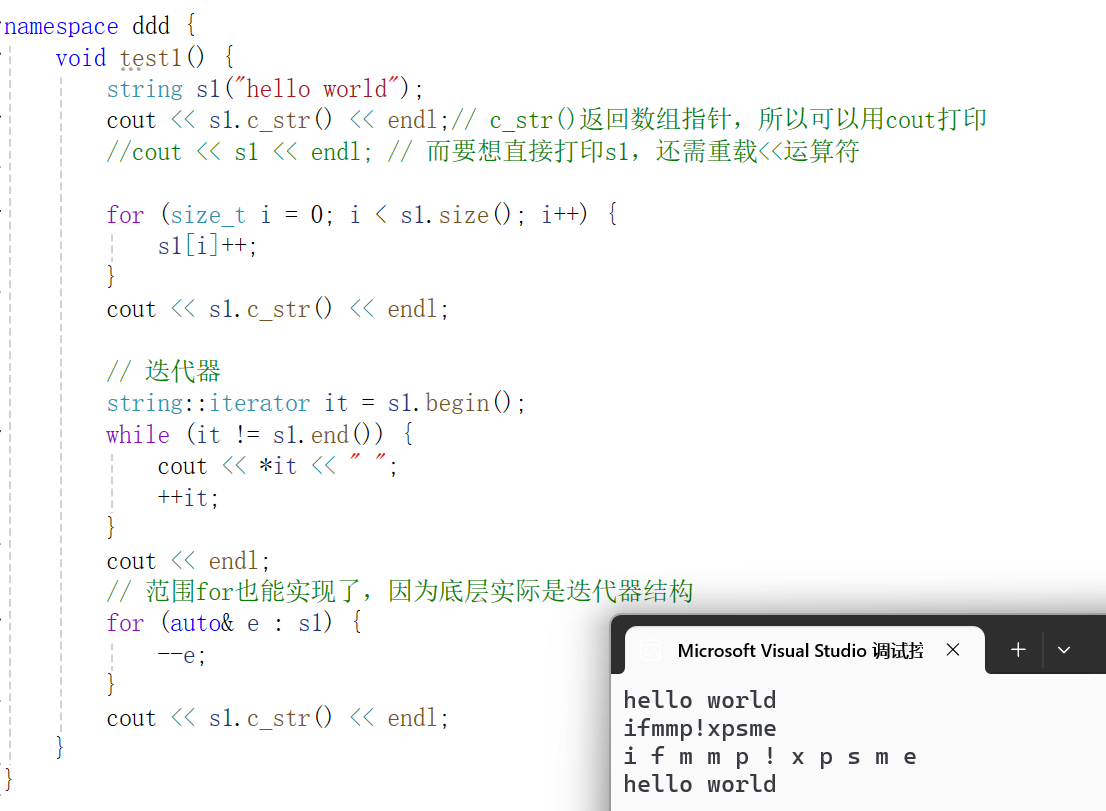
1.使用字符串初始化s1,成功
2.借助c_str()返回的数组指针进行打印,成功
3.使用重载运算符[ ]遍历并改变string的值,成功
4.迭代器遍历string并打印,成功
5.范围for遍历string并改变string的值,成功
7.reserve
void string::reserve(size_t n) {
// 暂时只实现扩容,不考虑缩容
if (n > _capacity) {
// C++没有配套扩容方式,且realloc大多数情况也是异地扩容,所以我们手动扩容即可
char* str = new char[n + 1];// 申请空间
//strcpy(str, _str);// 拷贝
memcpy(str, _str, _size + 1);
delete(_str);// 释放
_str = str;// 指向新空间
_capacity = n;// 修改capacity
}
}实现容器的扩容
8.push_back和append
void string::push_back(char ch) {
if (_size >= _capacity) {
//扩容
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::append(const char* str) {
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity) {
size_t newcapacity = 2 * _capacity;
if (len + _size > newcapacity) {
newcapacity = len + _size;
}
reserve(newcapacity);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}1.实现字符和字符串的插入,在空间不够时调用reserve进行扩容
2.还有一个问题是append插入时涉及到一个长字符串插入的问题,如果直接扩容两倍有可能空间还是不够,但如果都扩容成len + _size又会导致频繁扩容。所以对于短串采用二倍扩容,而对长串采用len + _size扩容
9.operator+=
string& string::operator+=(char ch) {
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* ch) {
append(ch);
return* this;
}+=重载的实质就是对push_back和append的封装
10.operator<<
// 流插入重载需要在全局
// 且通常需要成为友元来访问私有成员,但如果借用c_str()则不需要成员友元
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s){
// 直接使用c_str输出,但这样有个隐患,即遇到字符串内部含有'\0'会就会停止输出
//out << s.c_str();
for (size_t i; i <= s.size(); i++) {
out << s[i];
}
return out;
}1.operator<<声明需要在全局,而不是在类中,因为第一个参数需要是ostream&,而类成员函数默认第一个参数是this
2.如果采用直接out << s.c_str();的方式会导致问题,遇到'\0'就会停止流插入
测试代码:

可以感受cout << s2.c_str() << endl;和cout << s2 << endl;在使用效果上的区别。
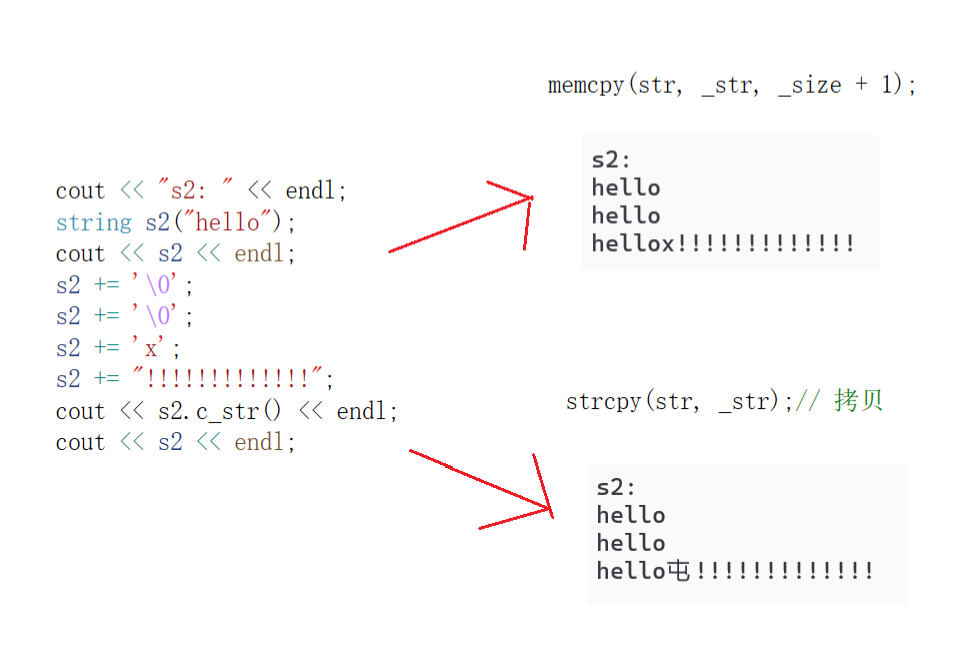
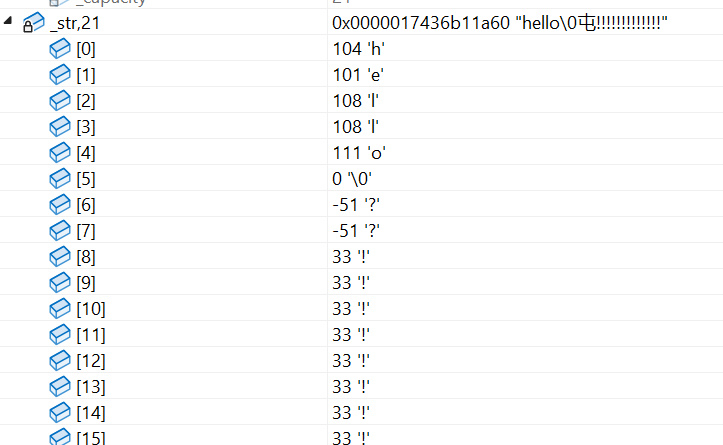
另外,reserve扩容拷贝时使用的strcpy也有类似的问题,strcpy在遇到'\0'时会停止拷贝,所以这个案例中strcpy只拷贝了"hello\0",但实际长度却更长,导致中间有两个位置没有拷贝过来,保留了两个随机值。
所以采用memcpy来代替strcpy,memcpy可以自己控制拷贝的长度
补充:如果运行后看到乱码,出现屯,烫这些字,说明是赋值出了问题,初始的随机值没有被赋值
11.insert
void string::insert(size_t pos, char ch){
assert(pos <= _size);
// 扩容
if (_size >= _capacity) {
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos) {
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
++_size;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str) {
assert(pos <= _size);
// 扩容
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity) {
size_t newcapacity = 2 * _capacity;
if (len + _size > newcapacity) {
newcapacity = len + _size;
}
reserve(newcapacity);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos) {
_str[end + len - 1] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
_str[pos + i] = str[i];
}
_size += len;
}函数重载,分别匹配插入字符和字符串
12.pop_back和erase
void pop_back();
void erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
static const size_t npos;void string::pop_back() {
_size--;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len) {
assert(pos < _size);
// 删除pos后的所有值
if (len == npos || len >= (_size - pos)) {
_size = pos;
_str[_size] = '\0';
return;
}
size_t i = pos + len;
memmove(_str + pos, _str + i, _size + 1 - i);
_size -= len;
}
const size_t string::npos = -1;1.pop_back()尾删直接_size--即可,然后把末尾置为'\0'
2.erase删除指定位置,指定长度的值,先移动再插入,用到了memmove函数
3.用到了npos变量,这个是string类的静态成员变量,且为公有
测试代码:
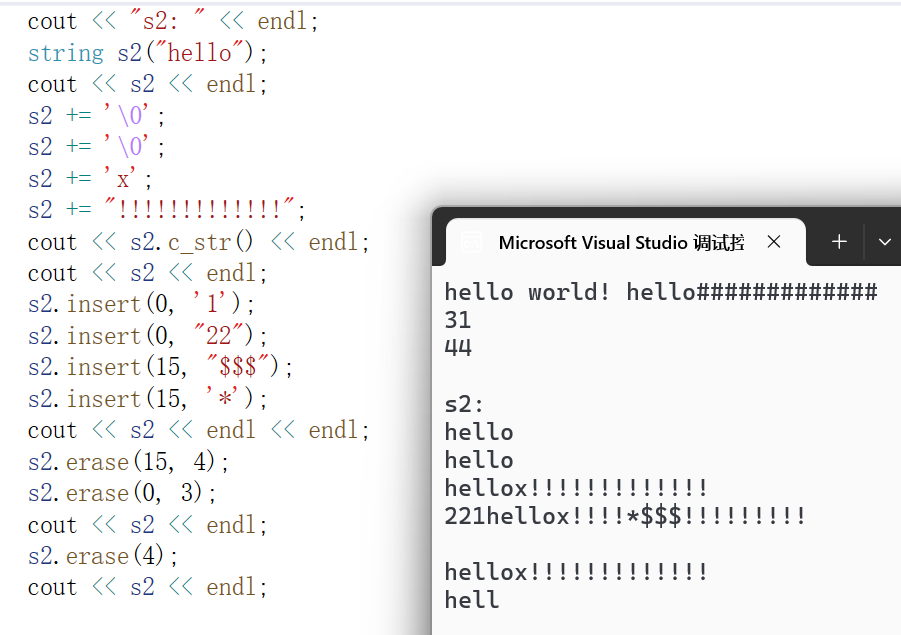
可以看到s2通过insert成功插入了数据,头插和中间插都没有问题
也可以通过erase删除指定位置数据,如果第二个参数缺省则删除pos之后的所有数据
13.find
size_t string::find(char ch, size_t pos = 0) const {
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++) {
if (ch == _str[i]) {
return i;
}
}
}
size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0) const {
// strstr函数,返回子串位置
const char* p1 = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (p1 == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return p1 - _str;
}
}查找字符较简单,查找字符串则使用了strstr函数来寻找子串位置
14.substr
// 生成子串并返回
string string::substr(size_t pos, size_t len) const{
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
len = _size - pos;
}
string ret;
ret.reserve(len);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
ret += _str[pos + i];
}
return ret;
}测试代码:
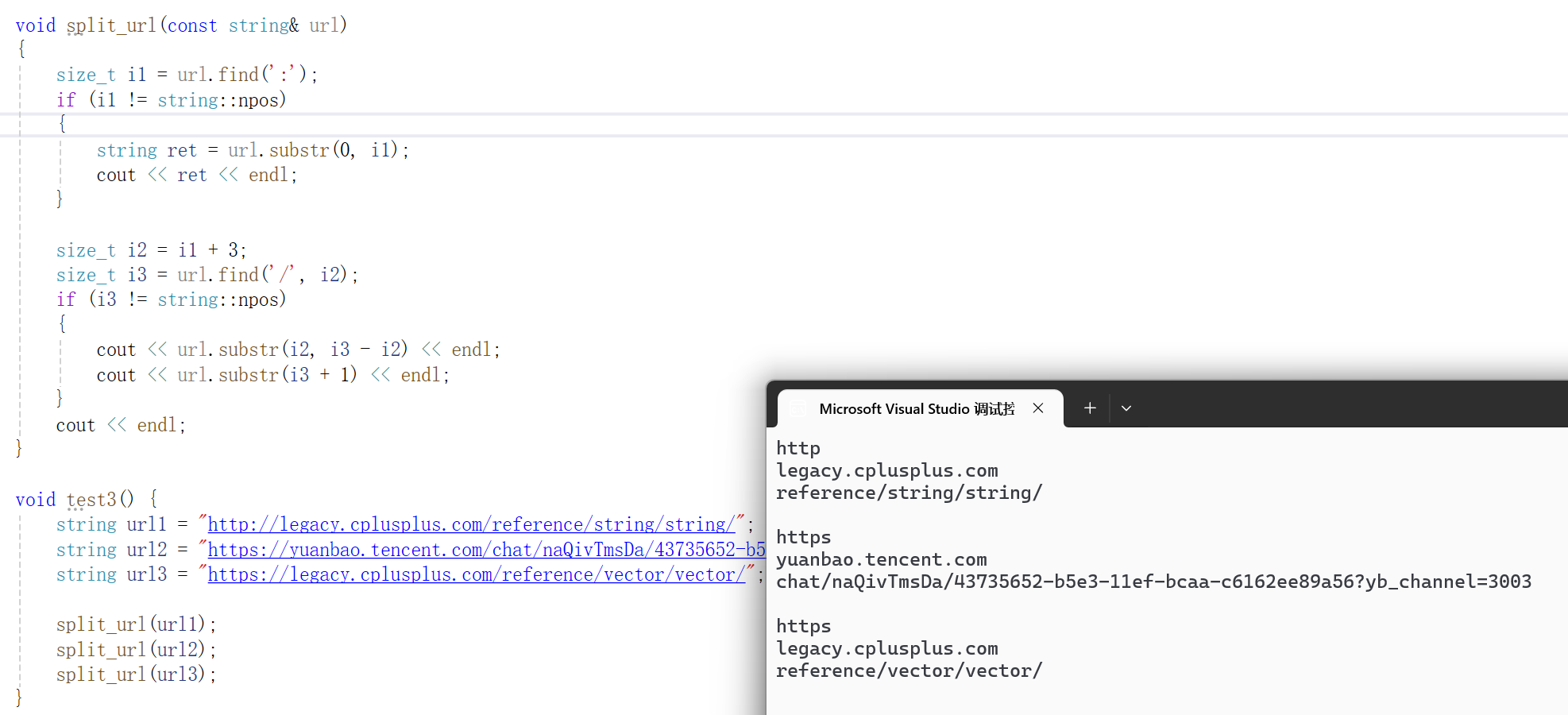
可以看到成功分割了网址
15.重载运算符<、<=、==、>、>=、!=
bool string::operator<(const string& s) const
{
size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size)
{
if (_str[i1] < s[i2])
{
return true;
}
else if (_str[i1] > s[i2])
{
return false;
}
else
{
++i1;
++i2;
}
}
return i2 < s._size;
}
bool string::operator<=(const string& s) const
{
return *this < s || *this == s;
}
bool string::operator>(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool string::operator>=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this < s);
}
bool string::operator==(const string& s) const
{
size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size)
{
if (_str[i1] != s[i2])
{
return false;
}
else
{
++i1;
++i2;
}
}
return i1 == _size && i2 == s._size;
}
bool string::operator!=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}完成 < 和 == 的实现,其余的使用直接复用即可
16.clear
void string::clear() {
_size = 0;
_str[0] = '\0';
}17.operator>>
// 流提取
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}1.读取in中的数据,碰到' '或'\n'时停止
2.但是常规的 in >> i 是把' '和'\n'当作终止符的,也就是根本读不进' '和'\n',所以我们重载时不能直接 in >> i 然后判断i是否等于' '和'\n',这样是恒成立的。所以需要用到get(),in.get()则是能够返回' '和'\n'的
3.而如果一个个读取,然后s += i的话,在面对长串输入时会导致频繁扩容,而如果提前开辟一个较大空间的话又会造成浪费。所以可以创建一个临时数组buff[ ],用于暂时存储,然后数组满了再一次性s += buff;,这样既能减少扩容次数,又能节约空间
18.getline
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s, char delim)
{
s.clear();
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != delim)
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}默认读取一整行,也可以指定终止字符
测试代码:
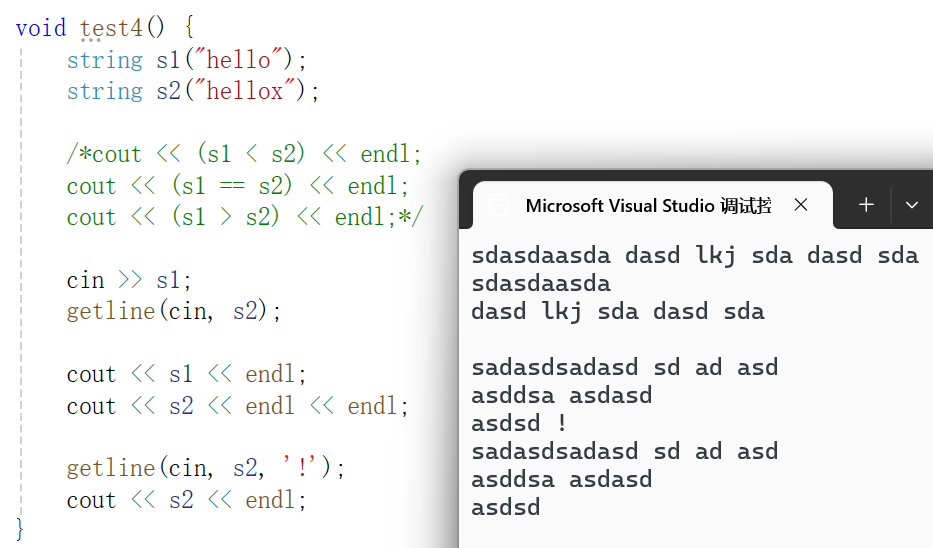
可以看到cin能读取一个字符串
getline默认能读取一行
getline输入第三个参数后可以一直读取,直到出现指定字符才结束
源码:
最后附上完整源码
string.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
//string的模拟实现
namespace ddd {
class string {
public:
// 模拟实现迭代器(但迭代器不是指针,只是用指针模拟)
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin();
iterator end();
typedef const char* const_iterator;
const_iterator begin() const;
const_iterator end() const;
//构造函数
//string();
string(const char* str = "");
//拷贝构造
string(const string& str);
//析构
~string();
const char* c_str() const;
size_t size() const;
size_t capacity() const;
char& operator[](size_t i);//重载[]
const char& operator[](size_t i) const;//重载[]const版本
void reserve(size_t n);
void push_back(char ch);
void append(const char* str);
string& operator+=(char ch);// 对push_back的封装
string& operator+=(const char* ch);// 对append1的封装
void insert(size_t pos, char ch);// 指定位置插入
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
void pop_back();
void erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0) const;// 查找
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0) const;
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
bool operator<(const string& s) const;
bool operator<=(const string& s) const;
bool operator>(const string& s) const;
bool operator>=(const string& s) const;
bool operator==(const string& s) const;
bool operator!=(const string& s) const;
void clear();
static const size_t npos;
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s);
istream& getline(istream& is, string& str, char delim = '\n');
}string.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"string.h"
namespace ddd {
//string::string()
// // 此处_str不能初始化为空,因为打印时空指针解引用程序会崩溃
// :_str(new char[1]{'\0'})// 所有初始化时应该有一个空间
// ,_size(0)
// ,_capacity(0)
//{}
string::string(const char* str)
// 一次构造重复使用了三次strlen函数,代价较大
//:_str(new char[strlen(str)+1])// strlen不包含'\0',所以要+1
//,_size(strlen(str))
//,_capacity(strlen(str))
// 优化,但需注意初始化顺序,应让_size第一个初始化
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_str = new char[_size + 1];
_capacity = _size;
strcpy(_str, str);// 拷贝str的数据,strcpy会连'\0'一起拷贝
}
//拷贝构造
string::string(const string& str) {
_str = new char[str.capacity() + 1];
_size = str.size();
_capacity = str.capacity();
memcpy(_str, str.c_str(), _size + 1);
}
string::~string() {}
const char* string::c_str() const{
return _str;
}
size_t string::size() const{
return _size;
}
size_t string::capacity() const{
return _capacity;
}
char& string::operator[](size_t i) {
assert(i < _size);
return _str[i];
}
const char& string::operator[](size_t i) const{
assert(i < _size);
return _str[i];
}
string::iterator string::begin(){
return _str;
}
string::iterator string::end() {
return _str + _size;
}
string::const_iterator string::begin() const {
return _str;
}
string::const_iterator string::end() const {
return _str + _size;
}
void string::reserve(size_t n) {
// 暂时只实现扩容,不考虑缩容
if (n > _capacity) {
// C++没有配套扩容方式,且realloc大多数情况也是异地扩容,所以我们手动扩容即可
char* str = new char[n + 1];// 申请空间
//strcpy(str, _str);// 拷贝
memcpy(str, _str, _size + 1);
delete(_str);// 释放
_str = str;// 指向新空间
_capacity = n;// 修改capacity
}
}
void string::push_back(char ch) {
if (_size >= _capacity) {
//扩容
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::append(const char* str) {
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity) {
size_t newcapacity = 2 * _capacity;
if (len + _size > newcapacity) {
newcapacity = len + _size;
}
reserve(newcapacity);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
string& string::operator+=(char ch) {
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* ch) {
append(ch);
return* this;
}
// 流插入重载需要在全局
// 且通常需要成为友元来访问私有成员,但如果借用c_str()则不需要成员友元
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s){
// 直接使用c_str输出,但这样有个隐患,即遇到字符串内部含有'\0'会就会停止输出
//out << s.c_str();
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
out << s[i];
}
return out;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, char ch){
assert(pos <= _size);
// 扩容
if (_size >= _capacity) {
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * _capacity;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos) {
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
++_size;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str) {
assert(pos <= _size);
// 扩容
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (len + _size > _capacity) {
size_t newcapacity = 2 * _capacity;
if (len + _size > newcapacity) {
newcapacity = len + _size;
}
reserve(newcapacity);
}
size_t end = _size + 1;
while (end > pos) {
_str[end + len - 1] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
_str[pos + i] = str[i];
}
_size += len;
}
void string::pop_back() {
_size--;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len) {
assert(pos < _size);
// 删除pos后的所有值
if (len == npos || len >= (_size - pos)) {
_size = pos;
_str[_size] = '\0';
return;
}
size_t i = pos + len;
memmove(_str + pos, _str + i, _size + 1 - i);
_size -= len;
}
size_t string::find(char ch, size_t pos) const {
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++) {
if (ch == _str[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos) const {
// strstr函数,返回子串位置
const char* p1 = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (p1 == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return p1 - _str;
}
}
// 生成子串并返回
string string::substr(size_t pos, size_t len) const{
if (len == npos || len >= _size - pos)
{
len = _size - pos;
}
string ret;
ret.reserve(len);
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
ret += _str[pos + i];
}
return ret;
}
bool string::operator<(const string& s) const
{
size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size)
{
if (_str[i1] < s[i2])
{
return true;
}
else if (_str[i1] > s[i2])
{
return false;
}
else
{
++i1;
++i2;
}
}
return i2 < s._size;
}
bool string::operator<=(const string& s) const
{
return *this < s || *this == s;
}
bool string::operator>(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool string::operator>=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this < s);
}
bool string::operator==(const string& s) const
{
size_t i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
while (i1 < _size && i2 < s._size)
{
if (_str[i1] != s[i2])
{
return false;
}
else
{
++i1;
++i2;
}
}
return i1 == _size && i2 == s._size;
}
bool string::operator!=(const string& s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
void string::clear() {
_size = 0;
_str[0] = '\0';
}
// 流提取
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
istream& getline(istream& in, string& s, char delim)
{
s.clear();
char buff[128];
int i = 0;
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != delim)
{
buff[i++] = ch;
if (i == 127)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
i = 0;
}
ch = in.get();
}
if (i > 0)
{
buff[i] = '\0';
s += buff;
}
return in;
}
const size_t string::npos = -1;
}test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"string.h"
namespace ddd {
void test1() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;// c_str()返回数组指针,所以可以用cout打印
//cout << s1 << endl; // 而要想直接打印s1,还需重载<<运算符
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) {
s1[i]++;
}
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
// 迭代器
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end()) {
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// 范围for也能实现了,因为底层实际是迭代器结构
for (auto& e : s1) {
--e;
}
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test2() {
string s1("hello world");
/*s1.push_back('!');
s1.append(" hello############");*/
s1 += '!';
s1 += " hello#############";
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;
cout << "s2: " << endl;
string s2("hello");
cout << s2 << endl;
s2 += '\0';
s2 += '\0';
s2 += 'x';
s2 += "!!!!!!!!!!!!!";
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.insert(0, '1');
s2.insert(0, "22");
s2.insert(15, "$$$");
s2.insert(15, '*');
cout << s2 << endl << endl;
s2.erase(15, 4);
s2.erase(0, 3);
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(4);
cout << s2 << endl;
}
void split_url(const string& url)
{
size_t i1 = url.find(':');
if (i1 != string::npos)
{
string ret = url.substr(0, i1);
cout << ret << endl;
}
size_t i2 = i1 + 3;
size_t i3 = url.find('/', i2);
if (i3 != string::npos)
{
cout << url.substr(i2, i3 - i2) << endl;
cout << url.substr(i3 + 1) << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test3() {
string url1 = "http://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/";
string url2 = "https://yuanbao.tencent.com/chat/naQivTmsDa/43735652-b5e3-11ef-bcaa-c6162ee89a56?yb_channel=3003";
string url3 = "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/";
split_url(url1);
split_url(url2);
split_url(url3);
}
void test4() {
string s1("hello");
string s2("hellox");
/*cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;*/
cin >> s1;
getline(cin, s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl << endl;
getline(cin, s2, '!');
cout << s2 << endl;
}
}
int main() {
//ddd::test1();
//ddd::test2();
//ddd::test3();
ddd::test4();
}总结
本篇博客到此结束了,要是觉得有用的话可以点赞、收藏加关注支持一下!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)