LangChain RunnableWithMessageHistory简化代码与使用
本文介绍了LangChain中RunnableWithMessageHistory类的使用方法,该工具类可自动管理聊天历史记录。主要内容包括: 核心功能:通过会话ID管理不同用户的对话历史,自动填充和存储消息 关键配置参数:包括输入输出消息键、历史消息键及会话历史工厂函数 实现示例:展示了完整的代码实现流程,包含历史存储初始化、链构建和包装过程 内部机制:解析了该类的运行流程,包括历史记录的加载、
01. RunnableWithMessageHistory 使用示例
在前面的示例中,我们将历史消息显示地传递给链,在链外单独处理历史消息的记忆存储。这是一种完全可接受的方法,除此之外,LangChain 还提供了一个名为 RunnableWithMessageHistory 的类/包裹器,能让链自动处理这个过程(填充+存储)。
类构造函数接收的参数如下:
- runnable:需要包装的链或者可运行的组件。
- get_session_history:一个工厂函数,它返回给定会话ID的消息历史记录。这样,您的链就可以通过加载不同对话的不同消息来同时处理多个用户。
- input_messages_key:人类的输入是哪一个键,用于指定输入的哪个部分应该在聊天历史中被跟踪和存储。
- output_messages_key:AI 的输出是哪一个键,指定要将哪个输出存储为历史记录。
- history_messages_key:历史消息使用哪一个键,用于指定以前的消息使用特定的变量在模板中格式化。
使用 RunnableWithMessageHistory 包装链后,就可以像正常链一样调用了,除此之外,还可以增加一个运行时配置来指定传递给工厂函数的 session_id 是什么,从哪里获取存储的历史消息。
示例代码如下
import dotenv
from langchain_community.chat_message_histories import FileChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.chat_history import BaseChatMessageHistory
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
from langchain_core.runnables.history import RunnableWithMessageHistory
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
dotenv.load_dotenv()
# 1.定义历史记忆存储
store = {}
# 2.工厂函数,用于获取指定会话的聊天历史
def get_session_history(session_id: str) -> BaseChatMessageHistory:
if session_id not in store:
store[session_id] = FileChatMessageHistory(f"chat_history_{session_id}.txt")
return store[session_id]
# 3.构建提示模板与大语言模型
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一个强大的聊天机器人,请根据用户的需求回复问题。"),
MessagesPlaceholder("history"),
("human", "{query}"),
])
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-16k")
# 4.构建链
chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# 5.包装链
with_message_chain = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
chain,
get_session_history,
input_messages_key="query",
history_messages_key="history",
)
while True:
query = input("Human: ")
if query == "q":
exit(0)
# 6.运行链并传递配置信息
response = with_message_chain.stream(
{"query": query},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "123456"}}
)
print("AI: ", flush=True, end="")
for chunk in response:
print(chunk, flush=True, end="")
print("")
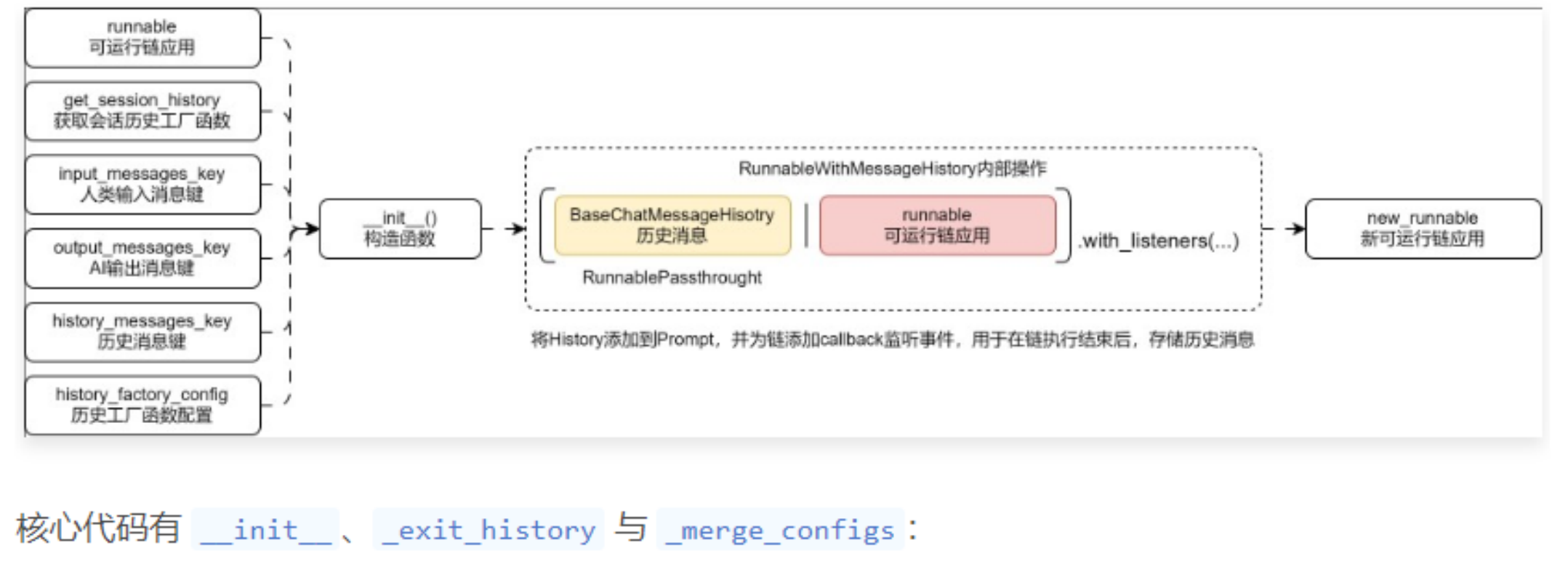
02. RunnableWithMessageHistory 运行流程
RunnableWithMessageHisotry 内部通过传递的运行时配置 session_id 获取到对应的消息历史实例,然后将消息历史实例组装用户输入字典,拼接到原始的 Runnable 可运行链应用中,并为新的 Runnable可运行链应用添加 callback 回调处理器,用于处理存储 LLM 生成的内容,并存储到消息历史记忆中。
整体的运行流程如下
def __init__(
self,
runnable: Union[
Runnable[
Union[MessagesOrDictWithMessages],
Union[str, BaseMessage, MessagesOrDictWithMessages],
],
LanguageModelLike,
],
get_session_history: GetSessionHistoryCallable,
*,
input_messages_key: Optional[str] = None,
output_messages_key: Optional[str] = None,
history_messages_key: Optional[str] = None,
history_factory_config: Optional[Sequence[ConfigurableFieldSpec]] = None,
**kwargs: Any,
) -> None:
history_chain: Runnable = RunnableLambda(
self._enter_history, self._aenter_history
).with_config(run_name="load_history")
messages_key = history_messages_key or input_messages_key
if messages_key:
history_chain = RunnablePassthrough.assign(
**{messages_key: history_chain}
).with_config(run_name="insert_history")
bound = (
history_chain | runnable.with_listeners(on_end=self._exit_history)
).with_config(run_name="RunnableWithMessageHistory")
if history_factory_config:
_config_specs = history_factory_config
else:
# If not provided, then we'll use the default session_id field
_config_specs = [
ConfigurableFieldSpec(
id="session_id",
annotation=str,
name="Session ID",
description="Unique identifier for a session.",
default="",
is_shared=True,
),
]
super().__init__(
get_session_history=get_session_history,
input_messages_key=input_messages_key,
output_messages_key=output_messages_key,
bound=bound,
history_messages_key=history_messages_key,
history_factory_config=_config_specs,
**kwargs,
)
def _exit_history(self, run: Run, config: RunnableConfig) -> None:
hist: BaseChatMessageHistory = config["configurable"]["message_history"]
# Get the input messages
inputs = load(run.inputs)
input_messages = self._get_input_messages(inputs)
# If historic messages were prepended to the input messages, remove them to
# avoid adding duplicate messages to history.
if not self.history_messages_key:
historic_messages = config["configurable"]["message_history"].messages
input_messages = input_messages[len(historic_messages) :]
# Get the output messages
output_val = load(run.outputs)
output_messages = self._get_output_messages(output_val)
hist.add_messages(input_messages + output_messages)
def _merge_configs(self, *configs: Optional[RunnableConfig]) -> RunnableConfig:
config = super()._merge_configs(*configs)
expected_keys = [field_spec.id for field_spec in self.history_factory_config]
configurable = config.get("configurable", {})
missing_keys = set(expected_keys) - set(configurable.keys())
if missing_keys:
example_input = {self.input_messages_key: "foo"}
example_configurable = {
missing_key: "[your-value-here]" for missing_key in missing_keys
}
example_config = {"configurable": example_configurable}
raise ValueError(
f"Missing keys {sorted(missing_keys)} in config['configurable'] "
f"Expected keys are {sorted(expected_keys)}."
f"When using via .invoke() or .stream(), pass in a config; "
f"e.g., chain.invoke({example_input}, {example_config})"
)
parameter_names = _get_parameter_names(self.get_session_history)
if len(expected_keys) == 1:
# If arity = 1, then invoke function by positional arguments
message_history = self.get_session_history(configurable[expected_keys[0]])
else:
# otherwise verify that names of keys patch and invoke by named arguments
if set(expected_keys) != set(parameter_names):
raise ValueError(
f"Expected keys {sorted(expected_keys)} do not match parameter "
f"names {sorted(parameter_names)} of get_session_history."
)
message_history = self.get_session_history(
**{key: configurable[key] for key in expected_keys}
)
config["configurable"]["message_history"] = message_history
return config
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献41条内容
已为社区贡献41条内容






所有评论(0)