使用 Vertex AI 构建 Prompt-to-SQL 系统
在实践中,构建 Prompt-to-SQL 就像构建一个普通的软件工程,中间需要一个语言模型:清晰的契约、可预测的解析器、优雅地处理故障的防护机制,以及指示何时迭代的指标。将其视为模型的世界。记录您实际发送的经过清理的提示、收到的 SQL 语句以及简短的解释。每次更改(例如提示调整、模型升级,甚至是库更新)时都运行这些提示,并跟踪执行率、列白名单的遵守情况、根据已知意图的过滤准确率以及系统请求澄清
将简单的语言转换为可靠的 SQL,与其说是神奇的提示符,不如说是建立用户、模型和数据库之间的精确关系。最可靠的系统始于定义一个明确而明确的契约,然后在代码中强制执行。其他一切——提示的艺术性、重试、缓存——都建立在这个基础上。
契约始于方言、范围内的单个表、精确的列列表以及默认的行限制。将其视为模型的世界。如果数据集包含同义词(例如“speed”、“kmh”和“speed_kmh”),请明确说明模型必须从给定的列中进行选择,并在没有合适的列时要求澄清。优秀的输出始于完善的上下文;发现模式(一小行样本就足够了),并每次都将其作为事实来源传递。
接下来是护栏。如果架构只允许SELECT在一个表上使用一个,请明确说明并验证。检查文本是否以 开头SELECT,是否拒绝 DDL/DML 或多个语句,以及是否仅引用允许的列。如果可能,请在访问数据库之前将请求的列与实时模式进行比较。这可以减少意外,并使错误处理变得简单——这正是您在生产环境中所需要的。
一致的提示形状会带来好处。保持系统消息稳定:提及方言、表格、列、单个示例记录和默认值LIMIT。保持用户消息专注于意图——过滤器、聚合、时间窗口、边界框——而不泄露实现细节。让模型返回应用程序可以确定性解析的严格 JSON:一个用于 SQL 的字段、一个简短的理由以及一个指示是否需要澄清的标志。如果标志为真,则 SQL 应该为空,并附带一个简洁的问题。这种约定使 UI 流程保持简单:要么执行,要么询问。
You are a SQL generator for agronomic operation points.
CONTEXT
• SQL DIALECT: {DIALECT}
• TABLE (single table only): {TABLE_NAME}
• COLUMNS (exact, case-sensitive): {COLUMNS_JSON_ARRAY}
• VALUES (example row, case-sensitive): {VALUES_JSON_ARRAY}
• TASK: From the user's request, produce ONE safe SELECT over {TABLE_NAME} only.
HARD RULES
1) Only SELECT. No DDL/DML/multiple statements.
2) Single table = {TABLE_NAME}. No JOINs.
3) Use only columns listed in COLUMNS.
4) Prefer simple predicates (ranges, =, IN, BETWEEN, LIKE) and basic aggregates.
5) Geospatial: use numeric lat/lon columns (e.g., lat BETWEEN a AND b AND lon BETWEEN c AND d).
6) Timestamps: use the column from COLUMNS; prefer ISO-8601 literals.
7) Always include LIMIT {DEFAULT_LIMIT} unless user asked otherwise.
8) If no suitable column exists, set "needs_clarification": true and DO NOT produce SQL.
9) Handle typos/synonyms only if a close match exists in COLUMNS.
10) STRICT JSON output (no markdown/code fences).
OUTPUT JSON SCHEMA
{
"sql": "string | empty if needs_clarification=true",
"reasoning": "short explanation",
"needs_clarification": "boolean",
"clarification_question": "string (optional)"
}由于模型有时会将答案包裹在代码围栏中或将其拆分成多个块,因此解析必须具有防御性。连接各个部分,去除多余的格式,并使用严格的错误处理机制解析 JSON。如果解析失败或调用超时,则提供安全的回退方案——设置澄清标志并返回一条有用的消息,以便对话继续进行,避免出现死胡同。
延迟控制主要在于减少往返次数。缓存提示符和模式快照的稳定部分。提供默认设置,LIMIT这样当用户只想快速浏览时,就无需获取数千行数据。跟踪时间的流向——排队、生成、解析、执行——并专注于最热门的路径。一次 LLM 调用通常会消耗比一次 SQL 查询更多的时间,因此请相应地调整优化力度。
最小集成足够小,可以一次性读完:获取示例行来构建列表,调用模型,在“需要说明”处分支,验证 SQL 语句并执行。大部分复杂性在于粘合代码(提示符的构建、解析和验证),而不是数据库层。保持粘合代码的可测试性,您将能够更改模型或提示符,而无需重写应用程序。
质量值得真正的衡量。使用您期望的 SQL 创建一小套自然语言提示。每次更改(例如提示调整、模型升级,甚至是库更新)时都运行这些提示,并跟踪执行率、列白名单的遵守情况、根据已知意图的过滤准确率以及系统请求澄清的频率。此处的少量自动化可以防止仅在负载下出现的静默回归。
良好的用户体验能将不确定性转化为动力。记录您实际发送的经过清理的提示、收到的 SQL 语句以及简短的解释。当模型发出疑问时,提出一个精确的问题并保存对话状态,这样用户就无需重复。如果数据库拒绝查询,则返回 SQL 语句、错误信息,以及(如果情况明显)一些小的修正。用户更容易原谅偶尔出现的“我不确定;是这个字段speed_kmh还是?”,而不是默默地忽略失败。speed_mph
与 Vertex AI 对话的客户端特意设计得很小:它构建一个稳定的系统提示(方言、单表、显式列列表、示例值、默认 LIMIT),附加用户请求,然后使用可配置模型(如 Gemini 2.5 Flash)调用 Vertex AI Java SDK(VertexAI、GenerativeModel)。响应被视为数据,而不是散文:代码栅栏被剥离,JSON 被解析,流程分支 -SELECT当模型发出不确定性信号或 SQL 为空时,执行已验证的或返回简洁的澄清问题。所有错误路径都会折叠到安全的后备(有界SELECT * … LIMIT N),因此 UI 永远不会死胡同。保持可观察性而不过度共享:记录形状和时间而不是原始提示或行值,并通过环境变量而不是硬编码来驱动项目、区域和模型。如果您的数据集包含地理空间字段,请保持提示指南的通用性(例如,显示如何使用lat/lon范围或距离排序),而无需嵌入私有表名或专有几何详细信息。这个包装器使数据库层变得无趣,模型可交换——改变配置,而不是应用程序设计。
package com.example.prompttosql;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.google.cloud.vertexai.VertexAI;
import com.google.cloud.vertexai.generativeai.GenerativeModel;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.util.List;
public class VertexAiSqlClient {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(VertexAiSqlClient.class);
private final String projectId;
private final String location;
private final String modelName;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public VertexAiSqlClient(String projectId, String location, String modelName) {
this.projectId = projectId;
this.location = location;
this.modelName = modelName;
}
public LlmSqlResult generateSql(
List<String> columns,
List<String> values,
String prompt,
String tableName,
int defaultLimit,
String dialect) {
if (projectId == null || projectId.isBlank()) {
log.warn("Vertex AI projectId not configured. Returning safe fallback.");
return new LlmSqlResult(
"SELECT * FROM " + tableName + " LIMIT " + defaultLimit,
"projectId missing; returned fallback",
false,
"",
"",
"");
}
final String systemPrompt = buildSystemPrompt(dialect, tableName, columns, values, defaultLimit);
final String combinedPrompt = systemPrompt + "\n\nUSER:\n" + prompt + "\n";
try {
final String text = callVertex(combinedPrompt);
// Strip fenced code (```json ... ```) if present
String payload = text;
if (payload.startsWith("```")) {
int first = payload.indexOf('{');
int last = payload.lastIndexOf('}');
if (first >= 0 && last > first) {
payload = payload.substring(first, last + 1);
}
}
JsonNode root = objectMapper.readTree(payload);
boolean needsClarification = root.path("needs_clarification").asBoolean(false);
String sql = root.path("sql").asText("");
String reasoning = root.path("reasoning").asText("");
String clarification = root.path("clarification_question").asText("");
String error = root.path("error").asText("");
String message = root.path("message").asText("");
if (needsClarification || sql.isBlank()) {
log.debug("Model requested clarification or returned empty SQL.");
return new LlmSqlResult(
"",
reasoning,
true,
clarification.isEmpty() ? "Could you clarify the desired columns/filters?" : clarification,
message,
error);
}
log.debug("Generated SQL ({} chars).", sql.length());
return new LlmSqlResult(sql, reasoning, false, "", message, error);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Vertex AI call failed: {}", e.toString());
return new LlmSqlResult(
"",
"Vertex error: " + e.getMessage(),
true,
"The model output was not valid JSON. Try rephrasing the request.",
"",
e.getMessage());
}
}
protected String callVertex(String combinedPrompt) throws Exception {
try (VertexAI vertexAi = new VertexAI(projectId, location)) {
GenerativeModel model = new GenerativeModel(modelName, vertexAi);
var response = model.generateContent(combinedPrompt);
log.debug("Vertex AI candidates: {}", response.getCandidatesCount());
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (!response.getCandidatesList().isEmpty()) {
var first = response.getCandidates(0);
var content = first.getContent();
for (int i = 0; i < content.getPartsCount(); i++) {
var p = content.getParts(i);
if (p.hasText()) sb.append(p.getText());
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
private String buildSystemPrompt(
String dialect, String tableName, List<String> columns, List<String> values, int defaultLimit) {
String columnsJson;
String valuesJson;
try {
columnsJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(columns);
valuesJson = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(values);
} catch (Exception e) {
columnsJson = "[]";
valuesJson = "[]";
}
return """
You are a SQL generator for a single relational table.
CONTEXT
- SQL DIALECT: %s
- TABLE (single table only): %s
- COLUMNS (exact, case-sensitive): %s
- VALUES (example values, case-sensitive): %s
- TASK: From the user's request, produce ONE safe SELECT statement over %s only.
HARD RULES (MUST FOLLOW)
1) Only SELECT is allowed. Absolutely NO INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE/TRUNCATE/CREATE/DROP/ALTER/GRANT/REVOKE.
2) Single table only = %s. No JOINs. No references to any other table.
3) Use only columns listed in COLUMNS for filters and projections.
4) Prefer simple predicates: ranges, equality, IN, BETWEEN, LIKE, and basic aggregates without joins.
5) Time filters must use the timestamp column if present and ISO-8601 literals when possible.
6) Always include LIMIT %d unless the user asked otherwise.
7) Never invent column names. If no close match exists, set "needs_clarification": true and DO NOT produce SQL.
8) Output must be STRICT JSON (no markdown, no comments, no fences).
OUTPUT JSON SCHEMA
{
"sql": "string | empty if needs_clarification=true",
"reasoning": "short explanation of column choices and filters",
"needs_clarification": "boolean",
"clarification_question": "string | optional when needs_clarification=true",
"error": "string | optional",
"message": "string | optional"
}
""".formatted(dialect, tableName, columnsJson, valuesJson, tableName, tableName, defaultLimit);
}
/** Minimal DTO for the LLM result. */
public record LlmSqlResult(
String sql,
String reasoning,
boolean needsClarification,
String clarificationQuestion,
String message,
String error) {}
}最后,将安全和隐私视为首要约束。不要让模型自行创建表名,而要注入它们。严格控制用户值。根据配置文件分离环境键和限制,并考虑采用更严格的生产模式,避免开放式、全模式的探索。如果数据敏感,请在上线前进行红队测试并运行越狱测试。最安全的系统是那些假设好奇心(包括人类和机器的好奇心)并围绕它进行设计的系统。
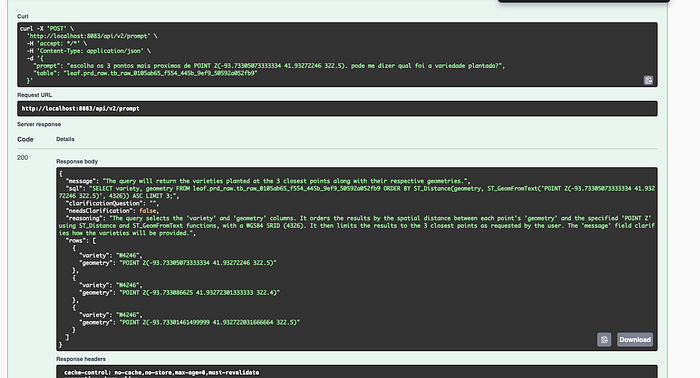
在实践中,构建 Prompt-to-SQL 就像构建一个普通的软件工程,中间需要一个语言模型:清晰的契约、可预测的解析器、优雅地处理故障的防护机制,以及指示何时迭代的指标。有了这些组件,您就可以逐步改进系统——交换模型、优化示例、调整限制——而不会危及稳定性。最终的结果不仅仅是按需 SQL,而是一个规范的工作流程,其中自然语言成为一种可靠的数据查询方式。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容







所有评论(0)