AI_agent rpc框架部分(一)
实现了四种通信模式(简单rpc通信、服务端流式rpc、客户端流式rpc、双向流式rpc),来适应不同的通信场景;(1)入口:客户端发起请求,a2a_client.cpp调用。
rpc框架实现
整体流程(大概)
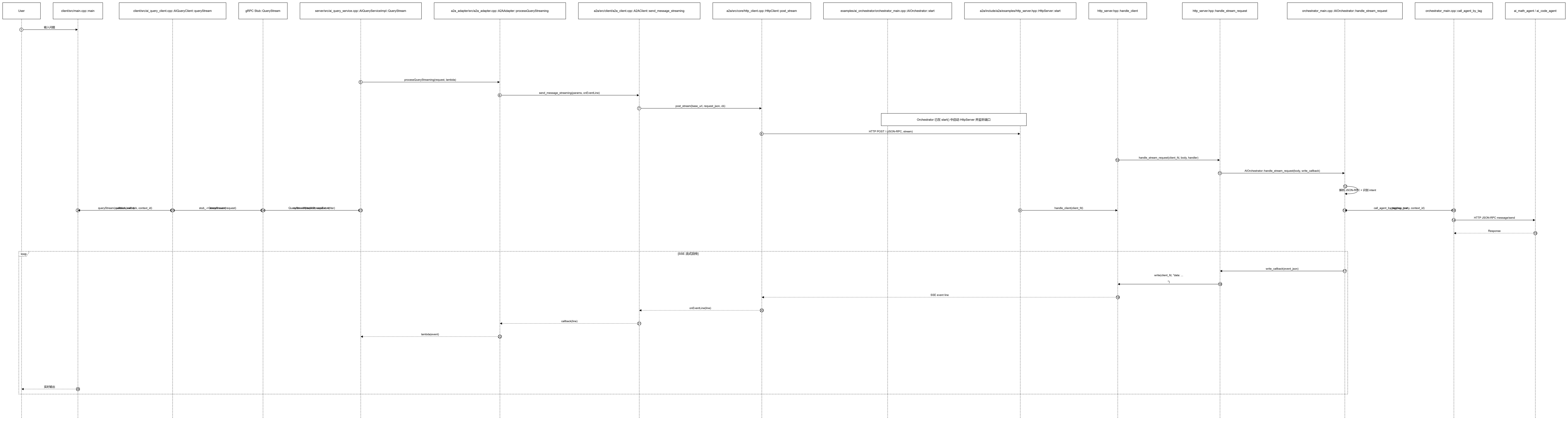
上面的图太模糊了,可以查看原图以用户流式请求为例,先说一下大致的流程
首先用户输入数据后agent-communication\client\src\main.cpp中的getline接收输入数据,client.queryStream处理消息
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
...
std::string line;
while (g_running) {
std::cout << "[" << context_id << (stream_mode ? "/流式" : "") << "] > ";
std::cout.flush();
//接收消息
if (!std::getline(std::cin, line)) {
// EOF 或输入错误,退出循环
if (std::cin.eof()) {
std::cout << "\n" << std::endl;
}
break;
}
// 检查是否收到退出信号
if (!g_running) {
break;
}
if (line == "/stream" || line == "/s") {
stream_mode = !stream_mode;
std::cout << "流式模式: " << (stream_mode ? "开启" : "关闭") << std::endl;
continue;
}
...
// 发送 AI 查询
std::cout << "\n思考中..." << std::endl;
if (stream_mode) {
// 流式查询
std::cout << "\nAI: ";
std::cout.flush();
//客户端开始调用处理函数
bool success = client.queryStream(line,
[](const agent_communication::AIStreamEvent& event) {
if (event.event_type() == "partial") {
std::cout << event.content();
std::cout.flush();
} else if (event.event_type() == "complete") {
std::cout << std::endl;
} else if (event.event_type() == "error") {
std::cout << "\n错误: " << event.content() << std::endl;
}
}, context_id, timeout_seconds);
if (!success) {
std::cout << "\n流式查询失败" << std::endl;
}
} else ...
}
agent-communication\client\src\ai_query_client.cpp的AIQueryClient::queryStream封装request消息,将request请求发送给server,读取返回的数据,调用callback进行处理
bool AIQueryClient::queryStream(
const std::string& question,
StreamEventCallback callback,
const std::string& context_id,
int timeout_seconds) {
//封装成request
agent_communication::AIQueryRequest request;
request.set_request_id(generateRequestId());
request.set_question(question);
request.set_context_id(context_id);
request.set_timeout_seconds(timeout_seconds);
return queryStream(request, callback);
}
bool AIQueryClient::queryStream(
const agent_communication::AIQueryRequest& request,
StreamEventCallback callback) {
if (!connected_) {
LOG_ERROR("AIQueryClient not connected");
return false;
}
if (!callback) {
LOG_ERROR("No callback provided for streaming query");
return false;
}
auto start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
grpc::ClientContext context;
// Set deadline
int timeout = request.timeout_seconds() > 0 ? request.timeout_seconds() : 60;
auto deadline = std::chrono::system_clock::now() +
std::chrono::seconds(timeout);
context.set_deadline(deadline);
LOG_INFO("Starting streaming AI query: " + request.request_id());
//发起gRPC的流式rpc调用并在客户端创建一个client对象
std::unique_ptr<grpc::ClientReader<agent_communication::AIStreamEvent>> reader(
stub_->QueryStream(&context, request));
if (!reader) {
LOG_ERROR("Failed to create stream reader");
return false;
}
agent_communication::AIStreamEvent event;
int event_count = 0;
//gRPC C++ 的流式读取接口
while (reader->Read(&event)) {
event_count++;
//读取数据后调用callback进行处理
callback(event);
// Check for completion or error
if (event.event_type() == "complete" || event.event_type() == "error") {
break;
}
}
grpc::Status status = reader->Finish();
auto end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
end_time - start_time);
if (status.ok()) {
LOG_INFO("Streaming AI query completed: " + request.request_id() +
" with " + std::to_string(event_count) + " events" +
" in " + std::to_string(duration.count()) + "ms");
return true;
} else {
LOG_ERROR("Streaming AI query failed: " + request.request_id() +
" - " + status.error_message());
return false;
}
}
server中的agent-communication\server\src\ai_query_service.cpp中的AIQueryServiceImpl::QueryStream接着进行处理,调用a2a_adapter_->processQueryStreaming接着处理
grpc::Status AIQueryServiceImpl::QueryStream(
grpc::ServerContext* context,
const agent_communication::AIQueryRequest* request,
grpc::ServerWriter<agent_communication::AIStreamEvent>* writer) {
...
bool success = true;
std::string error_message;
// Process streaming query
a2a_adapter_->processQueryStreaming(*request,
[&context, &writer, &success, &error_message](
const agent_communication::AIStreamEvent& event) {
// Check for cancellation
if (context->IsCancelled()) {
success = false;
error_message = "Request cancelled";
return;
}
// Write event to stream
if (!writer->Write(event)) {
success = false;
error_message = "Failed to write stream event";
}
});
...
}
agent-communication\a2a_adapter\src\a2a_adapter.cpp中的A2AAdapter::processQueryStreaming将request请求传换成A2A格式,然后发送给a2a_client_
void A2AAdapter::processQueryStreaming(
const agent_communication::AIQueryRequest& request,
std::function<void(const agent_communication::AIStreamEvent&)> callback) {
if (!initialized_ || !callback || !config_.enable_streaming) {
return;
}
try {
// Convert RPC request to A2A format
a2a::MessageSendParams params = request_adapter_->convertToA2A(request);
std::string context_id = params.context_id().value_or("");
// Use streaming API
// 注意:http_client按双换行符切分数据,每次回调收到完整的SSE事件
a2a_client_->send_message_streaming(params,
[this, &callback, &context_id](const std::string& event_line) {
// 跳过空行
if (event_line.empty() || event_line == "\n" || event_line == "\r\n") {
return;
}
// 解析SSE格式: "data: {...}\n" 或 "data: {...}"
std::string event_data = event_line;
// 移除行尾换行符
while (!event_data.empty() &&
(event_data.back() == '\n' || event_data.back() == '\r')) {
event_data.pop_back();
}
// 提取data:后面的内容
const std::string data_prefix = "data: ";
if (event_data.find(data_prefix) == 0) {
event_data = event_data.substr(data_prefix.length());
}
// 跳过空数据
if (event_data.empty()) {
return;
}
// 解析 JSON 响应,捕获所有 JSON 异常(包括 UTF-8 错误)
json j;
try {
j = json::parse(event_data);
} catch (const json::exception& e) {
// JSON 解析失败(包括 UTF-8 错误),跳过这个事件
return;
}
try {
// 检查是否有错误
if (j.contains("error")) {
agent_communication::AIStreamEvent event;
std::string error_msg = j["error"].value("message", "Unknown error");
response_adapter_->buildStreamEvent(
error_msg, context_id, "error", &event);
callback(event);
return;
}
// 检查是否有结果
if (j.contains("result")) {
auto& result = j["result"];
std::string type = result.value("type", "");
if (type == "chunk") {
// 流式内容块
std::string content = result.value("content", "");
agent_communication::AIStreamEvent event;
response_adapter_->buildStreamEvent(
content, context_id, "partial", &event);
callback(event);
} else if (type == "stream_start") {
// 流开始事件
agent_communication::AIStreamEvent event;
response_adapter_->buildStreamEvent(
"", context_id, "status", &event);
event.set_task_state("processing");
callback(event);
} else if (type == "stream_end") {
// 流结束事件 - 不在这里发送 complete,让外层处理
} else if (type == "intent") {
// 意图识别事件
agent_communication::AIStreamEvent event;
std::string intent = result.value("intent", "");
response_adapter_->buildStreamEvent(
"Intent: " + intent, context_id, "status", &event);
callback(event);
}
}
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
// 处理结果时出错,跳过
}
});
// Send completion event
agent_communication::AIStreamEvent complete_event;
response_adapter_->buildStreamEvent(
"", context_id, "complete", &complete_event);
callback(complete_event);
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
// Send error event
agent_communication::AIStreamEvent error_event;
response_adapter_->buildStreamEvent(
e.what(), request.context_id(), "error", &error_event);
callback(error_event);
}
}
agent-communication\a2a\src\client\a2a_client.cpp中的A2AClient::send_message_streaming发送post_stream消息
void A2AClient::send_message_streaming(const MessageSendParams& params,
std::function<void(const std::string&)> callback) {
// Serialize params to JSON
std::string params_json = params.to_json();
// Create JSON-RPC request
JsonRpcRequest request(generate_uuid(), A2AMethods::MESSAGE_STREAM, params_json);
std::string request_json = request.to_json();
// Send streaming POST request
impl_->http_client_.post_stream(
impl_->base_url_,
request_json,
"application/json",
callback
);
}
agent-communication\a2a\src\core\http_client.cpp中的HttpClient::post_stream就是封装的流式请求
void HttpClient::post_stream(const std::string& url,
const std::string& body,
const std::string& content_type,
std::function<void(const std::string&)> callback) {
CURL* curl = curl_easy_init();
if (!curl) {
throw A2AException("Failed to initialize CURL", ErrorCode::InternalError);
}
// 创建流式处理上下文,处理UTF-8边界问题
StreamContext ctx;
ctx.callback = &callback;
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_URL, url.c_str());
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_POST, 1L);
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, body.c_str());
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDSIZE, body.length());
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_WRITEFUNCTION, stream_callback);
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_WRITEDATA, &ctx); // 传递上下文而非直接传递callback
// 流式请求:禁用总超时,使用低速超时
// 如果60秒内没有收到任何数据才超时
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_TIMEOUT, 0L); // 禁用总超时
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_LIMIT, 1L); // 最低速度 1 byte/s
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_LOW_SPEED_TIME, 60L); // 60秒内低于最低速度则超时
// Set headers
struct curl_slist* header_list = nullptr;
header_list = curl_slist_append(header_list, ("Content-Type: " + content_type).c_str());
header_list = curl_slist_append(header_list, "Accept: text/event-stream");
for (const auto& [key, value] : impl_->headers_) {
std::string header = key + ": " + value;
header_list = curl_slist_append(header_list, header.c_str());
}
curl_easy_setopt(curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, header_list);
CURLcode res = curl_easy_perform(curl);
// 刷新剩余缓冲区
ctx.flush();
curl_slist_free_all(header_list);
curl_easy_cleanup(curl);
if (res != CURLE_OK) {
throw A2AException(
std::string("CURL error: ") + curl_easy_strerror(res),
ErrorCode::InternalError
);
}
}
之后agent-communication\examples\ai_orchestrator\orchestrator_main.cpp中的start(int port)会启动agent-communication\a2a\include\a2a\examples\http_server.hpp的start()会开始监听消息,收到消息后this->handle_client来进行处理
// 接受连接
while (running_) {
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t client_len = sizeof(client_addr);
// 程序运行到这行时,操作系统会让当前线程“睡觉”(挂起,Sleep)
//client_fd 对应的 内核中的TCP 连接(也就是 Orchestrator HTTP Server 与客户端之间的连接)。
//accept() 会返回一个 已经建立连接的 socket 描述符
int client_fd = accept(server_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &client_len);
if (client_fd < 0) {
continue;
}
// 处理请求(在新线程中)
std::thread([this, client_fd]() {
this->handle_client(client_fd);
}).detach();
}
agent-communication\a2a\include\a2a\examples\http_server.hpp中的handle_client处理请求,找到对应请求的处理函数
void handle_client(int client_fd) {
char buffer[8192] = {0};
ssize_t bytes_read = read(client_fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
if (bytes_read <= 0) {
close(client_fd);
return;
}
std::string request(buffer, bytes_read);
// 解析 HTTP 请求
std::istringstream request_stream(request);
std::string method, path, version;
request_stream >> method >> path >> version;
// 提取请求体
std::string body;
size_t body_pos = request.find("\r\n\r\n");
if (body_pos != std::string::npos) {
body = request.substr(body_pos + 4);
}
// 检查是否需要流式响应(通过检查请求体中的 method)
bool is_stream_request = false;
if (!body.empty()) {
// 简单检查是否包含 message/stream 方法
is_stream_request = (body.find("\"message/stream\"") != std::string::npos);
}
// 优先检查流式处理器
auto stream_it = stream_handlers_.find(path);
if (is_stream_request && stream_it != stream_handlers_.end()) {
handle_stream_request(client_fd, body, stream_it->second);
return;
}
// 查找普通处理器
std::string response_body;
int status_code = 200;
auto it = handlers_.find(path);
if (it != handlers_.end()) {
try {
response_body = it->second(body);
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
status_code = 500;
response_body = std::string("{\"error\":\"") + e.what() + "\"}";
}
} else {
status_code = 404;
response_body = "{\"error\":\"Not Found\"}";
}
// 构造 HTTP 响应
std::ostringstream response;
response << "HTTP/1.1 " << status_code << " OK\r\n";
response << "Content-Type: application/json\r\n";
response << "Content-Length: " << response_body.length() << "\r\n";
response << "Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *\r\n";
response << "\r\n";
response << response_body;
std::string response_str = response.str();
write(client_fd, response_str.c_str(), response_str.length());
close(client_fd);
}
handle_stream_request设置响应头,调用处理器handler
void handle_stream_request(int client_fd, const std::string& body, StreamHandler& handler) {
// 发送 SSE 响应头
std::ostringstream header;
header << "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n";
header << "Content-Type: text/event-stream\r\n";
header << "Cache-Control: no-cache\r\n";
header << "Connection: keep-alive\r\n";
header << "Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *\r\n";
header << "\r\n";
std::string header_str = header.str();
if (write(client_fd, header_str.c_str(), header_str.length()) < 0) {
close(client_fd);
return;
}
// 调用流式处理器,传入写入回调
try {
handler(body, [client_fd](const std::string& event_data) -> bool {
// 格式化为 SSE 事件
std::string sse_event = "data: " + event_data + "\n\n";
ssize_t written = write(client_fd, sse_event.c_str(), sse_event.length());
return written > 0;
});
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
// 发送错误事件
std::string error_event = "data: {\"error\":\"" + std::string(e.what()) + "\"}\n\n";
write(client_fd, error_event.c_str(), error_event.length());
}
close(client_fd);
}
agent-communication\examples\ai_orchestrator\orchestrator_main.cpp中的handle_stream_request处理流式请求 (message/stream)
void handle_stream_request(const std::string& body,
std::function<bool(const std::string&)> write_callback) {
try {
auto request_json = json::parse(body);
auto request = JsonRpcRequest::from_json(body);
if (request.method() != "message/stream") {
// 非流式方法,返回错误
json error_response = {
{"jsonrpc", "2.0"},
{"id", request.id()},
{"error", {
{"code", -32601},
{"message", "Method not found for streaming"}
}}
};
write_callback(error_response.dump());
return;
}
auto params_json = request_json["params"];
auto message = AgentMessage::from_json(params_json["message"].dump());
// 获取文本内容
std::string user_text;
if (!message.parts().empty()) {
auto text_part = dynamic_cast<TextPart*>(message.parts()[0].get());
if (text_part) {
user_text = text_part->text();
}
}
std::string context_id = message.context_id().value_or("default");
std::cout << "[Orchestrator] 收到流式消息: " << user_text << std::endl;
// 保存用户消息
save_message(context_id, message);
// 发送开始事件
json start_event = {
{"jsonrpc", "2.0"},
{"id", request.id()},
{"result", {
{"type", "stream_start"},
{"contextId", context_id}
}}
};
write_callback(start_event.dump());
// 识别意图
std::string intent = analyze_intent(user_text);
std::cout << "[Orchestrator] 识别意图: " << intent << std::endl;
// 发送意图识别事件
json intent_event = {
{"jsonrpc", "2.0"},
{"id", request.id()},
{"result", {
{"type", "intent"},
{"intent", intent}
}}
};
write_callback(intent_event.dump());
// 处理查询并流式返回
std::string response_text;
if (intent == "math") {
response_text = call_math_agent(user_text, context_id);
} else if (intent == "code") {
response_text = call_code_agent(user_text, context_id);
} else {
response_text = handle_general_query(user_text, context_id);
}
// UTF-8 安全的分块函数
auto utf8_safe_chunk = [](const std::string& text, size_t start, size_t max_len) -> std::string {
if (start >= text.length()) return "";
size_t end = std::min(start + max_len, text.length());
// 确保不在 UTF-8 多字节字符中间切断
while (end > start && end < text.length()) {
unsigned char c = static_cast<unsigned char>(text[end]);
// 如果是 UTF-8 后续字节 (10xxxxxx),向前移动
if ((c & 0xC0) == 0x80) {
end--;
} else {
break;
}
}
return text.substr(start, end - start);
};
// 流式输出:UTF-8 安全分块
const size_t chunk_size = 50;
size_t pos = 0;
while (pos < response_text.length()) {
std::string chunk = utf8_safe_chunk(response_text, pos, chunk_size);
if (chunk.empty()) break;
pos += chunk.length();
json chunk_event = {
{"jsonrpc", "2.0"},
{"id", request.id()},
{"result", {
{"type", "chunk"},
{"content", chunk}
}}
};
if (!write_callback(chunk_event.dump())) {
std::cerr << "[Orchestrator] 流式写入失败" << std::endl;
return;
}
// 小延迟模拟流式效果
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(10));
}
// 保存 Agent 响应
auto response_msg = AgentMessage::create()
.with_role(MessageRole::Agent)
.with_context_id(context_id);
response_msg.add_text_part(response_text);
save_message(context_id, response_msg);
// 发送完成事件
json complete_event = {
{"jsonrpc", "2.0"},
{"id", request.id()},
{"result", {
{"type", "stream_end"},
{"message", response_msg.to_json()}
}}
};
write_callback(complete_event.dump());
std::cout << "[Orchestrator] 流式响应完成" << std::endl;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "[Orchestrator] 流式处理错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
json error_event = {
{"jsonrpc", "2.0"},
{"id", "1"},
{"error", {
{"code", -32603},
{"message", e.what()}
}}
};
write_callback(error_event.dump());
}
}
根据意图识别选择对应的工作agent,比如是code agent
std::string call_code_agent(const std::string& query, const std::string& context_id) {
return call_agent_by_tag("code", query, context_id);
}
call_agent_by_tag查找指定的agent并发送请求
std::string call_agent_by_tag(const std::string& tag,
const std::string& query,
const std::string& context_id) {
try {
// 从注册中心查找 Agent
std::string agent_url = registry_client_.select_agent_by_tag(tag);
std::cout << "[Orchestrator] 调用 " << tag << " Agent: " << agent_url << std::endl;
// 构造请求
json request = {
{"jsonrpc", "2.0"},
{"id", "1"},
{"method", "message/send"},
{"params", {
{"message", {
{"role", "user"},
{"contextId", context_id},
{"parts", {{{"kind", "text"}, {"text", query}}}}
}},
{"historyLength", 5}
}}
};
// 发送请求
std::string response_body = SimpleHttpClient::post(agent_url, request.dump());
auto response_json = json::parse(response_body);
if (response_json.contains("result") &&
response_json["result"].contains("parts") &&
!response_json["result"]["parts"].empty()) {
return response_json["result"]["parts"][0]["text"].get<std::string>();
}
return "无法解析响应";
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "[Orchestrator] 调用 " << tag << " Agent 失败: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return "抱歉," + tag + " 服务暂时不可用,使用通用模型回答";
}
}
这样流式请求的链路就通了
四种通讯模式
心跳机制
心跳机制时序图
客户端实现1.启动心跳进程
// 文件: src/rpc_client.cpp:642-650
void RpcClient::startHeartbeat() {
if (heartbeat_running_) {
return; // 防止重复启动
}
heartbeat_running_ = true;
heartbeat_thread_ = std::thread([this]() {
heartbeatLoop(); // 在独立线程中运行心跳循环
});
}
2.心跳循环主题
// 文件: src/rpc_client.cpp:662-677
void RpcClient::heartbeatLoop() {
while (heartbeat_running_) {
if (connected_ && !current_agent_id_.empty()) {
// 发送心跳
if (!sendHeartbeat(current_agent_id_, current_agent_info_)) {
// ❌ 心跳失败处理
LOG_WARN("Heartbeat failed, attempting reconnection");
connected_ = false;
if (!reconnect()) {
LOG_ERROR("Failed to reconnect, stopping heartbeat");
break; // 重连失败,停止心跳
}
}
}
// 等待下一次心跳间隔(默认30秒)
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(config_.heartbeat_interval));
}
}
3.发送心跳请求
// 文件: src/rpc_client.cpp:420-455
bool RpcClient::sendHeartbeat(const std::string& agent_id,
const ServiceEndpoint& agent_info) {
if (!connected_) {
return false;
}
try {
// 构建心跳请求
agent_communication::HeartbeatRequest request;
request.set_agent_id(agent_id);
auto* info = request.mutable_agent_info();
info->set_host(agent_info.host);
info->set_port(agent_info.port);
info->set_service_name(agent_info.service_name);
info->set_version(agent_info.version);
agent_communication::HeartbeatResponse response;
grpc::ClientContext context;
// 设置超时(10秒)
auto deadline = std::chrono::system_clock::now() + std::chrono::seconds(10);
context.set_deadline(deadline);
// 发送 gRPC 请求
grpc::Status status = stub_->Heartbeat(&context, request, &response);
// 检查结果
if (status.ok() && response.status().code() == 0) {
return true;
} else {
LOG_WARN("Heartbeat failed: " +
(status.ok() ? response.status().message() : status.error_message()));
return false;
}
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
LOG_WARN("Heartbeat error: " + std::string(e.what()));
return false;
}
}
服务端实现1.处理心跳请求
// 文件: src/rpc_server.cpp:404-429
grpc::Status AgentCommunicationServiceImpl::Heartbeat(
grpc::ServerContext* context,
const agent_communication::HeartbeatRequest* request,
agent_communication::HeartbeatResponse* response) {
try {
// 记录指标
auto metrics = Metrics::getInstance();
metrics->recordRpcRequest("AgentCommunicationService", "Heartbeat", 0);
// 更新 Agent 心跳时间
updateAgentHeartbeat(request->agent_id());
// 返回成功响应
response->mutable_status()->set_code(0);
response->mutable_status()->set_message("Success");
response->set_server_time(/* 当前时间戳 */);
return grpc::Status::OK;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
// 服务器错误
LOG_ERROR("Error in Heartbeat: " + std::string(e.what()));
response->mutable_status()->set_code(2); // 错误码2:服务器内部错误
response->mutable_status()->set_message("Internal server error");
metrics->recordRpcError("AgentCommunicationService", "Heartbeat", "InternalError");
return grpc::Status::OK;
}
}
2.更新心跳时间戳
// 文件: src/rpc_server.cpp:105-111
void AgentCommunicationServiceImpl::updateAgentHeartbeat(const std::string& agent_id) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(agents_mutex_); // 线程安全
auto it = agents_.find(agent_id);
if (it != agents_.end()) {
it->second.last_heartbeat = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
}
}
3.清理离线 Agent
// 文件: src/rpc_server.cpp:113-128
void AgentCommunicationServiceImpl::cleanupOfflineAgents() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(agents_mutex_);
auto now = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto timeout = std::chrono::seconds(60); // 60秒超时
auto it = agents_.begin();
while (it != agents_.end()) {
if (now - it->second.last_heartbeat > timeout) {
// Agent 超时,清理资源
LOG_WARN("Agent offline, removing: " + it->first);
agent_message_queues_.erase(it->first); // 清理消息队列
it = agents_.erase(it); // 移除 Agent
} else {
++it;
}
}
}
重连机制
// 文件: client/src/rpc_client.cpp:234-255
bool RpcClient::reconnect() {
// 检查重试次数上限
if (connection_retry_count_ >= MAX_RETRY_COUNT) {
LOG_ERROR("Max reconnection attempts reached");
return false;
}
// 指数退避:第N次重连等待 N * RETRY_DELAY_MS 毫秒
std::this_thread::sleep_for(
std::chrono::milliseconds(RETRY_DELAY_MS * (connection_retry_count_ + 1)));
try {
setupChannel(); // 重新建立 gRPC 通道
connected_ = true;
connection_retry_count_ = 0; // 重置计数器
last_connection_time_ = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
LOG_INFO("Reconnected to server successfully");
return true;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
connection_retry_count_++; // 增加重试计数
LOG_ERROR("Reconnection failed: " + std::string(e.what()));
return false;
}
}
监控与指标
架构总览
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 性能监控系统架构 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 应用层(埋点) │ │
│ │ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐ │ │
│ │ │rpc_server │ │rpc_client │ │ai_query │ │a2a_adapter│ │ │
│ │ │ .cpp │ │ .cpp │ │service.cpp│ │ .cpp │ │ │
│ │ └─────┬─────┘ └─────┬─────┘ └─────┬─────┘ └─────┬─────┘ │ │
│ └────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Metrics 管理器(单例) │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ recordRpcRequest() | recordConnection() | recordMessage() | ...│ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ↓ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ MetricsCollector(指标收集器) │ │
│ │ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Counter │ │ Gauge │ │Histogram │ │ Summary │ │ │
│ │ │ 计数器 │ │ 仪表盘 │ │ 直方图 │ │ 摘要 │ │ │
│ │ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ↓ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ 导出层 │ │
│ │ exportPrometheus() exportJson() │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ ↓ ↓ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────┐ ┌────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Prometheus │ │ Grafana/ │ │ │
│ │ │ Server │ │ Dashboard │ │ │
│ │ └────────────┘ └────────────┘ │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
四种指标类型详解
Counter(计数器)特点:只能增加,不能减少,重启后归零
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:48-72
class CounterMetric : public Metric {
public:
void increment(double value = 1.0); // 增加
void set(double value); // 设置(只能比当前值大)
double get() const; // 获取当前值
void reset(); // 重置
private:
std::atomic<double> value_{0.0}; // 原子变量,线程安全
};
使用场景
- RPC 请求总数
- 错误发生次数
- 消息发送/接收总数
Gauge(仪表盘)特点:可增可减,表示瞬时值
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:74-99
class GaugeMetric : public Metric {
public:
void set(double value); // 设置
void increment(double value = 1.0); // 增加
void decrement(double value = 1.0); // 减少
double get() const; // 获取当前值
private:
std::atomic<double> value_{0.0};
};
使用场景
- 当前活跃连接数
- 内存使用量
- CPU 使用率
Histogram(直方图)特点:统计数据分布,按桶(bucket)分组
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:101-130
class HistogramMetric : public Metric {
public:
// 默认桶: 0.005, 0.01, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 10.0, ∞
HistogramMetric(const std::string& name,
const std::vector<double>& buckets = {...});
void observe(double value); // 记录一个观测值
double getSum() const; // 所有观测值的总和
uint64_t getCount() const; // 观测次数
std::vector<HistogramBucket> getBuckets() const; // 获取桶分布
private:
std::vector<HistogramBucket> buckets_;
std::atomic<double> sum_{0.0};
std::atomic<uint64_t> count_{0};
};
使用场景
- RPC 请求延迟分布
- 消息大小分布
Summary(摘要)特点:计算分位数(P50, P90, P95, P99)
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:132-165
class SummaryMetric : public Metric {
public:
// 默认分位数: 0.5, 0.9, 0.95, 0.99
SummaryMetric(const std::string& name,
const std::vector<double>& quantiles = {0.5, 0.9, 0.95, 0.99});
void observe(double value);
std::map<double, double> getQuantiles() const; // 获取各分位数值
private:
std::vector<double> values_; // 存储所有观测值
std::map<double, double> quantile_values_; // 分位数结果
};
使用场景
- 请求延迟的 P99 值
- 精确的性能 SLA 监控
四类监控指标的具体实现
RPC 请求指标
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:225-228
class Metrics {
// RPC相关指标
void recordRpcRequest(const std::string& service, const std::string& method, double duration_ms);
void recordRpcResponse(const std::string& service, const std::string& method, int status_code);
void recordRpcError(const std::string& service, const std::string& method, const std::string& error_type);
private:
std::shared_ptr<CounterMetric> rpc_request_counter_; // 请求计数器
std::shared_ptr<HistogramMetric> rpc_duration_histogram_; // 延迟直方图
std::shared_ptr<CounterMetric> rpc_error_counter_; // 错误计数器
};
//实现细节
// 文件: src/metrics.cpp:473-489
void Metrics::recordRpcRequest(const std::string& service,
const std::string& method,
double duration_ms) {
if (!rpc_request_counter_) {
initializeDefaultMetrics();
}
// 1. 增加请求计数
rpc_request_counter_->increment();
// 2. 记录延迟分布(转换为秒)
if (rpc_duration_histogram_) {
rpc_duration_histogram_->observe(duration_ms / 1000.0);
}
}
连接指标
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:230-232
void recordConnection(const std::string& service, bool success);
void recordDisconnection(const std::string& service);
private:
std::shared_ptr<GaugeMetric> active_connections_gauge_; // 活跃连接数
//实现细节
// 文件: src/metrics.cpp:503-518
void Metrics::recordConnection(const std::string& service, bool success) {
if (success) {
// 连接成功,活跃连接数 +1
if (active_connections_gauge_) {
active_connections_gauge_->increment();
}
}
}
void Metrics::recordDisconnection(const std::string& service) {
// 断开连接,活跃连接数 -1
if (active_connections_gauge_) {
active_connections_gauge_->decrement();
}
}
消息指标
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:234-236
void recordMessageSent(const std::string& message_type, size_t size);
void recordMessageReceived(const std::string& message_type, size_t size);
private:
std::shared_ptr<CounterMetric> message_counter_; // 消息计数器
//实现细节
// 文件: src/metrics.cpp:519-535
void Metrics::recordMessageSent(const std::string& message_type, size_t size) {
if (!message_counter_) {
initializeDefaultMetrics();
}
// 记录发送消息数量
message_counter_->increment();
// 可以额外记录消息大小到直方图
}
void Metrics::recordMessageReceived(const std::string& message_type, size_t size) {
if (!message_counter_) {
initializeDefaultMetrics();
}
message_counter_->increment();
}
系统资源指标
// 文件: include/agent_rpc/metrics.h:238-240
void recordMemoryUsage(size_t bytes);
void recordCpuUsage(double percentage);
private:
std::shared_ptr<GaugeMetric> memory_usage_gauge_; // 内存使用
std::shared_ptr<GaugeMetric> cpu_usage_gauge_; // CPU 使用
//实现细节
// 文件: src/metrics.cpp:537-553
void Metrics::recordMemoryUsage(size_t bytes) {
if (!memory_usage_gauge_) {
initializeDefaultMetrics();
}
memory_usage_gauge_->set(static_cast<double>(bytes));
}
void Metrics::recordCpuUsage(double percentage) {
if (!cpu_usage_gauge_) {
initializeDefaultMetrics();
}
cpu_usage_gauge_->set(percentage);
}
项目中的实际使用场景
场景 1:服务端 RPC 方法监控
// 文件: src/rpc_server.cpp:131-186
grpc::Status AgentCommunicationServiceImpl::SendMessage(...) {
try {
// 1️⃣ 方法开始:记录请求
auto metrics = Metrics::getInstance();
metrics->recordRpcRequest("AgentCommunicationService", "SendMessage", 0);
auto start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
// ... 业务逻辑 ...
// 2️⃣ 方法结束:记录耗时
auto end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
end_time - start_time);
metrics->recordRpcRequest("AgentCommunicationService", "SendMessage",
duration.count());
return grpc::Status::OK;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
// 3️⃣ 异常时:记录错误
auto metrics = Metrics::getInstance();
metrics->recordRpcError("AgentCommunicationService", "SendMessage",
"InternalError");
return grpc::Status(grpc::StatusCode::INTERNAL, e.what());
}
}
场景 2:客户端 RPC 调用监控
// 文件: src/rpc_client.cpp:71-113
bool RpcClient::sendMessage(const std::string& message, ...) {
try {
auto metrics = Metrics::getInstance();
auto start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
// ... gRPC 调用 ...
grpc::Status status = stub_->SendMessage(&context, request, &response);
auto end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
auto duration = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
end_time - start_time);
if (status.ok()) {
// ✅ 成功:记录请求和响应
metrics->recordRpcRequest("AgentCommunicationService", "SendMessage",
duration.count());
metrics->recordRpcResponse("AgentCommunicationService", "SendMessage",
response.status().code());
return true;
} else {
// ❌ gRPC 错误:记录错误类型
metrics->recordRpcError("AgentCommunicationService", "SendMessage",
"GrpcError");
return false;
}
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
metrics->recordRpcError("AgentCommunicationService", "SendMessage",
"Exception");
return false;
}
}
场景 3:AI 查询服务监控
// 文件: server/src/ai_query_service.cpp:229-242
void AIQueryServiceImpl::recordMetrics(const std::string& method,
int64_t duration_ms,
bool success) {
auto& metrics = common::Metrics::getInstance();
// 记录请求
metrics.recordRpcRequest("AIQueryService", method, duration_ms);
if (success) {
// 成功
metrics.recordRpcResponse("AIQueryService", method, 0);
} else {
// 失败
metrics.recordRpcError("AIQueryService", method, "Error");
}
}
场景 4:A2A 适配器专用指标
// 文件: a2a_adapter/include/agent_rpc/a2a_adapter/a2a_metrics.h
class A2AMetrics {
// 查询指标
void recordQueryRequest(const std::string& agent_id, bool streaming);
void recordQueryComplete(const std::string& agent_id, int64_t duration_ms, bool success);
void recordQueryError(const std::string& agent_id, const std::string& error_type);
// 任务指标
void recordTaskCreated(const std::string& task_id);
void recordTaskStateChange(const std::string& task_id, const std::string& from, const std::string& to);
void recordTaskComplete(const std::string& task_id, int64_t duration_ms, bool success);
// Agent 指标
void recordAgentRegistered(const std::string& agent_id);
void recordAgentUnregistered(const std::string& agent_id);
void recordAgentHealthCheck(const std::string& agent_id, bool healthy);
void recordAgentRouting(const std::string& from, const std::string& to, const std::string& skill);
// 连接指标
void recordConnectionAttempt(const std::string& target_url, bool success);
void recordMessageSent(const std::string& message_type, size_t size_bytes);
void recordMessageReceived(const std::string& message_type, size_t size_bytes);
private:
// 原子计数器
std::atomic<uint64_t> total_queries_{0};
std::atomic<uint64_t> successful_queries_{0};
std::atomic<uint64_t> failed_queries_{0};
std::atomic<uint64_t> streaming_queries_{0};
std::atomic<uint64_t> total_query_latency_ms_{0};
// ... 更多计数器
};
Prometheus 格式
// 文件: src/metrics.cpp:583-585
std::string Metrics::exportPrometheus() const {
return MetricsCollector::getInstance().exportPrometheus();
}
//输出格式
# HELP rpc_requests_total Total number of RPC requests
# TYPE rpc_requests_total counter
rpc_requests_total{service="AgentCommunicationService",method="SendMessage"} 1523
# HELP rpc_request_duration_seconds RPC request duration in seconds
# TYPE rpc_request_duration_seconds histogram
rpc_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.005"} 100
rpc_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.01"} 250
rpc_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.025"} 500
rpc_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="0.05"} 800
rpc_request_duration_seconds_bucket{le="+Inf"} 1523
rpc_request_duration_seconds_sum 45.67
rpc_request_duration_seconds_count 1523
# HELP active_connections Current active connections
# TYPE active_connections gauge
active_connections{service="AgentCommunicationService"} 15
# HELP memory_usage_bytes Current memory usage in bytes
# TYPE memory_usage_bytes gauge
memory_usage_bytes 134217728
JSON 格式
// 文件: src/metrics.cpp:587-589
std::string Metrics::exportJson() const {
return MetricsCollector::getInstance().exportJson();
}
//输出示例
{
"metrics": [
{
"name": "rpc_requests_total",
"type": "counter",
"value": 1523,
"labels": {
"service": "AgentCommunicationService",
"method": "SendMessage"
}
},
{
"name": "active_connections",
"type": "gauge",
"value": 15,
"labels": {
"service": "AgentCommunicationService"
}
},
{
"name": "memory_usage_bytes",
"type": "gauge",
"value": 134217728
}
]
}
熔断机制开发
加入熔断机制的好处
1.快速失败,节省资源
// 无熔断:每次请求都要等超时
auto response = client.query(question); // 等 30 秒...
// 有熔断:直接快速失败
if (circuit_breaker->getState() == CircuitState::OPEN) {
return "服务暂不可用"; // 立即返回
}
2. 防止级联故障(雪崩效应)
无熔断时的雪崩:
┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌────────┐
│ 用户端 │ → │ 网关 │ → │ 服务A │ → │ 服务B │ (宕机)
└────────┘ └────────┘ └────────┘ └────────┘
↑ ↑ ↑
线程阻塞 线程阻塞 线程阻塞
资源耗尽 资源耗尽 资源耗尽
└─────────────┴─────────────┴── 全部崩溃!
有熔断时:
┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│ 用户端 │ → │ 网关 │ → │ 服务A │ ✕ │ 熔断器 │ → 服务B(宕机)
└────────┘ └────────┘ └────────┘ └─────────┘
↑ │
正常返回 直接拒绝
"服务暂时不可用" 不再发送请求
3. 自动恢复能力
// 熔断器会自动尝试恢复
// 60秒后进入 HALF_OPEN 状态,放行少量请求测试
// 如果服务恢复正常,自动切回 CLOSED 状态
4. 可观测性
auto stats = circuit_breaker->getStats();
// 可以监控:
// - 总请求数、成功数、失败数
// - 被拒绝的请求数
// - 当前失败率
// - 熔断器状态
代码对应以及适用场景
熔断器头文件: -agent-communication/include/agent_rpc/circuit_breaker.h
1. 熔断器状态 (L9-14):
enum class CircuitState {
CLOSED, // 关闭状态 - 正常请求
OPEN, // 开启状态 - 熔断,拒绝请求
HALF_OPEN // 半开状态 - 尝试恢复
};
2. 熔断器配置 (L17-24):
struct CircuitBreakerConfig {
int failure_threshold = 5; // 失败阈值
int success_threshold = 3; // 半开状态下的成功阈值
std::chrono::milliseconds timeout = std::chrono::milliseconds(60000);
std::chrono::milliseconds half_open_timeout = std::chrono::milliseconds(30000);
double failure_rate_threshold = 0.5; // 失败率阈值
int min_request_count = 10; // 最小请求数量
};
3. 熔断器实现: -agent-communication/src/circuit_breaker.cpp
| 方法 | 功能 | 代码行 |
|---|---|---|
execute() |
执行请求,自动记录成功/失败 | L15-29 |
recordSuccess() |
记录成功,半开转关闭 | L34-48 |
recordFailure() |
记录失败,超阈值转开启 | L50-63 |
isRequestAllowed() |
判断是否允许请求 | L65-87 |
transitionToOpen() |
转换到开启状态 | L109-115 |
transitionToHalfOpen() |
转换到半开状态 | L117-128 |
transitionToClosed() |
转换到关闭状态 | L130-140 |
updateFailureRate() |
计算失败率 | L142-151 |
shouldAttemptReset() |
判断是否尝试恢复 | L153-158 |
4. 熔断器管理器 (L160-221):
class CircuitBreakerManager {
std::shared_ptr<CircuitBreaker> getCircuitBreaker(const std::string& service_name);
void removeCircuitBreaker(const std::string& service_name);
std::map<std::string, CircuitState> getAllStates() const;
void resetAll();
void updateConfig(const std::string& service_name, const CircuitBreakerConfig& config);
};
适用场景路径:-agent-communication/examples/ai_query_client.cpp
/**
* @file ai_query_client.cpp
* @brief AI Query RPC Client - 通过 gRPC 发送 AI 查询请求
*
* 这是项目的核心测试用例:
* - rpc_client 通过 gRPC 连接 rpc_server
* - rpc_server 通过 A2A 协议调用 Orchestrator
* - Orchestrator 路由到各个专业 Agent (Math Agent 等)
*/
#include "agent_rpc/client/ai_query_client.h"
#include "agent_rpc/common/rpc_framework.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <signal.h>
#include <string>
// ============================================================================
// [熔断机制集成示例 - 可选]
// 如需启用熔断保护,取消以下注释:
// #include "agent_rpc/circuit_breaker.h"
// 或使用 common 模块:
// #include "agent_rpc/common/circuit_breaker.h"
// ============================================================================
using namespace agent_rpc::client;
using namespace agent_rpc::common;
// ============================================================================
// [熔断机制命名空间 - 可选]
// 如需使用熔断器,取消以下注释:
// using agent_rpc::CircuitBreaker;
// using agent_rpc::CircuitBreakerManager;
// using agent_rpc::CircuitBreakerConfig;
// using agent_rpc::CircuitState;
// ============================================================================
// 全局变量用于优雅关闭
std::atomic<bool> g_running{true};
void signalHandler(int signal) {
std::cout << "\n收到信号 " << signal << ", 退出..." << std::endl;
g_running = false;
}
void printHelp() {
std::cout << "\n命令:" << std::endl;
std::cout << " /help - 显示帮助" << std::endl;
std::cout << " /stream - 切换流式模式" << std::endl;
std::cout << " /context <id> - 切换上下文" << std::endl;
std::cout << " /quit - 退出" << std::endl;
std::cout << "\n直接输入问题发送给 AI\n" << std::endl;
}
void printUsage(const char* program) {
std::cout << "用法: " << program << " <RPC_SERVER_ADDRESS>" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "参数:" << std::endl;
std::cout << " RPC_SERVER_ADDRESS - gRPC 服务器地址 (例如: localhost:50051)" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "示例:" << std::endl;
std::cout << " " << program << " localhost:50051" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "注意: 需要先启动以下服务:" << std::endl;
std::cout << " 1. ai_orchestrator 系统 (./start_system.sh)" << std::endl;
std::cout << " 2. rpc_server (./rpc_server)" << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 2) {
printUsage(argv[0]);
return 1;
}
std::string server_address = argv[1];
// 设置信号处理
signal(SIGINT, signalHandler);
signal(SIGTERM, signalHandler);
std::cout << "==========================================" << std::endl;
std::cout << "AI Query RPC Client" << std::endl;
std::cout << "==========================================" << std::endl;
std::cout << "连接到 RPC Server: " << server_address << std::endl;
// 创建 AI 查询客户端
AIQueryClient client;
// ========================================================================
// [熔断器初始化示例 - 可选]
// 为 AI 查询服务创建熔断器,提供服务容错保护:
//
// // 方式1:使用默认配置
// auto& cb_manager = CircuitBreakerManager::getInstance();
// auto circuit_breaker = cb_manager.getCircuitBreaker("ai_query_service");
//
// // 方式2:使用自定义配置
// CircuitBreakerConfig cb_config;
// cb_config.failure_threshold = 5; // 连续5次失败触发熔断
// cb_config.success_threshold = 3; // 半开状态3次成功恢复
// cb_config.timeout = std::chrono::milliseconds(30000); // 30秒超时后尝试恢复
// cb_config.failure_rate_threshold = 0.5; // 失败率超过50%触发熔断
// cb_config.min_request_count = 10; // 至少10次请求后才计算失败率
// auto circuit_breaker = std::make_shared<CircuitBreaker>(cb_config);
// ========================================================================
if (!client.connect(server_address)) {
std::cerr << "无法连接到服务器: " << server_address << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// ========================================================================
// [使用熔断器包装连接操作示例 - 可选]
// 连接操作可以用熔断器保护,防止服务不可用时频繁重试:
//
// bool connected = false;
// try {
// connected = circuit_breaker->execute([&]() {
// return client.connect(server_address);
// });
// } catch (const std::runtime_error& e) {
// // 熔断器开启时会抛出 "Circuit breaker is open" 异常
// std::cerr << "服务熔断中,稍后重试: " << e.what() << std::endl;
// return 1;
// }
// if (!connected) {
// std::cerr << "无法连接到服务器" << std::endl;
// return 1;
// }
// ========================================================================
std::cout << "连接成功!" << std::endl;
printHelp();
std::string context_id = "default";
bool stream_mode = false;
std::string line;
while (g_running) {
std::cout << "[" << context_id << (stream_mode ? "/流式" : "") << "] > ";
if (!std::getline(std::cin, line)) {
break;
}
if (line.empty()) continue;
// 处理命令
if (line == "/quit" || line == "/exit" || line == "/q") {
std::cout << "再见!" << std::endl;
break;
}
if (line == "/help" || line == "/h") {
printHelp();
continue;
}
if (line == "/stream" || line == "/s") {
stream_mode = !stream_mode;
std::cout << "流式模式: " << (stream_mode ? "开启" : "关闭") << std::endl;
continue;
}
if (line.substr(0, 9) == "/context " || line.substr(0, 3) == "/c ") {
size_t pos = line.find(' ');
if (pos != std::string::npos) {
context_id = line.substr(pos + 1);
std::cout << "切换到上下文: " << context_id << std::endl;
}
continue;
}
// 发送 AI 查询
std::cout << "\n思考中..." << std::endl;
// ====================================================================
// [熔断器状态检查示例 - 可选]
// 在发送请求前可以检查熔断器状态:
//
// CircuitState state = circuit_breaker->getState();
// if (state == CircuitState::OPEN) {
// std::cout << "⚠️ 服务熔断中,请稍后重试..." << std::endl;
// continue;
// } else if (state == CircuitState::HALF_OPEN) {
// std::cout << "ℹ️ 服务恢复测试中..." << std::endl;
// }
// ====================================================================
if (stream_mode) {
// 流式查询
std::cout << "\nAI: ";
bool success = client.queryStream(line,
[](const agent_communication::AIStreamEvent& event) {
if (event.event_type() == "partial") {
std::cout << event.content();
std::cout.flush();
} else if (event.event_type() == "complete") {
std::cout << std::endl;
} else if (event.event_type() == "error") {
std::cout << "\n错误: " << event.content() << std::endl;
}
}, context_id, 60);
if (!success) {
std::cout << "\n流式查询失败" << std::endl;
// ============================================================
// [熔断器记录失败示例 - 可选]
// circuit_breaker->recordFailure();
// ============================================================
}
// ================================================================
// [熔断器记录成功示例 - 可选]
// else {
// circuit_breaker->recordSuccess();
// }
// ================================================================
} else {
// 同步查询
auto response = client.query(line, context_id, 60);
// ================================================================
// [使用熔断器包装同步查询示例 - 可选]
// 推荐方式:使用 execute() 方法自动处理成功/失败记录
//
// try {
// auto response = circuit_breaker->execute([&]() {
// return client.query(line, context_id, 60);
// });
// // 处理响应...
// } catch (const std::runtime_error& e) {
// if (std::string(e.what()) == "Circuit breaker is open") {
// std::cout << "⚠️ 服务熔断中: " << e.what() << std::endl;
// } else {
// throw; // 重新抛出其他异常
// }
// }
// ================================================================
if (response.status().code() == 0) {
std::cout << "\nAI: " << response.answer() << std::endl;
if (!response.agent_name().empty()) {
std::cout << "[处理 Agent: " << response.agent_name()
<< ", 耗时: " << response.processing_time_ms() << "ms]" << std::endl;
}
// ============================================================
// [熔断器记录成功 - 可选]
// circuit_breaker->recordSuccess();
// ============================================================
} else {
std::cout << "\n错误: " << response.status().message() << std::endl;
// ============================================================
// [熔断器记录失败 - 可选]
// circuit_breaker->recordFailure();
// ============================================================
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
client.disconnect();
std::cout << "已断开连接" << std::endl;
// ========================================================================
// [熔断器统计信息示例 - 可选]
// 程序退出前可以打印熔断器统计信息:
//
// auto stats = circuit_breaker->getStats();
// std::cout << "\n========== 熔断器统计 ==========" << std::endl;
// std::cout << "总请求数: " << stats.total_requests << std::endl;
// std::cout << "成功请求: " << stats.successful_requests << std::endl;
// std::cout << "失败请求: " << stats.failed_requests << std::endl;
// std::cout << "被拒绝请求: " << stats.rejected_requests << std::endl;
// std::cout << "当前失败率: " << (stats.current_failure_rate * 100) << "%" << std::endl;
// std::cout << "当前状态: ";
// switch (circuit_breaker->getState()) {
// case CircuitState::CLOSED: std::cout << "CLOSED (正常)"; break;
// case CircuitState::OPEN: std::cout << "OPEN (熔断中)"; break;
// case CircuitState::HALF_OPEN: std::cout << "HALF_OPEN (恢复测试)"; break;
// }
// std::cout << std::endl;
// std::cout << "=================================" << std::endl;
// ========================================================================
return 0;
}
负载均衡机制
负载均衡整体架构
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 负载均衡系统架构 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ LoadBalancerFactory │
│ createLoadBalancer(strategy) │
│ │ │
│ ┌───────────────────────┼───────────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ │
│ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐
│ │RoundRobin│ │ Random │ │LeastConn │ │Weighted │ │Consistent│ │LeastResp │
│ │LoadBal │ │LoadBal │ │LoadBal │ │RoundRobin│ │Hash LB │ │Time LB │
│ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ └───────────┴───────────┴───────────┴───────────┴───────────┘ │
│ │ │
│ ↓ │
│ LoadBalancer 接口 (抽象基类) │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ selectEndpoint(endpoints) → Endpoint │ │
│ │ updateEndpoints(endpoints) │ │
│ │ markEndpointStatus(id, healthy) │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
轮询策略 (Round Robin)
原理
请求按顺序依次分配给每个服务器,循环往复
服务器: A B C A B C A B C
请求: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
实现代码
// 文件: src/load_balancer.cpp:11-33
ServiceEndpoint RoundRobinLoadBalancer::selectEndpoint(const std::vector<ServiceEndpoint>& endpoints) {
// 1. 过滤健康端点
std::vector<ServiceEndpoint> healthy_endpoints;
for (const auto& endpoint : endpoints) {
if (endpoint.is_healthy) {
healthy_endpoints.push_back(endpoint);
}
}
// 2. 轮询选择:原子操作获取并递增索引
size_t index = current_index_.fetch_add(1) % healthy_endpoints.size();
// ↑ 原子操作:获取当前值并+1
// ↑ 取模确保循环
return healthy_endpoints[index];
}
// 成员变量
std::atomic<size_t> current_index_{0}; // 原子计数器,线程安全
图解
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 轮询策略工作流程 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ current_index_ = 0 │
│ │
│ endpoints = [A, B, C] (3个健康服务器) │
│ │
│ 请求1: index = 0 % 3 = 0 → 选择 A, current_index_ = 1 │
│ 请求2: index = 1 % 3 = 1 → 选择 B, current_index_ = 2 │
│ 请求3: index = 2 % 3 = 2 → 选择 C, current_index_ = 3 │
│ 请求4: index = 3 % 3 = 0 → 选择 A, current_index_ = 4 │
│ 请求5: index = 4 % 3 = 1 → 选择 B, current_index_ = 5 │
│ ... │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
使用场景
- 服务器性能相近
- 无状态服务
- 简单高效
随机策略 (Random)
原理
每次请求随机选择一个服务器
服务器: B A C C A B C A A
请求: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
↑ 随机
实现代码
// 文件: src/load_balancer.cpp:54-76
ServiceEndpoint RandomLoadBalancer::selectEndpoint(const std::vector<ServiceEndpoint>& endpoints) {
// 1. 过滤健康端点
std::vector<ServiceEndpoint> healthy_endpoints;
for (const auto& endpoint : endpoints) {
if (endpoint.is_healthy) {
healthy_endpoints.push_back(endpoint);
}
}
// 2. 随机选择
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dis(0, healthy_endpoints.size() - 1);
// ↑ 均匀分布 [0, size-1]
return healthy_endpoints[dis(gen_)];
// ↑ 生成随机数
}
// 成员变量
std::random_device rd_; // 硬件随机数种子
mutable std::mt19937 gen_; // 梅森旋转随机数生成器
使用场景
- 服务器性能相近
- 简单场景
- 不需要均匀分布时
轮询策略 (Round Robin)
原理
实现代码
图解
使用场景
- 服务器性能相近
- 服务器性能相近
- 服务器性能相近
最少连接策略 (Least Connections)
原理
选择当前连接数最少的服务器
服务器 A: ████ (4 连接)
服务器 B: ██ (2 连接) ← 选择这个
服务器 C: ███ (3 连接)
实现代码
// 文件: src/load_balancer.cpp:96-127
ServiceEndpoint LeastConnectionsLoadBalancer::selectEndpoint(const std::vector<ServiceEndpoint>& endpoints) {
ServiceEndpoint* best_endpoint = nullptr;
int min_connections = INT_MAX;
for (const auto& endpoint : endpoints) {
if (!endpoint.is_healthy) continue;
std::string endpoint_id = endpoint.host + ":" + std::to_string(endpoint.port);
int connections = connection_counts_[endpoint_id]; // 获取当前连接数
if (connections < min_connections) {
min_connections = connections;
best_endpoint = const_cast<ServiceEndpoint*>(&endpoint);
}
}
// 选中后增加连接计数
connection_counts_[endpoint_id]++;
return *best_endpoint;
}
// 连接管理
void incrementConnections(const std::string& endpoint_id); // 建立连接时调用
void decrementConnections(const std::string& endpoint_id); // 断开连接时调用
图解
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 最少连接策略 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ connection_counts_ = { │
│ "A:8080": 4, │
│ "B:8080": 2, ← 最小 │
│ "C:8080": 3 │
│ } │
│ │
│ 新请求到达 → 选择 B:8080 │
│ connection_counts_["B:8080"]++ → 变为 3 │
│ │
│ 请求完成后 → 调用 decrementConnections("B:8080") │
│ connection_counts_["B:8080"]-- → 变回 2 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
使用场景
- 长连接服务
- 请求处理时间差异大
- 需要动态负载均衡
加权轮询策略 (Weighted Round Robin)
原理
根据服务器权重分配请求,权重高的分配更多
服务器 A (权重=5): █████
服务器 B (权重=3): ███
服务器 C (权重=2): ██
10个请求分配: A A A A A B B B C C
实现代码
// 文件: src/load_balancer.cpp:177-211
ServiceEndpoint WeightedRoundRobinLoadBalancer::selectEndpoint(const std::vector<ServiceEndpoint>& endpoints) {
WeightedEndpoint* best_endpoint = nullptr;
int max_current_weight = 0;
// 1. 遍历所有端点,累加权重
for (auto& endpoint : weighted_endpoints_) {
if (!endpoint.endpoint.is_healthy) continue;
// 当前权重 += 初始权重
endpoint.current_weight += endpoint.weight;
// 找出当前权重最大的
if (endpoint.current_weight > max_current_weight) {
max_current_weight = endpoint.current_weight;
best_endpoint = &endpoint;
}
}
// 2. 选中后减去自身权重
best_endpoint->current_weight -= best_endpoint->weight;
return best_endpoint->endpoint;
}
// 权重从 metadata 获取
auto it = endpoint.metadata.find("weight");
if (it != endpoint.metadata.end()) {
weighted_endpoint.weight = std::stoi(it->second);
}
图解
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 方式一:减去自身权重(代码实际实现) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ A=5, B=1, C=1 │
│ │
│ 请求1: A=5,B=1,C=1 → 选A → A=5-5=0 → A=0,B=1,C=1 │
│ 请求2: A=5,B=2,C=2 → 选A → A=5-5=0 → A=0,B=2,C=2 │
│ 请求3: A=5,B=3,C=3 → 选A → A=5-5=0 → A=0,B=3,C=3 │
│ 请求4: A=5,B=4,C=4 → 选A → A=5-5=0 → A=0,B=4,C=4 │
│ 请求5: A=5,B=5,C=5 → 选A → A=5-5=0 → A=0,B=5,C=5 │
│ 请求6: A=5,B=6,C=6 → 选B → B=6-1=5 → A=5,B=5,C=6 │
│ ... │
│ │
│ 问题:A 连续被选中很多次,不够平滑! │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 方式二:减去总权重(标准Nginx算法) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ A=5, B=1, C=1, 总权重=7 │
│ │
│ 请求1: A=5,B=1,C=1 → 选A → A=5-7=-2 → A=-2,B=1,C=1 │
│ 请求2: A=3,B=2,C=2 → 选A → A=3-7=-4 → A=-4,B=2,C=2 │
│ 请求3: A=1,B=3,C=3 → 选B → B=3-7=-4 → A=1,B=-4,C=3 │
│ 请求4: A=6,B=-3,C=4 → 选A → A=6-7=-1 → A=-1,B=-3,C=4 │
│ 请求5: A=4,B=-2,C=5 → 选C → C=5-7=-2 → A=4,B=-2,C=-2 │
│ 请求6: A=9,B=-1,C=-1 → 选A → ... │
│ 请求7: A=7,B=0,C=0 → 选A → ... │
│ │
│ 7次请求分配:A A B A C A A → A得5次, B得1次, C得1次 ✓ │
│ 而且分布是交错的,更平滑! │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
使用场景
- 服务器性能不同
- 需要手动控制流量分配
- 灰度发布
一致性哈希策略 (Consistent Hash)
原理
将服务器和请求都映射到一个哈希环上,请求顺时针找最近的服务器
0°
│
╭────┴────╮
╱ A ╲ 请求 X 的哈希值在 B 和 C 之间
│ │ → 顺时针找到 C
│ B │
╲ ╱
╰────┬────╯
│
C
实现代码
// 文件: src/load_balancer.cpp:249-362
ConsistentHashLoadBalancer::ConsistentHashLoadBalancer(int virtual_nodes)
: virtual_nodes_(virtual_nodes) {} // 默认 150 个虚拟节点
// 构建哈希环
void ConsistentHashLoadBalancer::buildHashRing() {
hash_ring_.clear();
for (const auto& pair : endpoints_) {
if (!pair.second.is_healthy) continue;
// 为每个物理节点创建 N 个虚拟节点
for (int i = 0; i < virtual_nodes_; ++i) {
std::string virtual_key = pair.first + "#" + std::to_string(i);
// "A:8080#0", "A:8080#1", ... "A:8080#149"
uint32_t hash_value = hash(virtual_key);
HashNode node;
node.key = virtual_key;
node.endpoint = pair.second;
node.hash = hash_value;
hash_ring_.push_back(node);
}
}
// 按哈希值排序
std::sort(hash_ring_.begin(), hash_ring_.end(),
[](const HashNode& a, const HashNode& b) {
return a.hash < b.hash;
});
}
// 查找端点(二分查找)
ServiceEndpoint ConsistentHashLoadBalancer::findEndpoint(uint32_t hash_value) {
// 找第一个哈希值 >= 目标值的节点
auto it = std::lower_bound(hash_ring_.begin(), hash_ring_.end(), hash_value,
[](const HashNode& node, uint32_t value) {
return node.hash < value;
});
// 环形结构:如果超出末尾,回到开头
if (it == hash_ring_.end()) {
it = hash_ring_.begin();
}
return it->endpoint;
}
图解
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 一致性哈希环(含虚拟节点) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 0 │
│ │ │
│ A#2 ─────┬┴┬───── B#0 │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ A#0 B#1 │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ C#1 A#1 │
│ │ │ │
│ │ ← 请求X的哈希值 │ │
│ │ 落在这里 │ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ C#0 ─────────────── B#2 │
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ ───────── │
│ │
│ 请求 X → hash("X") = 12345 → 顺时针找到 C#0 → 返回服务器 C │
│ │
│ 为什么用虚拟节点? │
│ - 3个物理节点只有3个点,分布不均匀 │
│ - 150个虚拟节点/物理节点 → 450个点,分布更均匀 │
│ - 添加/删除节点时,只影响相邻区域的请求 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
使用场景
- 分布式缓存(同一用户/数据总是路由到同一服务器)
- 有状态服务
- 需要会话保持
- 动态扩缩容时最小化数据迁移
解释
先理解普通哈希的问题
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 场景:你有3台缓存服务器,存放用户数据 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 普通哈希方法: │
│ 服务器编号 = hash(用户ID) % 服务器数量 │
│ │
│ 用户"张三" → hash("张三") = 12345 → 12345 % 3 = 0 → 服务器A │
│ 用户"李四" → hash("李四") = 67890 → 67890 % 3 = 1 → 服务器B │
│ 用户"王五" → hash("王五") = 11111 → 11111 % 3 = 2 → 服务器C │
│ │
│ 一切正常... │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 灾难来了:加了一台服务器,变成4台 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 现在要 % 4: │
│ │
│ 用户"张三" → 12345 % 4 = 1 → 服务器B (原来在A,变了!) │
│ 用户"李四" → 67890 % 4 = 2 → 服务器C (原来在B,变了!) │
│ 用户"王五" → 11111 % 4 = 3 → 服务器D (原来在C,变了!) │
│ │
│ 问题:几乎所有用户的数据都要迁移! │
│ - 缓存全部失效 │
│ - 数据库被大量请求压垮 │
│ - 系统崩溃! │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
一致性哈希的解决方案
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 想象一个圆形的"哈希环"(像钟表一样) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 12点 (哈希值=0) │
│ │ │
│ │ │
│ 10点 ──────────┼────────── 2点 │
│ ╲ │ ╱ │
│ ╲ [服务器A] ╱ │
│ ╲ │ ╱ │
│ 9点 ╲ │ ╱ 3点 │
│ ╲ │ ╱ │
│ ╲ │ ╱ │
│ ╲ │ ╱ │
│ 8点 [服务器B] 4点 │
│ ╱ │ ╲ │
│ ╱ │ ╲ │
│ 7点 ╱ │ ╲ 5点 │
│ ╱ [服务器C] ╲ │
│ ╱ │ ╲ │
│ ╱ │ ╲ │
│ 6点 ───────────┴─────────── 4点 │
│ │
│ 规则:把服务器和用户都放到环上,用户顺时针找最近的服务器 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
具体工作流程
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Step 1: 把服务器放到环上 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ hash("服务器A") = 1000 → 放在环的 1000 位置 │
│ hash("服务器B") = 5000 → 放在环的 5000 位置 │
│ hash("服务器C") = 8000 → 放在环的 8000 位置 │
│ │
│ 0 │
│ │ │
│ A(1000)┼ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ C(8000)─┤ ├─B(5000) │
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ │ │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Step 2: 用户请求来了,顺时针找最近的服务器 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 用户"张三" → hash("张三") = 3000 │
│ │
│ 0 │
│ │ │
│ A(1000)┼ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ 张三(3000)→ ╲ │
│ ↓ ╱ ╲ │
│ C(8000)─┤ ├─B(5000) ← 顺时针最近! │
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ ╲ ╱ │
│ │
│ 结果:张三的数据存到服务器B │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Step 3: 添加新服务器D时会发生什么? │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 新增 hash("服务器D") = 4000 │
│ │
│ 0 │
│ │ │
│ A(1000)┼ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ 张三(3000) ╲ │
│ ↓ ╲ │
│ C(8000)─┤ D(4000)─B(5000) │
│ ↑ │
│ 张三现在顺时针最近的是D了 │
│ │
│ 影响范围:只有 [3000, 4000] 区间的用户需要迁移到D │
│ 其他用户完全不受影响! │
│ │
│ 对比普通哈希:加一台服务器几乎所有数据都要迁移 │
│ 一致性哈希:只有 1/N 的数据需要迁移 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
虚拟节点的作用
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 问题:如果只有3个点,分布可能很不均匀 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ A 不均匀的情况: │
│ │ - A 覆盖的区间很大(从C到A) │
│ │ - C 覆盖的区间很小(从B到C) │
│ ────┼──── - 导致A的负载是C的好几倍 │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ ╱ ╲ │
│ C─────B │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 解决:每个服务器创建多个"虚拟节点" │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 服务器A → 创建 A#0, A#1, A#2, ... A#149 (150个虚拟节点) │
│ 服务器B → 创建 B#0, B#1, B#2, ... B#149 │
│ 服务器C → 创建 C#0, C#1, C#2, ... C#149 │
│ │
│ 环上现在有 450 个点,分布更均匀: │
│ │
│ A#0 B#47 │
│ ╲ │ ╱ │
│ C#12 ─┼─┼─┼─ A#88 │
│ ╱ │ ╲ │
│ B#3 │ C#99 │
│ │ │
│ A#45 │
│ │
│ 虽然点很多,但 A#xxx 都指向服务器A │
│ 用户找到 A#88,实际请求发到服务器A │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
最短响应时间策略 (Least Response Time)
原理
选择平均响应时间最短的服务器
服务器 A: 平均响应 50ms
服务器 B: 平均响应 20ms ← 选择这个
服务器 C: 平均响应 35ms
实现代码
// 文件: src/load_balancer.cpp:367-456
ServiceEndpoint LeastResponseTimeLoadBalancer::selectEndpoint(const std::vector<ServiceEndpoint>& endpoints) {
ServiceEndpoint* best_endpoint = nullptr;
std::chrono::milliseconds min_response_time = std::chrono::milliseconds::max();
for (const auto& endpoint : endpoints) {
if (!endpoint.is_healthy) continue;
std::string endpoint_id = endpoint.host + ":" + std::to_string(endpoint.port);
auto response_time = calculateAverageResponseTime(endpoint_id);
if (response_time < min_response_time) {
min_response_time = response_time;
best_endpoint = const_cast<ServiceEndpoint*>(&endpoint);
}
}
return *best_endpoint;
}
// 更新响应时间(请求完成后调用)
void LeastResponseTimeLoadBalancer::updateResponseTime(const std::string& endpoint_id,
std::chrono::milliseconds response_time) {
auto& stats = endpoint_stats_[endpoint_id];
stats.request_count++;
stats.last_update = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
// 指数移动平均:新值占 20%,旧值占 80%
if (stats.avg_response_time.count() == 0) {
stats.avg_response_time = response_time;
} else {
stats.avg_response_time = std::chrono::milliseconds(
(stats.avg_response_time.count() * 0.8) + (response_time.count() * 0.2)
);
// 平滑过渡,避免单次异常值影响太大
}
}
图解
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 指数移动平均(EMA)计算示例 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 初始: avg = 0 │
│ │
│ 请求1完成,耗时 100ms: │
│ avg = 100 (第一次直接赋值) │
│ │
│ 请求2完成,耗时 50ms: │
│ avg = 100 * 0.8 + 50 * 0.2 = 80 + 10 = 90ms │
│ │
│ 请求3完成,耗时 60ms: │
│ avg = 90 * 0.8 + 60 * 0.2 = 72 + 12 = 84ms │
│ │
│ 请求4完成,耗时 200ms(异常慢): │
│ avg = 84 * 0.8 + 200 * 0.2 = 67.2 + 40 = 107.2ms │
│ (异常值只贡献 20%,不会剧烈波动) │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
使用场景
- 服务器性能波动大
- 需要自适应负载均衡
- 对响应时间敏感的服务
工厂模式使用
// 文件: src/load_balancer.cpp:458-476
std::unique_ptr<LoadBalancer> LoadBalancerFactory::createLoadBalancer(LoadBalanceStrategy strategy) {
switch (strategy) {
case LoadBalanceStrategy::ROUND_ROBIN:
return std::make_unique<RoundRobinLoadBalancer>();
case LoadBalanceStrategy::RANDOM:
return std::make_unique<RandomLoadBalancer>();
case LoadBalanceStrategy::LEAST_CONNECTIONS:
return std::make_unique<LeastConnectionsLoadBalancer>();
case LoadBalanceStrategy::WEIGHTED_ROUND_ROBIN:
return std::make_unique<WeightedRoundRobinLoadBalancer>();
case LoadBalanceStrategy::CONSISTENT_HASH:
return std::make_unique<ConsistentHashLoadBalancer>();
case LoadBalanceStrategy::LEAST_RESPONSE_TIME:
return std::make_unique<LeastResponseTimeLoadBalancer>();
default:
return std::make_unique<RoundRobinLoadBalancer>();
}
}
使用示例
// 创建负载均衡器
auto lb = LoadBalancerFactory::createLoadBalancer(LoadBalanceStrategy::LEAST_CONNECTIONS);
// 更新服务端点列表
lb->updateEndpoints(endpoints);
// 选择端点发送请求
ServiceEndpoint selected = lb->selectEndpoint(endpoints);
// 标记端点健康状态
lb->markEndpointStatus("192.168.1.1:8080", false); // 标记为不健康
问题
mt19937 是什么
mt19937 = Mersenne Twister 19937
- Mersenne Twister:梅森旋转算法(一种随机数生成算法)
- 19937:算法的周期是 2^19937 - 1(一个超级大的数)
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ mt19937 = 高质量随机数生成器 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 类比: │
│ - rand() 像一个简单的骰子 → 便宜但不够"随机" │
│ - mt19937 像一个超复杂的随机摇奖机 → 更均匀、更难预测 │
│ │
│ 特点: │
│ 1. 周期极长:2^19937-1 次才会重复 │
│ 2. 分布均匀:每个数出现的概率相等 │
│ 3. 速度快:适合需要大量随机数的场景 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
mutable 关键字的含义
mutable = 即使在 const 成员函数中也可以修改
// 没有 mutable 时
ServiceEndpoint selectEndpoint(...) const { // const 函数
gen_(); // ❌ 错误!const 函数不能修改成员变量
}
// 有 mutable 时
ServiceEndpoint selectEndpoint(...) const {
gen_(); // ✓ OK!mutable 变量可以在 const 函数中修改
}
uniform_int_distribution解释
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dis(0, healthy_endpoints.size() - 1);
return healthy_endpoints[dis(gen_)];
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 第一行:创建"均匀分布生成器" │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ std::uniform_int_distribution<> dis(0, healthy_endpoints.size() - 1); │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ └─ 最大值(假设size=3,则最大值=2) │
│ │ │ └──── 最小值 │
│ │ └──────── 变量名 │
│ └───────────────────────────────────── 均匀整数分布类型 │
│ │
│ 假设 healthy_endpoints.size() = 3 │
│ dis 就是一个能生成 [0, 1, 2] 范围内整数的分布器 │
│ │
│ 类比:dis 就像一个"骰子模板",规定了骰子有哪些面(0,1,2) │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 第二行:生成随机数并取元素 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ return healthy_endpoints[dis(gen_)]; │
│ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ └─ gen_ 是随机数引擎(mt19937) │
│ │ └───── dis(gen_) 调用分布器,传入引擎 │
│ │ 返回一个 [0, 2] 范围的随机整数 │
│ └───────────────────────── 用随机数作为下标取数组元素 │
│ │
│ 执行过程: │
│ 1. gen_() 生成一个原始随机数,比如 3847291038474 │
│ 2. dis 把这个大数"映射"到 [0, 2] 范围,比如得到 1 │
│ 3. 返回 healthy_endpoints[1] │
│ │
│ 类比: │
│ - gen_ = 随机数发动机(输出原始随机数) │
│ - dis = 转换器(把原始随机数转成我们想要的范围) │
│ - dis(gen_) = 把发动机接到转换器上,得到最终结果 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
有状态服务 vs 无状态服务
通俗解释
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 无状态服务 (Stateless) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 类比:快餐店 │
│ - 你去任何一个窗口点餐都一样 │
│ - 服务员不需要"记住"你是谁 │
│ - 每次请求都带上所有信息(我要一个汉堡+可乐) │
│ │
│ 例子: │
│ - 计算服务:输入 2+3,返回 5 │
│ - 图片压缩服务:输入图片,返回压缩后的图片 │
│ - 无登录的API查询 │
│ │
│ 特点: │
│ - 请求可以发给任何一台服务器 │
│ - 服务器挂了,换一台继续用 │
│ - 容易扩展:加机器就行 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 有状态服务 (Stateful) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 类比:私人医生 │
│ - 你必须找你的专属医生 │
│ - 医生有你的病历(历史状态) │
│ - 换个医生,他不知道你的情况 │
│ │
│ 例子: │
│ - 购物车服务:服务器记住你的购物车内容 │
│ - 游戏服务器:服务器记住你的角色位置、血量 │
│ - WebSocket 长连接:服务器维护连接状态 │
│ - 分布式缓存:数据存在特定的服务器上 │
│ │
│ 特点: │
│ - 必须路由到"正确"的服务器 │
│ - 服务器挂了,状态可能丢失 │
│ - 扩展困难:需要迁移状态 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
为什么有状态服务需要一致性哈希
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 场景:分布式缓存(有状态) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ 用户"张三"的数据存在服务器B │
│ │
│ 如果用轮询: │
│ 请求1 → 服务器A → 没有张三的数据 → 去数据库查 │
│ 请求2 → 服务器B → 有数据 → 直接返回 │
│ 请求3 → 服务器C → 没有张三的数据 → 又去数据库查 │
│ → 缓存命中率很低! │
│ │
│ 如果用一致性哈希: │
│ 张三的请求 → 永远路由到服务器B │
│ 请求1 → 服务器B → 有数据 │
│ 请求2 → 服务器B → 有数据 │
│ 请求3 → 服务器B → 有数据 │
│ → 缓存命中率极高! │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
总结表格
| 特性 | 无状态服务 | 有状态服务 |
|---|---|---|
| 服务器是否需要记住用户 | ❌ 不需要 | ✅ 需要 |
| 请求可以发给任意服务器 | ✅ 可以 | ❌ 必须发给特定服务器 |
| 服务器挂了 | 换一台继续 | 状态可能丢失 |
| 扩容难度 | 简单 | 困难(需迁移数据) |
| 推荐负载均衡策略 | 轮询、随机 | 一致性哈希 |
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)