c++ STL笔记 6
初始化含义list<T> l1l1 是一个存放 T 类型数据的空 list利用 l1 构造 l2,l2 包含 l1 的所有数据同上l3 包含 n 个 vall4 包含 n 个默认 T 类型的数据l5 包含初始化列表提供的数据同上int main()//空链表//包含两个默认元素值的链表//包含3个4的链表//包含1,2,3,4的链表//把14的值赋值给l5Show(l1);Show(l2);Sho
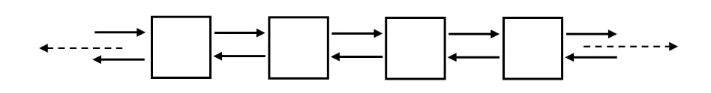
list双向链表
STL中list是一个双向循环列表:
使用list时需要包含头文件<list>
#include <list>list对象自带两个指针,分别指向第一个元素和最后一个元素;
list不支持随机访问。访问中间元素需要遍历,时间复杂度为O(n);访问头部与尾部元素时间复杂度为O(1);
list在任意位置进行插入和删除操作,时间复杂度为O(1);
定义与初始化
| 初始化 | 含义 |
| list<T> l1 | l1 是一个存放 T 类型数据的空 list |
| list<T> l2(l1) | 利用 l1 构造 l2,l2 包含 l1 的所有数据 |
| list<T> l2 = l1 | 同上 |
| list<T> l3(n, val) | l3 包含 n 个 val |
| list<T> l4(n) | l4 包含 n 个默认 T 类型的数据 |
| list<T> l5{a, b, c, ...} | l5 包含初始化列表提供的数据 |
| list<T> l5 = {a, b, c, ...} | 同上 |
void Show(const list<int>& l)
{
for (auto x : l)
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
list<int> l1; //空链表
list<int> l2(2); //包含两个默认元素值的链表
list<int> l3(3, 4); //包含3个4的链表
list<int> l4{ 1,2,3,4 }; //包含1,2,3,4的链表
list<int> l5(14); //把14的值赋值给l5
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
cout << "l3:"; Show(l3);
cout << "l4:"; Show(l4);
cout << "l5:"; Show(l5);
return 0;
}
list常用迭代器
list支持双向迭代器。
list迭代器不是随机迭代器,不能 +、- 数字。可以 ++、--。
list迭代器不能比较大小。可以 == 和 !=。
| 迭代器 | 含义 |
| l.begin() | 第一个元素的迭代器 |
| l.end() | 最后一个元素的下一个位置迭代器 |
| l.cbegin() | 第一个元素的常量迭代器 |
| l.cend() | 尾后常量迭代器 |
| l.rbegin() | 从后往前的第一个迭代器 |
| l.rend() | 从后往前的最后一个迭代器 |
| l.crbegin() | 从后往前的第一个常量迭代器 |
| l.crend() | 从后往前的最后一个常量迭代器 |
int main()
{
list<int> l{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
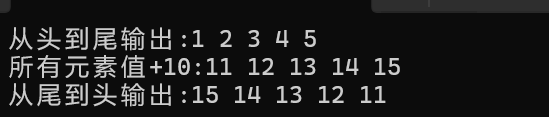
//从头到尾输出链表元素
cout << "从头到尾输出:";
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = l.cbegin(); it != l.cend(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
//把所有元素值+10
cout << "所有元素值+10:";
for (auto it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); ++it)
{
*it += 10;
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//从尾到头输出链表元素
cout << "从尾到头输出:";
for (auto it = l.crbegin(); it != l.crend(); ++it)
cout << *it << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
list常用运算符
| 运算符 | 含义 |
| l2 = l1 | 把 l1 的数据赋值给 l2 |
| l1 == l2 | 判断是否相等 |
| l1 != l2 | 判断是否不相等 |
| <, <=, >, >= | 判断大小关系,从头到尾依次比较 |
不支持[] |
int main()
{
list<int> l1{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
list<int> l2;
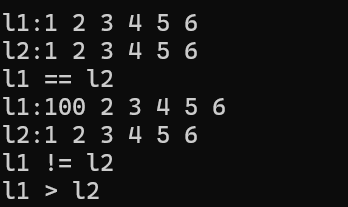
l2 = l1;//把l1的元素赋值给l2
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);//输出l1
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);//输出l2
if (l1 == l2)
cout << "l1 == l2" << endl;
l1.front() = 100;//把l1的第一元素改为100
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);//输出l1
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);//输出l2
if (l1 != l2)
cout << "l1 != l2" << endl;
if (l1 > l2)
cout << "l1 > l2" << endl;
else
cout << "l1 <= l2" << endl;
return 0;
}
list常用成员函数
| 成员函数 | 含义 | 成员函数 | 含义 |
| l.empty() | 判断是否为空 | l.push_back() | 尾插 |
| l.size() | 返回 l 的数据个数 | l.pop_back() | 尾删 |
| l.front() | 返回第一个元素的引用 | l.insert() | 插入一个或多个元素 |
| l.push_front() | 头插 | l.erase() | 删除一个或多个元素 |
| l.pop_front() | 头删 | l.swap() | 交换两个 list 的值 |
| l.back() | 返回最后一个元素的引用 | l.clear() | 清空数据 |
empty成员函数
判断list对象是否为空
size成员函数
获取list对象数据个数
int main()
{
list<int> l1;
if (l1.empty())//判空
cout << "l1是空的,数据个数=" << l1.size() << endl;
l1.assign({ 1,2,3,4,5 });
if (!l1.empty())
{
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l1不是空的,数据个数=" << l1.size() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
front成员函数
获取第一个元素的引用
push_front成员函数
从头部插入数据
pop_front成员函数
从头部删除数据
int main()
{
list<int> l1{ 1,2,3 };
l1.push_front(10);//头插
l1.push_front(20);
l1.push_front(30);
while (!l1.empty())
{
cout << l1.front() << " ";//输出l1的第一个元素
l1.pop_front();//删除第一个元素
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}![]()
back成员函数
获取最后一个元素的引用
push_back成员函数
尾部插入数据,可以自动扩容
pop_back成员函数
尾部删除数据
int main()
{
list<int> l2{ 10,20,30 };
l2.push_back(40);//尾插
l2.push_back(50);
l2.push_back(60);
while (!l2.empty())
{
cout << l2.back() << " ";//输出l2的最后元素
l2.pop_back();//删除最后一个元素
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}![]()
insert成员函数
插入一个或多个元素,时间复杂度为O(1)
int main()
{
list <int> l1{ 1, 2, 3 };
list <int> l2{ 4, 5, 6 };
list <int>::iterator Iter;
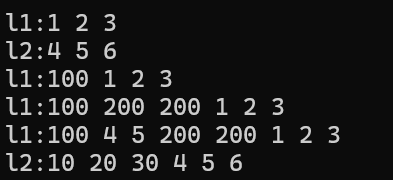
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
Iter = l1.begin();
l1.insert(Iter, 100);//在开始位置插入数字100
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
Iter = l1.begin();
Iter++;
l1.insert(Iter, 2, 200);//在Iter位置插入2个100
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
//在l1的begin后面插入l2的所有元素,不包含l2的最后一个
l1.insert(++l1.begin(), l2.begin(), --l2.end());
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l2.insert(l2.begin(), { 10,20,30 });//插入多个元素
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
return 0;
}
erase成员函数
删除一个或多个元素
int main()
{
list<int> l1{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.erase(l1.begin()); //删除一个元素
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.erase(l1.begin(), l1.end());//删除多个元素
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
return 0;
}
swap成员函数
交换两个list的值
int main()
{
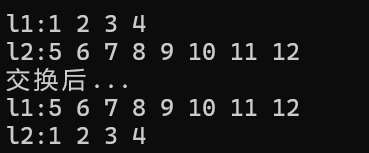
list<int> l1{ 1,2,3,4 };
list<int> l2{ 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 };
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
l1.swap(l2);//交换两个链表
cout << "交换后..." << endl;
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
return 0;
}
clear成员函数
清空数据
int main()
{
list<int> l1{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.clear();
cout << "清空后" << endl;
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
return 0;
}
list特有成员函数
| 成员函数 | 含义 |
| l.merge() | 链表合并 |
| l.remove(val) | 删除所有和val相同的元素 |
| l.remove_if() | 删除符合条件的元素 |
| l.reverse() | 反转链表中的元素 |
| l.sort() | 排序(默认为升序) |
| l.splice() | 链表连结 |
| l.unique() | 删除重复元素 |
merge特有成员函数
把两个链表的元素进行合并。
合并的前提:是原本两个链表必须按照合并的方法有序。
默认升序合并。
int main()
{
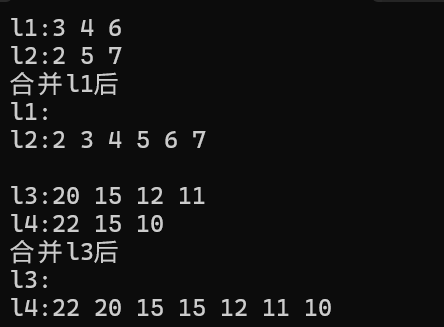
list <int> l1{ 3, 4, 6 };
list <int> l2{ 2, 5, 7 };
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
l2.merge(l1); //把l1合并到l2中,默认升序,前提l1,l2必须升序有序
cout << "合并l1后" << endl;
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
cout << endl;
list <int> l3{ 20, 15, 12,11 };
list <int> l4{ 22, 15, 10 };
cout << "l3:"; Show(l3);
cout << "l4:"; Show(l4);
l4.merge(l3, greater<int>());//按降序合并,前提l3,l4必须降序有序
cout << "合并l3后" << endl;
cout << "l3:"; Show(l3);
cout << "l4:"; Show(l4);
return 0;
}
remove特有成员函数
删除所有和_vel相同的值
int main()
{
list<int> l1{ 1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 4 };
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.remove(1);//删除所有值为1的元素
cout << "删除1后,";
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
return 0;
}![]()
remove_if特有成员函数
删除符合条件的元素
template <class T> class is_odd
{
public:
bool operator( ) (T& val)
{
return (val % 2) == 1;//奇数
}
};//奇数函数对象
int main()
{
list <int> l1{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.remove_if(is_odd<int>());//删除值为奇数的元素
cout << "删除奇数后,";
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
return 0;
}
reverse特有成员函数
将所有元素反序
int main()
{
list <int> l1{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.reverse();
cout << "反序后" << endl;
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
return 0;
}
sort特有成员函数
默认升序排序,可以提供排序依据
int main()
{
list <int> l1{7,2,3,1,4,9,8,6,5};
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.sort();//默认升序
cout << "排序后,";
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
l1.sort(greater<int>());//降序
cout << "降序排序后,";
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
return 0;
}
splice特有成员函数
链表连结:把一个链表的元素连结到另一个链表中。
它和merge的区别是:merge要求数据必须有序,而splice对数据没有要求。
int main()
{
list<int> l1{ 10, 11 };
list<int> l2{ 20, 21, 22 };
//把l2连结在l1的第二个位置
l1.splice(++l1.begin(), l2);
Show(l1);
list<int> l3{ 30, 31 };
list<int> l4{ 40, 41, 42, 43 };
//把l4连结在l3的最后面
l3.splice(l3.end(), l4);
Show(l3);
return 0;
}![]()
unique特有成员函数
删除相邻且重复的值,只保留一个
重复的值如果不相邻,不会删除
int main() {
list <int> l1{1,1,2,2,4,4,3,3,3,3,0};
list <int> l2{-1,1,1,3,3,3,5,5,-1};
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
cout << "删除过相邻且相同的数字后" << endl;
l1.unique();
l2.unique();
cout << "l1:"; Show(l1);
cout << "l2:"; Show(l2);
return 0;
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容






所有评论(0)