Crewai 挂载接入nmap的方法,让nmap扫描智能化
嗷嗷嗷嗷嗷嗷嗷嗷嗷
Crewai 挂载接入nmap的方法,让nmap扫描智能化
一、引言
crewai最核心的部分就是他能将一个任务分为多个agent和task,能够对其进行细分,并在足够完善的prompt的帮助下能够进行专业的问题分析和完成能力。所以如果我们可以在一个tool里加上crewai对任务分析的能力,那么就相当于给了工具一个能自己思考的能力,一个外置的大脑。
在日常工作中,像Nmap这类常用工具,虽能高效完成基础任务(如端口扫描),但缺乏自主决策与分析能力——例如扫描到开放端口后,无法自动判断是否需要进一步探测服务版本、是否存在安全风险,仍需人工介入解读结果、规划下一步操作。而通过CrewAI与工具的结合,为软件加装“外置大脑”,就能让工具具备自主思考、任务拆解、结果分析与持续优化的能力,实现从“被动执行指令”到“主动完成目标”的升级。
那么该如何实现呢?要给常用软件(以Nmap为例)加装可用的“智能大脑”,首先需明确其必然组成部分,再通过工具封装、大脑核心组件构建、全流程集成,完成整体落地。本文将详细拆解这一过程,并明确代码的附着位置,助力快速实现CrewAI+工具的智能化集成。
二、构建软件“智能大脑”的必然组成
无论对接何种常用软件(Nmap、curl、ping等),通过CrewAI构建的“智能大脑”,其核心组成缺一不可——这些组件分别对应“感知、思考、身份、记忆、执行”五大核心能力,协同实现工具的智能化升级。结合Nmap场景,各组成部分的定义、作用及对应实现载体如下:
2.1 感知层:工具封装
核心作用:作为大脑与目标软件(Nmap)的桥梁,负责接收大脑的指令、执行具体操作,并将操作结果(原始输出)反馈给大脑。没有感知层,大脑将与外部软件完全隔离,无法实现任何实际交互。
实现载体:针对目标软件的Python封装脚本。需将Nmap的命令行调用、输出结果捕获与格式化,封装为CrewAI可识别的Tool类,确保大脑能“调用”Nmap,且能“读懂”Nmap的输出。
2.2 认知层:大语言模型(LLM)
核心作用:负责理解任务目标、分析感知层反馈的结果、做出决策,是实现“自主思考”的核心。CrewAI本身依赖LLM作为认知基础,无需额外开发,但需配置正确的模型参数。
实现载体:CrewAI框架的LLM配置,确保大脑具备足够的分析与决策能力。
2.3 角色层:智能体(Agent)
核心作用:定义大脑的“专业身份”与行为逻辑,明确任务目标、工作背景与操作边界。例如对接Nmap时,可定义“网络安全扫描分析师”Agent,其行为将围绕“安全扫描、漏洞识别、风险评估”展开,而非通用的文本处理。
实现载体:CrewAI的Agent类。需指定Agent的role(角色)、goal(目标)、backstory(背景),并关联感知层的工具(NmapTool),让Agent知道“自己是谁、要做什么、能用什么工具”。
2.4 记忆层:上下文管理
核心作用:存储任务执行过程中的关键信息,包括历史操作记录、结果数据、决策依据等,确保大脑能基于上下文做出连贯决策。
实现载体:CrewAI框架内置的上下文管理机制。Agent在执行任务时,会自动记录当前任务的上下文信息,并传递给后续任务,实现“记忆延续”。
2.5 执行层:任务与流程
核心作用:将高层目标拆解为可执行的步骤(Task),并定义步骤的执行顺序(Process),确保大脑能有序推进任务、高效完成目标。
实现载体:CrewAI的Task类与Process类。
总结:感知层(工具封装)、认知层(LLM)、角色层(Agent)、记忆层(上下文)、执行层(Task+Process),是构建软件“智能大脑”的五大必然组成——缺少任意一环,大脑都无法实现完整的“思考-行动-反馈”闭环。
三、CrewAI+Nmap:智能大脑的完整实现流程
基于上述五大核心组成,以“让Nmap具备自主安全扫描能力”为目标,完整实现流程分为3步:环境准备→大脑核心组件构建→全流程集成运行。
3.1 第一步:环境准备与依赖安装
首先需搭建CrewAI与Nmap的运行环境,确保相关依赖包已安装,基础工具可正常调用:
- 安装系统依赖:确保本地已安装Nmap(可通过
nmap -v验证)。 - 安装Python依赖:创建虚拟环境后,安装CrewAI、工具封装所需依赖。
3.2 第二步:知识层构建——知识库与检索工具(knowledge_tool.py)
核心目标:构建一个“外置大脑”,存储Nmap操作手册和实战端口表,并提供检索工具供Agent查阅。
- 构建知识库:创建
knowledge/目录,存入nmap_cheatsheet.md(操作手册)和common_ports.md(常用端口表)。 - 封装检索工具:编写
knowledge_tool.py,实现对 Markdown 文件的关键词加权检索。
import os
import glob
from typing import Type
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from crewai.tools import BaseTool
class NmapKnowledgeInput(BaseModel):
"""Input schema for NmapKnowledgeTool."""
query: str = Field(..., description="A keyword or question about Nmap usage or Common Ports (e.g., 'stealth scan', 'database ports', 'web logic port').")
class NmapKnowledgeTool(BaseTool):
name: str = "Nmap & Security Knowledge Base"
description: str = (
"Use this tool to look up Nmap command flags, usage examples, and Common Port Lists. "
"Useful when you need to know which flags to use OR which specific ports to scan for a service (e.g., 'what ports are for database?')."
)
args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = NmapKnowledgeInput
def _run(self, query: str) -> str:
"""
Search all markdown files in the knowledge directory.
"""
# Define path relative to this file
current_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
knowledge_dir = os.path.join(current_dir, "knowledge")
# Get all .md files
md_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(knowledge_dir, "*.md"))
if not md_files:
return "Error: No knowledge base files found in 'knowledge' directory."
query_lower = query.lower()
keywords = query_lower.split()
all_relevant_sections = []
for file_path in md_files:
try:
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
content = f.read()
except Exception as e:
continue
# Split by headers (## ) to get sections
sections = content.split("## ")
for section in sections:
if not section.strip():
continue
# Re-add the header prefix for readability
full_section = "## " + section
section_lower = full_section.lower()
# Check if any query word appears in the section
# Weighted matching: If ALL keywords are present, it's a strong match
if all(k in section_lower for k in keywords):
all_relevant_sections.insert(0, f"[Source: {os.path.basename(file_path)}]\n{full_section.strip()}")
# If some keywords present, weak match
elif any(k in section_lower for k in keywords):
all_relevant_sections.append(f"[Source: {os.path.basename(file_path)}]\n{full_section.strip()}")
if not all_relevant_sections:
return (
f"No specific section found strictly matching '{query}'. "
"Try broader terms like 'scan', 'ports', 'database', or 'web'."
)
# Return top 3 matches to keep context small
return "\n\n---\n\n".join(all_relevant_sections[:3])
3.3 第三步:感知层实现——Nmap工具封装(nmap_tools.py)
核心目标:将Nmap的命令行操作封装为CrewAI可调用的Tool类,确保大脑能通过简单调用实现Nmap的功能,并获取格式化的结果。
import subprocess
from typing import Type
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from crewai.tools import BaseTool
class NmapInput(BaseModel):
"""Input schema for NmapTool."""
target: str = Field(..., description="The target IP address or hostname to scan.")
options: str = Field(default="-F", description="Nmap command line options (e.g., '-sV', '-F'). Default is '-F' (Fast scan).")
class NmapTool(BaseTool):
name: str = "System Nmap Scanner"
description: str = (
"Use this tool to scan a target network address using the local 'nmap' command. "
"It returns the raw text output of the scan. "
"Input requires a 'target' (IP/Domain) and optional 'options' (flags)."
)
args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = NmapInput
def _run(self, target: str, options: str = "-F") -> str:
# Construct the command safely
# We split options by space to pass them as separate arguments list
# Note: This is a basic implementation. In production, sanitize inputs strictly.
command = ["nmap"] + options.split() + [target]
print(f"DEBUG: Running command: {' '.join(command)}")
try:
# Run the command
result = subprocess.run(
command,
capture_output=True,
text=True,
# We don't enforce check=True immediately to capture stderr in the output if needed,
# but nmap usually returns non-zero on error.
)
if result.returncode != 0:
return f"Nmap Command Failed:\nstdout: {result.stdout}\nstderr: {result.stderr}"
return result.stdout
except FileNotFoundError:
return "Error: The 'nmap' command was not found on this system. Please install nmap (e.g., 'sudo apt install nmap')."
except Exception as e:
return f"Error executing nmap: {str(e)}"
3.4 第四步:大脑核心组件构建与集成(main.py)
核心目标:在main.py中集成六大必然组成,定义Agent(角色层)、Task(执行层)、LLM(认知层),调用nmap_tools.py(感知层)和 knowledge_tool.py(知识层),并依托CrewAI的内置记忆(记忆层),实现全流程智能化运行。
实现步骤(对应代码逻辑):
- 导入依赖:导入CrewAI核心类、NmapTool以及新增的NmapKnowledgeTool;
- 配置LLM(认知层):指定使用的大语言模型;
- 初始化工具(感知层 & 知识层):实例化NmapTool和NmapKnowledgeTool;
- 定义Agent(角色层):
- Layer 1 顾问:装备
NmapKnowledgeTool,负责查阅知识库并制定方案; - Layer 2 操作员:装备
NmapTool,负责执行; - Layer 3 报告员:负责总结;
- Layer 1 顾问:装备
- 创建Task(执行层):将高层目标拆解为子任务(查阅知识->制定方案->执行扫描->生成报告);
- 配置流程(执行层):定义串行工作流;
- 启动运行。
import os
import sys
import subprocess
from typing import Type
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from crewai import Agent, Task, Crew, Process, LLM
from crewai.tools import BaseTool
# Import the new Knowledge Tool
from knowledge_tool import NmapKnowledgeTool
# =============================================================================
# 0. TOOL DEFINITION
# =============================================================================
class NmapInput(BaseModel):
"""Input schema for NmapTool."""
target: str = Field(..., description="The target IP address or hostname to scan.")
options: str = Field(default="-F", description="Nmap command line options (e.g., '-sV', '-F'). Default is '-F' (Fast scan).")
class NmapTool(BaseTool):
name: str = "System Nmap Scanner"
description: str = (
"Use this tool to scan a target network address using the local 'nmap' command. "
"It returns the raw text output of the scan. "
"Input requires a 'target' (IP/Domain) and optional 'options' (flags)."
)
args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = NmapInput
def _run(self, target: str, options: str = "-F") -> str:
command = ["nmap"] + options.split() + [target]
print(f"DEBUG: Running command: {' '.join(command)}")
try:
result = subprocess.run(command, capture_output=True, text=True)
if result.returncode != 0:
return f"Nmap Command Failed:\nstdout: {result.stdout}\nstderr: {result.stderr}"
return result.stdout
except FileNotFoundError:
return "Error: The 'nmap' command was not found. Please install nmap."
except Exception as e:
return f"Error executing nmap: {str(e)}"
# =============================================================================
# 1. BRAIN CONFIGURATION (LLM)
# =============================================================================
LLM_API_KEY = os.getenv("LLM_API_KEY", "your-llm-api-key-here")
LLM_BASE_URL = os.getenv("LLM_BASE_URL", "https://your-llm-base-url-here/api/v1")
LLM_MODEL = os.getenv("LLM_MODEL", "your-llm-model-name-here")
my_llm = LLM(
model=f"openai/{LLM_MODEL}",
base_url=LLM_BASE_URL,
api_key=LLM_API_KEY
)
# =============================================================================
# 2. AGENTS (Personas - 3 Layers)
# =============================================================================
# Instantiate the Knowledge Tool
nmap_knowledge_tool = NmapKnowledgeTool()
# Layer 1: Understanding & Translation
# ------------------------------------
# Role: Translate natural language (vague) into technical specifications (precise).
consultant_agent = Agent(
role='Senior Security Consultant (Requirement Analyst)',
goal='Accurately interpret client security requirements from natural language and translate them into precise technical scanning specifications.',
backstory=(
"You are a world-class security consultant with a background in network engineering. "
"You have access to a specialized 'Nmap Reference Manual' (Knowledge Tool). "
"When you receive a user instruction, you should FIRST check the knowledge base if you are unsure about the best flags. "
"For example, if the user asks for a 'stealth scan', use the tool to find the recommended flags in the manual. "
"Your job is to ensure the technical team knows EXACTLY what to do based on vague user requests. "
"IMPORTANT RULES:\n"
"1. Consult the 'Nmap Reference Manual' for flag recommendations.\n"
"2. If a user provides an IP and asks to scan its 'subnet' or 'network', you must convert it to the network address (e.g., 192.168.1.100 -> 192.168.1.0/24)."
),
tools=[nmap_knowledge_tool], # Equipped with the Knowledge Tool
verbose=True,
allow_delegation=False,
llm=my_llm
)
# Layer 2: Execution & Operation
# ------------------------------------
# Role: Execute the tool strictly according to specs and return raw data.
operator_agent = Agent(
role='Network Reconnaissance Specialist (Nmap Operator)',
goal='Execute network scans with surgical precision using Nmap and provide raw, unfiltered technical data.',
backstory=(
"You are an elite Red Team operator specializing in reconnaissance. "
"You trust only raw data. You receive technical specs and execute them efficiently using the Nmap tool. "
"You do not interpret the business impact; you provide the facts—ports, services, versions, and OS fingerprints—exactly as the tool reveals them. "
"You are responsible for handling the tool's output and ensuring it is complete."
),
tools=[NmapTool()],
verbose=True,
allow_delegation=False,
llm=my_llm
)
# Layer 3: Analysis & Reporting
# ------------------------------------
# Role: Synthesize findings into a professional Chinese report.
reporting_agent = Agent(
role='Chief Information Security Officer (Reporting Analyst)',
goal='Synthesize technical findings into a comprehensive, professional security report in Chinese for stakeholders.',
backstory=(
"You are a CISO with decades of experience. "
"You take raw technical data and transform it into actionable intelligence. "
"You identify critical risks, explain technical details in accessible language (Chinese), and provide remediation advice. "
"Your reports are the gold standard in the industry: clear, structured, and insightful."
),
verbose=True,
allow_delegation=False,
llm=my_llm
)
# =============================================================================
# 3. TASKS (Planning - 3 Steps)
# =============================================================================
def create_analysis_task(user_input):
return Task(
description=(
f"Analyze the following client instruction: '{user_input}'.\n"
"1. **Knowledge Retrieval**: If the instruction contains terms like 'stealth', 'fast', 'OS detection', or 'UDP', use the 'Nmap Reference Manual' tool to find the correct flags.\n"
" - Example Query: 'stealth scan flags', 'host discovery only', 'version detection'.\n"
"2. **Intent Extraction**: Determine what the user really wants (e.g., Host Discovery, Port Scanning, OS Detection, Vulnerability Check).\n"
"3. **Target Definition**: Identify the IP, Subnet, or Domain. \n"
" - CRITICAL: If the user asks to scan the 'subnet' of a specific IP (e.g., 192.168.1.100), convert it to the /24 CIDR format (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24).\n"
"4. **Technical Specification**: Select the optimal 'nmap' flags based on your knowledge retrieval.\n"
"5. **Output**: Produce a clear technical directive for the Operator."
),
expected_output=(
"A structured technical directive containing:\n"
"- TARGET: <ip_or_cidr>\n"
"- FLAGS: <nmap_flags_string>\n"
"- SCAN_TYPE: <description_of_strategy>\n"
"- REASONING: <why_these_flags_were_chosen_based_on_knowledge_base>"
),
agent=consultant_agent
)
def create_execution_task():
return Task(
description=(
"1. **Receive Directive**: Read the technical directive provided by the Security Consultant.\n"
"2. **Execute Scan**: Use the 'System Nmap Scanner' tool strictly with the provided TARGET and FLAGS.\n"
"3. **Capture Output**: Ensure the full stdout from Nmap is captured.\n"
"4. **Pass-through**: Do not summarize yet; pass the raw data and a brief technical confirmation to the Reporting Analyst."
),
expected_output=(
"The raw output from the Nmap tool, accompanied by a brief confirmation of execution status (Success/Failure)."
),
agent=operator_agent
)
def create_reporting_task():
return Task(
description=(
"1. **Ingest Data**: Read the raw Nmap scan results provided by the Operator.\n"
"2. **Analyze Findings**: Identify open ports, running services, software versions, and OS details.\n"
"3. **Risk Assessment**: Evaluate the security implications of these findings (e.g., 'Old Apache version found', 'Telnet is insecure').\n"
"4. **Draft Report**: Write a FINAL report in **Chinese (中文)**.\n"
" - Use professional Markdown formatting.\n"
" - Include sections for: Executive Summary, Technical Findings (Table), Risk Analysis, and Recommendations."
),
expected_output=(
"一份完整的中文安全评估报告 (Markdown 格式),包含:\n"
"1. **执行摘要**: 简述扫描目标和整体安全状况。\n"
"2. **详细发现**: 列出端口、协议、服务、版本 (使用表格形式)。\n"
"3. **系统指纹**: 操作系统猜测 (如果有)。\n"
"4. **风险分析**: 对发现的高危端口或服务进行点评。\n"
"5. **加固建议**: 针对性的安全建议。"
),
agent=reporting_agent
)
# =============================================================================
# 4. EXECUTION (The Crew)
# =============================================================================
def main():
print("## 智能安全大脑 (Nmap-Brain) - 3 Layer Architecture + Knowledge Base ##")
print("---------------------------------------------------------------------")
print("架构说明:")
print(" [Layer 1] 顾问 Agent: 查阅知识库 -> 理解需求 -> 制定技术方案")
print(" [Layer 2] 操作 Agent: 执行工具 -> 获取原始数据")
print(" [Layer 3] 报告 Agent: 数据分析 -> 生成中文报告")
print("---------------------------------------------------------------------")
# Get input safely handling encoding issues
try:
user_instruction = input("请输入您的指令 (支持中文): ")
except UnicodeDecodeError:
# Fallback for environments with encoding issues (like some Docker containers or SSH sessions)
print("\n[!] 检测到输入编码错误,尝试使用系统默认编码读取...")
try:
user_instruction = sys.stdin.readline().strip()
except Exception:
print("无法读取输入。")
user_instruction = ""
if not user_instruction:
print("未检测到输入,默认扫描本机...")
user_instruction = "对本机 127.0.0.1 进行一次全面的服务版本和操作系统扫描"
# Define tasks
task1 = create_analysis_task(user_instruction)
task2 = create_execution_task()
task3 = create_reporting_task()
# Form the crew
crew = Crew(
agents=[consultant_agent, operator_agent, reporting_agent],
tasks=[task1, task2, task3],
process=Process.sequential
)
print(f"\n[+] 正在启动三层处理流程 (带知识库支持)...\n")
result = crew.kickoff()
print("\n\n########################")
print("## 最终安全报告 ##")
print("########################\n")
print(result)
# Save report
with open("security_report_v2.md", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(str(result))
print("\n[v] 报告已保存至 security_report_v2.md")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.4 第四步:运行与验证
将上述两个代码文件(nmap_tools.py、main.py)放在同一目录下,完成以下操作即可启动智能扫描:
- 替换main.py中的LLM API密钥;
- 打开终端,进入代码目录,执行命令:
python main.py;并告诉ai你需要进行什么样的扫描操作,且期待的结果是什么 - 观察终端输出:CrewAI将自动按顺序执行三个任务,调用Nmap工具完成扫描,分析结果并生成风险评估报告——整个过程无需人工干预,体现“大脑”的自主思考与执行能力。
3.5 第五步:运行与验证
将上述代码文件(main.py, nmap_tools.py, knowledge_tool.py, knowledge/)放在同一目录下,执行 python main.py。
- 用户输入:告诉ai你需要进行什么样的扫描操作,且期待的结果是什么。
- Layer 1 (顾问):自主调用
knowledge_tool查询知识库内容,生成 参数指令 - Layer 2 (操作):接收指令,调用 NmapTool 执行扫描。
- Layer 2 (操作):接收指令,调用
NmapTool执行扫描。 - Layer 3 (报告):生成中文风险报告。
在终端我们能看到agent在理解我们抽象的要求,自主查阅知识库的过程,然后将其转化成规范术语,报送给下一个agent
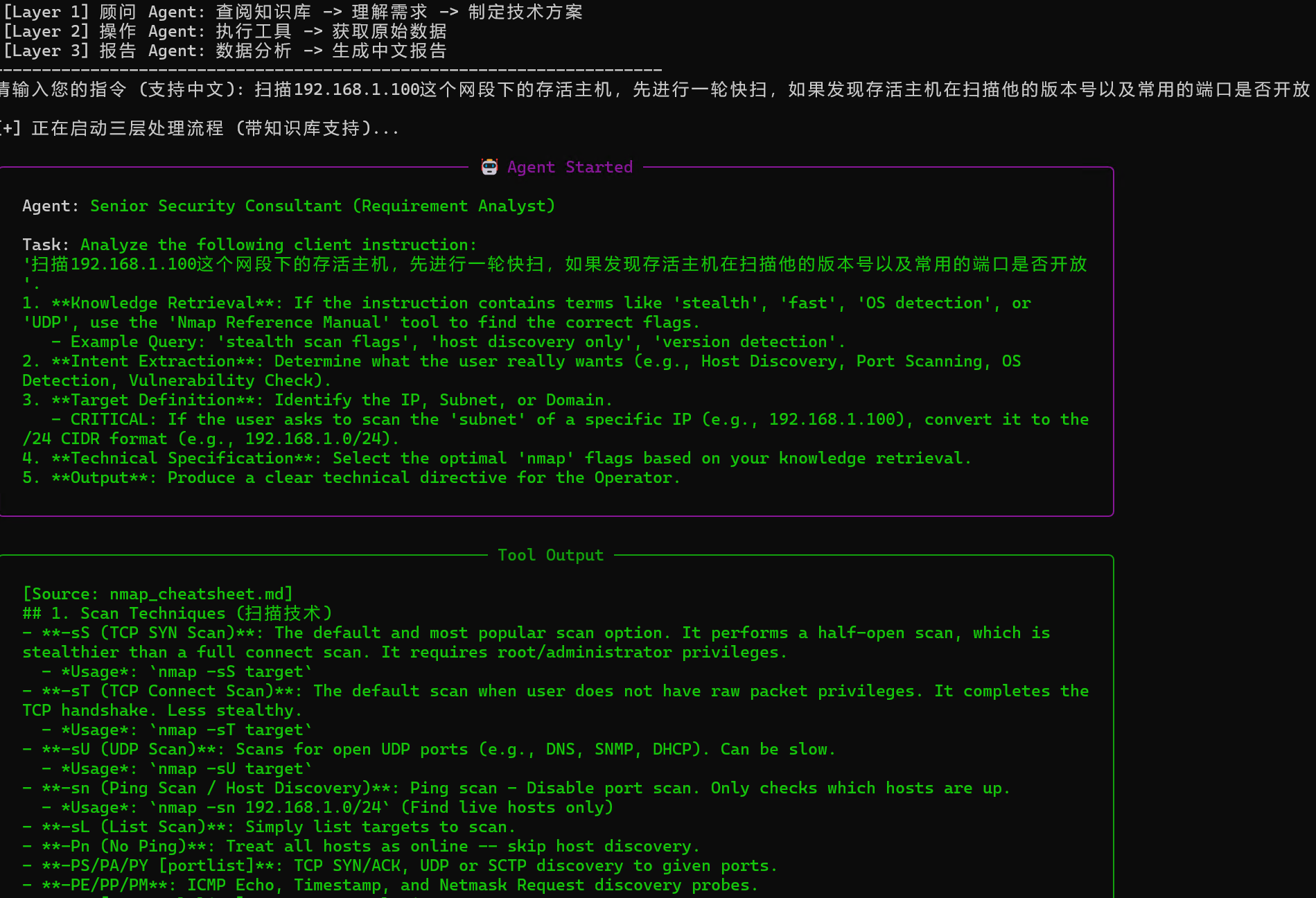
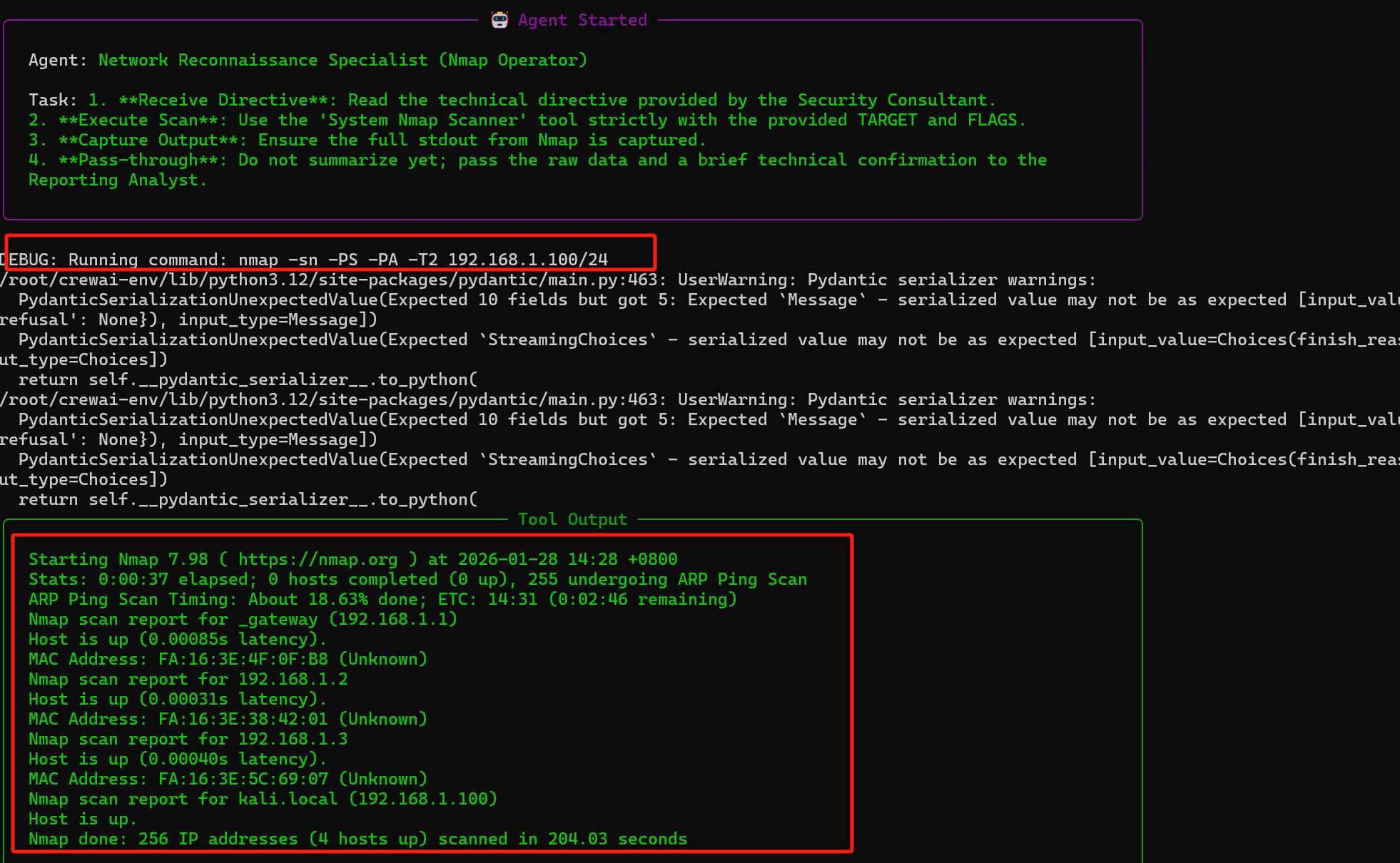
然后第二层的agent通过数据进行命令调用,并返回扫描结果
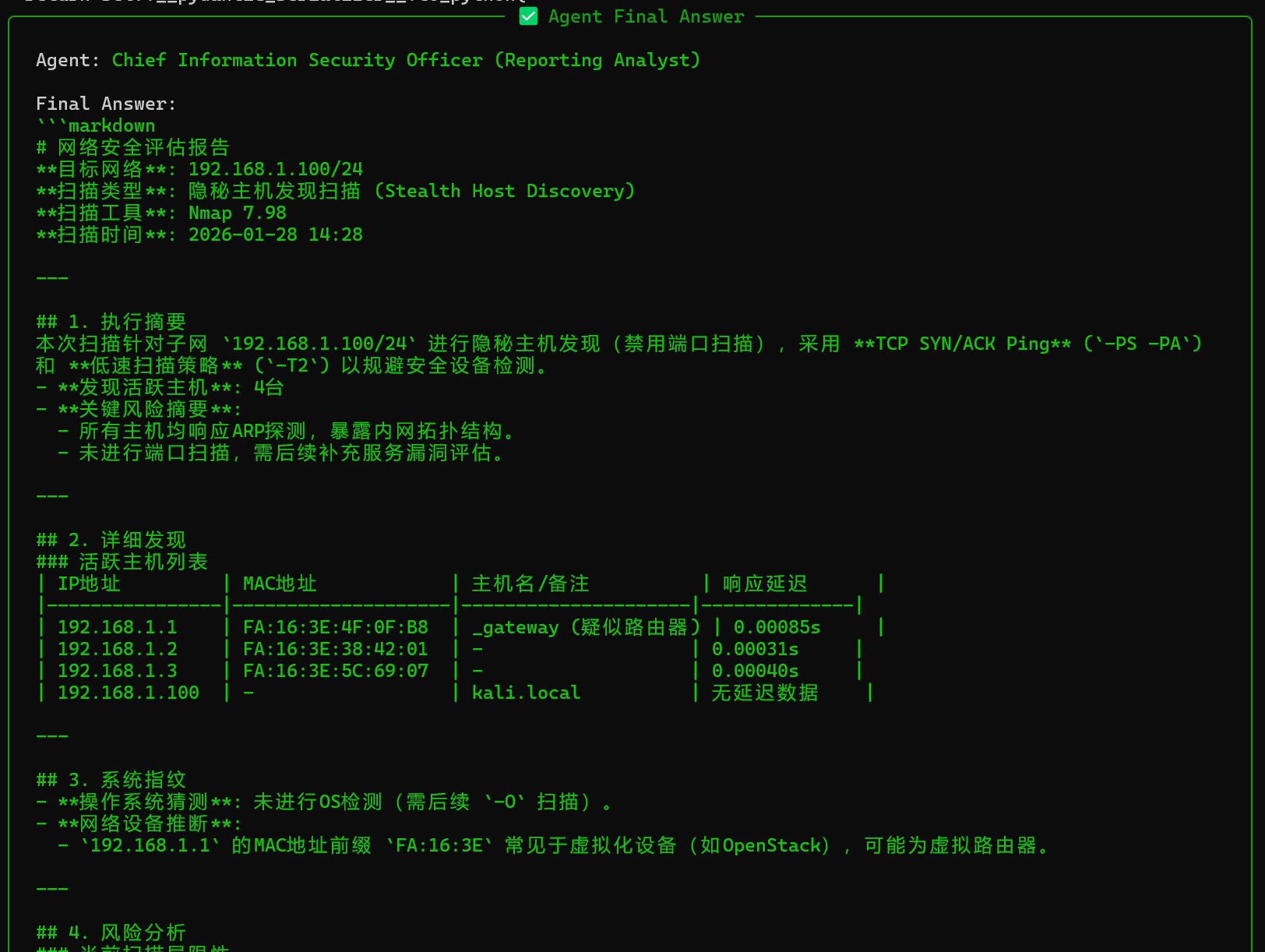
最后一层agent根据nmap扫描的结果,生成分析报告并返回
五、总结
给常用软件加装“智能大脑”,本质是通过CrewAI构建“感知-认知-角色-记忆-执行-知识”六大核心组成的闭环。,其中感知层(工具封装)是基础,认知层(LLM)是核心,角色层(Agent)是准则,记忆层(上下文)是连贯,执行层(Task+Process)是落地,知识层是对具体知识的查阅——六大组成缺一不可,共同实现工具的自主思考与智能执行。
以Nmap为例,通过nmap_tools.py完成感知层封装,通过main.py集成其他四大组成,即可实现“CrewAI+Nmap”的智能化升级。知识库的加入意味着你不需要修改代码来教 AI 新的扫描技巧,只需要把新的 Markdown 文档扔进 knowledge/ 文件夹,它就能立刻学会。该方案具备极强的扩展性,可轻松迁移到其他领域。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容






所有评论(0)