从零构建Agentic RAG系统:让AI像人一样思考,智能调用工具解决问题
本文详细介绍了如何构建一个Agentic RAG系统,该系统结合了检索增强生成(RAG)和AI Agent技术,能够智能地调用不同工具解决问题。文章首先解释RAG的基本概念和工作流程,然后展示如何将其与AI Agent结合形成Agentic RAG系统。通过使用自定义工具(包括RAG工具和网络搜索工具)和向量数据库,系统可以灵活检索公司内部信息或进行网络搜索,获取最新数据来回答用户问题。文中提供了
文章介绍了如何构建Agentic RAG系统,该系统能像人类一样思考,连续调用不同工具解决问题。首先解释了RAG(检索增强生成)的基本概念,然后展示了如何将其与AI Agent结合形成Agentic RAG。通过使用自定义工具和向量数据库,系统可以检索公司内部信息或进行网络搜索,智能地获取最新数据来回答用户问题。文章提供了完整的代码实现和示例,展示了系统如何根据查询类型自动选择合适的工具,最终生成准确的回答。
使用自定义工具和向量数据库创建Agentic RAG 系统的分步指南,让它学会向人一样不断思考连续调用不同工具解决问题
智能体人工智能正在迅速普及,现在是时候进行另一次详细的教程了,这不仅能帮助你构建你的第一个智能体 RAG 系统,还能让你深入了解它的组成部分。
我们的教程从 RAG 开始,再过渡到Agentic RAG 。
LLM 的内部知识有限,它基于训练数据和上下文长度。
为了确保LLM能够使用最新数据回答查询,我们可以使用相关数据集对其进行微调。这有助于提升LLM的内部知识水平。
不过,这里有个问题。
虽然微调可以提高 LLM 保持最新状态的性能,但由于数据经常过时,因此必须反复进行微调。
**另一方面, RAG(检索增强生成)**是一种通过将LLM连接到外部知识源来获取最新、可信信息的技术。
这使得LLM能够根据外部可验证的数据源动态生成响应,而不仅仅是根据其内部知识。
RAG 中的术语含义如下:
- 检索:从知识库/特定私有数据集中检索相关信息/文档的过程。
- 增强:将检索到的信息添加到LLM的输入上下文中的过程。
- 生成:LLM根据原始查询及其增强的上下文生成响应的过程。
典型的 RAG 流水线如下所示。
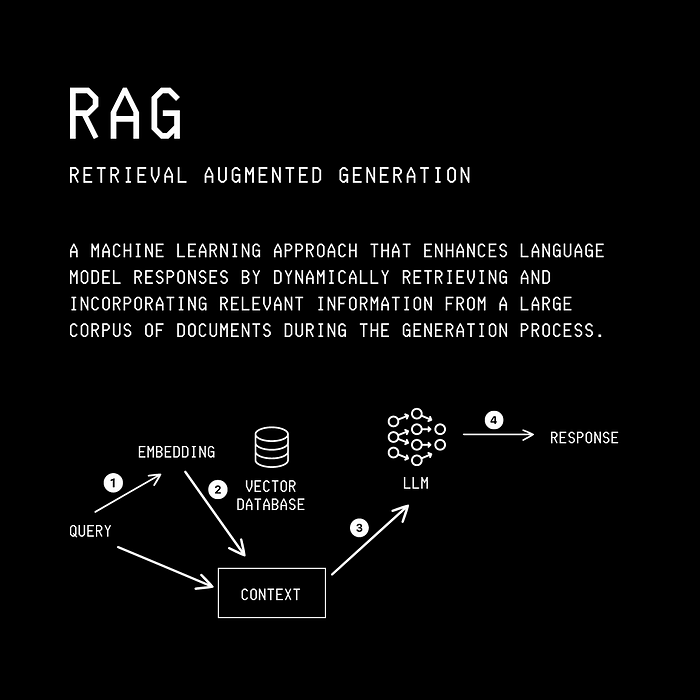
过程如下:
- 用户查询LLM
- 用户查询通过嵌入模型进行处理,该模型将查询转换为嵌入(密集向量)。
- 这种向量化查询(查询嵌入)用于搜索向量数据库。该搜索会从数据库中返回与查询最相关的前 K 个文档。
- 检索到的文档与原始用户查询相结合,并作为上下文传递给 LLM。
- LLM 生成响应并将其返回给用户。
请注意,此过程与通常的工作流程不同,在通常的工作流程中,用户查询 LLM 并根据 LLM 的内部信息直接获得响应。
Agentic RAG 是传统 RAG 系统的一项进步。
它涉及将传统的 RAG 与AI Agent相结合,AI Agent是能够推理、计划并采取多个步骤来完成任务的自主系统。
Agentic RAG 指的是Agent使用检索作为其工具之一。
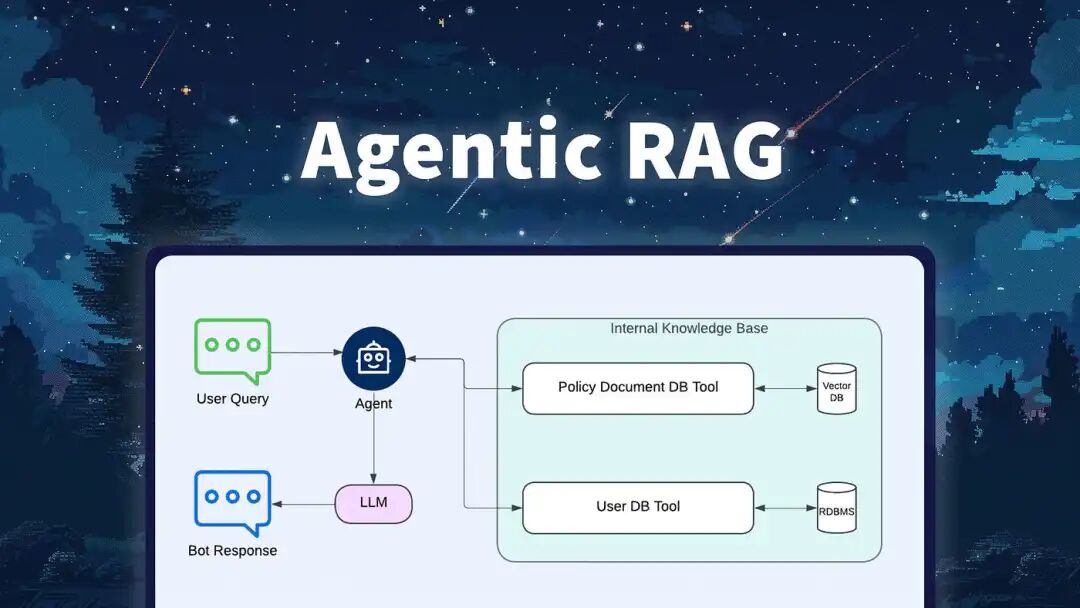
为了更好地理解它,我们将创建一个简单的客户聊天机器人,它可以动态地对公司的数据或互联网执行 RAG 操作。
安装软件包
我们首先安装软件包来构建我们的 Agentic RAG 系统,如下所示。
pip install sentence_transformers
pip install langgraph==1.0.7
pip install langchain_openai==1.1.7
pip install langchain-core==1.2.7
pip install google-search-results
我们将从头开始编写 RAG 和 Web 搜索工具。
建立公司向量数据库
我们首先实例化一个向量数据库,并向其中company_db添加关于我们假设的公司的信息。
# Set up our custom company vector database
company_db = VectorDatabase()
# Hypothetical company information
company_information = [
"Quantum Horizons Inc. is a pioneering space exploration company founded in 2030.",
"The company specializes in developing quantum-powered spacecraft for interplanetary travel.",
"With a team of 500 aerospace engineers and quantum physicists, Quantum Horizons is pushing the boundaries of space technology.",
"Their flagship project, the 'StarLeap', aims to reduce travel time to Mars from months to just weeks.",
"Quantum Horizons has established the first permanent research base on the Moon's far side.",
"The company's innovative quantum propulsion system has revolutionized the concept of space travel.",
"Headquartered in a state-of-the-art facility in Houston, Quantum Horizons also maintains orbital research stations.",
"They've partnered with major space agencies worldwide to advance human presence in the solar system.",
"Quantum Horizons' CEO, Dr. Zara Novak, is a former astronaut and a leading expert in quantum mechanics.",
"The company's mission is to make interplanetary travel accessible and establish humanity as a multi-planet species."
]
编写我们的rag工具
我们定制的 RAG 工具:
- 收到我们agent的提问
- 从向量数据库中检索与公司信息相关的信息(“检索”)
- 围绕问题构建上下文(“增强”)
- 使用LLM根据上下文生成答案(“生成”)
- 将答案返回给agent
@tool("RAG Tool")
def rag_tool(question: str) -> str:
"""Tool to search for relevant information from a vector database."""
# Encode the question
query_vec = model.encode(question)
# Get top 5 similar vector
results = company_db.search(query_vec, top_k = 5)
# Build context from the results
context = "\n".join([f"- {res['metadata']['sentence']}" for res in results])
# Return the answer
return context
编写网络搜索工具
我们的定制网络搜索工具使用Serper,它是谷歌搜索 API,可以实时获取网络信息。
首先,在他们的网站上注册并获取您的 API 密钥,即可获得一定 次数免费查询。接下来,按如下方式将此 API 密钥添加为环境变量。
os.environ["SERPER_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_API_KEY"
现在一切就绪,我们的自定义网络搜索工具将执行以下操作:
返回格式化的摘要,其中包含每个结果的标题、链接和摘要信息。
# Create custom Web search tool
@tool
def web_search_tool(query: str) -> str:
"""
Use this tool to search the internet for CURRENT events, news, and external knowledge.
CRITICAL: You MUST use this tool for any questions regarding 2024, 2025, 2026,
Nobel prizes, sports results, or real-time information.
"""
search = GoogleSearch({
# "as_dt":'exclude',#include
"q": query,
"api_key": os.environ.get("SERPER_API_KEY"),
})
results = search.get_dict()
# print(results)
# print(results['organic_results'])
# Get value associated with key "organic" else return []
search_results = results.get("organic_results", [])
if not search_results:
return "No search results found."
context = ""
for result in search_results:
title = result.get("title", "")
link = result.get("link", "")
snippet = result.get("snippet", "")
context += f"Title: {title}\nLink: {link}\nSnippet: {snippet}\n\n"
# print(context)
return f"Web Search Results:\n{context}"
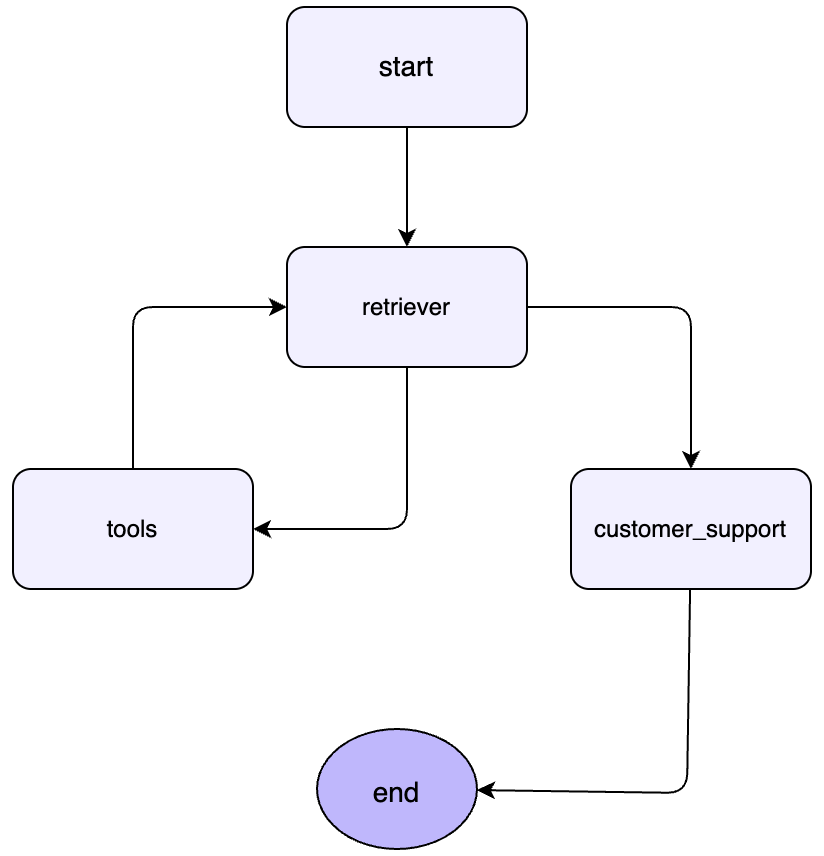
Langgraph的核心代码:
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model=MODEL,
api_key=API_KEY,
base_url=API_URL,
temperature=0
)
tools = [rag_tool, web_search_tool]
# 绑定工具到 LLM,这样 LLM 才知道可以调用它们
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
# 临时测试代码
# llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
response = llm_with_tools.invoke([HumanMessage(content="Hello")])
print(response)
# ==========================================
# 2. State (状态定义)
# ==========================================
class AgentState(TypedDict):
# 消息历史:存储所有对话记录(包括工具调用)
messages: Annotated[List[BaseMessage], add_messages]
# 用户原始查询
user_query: str
# 最终结果
final_answer: str
# ==========================================
# 3. Nodes (手动定义节点)
# ==========================================
# --- Node 1: Retriever Node (Core Logic) ---
import datetime
# ... (之前的代码)
def retriever_node(state: AgentState):
messages = state["messages"]
current_date = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
# --- 关键修改:将 Prompt 改为“回退策略 (Fallback Strategy)” ---
system_prompt_content = f"""You are a smart researcher assistant. Current Date: {current_date}.
Your Goal: Answer the user's question using the most reliable source.
### EXECUTION STRATEGY (Follow this strictly):
1. **PHASE 1: Check Internal Knowledge (RAG)**
- For ANY information query (technical, company, factual), ALWAYS start by calling 'rag_tool' first.
- Exception: Only skip RAG if the user is just saying "Hi" or asking for help writing a generic email.
2. **PHASE 2: Evaluate & Fallback**
- Look at the output from 'rag_tool'.
- **IF** the RAG context contains the answer -> Finalize the answer.
- **IF** the RAG context is empty, irrelevant, or doesn't fully answer the question -> **YOU MUST IMMEDIATELY call 'web_search_tool'**.
3. **PHASE 3: Final Answer**
- Use the info from Web Search to answer.
### CRITICAL RULES:
- Do NOT answer from your own memory if RAG fails. Search the web instead.
- If the user asks about "2024/2025/2026 events" or "News", and RAG fails, you MUST use web search.
User Query: {state['user_query']}
"""
# 逻辑保持不变:如果没有 SystemMessage 则添加
if isinstance(messages[0], SystemMessage):
input_messages = [SystemMessage(content=system_prompt_content)] + messages[1:]
else:
input_messages = [SystemMessage(content=system_prompt_content)] + messages
# 调用 LLM
response = llm_with_tools.invoke(input_messages)
# --- Debug 信息 (方便你观察它是否进行了“二次尝试”) ---
print(f"\nDEBUG [Retriever]: Processing step...")
if response.tool_calls:
print(f" -> Decision: Calling Tool: {[t['name'] for t in response.tool_calls]}")
else:
print(f" -> Decision: Responding directly (Content length: {len(response.content)})")
return {"messages": [response]}
# --- Node 2: Tool Execution Node ---
# 使用 LangGraph 内置的 ToolNode 来运行工具,这是最稳定的组件
tool_node = ToolNode(tools)
# --- Node 3: Customer Support Node ---
def customer_support_node(state: AgentState):
"""
客服代理。
当 Retriever 决定停止搜索并给出总结后,这个节点接手进行最终润色。
"""
# 获取 Retriever 的最后一条消息作为检索到的信息
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
retrieved_info = last_message.content
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", (
"You are a Senior Customer Support Agent.\n"
"Goal: Answer the user query using the retrieved info accurately and concisely.\n"
"If info is missing, apologize."
)),
("user", (
"User Query: {user_query}\n\n"
"Retrieved Context:\n{retrieved_info}"
))
])
chain = prompt | llm
response = chain.invoke({
"user_query": state["user_query"],
"retrieved_info": retrieved_info
})
return {"final_answer": response.content}
# ==========================================
# 4. Conditional Logic (路由逻辑)
# ==========================================
def route_retriever(state: AgentState):
"""
决定下一步去哪:
1. 如果 LLM 想要调用工具 -> 去 'tools' 节点
2. 如果 LLM 输出了文本(找到了信息) -> 去 'customer_support' 节点
"""
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
# 检查是否有工具调用请求
if last_message.tool_calls:
return "tools"
else:
return "customer_support"
# ==========================================
# 5. Graph Construction (构建图)
# ==========================================
workflow = StateGraph(AgentState)
# 添加节点
workflow.add_node("retriever", retriever_node)
workflow.add_node("tools", tool_node)
workflow.add_node("customer_support", customer_support_node)
# 设置入口
workflow.add_edge(START, "retriever")
# 设置条件边 (从 Retriever 出发)
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"retriever",
route_retriever,
{
"tools": "tools", # 如果决定调用工具,去 tools 节点
"customer_support": "customer_support" # 如果决定结束搜索,去客服节点
}
)
# 设置工具返回后的边 (工具执行完 -> 回到 Retriever 继续思考)
workflow.add_edge("tools", "retriever")
# 设置结束边
workflow.add_edge("customer_support", END)
# 编译
app = workflow.compile()
# ==========================================
# 6. Run (运行)
# ==========================================
def run_query(query: str):
print(f"\n--- Running for: {query} ---")
# 初始化状态,放入用户的查询
inputs = {
"user_query": query,
"messages": [HumanMessage(content=query)]
}
try:
# 运行图
result = app.invoke(inputs)
print(f"Final Result:\n{result['final_answer']}")
except Exception as e:
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Test 1: 需要 RAG
run_query("What is the name of the flagship project of the company?")
# Test 2: 需要 Web Search
run_query("Who won the Nobel prize in 2024 in Physics?")
核心流程图:
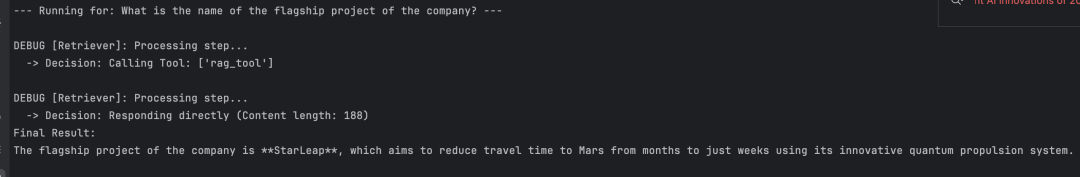
让我们运行第一个示例
run_query("What is the name of the flagship project of the company?")
调用 rag tool检索,其调用日志和结果如下:
运行另外一个示例,这个工具先调用rag tool,发现没有符合数据,然后开始调用web search tool
# Test 2: 需要 Web Search
run_query("Who won the Nobel prize in 2024 in Physics?")
其调用日志和结果如下所示:
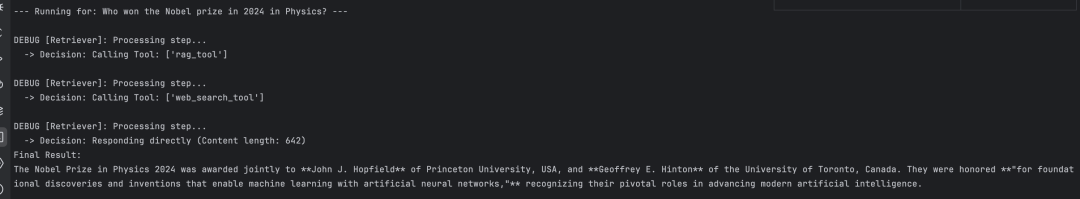
当无法找到正确回答用户查询的信息时,它会使用网络搜索工具。
成功后,系统会将此信息传递给高级客户支持节点,由其最终给出答案。
这种适应性正是 Agentic RAG 如此强大的原因,能连续调用不同工具来解决上下文缺失的问题,这点和人处理问题的逻辑保持一致。
AI大模型从0到精通全套学习大礼包
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
只要你是真心想学AI大模型,我这份资料就可以无偿共享给你学习。大模型行业确实也需要更多的有志之士加入进来,我也真心希望帮助大家学好这门技术,如果日后有什么学习上的问题,欢迎找我交流,有技术上面的问题,我是很愿意去帮助大家的!
如果你也想通过学大模型技术去帮助就业和转行,可以扫描下方链接👇👇
大模型重磅福利:入门进阶全套104G学习资源包免费分享!

01.从入门到精通的全套视频教程
包含提示词工程、RAG、Agent等技术点
02.AI大模型学习路线图(还有视频解说)
全过程AI大模型学习路线

03.学习电子书籍和技术文档
市面上的大模型书籍确实太多了,这些是我精选出来的

04.大模型面试题目详解


05.这些资料真的有用吗?
这份资料由我和鲁为民博士共同整理,鲁为民博士先后获得了北京清华大学学士和美国加州理工学院博士学位,在包括IEEE Transactions等学术期刊和诸多国际会议上发表了超过50篇学术论文、取得了多项美国和中国发明专利,同时还斩获了吴文俊人工智能科学技术奖。目前我正在和鲁博士共同进行人工智能的研究。
所有的视频由智泊AI老师录制,且资料与智泊AI共享,相互补充。这份学习大礼包应该算是现在最全面的大模型学习资料了。
资料内容涵盖了从入门到进阶的各类视频教程和实战项目,无论你是小白还是有些技术基础的,这份资料都绝对能帮助你提升薪资待遇,转行大模型岗位。


智泊AI始终秉持着“让每个人平等享受到优质教育资源”的育人理念,通过动态追踪大模型开发、数据标注伦理等前沿技术趋势,构建起"前沿课程+智能实训+精准就业"的高效培养体系。
课堂上不光教理论,还带着学员做了十多个真实项目。学员要亲自上手搞数据清洗、模型调优这些硬核操作,把课本知识变成真本事!

如果说你是以下人群中的其中一类,都可以来智泊AI学习人工智能,找到高薪工作,一次小小的“投资”换来的是终身受益!
应届毕业生:无工作经验但想要系统学习AI大模型技术,期待通过实战项目掌握核心技术。
零基础转型:非技术背景但关注AI应用场景,计划通过低代码工具实现“AI+行业”跨界。
业务赋能 突破瓶颈:传统开发者(Java/前端等)学习Transformer架构与LangChain框架,向AI全栈工程师转型。
👉获取方式:
😝有需要的小伙伴,可以保存图片到wx扫描二v码免费领取【保证100%免费】🆓
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献605条内容
已为社区贡献605条内容






所有评论(0)