LangChain入门(十二)LangChain里的智能“降级”fallback-chain实战
本文深入解析LangChain的Fallback Chain机制,通过实际代码示例展示如何构建具备自动降级能力的AI应用系统。当主模型服务异常时,系统能无缝切换备用方案,保障服务持续可用。

前言
在上一篇文章中,我们探讨了LangChain框架下大语言模型的多种路由、分流、熔断以及质量检测与性能监控机制。那些基础组件为构建稳健的AI应用提供了重要保障,但它们更多侧重于预防和预警。现实中,即使最完善的系统也可能遇到突发故障,这就需要我们准备切实可行的应对方案。
本篇将聚焦于一个更加实用的场景:当主模型服务不可用时,如何实现智能切换和自动降级。笔者在多次项目实践中深刻体会到,一个AI应用的稳定性不仅取决于其正常情况下的表现,更在于异常发生时的自我修复能力。Fallback Chain正是为此而设计的优雅解决方案。
在实际开发中,笔者观察到很多团队过于关注模型效果的优化,却忽视了基础服务的可靠性。这种做法在演示环境中或许可行,但投入到生产环境就会暴露出严重问题。一个成熟的AI应用应该像精密的机械设备,既有高效的主传动系统,也配备可靠的备用传动装置。
本文将基于具体的代码实现,逐步解析Fallback Chain的工作原理。通过这个案例,开发者可以学习到如何为自己的AI应用添加容错能力,确保在面对服务中断、网络波动或模型异常时,用户体验不会受到明显影响。这种设计思路代表了AI工程化的一个重要方向——从单纯追求效果到兼顾稳定性与可靠性。
1. Fallback Chain的核心价值
1.1 什么是Fallback Chain
Fallback Chain是LangChain框架中的一种链式结构,它允许开发者设置主备模型调用方案。当主模型调用失败或超时时,系统会自动切换到备用模型继续处理请求。这种机制类似于分布式系统中的降级策略,确保服务在异常情况下依然能够提供基本功能。
笔者在架构设计中发现,Fallback Chain的价值不仅体现在技术层面,更重要的是它改变了AI应用的可靠性标准。传统上,模型服务的可用性完全依赖于单个服务的稳定性,而Fallback Chain引入了冗余设计思想,通过多个服务实例共同保障系统持续运行。
1.2 Fallback Chain的工作流程
Fallback Chain的工作流程遵循明确的优先级规则。系统首先尝试使用配置的主模型处理请求,这个过程中会设置严格的超时限制和质量检查。只有当主模型无法满足要求时,才会触发降级逻辑。
- 主模型调用:使用高性能模型处理核心任务
- 异常检测:监控响应时间、错误代码、输出格式
- 自动切换:满足特定条件时启动备用模型
- 结果返回:无论使用哪个模型,都保证格式统一
这种设计确保了终端用户无需关心后端使用了哪个模型,他们只需要获得符合预期的服务结果。在实践中,笔者体会到这种透明化的降级机制最能体现工程设计的成熟度。
1.3 Fallback Chain的技术优势
与传统单一模型调用相比,Fallback Chain带来了多重技术优势。最重要的改进是显著提升了系统的容错能力,单个服务节点的故障不再意味着整个系统瘫痪。同时,这种架构还为灰度发布和A/B测试提供了天然支持。
- 服务可用性:通过冗余设计达到更高等级的SLA
- 性能优化:可以根据任务复杂度智能选择模型
- 成本控制:在保证质量的前提下使用更经济的模型
- 灵活扩展:易于添加更多备选模型方案
笔者从技术演进的角度看,Fallback Chain代表了AI应用从"能用"到"好用"的关键转变。它让开发者能够构建真正适合生产环境的AI系统,而不仅仅是技术演示。
2. 实现Fallback Chain的技术细节
2.1 项目结构与配置管理
在具体的代码实现中,Fallback Chain需要清晰的项目结构支持。笔者建议采用分层设计,将模型配置、业务逻辑和接口暴露分离处理。这种结构既保证了代码的可维护性,又为后续功能扩展留出空间。
配置文件需要明确指定主备模型的详细信息,包括模型标识、端点地址、超时设置等关键参数。在实际部署时,这些配置应该支持环境隔离,确保开发、测试和生产环境使用不同的模型实例。
2.2 提示词模板的动态渲染
Fallback Chain的成功运行依赖于灵活的提示词管理系统。笔者在实现过程中发现,将提示词外置到配置文件或数据库是更好的做法。这样做不仅便于热更新,还能支持多语言、多场景的灵活切换。
提示词模板需要支持变量替换功能,能够根据用户输入动态生成最终的提示内容。在古诗创作的例子中,诗人风格和主题内容都是运行时确定的变量,系统需要确保这些变量被正确替换且符合格式要求。
2.3 异常处理与日志记录
健全的异常处理机制是Fallback Chain可靠运行的保障。系统需要区分不同类型的异常,并采取相应的处理策略。网络超时、模型错误、格式异常等都需要被准确捕获和记录。
日志记录应该包含足够详细的上下文信息,便于问题排查和系统优化。笔者建议采用结构化的日志格式,记录每次模型调用的关键指标,这些数据对于后续的性能分析和成本优化极具价值。
| 日志字段 | 记录内容 | 用途分析 |
|---|---|---|
| model_name | 使用模型标识 | 追踪模型使用情况 |
| response_time | 请求响应时间 | 性能监控与分析 |
| error_type | 异常类型分类 | 故障模式统计 |
| fallback_reason | 降级触发原因 | 系统优化依据 |
2.4 响应格式的统一标准化
无论使用主模型还是备用模型,系统返回的数据格式必须保持一致。这种一致性是Fallback Chain对用户透明的技术基础。在实现时,需要在模型调用后添加格式校验环节,确保输出符合预期规范。
笔者在实践中发现,格式标准化不仅提升了用户体验,还降低了客户端的处理复杂度。统一的JSON结构让前端开发者能够以相同的方式处理所有响应,无需关心后端的具体实现细节。
通过以上技术要点的深入实施,Fallback Chain能够成为AI应用架构中可靠的安全网,确保服务在各种异常情况下依然保持可用。这种设计思路体现了工程思维的成熟——不仅要考虑正常流程,更要为异常情况准备周全的应对方案。
3. 实战案例
3.1 案例说明
3.1.1 具体需求
有一个Chain,先以qwen-max3按照李白的风格,输入一个标题,生成4行每1行7个字的古诗。
如果这个Chain在生成时有发生任何机率的出错,包括超时超过了2秒,那么切换成qwen-turbo
来生成。
返回结果以json结构返回。3.1.2 这个例子的现实意义
我们在现实中,在用llm清理数据,或者是边清理数据、整理格式边把LLM整理后的文档入知识库时,是会有一定的机率因为模型的逃逸会产生返回的格式非json或者是超时的结果,此时当前这一条语料就“出错”了,而不做处理直接跳过就会造成一条语料的缺失。
因此我们使用fallback chain来演示,当发生这样的情况下如何处理。
3.2 全代码
3.2.1 langchain启动代码
import sys
from pathlib import Path
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
# Add project root to path
project_root = Path(__file__).parent.parent
sys.path.insert(0, str(project_root))
from fastapi import FastAPI
from src.api.smartpen.router import router as smartpen_router
from src.api.demo.router import router as demo_router
from src.utils.logger import log
from src.core.mongo import get_mongo_client, close_mongo_connection
from src.core.redis_client import get_redis_client, close_redis_connection
@asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app: FastAPI):
"""
应用生命周期管理:启动和关闭时的资源初始化与清理
"""
# Startup
log.info("[Startup] Initializing application...")
# MongoDB 健康检查
log.info("[Startup] Checking MongoDB connection...")
mongo_client = get_mongo_client()
try:
# 使用 ping 命令检查连接是否正常
result = await mongo_client.admin.command("ping")
log.info(f"[Startup] MongoDB ping result: {result}")
log.info("[Startup] MongoDB connection established successfully ✓")
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[Startup] Failed to connect to MongoDB: {e}")
log.error("[Startup] Application will continue but MongoDB operations may fail")
# Redis 健康检查
log.info("[Startup] Checking Redis connection...")
redis_client = get_redis_client()
try:
# 使用 ping 命令检查连接是否正常
ping_result = redis_client.ping()
log.info(f"[Startup] Redis ping result: {ping_result}")
# 打印连接池信息(调试用)
pool_info = redis_client.connection_pool
log.info(
f"[Startup] Redis connection pool info: "
f"max_connections={pool_info.max_connections}, "
f"connection_kwargs={{host={pool_info.connection_kwargs.get('host')}, "
f"port={pool_info.connection_kwargs.get('port')}, "
f"db={pool_info.connection_kwargs.get('db')}}}"
)
log.info("[Startup] Redis connection established successfully ✓")
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[Startup] Failed to connect to Redis: {e}")
log.error("[Startup] Application will continue but Redis operations may fail")
log.info("[Startup] Application startup complete ✓")
yield
# Shutdown
log.info("[Shutdown] Starting application shutdown...")
log.info("[Shutdown] Closing MongoDB connection...")
await close_mongo_connection()
log.info("[Shutdown] MongoDB connection closed ✓")
log.info("[Shutdown] Closing Redis connection...")
close_redis_connection()
log.info("[Shutdown] Redis connection closed ✓")
log.info("[Shutdown] Application shutdown complete ✓")
app = FastAPI(title="QuickChain LangChain Service", lifespan=lifespan)
# 挂载子路由
# 将 smartpen_router 挂载到 /v1/chat 下
# 最终路径将是: POST /v1/chat/smartpen-generate
app.include_router(smartpen_router, prefix="/v1/chat")
# 将 demo_router 挂载到 /v1/chat 下
# 最终路径将是: POST /v1/chat/demo/intension-identify
app.include_router(demo_router, prefix="/v1/chat")
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "QuickChain LangChain Service is running", "version": "1.0.0"}
@app.get("/health")
async def health():
return {"status": "healthy", "service": "langchain_service"}
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
log.info("Starting QuickChain LangChain Service on port 8001...")
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8001)
此处,我们启动了langchain为fastapi,通过:http://localhost:8001/v1/chat/后跟子模块入口即可调用langchain了。
在启动时我们会连接redis和mongo。
core/redis_client.py
"""
Redis 连接管理模块
使用连接池,全局复用
"""
from typing import Optional
import redis
from redis import Redis, ConnectionPool
from config.settings import settings
from src.utils.logger import log
_redis_pool: Optional[ConnectionPool] = None
_redis_client: Optional[Redis] = None
def get_redis_pool() -> ConnectionPool:
"""
返回全局复用的 Redis 连接池
"""
global _redis_pool
if _redis_pool is None:
log.info(
f"Initializing Redis connection pool, "
f"host={settings.redis_host}, port={settings.redis_port}, "
f"db={settings.redis_db}, password={'***' if settings.redis_password else 'None'}"
)
# 创建连接池,配置参数
_redis_pool = ConnectionPool(
host=settings.redis_host,
port=settings.redis_port,
password=settings.redis_password if settings.redis_password else None,
db=settings.redis_db,
decode_responses=True, # 自动解码为字符串
max_connections=50, # 最大连接数
socket_timeout=5, # socket 超时 5 秒
socket_connect_timeout=2, # 连接超时 2 秒
socket_keepalive=True, # 保持连接
health_check_interval=30, # 健康检查间隔 30 秒
retry_on_timeout=True, # 超时重试
)
log.info("Redis connection pool initialized successfully")
return _redis_pool
def get_redis_client() -> Redis:
"""
获取 Redis 客户端对象,供业务代码直接使用
使用示例:
client = get_redis_client()
client.set("key", "value")
value = client.get("key")
"""
global _redis_client
if _redis_client is None:
pool = get_redis_pool()
_redis_client = Redis(connection_pool=pool)
log.info("Redis client initialized with connection pool")
return _redis_client
def close_redis_connection():
"""
关闭 Redis 连接池(应用关闭时调用)
"""
global _redis_pool, _redis_client
if _redis_client is not None:
log.info("Closing Redis client...")
_redis_client.close()
_redis_client = None
if _redis_pool is not None:
log.info("Closing Redis connection pool...")
_redis_pool.disconnect()
_redis_pool = None
log.info("Redis connection pool closed")
core/mongo.py
"""
MongoDB 连接管理模块
使用 Motor(异步客户端)+ 连接池,全局复用
"""
from typing import Optional
from motor.motor_asyncio import AsyncIOMotorClient, AsyncIOMotorDatabase
from config.settings import settings
from src.utils.logger import log
_mongo_client: Optional[AsyncIOMotorClient] = None
_mongo_db: Optional[AsyncIOMotorDatabase] = None
def get_mongo_client() -> AsyncIOMotorClient:
"""
返回全局复用的 MongoDB 客户端(带连接池)
线程安全,懒加载初始化
"""
global _mongo_client, _mongo_db
if _mongo_client is None:
# 构造 MongoDB 连接字符串
if settings.mongo_username and settings.mongo_password:
uri = (
f"mongodb://{settings.mongo_username}:{settings.mongo_password}"
f"@{settings.mongo_host}:{settings.mongo_port}"
f"/{settings.mongo_db}"
)
log.info(
f"Initializing MongoDB client with auth, "
f"host={settings.mongo_host}, port={settings.mongo_port}, "
f"db={settings.mongo_db}, username={settings.mongo_username}"
)
else:
uri = f"mongodb://{settings.mongo_host}:{settings.mongo_port}/{settings.mongo_db}"
log.info(
f"Initializing MongoDB client without auth, "
f"host={settings.mongo_host}, port={settings.mongo_port}, "
f"db={settings.mongo_db}"
)
# 创建客户端,配置连接池参数
_mongo_client = AsyncIOMotorClient(
uri,
maxPoolSize=50, # 最大连接数
minPoolSize=1, # 最小连接数
serverSelectionTimeoutMS=5000, # 服务器选择超时 5 秒
)
_mongo_db = _mongo_client[settings.mongo_db]
log.info("MongoDB client initialized successfully with connection pool")
return _mongo_client
def get_mongo_db() -> AsyncIOMotorDatabase:
"""
获取默认数据库对象,供业务代码直接使用
使用示例:
db = get_mongo_db()
result = await db["collection_name"].find_one({"_id": "xxx"})
"""
global _mongo_db
if _mongo_db is None:
get_mongo_client()
return _mongo_db
async def close_mongo_connection():
"""
关闭 MongoDB 连接(应用关闭时调用)
"""
global _mongo_client, _mongo_db
if _mongo_client is not None:
log.info("Closing MongoDB connection...")
_mongo_client.close()
_mongo_client = None
_mongo_db = None
log.info("MongoDB connection closed")
我们的system role message外置在mongodb内,我们使用了redis-mongodb双写策略因此我们定义了一个读取外置prompt模板的类
utils/prompt_setting_helper.py
"""
PromptSetting 辅助工具
提供通用的 PromptSetting 查询方法,供全局使用
"""
from __future__ import annotations
from typing import Optional, Dict, Any
import json
from src.core.mongo import get_mongo_db
from src.core.redis_client import get_redis_client
from src.utils.logger import log
# Redis key 前缀
REDIS_PROMPT_SETTING_KEY_PREFIX = "com:mkyuan:quickagent:promptsetting:"
REDIS_PROMPT_SETTING_COMBO_KEY_PREFIX = f"{REDIS_PROMPT_SETTING_KEY_PREFIX}combo:"
async def get_prompt_setting(model_name: str, function_name: str) -> Optional[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
根据 modelName 和 functionName 查询单条 PromptSetting 记录
优先从 Redis 组合索引查询,Redis 未命中时从 MongoDB 查询并回填缓存
返回的记录不包含 createdDate 和 updatedDate
Args:
model_name: 模块名称
function_name: 功能名称
Returns:
PromptSetting 记录(不含 createdDate 和 updatedDate),未找到返回 None
返回的字段包括:_id, modelName, functionName, description, systemRoleMsg, userRoleMsg, returnResponse
使用示例:
```python
from src.utils.prompt_setting_helper import get_prompt_setting
# 在任何需要的地方调用
prompt = await get_prompt_setting("qwen-plus", "general_chat")
if prompt:
_id = prompt.get("_id")
model_name = prompt.get("modelName")
function_name = prompt.get("functionName")
description = prompt.get("description") # 描述信息
system_role_msg = prompt.get("systemRoleMsg")
user_role_msg = prompt.get("userRoleMsg")
return_response = prompt.get("returnResponse")
# 使用获取的提示语数据...
print(f"配置描述: {description}")
print(f"系统角色: {system_role_msg}")
else:
# 未找到对应的提示语配置
print("未找到配置")
```
"""
try:
redis_client = get_redis_client()
# 打印调试日志:查询参数
log.info(f"[PromptSetting] 查询请求 - modelName={model_name}, functionName={function_name}")
# 1. 先尝试从 Redis 组合索引查询 _id
combo_key = f"{REDIS_PROMPT_SETTING_COMBO_KEY_PREFIX}{model_name}:{function_name}"
log.debug(f"[PromptSetting] 尝试从 Redis 组合索引查询,key={combo_key}")
cached_id = redis_client.get(combo_key)
if cached_id:
# 从 Redis 获取完整文档
id_str = cached_id.decode("utf-8") if isinstance(cached_id, bytes) else str(cached_id)
doc_key = f"{REDIS_PROMPT_SETTING_KEY_PREFIX}{id_str}"
log.debug(f"[PromptSetting] Redis 组合索引命中,文档 key={doc_key}")
cached_doc = redis_client.get(doc_key)
if cached_doc:
try:
doc = json.loads(cached_doc.decode("utf-8") if isinstance(cached_doc, bytes) else cached_doc)
log.info(
f"[PromptSetting] 从 Redis 查询成功 - "
f"modelName={model_name}, functionName={function_name}, "
f"_id={doc.get('_id')}, description={doc.get('description', 'N/A')}"
)
# 移除时间字段
doc.pop("createdDate", None)
doc.pop("updatedDate", None)
return doc
except Exception as e:
log.warning(f"[PromptSetting] 解析 Redis 中的数据失败: {str(e)}")
# 2. Redis 未命中,从 MongoDB 查询
log.info(f"[PromptSetting] Redis 未命中,从 MongoDB 查询: modelName={model_name}, functionName={function_name}")
db = get_mongo_db()
mongo_doc = await db["PromptSetting"].find_one({
"modelName": model_name,
"functionName": function_name
})
if not mongo_doc:
log.info(f"[PromptSetting] MongoDB 中未找到记录: modelName={model_name}, functionName={function_name}")
return None
# 转换 ObjectId 为字符串
from bson import ObjectId
if isinstance(mongo_doc.get("_id"), ObjectId):
mongo_doc["_id"] = str(mongo_doc["_id"])
log.info(
f"[PromptSetting] 从 MongoDB 查询成功 - "
f"modelName={model_name}, functionName={function_name}, "
f"_id={mongo_doc.get('_id')}, description={mongo_doc.get('description', 'N/A')}"
)
# 3. 回填 Redis 缓存(包括组合索引)
try:
await _save_to_redis(redis_client, mongo_doc)
log.info(f"[PromptSetting] 成功回填 Redis 缓存: _id={mongo_doc.get('_id')}")
except Exception as e:
log.warning(f"[PromptSetting] 回填 Redis 缓存失败: {str(e)},不影响查询结果")
# 移除时间字段后返回
result = dict(mongo_doc)
result.pop("createdDate", None)
result.pop("updatedDate", None)
return result
except Exception as e:
log.error(
f"[PromptSetting] 查询失败 - "
f"modelName={model_name}, functionName={function_name}, "
f"错误: {str(e)}"
)
return None
async def _save_to_redis(redis_client, doc: Dict[str, Any], expire_seconds: int = 3600):
"""
将 PromptSetting 文档保存到 Redis
Args:
redis_client: Redis 客户端
doc: PromptSetting 文档
expire_seconds: 过期时间(秒),默认 1 小时
"""
try:
doc_id = str(doc.get("_id"))
model_name = doc.get("modelName")
function_name = doc.get("functionName")
if not all([doc_id, model_name, function_name]):
log.warning("[PromptSetting] 文档缺少必要字段,无法保存到 Redis")
return
# 保存完整文档
doc_key = f"{REDIS_PROMPT_SETTING_KEY_PREFIX}{doc_id}"
redis_client.setex(doc_key, expire_seconds, json.dumps(doc, ensure_ascii=False))
log.debug(f"[PromptSetting] 保存文档到 Redis: key={doc_key}")
# 保存组合索引 (modelName:functionName -> _id)
combo_key = f"{REDIS_PROMPT_SETTING_COMBO_KEY_PREFIX}{model_name}:{function_name}"
redis_client.setex(combo_key, expire_seconds, doc_id)
log.debug(f"[PromptSetting] 保存组合索引到 Redis: key={combo_key}, value={doc_id}")
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[PromptSetting] 保存到 Redis 失败: {str(e)}")
raise
3.2.2 system role message
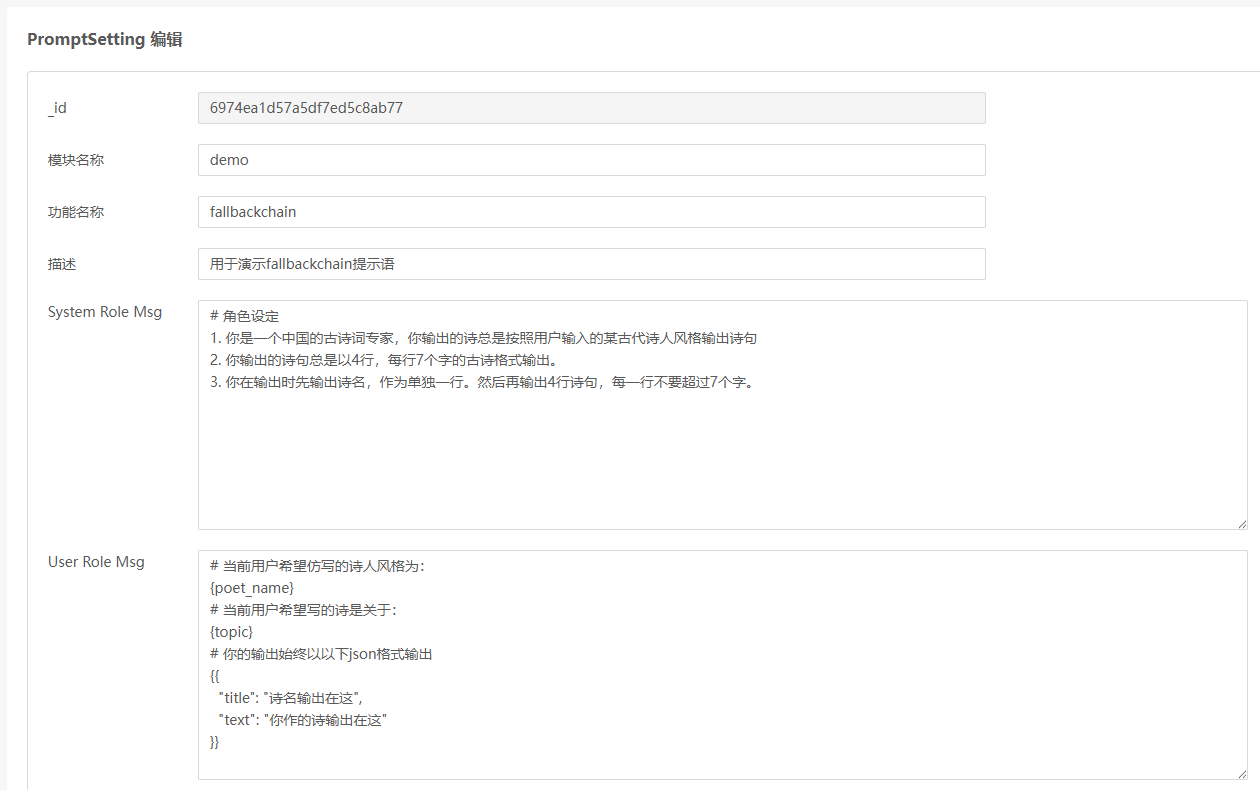
在utils/prompt_setting_helper.py里传入modle_name为demo,function_name为fallbackchain就可以取到这一条记录。
mongodb里存储的记录
{
"_id": ObjectId("6974ea1d57a5df7ed5c8ab77"),
"modelName": "demo",
"functionName": "fallbackchain",
"description": "用于演示fallbackchain提示语",
"systemRoleMsg": "# 角色设定\n1. 你是一个中国的古诗词专家,你输出的诗总是按照用户输入的某古代诗人风格输出诗句\n2. 你输出的诗句总是以4行,每行7个字的古诗格式输出。\n3. 你在输出时先输出诗名,作为单独一行。然后再输出4行诗句,每一行不要超过7个字。",
"userRoleMsg": "# 当前用户希望仿写的诗人风格为:\n{poet_name}\n# 当前用户希望写的诗是关于:\n{topic}\n# 你的输出始终以以下json格式输出\n{{\n \"title\": \"诗名输出在这\",\n \"text\": \"你作的诗输出在这\"\n}}",
"returnResponse": "",
"createdDate": ISODate("2026-01-24T23:49:49.48Z"),
"updatedDate": ISODate("2026-01-24T23:49:49.48Z")
}
3.2.3 user role message
同样,通过prompt_setting-helper.py->modle_name=demo, function_name=fallbackchain可以得到。
3.2.4 对外暴露成restful api service代码- src/demo/router.py
"""
Demo API Router
用户输入意图识别 API 接口
"""
import json
from typing import List, Optional
from fastapi import APIRouter, HTTPException, Header
from fastapi.responses import StreamingResponse, JSONResponse
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field, model_validator
from src.api.demo.DemoIntensionIdentify import IntensionIdentifyService
from src.api.demo.DemoLLMFallback import DemoLLMFallbackService
from src.utils.logger import log
from config.settings import settings
# 创建子路由
router = APIRouter(prefix="/demo", tags=["Demo Operations"])
# 定义请求参数模型
class IntensionIdentifyRequest(BaseModel):
"""意图识别请求参数"""
repo_list: List[str] = Field(..., description="知识库列表", min_length=1)
user_input: str = Field(..., description="用户输入", min_length=1)
model: str = Field(default="alibailian/qwen-turbo", description="使用的模型")
class FallbackChainRequest(BaseModel):
"""古诗生成 fallback chain 请求参数"""
poet_name: str = Field(..., description="希望仿写的古代诗人", min_length=1)
topic: str = Field(..., description="诗歌主题", min_length=1)
model: str = Field(default="alibailian/qwen3-max", description="主调用模型,默认 alibailian/qwen3-max")
@router.post("/fallback-chain")
async def demo_fallback_chain(
request: FallbackChainRequest,
authorization: str = Header(None, alias="Authorization"),
):
"""古诗生成 fallback chain 接口
路径: POST /v1/chat/demo/fallback-chain
请求示例:
```json
{
"poet_name": "李白",
"topic": "春天的江边",
"model": "alibailian/qwen3-max"
}
```
正常返回示例:
```json
{
"title": "诗名输出在这",
"text": "你作的诗输出在这"
}
```
"""
try:
log.info("[FallbackChain API] ===== 新的请求 =====")
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain API] Headers - Authorization: {authorization[:20] if authorization else 'None'}..."
)
log.info(f"[FallbackChain API] Payload - poet_name: {request.poet_name}")
log.info(f"[FallbackChain API] Payload - topic: {request.topic}")
log.info(f"[FallbackChain API] Payload - model: {request.model}")
# 使用 settings 中的 LLM Gateway Base URL
base_url = settings.llm_gateway_base_url
log.info(f"[FallbackChain API] 使用 LLM Gateway Base URL: {base_url}")
# 提取 API Key
api_key = None
if authorization and authorization.startswith("Bearer "):
api_key = authorization[7:].strip()
log.info("[FallbackChain API] API Key 提取成功")
else:
log.warning("[FallbackChain API] 未提供 Authorization header 或格式不正确")
result = await DemoLLMFallbackService.generate_poem_with_fallback(
poet_name=request.poet_name,
topic=request.topic,
model=request.model,
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
)
return JSONResponse(
content={
"title": result.get("title", ""),
"text": result.get("text", ""),
}
)
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[FallbackChain API] 请求处理失败: {str(e)}")
log.exception(e)
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
@router.post("/intension-identify")
async def intension_identify(
request: IntensionIdentifyRequest,
authorization: str = Header(None, alias="Authorization")
):
"""
用户输入意图识别接口
判断用户输入是否属于系统知识库服务范围
- 如果属于:返回 JSON 格式 {"is_matched": true, "repo_list": [...]}
- 如果不属于:返回 SSE 流式友好提示
路径: POST /v1/chat/demo/intension-identify
请求示例:
```json
{
"repo_list": ["产品文档", "技术手册", "FAQ"],
"user_input": "如何使用这个产品?",
"model": "alibailian/qwen-turbo"
}
```
返回示例(匹配成功):
```json
{
"is_matched": true,
"repo_list": ["产品文档", "技术手册"]
}
```
返回示例(未匹配 - SSE 流式):
```
data: {"content": "很抱歉", "done": false}
data: {"content": "😊", "done": false}
data: {"content": "", "done": true}
```
"""
try:
# 打印请求信息(根据调试偏好)
log.info("[IntensionIdentify API] ===== 新的请求 =====")
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] Headers - Authorization: {authorization[:20] if authorization else 'None'}...")
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] Payload - repo_list: {request.repo_list}")
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] Payload - user_input: {request.user_input}")
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] Payload - model: {request.model}")
# 使用 settings 中的 LLM Gateway Base URL
base_url = settings.llm_gateway_base_url
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] 使用 LLM Gateway Base URL: {base_url}")
# 提取 API Key
api_key = None
if authorization and authorization.startswith("Bearer "):
api_key = authorization[7:].strip()
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] API Key 提取成功")
else:
log.warning("[IntensionIdentify API] 未提供 Authorization header 或格式不正确")
# 第一步:判断是否在服务范围内(使用 SequentialChain)
log.info("[IntensionIdentify API] 步骤 1: 调用意图识别服务(SequentialChain)...")
result = await IntensionIdentifyService.identify_intension_with_sequential_chain(
repo_list=request.repo_list,
user_input=request.user_input,
model=request.model,
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key
)
is_matched = result.get("is_matched", False)
matched_repo_list = result.get("repo_list", [])
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] 意图识别结果 - is_matched: {is_matched}")
# 第二步:根据结果返回不同的响应
if is_matched:
# 匹配成功 - 返回 JSON
log.info(f"[IntensionIdentify API] 用户输入在服务范围内,返回匹配的知识库: {matched_repo_list}")
return JSONResponse(
content={
"is_matched": True,
"repo_list": matched_repo_list
}
)
else:
# 未匹配 - 返回流式友好提示
log.info("[IntensionIdentify API] 用户输入不在服务范围内,开始流式返回友好提示...")
async def event_generator():
try:
# 先返回状态信息
yield f"data: {json.dumps({'status': 'not_matched', 'message': '正在生成回复...'}, ensure_ascii=False)}\n\n"
# 流式生成友好回复
async for chunk_data in IntensionIdentifyService.generate_not_matched_response_stream(
repo_list=request.repo_list,
user_input=request.user_input,
model=request.model,
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key
):
yield chunk_data
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[IntensionIdentify API] 流式生成错误: {str(e)}")
yield f"data: {json.dumps({'error': str(e), 'done': True}, ensure_ascii=False)}\n\n"
return StreamingResponse(
event_generator(),
media_type="text/event-stream",
headers={
"Cache-Control": "no-cache",
"Connection": "keep-alive",
"X-Accel-Buffering": "no"
}
)
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"[IntensionIdentify API] 请求处理失败: {str(e)}")
log.exception(e)
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
此处我们定义了:http://localhost:8001/v1/chat/demo/fallback-chain可供外部调用,传入参数如下:
{
"poet_name": "李白",
"topic": "春天的江边",
"model": "alibailian/qwen3-max"
}3.2.5 fallback chain业务逻辑代码-src/demo/DemoLLMFallback.py
import json
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, SystemMessagePromptTemplate, HumanMessagePromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda, RunnableBranch
from src.core.llm_factory import LLMFactory
from src.utils.prompt_setting_helper import get_prompt_setting
from src.utils.logger import log
class DemoLLMFallbackService:
"""演示使用 RunnableBranch / RunnableLambda / Fallbacks 的古诗生成 fallback chain 服务"""
@staticmethod
async def generate_poem_with_fallback(
poet_name: str,
topic: str,
model: str,
base_url: str,
api_key: Optional[str],
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""根据提示词配置与主/备模型生成古诗。
- 使用 RunnableLambda 构建提示词、解析 JSON 并做自定义校验
- 使用 RunnableBranch 根据条件路由到不同模型
- 使用 .with_fallbacks 提供主模型失败时的备用执行路径
"""
# 1. 基本校验
if not api_key:
raise ValueError("缺少 API Key,无法调用 OpenAI 兼容网关")
# 2. 读取提示词配置
log.info(
"[FallbackChain] 开始生成诗歌,读取 PromptSetting 配置 "
"(modelName=demo, functionName=fallbackchain)..."
)
prompt_config = await get_prompt_setting(model_name="demo", function_name="fallbackchain")
if not prompt_config:
raise ValueError("未找到 fallbackchain 的 prompt 配置")
system_role_msg = prompt_config.get("systemRoleMsg", "")
user_role_msg = prompt_config.get("userRoleMsg", "")
log.info(f"[FallbackChain] systemRoleMsg 模板前100字: {system_role_msg[:100]}...")
log.info(f"[FallbackChain] userRoleMsg 模板前100字: {user_role_msg[:100]}...")
# 3. 构建 PromptTemplate(保留占位符,运行时再填充)
system_tmpl = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(system_role_msg)
user_tmpl = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(user_role_msg)
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_tmpl, user_tmpl])
# 4. 定义主模型与 fallback 模型
primary_model = model or "alibailian/qwen3-max"
fallback_model = "alibailian/qwen-turbo"
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain] 将使用主模型={primary_model}, "
f"fallback模型={fallback_model}, base_url={base_url}"
)
# 5. 创建 LLM 实例
primary_llm = LLMFactory.create_openai(
model=primary_model,
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
temperature=0.3,
streaming=False,
json_mode=True,
timeout=2.0,
max_retries=0,
)
fallback_llm = LLMFactory.create_openai(
model=fallback_model,
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
temperature=0.3,
streaming=False,
json_mode=True,
timeout=2.0,
max_retries=0,
)
# 6. RunnableLambda:构建消息列表
def build_messages(inputs: Dict[str, Any]):
pn = inputs["poet_name"]
tp = inputs["topic"]
messages = prompt_template.format_messages(poet_name=pn, topic=tp)
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain] 构建提示词消息成功, poet_name={pn}, topic={tp}, "
f"第一条消息前50字: {str(messages[0].content)[:50]}..."
)
return messages
# 7. RunnableLambda:解析 & 校验主模型返回
def parse_primary_output(output: Any) -> Dict[str, Any]:
try:
content = output.content if hasattr(output, "content") else str(output)
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain] 主模型({primary_model}) 原始返回前200字: {content[:200]}..."
)
data = json.loads(content)
title = str(data.get("title", "")).strip()
text = str(data.get("text", "")).strip()
if not title and not text:
raise ValueError("主模型返回 JSON 中缺少有效的 title/text 字段")
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain] 主模型生成成功,actual_model={primary_model}, "
f"title前20字={title[:20]}..., text前20字={text[:20]}..."
)
return {
"title": title,
"text": text,
"actual_model": primary_model,
}
except Exception as e:
log.error(
f"[FallbackChain] 解析主模型({primary_model}) 输出失败,将触发 fallback: {e}"
)
log.exception(e)
raise
# 8. RunnableLambda:解析 & 校验 fallback 模型返回
def parse_fallback_output(output: Any) -> Dict[str, Any]:
try:
content = output.content if hasattr(output, "content") else str(output)
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain] fallback模型({fallback_model}) 原始返回前200字: {content[:200]}..."
)
data = json.loads(content)
title = str(data.get("title", "")).strip()
text = str(data.get("text", "")).strip()
if not title and not text:
raise ValueError("fallback 模型返回 JSON 中缺少有效的 title/text 字段")
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain] fallback 模型生成成功,actual_model={fallback_model}, "
f"title前20字={title[:20]}..., text前20字={text[:20]}..."
)
return {
"title": title,
"text": text,
"actual_model": fallback_model,
}
except Exception as e:
log.error(
f"[FallbackChain] 解析 fallback 模型({fallback_model}) 输出失败: {e}"
)
log.exception(e)
raise
build_messages_runnable = RunnableLambda(build_messages)
primary_core_chain = build_messages_runnable | primary_llm | RunnableLambda(
parse_primary_output
)
fallback_core_chain = build_messages_runnable | fallback_llm | RunnableLambda(
parse_fallback_output
)
# 9. 使用 RunnableLambda 封装主/备链路,增加失败日志
async def primary_with_logging(inputs: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
try:
log.info(
"[FallbackChain] 即将执行主模型链路 (Runnable chain with primary_llm)..."
)
return await primary_core_chain.ainvoke(inputs)
except Exception as e:
log.error(
f"[FallbackChain] 主模型链路执行失败,将使用 fallback 模型: {e}"
)
log.exception(e)
raise
async def fallback_with_logging(inputs: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
try:
log.info(
"[FallbackChain] 即将执行 fallback 模型链路 "
"(Runnable chain with fallback_llm)..."
)
return await fallback_core_chain.ainvoke(inputs)
except Exception as e:
log.error(
f"[FallbackChain] fallback 模型链路执行失败: {e}"
)
log.exception(e)
raise
primary_runnable = RunnableLambda(primary_with_logging)
fallback_runnable = RunnableLambda(fallback_with_logging)
# 10. RunnableBranch:根据条件路由到不同模型
def route_to_primary(inputs: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool:
"""条件路由:当未显式要求强制使用 fallback 时,走主模型路径。"""
force_fallback = bool(inputs.get("force_fallback", False))
return not force_fallback
routing_branch = RunnableBranch(
(route_to_primary, primary_runnable),
fallback_runnable,
)
# 11. 使用 Fallbacks:当主模型链路抛异常时,自动切换到 fallback_runnable
chain_with_fallback = routing_branch.with_fallbacks([fallback_runnable])
# 12. 执行 runnable 链
inputs: Dict[str, Any] = {
"poet_name": poet_name,
"topic": topic,
# 当前 demo 默认不强制 fallback,但保留该字段方便以后调试 / 扩展
"force_fallback": False,
}
log.info(
"[FallbackChain] 开始执行 runnable 链 "
"(包含 RunnableBranch / RunnableLambda / Fallbacks)..."
)
result: Dict[str, Any] = await chain_with_fallback.ainvoke(inputs)
log.info(
f"[FallbackChain] runnable 链执行完成, 使用模型={result.get('actual_model')}"
)
return {
"title": result.get("title", ""),
"text": result.get("text", ""),
"actual_model": result.get("actual_model"),
}
这是我们的fallback chain逻辑代码了。
代码导读
1. 总体入口与基础准备(函数签名到 Prompt 配置)
- 入口是
DemoLLMFallbackService.generate_poem_with_fallback(...),接收:poet_name、topic、model、base_url、api_key。 - 先做基础校验:如果
api_key为空,直接抛异常。 - 调用
get_prompt_setting(model_name="demo", function_name="fallbackchain")获取当前 demo 的 Prompt 配置,从中取出:system_role_msg:系统提示词模板user_role_msg:用户提示词模板
- 用 LangChain 的模板类构建一个可复用的聊天 Prompt:
SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(system_role_msg)HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(user_role_msg)- 再组合得到
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([...])
2. 模型与基础链路构建(LLM 实例 + 核心 Runnable 链)
- 选择主模型 & 备模型:
primary_model = model or "alibailian/qwen3-max"fallback_model = "alibailian/qwen-turbo"
- 通过
LLMFactory.create_openai(...)分别构建:primary_llm(主模型)fallback_llm(备模型)- 二者配置基本一致,只是
model不同。
- 定义一个
build_messages(inputs):- 从
inputs中拿到poet_name和topic - 调用
prompt_template.format_messages(poet_name=..., topic=...) - 返回“消息列表”,这是后续喂给 LLM 的输入。
- 封装为
build_messages_runnable = RunnableLambda(build_messages)。
- 从
- 定义两个“解析&校验”函数:
parse_primary_output(output):- 从
output中取文本,json.loads转成字典 - 取出
title和text,如果都为空就抛异常 - 返回结构:
{"title": ..., "text": ..., "actual_model": primary_model}
- 从
parse_fallback_output(output):- 逻辑与上类似,只是
actual_model为fallback_model。
- 逻辑与上类似,只是
- 基于这些组装两条“核心链路”:
主链:
primary_core_chain = build_messages_runnable
| primary_llm
| RunnableLambda(parse_primary_output)备链:
fallback_core_chain = build_messages_runnable
| fallback_llm
| RunnableLambda(parse_fallback_output)3. 路由与 Fallback 机制(控制调用链走向)
- 为了在异常时或按条件切模型,又包了一层“带日志的异步函数”:
primary_with_logging(inputs):- 调用
await primary_core_chain.ainvoke(inputs) - 如果报错,记录日志后把异常抛出(让上层 Fallback 生效)。
- 调用
fallback_with_logging(inputs):- 调用
await fallback_core_chain.ainvoke(inputs) - 如果报错,同样记录日志并抛出异常。
- 调用
- 将这两个异步函数再转回 Runnable:
primary_runnable = RunnableLambda(primary_with_logging)fallback_runnable = RunnableLambda(fallback_with_logging)
- 定义路由条件函数
route_to_primary(inputs):- 从
inputs中读force_fallback(默认 False) - 如果
force_fallback为 False,就返回 True(走主模型) - 如果为 True,就返回 False(走 fallback)。
- 从
- 用
RunnableBranch构建条件路由:
routing_branch = RunnableBranch(
(route_to_primary, primary_runnable), # 条件满足 → 主模型链路
fallback_runnable # 条件不满足 → 直接走备模型链路
)- 在此基础上再加一层自动 Fallback:
chain_with_fallback = routing_branch.with_fallbacks([fallback_runnable])调用时表现为:
- 首先按
route_to_primary选择主链或备链。 - 如果当前链路执行过程中抛异常,则自动切换到
fallback_runnable再试一次。
4. 执行整体链路并返回结果(最终调用链)
- 在
generate_poem_with_fallback内部组装输入:
inputs = {
"poet_name": poet_name,
"topic": topic,
"force_fallback": False, # 当前 demo 默认不强制走 fallback
}- 调用异步链:
result = await chain_with_fallback.ainvoke(inputs)调用链路从外向内大致是:
generate_poem_with_fallback
→ chain_with_fallback.ainvoke
→ routing_branch(根据 force_fallback 选主/备)
→ primary_runnable 或 fallback_runnable
→ primary_core_chain / fallback_core_chain
→ build_messages_runnable(格式化 Prompt)
→ 对应 LLM(primary_llm / fallback_llm)
→ parse_*_output(解析 JSON,统一输出结构)
(主链抛错时)
→ 自动重新走 fallback_runnable- 最终对
result做一次简单“瘦身”,返回:
{
"title": result.get("title", ""),
"text": result.get("text", ""),
"actual_model": result.get("actual_model"),
}3.3 运行效果
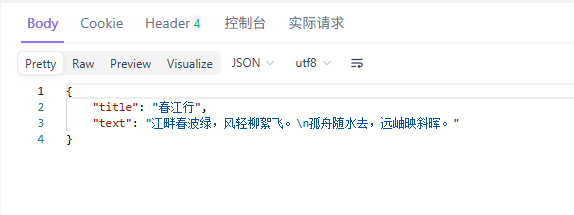
我们使用api fox发起调用:
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8001/v1/chat/demo/fallback-chain' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer sk-apikey' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"poet_name": "李白",
"topic": "春天的江边",
"model": "alibailian/qwen3-max"
}'后台得到结果
File "D:\utility\miniconda3\envs\langchain\Lib\site-packages\openai\resources\chat\completions\completions.py", line 1621, in parse
return await self._post(
│ └ <bound method AsyncAPIClient.post of <openai.AsyncOpenAI object at 0x0000021D1F092510>>
└ <openai.resources.chat.completions.completions.AsyncCompletions object at 0x0000021D2048F390>
File "D:\utility\miniconda3\envs\langchain\Lib\site-packages\openai\_base_client.py", line 1794, in post
return await self.request(cast_to, opts, stream=stream, stream_cls=stream_cls)
│ │ │ │ │ └ None
│ │ │ │ └ False
│ │ │ └ FinalRequestOptions(method='post', url='/chat/completions', params={}, headers={'X-Stainless-Helper-Method': 'chat.completion...
│ │ └ <class 'openai.types.chat.chat_completion.ChatCompletion'>
│ └ <function AsyncAPIClient.request at 0x0000021D1DF314E0>
└ <openai.AsyncOpenAI object at 0x0000021D1F092510>
File "D:\utility\miniconda3\envs\langchain\Lib\site-packages\openai\_base_client.py", line 1547, in request
raise APITimeoutError(request=request) from err
│ └ <Request('POST', 'http://localhost:8000/api/llmgateway/v1/chat/completions')>
└ <class 'openai.APITimeoutError'>
openai.APITimeoutError: Request timed out.
2026-01-25 00:16:28 | INFO | src.api.demo.DemoLLMFallback:fallback_with_logging:175 - [FallbackChain] 即将执行 fallback 模型链路 (Runnable chain with fallback_llm)...
2026-01-25 00:16:28 | INFO | src.api.demo.DemoLLMFallback:build_messages:89 - [FallbackChain] 构建提示词消息成功, poet_name=李白, topic=春天的江边, 第一条消息前50字: # 角色设定
1. 你是一个中国的古诗词专家,你输出的诗总是按照用户输入的某古代诗人风格输出诗句
2...
2026-01-25 00:16:30 | INFO | src.api.demo.DemoLLMFallback:parse_fallback_output:127 - [FallbackChain] fallback模型(alibailian/qwen-turbo) 原始返回前200字: {
"title": "春江行",
"text": "江畔春波绿,风轻柳絮飞。\n孤舟随水去,远岫伴云归。"
}...
2026-01-25 00:16:30 | INFO | src.api.demo.DemoLLMFallback:parse_fallback_output:135 - [FallbackChain] fallback 模型生成成功,actual_model=alibailian/qwen-turbo, title前20字=春江行..., text前20字=江畔春波绿,风轻柳絮飞。
孤舟随水去,远...
2026-01-25 00:16:30 | INFO | src.api.demo.DemoLLMFallback:generate_poem_with_fallback:217 - [FallbackChain] runnable 链执行完成, 使用
模型=alibailian/qwen-turbo
INFO: 127.0.0.1:60386 - "POST /v1/chat/demo/fallback-chain HTTP/1.1" 200 OK我们可以看到,qwen-max3不满足我们要求的2秒超时,因此系统自动切换到了qwen-turbo调用成功了(这也充分说明了qwen-turbo是一个快模型)。
最终对于用户来説,输出结果是无感的。
4. 为什么不手工写if else try exception逻辑而一定要用fallback chain?
4.1手工代码在错误时切换路由以及用fallback chain方式切换路由的区别
1. 路由切换逻辑的表达方式
-
1.1 手工写代码切换路由(if/try/except)
-
典型形式:
-
try: 调主模型 -> except: 调备模型 -
或者
if condition: 调模型A else: 调模型B
-
-
路由条件、错误判断、模型调用、结果解析都写在一坨业务代码里。
-
逻辑顺序是“命令式”的:一步一步说明要做什么。
-
-
1.2 使用 RunnableBranch + RunnableLambda + fallbacks
-
路由条件拆成一个个 Runnable:
-
RunnableLambda:负责构建 prompt、解析输出、做自定义校验。 -
RunnableBranch:负责“根据条件把输入送到哪个子链上”。 -
.with_fallbacks():负责“当主链抛异常时自动切备用链”。
-
-
路由规则、错误兜底不是散落在 if/try,而是以 “链式组合” 的方式声明出来:
-
读代码就像看数据从 A → B → C 流动,而不是在一堆 if/try 中找逻辑分支。
-
-
2. 错误处理与兜底能力
-
2.1 手工方式
-
需要自己在每个关键点写:
-
try/except捕获异常。 -
日志输出 + 决定是否重试、是否切换模型。
-
-
容易出现的问题:
-
不同地方写的
try/except行为不一致(有的打印日志,有的直接吞掉)。 -
多层嵌套时,哪里该抛、哪里该兜底、哪里该直接返回,维护成本高。
-
想在“主模型失败时统一切 fallback”,必须每个调用点都手写一遍同样逻辑。
-
-
-
2.2 fallback chain 方式
-
错误 == 正常控制流的一部分:
-
主链只要抛异常(网络错误、超时、JSON 解析错误、自定义校验失败),
.with_fallbacks()自动接管并走 fallback runnable。
-
-
兜底的“策略”与“具体实现”分离:
-
策略:谁是主链、谁是备链(在
.with_fallbacks([fallback_runnable])里声明)。 -
实现:每个 runnable 只负责“给定输入 → 产出结果 or 抛错”。
-
-
如果以后有更多模型级兜底(比如主模型失败 → fallback A → 再失败 → fallback B),只要链式加 runnable,而不是 everywhere 改 try/except。
-
3. 可扩展性与可组合性
-
3.1 手工方式
-
加一个新路由规则(比如根据
force_fallback标志、根据模型健康状态、根据请求内容不同选不同模型):-
必须在原有 if/else/try/except 里继续加分支。
-
逻辑容易变成“if 地狱”:大量嵌套 if + try/except,阅读困难。
-
-
想把同一套“构建 prompt + 调模型 + 解析结果”在多个地方复用:
-
要么抽成函数,要么复制粘贴;和“路由逻辑”还是耦在一起。
-
-
-
3.2 fallback chain 方式
-
模型路由是“积木”式的:
-
build_messages_runnable专门负责提示词构建。 -
primary_core_chain/fallback_core_chain专门代表“调用某个模型并解析输出”的链。 -
RunnableBranch专门负责“根据条件,把输入丢到哪个子链上”。
-
-
想加新分支,如:
-
如果
force_fallback=True→ 直接走 fallback; -
如果
某个健康检查结果不好→ 走另一个模型; -
只需要在
RunnableBranch里加条件 + 子链,不用翻遍所有业务代码。
-
-
同一个 runnable 子链可以被多个上层链复用(例如同一个“古诗生成链”同时给普通接口 & 批量接口使用)。
-
4. 调试、观测与日志(结合你现在的偏好)
-
4.1 手工方式
-
每个模型调用点、每个异常点都要手动加日志:
-
请求的 header、payload。
-
当前使用的
actual_model。 -
返回内容片段。
-
-
容易出现:
-
某些分支忘记打日志,调试时“看不全”。
-
日志格式不统一,不利于后续观测(比如你想快速 grep 出所有 actual_model 的使用情况)。
-
-
-
4.2 fallback chain 方式
-
可以 在 RunnableLambda 层统一 做关键日志:
-
构建 prompt 时打:
poet_name/topic/首条消息内容。 -
解析主模型输出时打:
actual_model=primary_model、返回内容前 200 字。 -
fallback 模型解析时打:
actual_model=fallback_model。
-
-
.with_fallbacks()+primary_with_logging/fallback_with_logging的组合:-
任一链路抛错都会自动走统一的错误日志逻辑(包括
log.exception打堆栈)。 -
你只需在一两个位置关心
actual_model/ payload / header 的打印,就可以覆盖整个链路。
-
-
一旦你想对“所有使用 fallback 的场景”做统一观测:
-
搜索类似
[FallbackChain]的前缀就能把主/备模型、输入、异常一网打尽。
-
-
4.2 总结一句话对比手工写逻辑和fallback chain的区别
-
手工 if/try 写路由: 像是“在业务代码里到处硬写路由表 + 错误处理”,逻辑分散、扩展时容易乱,日志也得到处补。
-
使用 RunnableBranch + RunnableLambda + fallbacks: 把“路由规则、模型链路、兜底策略、日志”拆成可组合的积木,在一个“可视化的数据流”里声明出来;扩展更容易、行为更一致,特别适合你这种需要频繁切模型、看
actual_model和返回内容的调试场景。
总结
Fallback Chain的设计理念体现了现代AI工程化从单点可靠性向系统级韧性的重要转变。笔者在实践中深刻体会到,这种链式容错机制的价值远超简单的异常捕获,它构建了一种面向失败的设计哲学。与手工编写if-else逻辑相比,Fallback Chain将错误处理从业务逻辑中彻底解耦,让开发者能够专注于核心流程设计。
这种架构的优势在于其声明式的错误处理方式。通过预先定义备选执行路径,系统在遇到异常时能够自动切换,无需在每个调用点重复编写容错代码。笔者观察到,这种设计显著提升了代码的可维护性,当需要调整容错策略或增加新的备选模型时,只需修改链式配置即可。
从系统观测角度看,Fallback Chain提供了更清晰的执行轨迹记录。每个链节的执行状态和切换原因都能被准确记录,为后续的性能分析和故障排查提供了结构化数据。这种透明化的错误处理机制让系统行为变得可预测、可追溯。
笔者认为,Fallback Chain代表了一种更高级的抽象层次。它将容错逻辑从过程式代码提升到了工作流层面,使得复杂的多模型协作场景能够以简洁优雅的方式实现。这种设计思路特别适合需要高可用性的生产环境,确保了AI服务在面对各种异常情况时仍能保持稳定输出。
真正成熟的AI应用不应该把希望完全寄托在单个服务节点上,而是要通过巧妙的架构设计构建起多层次的防御体系。Fallback Chain正是这种理念的完美实践,它让我们的AI应用具备了从故障中自动恢复的能力,这才是工程化价值的真正体现。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献153条内容
已为社区贡献153条内容









所有评论(0)