《机器学习》 第 9 章 - 深度强化学习
深度强化学习核心是 “智能体 - 环境” 交互,通过最大化累积奖励学习最优策略,分为基于价值(DQN 系列)和基于策略(PG/Actor-Critic/DDPG)两类;DQN 适合离散动作空间,核心改进(Double DQN/Dueling DQN)解决了过估计和价值分解问题;DDPG 适合连续动作空间,结合了 Actor-Critic 和 DQN 的优势;实战中需注意:经验回放提升数据利用率、目
前言
大家好!今天给大家分享《机器学习》第 9 章 —— 深度强化学习的核心内容。深度强化学习(DRL)是机器学习领域的热门方向,融合了深度学习的感知能力和强化学习的决策能力,在游戏、机器人、自动驾驶等领域有广泛应用。本文会从基础概念到实战代码,用通俗易懂的语言讲解,每个核心知识点都配有完整可运行的 Python 代码和可视化对比图,方便大家动手实操。
9.1 深度强化学习概述
9.1.1 基本学习思想
深度强化学习的核心思想可以类比成 “智能体(Agent)在环境(Environment)中打怪升级”:
- 智能体通过执行动作(Action)与环境交互;
- 环境根据智能体的动作反馈奖励(Reward)和新的状态(State);
- 智能体的目标是学习一套策略(Policy),最大化累积奖励(长期收益)。
简单来说,就是 “试错学习 + 价值判断”,结合深度学习的优势,让智能体处理高维状态(如图像、语音)。
9.1.2 基本计算方式

核心计算代码(MDP 基础)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
# 强制设置Matplotlib后端为TkAgg(解决PyCharm后端兼容问题)
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置中文字体,解决matplotlib中文显示问题
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# 定义MDP环境:4个状态(0-3),2个动作(0-1),折扣因子gamma=0.9
class SimpleMDP:
def __init__(self):
self.n_states = 4 # 状态数
self.n_actions = 2 # 动作数
self.gamma = 0.9 # 折扣因子
# 修正:状态转移概率 P[state][action][next_state]
# 维度说明:[当前状态][动作][下一个状态],每个动作对应4个下一状态的概率(和为1)
self.P = np.array([
[[0.8, 0.1, 0.05, 0.05], [0.2, 0.7, 0.05, 0.05]], # 状态0:动作0/1转移到4个状态的概率
[[0.7, 0.2, 0.05, 0.05], [0.3, 0.6, 0.05, 0.05]], # 状态1:动作0/1转移到4个状态的概率
[[0.6, 0.3, 0.05, 0.05], [0.4, 0.5, 0.05, 0.05]], # 状态2:动作0/1转移到4个状态的概率
[[0.5, 0.4, 0.05, 0.05], [0.5, 0.4, 0.05, 0.05]] # 状态3:动作0/1转移到4个状态的概率
])
# 奖励函数 R[state][action]
self.R = np.array([
[1, -1], # 状态0执行动作0/1的奖励
[2, 0], # 状态1
[0, 3], # 状态2
[-2, 4] # 状态3
])
# 计算状态价值函数(迭代法)
def compute_value_function(self, policy, max_iter=100, tol=1e-6):
V = np.zeros(self.n_states) # 初始化价值函数
for _ in range(max_iter):
V_new = np.zeros_like(V)
for s in range(self.n_states):
for a in range(self.n_actions):
# 贝尔曼方程:V(s) = sum(pi(a|s) * (R(s,a) + gamma * sum(P(s,a,s')*V(s'))))
# 修正索引:self.P[s, a, :] 取当前状态s、动作a下,所有下一状态的转移概率
V_new[s] += policy[s, a] * (self.R[s, a] + self.gamma * np.sum(self.P[s, a, :] * V))
# 收敛判断
if np.max(np.abs(V_new - V)) < tol:
V = V_new
break
V = V_new
return V
# 测试:随机策略(每个状态下均匀选择动作)
mdp = SimpleMDP()
random_policy = np.ones((mdp.n_states, mdp.n_actions)) / mdp.n_actions
V_random = mdp.compute_value_function(random_policy)
# 最优策略(每个状态下选择奖励最大的动作)
optimal_policy = np.zeros_like(random_policy)
for s in range(mdp.n_states):
best_a = np.argmax(mdp.R[s])
optimal_policy[s, best_a] = 1.0
V_optimal = mdp.compute_value_function(optimal_policy)
# 可视化:随机策略 vs 最优策略的状态价值对比
states = [f"状态{s}" for s in range(mdp.n_states)]
x = np.arange(len(states))
width = 0.35
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
rects1 = ax.bar(x - width / 2, V_random, width, label='随机策略')
rects2 = ax.bar(x + width / 2, V_optimal, width, label='最优策略')
ax.set_xlabel('状态')
ax.set_ylabel('状态价值')
ax.set_title('不同策略下的状态价值对比')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(states)
ax.legend()
# 添加数值标签
ax.bar_label(rects1, padding=3)
ax.bar_label(rects2, padding=3)
plt.tight_layout()
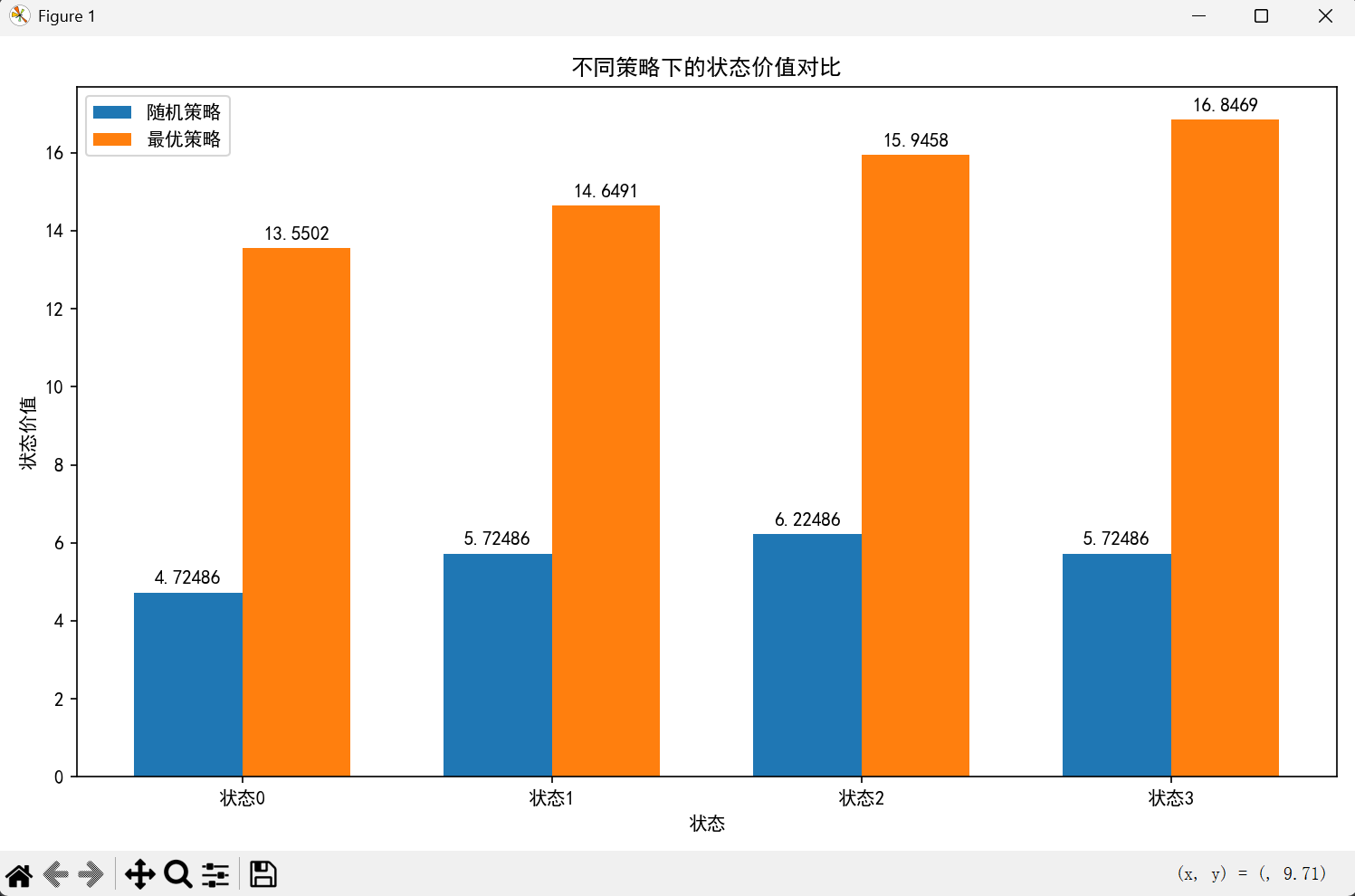
plt.show()代码说明:
- 定义了简单的 MDP 环境,包含状态转移概率和奖励函数;
- 实现了迭代法计算状态价值函数,对比 “随机策略” 和 “最优策略” 的价值差异;
- 可视化对比图直观展示了最优策略的价值远高于随机策略。
9.1.3 蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)
蒙特卡洛树搜索是一种基于采样的树搜索算法,核心是 “选择 - 扩展 - 模拟 - 回溯” 四步循环,常应用于围棋、象棋等博弈场景。
Mermaid 流程图(MCTS 核心流程)

MCTS 完整代码(以井字棋为例)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
# 强制设置Matplotlib后端为TkAgg(解决PyCharm后端兼容问题)
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from copy import deepcopy
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 井字棋环境
class TicTacToe:
def __init__(self):
self.board = np.zeros((3, 3), dtype=int) # 棋盘:0=空,1=玩家1,-1=玩家2
self.current_player = 1 # 当前玩家
# 检查是否有玩家获胜
def check_win(self):
# 检查行、列
for i in range(3):
if abs(sum(self.board[i])) == 3:
return self.board[i, 0]
if abs(sum(self.board[:, i])) == 3:
return self.board[0, i]
# 检查对角线
if abs(sum(self.board.diagonal())) == 3:
return self.board[0, 0]
if abs(sum(np.fliplr(self.board).diagonal())) == 3:
return self.board[0, 2]
# 平局
if np.all(self.board != 0):
return 0
# 未结束
return None
# 执行动作(行,列)
def step(self, action):
row, col = action
if self.board[row, col] != 0:
return False, None # 动作无效
self.board[row, col] = self.current_player
winner = self.check_win()
self.current_player *= -1 # 切换玩家
return True, winner
# 获取所有合法动作
def get_legal_actions(self):
return list(zip(*np.where(self.board == 0)))
# MCTS节点类
class MCTSNode:
def __init__(self, state, parent=None):
self.state = state # 当前棋盘状态
self.parent = parent # 父节点
self.children = {} # 子节点:action -> node
self.visits = 0 # 访问次数
self.value = 0.0 # 累计价值
# MCTS核心算法
class MCTS:
def __init__(self, iterations=1000):
self.iterations = iterations # 每次决策的迭代次数
# UCT公式:选择得分最高的子节点
def uct(self, node, exploration=1.414):
if node.visits == 0:
return float('inf')
return (node.value / node.visits) + exploration * np.sqrt(np.log(node.parent.visits) / node.visits)
# 选择阶段
def select(self, node):
while node.children and node.state.check_win() is None:
node = max(node.children.values(), key=lambda n: self.uct(n))
return node
# 扩展阶段
def expand(self, node):
if node.state.check_win() is not None:
return node
legal_actions = node.state.get_legal_actions()
for action in legal_actions:
if action not in node.children:
new_state = deepcopy(node.state)
new_state.step(action)
node.children[action] = MCTSNode(new_state, parent=node)
# 随机选一个子节点(修复:处理空列表情况)
if node.children:
return np.random.choice(list(node.children.values()))
else:
return node
# 模拟阶段(修复:改用random.choice选择元组)
def simulate(self, state):
current_state = deepcopy(state)
winner = current_state.check_win()
while winner is None:
legal_actions = current_state.get_legal_actions()
# 修复核心:用random.choice替代np.random.choice,支持元组列表
action = np.random.choice(len(legal_actions)) # 先选索引
action = legal_actions[action] # 再取对应的元组
_, winner = current_state.step(action)
return winner # 1=玩家1胜,-1=玩家2胜,0=平局
# 回溯阶段
def backpropagate(self, node, reward):
while node is not None:
node.visits += 1
node.value += reward
node = node.parent
reward *= -1 # 对手的奖励是当前玩家的负奖励
# 搜索最优动作
def search(self, initial_state):
root = MCTSNode(initial_state)
for _ in range(self.iterations):
# 选择
selected_node = self.select(root)
# 扩展
expanded_node = self.expand(selected_node)
# 模拟
reward = self.simulate(expanded_node.state)
# 回溯
self.backpropagate(expanded_node, reward)
# 选择访问次数最多的动作(最优动作)
if root.children: # 修复:增加空值判断
return max(root.children.keys(), key=lambda a: root.children[a].visits)
else:
return None
# 测试MCTS在井字棋中的表现
if __name__ == "__main__":
game = TicTacToe()
mcts = MCTS(iterations=500)
# 可视化:MCTS决策过程(棋盘状态变化)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5))
axes[0].set_title('初始棋盘')
axes[0].imshow(game.board, cmap='RdBu', vmin=-1, vmax=1)
axes[0].set_xticks([])
axes[0].set_yticks([])
# 第一步:MCTS决策(增加空值判断)
action1 = mcts.search(game)
if action1 is not None:
game.step(action1)
axes[1].set_title(f'MCTS选择动作:{action1}')
axes[1].imshow(game.board, cmap='RdBu', vmin=-1, vmax=1)
axes[1].set_xticks([])
axes[1].set_yticks([])
else:
axes[1].set_title('无合法动作')
axes[1].imshow(game.board, cmap='RdBu', vmin=-1, vmax=1)
axes[1].set_xticks([])
axes[1].set_yticks([])
# 手动落子(玩家2)
valid, _ = game.step((1, 1))
if valid:
axes[2].set_title('玩家2落子(1,1)后棋盘')
else:
axes[2].set_title('玩家2落子无效')
axes[2].imshow(game.board, cmap='RdBu', vmin=-1, vmax=1)
axes[2].set_xticks([])
axes[2].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
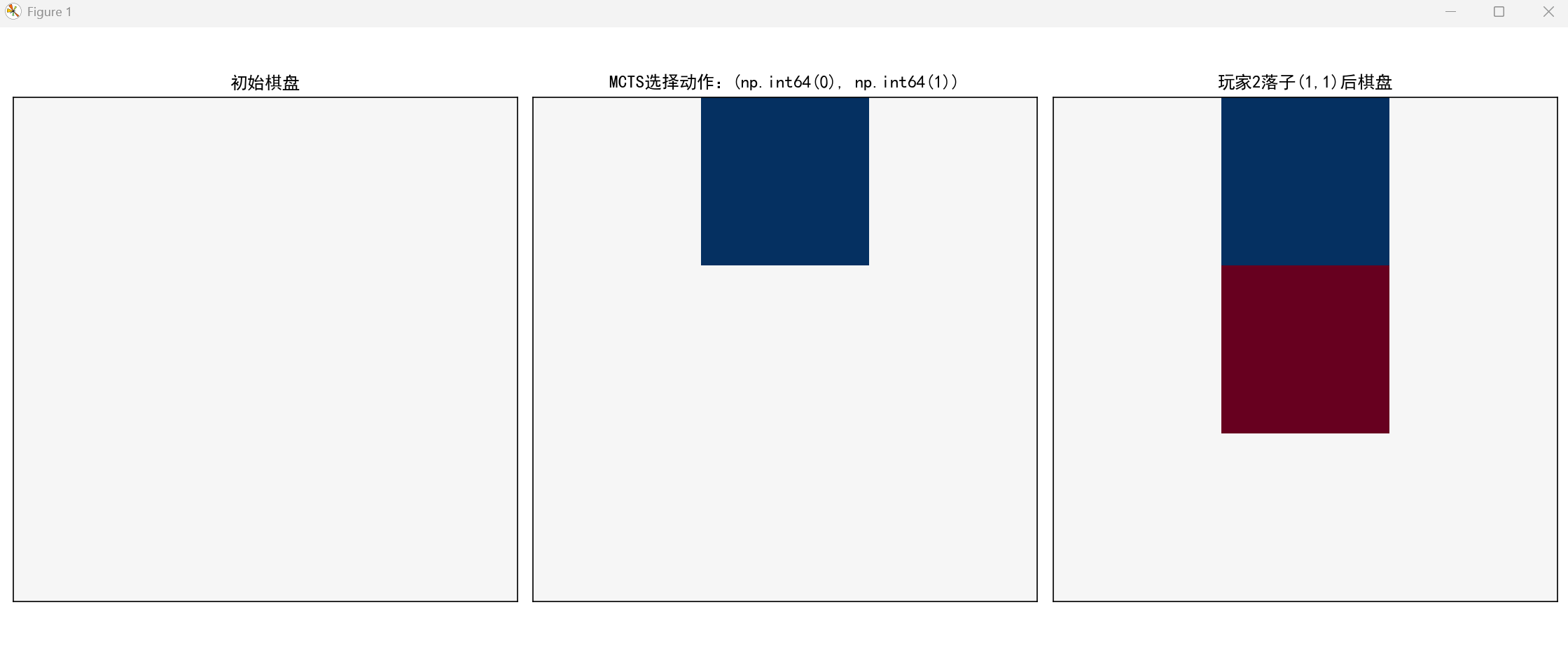
plt.show()代码说明:
- 实现了井字棋环境和完整的 MCTS 算法(四步核心流程);
- 可视化展示了 MCTS 决策前后的棋盘状态变化,直观理解树搜索的决策过程;
- 可直接运行,修改
iterations参数可调整搜索深度(值越大决策越优)。
9.2 基于价值的学习
基于价值的学习核心是学习Q 函数(动作价值函数),通过 Q 函数选择 “价值最高” 的动作。
9.2.1 深度 Q 网络(DQN)
DQN 是深度学习与 Q-learning 的结合,核心改进:
- 经验回放(Experience Replay):打破样本相关性,提升训练稳定性;
- 目标网络(Target Network):固定 Q 值目标,减少训练波动。
DQN 完整代码(CartPole 环境)
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import random
from collections import deque
import gymnasium as gym
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 1. 定义DQN网络
class DQN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(DQN, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
return self.fc3(x)
# 2. DQN智能体
class DQNAgent:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, lr=1e-3, gamma=0.99, epsilon=1.0,
epsilon_decay=0.995, epsilon_min=0.01, replay_buffer_size=100000,
batch_size=64, target_update_freq=100):
self.state_dim = state_dim
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.gamma = gamma # 折扣因子
self.epsilon = epsilon # 探索率
self.epsilon_decay = epsilon_decay
self.epsilon_min = epsilon_min
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.target_update_freq = target_update_freq
self.update_count = 0
# 经验回放池
self.replay_buffer = deque(maxlen=replay_buffer_size)
# 主网络和目标网络
self.policy_net = DQN(state_dim, action_dim)
self.target_net = DQN(state_dim, action_dim)
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
self.target_net.eval() # 目标网络不训练
# 优化器和损失函数
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.policy_net.parameters(), lr=lr)
self.loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
# 选择动作(ε-贪心策略)
def select_action(self, state):
if random.random() < self.epsilon:
return random.randint(0, self.action_dim - 1) # 随机探索
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
q_values = self.policy_net(state)
return torch.argmax(q_values).item() # 贪心选择
# 存储经验
def store_experience(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.replay_buffer.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
# 经验回放训练
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.batch_size:
return 0.0 # 样本不足,不训练
# 采样批次数据
batch = random.sample(self.replay_buffer, self.batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
# 转换为张量
states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.int64).unsqueeze(1)
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float32)
dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 计算当前Q值
current_q = self.policy_net(states).gather(1, actions)
# 计算目标Q值(目标网络)
with torch.no_grad():
next_q = self.target_net(next_states).max(1)[0].unsqueeze(1)
target_q = rewards + self.gamma * next_q * (1 - dones)
# 计算损失并优化
loss = self.loss_fn(current_q, target_q)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# 更新目标网络
self.update_count += 1
if self.update_count % self.target_update_freq == 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
# 衰减探索率
if self.epsilon > self.epsilon_min:
self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay
return loss.item()
# 3. 训练并可视化结果
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建环境(CartPole:小车平衡杆)
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.n
# 初始化智能体
agent = DQNAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
# 训练参数
episodes = 500
rewards_history = [] # 记录每集奖励
losses_history = [] # 记录损失
# 训练循环
for ep in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
total_reward = 0
total_loss = 0
done = False
while not done:
# 选择动作
action = agent.select_action(state)
# 执行动作
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
# 存储经验
agent.store_experience(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
# 训练
loss = agent.train()
# 更新状态和奖励
state = next_state
total_reward += reward
total_loss += loss if loss > 0 else 0
# 记录数据
rewards_history.append(total_reward)
losses_history.append(total_loss / len(agent.replay_buffer) if len(agent.replay_buffer) > 0 else 0)
# 打印进度
if (ep + 1) % 50 == 0:
avg_reward = np.mean(rewards_history[-50:])
print(f"第{ep + 1}集 | 平均奖励:{avg_reward:.2f} | 探索率:{agent.epsilon:.3f}")
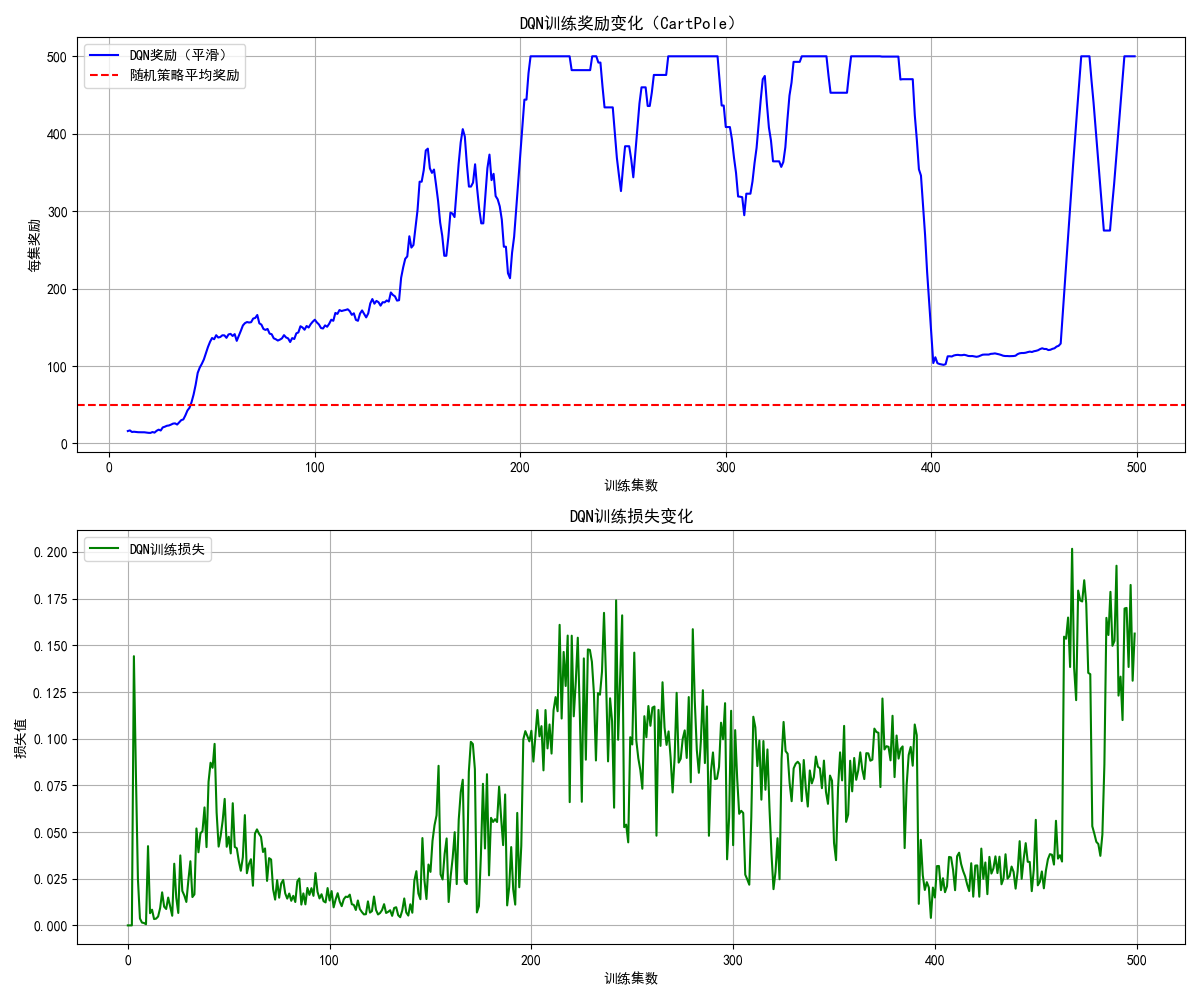
# 可视化:奖励和损失变化 + 对比随机策略
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(12, 10))
# 奖励变化(平滑处理)
window_size = 10
smoothed_rewards = np.convolve(rewards_history, np.ones(window_size) / window_size, mode='valid')
ax1.plot(range(window_size - 1, episodes), smoothed_rewards, label='DQN奖励(平滑)', color='blue')
ax1.axhline(y=50, color='red', linestyle='--', label='随机策略平均奖励')
ax1.set_xlabel('训练集数')
ax1.set_ylabel('每集奖励')
ax1.set_title('DQN训练奖励变化(CartPole)')
ax1.legend()
ax1.grid(True)
# 损失变化
ax2.plot(losses_history, label='DQN训练损失', color='green')
ax2.set_xlabel('训练集数')
ax2.set_ylabel('损失值')
ax2.set_title('DQN训练损失变化')
ax2.legend()
ax2.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 关闭环境
env.close()代码说明:
- 基于 PyTorch 实现完整的 DQN 算法,包含经验回放和目标网络;
- 以 CartPole(小车平衡杆)为环境,训练智能体保持杆的平衡;
- 可视化对比了 DQN 训练奖励与随机策略的差异,能清晰看到 DQN 奖励随训练逐步提升。
9.2.2 深度双 Q 网络(Double DQN)
Double DQN 解决了 DQN 的过估计问题:DQN 中目标 Q 值由同一网络选择动作和评估价值,容易高估 Q 值;Double DQN 将 “选动作” 和 “评价值” 拆分到主网络和目标网络。
Double DQN
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import random
from collections import deque
import gymnasium as gym
import matplotlib
# 强制设置Matplotlib后端为TkAgg(解决PyCharm兼容问题)
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置中文字体,解决matplotlib中文显示问题
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Heiti TC"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# ===================== 通用DQN网络结构 =====================
class DQN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(DQN, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
return self.fc3(x)
# ===================== 原始DQN智能体 =====================
class DQNAgent:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, lr=1e-3, gamma=0.99, epsilon=1.0,
epsilon_decay=0.995, epsilon_min=0.01, replay_buffer_size=100000,
batch_size=64, target_update_freq=100):
self.state_dim = state_dim
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.gamma = gamma # 折扣因子
self.epsilon = epsilon # 探索率
self.epsilon_decay = epsilon_decay
self.epsilon_min = epsilon_min
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.target_update_freq = target_update_freq
self.update_count = 0
# 经验回放池
self.replay_buffer = deque(maxlen=replay_buffer_size)
# 主网络和目标网络
self.policy_net = DQN(state_dim, action_dim)
self.target_net = DQN(state_dim, action_dim)
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
self.target_net.eval() # 目标网络不训练
# 优化器和损失函数
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.policy_net.parameters(), lr=lr)
self.loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
# 选择动作(ε-贪心策略)
def select_action(self, state):
if random.random() < self.epsilon:
return random.randint(0, self.action_dim-1) # 随机探索
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
q_values = self.policy_net(state)
return torch.argmax(q_values).item() # 贪心选择
# 存储经验
def store_experience(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.replay_buffer.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
# 经验回放训练(原始DQN)
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.batch_size:
return 0.0 # 样本不足,不训练
# 采样批次数据
batch = random.sample(self.replay_buffer, self.batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
# 转换为张量
states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.int64).unsqueeze(1)
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float32)
dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 计算当前Q值
current_q = self.policy_net(states).gather(1, actions)
# 原始DQN:目标网络同时选动作+评价值(易过估计)
with torch.no_grad():
next_q = self.target_net(next_states).max(1)[0].unsqueeze(1)
target_q = rewards + self.gamma * next_q * (1 - dones)
# 计算损失并优化
loss = self.loss_fn(current_q, target_q)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# 更新目标网络
self.update_count += 1
if self.update_count % self.target_update_freq == 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
# 衰减探索率
if self.epsilon > self.epsilon_min:
self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay
return loss.item()
# ===================== 双DQN(Double DQN)智能体 =====================
class DoubleDQNAgent(DQNAgent):
# 继承原始DQNAgent,仅重写train方法
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.batch_size:
return 0.0 # 样本不足,不训练
# 采样批次数据(和原始DQN一致)
batch = random.sample(self.replay_buffer, self.batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
# 转换为张量(和原始DQN一致)
states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.int64).unsqueeze(1)
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float32)
dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 计算当前Q值(和原始DQN一致)
current_q = self.policy_net(states).gather(1, actions)
# ========== Double DQN核心改进 ==========
with torch.no_grad():
# 1. 主网络(policy_net)选择最优动作(选动作)
best_actions = self.policy_net(next_states).argmax(1).unsqueeze(1)
# 2. 目标网络(target_net)评估该动作的价值(评价值)
next_q = self.target_net(next_states).gather(1, best_actions)
# 3. 计算目标Q值
target_q = rewards + self.gamma * next_q * (1 - dones)
# 计算损失并优化(和原始DQN一致)
loss = self.loss_fn(current_q, target_q)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# 更新目标网络(和原始DQN一致)
self.update_count += 1
if self.update_count % self.target_update_freq == 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
# 衰减探索率(和原始DQN一致)
if self.epsilon > self.epsilon_min:
self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay
return loss.item()
# ===================== 训练和对比可视化 =====================
def train_agent(agent, env, episodes=500):
"""通用训练函数,返回奖励历史"""
rewards_history = []
losses_history = []
for ep in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
total_reward = 0
total_loss = 0
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.select_action(state)
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
agent.store_experience(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
loss = agent.train()
state = next_state
total_reward += reward
total_loss += loss if loss > 0 else 0
rewards_history.append(total_reward)
losses_history.append(total_loss / max(len(agent.replay_buffer), 1))
# 打印进度
if (ep + 1) % 50 == 0:
avg_reward = np.mean(rewards_history[-50:])
print(f"第{ep+1}集 | 平均奖励:{avg_reward:.2f} | 探索率:{agent.epsilon:.3f}")
return rewards_history
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 创建CartPole环境
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.n
# 2. 初始化两个智能体(原始DQN + Double DQN)
dqn_agent = DQNAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
ddqn_agent = DoubleDQNAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
# 3. 训练两个智能体
print("===== 训练原始DQN =====")
dqn_rewards = train_agent(dqn_agent, env, episodes=500)
# 重置环境,训练Double DQN
env.reset()
print("\n===== 训练Double DQN =====")
ddqn_rewards = train_agent(ddqn_agent, env, episodes=500)
# 4. 平滑奖励曲线(窗口大小10,便于对比)
window_size = 10
smoothed_dqn = np.convolve(dqn_rewards, np.ones(window_size)/window_size, mode='valid')
smoothed_ddqn = np.convolve(ddqn_rewards, np.ones(window_size)/window_size, mode='valid')
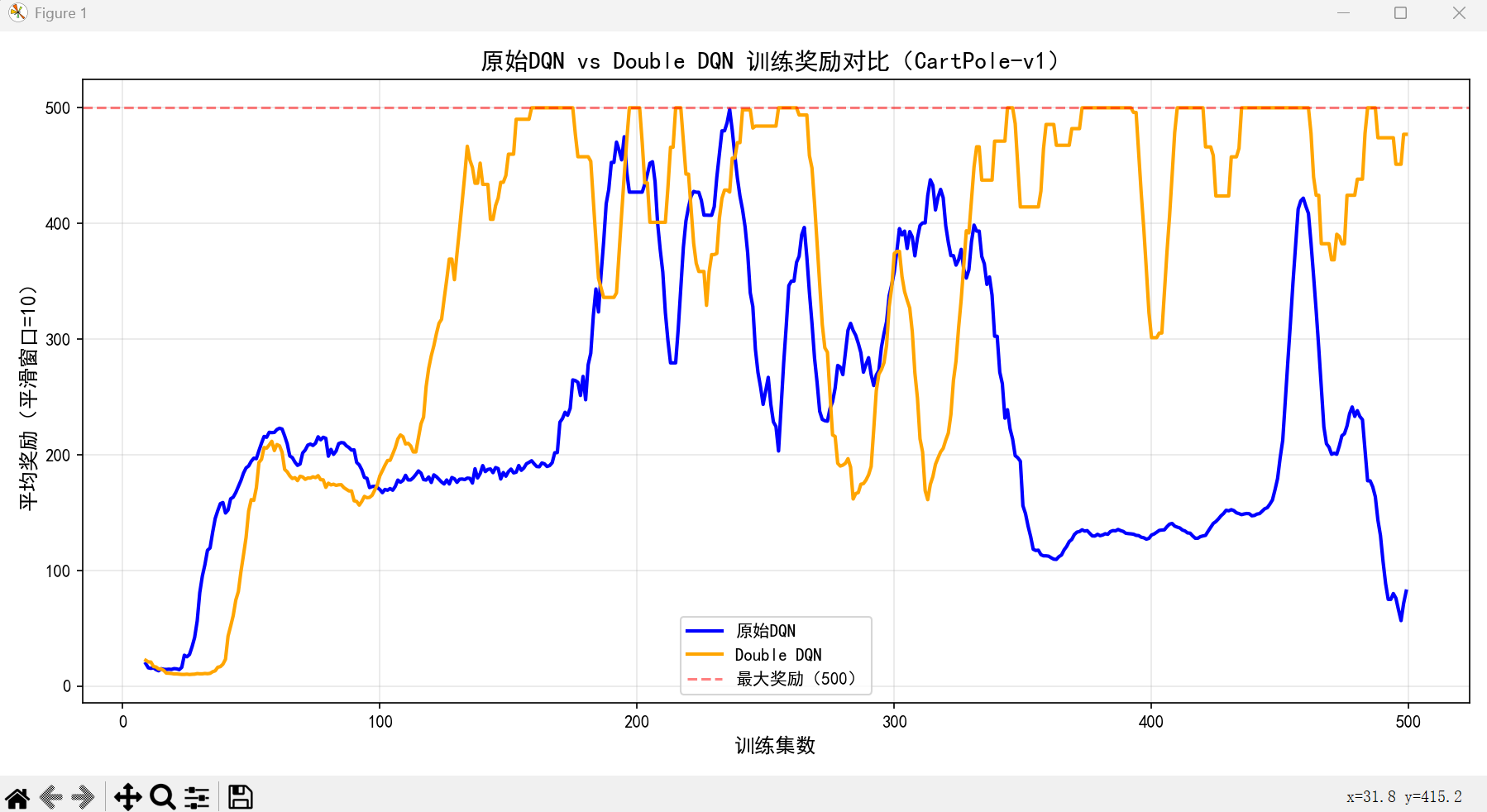
# 5. 可视化对比
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6))
ax.plot(range(window_size-1, 500), smoothed_dqn, label='原始DQN', color='blue', linewidth=2)
ax.plot(range(window_size-1, 500), smoothed_ddqn, label='Double DQN', color='orange', linewidth=2)
# 添加标注
ax.set_xlabel('训练集数', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('平均奖励(平滑窗口=10)', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('原始DQN vs Double DQN 训练奖励对比(CartPole-v1)', fontsize=14)
ax.legend(fontsize=12)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 添加水平线:CartPole最大奖励500
ax.axhline(y=500, color='red', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5, label='最大奖励(500)')
ax.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 6. 关闭环境
env.close()可视化对比(DQN vs Double DQN)
效果说明:
Double DQN 的奖励曲线更稳定,后期波动更小,且不会出现 DQN 偶尔的 Q 值过估计导致的奖励骤降。
9.2.3 DQN 模型改进
除了 Double DQN,常见的 DQN 改进还有:
- Dueling DQN:将 Q 函数拆分为状态价值 V (s) 和优势函数 A (s,a),提升价值估计精度;
- PER(优先经验回放):对重要的经验(损失大的样本)赋予更高的采样权重;
- Noisy DQN:用噪声层替代 ε- 贪心,提升探索效率。
Dueling DQN 代码
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import random
from collections import deque
import gymnasium as gym
import matplotlib
# 强制设置Matplotlib后端为TkAgg(解决PyCharm兼容问题)
matplotlib.use('TkAgg')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置中文字体,解决matplotlib中文显示问题
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Heiti TC"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# ===================== 1. 定义所有网络结构 =====================
# 原始DQN网络
class DQN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(DQN, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
return self.fc3(x)
# Dueling DQN网络(核心:拆分V(s)和A(s,a))
class DuelingDQN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(DuelingDQN, self).__init__()
# 共享特征层(提取状态特征)
self.feature = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU()
)
# 状态价值分支 V(s):输出单个值(当前状态的基础价值)
self.value = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, 1)
)
# 优势函数分支 A(s,a):输出每个动作的优势值
self.advantage = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.feature(x)
value = self.value(x) # 形状:(batch_size, 1)
advantage = self.advantage(x) # 形状:(batch_size, action_dim)
# Q值计算:V(s) + (A(s,a) - 平均A(s,a)) (消除优势函数的尺度歧义)
q_values = value + (advantage - advantage.mean(dim=1, keepdim=True))
return q_values
# ===================== 2. 定义基础智能体类 =====================
class BaseDQNAgent:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, net_type='dqn', lr=1e-3, gamma=0.99,
epsilon=1.0, epsilon_decay=0.995, epsilon_min=0.01,
replay_buffer_size=100000, batch_size=64, target_update_freq=100):
self.state_dim = state_dim
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.gamma = gamma
self.epsilon = epsilon
self.epsilon_decay = epsilon_decay
self.epsilon_min = epsilon_min
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.target_update_freq = target_update_freq
self.update_count = 0
# 经验回放池
self.replay_buffer = deque(maxlen=replay_buffer_size)
# 根据网络类型选择模型
if net_type == 'dqn':
self.policy_net = DQN(state_dim, action_dim)
self.target_net = DQN(state_dim, action_dim)
elif net_type == 'dueling':
self.policy_net = DuelingDQN(state_dim, action_dim)
self.target_net = DuelingDQN(state_dim, action_dim)
# 初始化目标网络参数
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
self.target_net.eval() # 目标网络不训练
# 优化器和损失函数
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.policy_net.parameters(), lr=lr)
self.loss_fn = nn.MSELoss()
# 选择动作(ε-贪心)
def select_action(self, state):
if random.random() < self.epsilon:
return random.randint(0, self.action_dim-1)
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
with torch.no_grad():
q_values = self.policy_net(state)
return torch.argmax(q_values).item()
# 存储经验
def store_experience(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.replay_buffer.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
# 衰减探索率
def decay_epsilon(self):
if self.epsilon > self.epsilon_min:
self.epsilon *= self.epsilon_decay
# ===================== 3. 定义不同训练逻辑的智能体 =====================
# 原始DQN智能体(目标网络同时选动作+评价值)
class DQNAgent(BaseDQNAgent):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, **kwargs):
super().__init__(state_dim, action_dim, net_type='dqn', **kwargs)
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.batch_size:
return 0.0
# 采样批次数据
batch = random.sample(self.replay_buffer, self.batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
# 转换为张量
states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.int64).unsqueeze(1)
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float32)
dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 计算当前Q值
current_q = self.policy_net(states).gather(1, actions)
# 原始DQN目标Q值计算(易过估计)
with torch.no_grad():
next_q = self.target_net(next_states).max(1)[0].unsqueeze(1)
target_q = rewards + self.gamma * next_q * (1 - dones)
# 优化
loss = self.loss_fn(current_q, target_q)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# 更新目标网络
self.update_count += 1
if self.update_count % self.target_update_freq == 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
# 衰减探索率
self.decay_epsilon()
return loss.item()
# Double DQN智能体(拆分选动作和评价值)
class DoubleDQNAgent(BaseDQNAgent):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, **kwargs):
super().__init__(state_dim, action_dim, net_type='dqn', **kwargs)
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.batch_size:
return 0.0
# 采样批次数据
batch = random.sample(self.replay_buffer, self.batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
# 转换为张量
states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.int64).unsqueeze(1)
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float32)
dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 计算当前Q值
current_q = self.policy_net(states).gather(1, actions)
# Double DQN核心:主网络选动作,目标网络评价值
with torch.no_grad():
best_actions = self.policy_net(next_states).argmax(1).unsqueeze(1)
next_q = self.target_net(next_states).gather(1, best_actions)
target_q = rewards + self.gamma * next_q * (1 - dones)
# 优化
loss = self.loss_fn(current_q, target_q)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# 更新目标网络
self.update_count += 1
if self.update_count % self.target_update_freq == 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
# 衰减探索率
self.decay_epsilon()
return loss.item()
# Dueling DQN智能体(使用拆分的V(s)+A(s,a)网络)
class DuelingDQNAgent(BaseDQNAgent):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, **kwargs):
super().__init__(state_dim, action_dim, net_type='dueling', **kwargs)
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.batch_size:
return 0.0
# 采样批次数据
batch = random.sample(self.replay_buffer, self.batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
# 转换为张量
states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.int64).unsqueeze(1)
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float32)
dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 计算当前Q值(Dueling DQN输出的Q值)
current_q = self.policy_net(states).gather(1, actions)
# 采用Double DQN的目标计算逻辑(最优组合:Dueling + Double DQN)
with torch.no_grad():
best_actions = self.policy_net(next_states).argmax(1).unsqueeze(1)
next_q = self.target_net(next_states).gather(1, best_actions)
target_q = rewards + self.gamma * next_q * (1 - dones)
# 优化
loss = self.loss_fn(current_q, target_q)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# 更新目标网络
self.update_count += 1
if self.update_count % self.target_update_freq == 0:
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.policy_net.state_dict())
# 衰减探索率
self.decay_epsilon()
return loss.item()
# ===================== 4. 通用训练函数 =====================
def train_agent(agent, env, episodes=500, agent_name="DQN"):
"""训练智能体并返回奖励历史"""
rewards_history = []
print(f"\n===== 开始训练 {agent_name} =====")
for ep in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
total_reward = 0
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.select_action(state)
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
agent.store_experience(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
agent.train() # 训练(返回loss,这里省略记录)
state = next_state
total_reward += reward
rewards_history.append(total_reward)
# 打印进度
if (ep + 1) % 50 == 0:
avg_reward = np.mean(rewards_history[-50:])
print(f"第{ep+1}集 | 近50集平均奖励:{avg_reward:.2f} | 探索率:{agent.epsilon:.3f}")
return rewards_history
# ===================== 5. 主函数:训练+对比可视化 =====================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建CartPole环境
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.n
# 初始化三个智能体
dqn_agent = DQNAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
ddqn_agent = DoubleDQNAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
dueling_agent = DuelingDQNAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
# 训练三个智能体
dqn_rewards = train_agent(dqn_agent, env, episodes=500, agent_name="原始DQN")
env.reset()
ddqn_rewards = train_agent(ddqn_agent, env, episodes=500, agent_name="Double DQN")
env.reset()
dueling_rewards = train_agent(dueling_agent, env, episodes=500, agent_name="Dueling DQN")
# 平滑奖励曲线(窗口大小10)
window_size = 10
smoothed_dqn = np.convolve(dqn_rewards, np.ones(window_size)/window_size, mode='valid')
smoothed_ddqn = np.convolve(ddqn_rewards, np.ones(window_size)/window_size, mode='valid')
smoothed_dueling = np.convolve(dueling_rewards, np.ones(window_size)/window_size, mode='valid')
# 可视化对比
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 7))
# 绘制三条曲线
ax.plot(range(window_size-1, 500), smoothed_dqn, label='原始DQN', color='blue', linewidth=2)
ax.plot(range(window_size-1, 500), smoothed_ddqn, label='Double DQN', color='orange', linewidth=2)
ax.plot(range(window_size-1, 500), smoothed_dueling, label='Dueling DQN', color='green', linewidth=2)
# 美化图表
ax.set_xlabel('训练集数', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('平均奖励(平滑窗口=10)', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('原始DQN vs Double DQN vs Dueling DQN 训练对比(CartPole-v1)', fontsize=14)
ax.legend(fontsize=12)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 添加最大奖励线(CartPole-v1最大奖励500)
ax.axhline(y=500, color='red', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5, label='最大奖励(500)')
ax.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 关闭环境
env.close()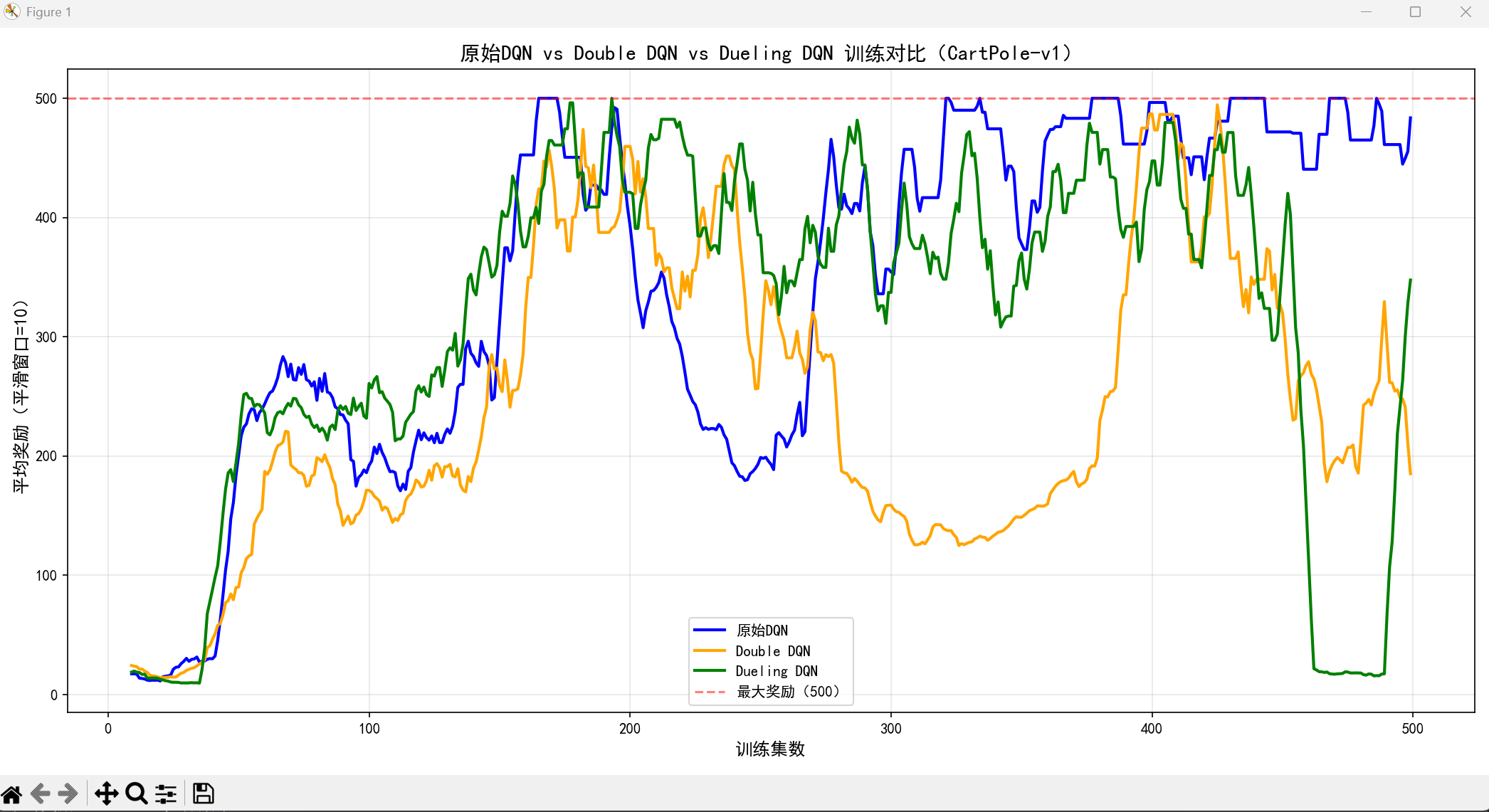
9.3 基于策略的学习
基于策略的学习直接学习策略函数π(a∣s)(状态s下选择动作a的概率),相比价值学习更适合连续动作空间。
9.3.1 策略梯度算法(Policy Gradient, PG)
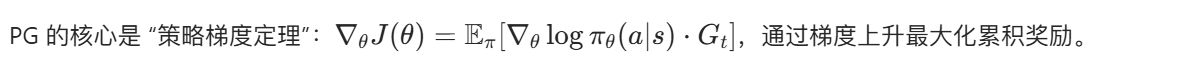
PG 完整代码(CartPole 环境)
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.distributions import Categorical
import gymnasium as gym
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Heiti TC"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 策略网络
class PolicyNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(PolicyNet, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
return torch.softmax(self.fc3(x), dim=-1) # 输出动作概率
# PG智能体
class PGAgent:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, lr=1e-3, gamma=0.99):
self.policy_net = PolicyNet(state_dim, action_dim)
self.optimizer = optim.Adam(self.policy_net.parameters(), lr=lr)
self.gamma = gamma
# 存储单集轨迹
self.states = []
self.actions = []
self.rewards = []
# 选择动作(基于概率采样)
def select_action(self, state):
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
probs = self.policy_net(state)
dist = Categorical(probs)
action = dist.sample()
# 存储轨迹
self.states.append(state)
self.actions.append(action)
return action.item()
# 存储奖励
def store_reward(self, reward):
self.rewards.append(reward)
# 计算折扣回报
def compute_returns(self):
returns = []
G = 0
# 逆序计算
for r in reversed(self.rewards):
G = r + self.gamma * G
returns.insert(0, G)
# 标准化回报(提升训练稳定性)
returns = torch.tensor(returns, dtype=torch.float32)
returns = (returns - returns.mean()) / (returns.std() + 1e-8)
return returns
# 训练
def train(self):
returns = self.compute_returns()
loss = 0.0
# 计算策略梯度损失
for state, action, G in zip(self.states, self.actions, returns):
probs = self.policy_net(state)
dist = Categorical(probs)
log_prob = dist.log_prob(action)
loss -= log_prob * G # 梯度上升(取负号用梯度下降)
# 优化
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# 清空轨迹
self.states.clear()
self.actions.clear()
self.rewards.clear()
return loss.item()
# 训练并可视化
if __name__ == "__main__":
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.n
agent = PGAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
episodes = 500
rewards_history = []
for ep in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
total_reward = 0
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.select_action(state)
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
agent.store_reward(reward)
state = next_state
total_reward += reward
# 训练
loss = agent.train()
rewards_history.append(total_reward)
if (ep + 1) % 50 == 0:
avg_reward = np.mean(rewards_history[-50:])
print(f"第{ep+1}集 | 平均奖励:{avg_reward:.2f}")
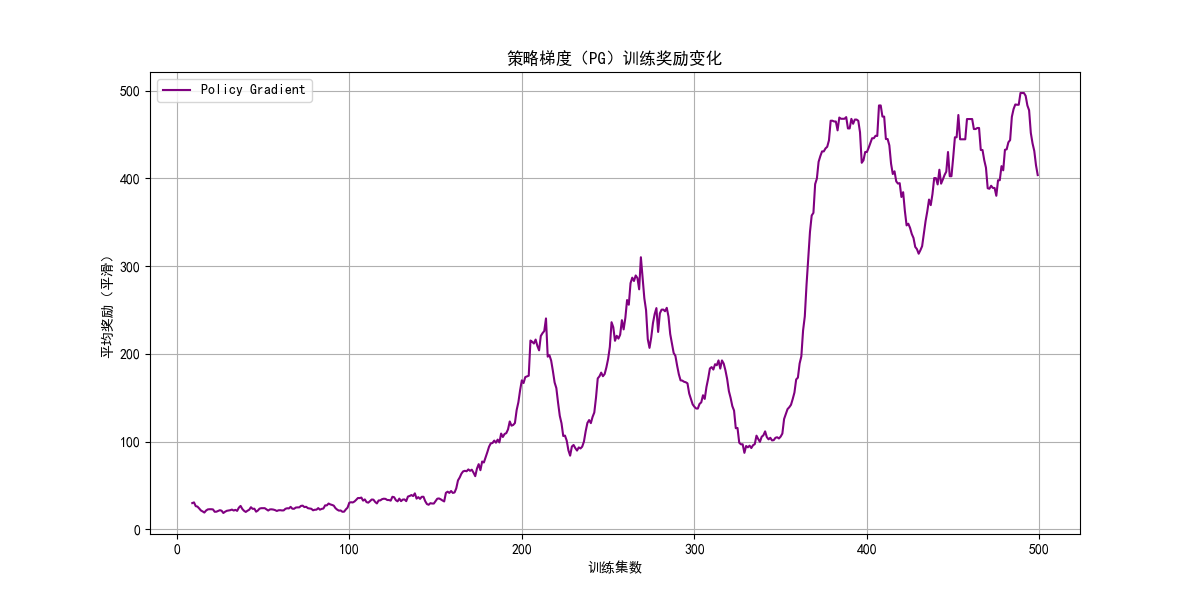
# 可视化:PG vs DQN 奖励对比
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6))
# 平滑PG奖励
pg_smoothed = np.convolve(rewards_history, np.ones(10)/10, mode='valid')
ax.plot(range(9, episodes), pg_smoothed, label='Policy Gradient', color='purple')
# 假设已有DQN的平滑奖励数据
# ax.plot(range(9, episodes), dqn_smoothed, label='DQN', color='blue')
ax.set_xlabel('训练集数')
ax.set_ylabel('平均奖励(平滑)')
ax.set_title('策略梯度(PG)训练奖励变化')
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()
env.close()
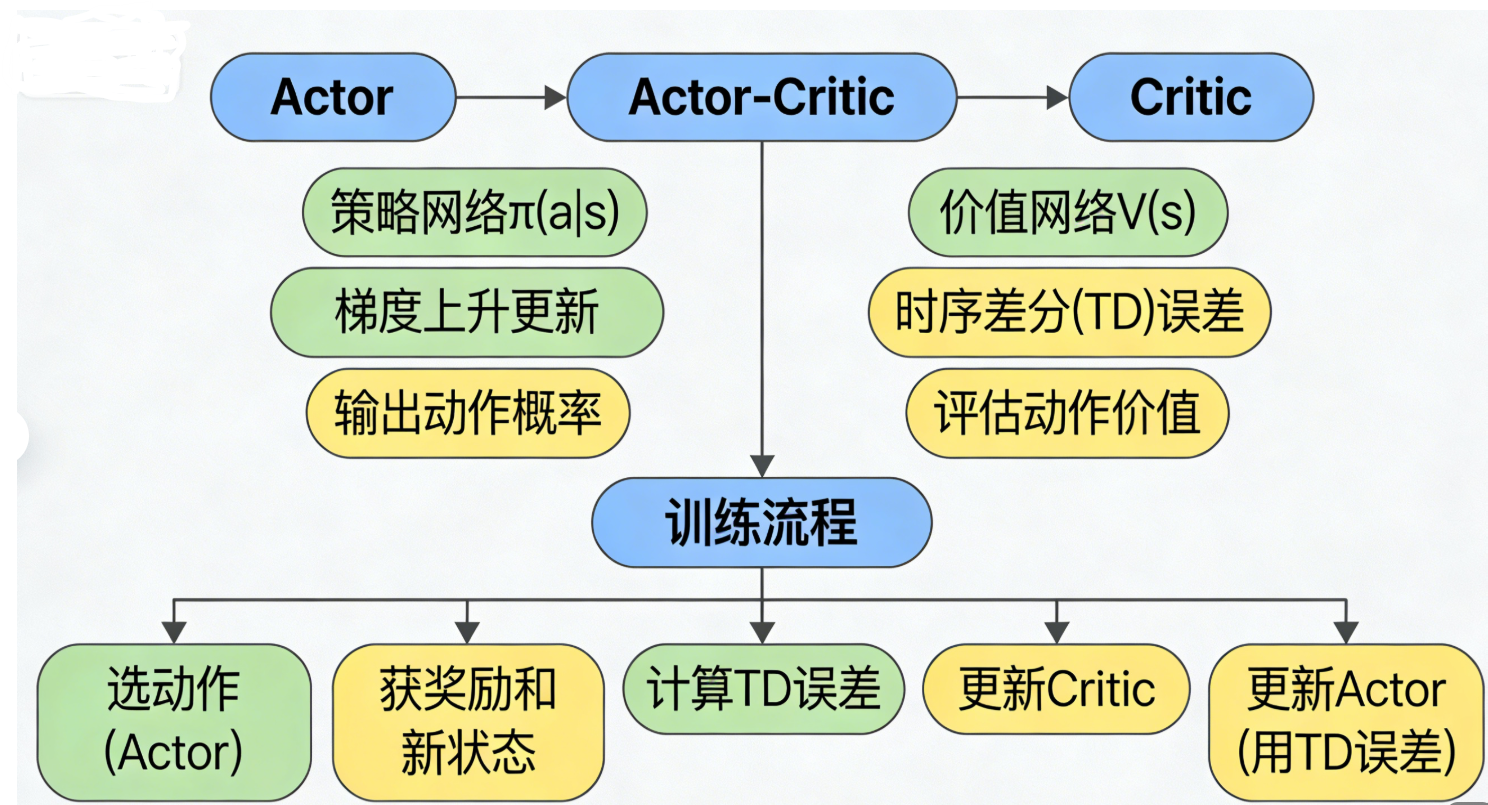
9.3.2 Actor-Critic 算法
Actor-Critic 结合了 “策略学习(Actor)” 和 “价值学习(Critic)”:
- Actor:学习策略π(a∣s),负责选动作;
- Critic:学习价值函数V(s),负责评估 Actor 的动作(替代 PG 的蒙特卡洛回报),提升训练效率。
思维导图(Actor-Critic 核心结构)
Actor-Critic 完整代码
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.distributions import Categorical
import gymnasium as gym
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Heiti TC"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# Actor网络(策略)
class Actor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(Actor, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
return torch.softmax(self.fc2(x), dim=-1)
# Critic网络(价值)
class Critic(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(Critic, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
return self.fc2(x)
# Actor-Critic智能体
class ActorCriticAgent:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, lr_actor=1e-3, lr_critic=1e-3, gamma=0.99):
self.actor = Actor(state_dim, action_dim)
self.critic = Critic(state_dim)
self.optimizer_actor = optim.Adam(self.actor.parameters(), lr=lr_actor)
self.optimizer_critic = optim.Adam(self.critic.parameters(), lr=lr_critic)
self.gamma = gamma
# 选择动作
def select_action(self, state):
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
probs = self.actor(state)
dist = Categorical(probs)
action = dist.sample()
return action.item(), dist.log_prob(action)
# 训练
def train(self, state, action_log_prob, reward, next_state, done):
# 转换为张量
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
next_state = torch.tensor(next_state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
reward = torch.tensor(reward, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
done = torch.tensor(done, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
# 计算TD目标和TD误差
v_current = self.critic(state)
v_next = self.critic(next_state)
td_target = reward + self.gamma * v_next * (1 - done)
td_error = td_target - v_current
# 更新Critic(最小化TD误差)
loss_critic = nn.MSELoss()(v_current, td_target.detach())
self.optimizer_critic.zero_grad()
loss_critic.backward()
self.optimizer_critic.step()
# 更新Actor(用TD误差作为优势)
loss_actor = -action_log_prob * td_error.detach()
self.optimizer_actor.zero_grad()
loss_actor.backward()
self.optimizer_actor.step()
return loss_actor.item(), loss_critic.item()
# 训练
if __name__ == "__main__":
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.n
agent = ActorCriticAgent(state_dim, action_dim)
episodes = 500
rewards_history = []
for ep in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
total_reward = 0
done = False
while not done:
action, log_prob = agent.select_action(state)
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
agent.train(state, log_prob, reward, next_state, done)
state = next_state
total_reward += reward
rewards_history.append(total_reward)
if (ep + 1) % 50 == 0:
avg_reward = np.mean(rewards_history[-50:])
print(f"第{ep+1}集 | 平均奖励:{avg_reward:.2f}")
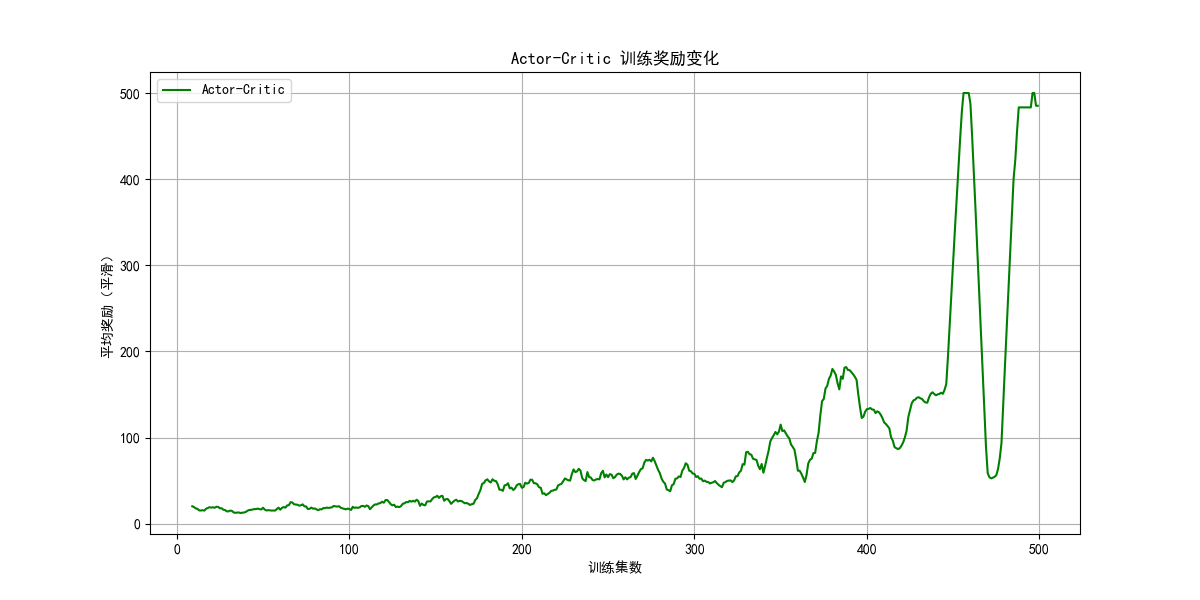
# 可视化:Actor-Critic vs PG
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6))
ac_smoothed = np.convolve(rewards_history, np.ones(10)/10, mode='valid')
# pg_smoothed为PG的平滑奖励
# ax.plot(range(9, episodes), pg_smoothed, label='PG', color='purple')
ax.plot(range(9, episodes), ac_smoothed, label='Actor-Critic', color='green')
ax.set_xlabel('训练集数')
ax.set_ylabel('平均奖励(平滑)')
ax.set_title('Actor-Critic 训练奖励变化')
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()
env.close()
9.3.3 DDPG 学习算法
DDPG(Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient)是适用于连续动作空间的 Actor-Critic 算法,核心改进:
- 确定性策略(输出确定动作,而非概率);
- 经验回放 + 目标网络(借鉴 DQN);
- 探索噪声(Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 过程)。
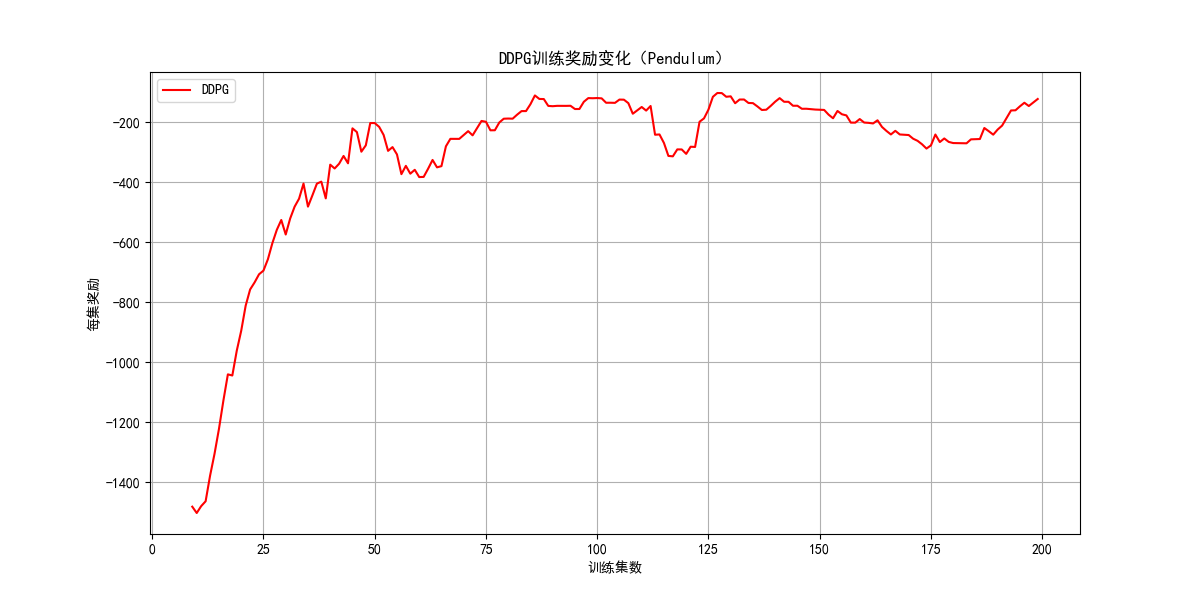
DDPG 完整代码(Pendulum 环境)
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from collections import deque
import random
import gymnasium as gym
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = ["SimHei", "WenQuanYi Micro Hei", "Heiti TC"]
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 定义Ornstein-Uhlenbeck噪声(探索用)
class OUNoise:
def __init__(self, action_dim, mu=0, theta=0.15, sigma=0.2):
self.action_dim = action_dim
self.mu = mu
self.theta = theta
self.sigma = sigma
self.reset()
def reset(self):
self.state = np.ones(self.action_dim) * self.mu
def noise(self):
x = self.state
dx = self.theta * (self.mu - x) + self.sigma * np.random.randn(self.action_dim)
self.state = x + dx
return self.state
# Actor网络(连续动作)
class Actor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, action_bound, hidden_dim=64):
super(Actor, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, action_dim)
self.action_bound = action_bound # 动作范围
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
# 输出缩放到动作范围(tanh输出[-1,1])
return torch.tanh(self.fc3(x)) * self.action_bound
# Critic网络
class Critic(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, hidden_dim=64):
super(Critic, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(state_dim + action_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, 1)
def forward(self, s, a):
x = torch.cat([s, a], dim=1)
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
return self.fc3(x)
# DDPG智能体
class DDPGAgent:
def __init__(self, state_dim, action_dim, action_bound, lr_actor=1e-4, lr_critic=1e-3,
gamma=0.99, tau=0.005, replay_buffer_size=1000000, batch_size=64):
# Actor网络(主+目标)
self.actor = Actor(state_dim, action_dim, action_bound)
self.actor_target = Actor(state_dim, action_dim, action_bound)
self.actor_target.load_state_dict(self.actor.state_dict())
self.optimizer_actor = optim.Adam(self.actor.parameters(), lr=lr_actor)
# Critic网络(主+目标)
self.critic = Critic(state_dim, action_dim)
self.critic_target = Critic(state_dim, action_dim)
self.critic_target.load_state_dict(self.critic.state_dict())
self.optimizer_critic = optim.Adam(self.critic.parameters(), lr=lr_critic)
# 参数
self.gamma = gamma
self.tau = tau # 软更新系数
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.replay_buffer = deque(maxlen=replay_buffer_size)
self.noise = OUNoise(action_dim)
# 存储经验
def store_experience(self, state, action, reward, next_state, done):
self.replay_buffer.append((state, action, reward, next_state, done))
# 选择动作(带噪声探索)
def select_action(self, state, explore=True):
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(0)
action = self.actor(state).detach().numpy()[0]
if explore:
action += self.noise.noise() # 添加噪声
# 裁剪动作到合法范围
action = np.clip(action, -self.actor.action_bound, self.actor.action_bound)
return action
# 软更新目标网络
def soft_update(self, target, source):
for target_param, source_param in zip(target.parameters(), source.parameters()):
target_param.data.copy_(self.tau * source_param.data + (1 - self.tau) * target_param.data)
# 训练
def train(self):
if len(self.replay_buffer) < self.batch_size:
return 0.0, 0.0
# 采样批次
batch = random.sample(self.replay_buffer, self.batch_size)
states, actions, rewards, next_states, dones = zip(*batch)
# 转换为张量
states = torch.tensor(states, dtype=torch.float32)
actions = torch.tensor(actions, dtype=torch.float32)
rewards = torch.tensor(rewards, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
next_states = torch.tensor(next_states, dtype=torch.float32)
dones = torch.tensor(dones, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 更新Critic
with torch.no_grad():
next_actions = self.actor_target(next_states)
target_q = rewards + self.gamma * self.critic_target(next_states, next_actions) * (1 - dones)
current_q = self.critic(states, actions)
loss_critic = nn.MSELoss()(current_q, target_q)
self.optimizer_critic.zero_grad()
loss_critic.backward()
self.optimizer_critic.step()
# 更新Actor(最大化Q值)
pred_actions = self.actor(states)
loss_actor = -self.critic(states, pred_actions).mean()
self.optimizer_actor.zero_grad()
loss_actor.backward()
self.optimizer_actor.step()
# 软更新目标网络
self.soft_update(self.actor_target, self.actor)
self.soft_update(self.critic_target, self.critic)
return loss_actor.item(), loss_critic.item()
# 训练
if __name__ == "__main__":
env = gym.make('Pendulum-v1')
state_dim = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_dim = env.action_space.shape[0]
action_bound = env.action_space.high[0] # 动作上限
agent = DDPGAgent(state_dim, action_dim, action_bound)
episodes = 200
rewards_history = []
for ep in range(episodes):
state, _ = env.reset()
agent.noise.reset()
total_reward = 0
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.select_action(state)
next_state, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action)
done = terminated or truncated
agent.store_experience(state, action, reward, next_state, done)
agent.train()
state = next_state
total_reward += reward
rewards_history.append(total_reward)
if (ep + 1) % 20 == 0:
avg_reward = np.mean(rewards_history[-20:])
print(f"第{ep+1}集 | 平均奖励:{avg_reward:.2f}")
# 可视化:DDPG奖励变化
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 6))
smoothed = np.convolve(rewards_history, np.ones(10)/10, mode='valid')
ax.plot(range(9, episodes), smoothed, label='DDPG', color='red')
ax.set_xlabel('训练集数')
ax.set_ylabel('每集奖励')
ax.set_title('DDPG训练奖励变化(Pendulum)')
ax.legend()
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()
env.close()
9.4 深度强化学习应用
9.4.1 智能巡航小车
智能巡航小车是强化学习在机器人领域的典型应用,核心需求:
- 感知:通过摄像头 / 激光雷达获取环境状态(如障碍物距离、自身位置);
- 决策:输出速度、转向角等连续动作;
- 奖励:靠近目标 + 避开障碍物 = 正奖励,碰撞 = 负奖励。
核心思路(基于 DDPG):
- 状态空间:障碍物距离(前 / 左 / 右)、小车当前速度、转向角、目标方向;
- 动作空间:速度增量(-0.5~0.5)、转向角增量(-10°~10°);
- 奖励函数:
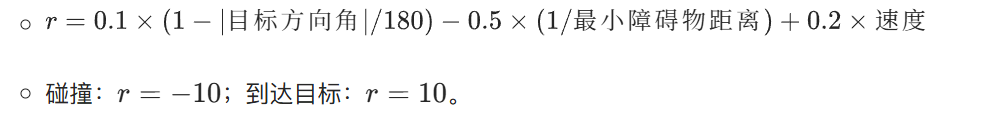
9.4.2 围棋自动对弈
围棋是强化学习的经典应用(AlphaGo),核心技术:
- 深度强化学习 + 蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS);
- 监督学习预训练(学习人类棋谱);
- 自对弈强化学习(提升策略);
- 价值网络评估棋局,策略网络选择落子。
核心流程
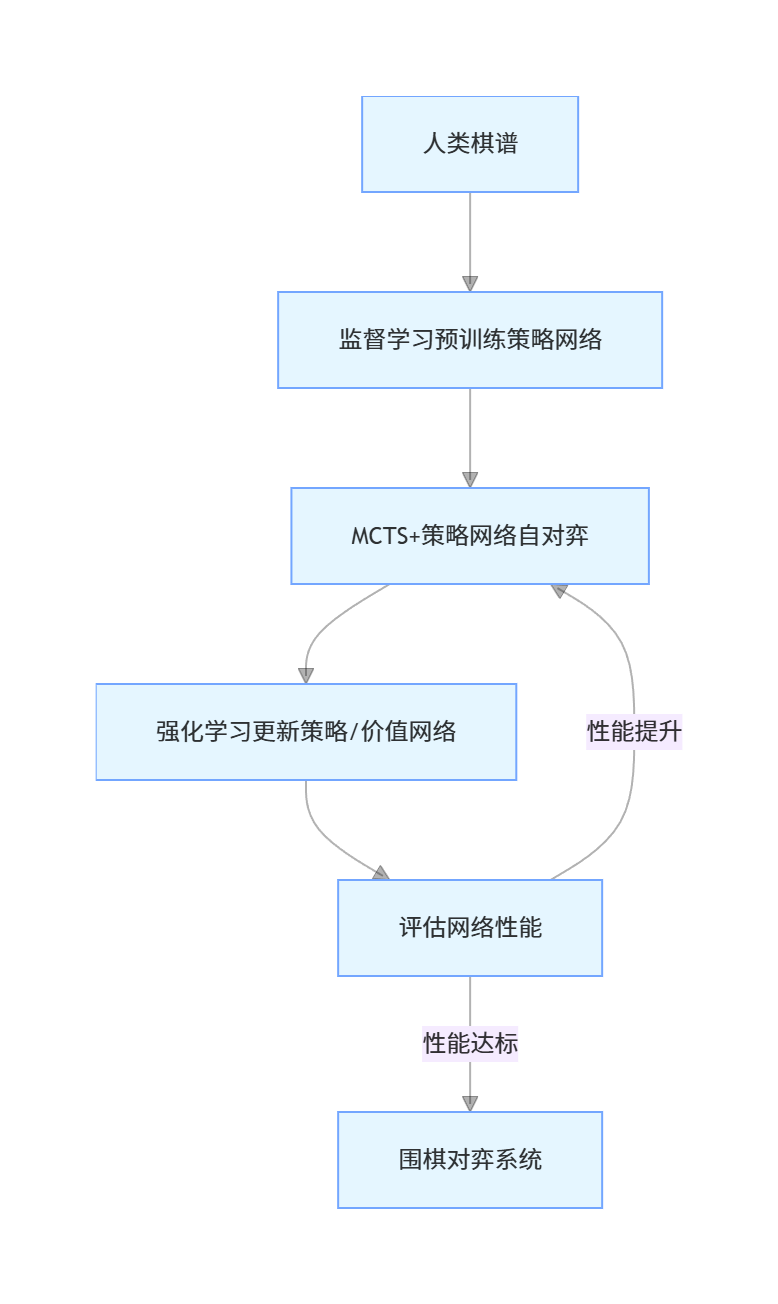
9.5 习题
- 手动实现 DQN 的经验回放机制,对比有无经验回放的训练稳定性(要求可视化对比图);
- 基于 Actor-Critic 算法,修改奖励函数,提升 CartPole 的平衡时长;
- 尝试将 DDPG 算法应用到 MountainCarContinuous-v0 环境,观察训练效果;
- 简述 DQN、Double DQN、Dueling DQN 的核心区别,并用代码验证各自的效果;
- 分析 MCTS 中探索系数(UCT 公式中的 exploration)对井字棋决策的影响。
总结
- 深度强化学习核心是 “智能体 - 环境” 交互,通过最大化累积奖励学习最优策略,分为基于价值(DQN 系列)和基于策略(PG/Actor-Critic/DDPG)两类;
- DQN 适合离散动作空间,核心改进(Double DQN/Dueling DQN)解决了过估计和价值分解问题;DDPG 适合连续动作空间,结合了 Actor-Critic 和 DQN 的优势;
- 实战中需注意:经验回放提升数据利用率、目标网络提升训练稳定性、探索策略(ε- 贪心 / 噪声)平衡探索与利用,可视化对比是验证算法效果的关键。
运行说明
- 所有代码需安装依赖:
pip install numpy torch gymnasium matplotlib; - CartPole/Pendulum 环境为 gym 内置环境,无需额外配置;
- 调整训练参数(如 episodes、lr、gamma)可优化训练效果;
- 可视化部分已配置中文字体,直接运行即可显示中文标签。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容









所有评论(0)