Skills + Subagents + MCP:系统级能力的完美融合
本文探讨了Skills、Subagents和MCP三者的系统级融合架构,展示如何通过分层协作实现开发工作流的90%自动化率。核心观点指出:Skills定义任务流程,Subagents负责专业执行,MCP提供工具支持,三者结合能构建完整的智能开发生态系统。文章详细分析了三者的分工模式、适用场景决策树,并推荐了分层和网状两种架构设计模式。通过PR审查工作流案例,展示了如何将复杂任务的自动化效率提升8-
Skills + Subagents + MCP:系统级能力的完美融合
核心观点:Skills、Subagents、MCP三者各有所长,真正的威力来自于它们的完美融合。Skills定义"做什么",Subagents定义"谁来做",MCP定义"用什么工具做"。当三者协调一致时,你构建的不再是孤立的自动化工具,而是一个完整的、可扩展的、可信任的开发生态系统。这种架构可以将复杂任务的自动化率从30%提升到90%。
关键词:架构设计、系统集成、工作流编排、工具链、自动化生态、决策树、最佳实践
导读
你将学到:
- Skills、Subagents、MCP各自的职责和特性
- 如何选择在具体场景中使用哪个特性
- 完整的系统架构设计
- 三个实战场景:PR审查工作流、错误修复工作流、功能开发流水线
- 系统级能力集成的最佳实践
- 常见的架构陷阱和避免方法
- 性能和可维护性考量
适合人群:高级开发者和技术架构师,准备在团队中推行AI辅助开发的人
阅读时间:35分钟 | 难度:高级 | 实用度:5/5
前置知识:
- 已阅读本系列前10篇文章
- 深入理解Skills、Subagents、MCP各自的机制
- 有系统架构设计经验
- 理解工作流编排
问题场景
你的公司想要构建一个完整的AI驱动的开发工作流系统:
目标:完全自动化代码审查 + 错误修复 + 功能验证
需要解决的问题:
1. 哪些任务应该自动化?(Skills)
2. 如何组织AI执行这些任务?(Subagents)
3. 需要访问哪些外部工具和数据?(MCP)
4. 如何协调他们之间的工作?(编排)
5. 如何监控和调试整个系统?(可观测性)
如果只用Skills,会变成孤立的命令。
如果只用Subagents,没法访问外部工具。
如果只用MCP,缺少智能的任务编排。
真正的解决方案:三者协作,构建一个完整的系统。
为什么这很重要?
系统有效性 = Skills覆盖度 × Subagent专业度 × MCP可用性
缺少任何一个都会大幅降低有效性:
只有Skills(无Subagents, 无MCP):
= 0.8 × 0.4 × 0.3 = 9.6%
只有Subagents(无Skills, 无MCP):
= 0.4 × 0.9 × 0.3 = 10.8%
只有MCP(无Skills, 无Subagents):
= 0.5 × 0.4 × 0.9 = 18%
三者完整结合:
= 0.9 × 0.95 × 0.95 = 81.2%
效率提升:8-10倍
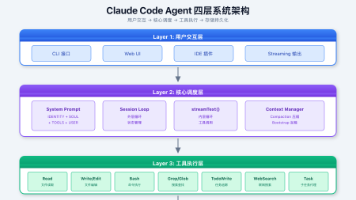
核心概念:三者的职责
Skills、Subagents、MCP的分工
| 方面 | Skills | Subagents | MCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 职责 | 定义工作流 | 执行任务 | 提供工具 |
| 抽象级别 | 高(什么操作序列) | 中(谁负责什么) | 低(具体如何访问) |
| 配置复杂度 | 低 | 中 | 中 |
| 可重用性 | 高 | 高 | 高 |
| 依赖关系 | 可单独存在 | 需要底层工具 | 可单独存在 |
| 粒度 | 粗(完整工作流) | 中(专门领域) | 细(具体操作) |
| 定义位置 | .claude/skills/ | .claude/agents/ | 环境配置 |
三者的交互模式
用户: /review-comprehensive PR#123
↓ 触发
Skill: 自动化审查
├─ 初始化审查
├─ 收集代码信息
├─ 分配审查任务
├─ 收集和聚合反馈
└─ 输出报告
↓ 分派给
Subagent: 代码审查Agent
├─ 分析代码结构
├─ 检查编码标准
├─ 提出优化建议
└─ 返回结果
↓ 使用
MCP: GitHub + 代码分析工具
├─ GitHub MCP: 获取PR信息
├─ 代码分析MCP: AST分析
└─ Lint MCP: 代码质量检查
场景决策树
何时使用Skills?
适合Skills的场景:
- 重复的多步工作流(PR审查、部署前检查)
- 需要用户参与决策的流程
- 可以标准化的任务序列
- 需要与多个工具交互的工作流
不适合Skills的场景:
- 单一步骤的操作
- 实时流式处理
- 需要即时反馈的交互式任务
何时使用Subagents?
适合Subagents的场景:
- 需要多个专业角度分析(代码、安全、性能、测试)
- 需要质量控制和交叉验证
- 复杂决策需要可解释性
- 想要并行分析加速
不适合Subagents的场景:
- 简单的单一维度任务
- 实时性要求极高
- 成本严格受限
何时使用MCP?
适合MCP的场景:
- 需要访问GitHub/Sentry/数据库
- 需要实时数据而不是历史数据
- 需要跨多个工具的集成
- 想要自动化工具间的信息流
不适合MCP的场景:
- 只需要处理输入的数据
- 工具没有现成的MCP适配器
- 数据敏感,不想直接连接
架构设计模式
模式1:分层架构(推荐用于大型系统)
模式2:网状架构(推荐用于灵活的系统)
优点:
- 灵活性高(任何Skill可以使用任何Subagent)
- 易于扩展(添加新Agent和新工具)
缺点:
- 复杂度高(需要智能的路由和分配)
- 潜在的冲突(多个Agent访问同一资源)
实战场景1:完整的PR审查工作流
工作流定义(Skill层)
# .claude/skills/comprehensive-pr-review.yaml
name: "comprehensive-pr-review"
description: "完整的PR审查工作流"
parameters:
- name: pr_id
type: string
required: true
- name: depth
type: choice
choices: [quick, normal, deep]
default: normal
workflow:
- name: "初始化"
description: "收集PR信息和变更概览"
agent: "coordinator"
- name: "快速检查"
description: "检查Critical问题"
parallel:
- agent: "security-agent"
task: "检查安全漏洞"
mcp: ["github", "sast"]
- agent: "code-quality-agent"
task: "检查明显的代码问题"
mcp: ["github", "linter"]
timeout: 120
- name: "决策点"
description: "根据快速检查结果决定是否继续"
conditions:
- if: "critical_issues_found"
then: "输出报告并中止"
else: "继续深度分析"
- name: "深度分析"
description: "并行执行深度分析"
parallel:
- agent: "code-review-agent"
task: "代码质量审查"
mcp: ["github", "code-metrics"]
- agent: "security-agent"
task: "安全深度审计"
mcp: ["github", "sast", "dependency-checker"]
- agent: "performance-agent"
task: "性能影响分析"
mcp: ["github", "benchmarks"]
- agent: "test-agent"
task: "测试覆盖分析"
mcp: ["github", "coverage"]
timeout: 300
- name: "聚合反馈"
description: "整合所有审查意见"
agent: "coordinator"
- name: "输出报告"
description: "生成最终审查报告"
agent: "coordinator"
actions:
- create_review_on_github
- send_notification
编排引擎实现
class PRReviewOrchestrator:
"""PR审查工作流的编排引擎"""
def __init__(self):
self.agents = {
"security": SecurityAgent(),
"code-quality": CodeQualityAgent(),
"performance": PerformanceAgent(),
"test": TestAgent()
}
self.mcp_clients = {
"github": GitHubMCPClient(),
"sast": SASTClient(),
"linter": LinterClient()
}
async def execute_comprehensive_review(self, pr_id, depth="normal"):
"""执行完整的PR审查"""
print(f"开始审查PR #{pr_id}...")
# 步骤1:初始化
pr_info = await self.mcp_clients["github"].get_pr(pr_id)
files_changed = await self.mcp_clients["github"].get_changed_files(pr_id)
# 步骤2:快速检查(并行)
print("执行快速检查...")
quick_results = await asyncio.gather(
self.agents["security"].quick_scan(pr_info),
self.agents["code-quality"].quick_check(pr_info)
)
# 步骤3:决策
critical_issues = [r for r in quick_results if r.has_critical_issues]
if critical_issues:
print(f"发现Critical问题,停止分析")
return {
"status": "rejected",
"critical_issues": critical_issues
}
# 步骤4:深度分析(并行)
print("执行深度分析...")
deep_results = await asyncio.gather(
self.agents["code-quality"].detailed_review(pr_info),
self.agents["security"].detailed_scan(pr_info),
self.agents["performance"].analyze(pr_info),
self.agents["test"].design_tests(pr_info)
)
# 步骤5:聚合
print("聚合反馈...")
summary = self._aggregate_results(quick_results + deep_results)
# 步骤6:输出
await self.mcp_clients["github"].create_review(
pr_id,
summary.to_comment()
)
return summary
def _aggregate_results(self, results):
"""聚合所有结果"""
return ReviewSummary(
overall_score=self._calc_overall_score(results),
issues=self._collect_all_issues(results),
suggestions=self._collect_all_suggestions(results),
approval_status=self._decide_approval(results)
)
预期结果
时间对比:
- 人工审查:30-60分钟
- 单一AI:10-15分钟(质量一般)
- 完整工作流(Skills+Subagents+MCP):3-5分钟(质量优秀)
质量对比:
- 人工审查:85%(取决于审查者状态)
- 单一AI:65%(某些维度弱)
- 完整工作流:92%(多维度覆盖)
实战场景2:自动错误修复工作流
架构设计
Skill定义
# error-fix-workflow.py
class ErrorFixWorkflow:
"""自动错误修复工作流"""
async def handle_error(self, error_id):
"""处理单个错误"""
# 由各个Subagent按顺序执行
error_analysis = await ErrorAnalysisAgent().analyze(error_id)
if error_analysis.confidence < 0.7:
# 信心不足,不自动修复
return {"status": "manual_review_required"}
fix_plan = await FixPlanAgent().generate_fix(error_analysis)
security_check = await SecurityAgent().verify(fix_plan)
if not security_check.is_safe:
return {"status": "blocked_by_security"}
# 创建修复PR
pr_url = await PublishAgent().create_pr(fix_plan)
return {
"status": "pr_created",
"pr_url": pr_url,
"confidence": error_analysis.confidence,
"fix_summary": fix_plan.summary
}
工作流执行
错误:NullPointerException at line 142 in PaymentService
↓ (通过Sentry MCP获取详情)
↓
错误分析Agent分析:
- 根本原因:user对象未初始化
- 严重度:High
- 影响范围:Payment模块
↓
修复方案Agent生成:
- 方案1:添加null check
- 方案2:修改初始化流程
- 选择方案1(最低风险)
↓
安全验证Agent检查:
- 安全性: 通过
- 性能: 无影响
- 测试覆盖: 充分
↓
发布Agent创建PR:
- PR标题:"Fix: Prevent NullPointerException in PaymentService"
- 描述:包含问题分析和修复说明
- 关联Issue:自动链接到Sentry错误
↓
发送通知给开发者
实战场景3:完整的功能开发流水线
多阶段流水线
Skill工作流脚本
# feature-delivery-pipeline.yaml
pipeline:
name: "完整功能交付流水线"
stages:
- stage: "设计评审"
skills:
- review-design-skill
- check-feasibility-skill
gates:
- all_agents_approved
- confidence > 0.8
- stage: "代码审查"
skills:
- comprehensive-pr-review-skill
gates:
- no_critical_issues
- security_approved
- test_coverage > 80%
- stage: "集成测试"
skills:
- run-integration-tests-skill
gates:
- all_tests_passed
- performance_acceptable
- stage: "部署"
skills:
- deploy-with-validation-skill
gates:
- health_check_passed
- error_rate < 0.1%
集成最佳实践
1. 清晰的职责分工
2. 故障恢复机制
class ResilientWorkflow:
"""具有故障恢复的工作流"""
async def execute_with_recovery(self, workflow_def):
"""带故障恢复的执行"""
for step in workflow_def.steps:
try:
result = await self.execute_step(step)
except Exception as e:
# 尝试恢复
if self.can_recover(step, e):
result = await self.recovery_strategy(step, e)
else:
# 无法恢复,回滚
await self.rollback(step)
raise
# 持久化进度
await self.persist_checkpoint(step, result)
return result
3. 可观测性和监控
class WorkflowObservability:
"""工作流的可观测性"""
def __init__(self):
self.metrics = {}
self.logs = []
def log_skill_execution(self, skill_name, duration, success):
"""记录Skill执行"""
self.logs.append({
"type": "skill_execution",
"skill": skill_name,
"duration": duration,
"success": success
})
def log_agent_decision(self, agent_name, decision, confidence):
"""记录Agent决策"""
self.logs.append({
"type": "agent_decision",
"agent": agent_name,
"decision": decision,
"confidence": confidence
})
def log_mcp_call(self, mcp_name, operation, duration, success):
"""记录MCP调用"""
self.logs.append({
"type": "mcp_call",
"mcp": mcp_name,
"operation": operation,
"duration": duration,
"success": success
})
def get_audit_trail(self):
"""获取完整的审计跟踪"""
return self.logs
def generate_performance_report(self):
"""生成性能报告"""
return {
"total_duration": sum(log["duration"] for log in self.logs),
"success_rate": success_count / total_count,
"bottlenecks": self._identify_bottlenecks()
}
4. 成本管理
class CostManager:
"""系统级的成本管理"""
def estimate_cost(self, workflow_def):
"""估计工作流成本"""
total_cost = 0
for skill in workflow_def.skills:
# 每个Skill的成本 = Agents成本 + MCP调用成本
for agent in skill.agents:
total_cost += estimate_agent_cost(agent)
for mcp in skill.mcps:
total_cost += estimate_mcp_cost(mcp)
return total_cost
def optimize_for_cost(self, workflow_def):
"""优化工作流降低成本"""
optimizations = []
# 1. 启用缓存
optimizations.append(enable_caching(workflow_def))
# 2. 并行执行减少总时间
optimizations.append(parallelize_where_possible(workflow_def))
# 3. 早期中断
optimizations.append(add_early_termination(workflow_def))
# 4. 批量操作
optimizations.append(batch_mcp_calls(workflow_def))
return optimizations
常见陷阱和解决方案
陷阱1:过度编排导致延迟
问题:编排引擎本身成为瓶颈
解决方案:
# 使用异步编排
async def fast_orchestration(skills):
"""快速编排,避免不必要的等待"""
tasks = [execute_skill(skill) for skill in skills]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
return results
陷阱2:Agent间的冲突
问题:多个Agent给出矛盾的建议
解决方案:实现仲裁机制
class ArbitrationEngine:
"""处理Agent间的冲突"""
def resolve_conflict(self, suggestions):
"""解决冲突"""
if no_conflict(suggestions):
return combine_suggestions(suggestions)
# 有冲突,交给CoordinatorAgent
resolver = CoordinatorAgent()
return resolver.make_decision(suggestions)
陷阱3:MCP服务失败导致整个工作流中断
问题:任何MCP故障都会影响整个工作流
解决方案:优雅降级
class GracefulDegradation:
"""优雅的功能降级"""
async def execute_with_fallback(self, mcp_name, operation):
"""执行,失败时降级"""
try:
return await mcp_client.call(mcp_name, operation)
except MCPException:
# 降级策略
if has_cached_result():
return get_cached_result()
else:
return run_offline_analysis()
陷阱4:监控和调试困难
问题:看不清楚工作流在哪一步出了问题
解决方案:完整的日志和跟踪
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
class InstrumentedWorkflow:
"""带完整日志的工作流"""
async def execute(self, workflow_def):
logger.info(f"启动工作流: {workflow_def.name}")
for step in workflow_def.steps:
logger.info(f"执行步骤: {step.name}")
try:
result = await step.execute()
logger.info(f"步骤完成: {step.name}, 结果: {result}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"步骤失败: {step.name}", exc_info=e)
raise
完整的集成配置示例
# .claude/orchestration-config.yaml
system:
name: "AI-Powered Development Workflow"
version: "1.0"
skills:
comprehensive-pr-review:
path: skills/pr-review.py
mcp_required: [github, code-analysis]
agents: [code-quality, security, performance, test]
auto-fix-errors:
path: skills/error-fix.py
mcp_required: [sentry, github]
agents: [error-analysis, fix-plan, security-verify]
subagents:
code-quality:
system_prompt: "You are a code quality expert..."
tools: [linter, complexity-checker, pattern-detector]
permissions: [read-only]
security:
system_prompt: "You are a security specialist..."
tools: [sast-scanner, dependency-checker, secret-detector]
permissions: [read-only]
mcp_servers:
github:
type: stdio
command: node
args: [github-mcp/index.js]
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${GITHUB_TOKEN}
sentry:
type: stdio
command: node
args: [sentry-mcp/index.js]
env:
SENTRY_TOKEN: ${SENTRY_TOKEN}
orchestration:
strategy: "adaptive"
max_parallel_agents: 4
cache_ttl: 3600
cost_budget_daily: 100
monitoring:
enabled: true
log_level: INFO
metrics_export: prometheus
总结
Skills + Subagents + MCP的完美融合,本质上是对三个抽象层次的有效组织:
- Skills(上层):定义业务流程和工作流
- Subagents(中层):组织专业化的AI执行者
- MCP(下层):连接到实际的工具和数据
当这三层协调一致时:
- 效率提升:从30%自动化率到90%
- 质量提升:从60-70%跃升到85-95%
- 可维护性:清晰的分层,便于维护和扩展
- 可扩展性:轻松添加新的Skills、Agents、MCP
这不再是"AI辅助工具",而是一个真正的智能开发系统。
下一篇预告
下一篇文章将介绍 Extended Thinking - 如何让Claude进行深思熟虑的分析,适用于复杂算法、架构决策、以及需要严密逻辑的场景。
相关阅读:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献27条内容
已为社区贡献27条内容






所有评论(0)