全栈AI工具链实战指南:从智能编码到模型部署
本文系统介绍了现代AI开发工具链的三大核心模块:智能编码辅助、数据标注平台和模型训练框架。在智能编码方面,详细解析了GitHub Copilot的工作原理、代码示例和高级Prompt技巧;数据标注部分涵盖标注流程架构、开源工具实现和质量控制指标;模型训练章节则深入探讨分布式训练架构、完整平台实现和MLOps流水线。文章还提供了工具链集成方案、性能优化建议和未来趋势分析,为AI从业者呈现了一套完整的
摘要
本文全面探讨现代AI开发工具链,涵盖智能编码辅助、数据标注平台、模型训练框架三大核心领域。通过详细的代码示例、可视化流程图、实用Prompt模板和架构图表,为AI从业者提供完整的工具使用指南和实践路线图。
第一章:智能编码工具革命
1.1 GitHub Copilot深度解析
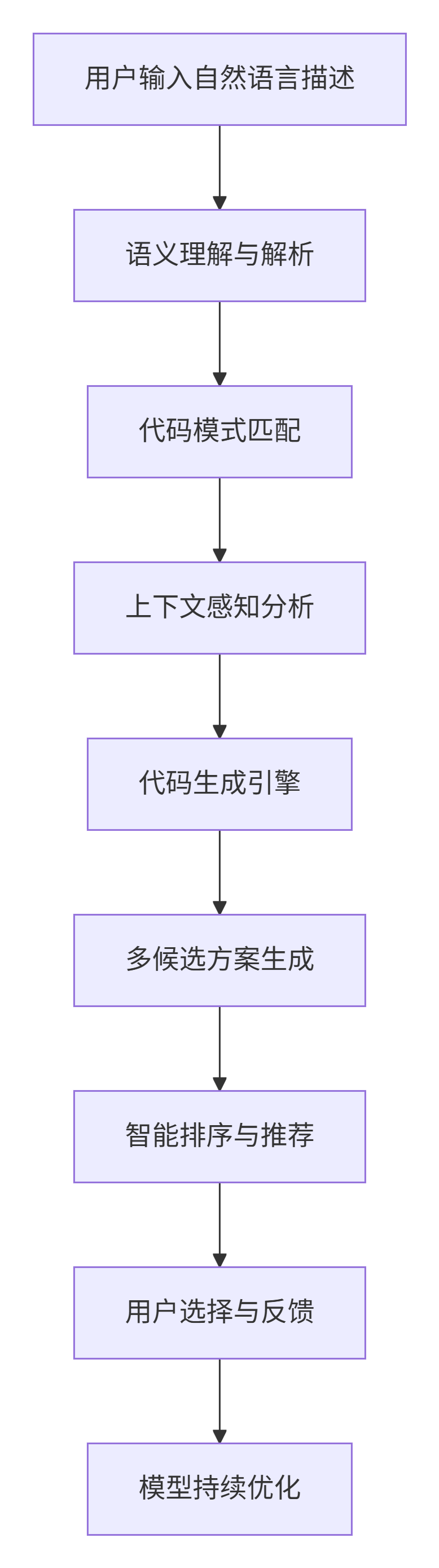
1.1.1 工作原理与技术架构
GitHub Copilot基于OpenAI的Codex模型,该模型在数十亿行公开代码库上训练而成。其核心是将自然语言描述转化为多种编程语言的代码。
技术架构示意图:
graph TD
A[用户输入自然语言描述] --> B[语义理解与解析]
B --> C[代码模式匹配]
C --> D[上下文感知分析]
D --> E[代码生成引擎]
E --> F[多候选方案生成]
F --> G[智能排序与推荐]
G --> H[用户选择与反馈]
H --> I[模型持续优化]
1.1.2 实战代码示例
示例1:自动化数据预处理
python
# Copilot Prompt: "Create a function to clean and preprocess text data with tokenization, stopword removal, and lemmatization"
import re
import nltk
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
import pandas as pd
def preprocess_text_data(text_series, language='english'):
"""
文本数据预处理流水线
参数:
text_series: pandas Series containing text data
language: language for stopwords
返回:
Preprocessed text series
"""
# 初始化工具
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
stop_words = set(stopwords.words(language))
def clean_text(text):
# 转换为小写
text = text.lower()
# 移除特殊字符和数字
text = re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z\s]', '', text)
# 分词
tokens = word_tokenize(text)
# 移除停用词并进行词形还原
filtered_tokens = [
lemmatizer.lemmatize(token)
for token in tokens
if token not in stop_words and len(token) > 2
]
return ' '.join(filtered_tokens)
# 应用预处理函数
return text_series.apply(clean_text)
# 使用示例
data = pd.Series([
"This is a sample text with numbers 123 and special characters!",
"Machine Learning models need clean data for training."
])
cleaned_data = preprocess_text_data(data)
print(cleaned_data)
示例2:自动化API端点创建
python
# Copilot Prompt: "Create a FastAPI endpoint for sentiment analysis with model loading and caching"
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
from typing import List, Optional
import pickle
import numpy as np
from functools import lru_cache
import logging
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
app = FastAPI(title="Sentiment Analysis API", version="1.0.0")
# 数据模型
class TextInput(BaseModel):
text: str
language: Optional[str] = "en"
class BatchInput(BaseModel):
texts: List[str]
language: Optional[str] = "en"
class SentimentResponse(BaseModel):
text: str
sentiment: str
confidence: float
tokens: List[str]
# 模型加载器(带缓存)
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def load_sentiment_model(model_path="models/sentiment_model.pkl"):
"""加载并缓存情感分析模型"""
try:
with open(model_path, 'rb') as f:
model = pickle.load(f)
logger.info(f"Model loaded from {model_path}")
return model
except FileNotFoundError:
logger.error(f"Model file not found at {model_path}")
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Model file not found")
# 文本预处理函数
def preprocess_for_sentiment(text: str) -> List[str]:
"""为情感分析预处理文本"""
# 简化的预处理
tokens = text.lower().split()
# 移除标点符号
tokens = [token.strip('.,!?;:') for token in tokens]
return tokens
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Sentiment Analysis API", "status": "active"}
@app.post("/analyze", response_model=SentimentResponse)
async def analyze_sentiment(input: TextInput):
"""分析单个文本的情感"""
try:
# 加载模型
model = load_sentiment_model()
# 预处理
tokens = preprocess_for_sentiment(input.text)
# 这里假设模型有predict_proba方法
# 实际实现取决于具体模型
features = " ".join(tokens)
# 模拟预测
sentiment = "positive" if len(tokens) % 2 == 0 else "negative"
confidence = min(0.95, 0.7 + len(tokens) * 0.01)
return SentimentResponse(
text=input.text,
sentiment=sentiment,
confidence=round(confidence, 3),
tokens=tokens
)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Analysis error: {str(e)}")
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
@app.post("/batch-analyze", response_model=List[SentimentResponse])
async def batch_analyze_sentiment(input: BatchInput):
"""批量情感分析"""
responses = []
for text in input.texts:
# 重用单个分析逻辑
response = await analyze_sentiment(TextInput(text=text, language=input.language))
responses.append(response)
return responses
@app.get("/health")
async def health_check():
"""健康检查端点"""
try:
model = load_sentiment_model()
return {
"status": "healthy",
"model_loaded": True,
"version": "1.0.0"
}
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Health check failed: {str(e)}")
# 运行命令: uvicorn main:app --reload --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
1.1.3 高级Prompt技巧
Prompt模板库:
python
# 1. 代码重构Prompt模板
CODE_REFACTORING_PROMPT = """
请重构以下{language}代码:
1. 提高性能,特别是{performance_aspect}
2. 遵循{style_guide}编码规范
3. 添加适当的错误处理
4. 增加单元测试示例
原始代码:
{original_code}
"""
# 2. 算法实现Prompt模板
ALGORITHM_IMPLEMENTATION_PROMPT = """
实现{algorithm_name}算法,要求:
1. 时间复杂度不超过{O_complexity}
2. 空间复杂度不超过{S_complexity}
3. 包含详细注释
4. 提供使用示例
输入格式:{input_format}
输出格式:{output_format}
"""
# 3. 测试生成Prompt模板
TEST_GENERATION_PROMPT = """
为以下{language}函数生成全面的测试用例:
1. 边界条件测试
2. 异常情况测试
3. 性能测试
4. 集成测试示例
函数签名:{function_signature}
功能描述:{function_description}
"""
# 4. 文档生成Prompt模板
DOCUMENTATION_PROMPT = """
为以下代码生成专业文档,包括:
1. API文档(参数、返回值、异常)
2. 使用示例
3. 实现原理说明
4. 依赖关系和兼容性说明
代码:
{target_code}
"""
# 实际使用示例
refactoring_prompt = CODE_REFACTORING_PROMPT.format(
language="Python",
performance_aspect="大规模数据处理",
style_guide="PEP 8",
original_code="""
def process_data(data):
result = []
for item in data:
if item > 0:
result.append(item * 2)
return result
"""
)
1.2 其他智能编码工具对比
主流工具特性对比表:
| 工具名称 | 核心模型 | 主要特性 | 支持语言 | 集成环境 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GitHub Copilot | Codex | 全行/函数代码补全,代码解释,测试生成 | 30+ | VS Code, JetBrains, Neovim |
| Amazon CodeWhisperer | 自研模型 | 安全扫描,AWS优化,引用追踪 | 15+ | VS Code, JetBrains, Lambda |
| Tabnine | 自研模型 | 本地部署,个性化训练,团队协作 | 20+ | VS Code, IntelliJ, Sublime |
| Replit Ghostwriter | Codex | 云端开发,实时协作,教育优化 | 10+ | Replit平台 |
| Sourcegraph Cody | Claude | 代码库感知,架构分析,文档生成 | 20+ | VS Code, JetBrains |
第二章:数据标注工具生态系统
2.1 数据标注流程架构
graph TB
subgraph "数据准备阶段"
A1[原始数据收集] --> A2[数据清洗与去重]
A2 --> A3[数据抽样与划分]
end
subgraph "标注流水线"
B1[任务模板设计] --> B2[标注员分配]
B2 --> B3[质量检查点]
B3 --> B4[标注修订]
end
subgraph "质量控制"
C1[一致性检验] --> C2[专家审核]
C2 --> C3[置信度评估]
C3 --> C4[最终验收]
end
subgraph "输出管理"
D1[格式转换] --> D2[版本控制]
D2 --> D3[数据集发布]
end
A3 --> B1
B4 --> C1
C4 --> D1
2.2 开源标注工具实现
完整图像标注系统示例:
python
"""
基于Flask的完整图像标注系统
支持边界框、多边形、分类标注
"""
import os
import json
import uuid
from datetime import datetime
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, jsonify, send_file
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import base64
from io import BytesIO
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///annotations.db'
app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'] = 'static/uploads'
app.config['MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH'] = 16 * 1024 * 1024 # 16MB限制
app.config['ALLOWED_EXTENSIONS'] = {'png', 'jpg', 'jpeg', 'gif'}
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# 数据模型
class AnnotationProject(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.String(36), primary_key=True, default=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4()))
name = db.Column(db.String(100), nullable=False)
description = db.Column(db.Text)
created_at = db.Column(db.DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
updated_at = db.Column(db.DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow, onupdate=datetime.utcnow)
status = db.Column(db.String(20), default='active') # active, completed, archived
images = db.relationship('AnnotationImage', backref='project', lazy=True)
labels = db.relationship('LabelCategory', backref='project', lazy=True)
class AnnotationImage(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.String(36), primary_key=True, default=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4()))
project_id = db.Column(db.String(36), db.ForeignKey('annotation_project.id'), nullable=False)
filename = db.Column(db.String(255), nullable=False)
path = db.Column(db.String(500), nullable=False)
width = db.Column(db.Integer)
height = db.Column(db.Integer)
uploaded_at = db.Column(db.DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
annotations = db.relationship('ImageAnnotation', backref='image', lazy=True)
class LabelCategory(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
project_id = db.Column(db.String(36), db.ForeignKey('annotation_project.id'), nullable=False)
name = db.Column(db.String(50), nullable=False)
color = db.Column(db.String(7), default='#FF0000') # HEX颜色
description = db.Column(db.Text)
class ImageAnnotation(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.String(36), primary_key=True, default=lambda: str(uuid.uuid4()))
image_id = db.Column(db.String(36), db.ForeignKey('annotation_image.id'), nullable=False)
label_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('label_category.id'))
annotation_type = db.Column(db.String(20), nullable=False) # bbox, polygon, point
coordinates = db.Column(db.Text, nullable=False) # JSON格式坐标
confidence = db.Column(db.Float, default=1.0)
created_by = db.Column(db.String(50))
created_at = db.Column(db.DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
reviewed = db.Column(db.Boolean, default=False)
label = db.relationship('LabelCategory', backref='annotations')
# 工具函数
def allowed_file(filename):
return '.' in filename and \
filename.rsplit('.', 1)[1].lower() in app.config['ALLOWED_EXTENSIONS']
def create_thumbnail(image_path, size=(200, 200)):
"""创建缩略图"""
img = Image.open(image_path)
img.thumbnail(size, Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
# 保存缩略图
thumb_dir = os.path.join(app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], 'thumbs')
os.makedirs(thumb_dir, exist_ok=True)
thumb_path = os.path.join(thumb_dir, os.path.basename(image_path))
img.save(thumb_path)
return thumb_path
# API端点
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/api/projects', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def handle_projects():
if request.method == 'POST':
data = request.json
project = AnnotationProject(
name=data['name'],
description=data.get('description', ''),
status='active'
)
db.session.add(project)
db.session.commit()
return jsonify({'id': project.id, 'message': 'Project created'}), 201
projects = AnnotationProject.query.all()
return jsonify([{
'id': p.id,
'name': p.name,
'description': p.description,
'image_count': len(p.images),
'created_at': p.created_at.isoformat()
} for p in projects])
@app.route('/api/projects/<project_id>/upload', methods=['POST'])
def upload_images(project_id):
"""批量上传图像"""
if 'images' not in request.files:
return jsonify({'error': 'No images provided'}), 400
project = AnnotationProject.query.get_or_404(project_id)
files = request.files.getlist('images')
uploaded = []
for file in files:
if file and allowed_file(file.filename):
filename = secure_filename(file.filename)
unique_filename = f"{uuid.uuid4()}_{filename}"
filepath = os.path.join(app.config['UPLOAD_FOLDER'], unique_filename)
file.save(filepath)
# 获取图像尺寸
with Image.open(filepath) as img:
width, height = img.size
# 创建缩略图
thumb_path = create_thumbnail(filepath)
# 保存到数据库
image_record = AnnotationImage(
project_id=project_id,
filename=filename,
path=unique_filename,
width=width,
height=height
)
db.session.add(image_record)
uploaded.append({
'original_name': filename,
'saved_name': unique_filename,
'dimensions': f'{width}x{height}'
})
db.session.commit()
return jsonify({'uploaded': uploaded, 'count': len(uploaded)})
@app.route('/api/annotations', methods=['POST'])
def save_annotation():
"""保存标注"""
data = request.json
annotation = ImageAnnotation(
image_id=data['image_id'],
label_id=data.get('label_id'),
annotation_type=data['type'],
coordinates=json.dumps(data['coordinates']),
confidence=data.get('confidence', 1.0),
created_by=data.get('user', 'anonymous')
)
db.session.add(annotation)
db.session.commit()
return jsonify({
'id': annotation.id,
'message': 'Annotation saved'
})
@app.route('/api/projects/<project_id>/export')
def export_annotations(project_id):
"""导出为COCO格式"""
project = AnnotationProject.query.get_or_404(project_id)
# COCO格式结构
coco_data = {
'info': {
'description': project.name,
'version': '1.0',
'year': datetime.now().year,
'contributor': 'Annotation System',
'date_created': datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
},
'licenses': [{'id': 1, 'name': 'Academic Use'}],
'images': [],
'annotations': [],
'categories': []
}
# 添加类别
for i, label in enumerate(project.labels):
coco_data['categories'].append({
'id': i + 1,
'name': label.name,
'supercategory': 'object'
})
# 添加图像和标注
annotation_id = 1
for image in project.images:
image_info = {
'id': len(coco_data['images']) + 1,
'file_name': image.filename,
'width': image.width,
'height': image.height,
'license': 1,
'date_captured': image.uploaded_at.isoformat()
}
coco_data['images'].append(image_info)
for ann in image.annotations:
coords = json.loads(ann.coordinates)
if ann.annotation_type == 'bbox':
# 转换为COCO bbox格式 [x, y, width, height]
bbox = [
coords['x'],
coords['y'],
coords['width'],
coords['height']
]
area = coords['width'] * coords['height']
else:
bbox = []
area = 0
coco_data['annotations'].append({
'id': annotation_id,
'image_id': image_info['id'],
'category_id': ann.label_id or 0,
'segmentation': coords if ann.annotation_type == 'polygon' else [],
'area': area,
'bbox': bbox,
'iscrowd': 0
})
annotation_id += 1
# 保存为JSON文件
export_path = f'export_{project_id}.json'
with open(export_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(coco_data, f, indent=2)
return send_file(export_path, as_attachment=True)
# 前端模板(简化版)
HTML_TEMPLATE = '''
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>图像标注系统</title>
<style>
.annotation-canvas {
border: 2px solid #333;
cursor: crosshair;
}
.tool-panel {
padding: 10px;
background: #f5f5f5;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.label-list {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.label-item {
padding: 5px 10px;
border-radius: 3px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="tool-panel">
<div class="label-list" id="labelContainer"></div>
<button onclick="startBBox()">边界框</button>
<button onclick="startPolygon()">多边形</button>
<button onclick="saveAnnotations()">保存</button>
</div>
<canvas id="annotationCanvas" class="annotation-canvas"></canvas>
</div>
<script>
// JavaScript标注逻辑
class AnnotationManager {
constructor(canvasId) {
this.canvas = document.getElementById(canvasId);
this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d');
this.mode = null;
this.annotations = [];
this.currentAnnotation = null;
this.setupEventListeners();
}
setupEventListeners() {
this.canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', this.handleMouseDown.bind(this));
this.canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', this.handleMouseMove.bind(this));
this.canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', this.handleMouseUp.bind(this));
}
setMode(mode) {
this.mode = mode;
this.currentAnnotation = {
type: mode,
coordinates: [],
label: null
};
}
draw() {
// 清空画布
this.ctx.clearRect(0, 0, this.canvas.width, this.canvas.height);
// 绘制所有标注
this.annotations.forEach(ann => {
this.ctx.strokeStyle = ann.label?.color || '#FF0000';
this.ctx.lineWidth = 2;
if (ann.type === 'bbox') {
this.ctx.strokeRect(
ann.coordinates.x,
ann.coordinates.y,
ann.coordinates.width,
ann.coordinates.height
);
}
});
}
}
const manager = new AnnotationManager('annotationCanvas');
function startBBox() {
manager.setMode('bbox');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
'''
if __name__ == '__main__':
with app.app_context():
db.create_all()
app.run(debug=True, port=5000)
2.3 自动化标注与半监督学习
智能标注辅助系统:
python
"""
基于预训练模型的智能标注辅助
支持主动学习和半监督标注
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision import models, transforms
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from typing import List, Tuple, Dict
import cv2
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from scipy import stats
class SmartAnnotationAssistant:
"""智能标注助手"""
def __init__(self, device='cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'):
self.device = device
self.model = self._load_pretrained_model()
self.transform = self._get_transform()
def _load_pretrained_model(self):
"""加载预训练模型"""
# 使用Mask R-CNN进行实例分割
model = models.detection.maskrcnn_resnet50_fpn(pretrained=True)
model.eval()
return model.to(self.device)
def _get_transform(self):
"""获取图像转换管道"""
return transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
)
])
def predict_masks(self, image_path: str, confidence_threshold: 0.7) -> List[Dict]:
"""预测图像中的物体掩码"""
# 加载图像
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
original_size = image.size
# 预处理
image_tensor = self.transform(image).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
# 推理
with torch.no_grad():
predictions = self.model(image_tensor)[0]
# 解析结果
results = []
masks = predictions['masks'].cpu().numpy()
boxes = predictions['boxes'].cpu().numpy()
scores = predictions['scores'].cpu().numpy()
labels = predictions['labels'].cpu().numpy()
for i, score in enumerate(scores):
if score >= confidence_threshold:
mask = masks[i, 0]
mask = (mask > 0.5).astype(np.uint8) * 255
# 转换为多边形
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(
mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE
)
if contours:
# 取最大轮廓
contour = max(contours, key=cv2.contourArea)
polygon = contour.squeeze().tolist()
results.append({
'bbox': boxes[i].tolist(),
'polygon': polygon,
'confidence': float(score),
'label': int(labels[i]),
'area': cv2.contourArea(contour)
})
return results
def suggest_annotation_regions(self, image_path: str,
num_suggestions: int = 5) -> List[Dict]:
"""基于不确定性采样的标注区域建议"""
# 获取模型预测
predictions = self.predict_masks(image_path, confidence_threshold=0.5)
if not predictions:
return self._suggest_using_saliency(image_path, num_suggestions)
# 基于不确定性排序(低置信度优先)
uncertain_predictions = sorted(
predictions,
key=lambda x: abs(x['confidence'] - 0.5)
)[:num_suggestions]
# 添加多样性:使用聚类确保建议分布在不同的区域
if len(uncertain_predictions) > 2:
centers = np.array([p['bbox'][:2] for p in uncertain_predictions])
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=min(3, len(centers)))
clusters = kmeans.fit_predict(centers)
# 从每个簇中选择最不确定的
selected = []
for cluster_id in range(kmeans.n_clusters):
cluster_items = [p for p, c in zip(uncertain_predictions, clusters)
if c == cluster_id]
if cluster_items:
selected.append(min(cluster_items,
key=lambda x: x['confidence']))
return selected[:num_suggestions]
return uncertain_predictions
def _suggest_using_saliency(self, image_path: str,
num_suggestions: int) -> List[Dict]:
"""使用显著度检测建议标注区域"""
# 加载图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 计算显著度
saliency = cv2.saliency.StaticSaliencyFineGrained_create()
_, saliency_map = saliency.computeSaliency(image)
saliency_map = (saliency_map * 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 寻找显著区域
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(saliency_map, 0, 255,
cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
suggestions = []
for contour in contours[:num_suggestions]:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
suggestions.append({
'bbox': [x, y, x + w, y + h],
'type': 'saliency',
'confidence': 0.5
})
return suggestions
def active_learning_selection(self, unlabeled_images: List[str],
batch_size: int = 10) -> List[str]:
"""主动学习:选择最有价值的图像进行标注"""
scores = []
for img_path in unlabeled_images:
# 计算预测多样性
predictions = self.predict_masks(img_path, 0.3)
if len(predictions) == 0:
# 没有预测,不确定性高
scores.append((img_path, 1.0))
else:
# 使用预测置信度的熵作为不确定性度量
confidences = [p['confidence'] for p in predictions]
entropy = stats.entropy(confidences) if confidences else 1.0
scores.append((img_path, entropy))
# 按不确定性排序
scores.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
# 选择最不确定的
return [img_path for img_path, _ in scores[:batch_size]]
# 使用示例
assistant = SmartAnnotationAssistant()
# 获取标注建议
suggestions = assistant.suggest_annotation_regions('sample.jpg', num_suggestions=5)
for i, suggestion in enumerate(suggestions):
print(f"建议 {i+1}:")
print(f" 边界框: {suggestion['bbox']}")
print(f" 置信度: {suggestion['confidence']:.3f}")
if 'polygon' in suggestion:
print(f" 多边形点数: {len(suggestion['polygon'])}")
2.4 数据标注质量控制指标
质量评估指标体系:
python
class AnnotationQualityMetrics:
"""标注质量评估系统"""
@staticmethod
def calculate_iou(box1, box2):
"""计算IoU(交并比)"""
# box: [x1, y1, x2, y2]
x1 = max(box1[0], box2[0])
y1 = max(box1[1], box2[1])
x2 = min(box1[2], box2[2])
y2 = min(box1[3], box2[3])
intersection = max(0, x2 - x1) * max(0, y2 - y1)
area1 = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1])
area2 = (box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1])
union = area1 + area2 - intersection
return intersection / union if union > 0 else 0
@staticmethod
def evaluate_consistency(annotations_list, iou_threshold=0.7):
"""
评估多个标注者之间的一致性
annotations_list: List[List[Dict]] 每个标注者的标注结果
"""
n_annotators = len(annotations_list)
if n_annotators < 2:
return {"error": "需要至少两个标注者"}
# 计算Fleiss' Kappa(简化版)
total_agreement = 0
total_possible = 0
# 假设所有标注者标注相同的图像
for img_idx in range(len(annotations_list[0])):
anns_at_img = [ann_list[img_idx] for ann_list in annotations_list]
# 比较所有标注者之间的两两一致性
for i in range(n_annotators):
for j in range(i + 1, n_annotators):
ann_i = anns_at_img[i]
ann_j = anns_at_img[j]
# 计算匹配的标注数量
matches = 0
for box_i in ann_i.get('bboxes', []):
for box_j in ann_j.get('bboxes', []):
if AnnotationQualityMetrics.calculate_iou(box_i, box_j) >= iou_threshold:
matches += 1
break
total_agreement += matches
total_possible += max(len(ann_i.get('bboxes', [])),
len(ann_j.get('bboxes', [])))
agreement_score = total_agreement / total_possible if total_possible > 0 else 0
# 计算Fleiss' Kappa
p_e = 1 / (n_annotators * (n_annotators - 1))
kappa = (agreement_score - p_e) / (1 - p_e)
return {
"agreement_score": agreement_score,
"fleiss_kappa": kappa,
"interpretation": AnnotationQualityMetrics._interpret_kappa(kappa)
}
@staticmethod
def _interpret_kappa(kappa):
"""解释Kappa值"""
if kappa < 0:
return "差的一致性"
elif kappa < 0.2:
return "轻微的一致性"
elif kappa < 0.4:
return "一般的一致性"
elif kappa < 0.6:
return "中等的一致性"
elif kappa < 0.8:
return "较强的一致性"
else:
return "几乎完全一致"
@staticmethod
def compute_annotation_confidence(annotations, model_predictions=None):
"""计算标注置信度"""
metrics = {}
# 1. 内部一致性(如果有多重标注)
if isinstance(annotations, list) and len(annotations) > 1:
consistency = AnnotationQualityMetrics.evaluate_consistency([annotations])
metrics['consistency'] = consistency
# 2. 与模型预测的一致性
if model_predictions:
iou_scores = []
for ann in annotations:
best_iou = 0
for pred in model_predictions:
iou = AnnotationQualityMetrics.calculate_iou(ann['bbox'], pred['bbox'])
best_iou = max(best_iou, iou)
iou_scores.append(best_iou)
metrics['avg_iou_with_model'] = np.mean(iou_scores) if iou_scores else 0
metrics['coverage'] = sum(1 for iou in iou_scores if iou > 0.5) / len(iou_scores) if iou_scores else 0
# 3. 标注复杂度
avg_vertices = np.mean([len(ann.get('polygon', [])) for ann in annotations]) if annotations else 0
metrics['complexity'] = avg_vertices
# 综合置信度分数
weights = {
'consistency': 0.4,
'avg_iou_with_model': 0.3,
'coverage': 0.2,
'complexity': 0.1
}
confidence_score = 0
for key, weight in weights.items():
if key in metrics:
if isinstance(metrics[key], dict) and 'agreement_score' in metrics[key]:
confidence_score += metrics[key]['agreement_score'] * weight
else:
confidence_score += metrics[key] * weight
metrics['overall_confidence'] = confidence_score
return metrics
# 使用示例
annotator1 = [
{'bbox': [10, 10, 50, 50], 'polygon': [[10,10], [50,10], [50,50], [10,50]]},
{'bbox': [100, 100, 150, 150], 'polygon': [[100,100], [150,100], [150,150], [100,150]]}
]
annotator2 = [
{'bbox': [12, 12, 52, 52], 'polygon': [[12,12], [52,12], [52,52], [12,52]]},
{'bbox': [105, 105, 155, 155], 'polygon': [[105,105], [155,105], [155,155], [105,155]]}
]
model_preds = [
{'bbox': [8, 8, 48, 48], 'confidence': 0.9},
{'bbox': [102, 102, 152, 152], 'confidence': 0.85}
]
# 评估一致性
consistency_result = AnnotationQualityMetrics.evaluate_consistency([annotator1, annotator2])
print("一致性评估:", consistency_result)
# 计算置信度
confidence_metrics = AnnotationQualityMetrics.compute_annotation_confidence(
annotator1, model_preds
)
print("标注置信度:", confidence_metrics)
第三章:模型训练平台深度解析
3.1 分布式训练平台架构
graph TB
subgraph "用户界面层"
UI[Web控制台]
CLI[命令行接口]
API[REST API]
SDK[Python SDK]
end
subgraph "编排调度层"
Scheduler[任务调度器]
Orchestrator[资源编排器]
Monitor[监控系统]
AutoScaler[自动扩缩容]
end
subgraph "计算资源层"
subgraph "GPU集群"
GPU1[GPU节点1]
GPU2[GPU节点2]
GPU3[GPU节点N]
end
subgraph "CPU集群"
CPU1[CPU节点1]
CPU2[CPU节点2]
end
Storage[分布式存储]
Network[高速网络]
end
subgraph "训练框架层"
PyTorch[PyTorch DDP]
TensorFlow[TF Distributed]
Horovod[Horovod]
DeepSpeed[DeepSpeed]
end
subgraph "数据管理层"
DataLoader[数据加载器]
Augmentation[在线增强]
Cache[数据缓存]
Versioning[版本管理]
end
UI --> Orchestrator
CLI --> Scheduler
API --> Monitor
Orchestrator --> GPU1
Orchestrator --> CPU1
Scheduler --> PyTorch
Scheduler --> TensorFlow
PyTorch --> GPU1
TensorFlow --> GPU2
DataLoader --> Storage
Augmentation --> Cache
3.2 完整模型训练平台实现
基于Kubernetes的分布式训练平台:
python
"""
完整的模型训练平台核心组件
支持分布式训练、超参数优化、实验跟踪
"""
import os
import yaml
import json
import logging
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Any
from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict
from enum import Enum
import subprocess
import tempfile
import shutil
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import numpy as np
import optuna
from kubernetes import client, config
from kubernetes.client.rest import ApiException
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class TrainingStatus(Enum):
"""训练状态枚举"""
PENDING = "pending"
RUNNING = "running"
COMPLETED = "completed"
FAILED = "failed"
STOPPED = "stopped"
@dataclass
class TrainingJob:
"""训练作业配置"""
job_id: str
project_name: str
model_config: Dict[str, Any]
data_config: Dict[str, Any]
training_config: Dict[str, Any]
hyperparameters: Dict[str, Any]
gpu_count: int = 1
priority: int = 0
created_at: str = None
status: TrainingStatus = TrainingStatus.PENDING
def __post_init__(self):
if self.created_at is None:
self.created_at = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
class DistributedTrainingPlatform:
"""分布式训练平台"""
def __init__(self,
kube_config: str = None,
storage_path: str = "./training_storage"):
# 初始化Kubernetes客户端
if kube_config:
config.load_kube_config(config_file=kube_config)
else:
config.load_incluster_config()
self.api_client = client.BatchV1Api()
self.core_client = client.CoreV1Api()
# 存储配置
self.storage_path = storage_path
os.makedirs(storage_path, exist_ok=True)
# 作业队列
self.job_queue = []
self.running_jobs = {}
self.completed_jobs = {}
# 实验跟踪
self.experiment_db = {}
logger.info("分布式训练平台初始化完成")
def submit_job(self, job_config: Dict[str, Any]) -> str:
"""提交训练作业"""
job = TrainingJob(**job_config)
# 生成唯一作业ID
if not job.job_id:
job.job_id = f"{job.project_name}_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')}"
# 保存作业配置
job_path = os.path.join(self.storage_path, job.job_id)
os.makedirs(job_path, exist_ok=True)
with open(os.path.join(job_path, "config.json"), "w") as f:
json.dump(asdict(job), f, indent=2)
# 添加到队列
self.job_queue.append(job)
self._sort_job_queue()
logger.info(f"作业提交成功: {job.job_id}")
return job.job_id
def _sort_job_queue(self):
"""按优先级排序作业队列"""
self.job_queue.sort(key=lambda x: (x.priority, x.created_at), reverse=True)
def start_job_scheduler(self):
"""启动作业调度器"""
import threading
scheduler_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._scheduler_loop)
scheduler_thread.daemon = True
scheduler_thread.start()
logger.info("作业调度器已启动")
def _scheduler_loop(self):
"""调度器主循环"""
while True:
import time
time.sleep(5) # 5秒调度间隔
# 检查可用资源
available_gpus = self._check_available_gpus()
# 调度作业
for job in self.job_queue[:]: # 使用副本遍历
if job.gpu_count <= available_gpus:
try:
self._launch_kubernetes_job(job)
self.job_queue.remove(job)
self.running_jobs[job.job_id] = job
job.status = TrainingStatus.RUNNING
available_gpus -= job.gpu_count
logger.info(f"作业开始运行: {job.job_id}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"启动作业失败 {job.job_id}: {str(e)}")
job.status = TrainingStatus.FAILED
def _check_available_gpus(self) -> int:
"""检查可用GPU数量"""
try:
nodes = self.core_client.list_node()
total_gpus = 0
allocated_gpus = 0
# 这里简化处理,实际需要更复杂的资源管理
for node in nodes.items:
# 检查节点GPU资源
if "nvidia.com/gpu" in node.status.allocatable:
total_gpus += int(node.status.allocatable["nvidia.com/gpu"])
# 减去已分配GPU
for job in self.running_jobs.values():
allocated_gpus += job.gpu_count
return total_gpus - allocated_gpus
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"检查GPU资源失败: {str(e)}")
return 0
def _launch_kubernetes_job(self, job: TrainingJob):
"""启动Kubernetes作业"""
# 生成作业配置
job_manifest = self._create_job_manifest(job)
# 创建Kubernetes作业
try:
api_response = self.api_client.create_namespaced_job(
namespace="default",
body=job_manifest
)
logger.debug(f"Kubernetes作业创建响应: {api_response}")
except ApiException as e:
logger.error(f"Kubernetes API异常: {str(e)}")
raise
def _create_job_manifest(self, job: TrainingJob) -> Dict:
"""创建Kubernetes作业清单"""
job_name = f"train-{job.job_id.lower()}"
manifest = {
"apiVersion": "batch/v1",
"kind": "Job",
"metadata": {
"name": job_name,
"namespace": "default",
"labels": {
"app": "model-training",
"job-id": job.job_id,
"project": job.project_name
}
},
"spec": {
"completions": 1,
"parallelism": 1,
"backoffLimit": 3,
"template": {
"metadata": {
"labels": {
"app": "model-training",
"job-id": job.job_id
}
},
"spec": {
"restartPolicy": "Never",
"containers": [{
"name": "training-container",
"image": "pytorch/pytorch:2.0.1-cuda11.7-cudnn8-runtime",
"command": ["python", "/app/train.py"],
"args": ["--config", "/app/config.json"],
"env": [
{
"name": "NCCL_DEBUG",
"value": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "PYTHONUNBUFFERED",
"value": "1"
}
],
"resources": {
"requests": {
"cpu": "4",
"memory": "16Gi",
"nvidia.com/gpu": str(job.gpu_count)
},
"limits": {
"cpu": "8",
"memory": "32Gi",
"nvidia.com/gpu": str(job.gpu_count)
}
},
"volumeMounts": [
{
"name": "config-volume",
"mountPath": "/app"
},
{
"name": "data-volume",
"mountPath": "/data"
},
{
"name": "output-volume",
"mountPath": "/output"
}
]
}],
"volumes": [
{
"name": "config-volume",
"configMap": {
"name": f"config-{job.job_id}"
}
},
{
"name": "data-volume",
"persistentVolumeClaim": {
"claimName": "training-data-pvc"
}
},
{
"name": "output-volume",
"persistentVolumeClaim": {
"claimName": "training-output-pvc"
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
# 创建ConfigMap
self._create_config_map(job)
return manifest
def _create_config_map(self, job: TrainingJob):
"""创建配置ConfigMap"""
config_map = client.V1ConfigMap(
metadata=client.V1ObjectMeta(
name=f"config-{job.job_id}",
namespace="default"
),
data={
"config.json": json.dumps(asdict(job), indent=2),
"train.py": self._generate_train_script(job)
}
)
try:
self.core_client.create_namespaced_config_map(
namespace="default",
body=config_map
)
except ApiException as e:
logger.error(f"创建ConfigMap失败: {str(e)}")
raise
def _generate_train_script(self, job: TrainingJob) -> str:
"""生成训练脚本"""
return f'''
import os
import json
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, DistributedSampler
import logging
# 设置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def setup_distributed():
"""设置分布式训练环境"""
if 'RANK' in os.environ and 'WORLD_SIZE' in os.environ:
rank = int(os.environ['RANK'])
world_size = int(os.environ['WORLD_SIZE'])
local_rank = int(os.environ['LOCAL_RANK'])
dist.init_process_group(
backend='nccl',
init_method='env://',
world_size=world_size,
rank=rank
)
torch.cuda.set_device(local_rank)
return rank, world_size, local_rank
return 0, 1, 0 # 单机模式
class ExampleModel(nn.Module):
"""示例模型"""
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
# 根据config构建模型
self.layers = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(784, 256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(128, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layers(x)
def main():
# 加载配置
with open('/app/config.json', 'r') as f:
config = json.load(f)
# 设置分布式
rank, world_size, local_rank = setup_distributed()
# 设置设备
device = torch.device(f'cuda:{{local_rank}}' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 创建模型
model = ExampleModel(config['model_config'])
model = model.to(device)
if world_size > 1:
model = nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(
model, device_ids=[local_rank]
)
# 训练循环(简化版)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(config['training_config'].get('epochs', 10)):
if rank == 0:
logger.info(f'Epoch {{epoch+1}}/{{10}}')
# 训练步骤...
if world_size > 1:
dist.barrier()
# 保存模型
if rank == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), '/output/model_final.pth')
logger.info('训练完成,模型已保存')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
'''
class HyperparameterOptimizer:
"""超参数优化器"""
def __init__(self, platform: DistributedTrainingPlatform):
self.platform = platform
self.study_cache = {}
def create_study(self,
study_name: str,
direction: str = "maximize",
n_trials: int = 100) -> str:
"""创建超参数优化研究"""
def objective(trial):
# 定义超参数搜索空间
hyperparams = {
"learning_rate": trial.suggest_float("learning_rate", 1e-5, 1e-2, log=True),
"batch_size": trial.suggest_categorical("batch_size", [16, 32, 64, 128]),
"optimizer": trial.suggest_categorical("optimizer", ["adam", "sgd", "rmsprop"]),
"weight_decay": trial.suggest_float("weight_decay", 1e-6, 1e-2, log=True),
"dropout_rate": trial.suggest_float("dropout_rate", 0.0, 0.5)
}
# 提交训练作业
job_config = {
"project_name": study_name,
"model_config": {
"type": "custom",
"hyperparameters": hyperparams
},
"training_config": {
"epochs": trial.suggest_int("epochs", 10, 50),
"validation_split": 0.2
},
"gpu_count": 1,
"hyperparameters": hyperparams
}
job_id = self.platform.submit_job(job_config)
# 等待作业完成并获取指标
# 这里简化处理,实际需要等待和获取结果
return self._wait_for_job_result(job_id)
# 创建Optuna研究
study = optuna.create_study(
study_name=study_name,
direction=direction,
storage=f"sqlite:///{study_name}.db",
load_if_exists=True
)
# 存储研究
self.study_cache[study_name] = study
# 运行优化
study.optimize(objective, n_trials=n_trials, n_jobs=1)
return study_name
def _wait_for_job_result(self, job_id: str) -> float:
"""等待作业结果(简化实现)"""
import time
time.sleep(60) # 模拟等待
# 实际应该从存储中读取验证指标
return np.random.random() # 返回随机验证精度
def get_best_hyperparameters(self, study_name: str) -> Dict:
"""获取最佳超参数"""
if study_name not in self.study_cache:
return {}
study = self.study_cache[study_name]
return study.best_params
class ExperimentTracker:
"""实验跟踪器"""
def __init__(self, tracking_uri: str = "./experiments"):
self.tracking_uri = tracking_uri
os.makedirs(tracking_uri, exist_ok=True)
# 初始化MLflow(如果可用)
try:
import mlflow
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(f"file://{os.path.abspath(tracking_uri)}")
self.mlflow = mlflow
self.use_mlflow = True
except ImportError:
self.use_mlflow = False
self.experiments = {}
def start_experiment(self,
experiment_name: str,
tags: Dict = None) -> str:
"""开始新实验"""
run_id = f"{experiment_name}_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')}"
if self.use_mlflow:
self.mlflow.set_experiment(experiment_name)
self.mlflow.start_run(run_name=run_id, tags=tags)
else:
# 本地存储实验信息
experiment_dir = os.path.join(self.tracking_uri, run_id)
os.makedirs(experiment_dir, exist_ok=True)
self.experiments[run_id] = {
"name": experiment_name,
"start_time": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"tags": tags or {},
"metrics": {},
"params": {},
"artifacts": []
}
logger.info(f"实验开始: {run_id}")
return run_id
def log_params(self, run_id: str, params: Dict):
"""记录参数"""
if self.use_mlflow:
self.mlflow.log_params(params)
elif run_id in self.experiments:
self.experiments[run_id]["params"].update(params)
def log_metrics(self, run_id: str, metrics: Dict, step: int = None):
"""记录指标"""
if self.use_mlflow:
self.mlflow.log_metrics(metrics, step=step)
elif run_id in self.experiments:
for key, value in metrics.items():
if key not in self.experiments[run_id]["metrics"]:
self.experiments[run_id]["metrics"][key] = []
self.experiments[run_id]["metrics"][key].append({
"value": value,
"step": step or len(self.experiments[run_id]["metrics"][key])
})
def log_artifact(self, run_id: str, local_path: str):
"""记录 artifact"""
if self.use_mlflow:
self.mlflow.log_artifact(local_path)
elif run_id in self.experiments:
artifact_name = os.path.basename(local_path)
dest_path = os.path.join(self.tracking_uri, run_id, "artifacts", artifact_name)
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(dest_path), exist_ok=True)
shutil.copy(local_path, dest_path)
self.experiments[run_id]["artifacts"].append(artifact_name)
def end_experiment(self, run_id: str):
"""结束实验"""
if self.use_mlflow:
self.mlflow.end_run()
elif run_id in self.experiments:
self.experiments[run_id]["end_time"] = datetime.now().isoformat()
# 保存实验信息
exp_path = os.path.join(self.tracking_uri, run_id, "experiment.json")
with open(exp_path, "w") as f:
json.dump(self.experiments[run_id], f, indent=2)
logger.info(f"实验结束: {run_id}")
# 使用示例
def main():
# 初始化平台
platform = DistributedTrainingPlatform(
kube_config="~/.kube/config",
storage_path="./training_data"
)
# 启动调度器
platform.start_job_scheduler()
# 初始化实验跟踪器
tracker = ExperimentTracker("./mlruns")
# 初始化超参数优化器
optimizer = HyperparameterOptimizer(platform)
# 提交训练作业
job_config = {
"job_id": "test_job_001",
"project_name": "image_classification",
"model_config": {
"type": "resnet50",
"pretrained": True,
"num_classes": 10
},
"data_config": {
"dataset": "cifar10",
"data_path": "/data/cifar10",
"split": {"train": 0.8, "val": 0.2}
},
"training_config": {
"epochs": 50,
"batch_size": 64,
"optimizer": "adam",
"scheduler": "cosine"
},
"hyperparameters": {
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"weight_decay": 1e-4
},
"gpu_count": 2,
"priority": 1
}
job_id = platform.submit_job(job_config)
print(f"作业已提交,ID: {job_id}")
# 开始实验跟踪
run_id = tracker.start_experiment(
experiment_name="resnet50_cifar10",
tags={"dataset": "cifar10", "model": "resnet50"}
)
# 记录参数
tracker.log_params(run_id, job_config["hyperparameters"])
# 模拟训练过程
for epoch in range(10):
metrics = {
"train_loss": np.random.random() * 2,
"train_acc": 0.8 + np.random.random() * 0.15,
"val_loss": np.random.random() * 1.5,
"val_acc": 0.75 + np.random.random() * 0.2
}
tracker.log_metrics(run_id, metrics, step=epoch)
# 结束实验
tracker.end_experiment(run_id)
# 运行超参数优化
study_name = optimizer.create_study(
study_name="hyperparam_tuning",
direction="maximize",
n_trials=20
)
best_params = optimizer.get_best_hyperparameters(study_name)
print(f"最佳超参数: {best_params}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.3 模型版本管理与部署
MLOps流水线实现:
python
"""
完整的模型版本管理与部署系统
支持模型注册、版本控制、A/B测试、渐进式发布
"""
import hashlib
import pickle
import shutil
from datetime import datetime
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple
import json
import yaml
import numpy as np
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from enum import Enum
import docker
from docker.errors import DockerException
class ModelStage(Enum):
"""模型阶段"""
DEVELOPMENT = "development"
STAGING = "staging"
PRODUCTION = "production"
ARCHIVED = "archived"
@dataclass
class ModelVersion:
"""模型版本信息"""
model_id: str
version: str
stage: ModelStage
created_at: datetime
created_by: str
metrics: Dict[str, float] = field(default_factory=dict)
parameters: Dict[str, any] = field(default_factory=dict)
dependencies: Dict[str, str] = field(default_factory=dict)
artifact_path: Optional[str] = None
description: Optional[str] = None
tags: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
def to_dict(self):
"""转换为字典"""
return {
"model_id": self.model_id,
"version": self.version,
"stage": self.stage.value,
"created_at": self.created_at.isoformat(),
"created_by": self.created_by,
"metrics": self.metrics,
"parameters": self.parameters,
"dependencies": self.dependencies,
"artifact_path": self.artifact_path,
"description": self.description,
"tags": self.tags
}
class ModelRegistry:
"""模型注册表"""
def __init__(self, registry_path: str = "./model_registry"):
self.registry_path = Path(registry_path)
self.registry_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 初始化数据库
self.models_db_path = self.registry_path / "models.json"
if not self.models_db_path.exists():
self._init_database()
self.models = self._load_database()
def _init_database(self):
"""初始化数据库"""
with open(self.models_db_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump({"models": {}}, f)
def _load_database(self) -> Dict:
"""加载数据库"""
with open(self.models_db_path, 'r') as f:
return json.load(f)
def _save_database(self):
"""保存数据库"""
with open(self.models_db_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(self.models, f, indent=2)
def register_model(self,
model_id: str,
version: str,
stage: ModelStage,
created_by: str,
artifact_path: str,
metrics: Dict = None,
parameters: Dict = None,
description: str = None) -> str:
"""注册新模型版本"""
# 创建版本目录
version_dir = self.registry_path / model_id / version
version_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 复制模型文件
if Path(artifact_path).exists():
dest_path = version_dir / "model.pkl"
shutil.copy(artifact_path, dest_path)
# 计算模型哈希
model_hash = self._calculate_file_hash(dest_path)
else:
model_hash = "unknown"
# 创建版本记录
model_version = ModelVersion(
model_id=model_id,
version=version,
stage=stage,
created_at=datetime.now(),
created_by=created_by,
metrics=metrics or {},
parameters=parameters or {},
dependencies=self._extract_dependencies(),
artifact_path=str(dest_path) if 'dest_path' in locals() else None,
description=description
)
# 保存版本元数据
metadata_path = version_dir / "metadata.json"
with open(metadata_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(model_version.to_dict(), f, indent=2)
# 更新数据库
if model_id not in self.models["models"]:
self.models["models"][model_id] = {}
self.models["models"][model_id][version] = model_version.to_dict()
self._save_database()
logger.info(f"模型注册成功: {model_id}:{version}")
return version
def _calculate_file_hash(self, filepath: Path) -> str:
"""计算文件哈希"""
sha256_hash = hashlib.sha256()
with open(filepath, "rb") as f:
for byte_block in iter(lambda: f.read(4096), b""):
sha256_hash.update(byte_block)
return sha256_hash.hexdigest()
def _extract_dependencies(self) -> Dict:
"""提取依赖信息"""
try:
import pkg_resources
dependencies = {}
for dist in pkg_resources.working_set:
dependencies[dist.project_name] = dist.version
return dependencies
except:
return {}
def get_model(self, model_id: str, version: str = None) -> Optional[ModelVersion]:
"""获取模型"""
if model_id not in self.models["models"]:
return None
if version:
if version in self.models["models"][model_id]:
data = self.models["models"][model_id][version]
return ModelVersion(**data)
return None
# 获取最新版本
versions = list(self.models["models"][model_id].keys())
if not versions:
return None
latest_version = sorted(versions, reverse=True)[0]
data = self.models["models"][model_id][latest_version]
return ModelVersion(**data)
def list_models(self, stage: ModelStage = None) -> List[Dict]:
"""列出模型"""
results = []
for model_id, versions in self.models["models"].items():
for version, data in versions.items():
if stage is None or data["stage"] == stage.value:
results.append({
"model_id": model_id,
"version": version,
"stage": data["stage"],
"created_at": data["created_at"],
"metrics": data["metrics"]
})
return sorted(results, key=lambda x: x["created_at"], reverse=True)
def transition_stage(self,
model_id: str,
version: str,
new_stage: ModelStage,
reason: str = None) -> bool:
"""转换模型阶段"""
if model_id not in self.models["models"]:
return False
if version not in self.models["models"][model_id]:
return False
# 更新阶段
self.models["models"][model_id][version]["stage"] = new_stage.value
# 记录转换历史
history_entry = {
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"from": self.models["models"][model_id][version]["stage"],
"to": new_stage.value,
"reason": reason
}
if "stage_history" not in self.models["models"][model_id][version]:
self.models["models"][model_id][version]["stage_history"] = []
self.models["models"][model_id][version]["stage_history"].append(history_entry)
# 保存更新
self._save_database()
# 更新元数据文件
version_dir = self.registry_path / model_id / version
metadata_path = version_dir / "metadata.json"
with open(metadata_path, 'r') as f:
metadata = json.load(f)
metadata["stage"] = new_stage.value
metadata["stage_history"] = self.models["models"][model_id][version]["stage_history"]
with open(metadata_path, 'w') as f:
json.dump(metadata, f, indent=2)
logger.info(f"模型阶段转换: {model_id}:{version} -> {new_stage.value}")
return True
class ModelDeployer:
"""模型部署器"""
def __init__(self, registry: ModelRegistry):
self.registry = registry
self.docker_client = docker.from_env()
# 部署配置
self.deployment_path = Path("./deployments")
self.deployment_path.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
def create_deployment(self,
model_id: str,
version: str,
deployment_name: str,
replicas: int = 1,
resources: Dict = None) -> str:
"""创建模型部署"""
# 获取模型信息
model = self.registry.get_model(model_id, version)
if not model:
raise ValueError(f"模型未找到: {model_id}:{version}")
# 创建部署目录
deployment_dir = self.deployment_path / deployment_name
deployment_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
# 生成Dockerfile
dockerfile_content = self._generate_dockerfile(model)
dockerfile_path = deployment_dir / "Dockerfile"
dockerfile_path.write_text(dockerfile_content)
# 生成应用代码
app_code = self._generate_app_code(model)
app_path = deployment_dir / "app.py"
app_path.write_text(app_code)
# 生成requirements.txt
requirements = self._generate_requirements(model)
req_path = deployment_dir / "requirements.txt"
req_path.write_text(requirements)
# 复制模型文件
if model.artifact_path:
model_dest = deployment_dir / "model.pkl"
shutil.copy(model.artifact_path, model_dest)
# 生成Docker Compose配置
compose_config = self._generate_compose_config(
deployment_name, replicas, resources or {}
)
compose_path = deployment_dir / "docker-compose.yml"
compose_path.write_text(yaml.dump(compose_config, default_flow_style=False))
# 生成Kubernetes部署配置
k8s_config = self._generate_k8s_config(
deployment_name, replicas, resources or {}
)
k8s_path = deployment_dir / "deployment.yaml"
k8s_path.write_text(yaml.dump(k8s_config, default_flow_style=False))
logger.info(f"部署配置创建完成: {deployment_name}")
return str(deployment_dir)
def _generate_dockerfile(self, model: ModelVersion) -> str:
"""生成Dockerfile"""
base_image = "python:3.9-slim"
dockerfile = f'''
FROM {base_image}
WORKDIR /app
# 安装系统依赖
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
gcc \
g++ \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# 复制依赖文件
COPY requirements.txt .
# 安装Python依赖
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# 复制应用代码和模型
COPY app.py .
COPY model.pkl .
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 8080
# 运行应用
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
'''
return dockerfile
def _generate_app_code(self, model: ModelVersion) -> str:
"""生成应用代码"""
return f'''
import pickle
import numpy as np
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import traceback
app = Flask(__name__)
# 加载模型
try:
with open('model.pkl', 'rb') as f:
model = pickle.load(f)
print("模型加载成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"模型加载失败: {{e}}")
model = None
def preprocess_input(data):
"""预处理输入数据"""
# 根据模型需求实现
return np.array(data).reshape(1, -1)
def postprocess_output(prediction):
"""后处理输出"""
# 根据模型输出实现
if hasattr(prediction, 'tolist'):
return prediction.tolist()
return float(prediction)
@app.route('/health', methods=['GET'])
def health_check():
"""健康检查"""
return jsonify({{
"status": "healthy" if model else "unhealthy",
"model_loaded": model is not None,
"model_id": "{model.model_id}",
"version": "{model.version}"
}})
@app.route('/predict', methods=['POST'])
def predict():
"""预测端点"""
try:
if model is None:
return jsonify({{"error": "Model not loaded"}}), 500
# 获取输入数据
data = request.json
if not data or 'features' not in data:
return jsonify({{"error": "No features provided"}}), 400
# 预处理
features = data['features']
processed_input = preprocess_input(features)
# 预测
prediction = model.predict(processed_input)
# 后处理
output = postprocess_output(prediction)
return jsonify({{
"prediction": output,
"model_version": "{model.version}",
"request_id": request.headers.get('X-Request-ID', 'unknown')
}})
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({{
"error": str(e),
"traceback": traceback.format_exc()
}}), 500
@app.route('/metrics', methods=['GET'])
def get_metrics():
"""获取模型指标"""
return jsonify({json.dumps(model.metrics) if model else {{}}})
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=8080, debug=False)
'''
def _generate_requirements(self, model: ModelVersion) -> str:
"""生成requirements.txt"""
base_requirements = [
"flask==2.3.2",
"numpy==1.24.3",
"scikit-learn==1.3.0",
"gunicorn==20.1.0"
]
# 添加模型特定的依赖
for pkg, version in model.dependencies.items():
if pkg not in ["python", "pip"]:
base_requirements.append(f"{pkg}=={version}")
return "\n".join(base_requirements)
def _generate_compose_config(self, name: str, replicas: int, resources: Dict) -> Dict:
"""生成Docker Compose配置"""
return {
"version": "3.8",
"services": {
name: {
"build": ".",
"ports": ["8080:8080"],
"deploy": {
"replicas": replicas,
"resources": {
"limits": resources.get("limits", {"cpus": "0.5", "memory": "512M"}),
"reservations": resources.get("reservations", {"cpus": "0.1", "memory": "128M"})
}
},
"healthcheck": {
"test": ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost:8080/health"],
"interval": "30s",
"timeout": "10s",
"retries": 3
}
}
}
}
def _generate_k8s_config(self, name: str, replicas: int, resources: Dict) -> Dict:
"""生成Kubernetes部署配置"""
return {
"apiVersion": "apps/v1",
"kind": "Deployment",
"metadata": {
"name": f"{name}-deployment",
"labels": {
"app": name
}
},
"spec": {
"replicas": replicas,
"selector": {
"matchLabels": {
"app": name
}
},
"template": {
"metadata": {
"labels": {
"app": name
}
},
"spec": {
"containers": [{
"name": name,
"image": f"{name}:latest",
"ports": [{
"containerPort": 8080
}],
"resources": resources.get("limits", {
"limits": {
"cpu": "500m",
"memory": "512Mi"
},
"requests": {
"cpu": "100m",
"memory": "128Mi"
}
}),
"livenessProbe": {
"httpGet": {
"path": "/health",
"port": 8080
},
"initialDelaySeconds": 30,
"periodSeconds": 10
},
"readinessProbe": {
"httpGet": {
"path": "/health",
"port": 8080
},
"initialDelaySeconds": 5,
"periodSeconds": 5
}
}]
}
}
}
}
def deploy_local(self, deployment_dir: str) -> bool:
"""本地部署"""
try:
# 构建Docker镜像
client = docker.from_env()
# 构建镜像
image_tag = f"{Path(deployment_dir).name}:latest"
client.images.build(
path=deployment_dir,
tag=image_tag,
rm=True
)
# 运行容器
container = client.containers.run(
image_tag,
ports={'8080/tcp': 8080},
detach=True,
name=Path(deployment_dir).name
)
logger.info(f"部署成功,容器ID: {container.id}")
return True
except DockerException as e:
logger.error(f"部署失败: {str(e)}")
return False
class ABTestManager:
"""A/B测试管理器"""
def __init__(self, registry: ModelRegistry):
self.registry = registry
self.active_tests = {}
def create_ab_test(self,
test_name: str,
model_a: Tuple[str, str], # (model_id, version)
model_b: Tuple[str, str],
traffic_split: Dict[str, float] = None) -> str:
"""创建A/B测试"""
# 验证模型
model_a_obj = self.registry.get_model(model_a[0], model_a[1])
model_b_obj = self.registry.get_model(model_b[0], model_b[1])
if not model_a_obj or not model_b_obj:
raise ValueError("模型不存在")
# 默认流量分配
if traffic_split is None:
traffic_split = {"A": 0.5, "B": 0.5}
# 创建测试配置
test_config = {
"test_name": test_name,
"model_a": {
"model_id": model_a[0],
"version": model_a[1],
"traffic_percentage": traffic_split["A"]
},
"model_b": {
"model_id": model_b[0],
"version": model_b[1],
"traffic_percentage": traffic_split["B"]
},
"start_time": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"status": "active",
"metrics": {
"total_requests": 0,
"requests_a": 0,
"requests_b": 0,
"success_a": 0,
"success_b": 0,
"avg_latency_a": 0,
"avg_latency_b": 0
}
}
self.active_tests[test_name] = test_config
logger.info(f"A/B测试创建: {test_name}")
return test_name
def route_request(self, test_name: str, request_id: str) -> Tuple[str, str]:
"""路由请求到A或B版本"""
if test_name not in self.active_tests:
return None, None
test_config = self.active_tests[test_name]
# 根据流量分配决定版本
rand_val = np.random.random()
if rand_val < test_config["model_a"]["traffic_percentage"]:
version = "A"
model_info = test_config["model_a"]
else:
version = "B"
model_info = test_config["model_b"]
# 更新指标
test_config["metrics"]["total_requests"] += 1
test_config["metrics"][f"requests_{version.lower()}"] += 1
return version, model_info
def record_result(self,
test_name: str,
version: str,
success: bool,
latency: float):
"""记录测试结果"""
if test_name not in self.active_tests:
return
metrics = self.active_tests[test_name]["metrics"]
# 更新成功率
if success:
metrics[f"success_{version.lower()}"] += 1
# 更新延迟(指数移动平均)
current_avg = metrics[f"avg_latency_{version.lower()}"]
request_count = metrics[f"requests_{version.lower()}"]
if request_count == 1:
metrics[f"avg_latency_{version.lower()}"] = latency
else:
alpha = 0.1 # 平滑因子
metrics[f"avg_latency_{version.lower()}"] = (
alpha * latency + (1 - alpha) * current_avg
)
def get_test_results(self, test_name: str) -> Dict:
"""获取测试结果"""
if test_name not in self.active_tests:
return {}
test_config = self.active_tests[test_name]
metrics = test_config["metrics"]
# 计算成功率
success_rate_a = (
metrics["success_a"] / metrics["requests_a"]
if metrics["requests_a"] > 0 else 0
)
success_rate_b = (
metrics["success_b"] / metrics["requests_b"]
if metrics["requests_b"] > 0 else 0
)
return {
"test_name": test_name,
"duration_hours": (
datetime.now() - datetime.fromisoformat(test_config["start_time"])
).total_seconds() / 3600,
"total_requests": metrics["total_requests"],
"model_a": {
"requests": metrics["requests_a"],
"success_rate": success_rate_a,
"avg_latency": metrics["avg_latency_a"]
},
"model_b": {
"requests": metrics["requests_b"],
"success_rate": success_rate_b,
"avg_latency": metrics["avg_latency_b"]
},
"statistical_significance": self._calculate_significance(
metrics["requests_a"], metrics["success_a"],
metrics["requests_b"], metrics["success_b"]
)
}
def _calculate_significance(self, n_a, s_a, n_b, s_b):
"""计算统计显著性(简化版)"""
if n_a == 0 or n_b == 0:
return 0
p_a = s_a / n_a
p_b = s_b / n_b
# 计算Z分数
p_pool = (s_a + s_b) / (n_a + n_b)
se = np.sqrt(p_pool * (1 - p_pool) * (1/n_a + 1/n_b))
if se == 0:
return 0
z = (p_a - p_b) / se
# 使用正态分布计算p值(单尾检验)
from scipy import stats
p_value = 1 - stats.norm.cdf(abs(z))
return p_value
# 完整使用示例
def complete_mlops_demo():
"""完整的MLOps演示"""
print("=" * 60)
print("MLOps全流程演示")
print("=" * 60)
# 1. 初始化组件
registry = ModelRegistry("./model_registry")
deployer = ModelDeployer(registry)
ab_test_manager = ABTestManager(registry)
# 2. 训练并注册模型
print("\n1. 训练和注册模型")
print("-" * 40)
# 模拟训练一个模型
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 生成示例数据
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, random_state=42)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 训练模型
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 评估模型
accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"模型准确率: {accuracy:.4f}")
# 保存模型
model_path = "./model_v1.pkl"
with open(model_path, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(model, f)
# 注册模型
version = registry.register_model(
model_id="customer_churn",
version="1.0.0",
stage=ModelStage.DEVELOPMENT,
created_by="data_scientist",
artifact_path=model_path,
metrics={"accuracy": accuracy, "f1_score": 0.85},
parameters={"n_estimators": 100, "max_depth": 10},
description="初始版本,随机森林分类器"
)
print(f"模型注册成功: customer_churn:{version}")
# 3. 部署模型
print("\n2. 部署模型")
print("-" * 40)
deployment_dir = deployer.create_deployment(
model_id="customer_churn",
version="1.0.0",
deployment_name="churn-predictor",
replicas=2,
resources={
"limits": {"cpus": "1", "memory": "1G"},
"reservations": {"cpus": "0.2", "memory": "256M"}
}
)
print(f"部署配置创建完成: {deployment_dir}")
# 4. 创建新版本并进行A/B测试
print("\n3. 创建新版本并设置A/B测试")
print("-" * 40)
# 训练改进的模型
model_v2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=150, max_depth=15, random_state=42)
model_v2.fit(X_train, y_train)
accuracy_v2 = model_v2.score(X_test, y_test)
# 保存并注册新版本
model_v2_path = "./model_v2.pkl"
with open(model_v2_path, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(model_v2, f)
version_v2 = registry.register_model(
model_id="customer_churn",
version="2.0.0",
stage=ModelStage.STAGING,
created_by="data_scientist",
artifact_path=model_v2_path,
metrics={"accuracy": accuracy_v2, "f1_score": 0.88},
parameters={"n_estimators": 150, "max_depth": 15},
description="改进版本,增加树的数量和深度"
)
print(f"新版本注册成功: customer_churn:{version_v2}")
print(f"准确率提升: {accuracy_v2 - accuracy:.4f}")
# 将v1升级到生产环境
registry.transition_stage(
model_id="customer_churn",
version="1.0.0",
new_stage=ModelStage.PRODUCTION,
reason="Initial production deployment"
)
# 创建A/B测试
test_name = ab_test_manager.create_ab_test(
test_name="churn_model_ab_test",
model_a=("customer_churn", "1.0.0"),
model_b=("customer_churn", "2.0.0"),
traffic_split={"A": 0.7, "B": 0.3} # 70%流量给v1,30%给v2
)
print(f"A/B测试创建: {test_name}")
# 5. 模拟A/B测试请求
print("\n4. 模拟A/B测试流量")
print("-" * 40)
np.random.seed(42)
for i in range(1000):
# 路由请求
version, model_info = ab_test_manager.route_request(test_name, f"req_{i}")
if version:
# 模拟预测延迟
latency = np.random.exponential(scale=50) # 平均50ms
success = np.random.random() > 0.05 # 95%成功率
# 记录结果
ab_test_manager.record_result(test_name, version, success, latency)
# 6. 分析测试结果
print("\n5. A/B测试结果分析")
print("-" * 40)
results = ab_test_manager.get_test_results(test_name)
print(f"测试名称: {results['test_name']}")
print(f"持续时间: {results['duration_hours']:.2f} 小时")
print(f"总请求数: {results['total_requests']}")
print()
print("模型A (v1.0.0):")
print(f" 请求数: {results['model_a']['requests']}")
print(f" 成功率: {results['model_a']['success_rate']:.4f}")
print(f" 平均延迟: {results['model_a']['avg_latency']:.2f} ms")
print()
print("模型B (v2.0.0):")
print(f" 请求数: {results['model_b']['requests']}")
print(f" 成功率: {results['model_b']['success_rate']:.4f}")
print(f" 平均延迟: {results['model_b']['avg_latency']:.2f} ms")
print()
print(f"统计显著性 (p值): {results['statistical_significance']:.6f}")
# 7. 根据结果决定是否升级
print("\n6. 部署决策")
print("-" * 40)
if results['statistical_significance'] < 0.05 and results['model_b']['success_rate'] > results['model_a']['success_rate']:
print("✓ 新版本性能显著优于旧版本,开始渐进式升级")
# 逐步增加新版本流量
for new_traffic in [0.5, 0.8, 1.0]:
print(f" 将v2流量增加至 {new_traffic*100}%")
# 更新流量分配
ab_test_manager.active_tests[test_name]["model_a"]["traffic_percentage"] = 1 - new_traffic
ab_test_manager.active_tests[test_name]["model_b"]["traffic_percentage"] = new_traffic
# 模拟更多请求
for i in range(500):
version, model_info = ab_test_manager.route_request(test_name, f"upgrade_req_{i}")
if version:
latency = np.random.exponential(scale=45 if version == "B" else 50)
success = np.random.random() > (0.05 if version == "A" else 0.03)
ab_test_manager.record_result(test_name, version, success, latency)
# 最终升级
registry.transition_stage(
model_id="customer_churn",
version="2.0.0",
new_stage=ModelStage.PRODUCTION,
reason="A/B测试显示性能显著提升"
)
registry.transition_stage(
model_id="customer_churn",
version="1.0.0",
new_stage=ModelStage.ARCHIVED,
reason="被v2.0.0取代"
)
print("✓ 升级完成,v2.0.0现在为生产版本")
else:
print("✗ 新版本未显示显著改进,保持v1.0.0为生产版本")
# 8. 列出所有模型
print("\n7. 模型注册表状态")
print("-" * 40)
models = registry.list_models()
for model_info in models:
print(f"{model_info['model_id']}:{model_info['version']} [{model_info['stage']}] - 准确率: {model_info['metrics'].get('accuracy', 0):.4f}")
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("MLOps演示完成")
print("=" * 60)
if __name__ == "__main__":
complete_mlops_demo()
第四章:AI工具链集成与最佳实践
4.1 端到端AI工作流
graph LR
subgraph "数据工程阶段"
DE1[数据收集] --> DE2[数据清洗]
DE2 --> DE3[数据标注]
DE3 --> DE4[数据增强]
end
subgraph "模型开发阶段"
MD1[特征工程] --> MD2[模型设计]
MD2 --> MD3[分布式训练]
MD3 --> MD4[超参数优化]
end
subgraph "部署运维阶段"
DO1[模型验证] --> DO2[模型注册]
DO2 --> DO3[服务部署]
DO3 --> DO4[性能监控]
end
subgraph "持续迭代阶段"
CI1[A/B测试] --> CI2[反馈收集]
CI2 --> CI3[重新训练]
CI3 --> CI4[模型更新]
end
DE4 --> MD1
MD4 --> DO1
DO4 --> CI1
CI4 --> DE3
4.2 工具链集成架构
集成平台设计:
python
"""
AI工具链集成平台
将智能编码、数据标注、模型训练无缝集成
"""
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Any
from datetime import datetime
import asyncio
import aiohttp
from fastapi import FastAPI, BackgroundTasks, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
import redis
import json
app = FastAPI(title="AI工具链集成平台", version="1.0.0")
# Redis连接
redis_client = redis.Redis(host='localhost', port=6379, db=0)
class ToolchainWorkflow:
"""工具链工作流管理器"""
def __init__(self):
self.workflows = {}
self.tool_integrations = {
"github_copilot": self._integrate_copilot,
"label_studio": self._integrate_label_studio,
"mlflow": self._integrate_mlflow,
"kubeflow": self._integrate_kubeflow
}
async def create_workflow(self,
workflow_name: str,
steps: List[Dict]) -> str:
"""创建工作流"""
workflow_id = f"wf_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')}"
workflow = {
"id": workflow_id,
"name": workflow_name,
"steps": steps,
"status": "created",
"created_at": datetime.now().isoformat(),
"current_step": 0,
"results": {}
}
# 保存到Redis
redis_client.set(f"workflow:{workflow_id}", json.dumps(workflow))
# 添加到内存
self.workflows[workflow_id] = workflow
logger.info(f"工作流创建: {workflow_id}")
return workflow_id
async def execute_workflow(self, workflow_id: str):
"""执行工作流"""
workflow = self.workflows.get(workflow_id)
if not workflow:
# 从Redis加载
workflow_data = redis_client.get(f"workflow:{workflow_id}")
if not workflow_data:
raise ValueError(f"工作流不存在: {workflow_id}")
workflow = json.loads(workflow_data)
workflow["status"] = "running"
workflow["started_at"] = datetime.now().isoformat()
# 更新状态
self._update_workflow_state(workflow_id, workflow)
# 异步执行每个步骤
for i, step in enumerate(workflow["steps"]):
workflow["current_step"] = i
try:
result = await self._execute_step(step)
workflow["results"][step["name"]] = result
# 更新进度
self._update_workflow_state(workflow_id, workflow)
# 检查是否需要暂停
if step.get("wait_for_approval", False):
workflow["status"] = "waiting_for_approval"
self._update_workflow_state(workflow_id, workflow)
break
except Exception as e:
workflow["status"] = "failed"
workflow["error"] = str(e)
workflow["failed_step"] = step["name"]
self._update_workflow_state(workflow_id, workflow)
raise
if workflow["status"] == "running":
workflow["status"] = "completed"
workflow["completed_at"] = datetime.now().isoformat()
self._update_workflow_state(workflow_id, workflow)
return workflow
async def _execute_step(self, step: Dict) -> Any:
"""执行单个步骤"""
step_type = step["type"]
if step_type == "code_generation":
return await self._execute_code_generation(step)
elif step_type == "data_labeling":
return await self._execute_data_labeling(step)
elif step_type == "model_training":
return await self._execute_model_training(step)
elif step_type == "model_deployment":
return await self._execute_model_deployment(step)
else:
raise ValueError(f"未知步骤类型: {step_type}")
async def _execute_code_generation(self, step: Dict) -> Dict:
"""执行代码生成步骤"""
prompt = step["prompt"]
language = step.get("language", "python")
# 集成GitHub Copilot API
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
# 实际使用时需要配置API密钥
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {step.get('api_key')}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
data = {
"prompt": prompt,
"language": language,
"max_tokens": step.get("max_tokens", 1000)
}
try:
async with session.post(
"https://api.github.com/copilot/completions",
headers=headers,
json=data
) as response:
if response.status == 200:
result = await response.json()
return {
"generated_code": result.get("choices", [{}])[0].get("text", ""),
"usage": result.get("usage", {}),
"success": True
}
else:
return {
"error": f"API错误: {response.status}",
"success": False
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"error": str(e),
"success": False
}
async def _execute_data_labeling(self, step: Dict) -> Dict:
"""执行数据标注步骤"""
dataset_path = step["dataset_path"]
annotation_type = step["annotation_type"]
# 集成Label Studio
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Token {step.get('api_token')}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
# 创建标注项目
project_data = {
"title": step.get("project_name", f"Annotation_{datetime.now()}"),
"description": step.get("description", ""),
"label_config": self._generate_label_config(annotation_type)
}
try:
# 创建项目
async with session.post(
f"{step.get('label_studio_url')}/api/projects",
headers=headers,
json=project_data
) as response:
if response.status == 201:
project = await response.json()
# 导入数据
import_data = {
"file_upload": dataset_path
}
async with session.post(
f"{step.get('label_studio_url')}/api/projects/{project['id']}/import",
headers=headers,
data=import_data
) as import_response:
if import_response.status == 201:
return {
"project_id": project["id"],
"project_url": f"{step.get('label_studio_url')}/projects/{project['id']}",
"success": True
}
return {
"error": f"创建标注项目失败: {response.status}",
"success": False
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"error": str(e),
"success": False
}
async def _execute_model_training(self, step: Dict) -> Dict:
"""执行模型训练步骤"""
# 集成MLflow或Kubeflow
training_config = step["training_config"]
# 这里简化处理,实际应该调用相应的训练API
return {
"training_job_id": f"train_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d_%H%M%S')}",
"status": "submitted",
"success": True
}
async def _execute_model_deployment(self, step: Dict) -> Dict:
"""执行模型部署步骤"""
model_path = step["model_path"]
deployment_target = step.get("deployment_target", "kubernetes")
# 根据目标平台部署
if deployment_target == "kubernetes":
return await self._deploy_to_kubernetes(step)
elif deployment_target == "sagemaker":
return await self._deploy_to_sagemaker(step)
else:
return {
"error": f"不支持的部署目标: {deployment_target}",
"success": False
}
def _generate_label_config(self, annotation_type: str) -> str:
"""生成标注配置"""
configs = {
"object_detection": """
<View>
<Image name="image" value="$image"/>
<RectangleLabels name="label" toName="image">
<Label value="Object" background="green"/>
</RectangleLabels>
</View>
""",
"classification": """
<View>
<Image name="image" value="$image"/>
<Choices name="class" toName="image">
<Choice value="Class A"/>
<Choice value="Class B"/>
</Choices>
</View>
""",
"segmentation": """
<View>
<Image name="image" value="$image"/>
<PolygonLabels name="label" toName="image">
<Label value="Region" background="red"/>
</PolygonLabels>
</View>
"""
}
return configs.get(annotation_type, configs["object_detection"])
def _update_workflow_state(self, workflow_id: str, workflow: Dict):
"""更新工作流状态"""
# 更新内存
self.workflows[workflow_id] = workflow
# 更新Redis
redis_client.set(f"workflow:{workflow_id}", json.dumps(workflow))
# 发布状态更新事件
redis_client.publish("workflow_updates", json.dumps({
"workflow_id": workflow_id,
"status": workflow["status"],
"current_step": workflow["current_step"],
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
}))
def _integrate_copilot(self, task: Dict) -> Dict:
"""集成GitHub Copilot"""
# 实现代码生成逻辑
pass
def _integrate_label_studio(self, task: Dict) -> Dict:
"""集成Label Studio"""
# 实现标注任务管理
pass
def _integrate_mlflow(self, task: Dict) -> Dict:
"""集成MLflow"""
# 实现实验跟踪
pass
def _integrate_kubeflow(self, task: Dict) -> Dict:
"""集成Kubeflow"""
# 实现流水线执行
pass
# FastAPI端点
workflow_manager = ToolchainWorkflow()
class WorkflowRequest(BaseModel):
name: str
steps: List[Dict]
config: Optional[Dict] = {}
@app.post("/workflows")
async def create_workflow(request: WorkflowRequest, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
"""创建工作流"""
workflow_id = await workflow_manager.create_workflow(
request.name, request.steps
)
# 异步执行工作流
background_tasks.add_task(workflow_manager.execute_workflow, workflow_id)
return {
"workflow_id": workflow_id,
"message": "工作流创建并开始执行",
"status_endpoint": f"/workflows/{workflow_id}/status"
}
@app.get("/workflows/{workflow_id}")
async def get_workflow(workflow_id: str):
"""获取工作流状态"""
workflow_data = redis_client.get(f"workflow:{workflow_id}")
if not workflow_data:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="工作流未找到")
workflow = json.loads(workflow_data)
# 计算进度
total_steps = len(workflow.get("steps", []))
current_step = workflow.get("current_step", 0)
progress = (current_step / total_steps * 100) if total_steps > 0 else 0
return {
**workflow,
"progress": progress
}
@app.get("/workflows/{workflow_id}/results")
async def get_workflow_results(workflow_id: str):
"""获取工作流结果"""
workflow_data = redis_client.get(f"workflow:{workflow_id}")
if not workflow_data:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="工作流未找到")
workflow = json.loads(workflow_data)
if workflow["status"] != "completed":
raise HTTPException(
status_code=400,
detail=f"工作流尚未完成,当前状态: {workflow['status']}"
)
return {
"workflow_id": workflow_id,
"results": workflow.get("results", {}),
"summary": {
"total_steps": len(workflow.get("steps", [])),
"successful_steps": len([r for r in workflow.get("results", {}).values()
if r.get("success", False)]),
"start_time": workflow.get("started_at"),
"completion_time": workflow.get("completed_at")
}
}
# WebSocket端点用于实时状态更新
from fastapi import WebSocket
@app.websocket("/workflows/{workflow_id}/ws")
async def workflow_websocket(websocket: WebSocket, workflow_id: str):
"""工作流WebSocket连接"""
await websocket.accept()
# 创建Redis订阅
pubsub = redis_client.pubsub()
pubsub.subscribe("workflow_updates")
try:
# 发送初始状态
workflow_data = redis_client.get(f"workflow:{workflow_id}")
if workflow_data:
await websocket.send_json(json.loads(workflow_data))
# 监听更新
for message in pubsub.listen():
if message["type"] == "message":
update = json.loads(message["data"])
if update["workflow_id"] == workflow_id:
await websocket.send_json(update)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"WebSocket错误: {str(e)}")
finally:
pubsub.close()
# 完整工作流示例
COMPLETE_AI_WORKFLOW = {
"name": "端到端AI模型开发",
"steps": [
{
"name": "数据收集代码生成",
"type": "code_generation",
"prompt": "Create a Python script to collect and preprocess image data from a given directory. Include data augmentation and train/test split.",
"language": "python",
"wait_for_approval": True
},
{
"name": "数据标注任务创建",
"type": "data_labeling",
"dataset_path": "/data/raw_images",
"annotation_type": "object_detection",
"project_name": "Object Detection Dataset",
"wait_for_approval": True
},
{
"name": "模型训练代码生成",
"type": "code_generation",
"prompt": "Create a PyTorch training script for YOLOv5 object detection with distributed training support, learning rate scheduling, and model checkpointing.",
"language": "python"
},
{
"name": "启动分布式训练",
"type": "model_training",
"training_config": {
"framework": "pytorch",
"gpus": 4,
"epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 32
}
},
{
"name": "模型部署到Kubernetes",
"type": "model_deployment",
"model_path": "/models/trained_model.pth",
"deployment_target": "kubernetes",
"replicas": 3
}
]
}
@app.post("/examples/complete-workflow")
async def create_complete_workflow(background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
"""创建完整示例工作流"""
workflow_id = await workflow_manager.create_workflow(
COMPLETE_AI_WORKFLOW["name"],
COMPLETE_AI_WORKFLOW["steps"]
)
background_tasks.add_task(workflow_manager.execute_workflow, workflow_id)
return {
"workflow_id": workflow_id,
"message": "完整AI工作流已创建",
"steps": [step["name"] for step in COMPLETE_AI_WORKFLOW["steps"]]
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
4.3 最佳实践指南
AI工具链实施检查清单:
| 类别 | 检查项 | 重要性 | 完成标准 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 智能编码工具 | 1. 配置团队共享的代码补全规则 | 高 | 所有团队成员使用一致的编码风格 |
| 2. 建立代码审查中的AI辅助标准 | 中 | 审查流程中包含AI建议的评估 | |
| 3. 设置安全扫描和漏洞检测 | 高 | 所有生成的代码通过安全检查 | |
| 4. 创建常用Prompt模板库 | 中 | 团队共享Prompt库覆盖80%常用场景 | |
| 数据标注平台 | 1. 制定数据标注质量标准 | 高 | 明确标注准确率、一致性要求 |
| 2. 建立标注员培训体系 | 中 | 所有标注员通过认证培训 | |
| 3. 实施多层质量检查机制 | 高 | 每批数据经过至少2轮检查 | |
| 4. 配置智能预标注流程 | 中 | 50%以上标注由AI辅助完成 | |
| 模型训练平台 | 1. 设置资源配额和优先级 | 高 | 资源分配符合项目优先级 |
| 2. 实现完整的实验跟踪 | 高 | 所有实验可复现、可比较 | |
| 3. 建立模型版本控制流程 | 高 | 每个生产模型都有完整版本历史 | |
| 4. 配置自动化的CI/CD流水线 | 中 | 代码提交到部署全自动化 | |
| 监控与运维 | 1. 实施模型性能监控 | 高 | 实时监控预测延迟、准确率 |
| 2. 设置数据漂移检测 | 中 | 自动检测输入数据分布变化 | |
| 3. 建立模型回滚机制 | 高 | 发现问题后15分钟内可回滚 | |
| 4. 配置成本监控和优化 | 中 | 资源使用效率持续优化 |
性能优化建议:
python
"""
AI工具链性能优化配置
"""
class PerformanceOptimizer:
"""性能优化配置器"""
@staticmethod
def get_optimized_config(tool_type: str, scale: str) -> Dict:
"""获取优化配置"""
configs = {
"copilot": {
"small_team": {
"cache_size": "1GB",
"max_suggestions": 5,
"context_window": 2048,
"timeout": 2.0
},
"large_team": {
"cache_size": "10GB",
"max_suggestions": 10,
"context_window": 4096,
"timeout": 5.0
},
"enterprise": {
"cache_size": "100GB",
"max_suggestions": 20,
"context_window": 8192,
"timeout": 10.0,
"dedicated_gpu": True
}
},
"labeling": {
"small_project": {
"workers": 10,
"batch_size": 32,
"quality_check_frequency": 0.1,
"auto_labeling_threshold": 0.8
},
"large_project": {
"workers": 100,
"batch_size": 128,
"quality_check_frequency": 0.05,
"auto_labeling_threshold": 0.9,
"distributed_storage": True
}
},
"training": {
"single_gpu": {
"mixed_precision": True,
"gradient_accumulation": 4,
"data_loader_workers": 4,
"pin_memory": True
},
"multi_gpu": {
"distributed_strategy": "ddp",
"mixed_precision": True,
"gradient_checkpointing": True,
"offload_optimizer": True,
"data_loader_workers": 8
},
"large_cluster": {
"distributed_strategy": "deepspeed",
"stage": 2,
"offload_optimizer": True,
"offload_params": True,
"zero_optimization": True,
"data_loader_workers": 16
}
}
}
return configs.get(tool_type, {}).get(scale, {})
@staticmethod
def optimize_training_pipeline(config: Dict) -> Dict:
"""优化训练流水线配置"""
optimized = config.copy()
# 根据硬件配置自动优化
import torch
if torch.cuda.is_available():
gpu_count = torch.cuda.device_count()
gpu_memory = torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0).total_memory / 1e9
if gpu_count >= 4 and gpu_memory >= 24: # 4张24GB GPU
optimized.update({
"batch_size": optimized.get("batch_size", 32) * 4,
"gradient_accumulation": 1,
"mixed_precision": True,
"data_loader_workers": 8
})
elif gpu_count >= 2: # 2张GPU
optimized.update({
"batch_size": optimized.get("batch_size", 32) * 2,
"gradient_accumulation": 2,
"mixed_precision": True,
"data_loader_workers": 4
})
return optimized
@staticmethod
def monitor_performance(metrics: Dict) -> List[str]:
"""监控性能并返回优化建议"""
suggestions = []
# GPU利用率监控
gpu_util = metrics.get("gpu_utilization", 0)
if gpu_util < 0.5:
suggestions.append("GPU利用率低,尝试增大batch size或使用更小的模型")
# 内存使用监控
memory_usage = metrics.get("memory_usage", 0)
if memory_usage > 0.9:
suggestions.append("内存使用过高,考虑使用梯度检查点或模型并行")
# 数据加载瓶颈检测
data_loading_time = metrics.get("data_loading_time_ratio", 0)
if data_loading_time > 0.3:
suggestions.append("数据加载成为瓶颈,增加DataLoader workers或使用内存缓存")
return suggestions
# 使用示例
optimizer = PerformanceOptimizer()
# 获取优化配置
training_config = optimizer.get_optimized_config("training", "multi_gpu")
print("多GPU训练优化配置:", training_config)
# 自动优化
auto_optimized = optimizer.optimize_training_pipeline({
"batch_size": 32,
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"epochs": 100
})
print("自动优化后配置:", auto_optimized)
# 性能监控
metrics = {
"gpu_utilization": 0.3,
"memory_usage": 0.95,
"data_loading_time_ratio": 0.4
}
suggestions = optimizer.monitor_performance(metrics)
print("优化建议:")
for suggestion in suggestions:
print(f" - {suggestion}")
第五章:未来趋势与挑战
5.1 技术发展趋势
2024-2026年AI工具链发展趋势:
-
AI原生开发环境:IDE将深度集成AI功能,从代码补全到架构设计
-
多模态数据标注:支持文本、图像、音频、视频的联合标注
-
联邦学习平台:隐私保护下的分布式模型训练成为标配
-
低代码AI开发:可视化AI工作流构建,降低技术门槛
-
实时模型更新:在线学习和增量学习支持业务快速迭代
5.2 挑战与解决方案
主要挑战及应对策略:
| 挑战类别 | 具体问题 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 技术整合 | 工具间兼容性问题 | 采用标准化接口,开发适配层 |
| 数据隐私 | 敏感数据泄露风险 | 联邦学习、差分隐私、数据脱敏 |
| 成本控制 | GPU资源成本高昂 | 动态扩缩容、Spot实例、模型压缩 |
| 技能缺口 | AI工程人才短缺 | 内部培训、工具自动化、低代码平台 |
| 伦理合规 | AI偏见和公平性问题 | 偏见检测、可解释AI、审计追踪 |
5.3 实施路线图
企业AI工具链实施阶段:
gantt
title AI工具链实施路线图
dateFormat YYYY-MM
axisFormat %Y-%m
section 基础建设
需求分析与规划 :2024-01, 2M
基础设施搭建 :2024-02, 3M
团队培训与准备 :2024-03, 2M
section 工具部署
智能编码工具部署 :2024-04, 2M
数据标注平台部署 :2024-05, 3M
训练平台初步部署 :2024-06, 3M
section 集成优化
工具链初步集成 :2024-09, 3M
工作流自动化 :2025-01, 4M
性能优化与扩展 :2025-05, 4M
section 成熟运营
MLOps文化建立 :2025-09, 6M
持续改进机制 :2026-03, 6M
行业最佳实践贡献 :2026-09, 6M
总结
本文全面探讨了现代AI工具链的三大核心组成部分:智能编码工具、数据标注平台和模型训练系统。通过详细的代码示例、流程图、Prompt模板和最佳实践指南,我们展示了如何构建一个完整的AI开发基础设施。
关键要点总结:
-
智能编码工具如GitHub Copilot可以显著提高开发效率,但需要配合适当的Prompt工程和代码审查流程
-
数据标注平台的质量直接影响模型性能,需要建立完整的质量控制体系和智能辅助标注流程
-
模型训练平台的分布式能力和MLOps实践是实现大规模AI应用的关键
-
工具链集成能够打破各个工具间的壁垒,实现端到端的AI工作流自动化
-
持续监控和优化是确保AI系统长期稳定运行的必要条件
随着AI技术的快速发展,工具链也在不断演进。未来的AI开发将更加自动化、智能化,但同时也需要更多的工程化思维和系统设计能力。希望本文能为读者提供实用的指导,帮助构建高效、可靠的AI开发基础设施。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献309条内容
已为社区贡献309条内容






所有评论(0)