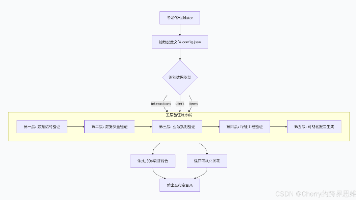
提示模板与大模型交互
模型类型推荐输入格式对应模板类BaseLLM(如OllamaLLMstr或(如ChatOllama或最佳实践不要混用:不要把列表传给,会报错。统一接口:若不确定模型类型,可通过让 LangChain 自动处理转换。
·
在 LangChain 中,提示模板(Prompt Template)是连接用户输入与大语言模型(LLM)的关键桥梁。通过模板,我们可以将动态变量安全、规范地注入到提示中,再交由 LLM 进行推理。
1.1 基础示例:使用 PromptTemplate + OllamaLLM
from langchain_ollama.llms import OllamaLLM
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
import datetime
# 初始化本地 LLM(使用 Ollama 托管的 Qwen3 4B 模型)
llm = OllamaLLM(model="qwen3:4b")
def get_datetime():
now = datetime.datetime.now()
return now.strftime("%m/%d/%Y, %H:%M:%S")
# 定义提示模板(显式声明变量)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="告诉我{city}在{year}年{date}的平均气温",
input_variables=["city", "year", "date"]
)
# 方式一:直接格式化后调用 LLM
message1 = prompt.format(city="上海", year=2025, date=get_datetime())
response1 = llm.invoke(message1)
print(response1)
print("*" * 100)
# 方式二:使用 partial() 预填充部分或全部变量
partial_prompt = prompt.partial(city="成都", date=get_datetime(), year="2025")
response2 = llm.invoke(partial_prompt.format()) # 无需传参
print(response2)说明:
prompt.format()返回的是 字符串(str)llm.invoke()接受该字符串作为输入partial()创建了一个新模板,其部分变量已被固化,后续调用更简洁
1.2 llm.invoke() 的输入类型详解
LangChain 的 invoke() 方法支持多种输入格式,具体取决于所使用的 LLM 类型:
| 输入类型 | 适用场景 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
str |
基础文本推理(适用于非聊天型 LLM) | "你好,请介绍一下量子计算。" |
PromptValue |
使用 PromptTemplate 或 ChatPromptTemplate 生成的中间表示 |
prompt.format_prompt(...) |
List[BaseMessage] |
聊天模型(ChatModel)多轮对话 | [SystemMessage(...), HumanMessage(...)] |
关键区别:基础 LLM vs 聊天模型(ChatModel)
| 特性 | 基础 LLM(如 OllamaLLM, OpenAI 非 chat) |
聊天模型(如 ChatOpenAI, ChatOllama) |
|---|---|---|
| 输入格式 | 字符串(str) 或 PromptValue | 消息列表(List[BaseMessage]) |
| 是否支持角色 | 不支持 | 支持 system / user / assistant |
| 推荐模板 | PromptTemplate |
ChatPromptTemplate |
| 典型用途 | 单次指令、文本生成 | 对话系统、带上下文的问答 |
重要提醒:
- 如果你使用的是
OllamaLLM(继承自BaseLLM),它不接受BaseMessage列表,只接受str。- 若想使用聊天格式,应改用
ChatOllama(属于BaseChatModel)。
1.3 正确选择输入类型
场景1:简单单轮问答(推荐用 str)
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
llm = OllamaLLM(model="qwen3:4b")
response = llm.invoke("解释一下牛顿第一定律。")
场景2:带变量的模板(推荐用 PromptTemplate → str)
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
llm = OllamaLLM(model="qwen3:4b")
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("用{language}解释{concept}")
text = prompt.format(language="中文", concept="相对论")
response = llm.invoke(text)场景3:多轮对话(必须用 ChatPromptTemplate + ChatModel)
from langchain_ollama.chat_models import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
chat_llm = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:4b")
chat_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一名耐心的数学老师。"),
("human", "如何解方程 {equation}?")
])
messages = chat_template.format_messages(equation="x^2 - 4 = 0")
response = chat_llm.invoke(messages) # messages 是 List[BaseMessage]1.4 总结:输入类型与模型匹配关系
| 模型类型 | 推荐输入格式 | 对应模板类 |
|---|---|---|
BaseLLM(如 OllamaLLM) |
str 或 PromptValue.to_string() |
PromptTemplate |
BaseChatModel(如 ChatOllama) |
List[BaseMessage] 或 PromptValue.to_messages() |
ChatPromptTemplate |
最佳实践:
- 不要混用:不要把
BaseMessage列表传给OllamaLLM.invoke(),会报错。- 统一接口:若不确定模型类型,可通过
.invoke(prompt_value)让 LangChain 自动处理转换。
1.5 补充:PromptValue 的作用
PromptValue 是 LangChain 内部用于统一提示表示的抽象类:
.to_string()→ 返回str.to_messages()→ 返回List[BaseMessage]
pv = prompt.format_prompt(city="北京", year=2025, date=get_datetime())
print(pv.to_string()) # 用于基础 LLM
# print(pv.to_messages()) # 仅当 prompt 是 ChatPromptTemplate 时有效1.6结论
PromptTemplate+OllamaLLM→ 生成字符串 → 调用invoke(str)ChatPromptTemplate+ChatOllama→ 生成消息列表 → 调用invoke(List[BaseMessage])partial()可预填充变量,提升复用性和链式调用效率
2.1 LLM.invoke() 输入类型详解
核心结论
| 输入类型 | 类型说明 | 适用模型 | 使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
str |
普通字符串 | 基础 LLM(如 OllamaLLM, OpenAI 非聊天接口) |
简单文本推理 |
PromptValue |
LangChain 内部提示对象,可转换为 str 或 List[BaseMessage] |
所有 LLM / ChatModel | 使用 PromptTemplate 后的中间表示 |
List[BaseMessage] |
消息列表,包含角色(system/human/ai) | 聊天模型(ChatModel) | 多轮对话、复杂交互 |
注意:
PromptValue是一种“统一中间格式”,它能适配不同类型的模型输出需求。
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
llm = OllamaLLM(model="qwen3:4b")
prompt1 = PromptTemplate.from_template("你好,{name}!")
prompt_value1 = prompt1.format(name="小明") # 返回 str
prompt_value2 = prompt1.format_prompt(name="小明") # 返回 PromptValue
response1 = llm.invoke(prompt_value1) # 字符串输入
response2 = llm.invoke(prompt_value2) # PromptValue 输入 输出结果:
print(type(prompt_value1)) # <class 'str'>
print(type(prompt_value2)) # <class 'langchain_core.prompts.prompt.PromptValue'>解释:
format()→ 返回 纯字符串format_prompt()→ 返回 PromptValue 对象
结果说明:
response1和response2实际上是等价的,因为:
prompt_value1 == prompt_value2.to_string() # Truellm.invoke()在内部会自动调用.to_string()将PromptValue转换为str,再传给底层模型。
因此:
PromptValue可以直接用于基础 LLM 的invoke()方法。
2.2ChatModel 场景:使用 List[BaseMessage]
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
chat_llm = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:4b")
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="你是一个有帮助的助手。"),
HumanMessage(content="今天天气怎么样?")
]
print(type(messages)) # <class 'list'>
response = chat_llm.invoke(messages)
print(response)输出结果:
messages是一个List[BaseMessage]chat_llm.invoke(messages)成功执行,并返回一个AIMessage对象(含模型回复)
这种方式适用于支持多轮对话的 ChatModel,例如:
ChatOpenAIChatOllamaChatAnthropic
3.完整示例对比
示例1:基础 LLM + 字符串输入
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM
llm = OllamaLLM(model="qwen3:4b")
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template("你是{role},请回答:{question}")
text = prompt.format(role="物理老师", question="什么是量子纠缠?")
response = llm.invoke(text)
print(response)示例2:基础 LLM + PromptValue 输入
pv = prompt.format_prompt(role="物理老师", question="什么是量子纠缠?")
response = llm.invoke(pv) # 自动转为字符串
print(response)示例3:聊天模型 + 消息列表输入
from langchain_ollama import ChatOllama
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
chat_llm = ChatOllama(model="qwen3:4b")
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="你是一名专业的物理教师。"),
HumanMessage(content="解释一下量子纠缠。")
]
response = chat_llm.invoke(messages)
print(response.content)from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一个助手。"),
("human", "你好!")
])
pv = chat_prompt.format_prompt()
messages = pv.to_messages() # 可以转换为消息列表更多推荐
 已为社区贡献18条内容
已为社区贡献18条内容






所有评论(0)