LangGraph-智能体中Tool的定义
1.Tool:在构建Agent 时,您需要为其提供一个它可以使用的工具列表。
除了实际调用的函数之外,工具还包括几个组件:

ps:如果工具具有好的,名称/描述/args_schema,模型将会有更好的表现
2.智能体调用的时候有4条消息:
1.Human Message,用户输入的消息
2.AI Message,调用工具的指令
3.Tool Message,工具执行之后的结果
4.AI Message,对第三步结果的总结,如果return_direct定义为True,此步骤就省略了,执行到第三步就结果。
3.LangChain 支持从以下对象创建工具:
1.函数;
2.Langchain Runables;
3.通过BaseTool的子类化-这是最灵活的方法,它提供了最大的控制程度,但代价是需要付出更多的努力和编写更多的代码。
ps:还有MCP,这里暂时不讲
3.1--函数的定义方式
这个 @tool 装饰器是定义自定义工具的最简单方法。默认情况下,装饰器使用函数名称作为工具名称,但可以通过将字符串作为第一个参数传递来覆盖。此外,装饰器将使用函数的文档字符串作为工具的描述 - 因此必须提供文档字符串。请注意,@tool 支持解析注释、嵌套模式和其他特性,有几种常见的方法,此次列举几种常见的方法
3.1.1--第一种
@tool()
def calculate1(a:float,b:float,opeartion:str) -> float:
"""工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果"""
print(f"调用calculate工具,第一个数字:{a},第二个数字:{b},运算类型:{opeartion}")
result=0.0
match opeartion:
case "add":
result=a+b
case "subtract":
result=a-b
case "multiply":
result=a*b
case "divide":
if b!=0:
result=a/b
else:
raise ValueError("除数不能为0")
return result
print(calculate1.name)
print(calculate1.description)
print(calculate1.args)
print(calculate1.args_schema.model_json_schema())
print(calculate1.return_direct)这种方式比较简单,但是缺乏对参数的描述,可能会造成模型的了解错误,不推荐使用,此模块单独运行的结果如下:
--calculate1
--工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果
--{'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'number'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'number'}, 'opeartion': {'title': 'Opeartion', 'type': 'string'}}
--{'description': '工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果', 'properties': {'a': {'title': 'A', 'type': 'number'}, 'b': {'title': 'B', 'type': 'number'}, 'opeartion': {'title': 'Opeartion', 'type': 'string'}}, 'required': ['a', 'b', 'opeartion'], 'title': 'calculate1', 'type': 'object'}
--False
3.1.2--第二种
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from pydantic import BaseModel,Field
class CalculateArgs(BaseModel):
a:float=Field(description='第一个需要输入的数字')
b:float=Field(description='第二个需要输入的数字')
operation:str=Field(description='运算类型,add,subtract,multiply,divide')
@tool('calculate',args_schema=CalculateArgs)
def calculate2(a:float,b:float,opeartion:str) -> float:
"""工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果"""
print(f"调用calculate工具,第一个数字:{a},第二个数字:{b},运算类型:{opeartion}")
result=0.0
match opeartion:
case "add":
result=a+b
case "subtract":
result=a-b
case "multiply":
result=a*b
case "divide":
if b!=0:
result=a/b
else:
raise ValueError("除数不能为0")
return result
print(calculate2.name)
print(calculate2.description)
print(calculate2.args)
print(calculate2.args_schema.model_json_schema())
print(calculate2.return_direct)上图是tool模块的代码,单独运行此模块的结果如下:
--calculate
--工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果
--{'a': {'description': '第一个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'A', 'type': 'number'}, 'b': {'description': '第二个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'B', 'type': 'number'}, 'operation': {'description': '运算类型,add,subtract,multiply,divide', 'title': 'Operation', 'type': 'string'}}
--{'properties': {'a': {'description': '第一个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'A', 'type': 'number'}, 'b': {'description': '第二个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'B', 'type': 'number'}, 'operation': {'description': '运算类型,add,subtract,multiply,divide', 'title': 'Operation', 'type': 'string'}}, 'required': ['a', 'b', 'operation'], 'title': 'CalculateArgs', 'type': 'object'}
--False
3.1.3--第三种
from typing import Annotated
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from pydantic import BaseModel,Field
@tool('calculate')
def calculate3(
a:Annotated[float,'第一个需要输入的数字'],
b:Annotated[float,'第二个需要输入的数字'],
operation:Annotated[str,'运算类型,add,subtract,multiply,divide'],) -> float:
"""工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果"""
print(f"调用calculate工具,第一个数字:{a},第二个数字:{b},运算类型:{operation}")
result=0.0
match operation:
case "add":
result=a+b
case "subtract":
result=a-b
case "multiply":
result=a*b
case "divide":
if b!=0:
result=a/b
else:
raise ValueError("除数不能为0")
return result
print(calculate3.name)
print(calculate3.description)
print(calculate3.args)
print(calculate3.args_schema.model_json_schema())
print(calculate3.return_direct)
print(calculate3.invoke({'a': 2, 'b': 3, 'operation': 'multiply'}))上图是tool模块的代码,单独运行此模块的结果如下:
--calculate
--工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果
--{'a': {'description': '第一个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'A', 'type': 'number'}, 'b': {'description': '第二个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'B', 'type': 'number'}, 'operation': {'description': '运算类型,add,subtract,multiply,divide', 'title': 'Operation', 'type': 'string'}}
--{'description': '工具函数:计算两个数字的运算结果', 'properties': {'a': {'description': '第一个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'A', 'type': 'number'}, 'b': {'description': '第二个需要输入的数字', 'title': 'B', 'type': 'number'}, 'operation': {'description': '运算类型,add,subtract,multiply,divide', 'title': 'Operation', 'type': 'string'}}, 'required': ['a', 'b', 'operation'], 'title': 'calculate', 'type': 'object'}
--False
--调用calculate工具,第一个数字:2.0,第二个数字:3.0,运算类型:multiply
6.0
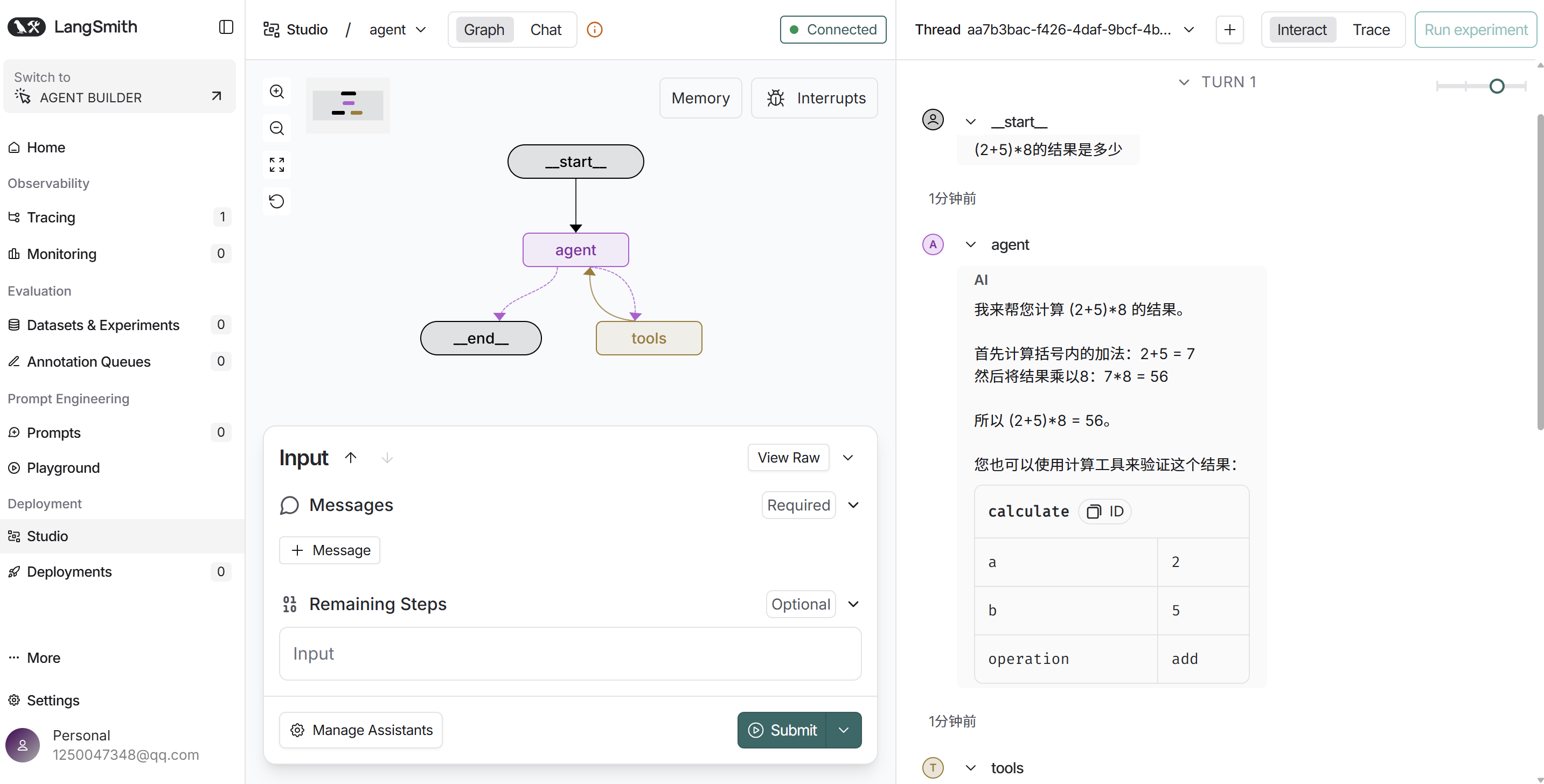
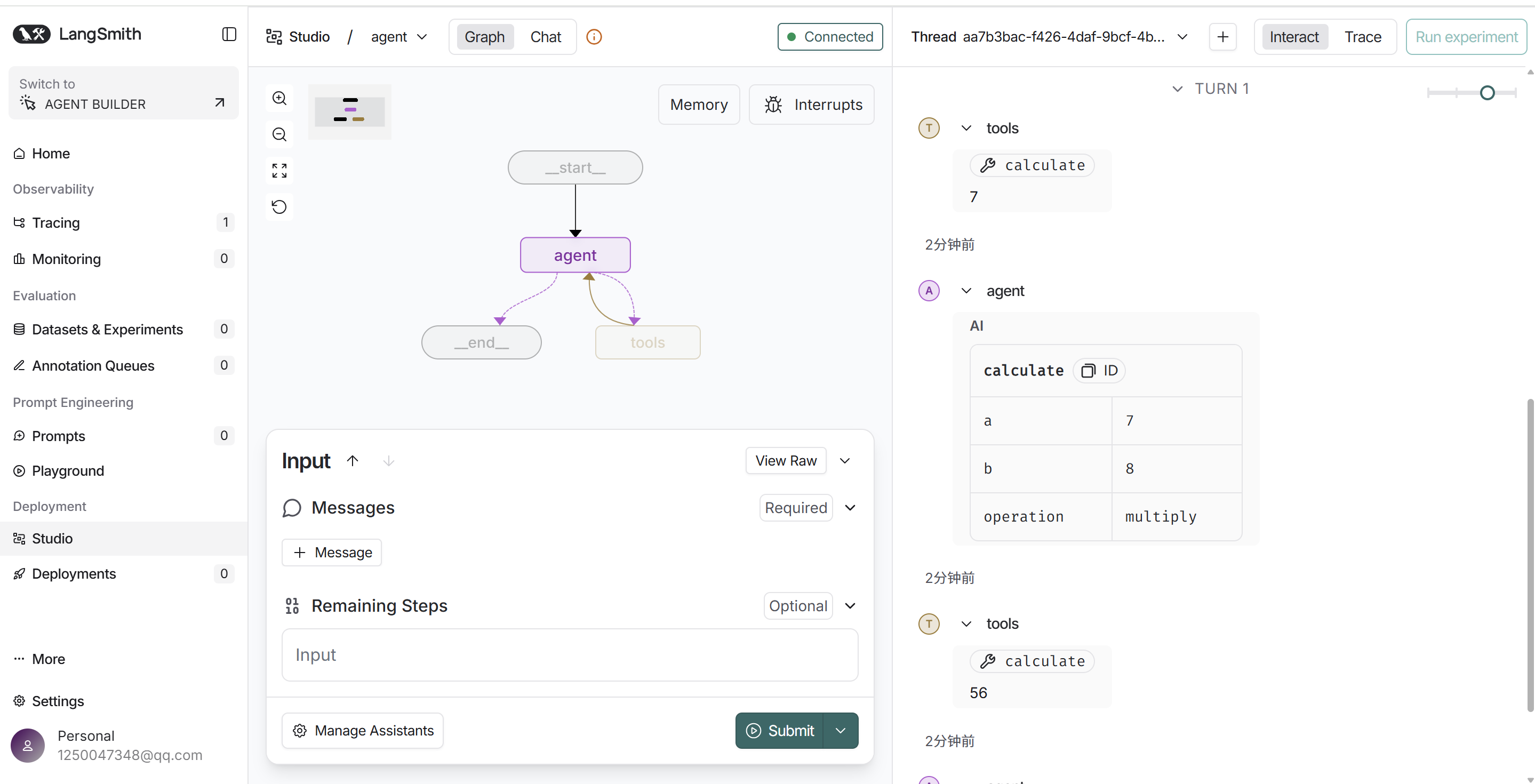
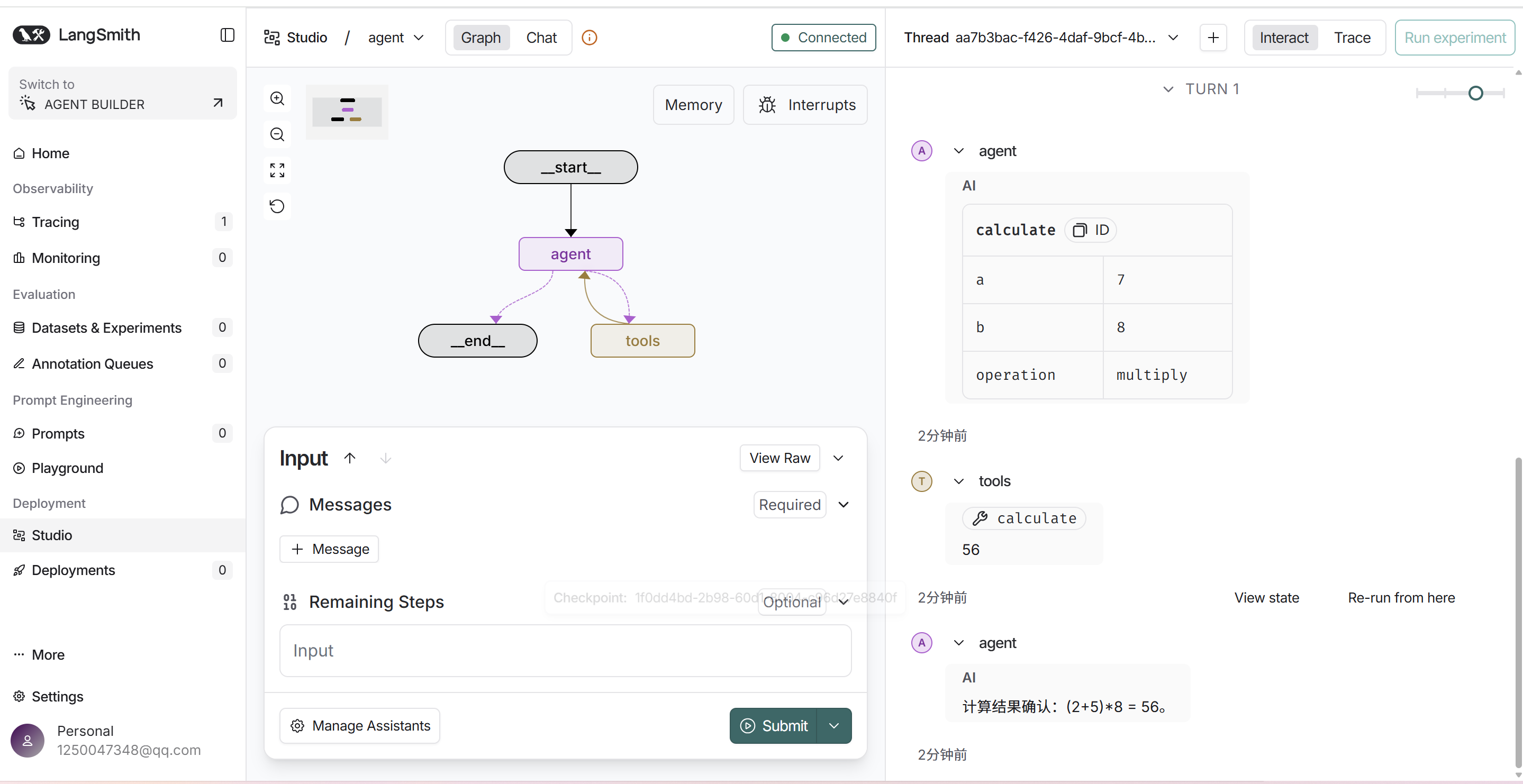
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from agent.tools.tool_demo2 import calculate2
from my_llm import llm
graph = create_react_agent(
llm,
tools=[calculate2],
prompt="你是一个智能助手"
)上图是graph.py的代码,启动langgraph的本地服务后,运行结果如下图,看右侧的运行结果
3.2--从可运行对象(Runable创建工具)
接受字符串或 dict 输入的 LangChain Runnables 可以使用 as_tool 方法转换为工具,该方法允许为参数指定名称、描述和其他模式信息。
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel,Field
from my_llm import llm
prompt=(#外层模板
PromptTemplate.from_template("帮我生成一个简短的关于{topic}报幕词,")
+",要求:1.内容搞笑点"
+"2.输出的内容采用{language}"
)
chain=prompt|llm|StrOutputParser
class ToolArgs(BaseModel):
topic: str = Field(default="", description='报幕词的主题')
language: str = Field(default="中文", description='报幕词采用的语言')
runnable_tool=chain.as_tool(
name='chain_tool',
description='这是一个生成报幕词的工具',
args_schema=ToolArgs,
)
print(runnable_tool.args_schema.model_json_schema())
print(runnable_tool.name)
print(runnable_tool.description)上图是tool模块的代码,单独运行此模块的结果如下:
--{'properties': {'topic': {'default': '', 'description': '报幕词的主题', 'title': 'Topic', 'type': 'string'}, 'language': {'default': '中文', 'description': '报幕词采用的语言', 'title': 'Language', 'type': 'string'}}, 'title': 'ToolArgs', 'type': 'object'}
--chain_tool
--这是一个生成报幕词的工具
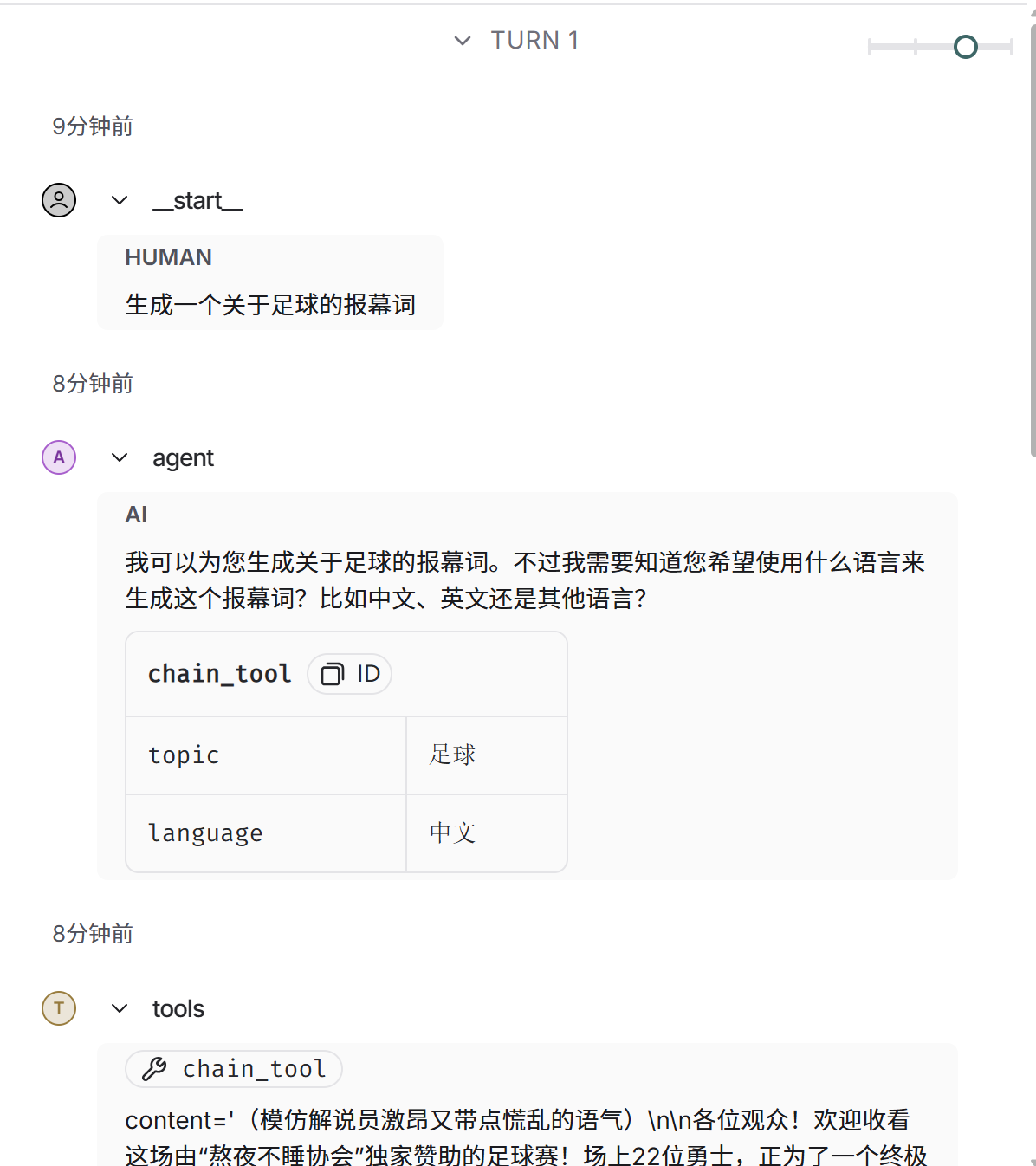
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from agent.tools.tool_demo2 import calculate2
from my_llm import llm
from agent.tools.tool_demo6 import runnable_tool
graph = create_react_agent(
llm,
tools=[calculate2,runnable_tool],
prompt="你是一个智能助手"
)上图是graph.py的代码,启动langgraph的本地服务后,就可以运行
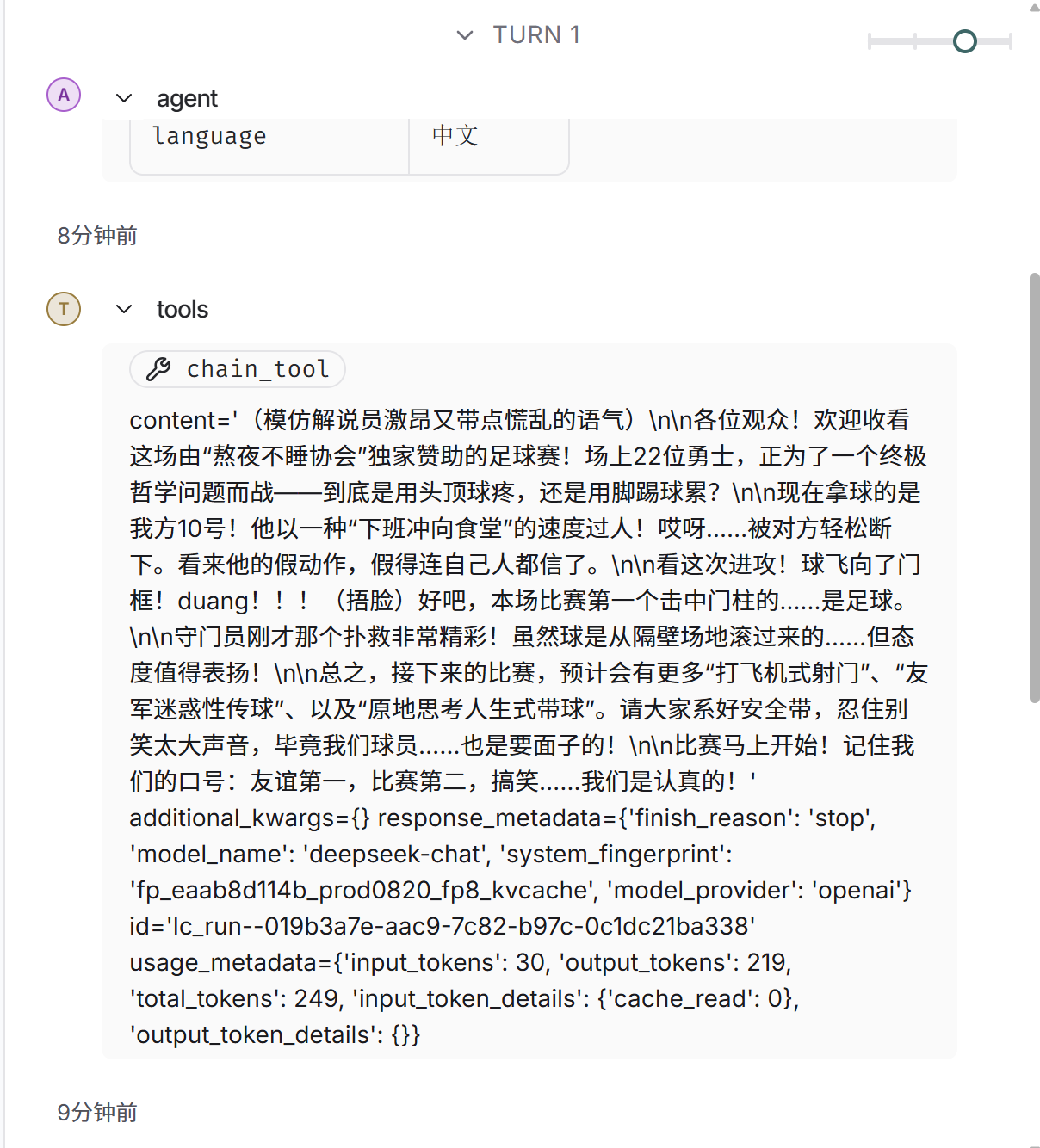

3.3--从可运行对象(Runable创建工具)
通过从 BaseTool 子类化来定义自定义工具
from typing import Any, Type
from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from zhipuai import ZhipuAI
zhipuai_client = ZhipuAI(api_key='xxxxx')
class SearchArgs(BaseModel):
query: str = Field(description="需要进行网络搜索的信息。")
# 网络搜索的工具
class MySearchTool(BaseTool):
# 工具名字
name: str = "search_tool"
description: str = '用于查询实时信息(如天气、新闻、资讯)的工具,当需要获取当前或最新信息时调用,参数为query(查询内容)'
return_direct: bool = False
args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = SearchArgs
def _run(self, query) -> str:
try:
# print("执行我的Python中的工具,输入的参数为:", query)
response = zhipuai_client.web_search.web_search(
search_engine="search_pro",
search_query=query
)
# print(response)
if response.search_result:
return "\n\n".join([d.content for d in response.search_result])
return '没有搜索到任何内容!'
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return '没有搜索到任何内容!'
search_tool = MySearchTool()
print(search_tool.name)
print(search_tool.description)
print(search_tool.args_schema.model_json_schema())
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 单独测试工具
result = search_tool.run({"query": "今天深圳的天气怎么样"})
print("工具返回结果:", result)此模块单独运行的结果如下:

graph.py中的代码如下:
from langchain_core.messages import AnyMessage
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
#from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langgraph.prebuilt.chat_agent_executor import AgentState, create_react_agent
from agent.tools.tool_demo2 import calculate2
from agent.tools.tool_demo6 import runnable_tool
from agent.tools.tool_demo7 import MySearchTool, search_tool
from my_llm import llm
def prompt(state:AgentState,config:RunnableConfig) -> list[AnyMessage]:
user_name=config['configurable'].get('user_name','zs')
print(user_name)
system_message=f"你是一个智能助手,当前的用户名字是:{'user_name'}"
return [{'role':'system','content':system_message}] + state['messages']
graph = create_react_agent(
llm,
tools=[search_tool,calculate2,runnable_tool],
prompt ="""你是一个助手,遵循以下规则:
1. 当用户询问实时信息(如天气、新闻、当前数据),必须调用search_tool工具查询,不能直接回答;
2. 工具返回结果后,整理成自然语言回复用户;
3. 其他任务可直接处理。""",
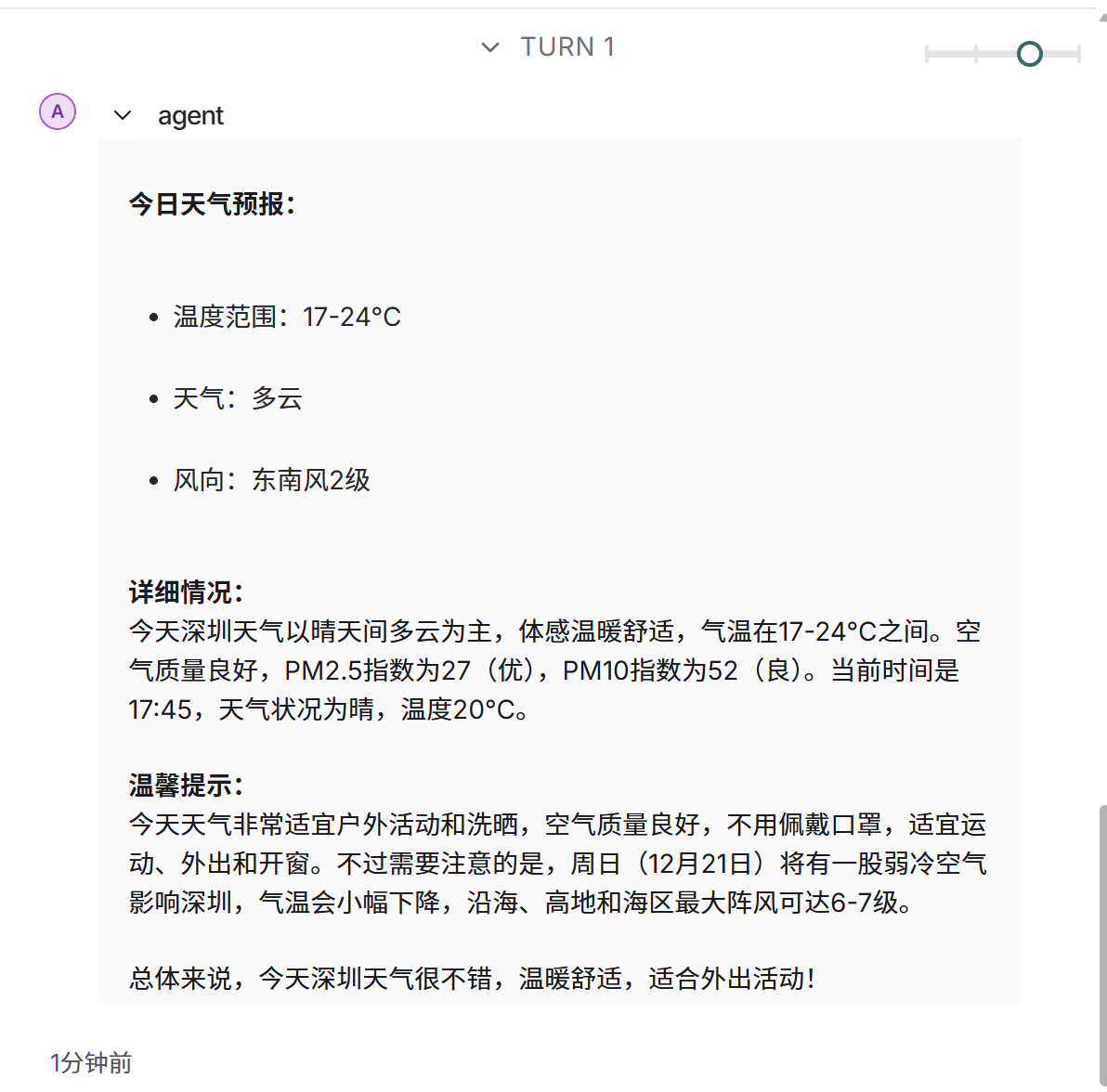
)上图是graph.py的代码,启动langgraph的本地服务后,运行结果如下图
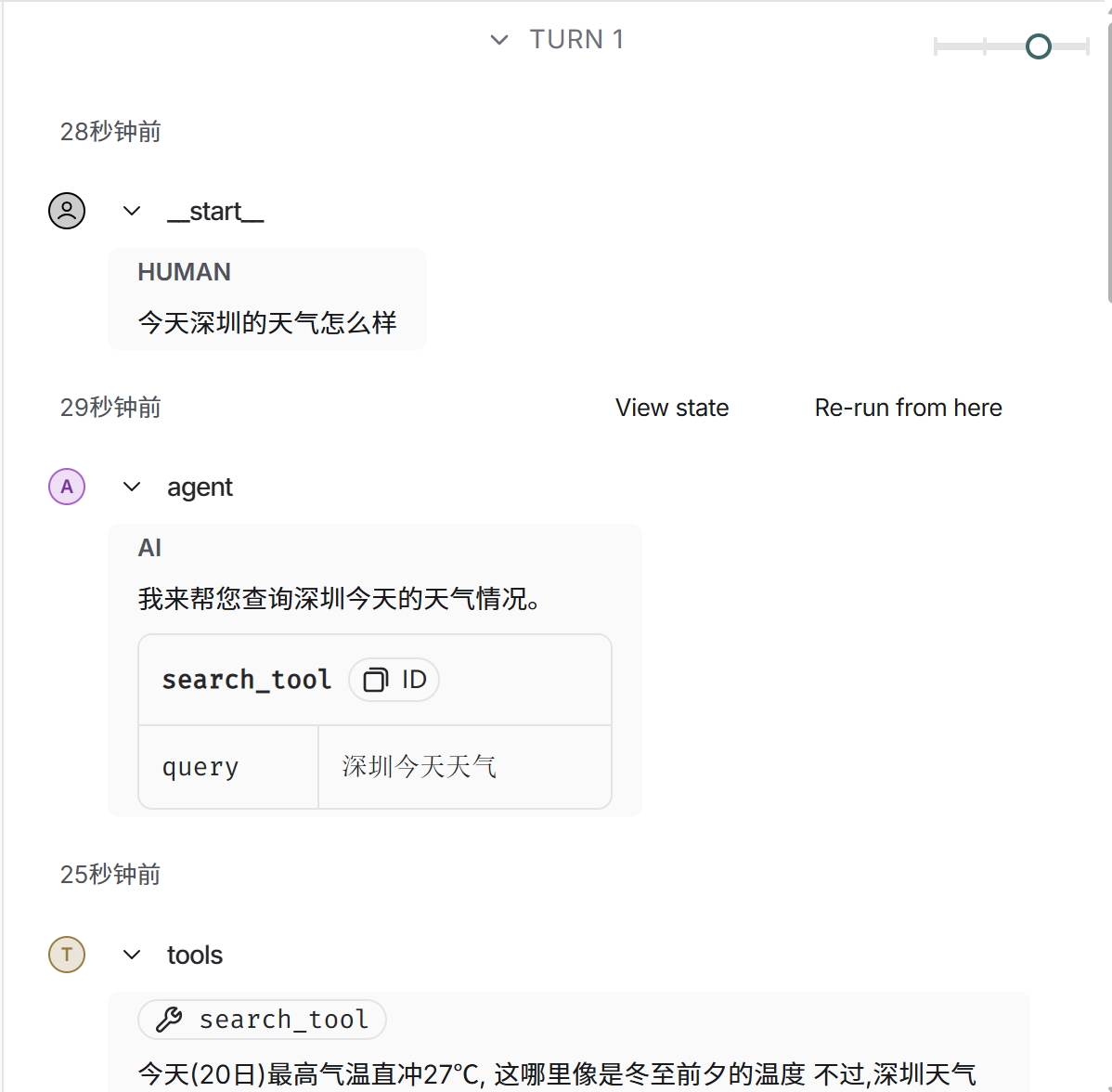
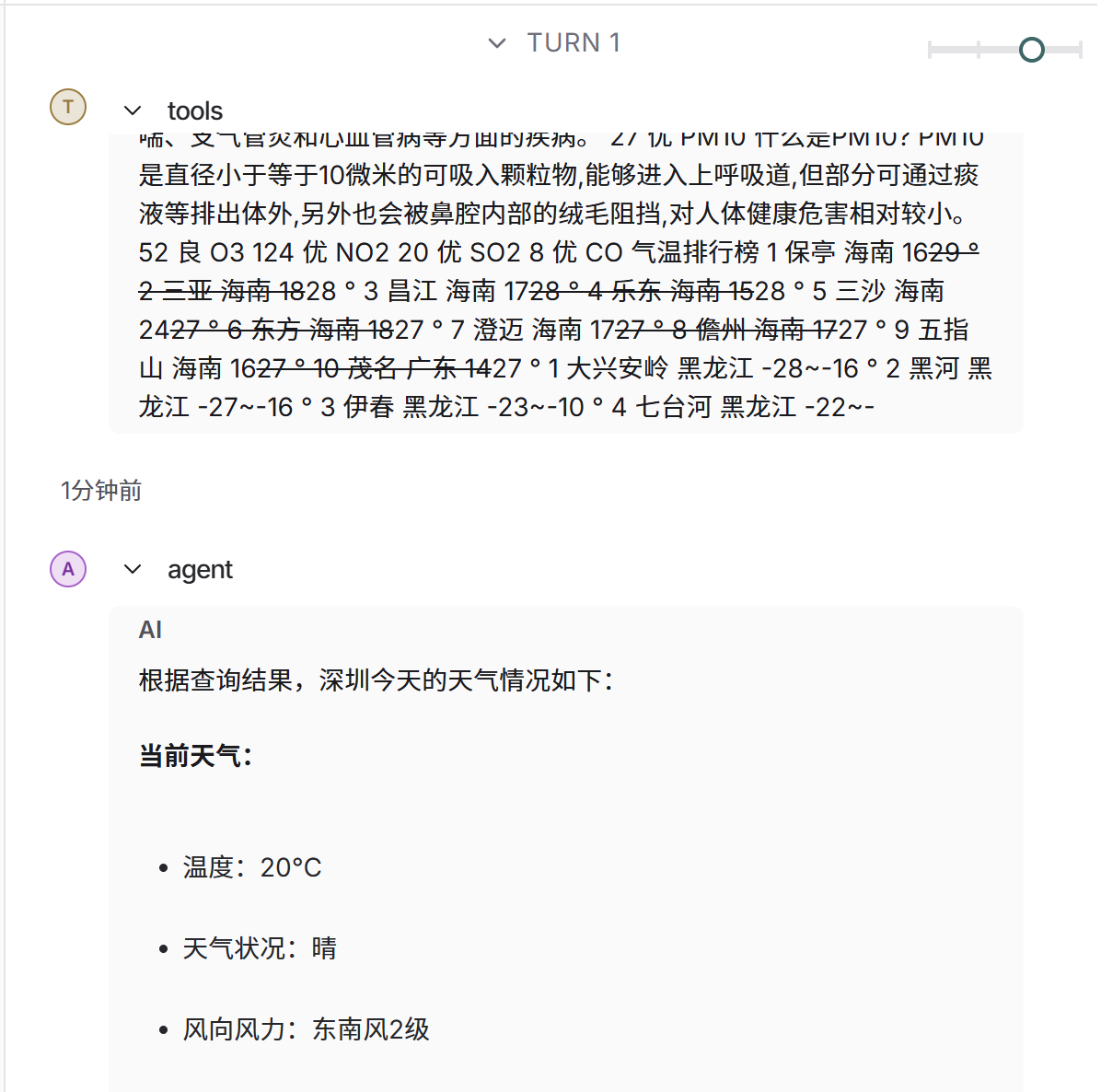
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)