Yolo使用教程
print(f"警告: 未知标签 '{label_name}',跳过此标注")print(f"成功转换: {json_file} -> {base_name}.txt")Train:训练集 图片和标签的合集就叫做训练集 图片文件夹名称images标签文件夹名称 labels。print(f"转换 {json_file} 时出错: {e}")将LabelMe目录中的所有JSON文件转换为YOLO T
一、已有模型的使用
打开YOLO官方地址
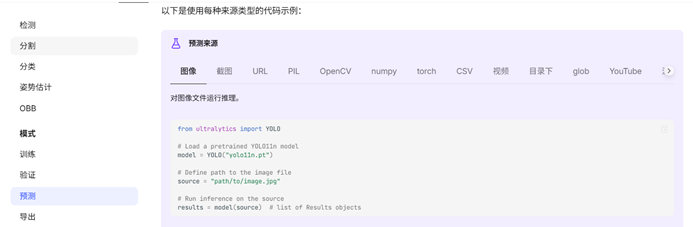
代码如下:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a pretrained YOLO11n model 从不知道什么地方下载训练好的模型
model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt")
# Define path to the image file 定
你的检测素材路径。格式
source = "path/to/image.jpg"
# Run inference on the source 定义你要怎样运行这个模型 一般把 show 改为 True
#像这样 results = model(source,show = True)
results = model(source) # list of Results objects二、训练自己的模型(要用标注工具做好训练集与验证集的)
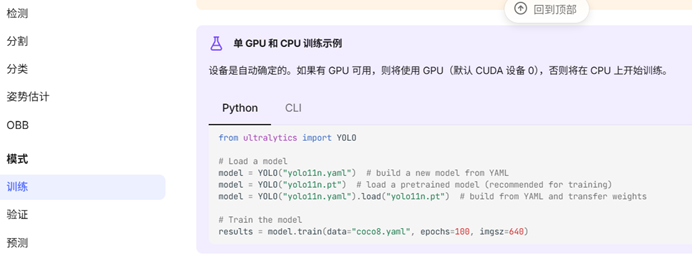
文件夹层级关系
Run_Mode/
├── Train/
│ ├── Images/
│ └── Labels/
├── Val/
│ ├── Images/
│ └── Labels/
└── xxxxxx.yaml
Train:训练集 图片和标签的合集就叫做训练集 图片文件夹名称images 标签文件夹名称 labels
Val:验证集 图片和标签的合集就叫做训练集 图片文件夹名称images 标签文件夹名称 labels
【训练集和验证集的内容不能重复】
【验证集是训练集的10%-20%】
【或者说训练集与验证机8:2】
Yaml文件格式:
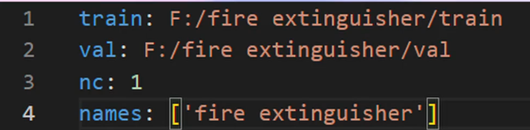
把配置文件(yaml)路径放到data处即可
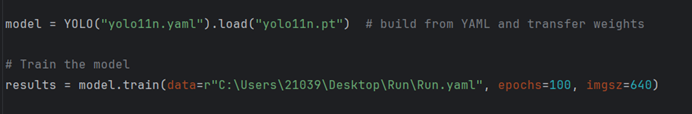
代码:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
#model = YOLO("yolo11n.yaml") # build a new model from YAML
#model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO("yolo11n.yaml").load("yolo11n.pt") # build from YAML and transfer weights
# Train the model 把配置文件(yaml)路径放到data处即可
results = model.train(data="coco8.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640)训练集的构建
数据类型转换
import json
import os
def labelme_polygon_to_yolo_bbox_directory(labelme_json_dir, output_dir, class_mapping=None):
"""将LabelMe目录中的所有JSON文件转换为YOLO TXT格式"""
# 默认类别映射(根据你的实际类别修改)
if class_mapping is None:
class_mapping = {
"person": 0, # 类别0
"car": 1, # 类别1
"bicycle": 2, # 类别2
# 添加更多类别...
}
# 确保输出目录存在
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 遍历目录中的所有JSON文件
for json_file in os.listdir(labelme_json_dir):
if json_file.endswith('.json'):
json_path = os.path.join(labelme_json_dir, json_file)
try:
with open(json_path, 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 创建对应的TXT文件名
base_name = os.path.splitext(json_file)[0]
txt_path = os.path.join(output_dir, f"{base_name}.txt")
img_height = data.get('imageHeight', 640)
img_width = data.get('imageWidth', 480)
with open(txt_path, 'w') as f:
for shape in data.get('shapes', []):
if shape.get('shape_type') == 'polygon':
label_name = shape.get('label', '')
points = shape.get('points', [])
if len(points) < 2:
continue # 跳过无效的多边形
# 获取类别ID
if label_name in class_mapping:
class_id = class_mapping[label_name]
else:
print(f"警告: 未知标签 '{label_name}',跳过此标注")
continue
# 计算外接矩形
x_coords = [p[0] for p in points]
y_coords = [p[1] for p in points]
x_min = min(x_coords)
x_max = max(x_coords)
y_min = min(y_coords)
y_max = max(y_coords)
# 转换为YOLO格式
x_center = (x_min + x_max) / 2 / img_width
y_center = (y_min + y_max) / 2 / img_height
width = (x_max - x_min) / img_width
height = (y_max - y_min) / img_height
# 确保坐标在0-1范围内
x_center = max(0, min(1, x_center))
y_center = max(0, min(1, y_center))
width = max(0, min(1, width))
height = max(0, min(1, height))
# 写入YOLO格式,包含正确的类别ID
f.write(f"{class_id} {x_center:.6f} {y_center:.6f} {width:.6f} {height:.6f}\n")
print(f"成功转换: {json_file} -> {base_name}.txt")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换 {json_file} 时出错: {e}")
# 使用示例
labelme_polygon_to_yolo_bbox_directory(
labelme_json_dir=r"C:\Users\21039\Desktop\Run\val\json",
output_dir=r"C:\Users\21039\Desktop\Run\val\labels",
class_mapping={
"cat": 0, # 猫 - 类别0
"dog": 1, # 狗 - 类别1
"bird": 2, # 鸟 - 类别2
}Model的参数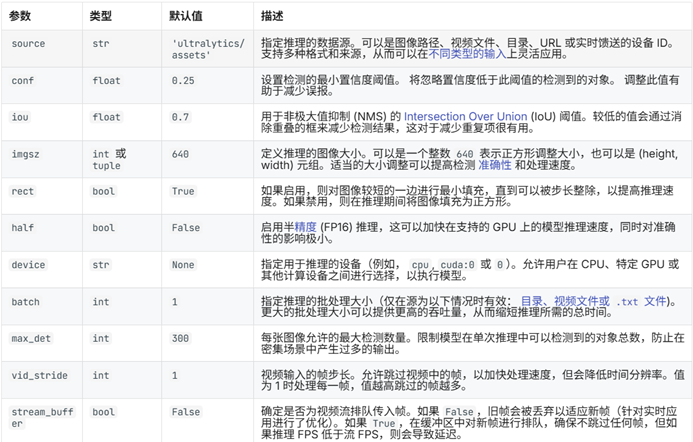
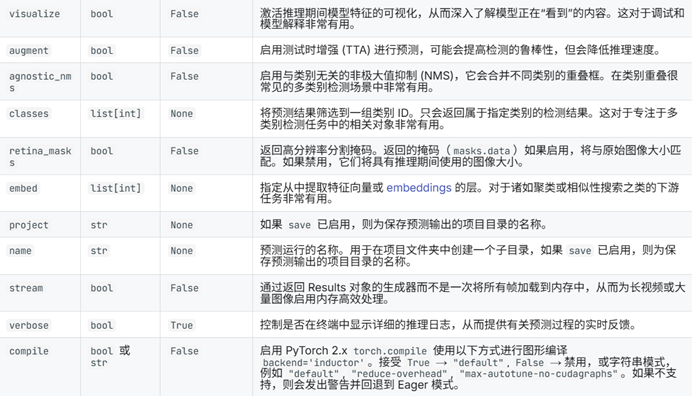

补充 ::
另一种数据处理方式
2. 输入文件层级要求
原始数据目录/
├── image_dir/ # 所有原始图片(.jpg/png)
│ ├── image1.jpg
│ ├── image2.jpg
│ └── ...
└── txt_dir/ # 所有标签文件(.txt/json)
├── image1.txt
├── image2.txt
└── ...
数据处理代码
import shutil
import random
import os
import argparse
import json
# 支持的图片格式列表
SUPPORTED_IMAGE_FORMATS = ['.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.bmp', '.tiff', '.tif']
# 检查文件夹是否存在
def mkdir(path):
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
def find_image_file(image_dir, base_name):
"""根据基础文件名查找图片文件,支持多种格式"""
for ext in SUPPORTED_IMAGE_FORMATS:
image_path = os.path.join(image_dir, base_name + ext)
if os.path.exists(image_path):
return image_path
return None
def convert_labelme_to_yolo_bbox(json_path, output_txt_path, class_mapping=None):
"""将单个LabelMe JSON文件转换为YOLO TXT格式"""
# 默认类别映射(根据你的实际类别修改)
if class_mapping is None:
class_mapping = {
"person": 0, # 类别0
"car": 1, # 类别1
"bicycle": 2, # 类别2
# 添加更多类别...
}
try:
with open(json_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
img_height = data.get('imageHeight', 640)
img_width = data.get('imageWidth', 480)
with open(output_txt_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for shape in data.get('shapes', []):
if shape.get('shape_type') == 'polygon':
label_name = shape.get('label', '')
points = shape.get('points', [])
if len(points) < 2:
continue # 跳过无效的多边形
# 获取类别ID
if label_name in class_mapping:
class_id = class_mapping[label_name]
else:
print(f"警告: 未知标签 '{label_name}',跳过此标注")
continue
# 计算外接矩形
x_coords = [p[0] for p in points]
y_coords = [p[1] for p in points]
x_min = min(x_coords)
x_max = max(x_coords)
y_min = min(y_coords)
y_max = max(y_coords)
# 转换为YOLO格式
x_center = (x_min + x_max) / 2 / img_width
y_center = (y_min + y_max) / 2 / img_height
width = (x_max - x_min) / img_width
height = (y_max - y_min) / img_height
# 确保坐标在0-1范围内
x_center = max(0, min(1, x_center))
y_center = max(0, min(1, y_center))
width = max(0, min(1, width))
height = max(0, min(1, height))
# 写入YOLO格式,包含正确的类别ID
f.write(f"{class_id} {x_center:.6f} {y_center:.6f} {width:.6f} {height:.6f}\n")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换 {json_path} 时出错: {e}")
return False
def process_annotation_files(txt_dir, temp_txt_dir, class_mapping=None):
"""处理标注文件:如果是json则转换为txt,如果是txt则直接复制"""
mkdir(temp_txt_dir)
# 获取所有标注文件
annotation_files = [f for f in os.listdir(txt_dir) if f.endswith('.txt') or f.endswith('.json')]
for ann_file in annotation_files:
base_name = os.path.splitext(ann_file)[0]
src_path = os.path.join(txt_dir, ann_file)
dst_path = os.path.join(temp_txt_dir, base_name + '.txt')
if ann_file.endswith('.json'):
# JSON文件:转换为TXT
print(f"转换JSON文件: {ann_file} -> {base_name}.txt")
convert_labelme_to_yolo_bbox(src_path, dst_path, class_mapping)
else:
# TXT文件:直接复制
print(f"复制TXT文件: {ann_file}")
shutil.copyfile(src_path, dst_path)
return temp_txt_dir
def main(image_dir, txt_dir, save_dir, class_mapping=None):
# 创建临时目录用于存放处理后的TXT文件
temp_txt_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'temp_txt')
# 处理标注文件:JSON转TXT或直接复制TXT
processed_txt_dir = process_annotation_files(txt_dir, temp_txt_dir, class_mapping)
# 创建文件夹
mkdir(save_dir)
images_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'images')
labels_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'labels')
img_train_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'train')
img_test_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'test')
img_val_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'val')
label_train_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'train')
label_test_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'test')
label_val_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'val')
mkdir(images_dir)
mkdir(labels_dir)
mkdir(img_train_path)
mkdir(img_test_path)
mkdir(img_val_path)
mkdir(label_train_path)
mkdir(label_test_path)
mkdir(label_val_path)
# 数据集划分比例,训练集75%,验证集15%,测试集15%,按需修改
train_percent = 0.9
val_percent = 0.1
test_percent = 0
total_txt = os.listdir(processed_txt_dir)
num_txt = len(total_txt)
list_all_txt = range(num_txt) # 范围 range(0, num)
num_train = int(num_txt * train_percent)
num_val = int(num_txt * val_percent)
num_test = num_txt - num_train - num_val
train = random.sample(list_all_txt, num_train)
# 在全部数据集中取出train
val_test = [i for i in list_all_txt if not i in train]
# 再从val_test取出num_val个元素,val_test剩下的元素就是test
val = random.sample(val_test, num_val)
print("训练集数目:{}, 验证集数目:{},测试集数目:{}".format(len(train), len(val), len(val_test) - len(val)))
for i in list_all_txt:
name = total_txt[i][:-4] # 去掉.txt后缀
# 查找对应的图片文件
srcImage = find_image_file(image_dir, name)
srcLabel = os.path.join(processed_txt_dir, name + '.txt')
if srcImage is None:
print(f"警告: 找不到与标注文件 {name}.txt 对应的图片文件")
continue
# 获取图片文件的扩展名
_, image_ext = os.path.splitext(srcImage)
if i in train:
dst_train_Image = os.path.join(img_train_path, name + image_ext)
dst_train_Label = os.path.join(label_train_path, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_train_Image)
shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_train_Label)
elif i in val:
dst_val_Image = os.path.join(img_val_path, name + image_ext)
dst_val_Label = os.path.join(label_val_path, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_val_Image)
shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_val_Label)
else:
dst_test_Image = os.path.join(img_test_path, name + image_ext)
dst_test_Label = os.path.join(label_test_path, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_test_Image)
shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_test_Label)
# 清理临时目录
try:
shutil.rmtree(temp_txt_dir)
print("临时目录已清理")
except:
print("警告: 临时目录清理失败")
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
使用示例:
python split_datasets.py --image-dir my_datasets/color_rings/imgs --txt-dir my_datasets/color_rings/annotations --save-dir my_datasets/color_rings/train_data
注意:txt-dir目录可以包含.txt文件或.json文件,程序会自动处理
"""
# 在这里定义你的类别映射
CLASS_MAPPING = {
"bucket": 0, # 猫 - 类别0
# 根据你的实际类别添加更多映射...
}
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='split datasets to train,val,test params')
parser.add_argument('--image-dir', type=str, default=r'C:\Users\21039\Desktop\Test\images',
help='image path dir')
parser.add_argument('--txt-dir', type=str, default=r'C:\Users\21039\Desktop\Test\labels',
help='annotation path dir (can contain .txt or .json files)')
parser.add_argument('--save-dir', default=r'C:\Users\21039\Desktop\Test\sava', type=str,
help='save dir')
args = parser.parse_args()
image_dir = args.image_dir
txt_dir = args.txt_dir
save_dir = args.save_dir
main(image_dir, txt_dir, save_dir, CLASS_MAPPING)- 转换程序输出 → YAML配置路径
save_dir/ path: ../datasets/coco8
├── images/ train: images/train
│ ├── train/ val: images/val
│ ├── val/
│ └── test/
└── labels/
├── train/
├── val/
└── test/
示例代码:
path: ../datasets/coco8 # dataset root dir
train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes (有几个写几个就行了)
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
2: car
3: motorcycle
# ⋮
# ⋮更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)