SpringBoot集成本地Ollama部署大模型,调用MCP服务demo示例
Ollama是一个本地运行大型语言模型的工具,支持Llama、Mistral等开源模型。安装方法包括Windows下载安装包或Linux使用命令行安装,安装后可通过命令验证。用户可从模型广场选择并下载模型,运行后即可本地使用。此外,文章介绍了MCP服务(Model Context Protocol),这是一种让AI模型调用外部工具的协议,通过SpringBoot开发示例展示了天气查询服务的实现,包
Ollama本地安装大模型
Ollama是什么
Ollama 是一个让用户能够在本地计算机上轻松运行、管理和部署大型语言模型的工具。它支持多种开源模型,包括 Llama、Mistral、CodeLlama 等。官网地址https://ollama.com/
本地部署
首先,需要先安装Ollama程序,这里以windows为例,去官网https://ollama.com/download下载安装包
linux系统通过命令curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh一键安装,安装完成后,通过命令ollama --version验证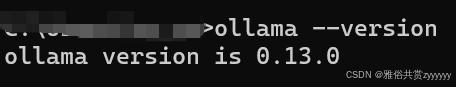
然后,我们去模型广场看一下都可以安装哪些模型,官网https://ollama.com/search,然后点击想要部署的模型,进到详情页,复制命令即可下载部署ollama run gpt-oss:20b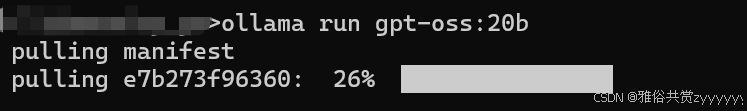
安装完成后,默认启动,这时,可以问一些问题,至此,本地通过Ollama部署大模型完成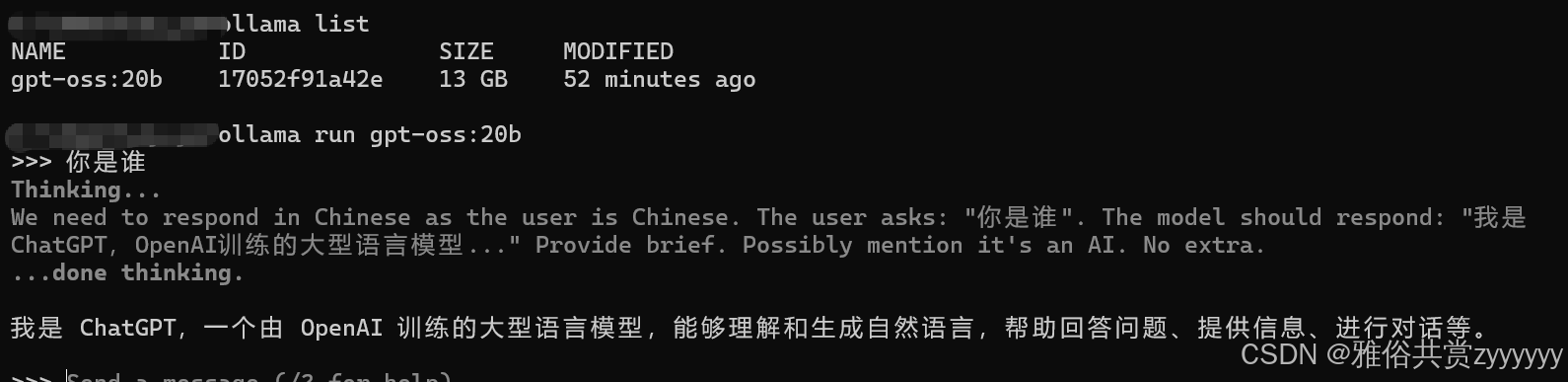
MCP服务
MCP是什么
MCP(Model Context Protocol)服务是一种协议,用于在AI应用和外部工具/服务之间建立标准化的通信方式。它允许AI模型动态调用外部工具,扩展模型的能力。我们知道大模型是基于训练数据的,无法获取最新的天气、新闻等事实信息,无法访问企业内部数据或私有信息,通过MCP服务,我们可以将外部API调用、内部系统调用包装,提供给大模型使用。
SpringBoot开发MCP服务
需要准备SpringBoot3.x版本以及jdk17+版本,首先,引入相关依赖
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring-ai.version>1.0.0</spring-ai.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-bom</artifactId>
<version>${spring-ai.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring AI MCP Server -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webmvc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.nashorn</groupId>
<artifactId>nashorn-core</artifactId>
<version>15.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
开发MCP服务能力,例如天气查询,这里通过MOCK方式
@Service
@Slf4j
public class WeatherService {
private final Map<String, String> cityWeatherData;
private final Random random = new Random();
public WeatherService() {
// 模拟天气数据
cityWeatherData = new HashMap<>();
cityWeatherData.put("北京", "晴, 25°C, 湿度 60%");
cityWeatherData.put("上海", "多云, 28°C, 湿度 70%");
cityWeatherData.put("广州", "雨, 30°C, 湿度 85%");
cityWeatherData.put("深圳", "晴, 32°C, 湿度 75%");
cityWeatherData.put("杭州", "阴, 26°C, 湿度 65%");
}
@Tool(description = "根据城市名称获取实时天气信息")
public String getWeatherByCity(
@ToolParam(description = "城市名称,例如:北京、上海、广州") String city) {
log.info("getWeatherByCity city: {}", city);
if (city == null || city.trim().isEmpty()) {
return "错误:城市名称不能为空";
}
String weather = cityWeatherData.get(city);
if (weather != null) {
return String.format("城市【%s】的天气:%s", city, weather);
} else {
// 如果城市不在预设列表中,生成随机天气
String[] conditions = {"晴", "多云", "阴", "小雨"};
String condition = conditions[random.nextInt(conditions.length)];
int temperature = 20 + random.nextInt(15); // 20-35°C
int humidity = 50 + random.nextInt(40); // 50-90%
return String.format("城市【%s】的天气:%s, %d°C, 湿度 %d%%",
city, condition, temperature, humidity);
}
}
@Tool(description = "获取未来几天的天气预报")
public String getWeatherForecast(
@ToolParam(description = "城市名称") String city,
@ToolParam(description = "预报天数,1-7天") int days) {
log.info("getWeatherForecast city: {}, days: {}", city, days);
if (days < 1 || days > 7) {
return "错误:预报天数应在1-7天范围内";
}
StringBuilder forecast = new StringBuilder();
forecast.append(String.format("【%s】未来%d天天气预报:\n", city, days));
String[] conditions = {"晴", "多云", "阴", "小雨", "中雨", "雷阵雨"};
for (int i = 1; i <= days; i++) {
String condition = conditions[random.nextInt(conditions.length)];
int minTemp = 18 + random.nextInt(10);
int maxTemp = minTemp + 5 + random.nextInt(5);
forecast.append(String.format("第%d天:%s,温度 %d-%d°C\n",
i, condition, minTemp, maxTemp));
}
return forecast.toString();
}
@Tool(description = "获取空气质量指数(AQI)")
public String getAirQuality(
@ToolParam(description = "城市名称") String city) {
log.info("getAirQuality city: {}", city);
String[] levels = {"优", "良", "轻度污染", "中度污染", "重度污染"};
String level = levels[random.nextInt(levels.length)];
int aqi = 20 + random.nextInt(200); // 20-220
return String.format("城市【%s】的空气质量:AQI指数 %d,等级 %s", city, aqi, level);
}
}
然后,配置一个管理嘞对外暴露这些工具,也就是MCP服务
@Configuration
public class McpConfig {
@Bean
public ToolCallbackProvider weatherTools(WeatherService weatherService){
return MethodToolCallbackProvider.builder()
.toolObjects(weatherService)
.build();
}
}
最后,添加相应的配置
server.port=9090
spring.ai.mcp.server.name=mcp-sdk-server-demo
spring.ai.mcp.server.version=1.0.0
# sync表示同步通信模式,在这种模式下,客户端发送请求后,服务器会立即处理并返回结果
spring.ai.mcp.server.type=sync
# sse-endpoint配置 SSE 服务器的端点路径,当使用异步或流式模式时,客户端会通过这个端点连接到 SSE 服务器
spring.ai.mcp.server.sse-endpoint=/sse
启动MCP服务即可,然后访问http://localhost:9090/sse可以看到响应信息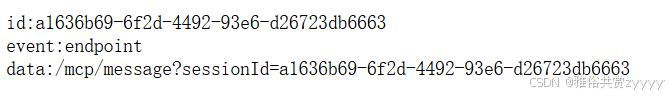
智能体服务
什么是智能体
在Spring AI的上下文中,智能体通常由一个大语言模型(LLM)作为核心,并配备了一系列工具(例如MCP服务提供的工具)来扩展其能力。智能体可以根据用户输入决定是否调用工具、调用哪个工具,并将工具的结果整合到对用户的响应中。简单来说,智能体 = 大语言模型 + 工具调用能力 + 决策逻辑。在我们的例子中,我们有一个MCP服务(工具服务器)和一个智能体(AI应用)。智能体通过MCP客户端调用MCP服务器上的工具,从而获取实时天气、进行计算等。
SpringBoot开发智能体Demo
引入必要的依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring AI Ollama 适配器(调用本地 Ollama 模型) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<!-- <artifactId>spring-ai-ollama-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>-->
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-ollama</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-M7</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring AI MCP 客户端(调用 MCP 服务工具)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-mcp-client</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-M7</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
定义MCP客户端,用来调用MCP服务端
@Service
@Slf4j
public class McpClientService {
private McpSyncClient syncClient;
@Value("${mcp.server.url:http://localhost:9090}")
private String mcpServerUrl;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
connectToMcpServer();
}
/**
* 连接到MCP服务器
*/
private void connectToMcpServer() {
try {
String fullUrl = mcpServerUrl;
log.info("🔄 正在连接 MCP 服务器: {}", fullUrl);
HttpClientSseClientTransport transport = new HttpClientSseClientTransport(fullUrl);
this.syncClient = McpClient.sync(transport).build();
this.syncClient.initialize();
// 测试连接
testConnection();
log.info("✅ MCP 客户端连接成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("❌ MCP 客户端连接失败: {}", e.getMessage());
this.syncClient = null;
// 可以添加重试逻辑
scheduleReconnect();
}
}
/**
* 重连机制
*/
private void scheduleReconnect() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000); // 5秒后重试
connectToMcpServer();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
/**
* 测试连接并列出可用工具
*/
public void testConnection() {
log.info("🧪 测试 MCP 客户端连接...");
List<String> tools = listAvailableTools();
if (tools.isEmpty()) {
log.warn("⚠️ 未找到可用工具,请检查 MCP 服务配置");
} else {
log.info("✅ 发现 {} 个可用工具: {}", tools.size(), tools);
}
}
/**
* 列出所有可用工具
*/
public List<String> listAvailableTools() {
if (!isConnected()) {
log.warn("⚠️ MCP 客户端未连接");
return Collections.emptyList();
}
try {
McpSchema.ListToolsResult result = syncClient.listTools();
List<String> toolNames = result.tools().stream()
.map(McpSchema.Tool::name)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return toolNames;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("❌ 列出工具失败: {}", e.getMessage());
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
/**
* 检查连接状态
*/
public boolean isConnected() {
return syncClient != null;
}
/**
* 调用 MCP 工具
*/
public String callTool(String toolName, Map<String, Object> params) {
if (!isConnected()) {
log.warn("⚠️ MCP 客户端未连接,尝试重新连接...");
connectToMcpServer();
if (!isConnected()) {
return "错误:MCP 服务不可用,请检查服务是否启动";
}
}
try {
log.info("🛠️ 调用工具: {},参数: {}", toolName, params);
McpSchema.CallToolRequest request = new McpSchema.CallToolRequest(toolName, params);
McpSchema.CallToolResult result = syncClient.callTool(request);
String content = result.content().toString();
log.info("✅ 工具调用成功: {}", content);
return content;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("❌ 工具调用失败: {}", e.getMessage());
return "工具调用错误: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
if (syncClient != null) {
try {
syncClient.closeGracefully();
log.info("🔌 MCP 客户端连接已关闭");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("⚠️ 关闭连接时出错: {}", e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public List<McpSchema.Tool> listTools() {
if (!isConnected()) {
log.warn("⚠️ MCP 客户端未连接");
return Collections.emptyList();
}
try {
McpSchema.ListToolsResult result = syncClient.listTools();
List<McpSchema.Tool> tools = result.tools();
return tools;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("❌ 列出工具失败: {}", e.getMessage());
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
}
定义一个工具注册类,Spring AI框架通过@Tool注解来识别和注册工具。当Agent需要调用工具时,它可以通过这些注册的工具来执行具体操作
@Service
public class McpServiceRegister {
@Autowired
private McpClientService mcpClientService;
@Tool(name = "getWeatherByCity", description = "根据城市名称查询实时天气信息")
public String getWeatherByCity(
@ToolParam(description = "城市名称,例如:北京、上海、广州") String city) {
Map<String, Object> params = Map.of("city", city);
return mcpClientService.callTool("getWeatherByCity", params);
}
@Tool(name = "getWeatherForecast", description = "获取未来几天的天气预报")
public String getWeatherForecast(
@ToolParam(description = "城市名称") String city,
@ToolParam(description = "预报天数,1-7天") int days) {
Map<String, Object> params = Map.of("city", city, "days", days);
return mcpClientService.callTool("getWeatherForecast", params);
}
@Tool(name = "getAirQuality", description = "获取空气质量指数(AQI)")
public String getAirQuality(
@ToolParam(description = "城市名称") String city) {
Map<String, Object> params = Map.of("city", city);
return mcpClientService.callTool("getAirQuality", params);
}
}
然后,还需要一个工具回调类,这个 Bean 负责将 McpServiceRegister中所有使用 @Tool注解的方法注册为 AI 模型可以调用的工具。这样,当 AI 模型在处理用户请求时,它能够知道有哪些工具可用,以及如何调用这些工具。
@Configuration
public class McpConfig {
@Bean
@Primary
public ToolCallbackProvider toolCallbackProvider(McpServiceRegister mcpServiceRegister) {
return MethodToolCallbackProvider.builder()
.toolObjects(mcpServiceRegister)
.build();
}
}
这样,我们就可以理解为什么MCP服务端已经定义了工具,为什么还要在客户端重新写一次工具注册,因为我们的工具回调需要传入工具,而我们没有实现工具自动发现注册,因此通过这种方式将工具注册进来。
最后,实现一个聊天接口,通过对prompt(提示词)的定义,给模型一个任务描述或问题,模型基于这个Prompt来生成相应的回答或内容。
@RestController
public class McpController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private static final String SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
你是一个智能助手,请根据问题类型选择合适的回答方式:
## 可用工具(仅用于特定问题):
1. 天气相关工具:
- getWeatherByCity: 查询城市实时天气
- getWeatherForecast: 获取天气预报
- getAirQuality: 获取空气质量
2. 计算相关工具:
- calculate: 执行数学计算
- convertUnit: 单位换算
## 回答规则:
### 必须调用工具的情况(工具类问题):
- 询问具体城市天气、天气预报、空气质量
- 询问数学计算、算术表达式
- 询问单位换算(温度、长度等)
### 使用自身知识回答的情况(非工具类问题):
- 一般性知识问答、常识问题
- 聊天、问候、自我介绍
- 编程、技术问题
- 历史、文化、科学等知识性问题
- 建议、意见、创意类问题
### 禁止行为:
- 对于非工具类问题,不要尝试调用工具
- 不要编造天气或计算数据
- 不确定时如实告知,不要猜测
### 注意:
- 当你调用工具获取信息后,必须基于工具返回的结果来回答用户
- 不要拒绝使用工具返回的数据,这些数据是专门为用户问题准备的
- 如果工具返回了计算结果,直接使用该结果回答用户
## 示例:
用户:北京天气怎么样? → 调用getWeatherByCity工具
用户:计算2+3 * 4 → 调用calculate工具
用户:你好! → 用自身知识友好回应
用户:Java是什么? → 用自身知识解释
用户:给我讲个笑话 → 用自身知识创作笑话
请根据问题类型智能选择回答方式。
""";
@Autowired
public McpController(OllamaChatModel ollamaChatModel,
ToolCallbackProvider toolCallbackProvider) {
this.chatClient = buildChatClient(ollamaChatModel, toolCallbackProvider);
}
private ChatClient buildChatClient(OllamaChatModel chatModel,
ToolCallbackProvider toolCallbackProvider) {
return ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(toolCallbackProvider.getToolCallbacks())
.build();
}
@RequestMapping("/mcp")
public String mcp(@RequestParam String message) {
return chatClient.prompt(SYSTEM_PROMPT)
.user(message)
.call()
.content();
}
}
然后配置智能体相关配置
server.port=9091
server.servlet.context-path=/agent
spring.application.name=ollama-agent-demo
#本地模型API地址
spring.ai.ollama.base-url=http://127.0.0.1:11434/
#模型名称
spring.ai.ollama.chat.model=gpt-oss:20b
#控制生成文本的随机性:温度值越高,生成的文本越随机、越有创造性;温度值越低,生成的文本越确定、越保守
spring.ai.ollama.chat.options.temperature=0.1
#控制候选词的范围:从概率最高的词开始累加,直到累计概率达到 top-p 值,然后只从这个集合中采样
spring.ai.ollama.chat.options.top-p=0.5
#限制候选词的数量:只从概率最高的 k 个词中选择
spring.ai.ollama.chat.options.top-k=10
#开启MCP服务调用
spring.ai.mcp.client.enabled=true
spring.ai.mcp.client.sse.connections.mcp-sdk-server-demo.url=http://localhost:9090
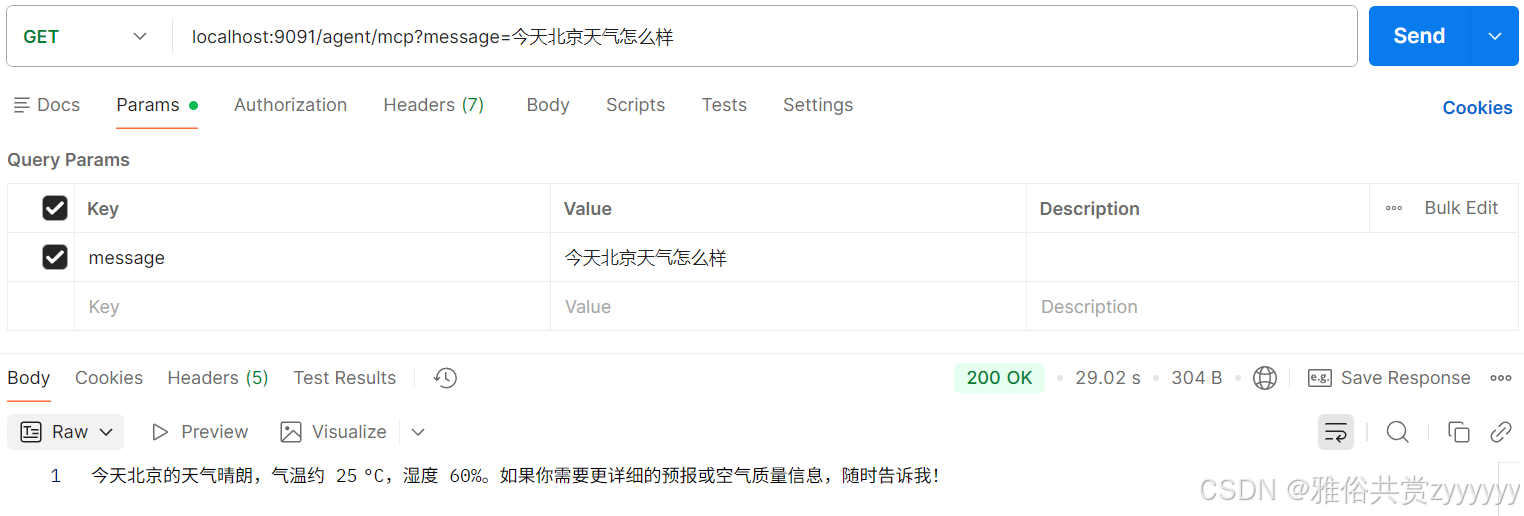
然后我们启动这个智能体Demo,通过接口方式调用测试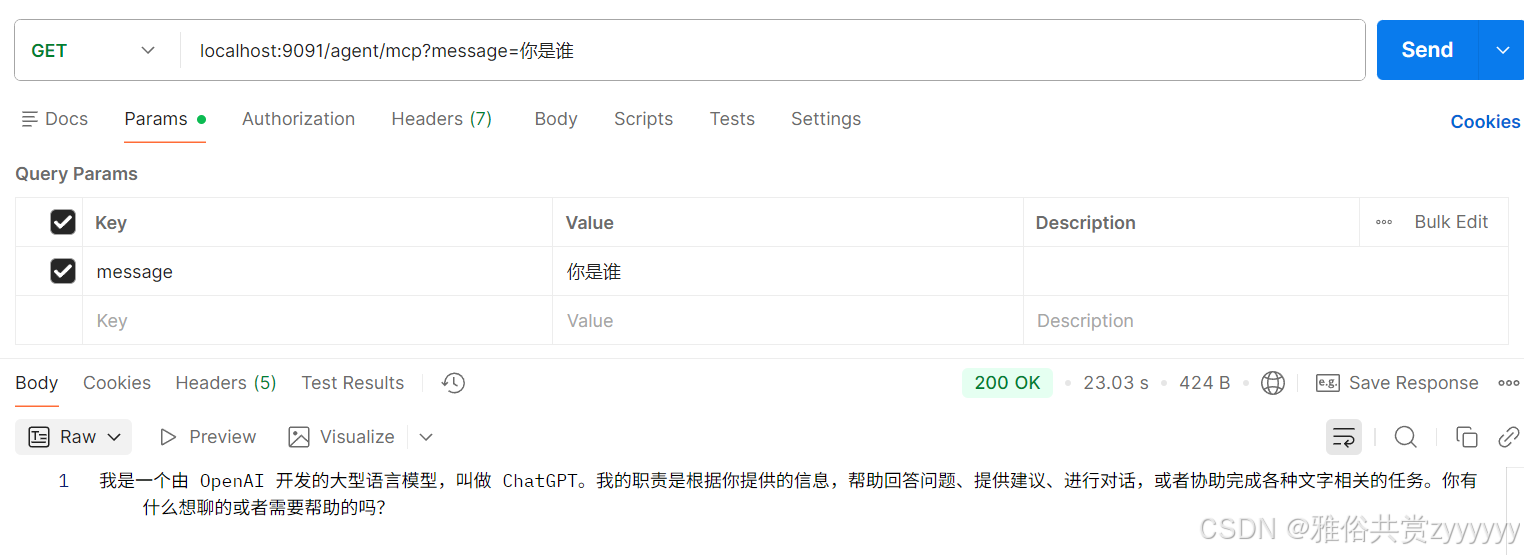
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容






所有评论(0)