1. Agent 介绍 ——【Google 5-Day AI Agents】
AI Agent 定义:Model(模型) TOOLS(工具) Orchestration-Layer(编排) Runtime -Services (运行服务) 四个要素的结合。Model(大脑): 处理信息、评估选项、做出抉择Tools(双手): API拓展、调用代码函数、与外部知识(数据库)连接Orchestration Layer(神经系统): 任务规划(React)、管理记忆、决策调度(t
1. 白皮书
第一天的白皮书介绍了 AI agents 基础知识,还进一步介绍了 agents 的能力分类体系、agents 落地运维规范、多 agents 协作与安全性等内容
1.1. AI Agents 简介
AI Agent 定义:Model(模型) TOOLS(工具) Orchestration-Layer(编排) Runtime -Services (运行服务) 四个要素的结合。
- Model(大脑): 处理信息、评估选项、做出抉择
- Tools(双手): API拓展、调用代码函数、与外部知识(数据库)连接
- Orchestration Layer(神经系统): 任务规划(React)、管理记忆、决策调度(think-action-observe)
- Deployment(躯干): 托管部署、监控、日志记录等
Agent 开发者像一个导演,不需要编写每一行代码,而是搭建场景(instructions and prompts),配置演员(tools and APIs),提供私域信息(data)。主要目的是引导大模型呈现出预期的表现。
LLM 最大的特点就是灵活,导致她很难可靠且完美的完成某一特定任务。从 prompt engineering 到 context engineering,我们的目的是引导 LLM 生成期望的输出。
每次调用她,我们会输入:指令、事实依据、Tools、示例、会话历史、私域数据等等,在上下文窗口中填入恰到好处的信息,然后获得我们需要的输出(模型唯一的作用:输入->输出)。而 Agent 则是通过管理我们的输入来进行工作。
Agent 善后:追踪(Traces)和日志(Logs)监控Agent的思考过程和执行链路,定位到与预期执行链路不符的偏差点。开发者的职责是提供关键组件:专业领域知识、明确的角色设定、工具的无缝集成。在初始prompt设计完善的基础上,还要多场景边缘性测试然后持续全面评估并优化。
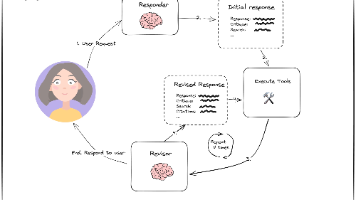
本质上:Agent 是一个专注于管理上下文窗口的系统。它始终处于持续不断的循环过程中:整合上下文、给模型提供prompt、观察模型结果,然后为下一步重新整合上下文。这里的上下文可能包括:指令、用户输入、会话历史、长期记忆、来自权威来源的基础信息、可使用的工具,以及已调用工具返回的结果等。这种对模型的精细化管理,能让模型更有效的工作。
Agent 工作流程
Agent 通过一个持续的循环过程来实现其目标:
- 获取任务:用户提出一个需求
- 扫描场景:Agent 收集现有能解决用于需求的知识(memory history tools database等)
- 深入思考:根据1和2进行循环推理制定执行计划
- 采取行动:模型决策后开始调用Tools操作
- 观察并迭代:观察Tools返回结果,循环tool->observe->think->tool…
这种" think、act、observe"的循环会持续进行——由编排层管理,由模型进行推理,由工具执行,直到智能体的内部计划完成且初始任务达成。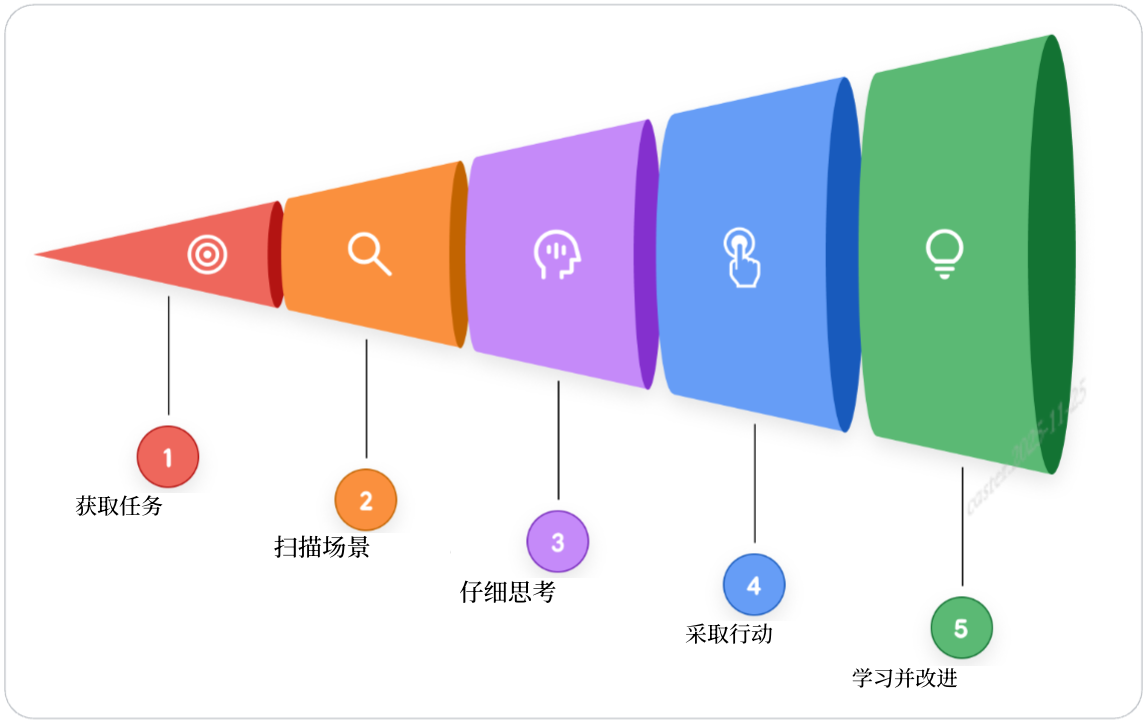
1.2. Agentic 系统分类法
理解前面提到的 Agent 5步工作流程后,我们需要了解到这个循环的复杂性是可变的。对于架构师来说,我们要根据我们需求的难易和复杂度决定构建何种复杂程度的Agent。
Agentic system 从简单到复杂可以分为以下五个级别: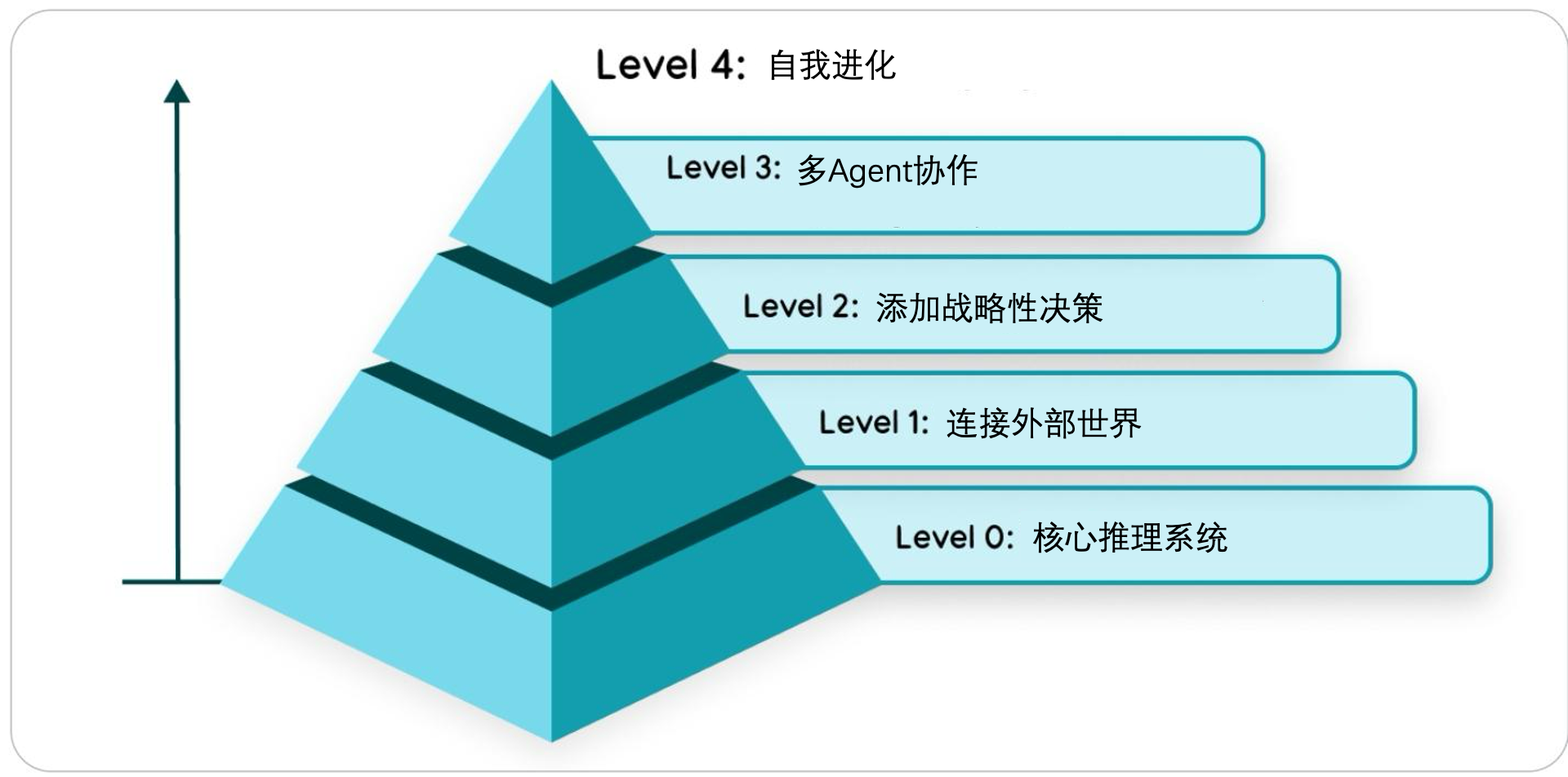
1.2.1. LLM
大模型仅基于训练数据回答问题,无任何Tools、实时数据知识和记忆等等
1.2.2. LLM + Tools
大模型可以决策调用Tools去进行检索实时数据、调用API等等丰富自己的知识和执行能力(与外部世界交互)
1.2.3. LLM + Tools + Context-Engineering
通过高质量的上下文管控LLM有限的注意力,战略性规划复杂、多模块任务
1.2.4. (LLM + Tools + Context-Engineering) x n
在上一步的基础上,构造多个agents进行协作分工,主agent管理多个subagents
1.2.5. Self Evolving
Agent 能够识别自身能力的不足,并动态创建 Tools 甚至 Subagent 来弥补这些不足, 赋予 Agent 主动拓张自己能力的能力,自我进化。
1.3. Agent 核心架构:模型、工具与编排
落地三个组件从概念到代码的实现,具体架构如何设计
1.3.1. Model:Agent的大脑
LLM 是推理核心,选择要素:
- 卓越的推理能力
- 应对复杂多步骤任务
- 可靠的工具调用能力
- 成本…
具体落地方案:
- 针对你的业务用各个模型进行测试,做出在质量、速度和价格上的最佳选择。
- 可以在 Agent 内根据不同需求的难易程度选择不同的模型,组件多模型团队。
- 模型会不段进化,Agent系统要具备持续集成新模型的能力。
1.3.2. Tools
Tools 使 Agent 能够超越其静态的训练数据,获取实时信息并在现实世界中采取行动。一个强大的 Tool 接口包含三个环节:定义功能、调用以及观察结果。几种主要的工具类型如下:
1.3.2.1. 检索信息
google-search、RAG、查询向量数据库、查询私域数据文档、自然语言转SQL查询结构化数据库等等
1.3.2.2. 执行操作
行动类工具:发邮件、执行Python脚本、Human-in-the-Loop、操作浏览器等
1.3.2.3. 函数调用
可靠的进行函数调用,依赖MCP等规范
1.3.3. The Orchestration Layer
编排层是连接 LLM 和 Tools 的神经网络,运行Think, Act,Observe"循环的引擎,控制 Agent 行为的状态机(可以参考 LangGraph 框架)
1.3.3.1. 核心设计
- Agent 自主程度:(自由)React -> Workflow(限制)
- 实现方式:(快速简单)无代码 -> 代码优先(复杂控制)
- 框架选择:多模型支持、具备可观测性
1.3.3.2. 借助领域知识和角色定位
开发者最有力的干预模型手段是向 Agent 传授领域知识并赋予其独特的角色设定,通过 System Prompt 或一组核心指令来实现,作为 Agent 的行为准则。
例:你是xxx、你有哪些限制、期望输出的格式、语气、何时为何使用tools等等,并提供几个场景示例。
1.3.3.3. 用上下文增强
- 短期记忆:当前会话的循环历史记录,Human、AI、Tools 的 Message
- 长期记忆:夸会话持久性存储,会话记录落盘和恢复
1.3.3.4. 多智能体协作
任务复杂性提高,单一超级 Agent 效率低下,需要组建 Agents 专家团队各司其职。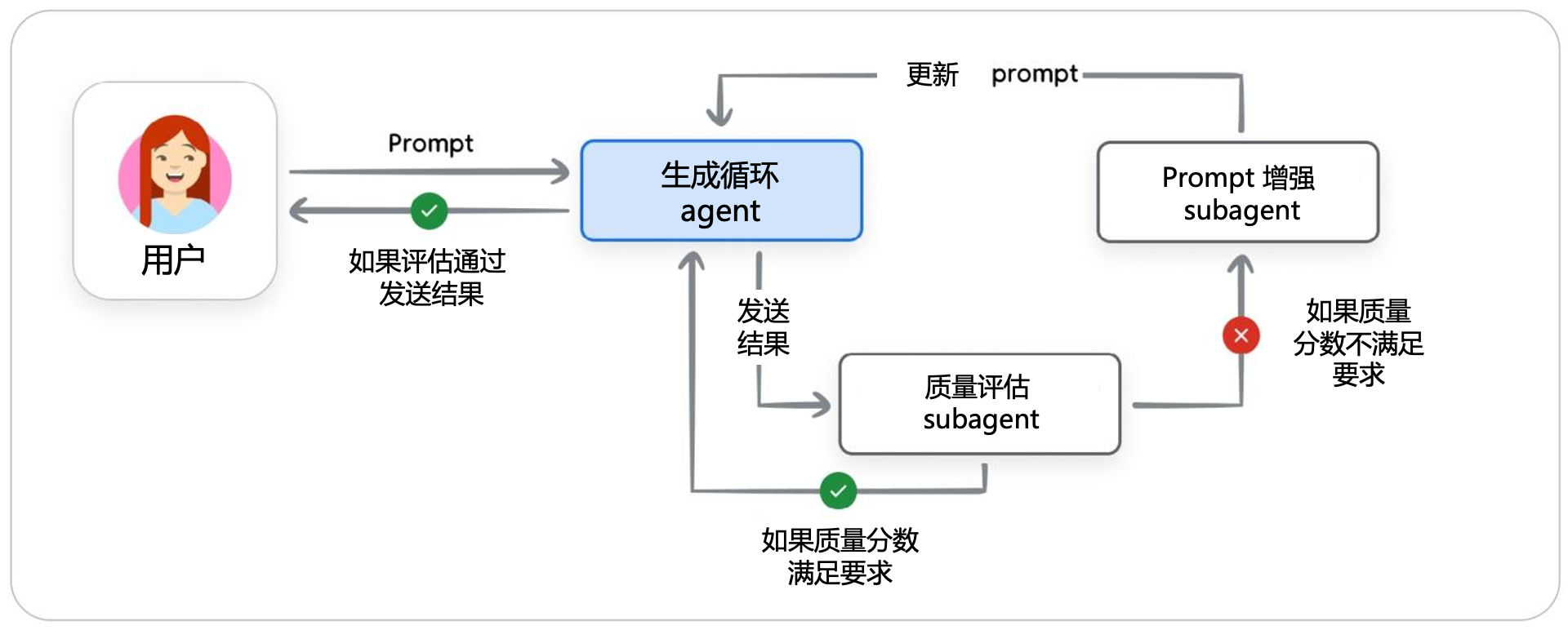
迭代优化模式会创建一个反馈循环,使用“生成循环”智能体创建内容,并使用“质量评估”智能体根据……进行评估,然后使用“Prompt 增强”执行体增强。
对于更线性的 Workflow,序列模式更合适,它就像一条数字装配线,一个 Agent 的输出直接成为下一个 Agent 的输入。
对于高风险任务,Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) 模式至关重要,它会在Workflow中设置一个刻意的停顿,以便在 Agent 采取重大行动前获得 Human 的批准。
1.3.4. 部署与服务化
Agent 只是一种新的软件形式,很多软件部署原则仍然适用(docker CI/CD等),额外需要注意的是会话历史记录、长期记忆记录和客观性性等内容。
Google 的 Agent 专用部署运行平台 Vertex AI Agent Engine: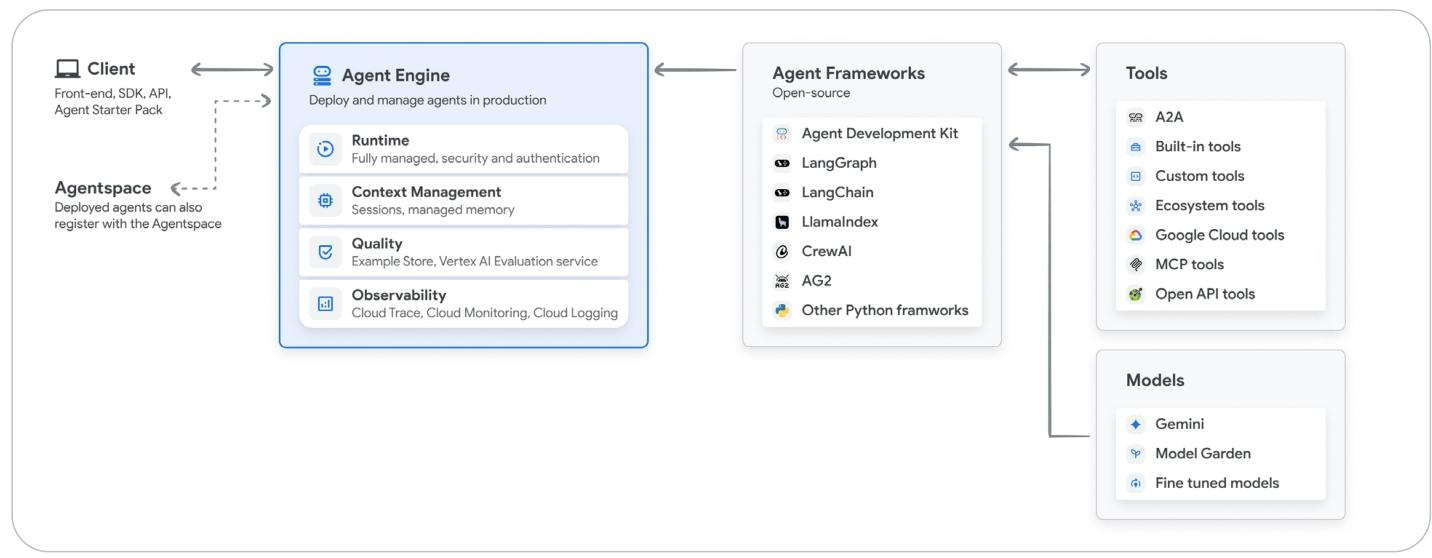
1.3.5. Agents 运维:应对不可预测性
从传统确定性软件到随机的 Agentic 系统转变,需要一种新的理念。由于语言的复杂性,通常我们需要用 LLM 来评估 Agent 的工作质量:完成了所有应该做的、没做不该做的、回复语气得当等等。
生成式人工智能(GenAI)的发展主要有两个领域:模型开发和应用开发,运维方式继承关系如下: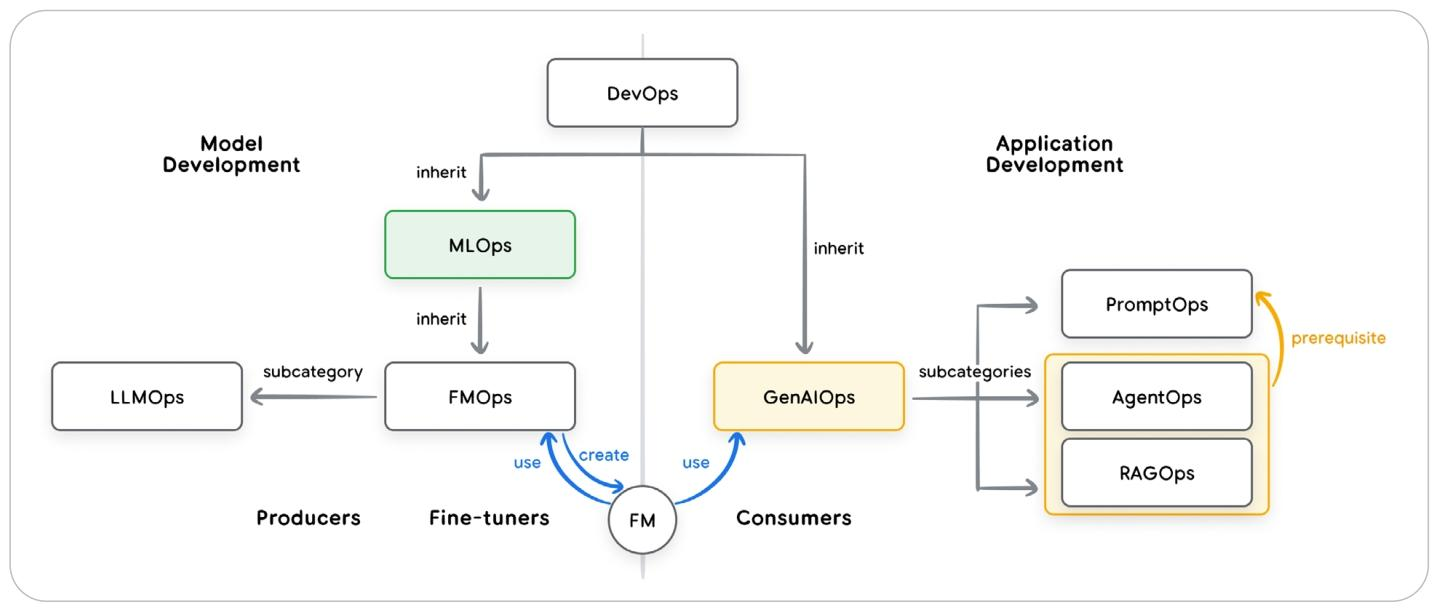
1.3.5.1. A/B 测试来衡量指标
明确当前业务背景下,模型工作产出的具体指标(KPI),构建KPI的可观测策略,量化测试模型的工作效果。
1.3.5.2. 让 LLM 评判
某些业务无法设定标准答案,通过让领域专家(精通此业务人员)提供预定义的标准,来叫 LLM 评判 Agent 的工作产出
1.3.5.3. 新版本能不能上?
- 一旦你自动化了数十个评估场景并建立了可信赖的质量评分体系,你就可以放心的开始迭代升级的 Agent 了。新版本在整个评估数据集上运行测试,将分数与现版本进行对比(自动化评估)。
- 还要额外考虑的因素:延迟、成本和任务的成功率等。
- 采用A/B部署方式,收集生产指标结合模型评分体系一起决定新版本能不能上?
1.3.5.4. 追踪调试你的 Agent
可以使用类似 OpenTelemetry 这种客观性追踪调用链路和日志的工具去查看你 Agent 的异常问题。观察发送给模型的Prompt、模型内部推理过程、选择的Tool和参数以及Tool返回结果等。
1.3.5.5. 用户反馈的重要性
获取用户反馈并形成一个新的评估数据集用于测试你的 Agent,可以让系统对用户反馈的问题具有免疫性。
1.3.6. Agent 交互
高质量的 Agent 需要与其他 Agents 和用户连接起来,你需要思考如何将你的 Agent 融入到更广泛的生态系统之中。
1.3.6.1. Agents & 人
- 通过用户界面提供给用户,比如聊天机器人:用户输入,Agent 接收处理并返回一段文本给到用户。
- 控制你的电脑,比如操作浏览器:打开小红书,输入XXX,进行搜索。
- 渲染你的UI,根据你的问题需求热生成UI界面进行展示交互
- 访问你的摄像头麦克风直接获取的你感官世界获取的信息进行回应。
1.3.6.2. Agents & Agents
不同团队的不同专业 Agents 连接起来需要通用标准:
- 发现: 我的 Agent 如何找到其他的 Agents 并了解他们的功能?
- 通信: 如何确保他们使用相同的语言交互?
Agent2Agent(A2A)协议 :为解决该问题而设计的开放式标准,它相当于智能体生态中的 “通用握手协议”:
- 通过 A2A 协议,任何智能体都能发布一份名为 “智能体名片(Agent Card)” 的数字化文件。这份简洁的 JSON 格式文件会公示智能体的核心能力、网络端点(用于通信连接的地址),以及与该智能体交互所需的安全凭证。这种设计让 “智能体发现” 过程变得简单且标准化。
- A2A 协议与 MCP 的定位不同:MCP 侧重处理事务性请求(如订单查询、数据调取等单一明确的任务指令),而 A2A 通信则通常用于辅助完成更复杂的问题解决流程(如多智能体协作拆解项目、联合分析跨领域数据等)。
- Agent 被发现后,会采用面向任务的架构进行通信。与简单的 “请求 - 响应” 模式不同,Agents 间的交互以异步 “任务” 形式构建:client agent 向 server agent 发送任务请求,随后 server agent 可通过长连接实时流式返回更新信息。
- 这种稳健、标准化的通信协议是实现 Level 3 multi-agent systems 的关键一环,借助 A2A 协议,原本零散孤立的 Agents 集合,被转化为一个真正具备互操作性的生态系统。
1.3.6.3. Agent & 金钱
是否允许 Agent 代表用户安全可靠地进行交易?出了问题责任在谁?
Agent支付协议:Agent Payments Protocol (AP2)
1.3.7. Agent Security
Agent 的实用性和安全性具备冲突:
- 实用性:赋予它更多的权利(发邮件、增删改查数据库)
- 安全性:限制他有害的行为(删库跑路、敏感数据泄露)
- 硬编码规则,为 Agent 提供可预测、可审计的硬性限制 Prompt(禁止删除表)
- 训练模型或者小模型对操作进行安全检查
1.3.7.1 Agent ID:一类新型主体
Agent 不仅仅是一段代码,它是一个自主的参与者,是一种需要自身可验证身份的新型主体。就像员工会领到工牌一样,平台上的每个智能体都必须获得一个安全、可验证的“数字护照”。
对每个身份进行验证并为所有身份设置访问控制,是 Agents 安全的基础。一旦 Agents 拥有可通过加密方式验证的身份,就可以为其赋予特定的、最小权限的许可(不同系统间权限隔离)。它能确保单个 Agent 被入侵或行为异常,潜在的影响范围也能得到控制。
1.3.7.2 访问约束策略
策略的本质是授权(你能干啥)而非认证(你是谁),需通过 “最小权限原则” 约束访问范围。Agentic 系统的权限关系更复杂,策略需延伸到 Agent 交互的所有关键环节:
- Agents: 限制自身能力
- Tools: 控制工具使用范围
- SubAgents: 限制子 Agents 能力
- Context: 管控上下文敏感信息
- Remote Agent: 跨系统远程 Agent 的访问
1.3.7.3 ADK 智能体的保护
ADK 采用:
- 身份验证(Agent Identity)
- 建立访问策略(授权你能干啥)
- 工具和 SubAgents 内置防护
- AI 动态防护(before_tool_callback工具调用前回调、AI插件实时监控输入输出)
- 托管安全服务(Model Armor)
的混合方案,既让 Agent 具备强大功能,又能保证其可信任性和安全性。
1.3.8. 扩展单个 Agent 到 Agents 集群
单个到数百个的扩张管理起来会很复杂,需要更好的架构性设计。
1.3.8.1 安全和隐私
纵深防御策略:从数据层开始,到控制输入输出、Prompt防火墙等(企业级别的数据保护)
1.3.8.2 Agents 治理
agent sprawl(智能体蔓延):随着多执行体复杂交互网络的出现,需要一个作为所有智能体活动控制平面的中央网关:可以检查、路由、监控和管理每一次 Agents 之间的交互。
- 运行时策略:验证身份和授权操作,跟踪记录 Agent 行为日志和指标
- 集中式管理:Agents Tools 注册表系统(管理界面)
1.3.8.3 成本和可靠性
企业级智能体必须既可靠又具成本效益。
1.3.9. 进化和学习
现实环境中政策、技术和数据不断变化,Agents 需要具备成为老古董的能力。
1.3.9.1 智能体如何学习和自我进化
和人类相似,Agent 从经验和外部信息中学习。
- 运行过程中通过日志和跟踪记录积累失败和成功的经验
- 外部数据源更新,私域知识的更新
- 增强型上下文工程:持续优化Prompt、示例和内存中用于检索的信息
- Tool的新增和优化:获取、创建、修改 Tool
示例:
- 学习新的合规指南
金融企业必须在符合隐私和监管规则的前提下给用户提供报告
Querying Agent: 响应用户请求检索原始数据
Reporting Agent: 总结数据生成报告
Critiquing Agent: 根据已知合规指南对报告进行审查,模糊场景提交给人工干预
Learning Agent: 学习整个流程尤其是人工专家干预部分,将人工反馈归纳为新的合规指南中的一条。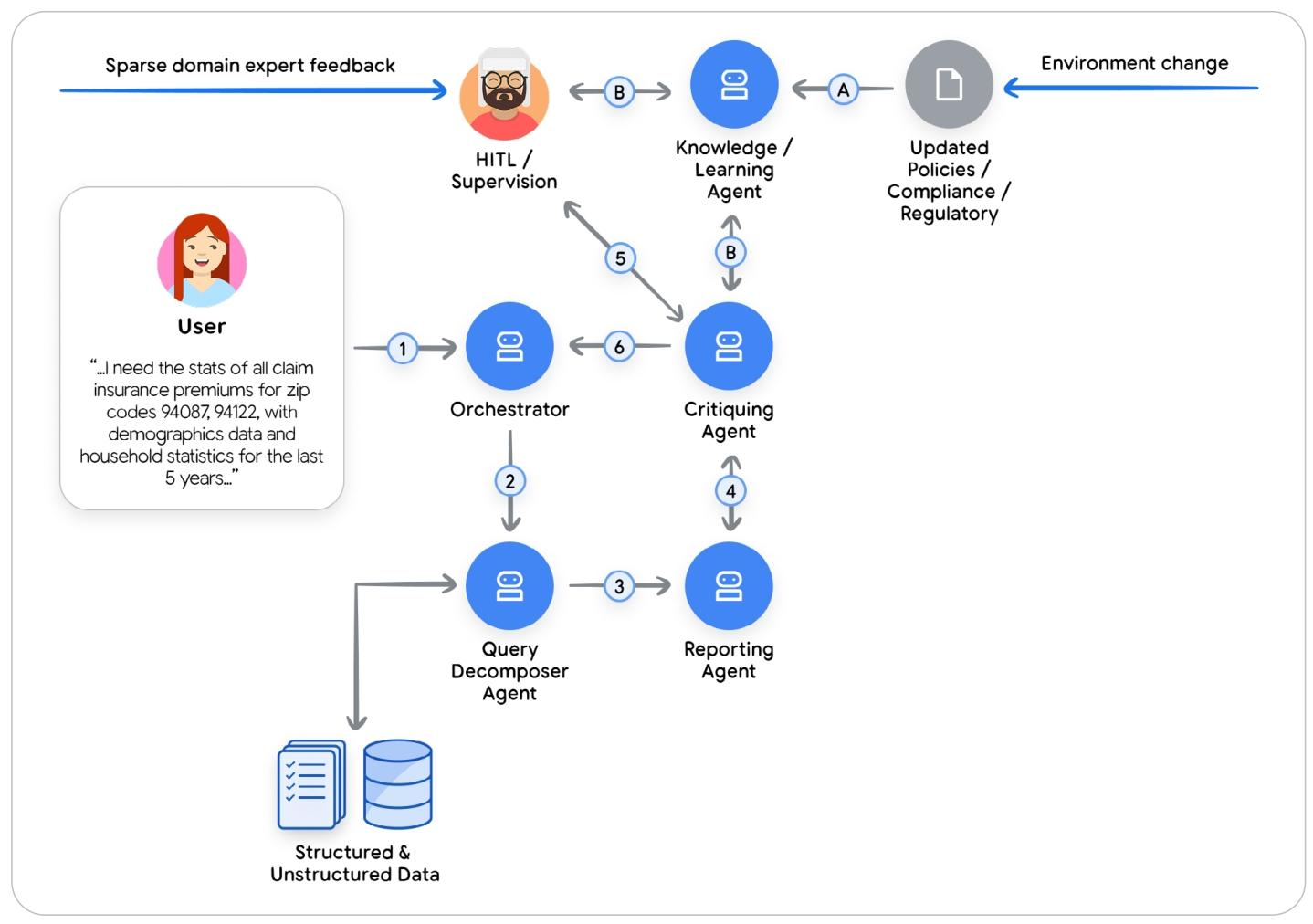
1.3.9.2 模拟与 Agent 训练平台
离线过程中而非运行时获取的信息来优化 Agents 能力。
模拟环境、使用高级模拟数据生成器、与领域专家咨询获取指导。
1.4. 高级 Agents 示例
自己随便看看就好
1.4.1. Google Co-Scientist
1.4.2. AlphaEvolve Agent
1.5. 总结
生成式人工智能智能体标志着一次关键的进化,将人工智能从单纯的内容创作,转变为解决问题过程中积极且自主的搭档。
Agent 三个基本组件:Model Tools Orchestration-Layer 组合在一起实现了连续的 “Think, Act, Observe” 循环链路。
Agent 开发者的工作变成了引导、约束和调试 Agent 行为。
2. 代码实验室
2.1. first AI agent
基础模型对话中加入谷歌查询 Tool 来达到根据用户需求实时进行谷歌搜索的能力
root_agent = Agent(
name="helpful_assistant",
model=Gemini(
model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite",
retry_options=retry_config
),
description="A simple agent that can answer general questions.",
instruction="You are a helpful assistant. Use Google Search for current info or if unsure.",
tools=[google_search],
)
print("✅ Root Agent defined.")
2.2. first multi-agent system
2.2.1. Research & Summarization System
主 agent 调用检索 agent 和总结 agent 实现检索总结系统
- ResearchAgent 负责使用谷歌搜索Tool进行数据检索
# Research Agent: Its job is to use the google_search tool and present findings. research_agent = Agent( name="ResearchAgent", model=Gemini( model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite", retry_options=retry_config ), instruction="""You are a specialized research agent. Your only job is to use the google_search tool to find 2-3 pieces of relevant information on the given topic and present the findings with citations.""", tools=[google_search], output_key="research_findings", # The result of this agent will be stored in the session state with this key. ) print("✅ research_agent created.") - SummarizerAgent 负责总结ResearchAgent 的检索结果
# Summarizer Agent: Its job is to summarize the text it receives. summarizer_agent = Agent( name="SummarizerAgent", model=Gemini( model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite", retry_options=retry_config ), # The instruction is modified to request a bulleted list for a clear output format. instruction="""Read the provided research findings: {research_findings} Create a concise summary as a bulleted list with 3-5 key points.""", output_key="final_summary", ) print("✅ summarizer_agent created.") - ResearchCoordinator 作为 Root 负责启动任务调用两个 AgentTool
# Root Coordinator: Orchestrates the workflow by calling the sub-agents as tools. root_agent = Agent( name="ResearchCoordinator", model=Gemini( model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite", retry_options=retry_config ), # This instruction tells the root agent HOW to use its tools (which are the other agents). instruction="""You are a research coordinator. Your goal is to answer the user's query by orchestrating a workflow. 1. First, you MUST call the `ResearchAgent` tool to find relevant information on the topic provided by the user. 2. Next, after receiving the research findings, you MUST call the `SummarizerAgent` tool to create a concise summary. 3. Finally, present the final summary clearly to the user as your response.""", # We wrap the sub-agents in `AgentTool` to make them callable tools for the root agent. tools=[AgentTool(research_agent), AgentTool(summarizer_agent)], ) print("✅ root_agent created.") - 通过 ResearchCoordinator 启动主流程
runner = InMemoryRunner(agent=root_agent) response = await runner.run_debug( "What are the latest advancements in quantum computing and what do they mean for AI?" )
2.2.2. Blog Post Creation with Sequential Agents
确定链路workflow demo,使用顺序链路调用 Agents 创建博客文章
- Outline Agent : 为给定主题创建博客大纲
- Writer Agent : 撰写博客文章
- Editor Agent : 编辑博客文章草稿,使其清晰且结构合理

与上一个demo类似,三个子 Agent 由主 Agent 整合为 SequentialAgent(顺序性Agent)即可:
root_agent = SequentialAgent(
name="BlogPipeline",
sub_agents=[outline_agent, writer_agent, editor_agent],
)
print("✅ Sequential Agent created.")
2.2.3. Parallel Multi-Topic Research
当你有多个独立任务时,你可以使用 ParallelAgent 同时运行所有这些任务。该 Agent 会并发执行其所有子 Agent,显著加快工作流程。所有并行任务完成后,你就可以将它们的合并结果传递到最后的 “聚合” 步骤。
一个包含四个 Agents 的系统:
- Tech Researcher :研究人工智能 / 机器学习新闻和趋势
- Health Researcher :研究近期医疗新闻和趋势
- Finance Researcher :研究金融和金融科技新闻和趋势
- Aggregator Agent :将所有研究成果整合为一份摘要
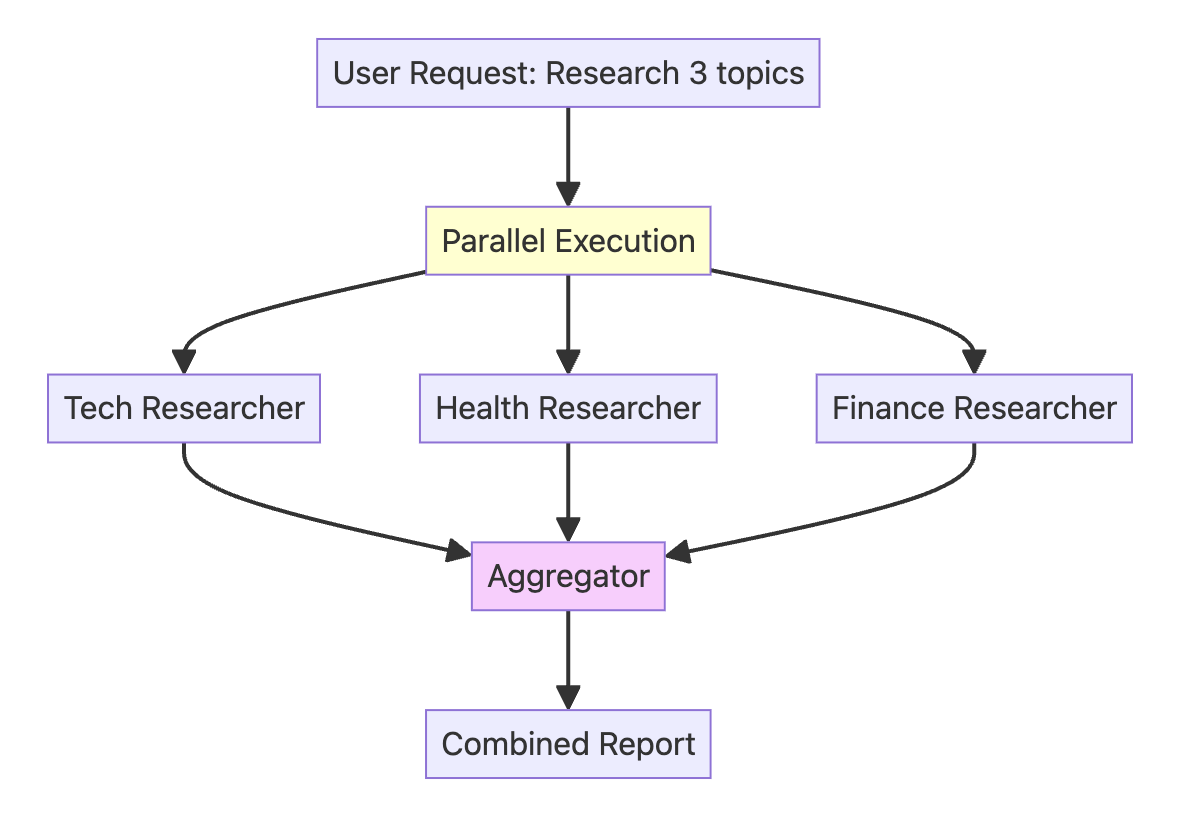
前三个 Researcher 均为带有谷歌搜索 Tool 的** Agent **,不再赘述。
Aggregator Agent 代码如下,将三个 Researcher 结果和总结需求提交给 LLM :
# The AggregatorAgent runs *after* the parallel step to synthesize the results.
aggregator_agent = Agent(
name="AggregatorAgent",
model=Gemini(
model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite",
retry_options=retry_config
),
# It uses placeholders to inject the outputs from the parallel agents, which are now in the session state.
instruction="""Combine these three research findings into a single executive summary:
**Technology Trends:**
{tech_research}
**Health Breakthroughs:**
{health_research}
**Finance Innovations:**
{finance_research}
Your summary should highlight common themes, surprising connections, and the most important key takeaways from all three reports. The final summary should be around 200 words.""",
output_key="executive_summary", # This will be the final output of the entire system.
)
print("✅ aggregator_agent created.")
并发执行方式如下:
主 Agent 为顺序链路 Agent,先执行 parallel_research_team 然后执行aggregator_agent。
parallel_research_team 为并行 Agent,同时执行三个researcher。
# The ParallelAgent runs all its sub-agents simultaneously.
parallel_research_team = ParallelAgent(
name="ParallelResearchTeam",
sub_agents=[tech_researcher, health_researcher, finance_researcher],
)
# This SequentialAgent defines the high-level workflow: run the parallel team first, then run the aggregator.
root_agent = SequentialAgent(
name="ResearchSystem",
sub_agents=[parallel_research_team, aggregator_agent],
)
runner = InMemoryRunner(agent=root_agent)
response = await runner.run_debug(
"Run the daily executive briefing on Tech, Health, and Finance"
)
2.2.4. Iterative Story Refinement
当一项任务需要通过反馈和修订循环来改进时,你可以使用循环代理(LoopAgent)。循环代理会重复运行一组子代理,直到满足特定条件或达到最大迭代次数。这就形成了一个优化周期,使代理系统能够不断改进自己的工作。
一个包含两个 Agents 的系统:
- Writer Agent :撰写短篇小说草稿
- Critic Agent :审阅并评论短篇小说,提出改进建议

- 初始化撰写小说 Agent :
# This agent runs ONCE at the beginning to create the first draft. initial_writer_agent = Agent( name="InitialWriterAgent", model=Gemini( model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite", retry_options=retry_config ), instruction="""Based on the user's prompt, write the first draft of a short story (around 100-150 words). Output only the story text, with no introduction or explanation.""", output_key="current_story", # Stores the first draft in the state. ) print("✅ initial_writer_agent created.") - 评价小说 Agent,如果通过返回
APPROVED,否则给出修改建议:# This agent's only job is to provide feedback or the approval signal. It has no tools. critic_agent = Agent( name="CriticAgent", model=Gemini( model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite", retry_options=retry_config ), instruction="""You are a constructive story critic. Review the story provided below. Story: {current_story} Evaluate the story's plot, characters, and pacing. - If the story is well-written and complete, you MUST respond with the exact phrase: "APPROVED" - Otherwise, provide 2-3 specific, actionable suggestions for improvement.""", output_key="critique", # Stores the feedback in the state. ) print("✅ critic_agent created.") - 当评论通过返回
APPROVED退出循环用的函数:# This is the function that the RefinerAgent will call to exit the loop. def exit_loop(): """Call this function ONLY when the critique is 'APPROVED', indicating the story is finished and no more changes are needed.""" return {"status": "approved", "message": "Story approved. Exiting refinement loop."} print("✅ exit_loop function created.") - 指挥上面三个部分协作的 Agent:
# This agent refines the story based on critique OR calls the exit_loop function. refiner_agent = Agent( name="RefinerAgent", model=Gemini( model="gemini-2.5-flash-lite", retry_options=retry_config ), instruction="""You are a story refiner. You have a story draft and critique. Story Draft: {current_story} Critique: {critique} Your task is to analyze the critique. - IF the critique is EXACTLY "APPROVED", you MUST call the `exit_loop` function and nothing else. - OTHERWISE, rewrite the story draft to fully incorporate the feedback from the critique.""", output_key="current_story", # It overwrites the story with the new, refined version. tools=[ FunctionTool(exit_loop) ], # The tool is now correctly initialized with the function reference. ) print("✅ refiner_agent created.") - 程序的主 Agent构造
主 Agent 先顺序链路执行 initial_writer_agent 初始化故事,然后执行 story_refinement_loop 进入 LoopAgent,循环调用 critic_agent 对故事评价和 refiner_agent 指挥1、2、3部分协作。# The LoopAgent contains the agents that will run repeatedly: Critic -> Refiner. story_refinement_loop = LoopAgent( name="StoryRefinementLoop", sub_agents=[critic_agent, refiner_agent], max_iterations=2, # Prevents infinite loops ) # The root agent is a SequentialAgent that defines the overall workflow: Initial Write -> Refinement Loop. root_agent = SequentialAgent( name="StoryPipeline", sub_agents=[initial_writer_agent, story_refinement_loop], ) print("✅ Loop and Sequential Agents created.") runner = InMemoryRunner(agent=root_agent) response = await runner.run_debug( "Write a short story about a lighthouse keeper who discovers a mysterious, glowing map" )
2.3. 选择合适的 Agent 模式
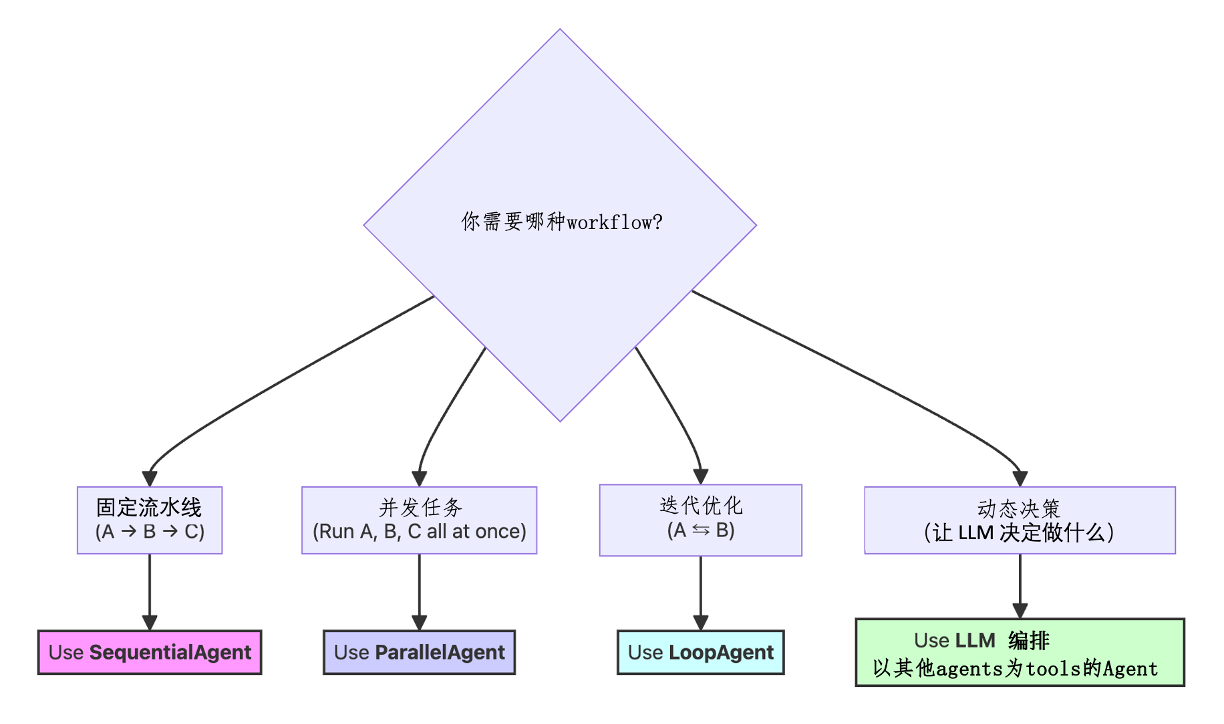
| Agent 类型 | 适用场景 | 示例 | 核心特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LLM 编排 | 需要动态协调调度的场景 | 研究 + 总结 | 由LLM决定调用组件 |
| Sequential | 任务顺序有要求、需线性执行的场景 | 列大纲 → 撰写 → 编辑 | 执行顺序固定可确定 |
| Parallel | 任务相互独立、需提升效率的场景 | 多主题研究 | 多个任务并发执行 |
| Loop | 需要迭代优化、持续改进的场景 | 撰写者 + 评论者协同优化 | 通过重复循环提升质量 |
参考文献:
5-Day AI Agents Intensive Course with Google
Introduction to Agents
Day 1a - From Prompt to Action
Day 1b - Agent Architectures
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)