LeetCode Daily Challenge#Day 03--Linked list (203,206)
🗓️。
🗓️Day 03 – Linked list.
Topics: Linked List
Problem solved:
#203 - Remove Linked List Elements
#206 - Reverse Linked List
文章目录
📚Concept Review – What is linked list?
A linked list is a linear data strcture that made up of nodes. Each nodes contains some infomation, such as value, pointer.
Highlight
- Dynamic size
- Don’t need contiguous memory
- Can’t access randomly
- Easy for insert or delete
🧩Problem solution – 203. Remove Linked List Elements
💡Problem description
Given the head of a linked list and an integer val, remove all the nodes of the linked list that has Node.val == val, and return the new head.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
Output: [1,2,3,4,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [], val = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
Output: []
-
Constraints:
-
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 10 4].
1 <= Node.val <= 50
0 <= val <= 50
🧭Thought Process
If the head need to be removed, then we just move the pointer head to the next one. Besides, it is just cur->next = next->next.
💻Code Implementation
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
while (head != NULL) {
if (head->val == val) {
head = head->next;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (head == NULL)
return head;
ListNode* h = head;
ListNode* n = head->next;
while (n != NULL) {
if (n->val == val) {
h->next = n->next;
n = h->next;
} else {
h = h->next;
n = h->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};
⏱️Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
🧩Problem solution – 206. Reverse Linked List
💡Problem description
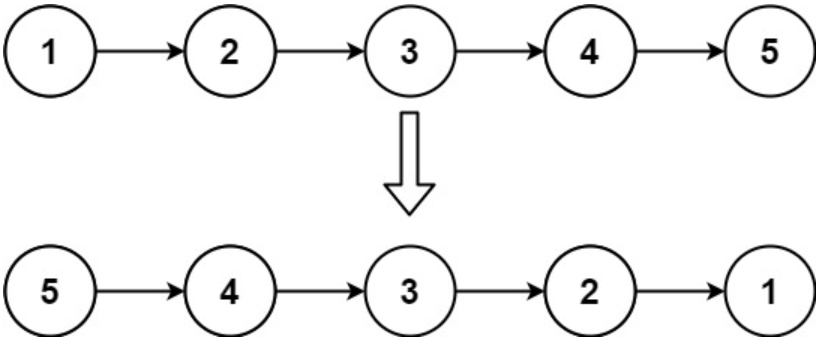
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
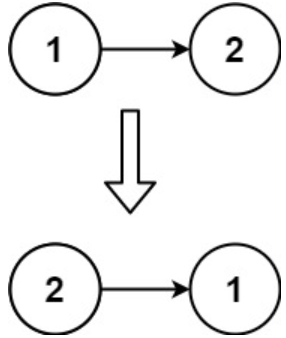
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
-
Constraints:
-
The number of nodes in the list is the range [0, 5000].
-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
🧭Thought Process
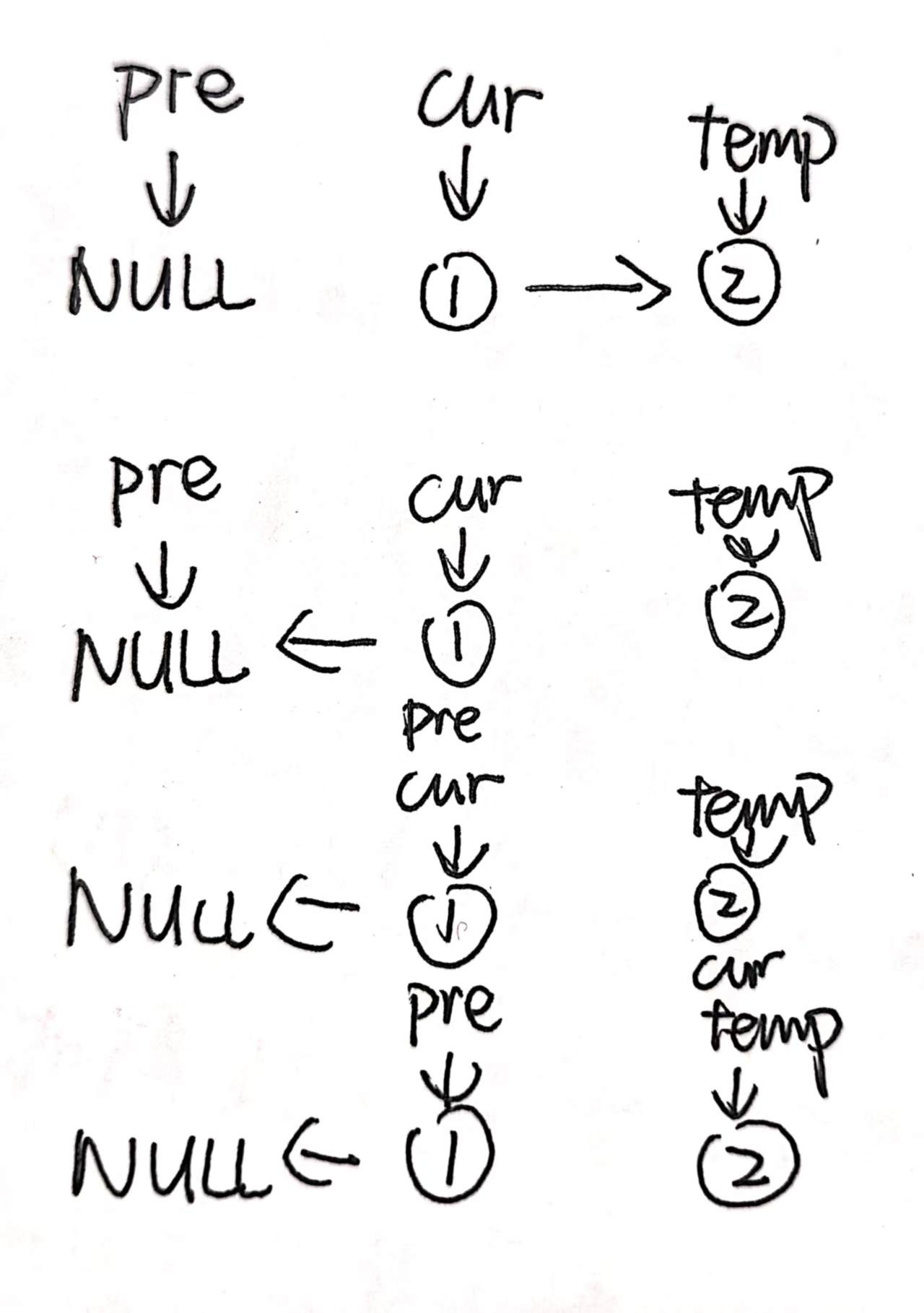
💻Code Implementation
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* pre = NULL;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* temp;
while(cur!=NULL){
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
⏱️Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容









所有评论(0)