spiderdemo第三题
笔者已经通过,直接给出结果哈哈哈哈哈哈哈网址如下T3-protobuf挑战直接给出全部代码lib.rsinclude!(concat!(env!// 绑定静态方法 hash)).send().await.unwrap().bytes().await.unwrap().unwrap().numbers.iter()page: 1,timestamp,signature,目录结构md5.js的改动运行
目录
获取ChallengeRequest、ChallengeResponse并使用
前言
笔者已经通过,直接给出结果

哈哈哈哈哈哈哈
网址如下
正文
整个流程
说实话,笔者现在非常喜欢搞这个流程
- 下载js文件
- html里面发送请求
- mitmproxy代理
- 获取数据
而这道题也是如下
分析
什么都不用说,发送请求,如下
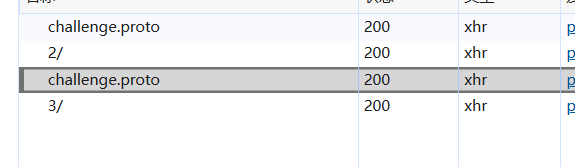
发现有个challeng.proto文件
proto的介绍和基础使用-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41358574/article/details/123903840语言指南 (proto 3) | Protocol Buffers 文档 - ProtoBuf 文档
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41358574/article/details/123903840语言指南 (proto 3) | Protocol Buffers 文档 - ProtoBuf 文档![]() https://protobuf.com.cn/programming-guides/proto3/这好像是一种数据传输方式。
https://protobuf.com.cn/programming-guides/proto3/这好像是一种数据传输方式。
总之,不重要。
可以发现这个proto文件的内容不会发送变化。
还可以发现参数,如下
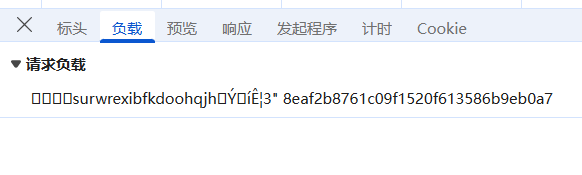
看不懂,不知道是什么东西,像乱码一样
看一下堆栈的调用
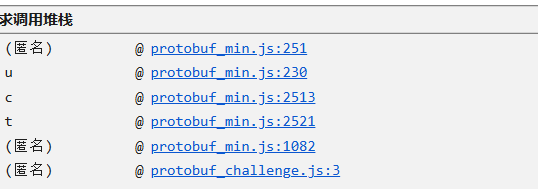
发现两个js文件protobuf_challenge.js和 protobuf_min.js
笔者启动了本地t替换,把 protobuf_min.js格式化了,好看点
不用多说,直接下载下来分别叫,index.js和proto.js
在html文件中加载这两个js文件,看看有什么事情发生吗
控制台有与页面有关的报错,不重要。
再看看堆栈调用的过程
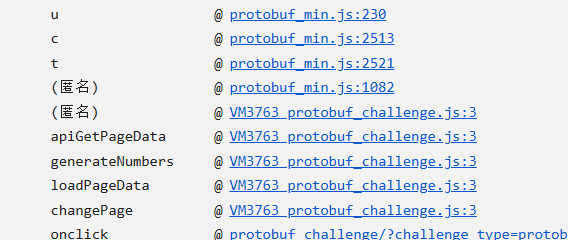
不装了,可以发现一个关键的东西apiGetPageData
在本地文件搜索关键字api,可以发现如下东西
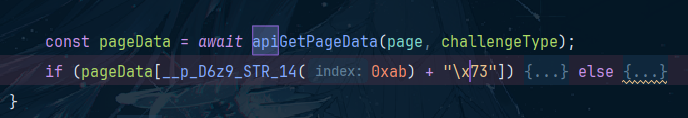
哦,笔者明白了,page显示是页数,challengeType显示是protobuf_challenge这个字符串
为什么是protobuf_challenge,标题写着的。
笔者自信,就是这个。
可以添加一行打印语句
如下
没问题
总之,确定两个参数
探索
笔者在html文件执行看看
<script type="module">
const pageData = await apiGetPageData(1, "");
</script>运行,然后报错
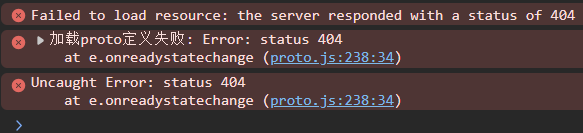
没有发现了proto文件
意料之中,毕竟还没下载这个文件
看请求
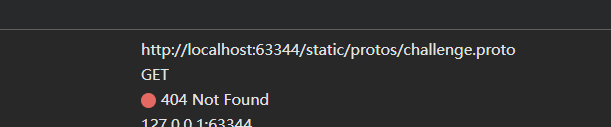
63344是pycharm 的内置端口,这个static路径怎么办
这里其实给笔者整懵逼了,该怎么搞出一个static

笔者的路径是这样的,文件路径就是路由路径
但是就算笔者创建一个stataic目录,也不行
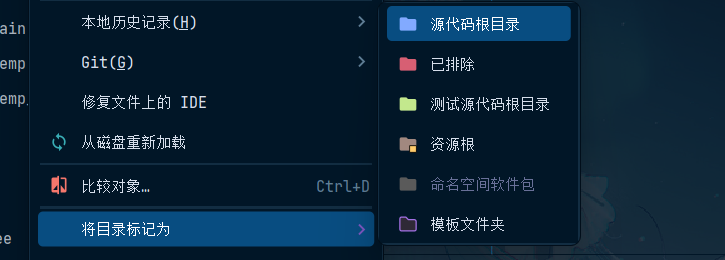
如果把T3目录标记成源代码目录,还是不行
总之,有个项目根目录,笔者还考虑一下,怎么搞,
但是,笔者突然想到,
新建一个static目录,pycharm把它作为项目的根目录,目录结构如下

把static作为根目录,创建和下载对应的文件
把html文件也放到static目录下
再次打开,结果如下
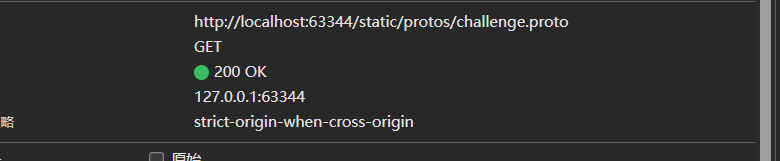
哈哈哈哈哈哈哈,成功了,把static作为项目的根目录,有点意思
虽然请求报错了
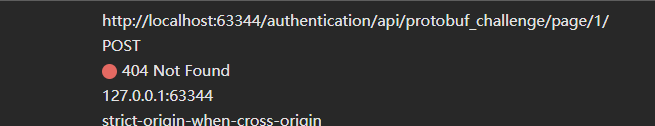
但是,可以发现,参数
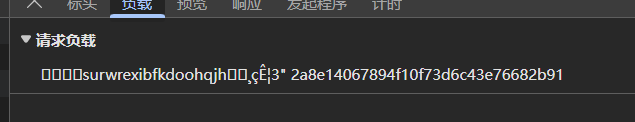
已经有参数了,哈哈哈哈哈哈哈,好好好
但是,笔者突然意思到一个小问题,请求具体在哪里发生的???????
=======行,明天再说,不慌------------------------------
好,继续。
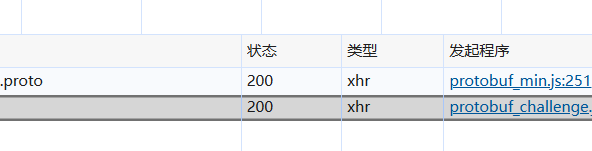
可以发现请求的类型是xhr,而且是在spiderdemo页面的protobuf_challenge.js触发
请求地址是https://www.spiderdemo.cn/authentication/api/protobuf_challenge/page/1/
说白了,在本地的index.js发送了请求,类型是xhr
XMLHttpRequest - Web API | MDN![]() https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/XMLHttpRequest直接在本地index.js中搜关键字XMLHttpRequest,如下
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/XMLHttpRequest直接在本地index.js中搜关键字XMLHttpRequest,如下
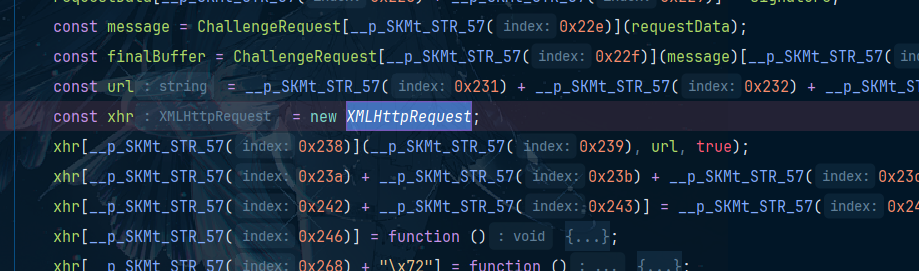
很显然,这个发送的请求。
前面有个url,在本地调用看看,在xhr那个打个断点
可以发现如下东西
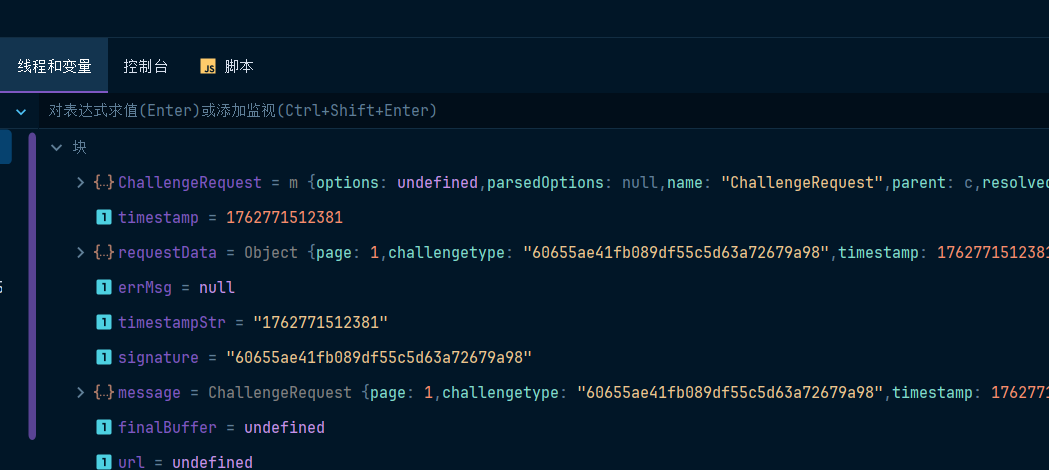
ChallengeRequest是什么东西?

就是proto定义的一个类型。还有ChallengeResponse
注意到前面url的东西
![]()
有个__p_SKMt_STR_57,这是什么
打印出来看看
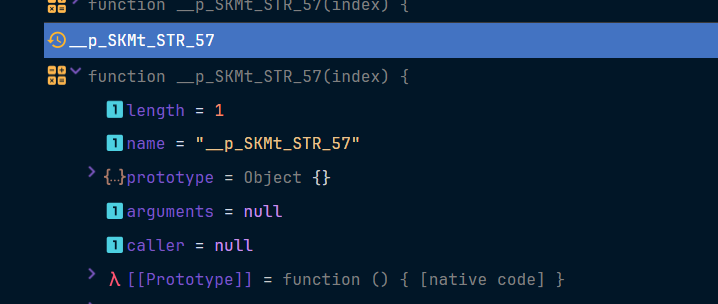
发现是一个函数,哦
笔者右键选择对表达式求值或者alt+F8

求个值看看,结果如下
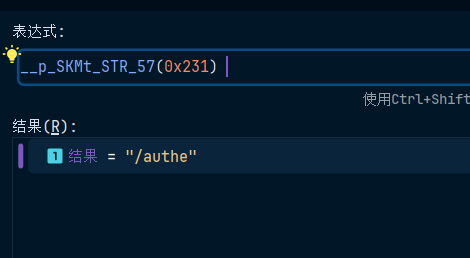
说明__p_SKMt_STR_57(0x231)就是字符串/authe
把全部url进行求值,结果如下
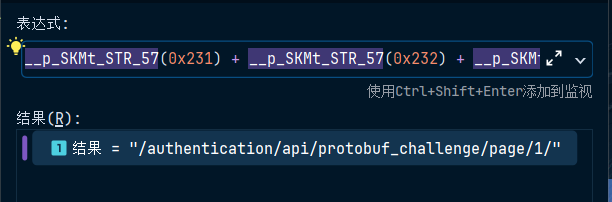
那么显然,这个就是路由,笔者将其发送到本机的8082端口
可以看一下其他东西
__p_SKMt_STR_57(0x238)——open
__p_SKMt_STR_57(0x239)——post
...
直言的说,全部都可以解出来,没必要
直接在最前面添加地址就可以了

代理脚本
启动代理
mitmweb --mode reverse:https://www.spiderdemo.cn -p 8082 -s proxy.py
运行html,
这个响应好像是二进制数据,还看不到
打印出来看看
<script type="module">
const res = await apiGetPageData(1, 'protobuf_challenge');
console.log(res)
</script>没问题
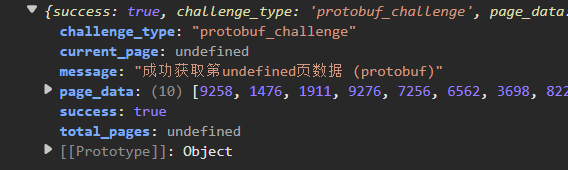
还有一个undefined,去官网试试,结果如下
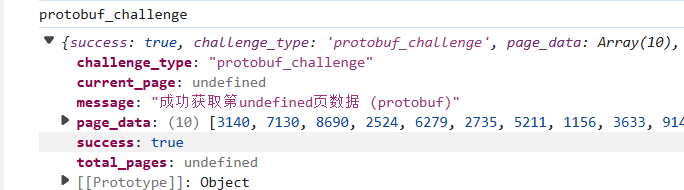
还是undefined,哦,难道是网站有bug?
网站小的bug
哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈,笔者分析了一下,确实是个bug
笔者直接给出关键信息
如下
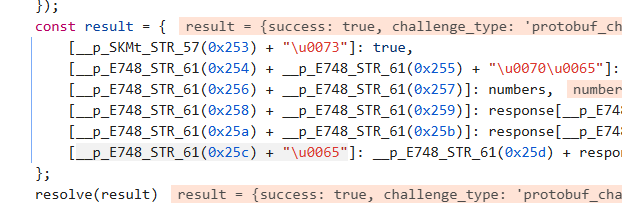
这个result就是返回的信息,但是最后一个
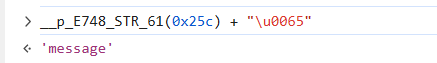
可以看成是message,其中的数据
response[__p_E748_STR_61(0x258) + __p_E748_STR_61(0x259)]
是undefined
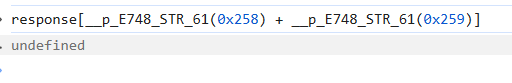
为什么是undefined
因为__p_E748_STR_61(0x258) + __p_E748_STR_61(0x259)是current_page
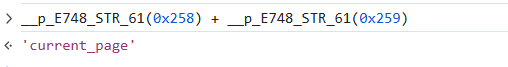
但是在proto文件的定义中
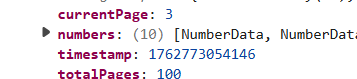
只有currentPage,因此出现了bug
笑死,哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈
解混淆
首先,笔者在mitmweb中,看到了请求的参数
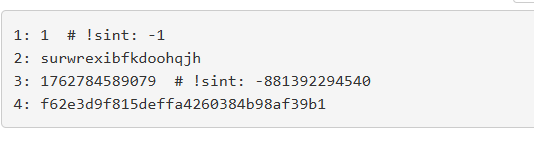
对照proto中的定义可以看出,四个参数对应的含义
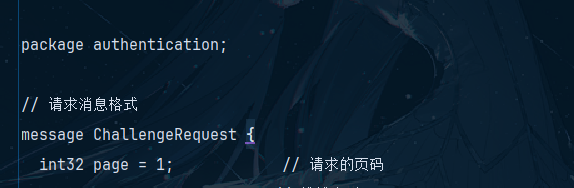
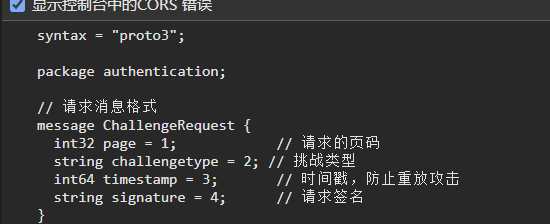
message ChallengeRequest {
int32 page = 1; // 请求的页码
string challengetype = 2; // 挑战类型
int64 timestamp = 3; // 时间戳,防止重放攻击
string signature = 4; // 请求签名
}看来是对challengetype和signature 进行了加密
其中signature使用了md_sign 这个类中的方法,笔者直接给出解混淆的代码,如下
class md_sign {
static F(x, y, z) {
return ~x & z | y & x
}
static G(x, y, z) {
return x & y | x & z | y & z
}
static H(x, y, z) {
return x ^ y ^ z
}
static rot(x, n) {
return x << n | x >>> 32 - n
}
static round1(a, b, c, d, k, s) {
return this.rot(a + this.F(b, c, d) + k, s)
}
static round2(a, b, c, d, k, s) {
return this.rot(a + this.G(b, c, d) + k + 0x5a827999, s)
}
static round3(a, b, c, d, k, s) {
return this.rot(a + this.H(b, c, d) + k + 0x6ed9eba1, s)
}
static padMessage(bytes) {
const bits = bytes.length * 8, padded = [...bytes];
padded.push(0x80);
while ((padded.length % 64) !== 56) padded.push(0);
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) padded.push(bits >>> i * 8 & 0xff);
return padded;
}
static hash(inputBytes) {
const padded = this.padMessage(inputBytes);
let A = 0x67452301;
let B = 0xefcdab89;
let C = 0x98badcfe;
let D = 0x10325476;
for (let block = 0x0; block < padded.length / 0x40; block++) {
const M = new Array(0x10);
for (let i = 0x0; i < 0x10; i++) {
const offset = block * 0x40 + i * 0x4;
M[i] = padded[offset] & 0xff | (padded[offset + 0x1] & 0xff) << 0x8 | (padded[offset + 0x2] & 0xff) << 0x10 | (padded[offset + 0x3] & 0xff) << 0x18
}
let AA = A;
let BB = B;
let CC = C;
let DD = D;
AA = this.round1(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x0], 0x3);
DD = this.round1(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x1], 0x7);
CC = this.round1(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x2], 0xb);
BB = this.round1(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0x3], 0x13);
AA = this.round1(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x4], 0x3);
DD = this.round1(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x5], 0x7);
CC = this.round1(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x6], 0xb);
BB = this.round1(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0x7], 0x13);
AA = this.round1(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x8], 0x3);
DD = this.round1(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x9], 0x7);
CC = this.round1(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0xa], 0xb);
BB = this.round1(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xb], 0x13);
AA = this.round1(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0xc], 0x3);
DD = this.round1(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0xd], 0x7);
CC = this.round1(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0xe], 0xb);
BB = this.round1(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xf], 0x13);
AA = this.round2(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x0], 0x3);
DD = this.round2(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x4], 0x5);
CC = this.round2(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x8], 0x9);
BB = this.round2(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xc], 0xd);
AA = this.round2(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x1], 0x3);
DD = this.round2(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x5], 0x5);
CC = this.round2(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x9], 0x9);
BB = this.round2(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xd], 0xd);
AA = this.round2(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x2], 0x3);
DD = this.round2(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x6], 0x5);
CC = this.round2(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0xa], 0x9);
BB = this.round2(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xe], 0xd);
AA = this.round2(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x3], 0x3);
DD = this.round2(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x7], 0x5);
CC = this.round2(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0xb], 0x9);
BB = this.round2(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xf], 0xd);
/* 第 3 轮 16 步:显式调用 round3,无混淆 */
AA = this.round3(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x0], 0x3);
DD = this.round3(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x8], 0x9);
CC = this.round3(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x4], 0xb);
BB = this.round3(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xc], 0xf);
AA = this.round3(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x2], 0x3);
DD = this.round3(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0xa], 0x9);
CC = this.round3(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x6], 0xb);
BB = this.round3(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xe], 0xf);
AA = this.round3(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x1], 0x3);
DD = this.round3(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0x9], 0x9);
CC = this.round3(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x5], 0xb);
BB = this.round3(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xd], 0xf);
AA = this.round3(AA, BB, CC, DD, M[0x3], 0x3);
DD = this.round3(DD, AA, BB, CC, M[0xb], 0x9);
CC = this.round3(CC, DD, AA, BB, M[0x7], 0xb);
BB = this.round3(BB, CC, DD, AA, M[0xf], 0xf);
A = A + AA >>> 0x0;
B = B + BB >>> 0x0;
C = C + CC >>> 0x0;
D = D + DD >>> 0x0
}
const result = [A & 0xff, A >>> 0x8 & 0xff, A >>> 0x10 & 0xff, A >>> 0x18 & 0xff, B & 0xff, B >>> 0x8 & 0xff, B >>> 0x10 & 0xff, B >>> 0x18 & 0xff, C & 0xff, C >>> 0x8 & 0xff, C >>> 0x10 & 0xff, C >>> 0x18 & 0xff, D & 0xff, D >>> 0x8 & 0xff, D >>> 0x10 & 0xff, D >>> 0x18 & 0xff];
return result.map(b => {
return b.toString(0x10).padStart(0x2, "0")
}).join("")
}
}为什么要给出这个代码,一看,觉得是md5加密,但是,不对劲
看下面
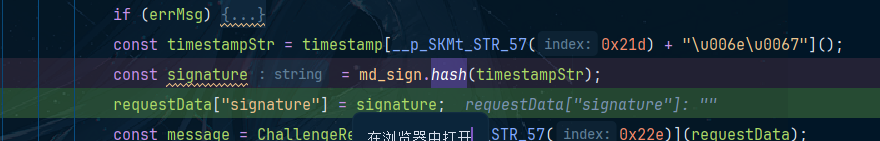
这个是调用其中的hash方法,把时间戳传进去,但是,笔者对123456进行加密
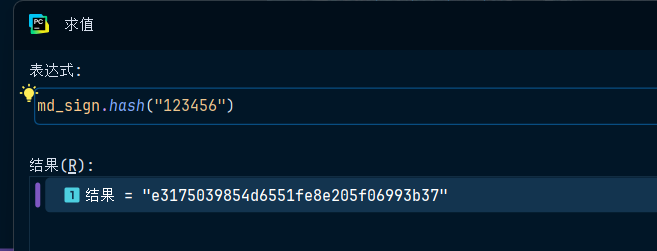
发现不对劲,结果应该是e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e
有问题。
因此,笔者就把这个js解混淆,一看,确实不是标准的,
一文详解 MD5 信息摘要算法 - bjxiaxueliang - 博客园![]() https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaxveliang/p/15004954.htmlshifts不是标准的,缺少了round4。
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaxveliang/p/15004954.htmlshifts不是标准的,缺少了round4。
总之,解开了。
challenget_type加密后是surwrexibfkdoohqjh,这好像是个定值,不会变化。
===============就这样,明天再说=============
js使用proto文件
继续搞事情
加载依赖
正好学习一下这个proto,这个东西,怎么使用
前端如何对接protobuf | PingCode智库![]() https://docs.pingcode.com/baike/2563896笔者新建一个html文件,加载依赖protobuf的关键依赖
https://docs.pingcode.com/baike/2563896笔者新建一个html文件,加载依赖protobuf的关键依赖
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/protobufjs/7.5.4/protobuf.min.js"></script>对应proto文件,就使用这道题的challenge.proto
加载proto文件
<script type="module">
const root = await protobuf.load('/static/protos/challenge.proto');
</script>结果如下
没问题。
获取ChallengeRequest、ChallengeResponse并使用
在proto文件,有个package,相当于包的名字,需要使用
即,代码如下
const ChallengeRequest=root.lookup('authentication.ChallengeRequest')
const ChallengeResponse=root.lookup('authentication.ChallengeResponse')
console.log(ChallengeRequest)
console.log(ChallengeResponse)有点多的属性
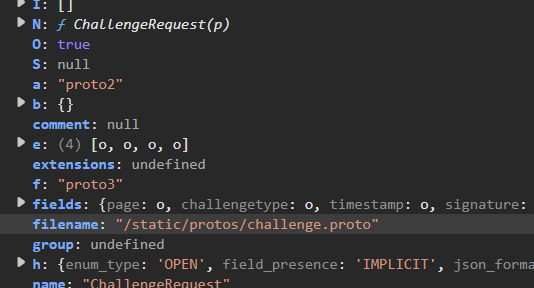
在fieldsArray发现了关键的东西
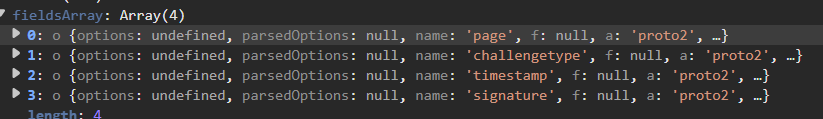
这个ChallengeRequest就类似于rust中的结构体,其中的page、challengetype等就是其中的字段。差不多
现在还没有初始化ChallengeRequest,需要初始化,比如
const req = ChallengeRequest.create({
page: 1,
challengetype: 'protobuf_challenge',
timestamp: Date.now(),
signature: '123456'
});结果如下
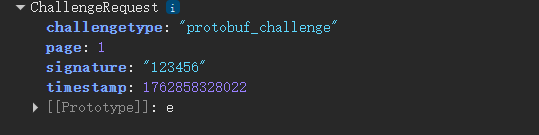
发送请求于与响应
使用ChallengeRequest和ChallengeResponse出来请求和响应
直接给出代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="./js/protobuf.min.js"></script>
<script src="./js/md5.js"></script>
<script type="module">
const root = await protobuf.load('/static/protos/challenge.proto');
const ChallengeRequest = root.lookup('authentication.ChallengeRequest')
const ChallengeResponse = root.lookup('authentication.ChallengeResponse')
let t = Date.now()
const req = ChallengeRequest.create({
page: 1,
challengetype: 'surwrexibfkdoohqjh',
timestamp: t.toString(),
signature: md_sign.hash(t.toString())
});
const buffer = ChallengeRequest.encode(req).finish();
console.log(buffer instanceof Uint8Array, buffer);
const res = await fetch('http://localhost:8082/authentication/api/protobuf_challenge/page/1/', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-protobuf'
},
body: buffer
});
const respBuf = new Uint8Array(await res.arrayBuffer());
const resp = ChallengeResponse.decode(respBuf);
console.log(resp)
const sum = resp.numbers.reduce((s, item) => s + item.value, 0);
console.log(sum)
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>md5.js就是前面解混淆的函数所在的文件
结果如下
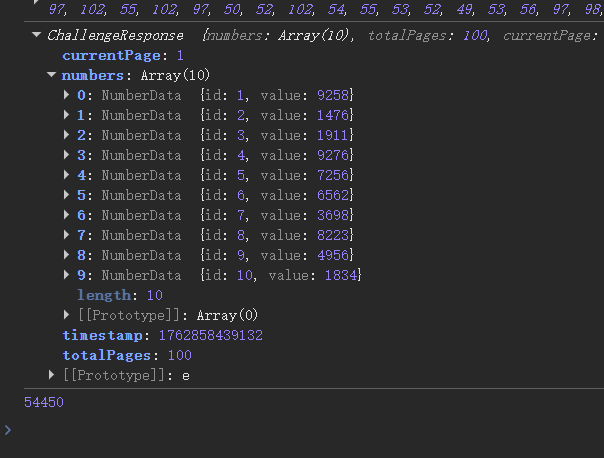
没什么问题
使用rust或者python应该也可以搞,笔者懒得搞了,就这样。
proto与rust
按道理来说,这篇博客已经完成了,笔者有其他想法,先使用rust来操作一些proto
新建一个项目
cargo new proto-rs
玩一玩。一些参考
https://protobuf.com.cn/reference/rust/![]() https://protobuf.com.cn/reference/rust/深入掌握 Prost:Rust 中 Protocol Buffers 的高级应用与实战技巧 - 知乎
https://protobuf.com.cn/reference/rust/深入掌握 Prost:Rust 中 Protocol Buffers 的高级应用与实战技巧 - 知乎![]() https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/694261734andrewhickman/prost-reflect: A protobuf library extending prost with reflection support and dynamic messages.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/694261734andrewhickman/prost-reflect: A protobuf library extending prost with reflection support and dynamic messages.![]() https://github.com/andrewhickman/prost-reflect
https://github.com/andrewhickman/prost-reflect
看来可以使用prost-reflect和prost这两个crate。
直接给出Cargo.toml文件
[package]
name = "proto-rs"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2024"
[dependencies]
serde_json = "1.0.145"
prost-reflect = {version = "0.16.2",features = ["serde","text-format"]}
prost = {version = "0.14.1"}
protox = {version = "0.9.0"}
[build-dependencies]
prost-build = {version = "0.14.1"}静态代码生成
先使用prost来试试
首先,把这个challenge.proto文件放到src/proto目录下。
目录如下
然后在build.rs中,其中的代码如下
use std::io::Result;
fn main()-> Result<()> {
prost_build::compile_protos(&["src/proto/challenge.proto"],
&["src/proto/"])?;
println!("cargo:rerun-if-changed=src/proto/challenge.proto");
Ok(())
}
构建
cargo build
然后,就可以在target/{debug|release}/build/{crate}-{hash}/out/发现如下文件
就会生成authentication.rs文件,如下
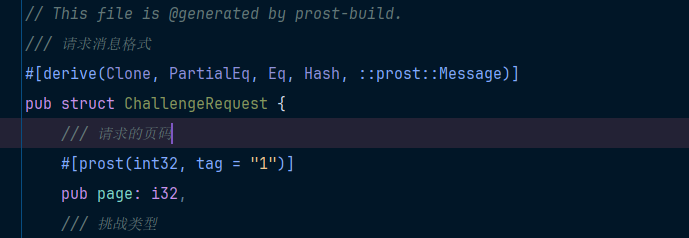
没问题
在main.rs中导入并运行
include!(concat!(env!("OUT_DIR"), "/authentication.rs"));
fn main() {
let request = ChallengeRequest {
page: 1,
challengetype: "protobuf_challenge".to_string(),
timestamp: 1234567890123,
signature: "666".to_string(),
};
let n1=NumberData{
id:1,
value:1,
};
let n2=NumberData{
id:2,
value:2,
};
let resp=ChallengeResponse{
numbers:vec![n1,n2],
total_pages:100,
current_page:1,
timestamp:1234567890123,
signature:"666".to_string()
};
println!("request: {:?}", request);
println!("resp: {:?}", resp);
}
结果如下,没问题

动态加载
动态加载
这个动态加载还挺麻烦的,笔者学习了一下。
reflect的英文意思是反射,实际上动态加载proto文件,就是使用了反射,类似于java的反射
当然,没有java那么强大。
首先,初始化一个DescriptorPool
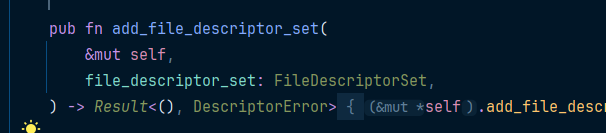
let mut pool = DescriptorPool::new();pool有个方法add_file_descriptor_set
需要传入一个FileDescriptorSet,那么就还需要获取这个
为了获取 FileDescriptorSet,需要使用protox,而protox有一个complie方法
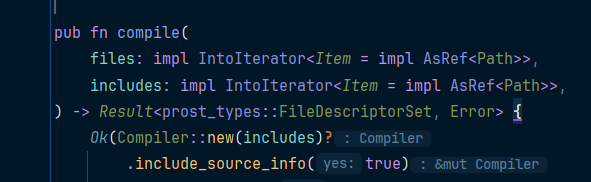
函数签名如下
pub fn compile(
files: impl IntoIterator<Item = impl AsRef<Path>>,
includes: impl IntoIterator<Item = impl AsRef<Path>>,
) -> Result<prost_types::FileDescriptorSet, Error>impl IntoIterator表示任何可以转换为迭代器的类型
Item = impl AsRef<Path>表示迭代器产生的每个元素必须实现 AsRef<Path>
成功则返回prost_types::FileDescriptorSet
这就非常的灵活,可以传vec,也可以传 &str,或者传PathBuf
但是传字符串会被作为文件路径去使用
因此,代码如下
let file_descriptor = protox::compile(&["src/proto/challenge.proto"], &["src/proto"])?;
调用add_file_descriptor_set
pool.add_file_descriptor_set(file_descriptor)?;现在就完成了proto文件的初始化。
后面就使其中的message的初始化,笔者以ChallengeRequest 为例子
还是类似,需要一个东西把ChallengeRequest 反射出来,
首先,在 Protocol Buffers 中,message是一个关键字,用于创建了一个复合数据类型(类似于 Rust 的 struct 或 Java 的 class)。
那么需要把message反射出来,这就需要使用prost-reflect中的MessageDescriptor这个结构体
如何才能获取这个结构体?这就需要使用DescriptorPool中的get_message_by_name这个方法
这一步其实javascript获取proto里面的message差不多,那么rust中的代码如下
let request_descriptor = pool
.get_message_by_name("authentication.ChallengeRequest")
.ok_or("ChallengeRequest 未找到")?;这个request_descriptor 的类型就是MessageDescriptor,但是还没完。
这个MessageDescriptor是什么???
MessageDescriptor这个东西,该怎么说,笔者的理解,
就是认为这个MessageDescriptor是一个“工厂”,一个工厂,并不是产品,需要再进一步,
需要生成出产品——DynamicMessage。
因此,代码如下
let mut request = DynamicMessage::new(request_descriptor);现在就生成出来这个产品ChallengeRequest ,但是里面什么都没有,需要放东西
而放东西的方法——set_field_by_name
因此,代码如下
request.set_field_by_name("page", Value::I32(1));
request.set_field_by_name("challengetype", Value::String("6666".to_string()));
request.set_field_by_name("timestamp", Value::I64(123));
request.set_field_by_name("signature", Value::String("signature".to_string()));至此,才完成了ChallengeRequest 的初始化
总之,还是比较麻烦的。
笔者直接给出全部的代码
use prost::Message;
use prost_reflect::{DescriptorPool, DynamicMessage, Value, ReflectMessage};
use std::collections::HashMap;
fn create_dynamic_request() -> Result<String, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let mut pool = DescriptorPool::new();
let file_descriptor = protox::compile(&["src/proto/challenge.proto"], &["src/proto"])?;
pool.add_file_descriptor_set(file_descriptor)?;
let request_descriptor = pool
.get_message_by_name("authentication.ChallengeRequest")
.ok_or("ChallengeRequest 未找到")?;
let mut request = DynamicMessage::new(request_descriptor);
request.set_field_by_name("page", Value::I32(1));
request.set_field_by_name("challengetype", Value::String("6666".to_string()));
request.set_field_by_name("timestamp", Value::I64(123));
request.set_field_by_name("signature", Value::String("signature".to_string()));
Ok(serde_json::to_string(&request)?)
}
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
println!("=== 动态生成 ChallengeRequest ===");
let request = create_dynamic_request()?;
println!("{}",request);
Ok(())
}打印结果如下

可以的,不是,有点麻烦的。
wasm和proto
笔者决定再进一步,在wasm里面获取proto文件,然后初始化,编写爬虫,行。
=================先这样吧,明天再说===============
好。
首先,初始化一个wasm项目
wasm-pack new wasm-proto
删除没有用的文件
新建一个examples,里面新建一个html文件,打包wasm项目到examples里面
顺便把static目录和proto文件也复制过来。
笔者使用cargo-make打包,其中Makefile.toml文件的内容如下
[tasks.build-wasm]
command = "wasm-pack"
args = ["build", "--target", "web", "--out-dir", "./examples/pkg", "--no-pack"]
打包后,目录如下
后面的流程其实很简单
- 初始化wasm
- 获取proto文件
- 动态加载message,生成参数
- 发送请求
- 处理响应
首先,考虑如何获取wasm文件,看看地址和路由
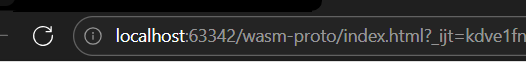
可以确定proto文件的路由是/wasm-proto/static/protos/challenge.proto
加载proto文件
其中关键代码如下
async fn get_proto() -> Result<String, JsValue> {
let window = window().ok_or("无 window 对象")?;
let origin = window.location().origin().map_err(|_| "获取 origin 失败")?;
let url = format!("{}/wasm-proto/static/protos/challenge.proto", origin);
let content = reqwest::get(&url)
.await
.map_err(|e| JsValue::from_str(&e.to_string()))?
.text()
.await
.map_err(|e| JsValue::from_str(&e.to_string()))?;
Ok(content)
}
#[wasm_bindgen(start)]
pub async fn main(){
let result=get_proto().await.map_err(|e| "ggg".to_string()).unwrap();
log_1(&JsValue::from_str(&result))
}
#[wasm_bindgen(start)]这个属性宏中有一个参数start,使用了,在初始化的时候就会执行这个函数,就会初始化proto文件
打包,运行,结果如下

可以看到加载了wasm文件和proto文件
也输出了,说明加载没问题
=====明天再说==========
映射message
笔者发现自己考虑的不是很好,笔者发现关键文件,protox这个compile这个方法,需要传入路径,但笔者前面获取的是字符串,那搞了寂寞,使用不了,笔者尝试了,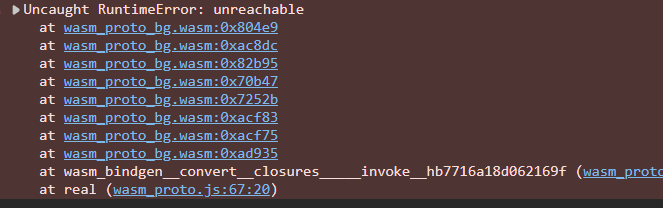 。
。
怎么办?
怎么办?
怎么办?
动态加载的文件不能使用。既然如此,静态操作,使用prost,反正proto文件不会变化的。
静态编译,直接给出结果,如下
在lib.rs中导入
use prost::Message;
include!(concat!(env!("OUT_DIR"), "/authentication.rs"));那么,后面的事情就不必多说。
最后的代码
直接给出全部代码
lib.rs
use prost::Message;
use protox::Error;
use reqwest::Client;
use wasm_bindgen::prelude::*;
use web_sys::{console::log_1, window};
include!(concat!(env!("OUT_DIR"), "/authentication.rs"));
#[wasm_bindgen(module = "/md5.js")]
extern "C" {
type MdSign;
// 绑定静态方法 hash
#[wasm_bindgen(static_method_of = MdSign)]
fn hash(timestamp: String) -> String;
}
fn get_timestamp() -> i64 {
#[wasm_bindgen]
extern "C" {
#[wasm_bindgen(js_namespace = Date)]
fn now() -> f64;
}
now() as i64
}
fn generate_signature(timestamp: i64) -> String {
MdSign::hash(timestamp.to_string())
}
async fn send_request(page: i32, body: &[u8]) {
log_1(&JsValue::from(ChallengeResponse::decode(&mut
Client::new()
.post(format!(
"http://localhost:8082/authentication/api/protobuf_challenge/page/{page}/"
))
.body(body.to_vec())
.send()
.await
.unwrap()
.bytes()
.await
.unwrap()
)
.unwrap()
.numbers
.iter()
.map(|n|n.value)
.sum::<i32>()))
}
#[wasm_bindgen(start)]
pub async fn main() {
let timestamp = get_timestamp();
let signature = generate_signature(timestamp.clone());
let request = ChallengeRequest {
page: 1,
challengetype: "surwrexibfkdoohqjh".to_string(),
timestamp,
signature,
};
let mut buf = Vec::new();
request.encode(&mut buf).unwrap();
send_request(1, &buf).await;
}
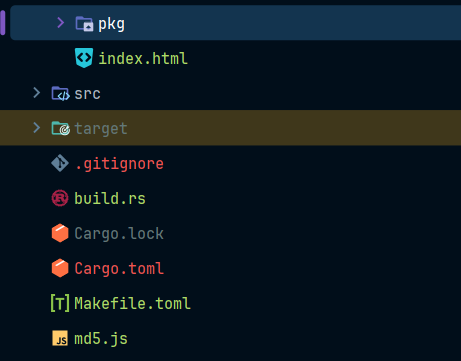
目录结构
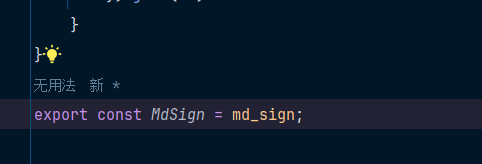
md5.js的改动
运行,启动代理。结果如下
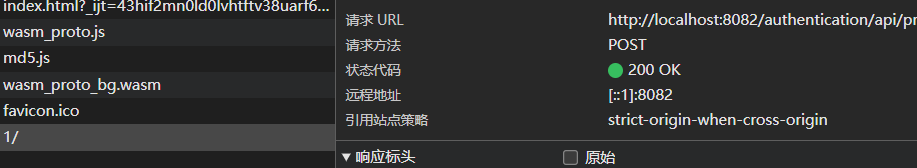
没问题。
终于完成了。
总结
经过了多天,其实这个proto问题和wasm差不多,都是需要获取某个东西,然后使用这个东西。
就没了。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容








所有评论(0)