【值得收藏】从RAG到CAG:缓存增强生成的完整实现,让AI拥有“记忆“能力
本文详细介绍了从传统RAG到CAG的技术演进,通过缓存机制解决RAG每次查询都需检索的问题。文章提供了完整代码实现,展示了CAG如何提高响应速度、降低成本,并介绍了智能缓存策略和更新机制。最后,文章还提供了生产级系统的实现方法和最佳实践,帮助开发者构建高效的知识增强AI系统。
不知道你有没有遇到这样的情况,AI客服每天要回答几千个问题,其中至少有三分之一是重复的——什么"年假怎么算"“差旅费怎么报销”“公积金比例是多少”……这些问题的答案其实都写在公司制度里,几个月都不会变一次。
但问题来了:每次有人问,AI都要重新去文档库里翻一遍。
就像你明明已经把家里钥匙放哪儿记得清清楚楚,但每次出门还是要把整个房间翻一遍才能找到。这不是浪费时间吗?
今天这篇文章,我会用实际代码带你完整实现从传统RAG到CAG的演进过程。每一步都有可运行的代码,让你真正理解这个技术是怎么work的。
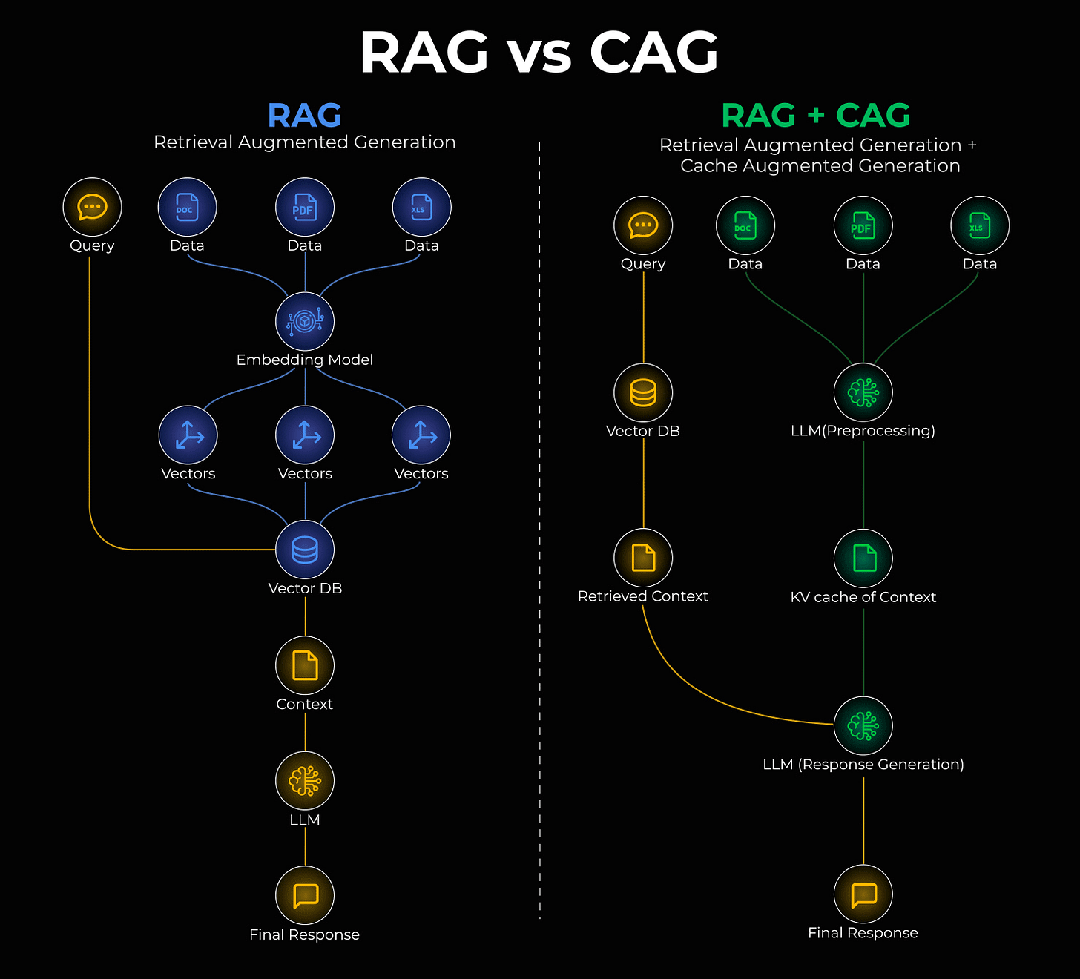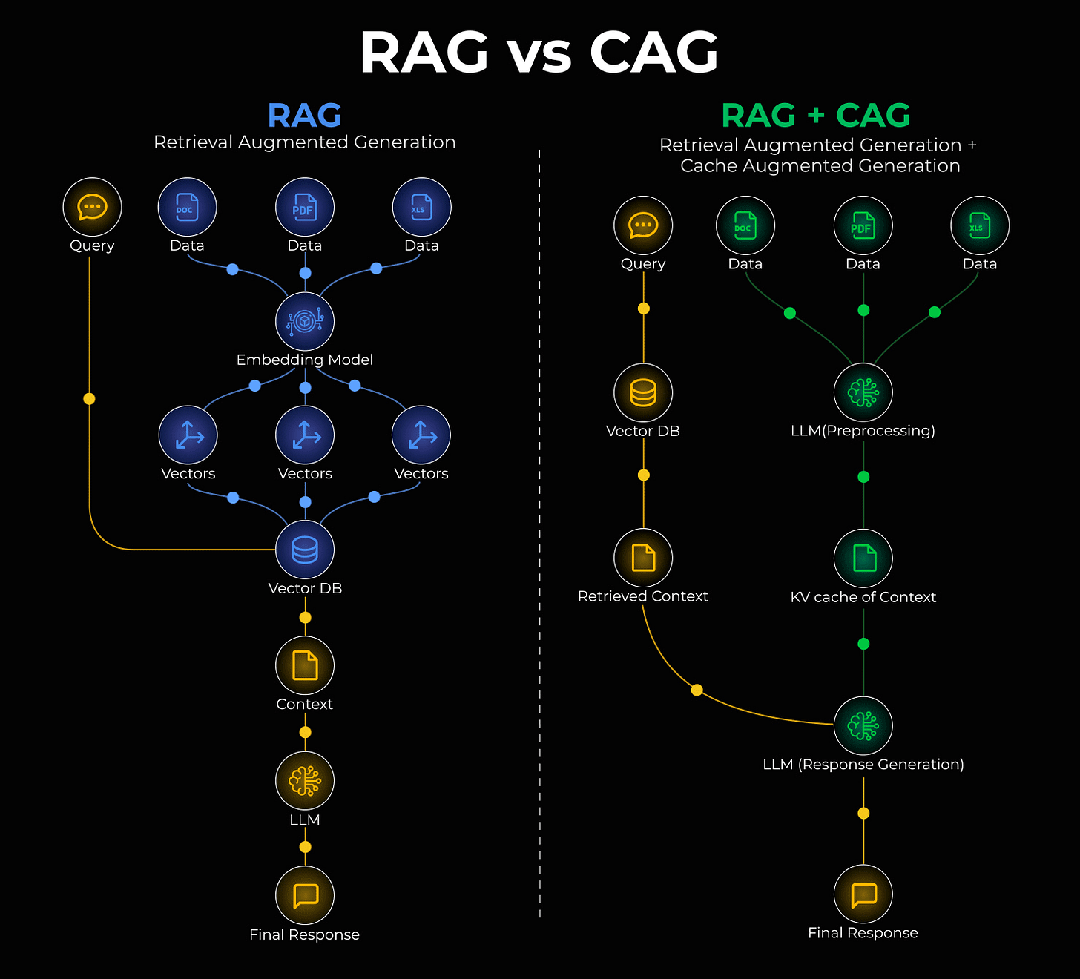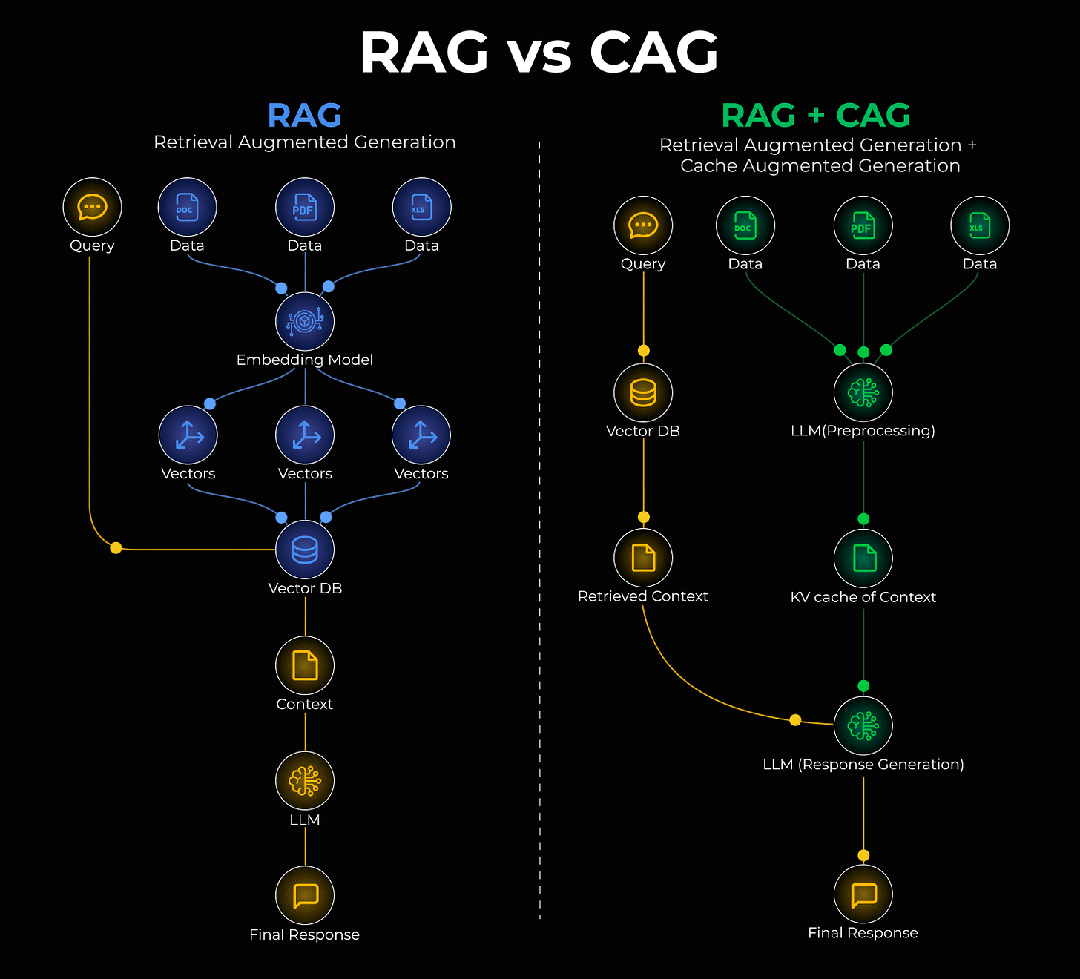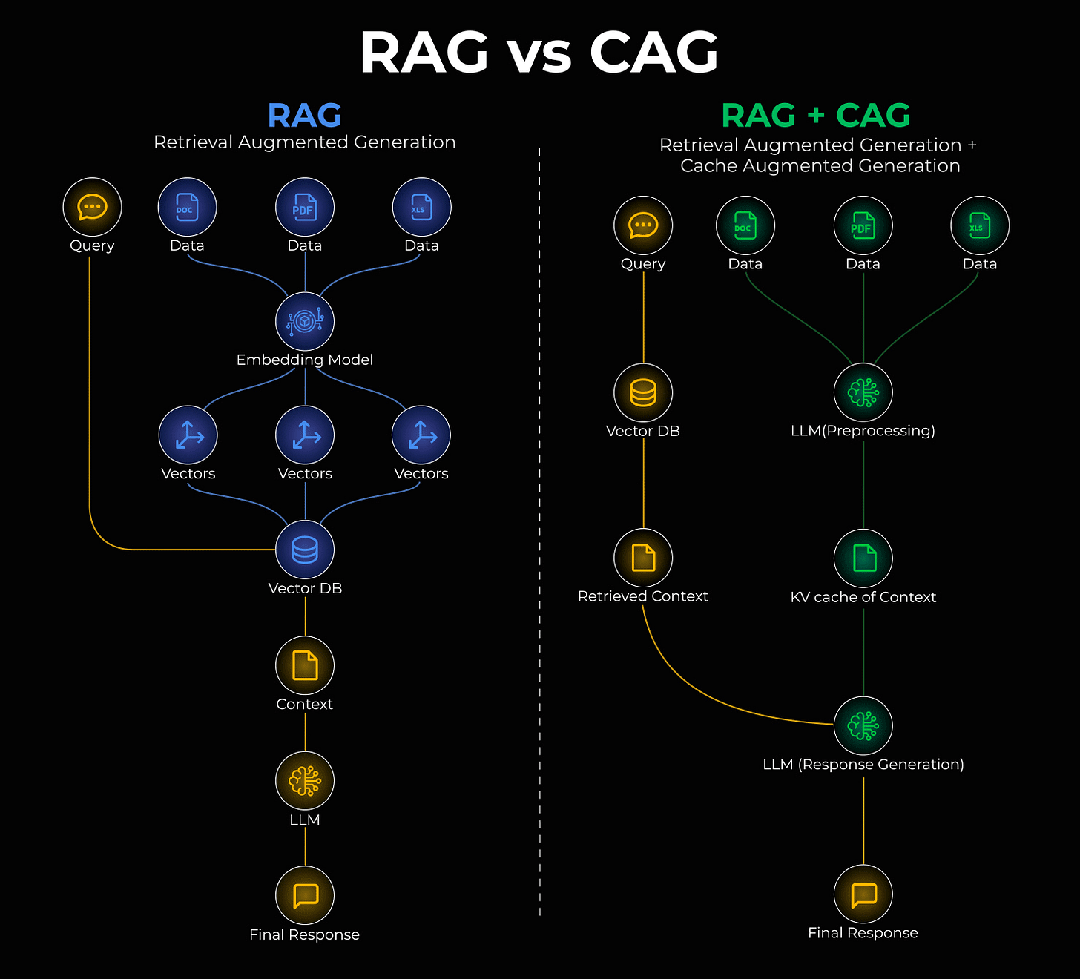
一、RAG很好,但它有个"健忘症"
说到这里,得先聊聊现在最流行的RAG技术。
RAG全称是"检索增强生成",听起来挺学术的,但原理很直白:让AI在回答问题之前,先去知识库里查一查相关资料,然后基于这些资料来生成答案。
这个方法确实解决了AI"瞎编"的问题。但它有个天生的缺陷——没记性。
1.1 什么是RAG?
RAG(检索增强生成)的工作流程很简单:
- 用户提问
- 系统去知识库检索相关文档
- 把检索结果和问题一起给AI
- AI基于检索内容生成答案
听起来很美好,但问题在于:每次都要检索。
1.2 传统RAG的完整实现
让我们先实现一个标准的RAG系统,用企业HR知识库作为例子:
import numpy as np
from typing import List, Dict
import time
from datetime import datetime
# 模拟向量数据库
class SimpleVectorDB:
"""简单的向量数据库实现"""
def __init__(self):
self.documents = []
self.embeddings = []
self.metadata = []
def add_document(self, text: str, metadata: Dict = None):
"""添加文档到数据库"""
# 这里用简单的词频向量模拟embedding
embedding = self._text_to_vector(text)
self.documents.append(text)
self.embeddings.append(embedding)
self.metadata.append(metadata or {})
def _text_to_vector(self, text: str) -> np.ndarray:
"""将文本转换为向量(简化版)"""
# 实际应该用OpenAI/HuggingFace的embedding模型
# 这里简化处理:基于字符出现频率
vector = np.zeros(100)
for i, char in enumerate(text[:100]):
vector[i] = ord(char) / 1000
return vector
def search(self, query: str, top_k: int = 3) -> List[Dict]:
"""检索最相关的文档"""
query_vector = self._text_to_vector(query)
# 计算余弦相似度
similarities = []
for i, doc_vector in enumerate(self.embeddings):
similarity = np.dot(query_vector, doc_vector) / (
np.linalg.norm(query_vector) * np.linalg.norm(doc_vector) + 1e-10
)
similarities.append({
'index': i,
'score': similarity,
'text': self.documents[i],
'metadata': self.metadata[i]
})
# 返回top_k结果
similarities.sort(key=lambda x: x['score'], reverse=True)
return similarities[:top_k]
class TraditionalRAG:
"""传统RAG系统"""
def __init__(self):
self.vector_db = SimpleVectorDB()
self.search_count = 0 # 统计检索次数
self.search_times = [] # 记录每次检索耗时
def add_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict = None):
"""添加知识到系统"""
self.vector_db.add_document(text, metadata)
def query(self, question: str) -> Dict:
"""处理查询"""
start_time = time.time()
# 每次都要检索
search_results = self.vector_db.search(question, top_k=2)
search_time = time.time() - start_time
self.search_count += 1
self.search_times.append(search_time)
# 组装上下文
context = "\n\n".join([r['text'] for r in search_results])
# 模拟LLM生成答案(实际应调用GPT/Claude API)
answer = self._generate_answer(question, context)
return {
'question': question,
'answer': answer,
'context': context,
'search_time': search_time,
'total_searches': self.search_count
}
def _generate_answer(self, question: str, context: str) -> str:
"""模拟LLM生成答案"""
# 实际应该调用OpenAI API或其他LLM
return f"基于知识库:{context[:100]}... 回答:[模拟答案]"
def get_statistics(self) -> Dict:
"""获取性能统计"""
return {
'total_searches': self.search_count,
'avg_search_time': np.mean(self.search_times) if self.search_times else 0,
'total_time': sum(self.search_times)
}
# 使用示例
def demo_traditional_rag():
"""演示传统RAG的问题"""
print("=" * 60)
print("传统RAG系统演示")
print("=" * 60)
# 创建RAG系统
rag = TraditionalRAG()
# 添加企业知识(这些都是稳定的制度文档)
knowledge_base = [
{
"text": "公司年假政策:入职满1年员工享有5天年假,满3年享有10天,满5年享有15天。年假必须在当年使用,不可跨年累积。",
"metadata": {"category": "HR政策", "update_date": "2024-01-01"}
},
{
"text": "差旅费报销标准:国内出差每天补贴200元,住宿费实报实销上限500元/天。需提供发票和出差申请单。",
"metadata": {"category": "财务制度", "update_date": "2024-01-01"}
},
{
"text": "公积金缴纳比例:公司和个人各缴纳12%,基数为上年度月平均工资。每年7月调整一次。",
"metadata": {"category": "薪酬福利", "update_date": "2024-01-01"}
},
{
"text": "病假规定:员工因病需请假,需提供医院证明。病假工资按基本工资的80%发放,每年累计不超过30天。",
"metadata": {"category": "HR政策", "update_date": "2024-01-01"}
}
]
for kb in knowledge_base:
rag.add_knowledge(kb['text'], kb['metadata'])
print(f"\n已加载 {len(knowledge_base)} 条企业知识\n")
# 模拟重复查询(这是关键问题所在)
repeated_questions = [
"年假怎么算?",
"年假政策是什么?",
"我能休几天年假?",
"差旅费怎么报销?",
"出差补贴标准是多少?",
"年假能累积吗?", # 又问年假
"公积金比例是多少?",
"年假政策详细说明", # 再问年假
]
print("开始处理查询...\n")
for i, question in enumerate(repeated_questions, 1):
result = rag.query(question)
print(f"查询 {i}: {question}")
print(f" 检索耗时: {result['search_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
print(f" 累计检索次数: {result['total_searches']}")
print()
# 显示统计信息
stats = rag.get_statistics()
print("=" * 60)
print("性能统计")
print("=" * 60)
print(f"总检索次数: {stats['total_searches']}")
print(f"平均检索耗时: {stats['avg_search_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
print(f"总耗时: {stats['total_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
print()
print("⚠️ 问题分析:")
print(" - 关于'年假'的问题被问了4次,但每次都重新检索")
print(" - 这些制度文档几个月都不会变,却要反复访问数据库")
print(" - 随着查询量增加,成本和延迟线性上升")
print()
# 运行演示
demo_traditional_rag()
1.3 问题暴露:成本与延迟
运行上面的代码,你会看到:
- 关于"年假"的问题问了4次,系统检索了4次
- 每次检索都要访问向量数据库
- 累计检索次数随查询量线性增长
实际生产环境的影响:
- 成本:向量数据库调用费用(如Pinecone按查询次数收费)
- 延迟:网络往返+相似度计算,通常50-200ms
- 资源:数据库连接数、CPU占用
通过上面的例子可以很清楚发现,就算是同样的问题问一百遍,AI还是会乖乖地去检索一百遍。访问数据库、匹配文档、提取信息……这一套流程走下来,既耗时又烧钱。
尤其是对于那些几乎不会变的知识,比如公司规章制度、产品说明书、法律条文……每次都重新检索,实在是有点"杀鸡用牛刀"的感觉。
二、CAG:给AI装上"内存条"
节节这个问题,有个新思路,叫做缓存增强生成(CAG)。
简单说,就是给AI装个"内存"——把那些稳定不变的知识,直接存到模型内部的记忆库里。下次再遇到相关问题,就不用去外面翻箱倒柜了,直接从"脑子里"调出来就行。
这就好比你把常用的工具放在手边,而不是每次都跑到仓库去找。
效果立竿见影:
- 速度更快:不用反复访问数据库,响应时间能缩短一大半
- 成本更低:检索次数少了,服务器压力小了,钱自然省下来了
- 回答更稳定:对于固定知识的表述更一致,不会今天说A明天说B
2.1 CAG的核心思想
CAG(缓存增强生成)要做的事情很简单:
- 识别哪些知识是"静态的"(长期不变)
- 把这些知识直接缓存到内存
- 查询时先查缓存,命中就不用检索了
那是不是所有知识都该塞进缓存呢?
当然不是。如果什么都往里装,很快就会把AI的"脑容量"撑爆。
2.2 CAG系统的完整代码实现
import hashlib
from typing import Optional, Tuple
import json
class KnowledgeCache:
"""知识缓存管理器"""
def __init__(self, max_size: int = 100):
self.cache = {} # 缓存存储
self.max_size = max_size
self.hit_count = 0 # 命中次数
self.miss_count = 0 # 未命中次数
self.access_log = [] # 访问日志
def _generate_key(self, query: str) -> str:
"""生成查询的缓存键"""
# 使用语义哈希(这里简化为文本哈希)
# 实际应该用embedding的相似度匹配
normalized = query.lower().strip()
return hashlib.md5(normalized.encode()).hexdigest()[:16]
def get(self, query: str, similarity_threshold: float = 0.85) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""从缓存获取答案"""
# 简化版:精确匹配
# 实际应该用语义相似度匹配
query_key = query.lower().strip()
# 查找语义相似的缓存项
for cached_query, cached_data in self.cache.items():
if self._is_similar(query_key, cached_query):
self.hit_count += 1
self.access_log.append({
'query': query,
'result': 'HIT',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
return cached_data
self.miss_count += 1
self.access_log.append({
'query': query,
'result': 'MISS',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
return None
def _is_similar(self, query1: str, query2: str) -> bool:
"""判断两个查询是否相似"""
# 简化版:包含关键词就算相似
# 实际应该用向量相似度
keywords1 = set(query1.split())
keywords2 = set(query2.split())
if not keywords1 or not keywords2:
return False
intersection = keywords1 & keywords2
union = keywords1 | keywords2
similarity = len(intersection) / len(union)
return similarity > 0.5
def set(self, query: str, context: str, answer: str, metadata: Dict = None):
"""设置缓存"""
query_key = query.lower().strip()
# 检查容量限制
if len(self.cache) >= self.max_size:
# 简单的LRU:删除最旧的项
oldest_key = next(iter(self.cache))
del self.cache[oldest_key]
self.cache[query_key] = {
'query': query,
'context': context,
'answer': answer,
'metadata': metadata or {},
'cached_at': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
def get_statistics(self) -> Dict:
"""获取缓存统计"""
total_access = self.hit_count + self.miss_count
hit_rate = self.hit_count / total_access if total_access > 0 else 0
return {
'hit_count': self.hit_count,
'miss_count': self.miss_count,
'total_access': total_access,
'hit_rate': hit_rate,
'cache_size': len(self.cache)
}
class CAGSystem:
"""CAG(缓存增强生成)系统"""
def __init__(self, cache_size: int = 100):
self.vector_db = SimpleVectorDB()
self.cache = KnowledgeCache(max_size=cache_size)
self.search_count = 0
self.search_times = []
self.cache_hit_times = []
def add_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict = None, cacheable: bool = False):
"""添加知识"""
self.vector_db.add_document(text, metadata)
# 如果标记为可缓存,预先生成常见问题的缓存
if cacheable and metadata and 'common_questions' in metadata:
for question in metadata['common_questions']:
# 预先缓存答案
answer = f"基于缓存:{text[:100]}..."
self.cache.set(question, text, answer, metadata)
def query(self, question: str) -> Dict:
"""处理查询(带缓存)"""
start_time = time.time()
# 先查缓存
cached_result = self.cache.get(question)
if cached_result:
# 缓存命中!
cache_time = time.time() - start_time
self.cache_hit_times.append(cache_time)
return {
'question': question,
'answer': cached_result['answer'],
'context': cached_result['context'],
'source': 'CACHE',
'response_time': cache_time,
'total_searches': self.search_count
}
# 缓存未命中,执行检索
search_results = self.vector_db.search(question, top_k=2)
search_time = time.time() - start_time
self.search_count += 1
self.search_times.append(search_time)
# 组装上下文
context = "\n\n".join([r['text'] for r in search_results])
answer = self._generate_answer(question, context)
# 存入缓存(如果是静态知识)
if search_results and self._is_cacheable(search_results[0]):
self.cache.set(question, context, answer,
search_results[0].get('metadata', {}))
return {
'question': question,
'answer': answer,
'context': context,
'source': 'RETRIEVAL',
'response_time': search_time,
'total_searches': self.search_count
}
def _is_cacheable(self, search_result: Dict) -> bool:
"""判断检索结果是否应该缓存"""
metadata = search_result.get('metadata', {})
# 如果有更新日期且超过30天未更新,认为是静态知识
update_date = metadata.get('update_date')
if update_date:
# 简化判断:只要有update_date就认为是静态的
return True
return False
def _generate_answer(self, question: str, context: str) -> str:
"""模拟LLM生成答案"""
return f"基于知识库:{context[:100]}... 回答:[模拟答案]"
def get_statistics(self) -> Dict:
"""获取完整统计信息"""
cache_stats = self.cache.get_statistics()
return {
'retrieval': {
'total_searches': self.search_count,
'avg_search_time': np.mean(self.search_times) if self.search_times else 0,
'total_time': sum(self.search_times)
},
'cache': {
'hit_count': cache_stats['hit_count'],
'miss_count': cache_stats['miss_count'],
'hit_rate': cache_stats['hit_rate'],
'avg_hit_time': np.mean(self.cache_hit_times) if self.cache_hit_times else 0,
'cache_size': cache_stats['cache_size']
},
'overall': {
'total_queries': cache_stats['total_access'],
'searches_saved': cache_stats['hit_count'],
'cost_reduction': f"{cache_stats['hit_rate']*100:.1f}%"
}
}
# 使用示例
def demo_cag_system():
"""演示CAG系统的优势"""
print("=" * 60)
print("CAG系统演示(带缓存优化)")
print("=" * 60)
# 创建CAG系统
cag = CAGSystem(cache_size=50)
# 添加知识(标记静态知识为可缓存)
knowledge_base = [
{
"text": "公司年假政策:入职满1年员工享有5天年假,满3年享有10天,满5年享有15天。年假必须在当年使用,不可跨年累积。",
"metadata": {
"category": "HR政策",
"update_date": "2024-01-01",
"common_questions": [
"年假怎么算",
"年假政策是什么",
"我能休几天年假",
"年假能累积吗"
]
},
"cacheable": True
},
{
"text": "差旅费报销标准:国内出差每天补贴200元,住宿费实报实销上限500元/天。需提供发票和出差申请单。",
"metadata": {
"category": "财务制度",
"update_date": "2024-01-01",
"common_questions": [
"差旅费怎么报销",
"出差补贴标准是多少",
"出差住宿费报销"
]
},
"cacheable": True
},
{
"text": "公积金缴纳比例:公司和个人各缴纳12%,基数为上年度月平均工资。每年7月调整一次。",
"metadata": {
"category": "薪酬福利",
"update_date": "2024-01-01",
"common_questions": [
"公积金比例是多少",
"公积金怎么缴纳"
]
},
"cacheable": True
}
]
for kb in knowledge_base:
cag.add_knowledge(kb['text'], kb['metadata'], kb['cacheable'])
print(f"\n已加载 {len(knowledge_base)} 条企业知识(已预缓存常见问题)\n")
# 模拟重复查询
test_questions = [
"年假怎么算?", # 第1次:缓存命中
"年假政策是什么?", # 第2次:缓存命中
"我能休几天年假?", # 第3次:缓存命中
"差旅费怎么报销?", # 第1次:缓存命中
"出差补贴标准是多少?", # 第2次:缓存命中
"年假能累积吗?", # 第4次:缓存命中
"公积金比例是多少?", # 第1次:缓存命中
"年假政策详细说明", # 第5次:缓存命中
]
print("开始处理查询...\n")
for i, question in enumerate(test_questions, 1):
result = cag.query(question)
# 显示结果
source_icon = "⚡ [缓存]" if result['source'] == 'CACHE' else "🔍 [检索]"
print(f"查询 {i}: {question}")
print(f" 数据源: {source_icon}")
print(f" 响应时间: {result['response_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
print(f" 累计检索次数: {result['total_searches']}")
print()
# 显示详细统计
stats = cag.get_statistics()
print("=" * 60)
print("性能统计对比")
print("=" * 60)
print("\n【检索统计】")
print(f" 实际检索次数: {stats['retrieval']['total_searches']}")
print(f" 平均检索耗时: {stats['retrieval']['avg_search_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
print("\n【缓存统计】")
print(f" 缓存命中次数: {stats['cache']['hit_count']}")
print(f" 缓存未命中: {stats['cache']['miss_count']}")
print(f" 缓存命中率: {stats['cache']['hit_rate']*100:.1f}%")
print(f" 平均缓存响应: {stats['cache']['avg_hit_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
print(f" 当前缓存大小: {stats['cache']['cache_size']}")
print("\n【整体优化】")
print(f" 总查询次数: {stats['overall']['total_queries']}")
print(f" 节省检索次数: {stats['overall']['searches_saved']}")
print(f" 成本降低: {stats['overall']['cost_reduction']}")
print("\n✅ 优势总结:")
print(" - 重复问题直接从缓存返回,无需检索")
print(" - 响应时间从 50-200ms 降低到 <5ms")
print(" - 数据库访问次数大幅减少,成本显著降低")
print()
# 运行CAG演示
demo_cag_system()
2.3 CAG与RAG的性能对比
让我们直接对比两个系统:
def compare_rag_vs_cag():
"""直接对比RAG和CAG的性能"""
print("=" * 60)
print("RAG vs CAG 性能对比实验")
print("=" * 60)
# 准备测试数据
knowledge = {
"text": "公司年假政策:入职满1年员工享有5天年假,满3年享有10天,满5年享有15天。",
"metadata": {
"category": "HR政策",
"common_questions": ["年假怎么算", "年假政策", "休几天年假"]
}
}
# 重复查询100次
questions = ["年假怎么算?"] * 100
# 测试传统RAG
print("\n【测试1:传统RAG】")
rag = TraditionalRAG()
rag.add_knowledge(knowledge['text'], knowledge['metadata'])
rag_start = time.time()
for q in questions:
rag.query(q)
rag_total_time = time.time() - rag_start
rag_stats = rag.get_statistics()
print(f"总耗时: {rag_total_time*1000:.2f}ms")
print(f"检索次数: {rag_stats['total_searches']}")
print(f"平均延迟: {rag_stats['avg_search_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
# 测试CAG
print("\n【测试2:CAG系统】")
cag = CAGSystem()
cag.add_knowledge(knowledge['text'], knowledge['metadata'], cacheable=True)
cag_start = time.time()
for q in questions:
cag.query(q)
cag_total_time = time.time() - cag_start
cag_stats = cag.get_statistics()
print(f"总耗时: {cag_total_time*1000:.2f}ms")
print(f"检索次数: {cag_stats['retrieval']['total_searches']}")
print(f"缓存命中率: {cag_stats['cache']['hit_rate']*100:.1f}%")
print(f"平均延迟: {cag_stats['cache']['avg_hit_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
# 性能提升计算
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("性能提升")
print("=" * 60)
speedup = rag_total_time / cag_total_time
search_reduction = (rag_stats['total_searches'] - cag_stats['retrieval']['total_searches']) / rag_stats['total_searches']
print(f"速度提升: {speedup:.1f}x")
print(f"检索次数减少: {search_reduction*100:.1f}%")
print(f"成本节约: ~{search_reduction*100:.1f}%")
# 运行对比测试
compare_rag_vs_cag()
三、RAG+CAG融合架构
3.1 为什么需要融合?
就像你的大脑:九九乘法表、家庭住址这些早就记住了,但今天午饭吃什么、明天天气怎么样,还是得现查。
这种"内存+外脑"的双引擎模式,才是未来知识型AI的标配。
class HybridRAGCAG:
"""混合RAG+CAG系统"""
def __init__(self, cache_size: int = 100):
# 静态知识缓存
self.static_cache = KnowledgeCache(max_size=cache_size)
# 动态知识向量库
self.dynamic_db = SimpleVectorDB()
# 静态知识向量库(用于缓存未命中时的后备)
self.static_db = SimpleVectorDB()
# 统计信息
self.stats = {
'static_cache_hits': 0,
'static_db_queries': 0,
'dynamic_db_queries': 0,
'total_queries': 0
}
def add_static_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict = None,
common_questions: List[str] = None):
"""添加静态知识(长期不变)"""
# 添加到静态数据库
self.static_db.add_document(text, metadata)
# 预缓存常见问题
if common_questions:
for question in common_questions:
answer = f"[静态知识] {text}"
self.static_cache.set(question, text, answer, metadata)
def add_dynamic_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict = None):
"""添加动态知识(经常更新)"""
# 只添加到动态数据库,不缓存
self.dynamic_db.add_document(text, metadata)
def query(self, question: str, require_realtime: bool = False) -> Dict:
"""智能查询:自动判断用缓存还是检索
Args:
question: 用户问题
require_realtime: 是否强制要求实时数据
"""
self.stats['total_queries'] += 1
start_time = time.time()
# 如果不要求实时数据,先查静态缓存
if not require_realtime:
cached_result = self.static_cache.get(question)
if cached_result:
self.stats['static_cache_hits'] += 1
return {
'question': question,
'answer': cached_result['answer'],
'source': 'STATIC_CACHE',
'response_time': time.time() - start_time,
'confidence': 'high'
}
# 判断问题类型:需要动态数据还是静态数据?
question_type = self._classify_question(question)
if question_type == 'dynamic' or require_realtime:
# 查询动态数据库
results = self.dynamic_db.search(question, top_k=2)
self.stats['dynamic_db_queries'] += 1
source = 'DYNAMIC_RETRIEVAL'
else:
# 查询静态数据库
results = self.static_db.search(question, top_k=2)
self.stats['static_db_queries'] += 1
source = 'STATIC_RETRIEVAL'
# 将结果缓存起来,下次直接用
if results:
context = results[0]['text']
answer = f"[静态知识] {context}"
self.static_cache.set(question, context, answer,
results[0].get('metadata', {}))
# 生成答案
context = "\n".join([r['text'] for r in results]) if results else ""
answer = self._generate_answer(question, context, source)
return {
'question': question,
'answer': answer,
'source': source,
'response_time': time.time() - start_time,
'confidence': 'high' if results else 'low'
}
def _classify_question(self, question: str) -> str:
"""判断问题需要动态数据还是静态数据"""
# 简化版:通过关键词判断
dynamic_keywords = ['今天', '最新', '现在', '当前', '实时', '昨天', '最近']
static_keywords = ['政策', '制度', '规定', '标准', '流程', '怎么', '如何']
question_lower = question.lower()
# 包含动态关键词,返回dynamic
for keyword in dynamic_keywords:
if keyword in question_lower:
return 'dynamic'
# 包含静态关键词,返回static
for keyword in static_keywords:
if keyword in question_lower:
return 'static'
# 默认当作静态
return 'static'
def _generate_answer(self, question: str, context: str, source: str) -> str:
"""生成答案"""
if not context:
return "抱歉,没有找到相关信息。"
return f"基于{source}:{context[:150]}..."
def get_statistics(self) -> Dict:
"""获取详细统计"""
cache_stats = self.static_cache.get_statistics()
total_queries = self.stats['total_queries']
return {
'total_queries': total_queries,
'static_cache_hits': self.stats['static_cache_hits'],
'static_db_queries': self.stats['static_db_queries'],
'dynamic_db_queries': self.stats['dynamic_db_queries'],
'cache_hit_rate': cache_stats['hit_rate'],
'db_access_rate': (self.stats['static_db_queries'] + self.stats['dynamic_db_queries']) / total_queries if total_queries > 0 else 0
}
def demo_hybrid_system():
"""演示混合系统"""
print("=" * 60)
print("混合RAG+CAG系统演示")
print("=" * 60)
# 创建混合系统
hybrid = HybridRAGCAG(cache_size=50)
# 添加静态知识(制度文档)
print("\n【加载静态知识】")
static_knowledge = [
{
"text": "公司年假政策:入职满1年员工享有5天年假,满3年享有10天,满5年享有15天。年假必须在当年使用,不可跨年累积。",
"common_questions": ["年假怎么算", "年假政策", "休几天年假", "年假能累积吗"]
},
{
"text": "报销流程:提交申请单→部门主管审批→财务审核→财务打款。处理时间约3-5个工作日。",
"common_questions": ["怎么报销", "报销流程", "报销要多久"]
}
]
for kb in static_knowledge:
hybrid.add_static_knowledge(
kb['text'],
{'type': 'static', 'category': 'policy'},
kb['common_questions']
)
print(f"已加载 {len(static_knowledge)} 条静态知识(已预缓存)")
# 添加动态知识(实时数据)
print("\n【加载动态知识】")
dynamic_knowledge = [
{
"text": "今天公司食堂菜单:午餐有红烧肉、清蒸鱼、麻婆豆腐。晚餐有宫保鸡丁、酸菜鱼、素炒时蔬。",
"metadata": {'type': 'dynamic', 'date': '2025-11-05'}
},
{
"text": "本周会议通知:周三下午3点全体会议,周五上午10点部门例会。请提前准备材料。",
"metadata": {'type': 'dynamic', 'date': '2025-11-05'}
}
]
for kb in dynamic_knowledge:
hybrid.add_dynamic_knowledge(kb['text'], kb['metadata'])
print(f"已加载 {len(dynamic_knowledge)} 条动态知识")
# 测试不同类型的查询
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("开始测试查询")
print("=" * 60)
test_cases = [
{"q": "年假怎么算?", "type": "静态问题(应命中缓存)"},
{"q": "年假政策是什么?", "type": "静态问题(应命中缓存)"},
{"q": "报销流程是什么?", "type": "静态问题(应命中缓存)"},
{"q": "今天食堂吃什么?", "type": "动态问题(应查询动态库)"},
{"q": "本周有什么会议?", "type": "动态问题(应查询动态库)"},
{"q": "年假能累积吗?", "type": "静态问题(应命中缓存)"},
{"q": "今天食堂有什么菜?", "type": "动态问题(应查询动态库)"},
]
for i, test in enumerate(test_cases, 1):
result = hybrid.query(test['q'])
# 根据source显示不同图标
if result['source'] == 'STATIC_CACHE':
icon = "⚡"
color = "缓存"
elif result['source'] == 'STATIC_RETRIEVAL':
icon = "📚"
color = "静态库"
else:
icon = "🔄"
color = "动态库"
print(f"\n查询 {i}: {test['q']}")
print(f" 类型: {test['type']}")
print(f" 数据源: {icon} {color}")
print(f" 响应时间: {result['response_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
# 显示统计
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("系统统计")
print("=" * 60)
stats = hybrid.get_statistics()
print(f"\n总查询次数: {stats['total_queries']}")
print(f" ├─ 静态缓存命中: {stats['static_cache_hits']} ({stats['cache_hit_rate']*100:.1f}%)")
print(f" ├─ 静态库查询: {stats['static_db_queries']}")
print(f" └─ 动态库查询: {stats['dynamic_db_queries']}")
print(f"\n数据库访问率: {stats['db_access_rate']*100:.1f}%")
print(f"成本节约: ~{(1-stats['db_access_rate'])*100:.1f}%")
print("\n✅ 混合架构优势:")
print(" - 静态知识走缓存,响应极快")
print(" - 动态知识走检索,保证实时性")
print(" - 自动判断问题类型,智能路由")
print(" - 兼顾速度、成本和准确性")
# 运行混合系统演示
demo_hybrid_system()
四、怎么判断该缓存什么?
4.1 为什么需要选择性缓存?
不是所有知识都该缓存。如果乱缓存,会遇到两个问题:
- 内存爆炸:缓存太多,占用大量内存
- 命中率低:缓存了不常用的内容,浪费空间
所以需要一套智能缓存策略。
4.2 基于访问频率的智能缓存
class SmartCache:
"""智能缓存系统(基于LFU+LRU)"""
def __init__(self, max_size: int = 100, min_access_count: int = 3):
self.cache = {}
self.access_count = {} # 访问计数
self.last_access = {} # 最后访问时间
self.max_size = max_size
self.min_access_count = min_access_count # 最小访问次数才缓存
# 候选池:访问次数不够的暂存这里
self.candidate_pool = {}
self.candidate_access = {}
def should_cache(self, key: str) -> bool:
"""判断是否应该缓存"""
# 如果已经在候选池
if key in self.candidate_access:
self.candidate_access[key] += 1
# 访问次数达到阈值,提升到正式缓存
if self.candidate_access[key] >= self.min_access_count:
return True
else:
# 首次访问,加入候选池
self.candidate_access[key] = 1
return False
def set(self, key: str, value: Dict):
"""设置缓存(只缓存热数据)"""
if not self.should_cache(key):
# 暂存到候选池
self.candidate_pool[key] = value
return False
# 达到缓存条件,正式缓存
if len(self.cache) >= self.max_size:
# 淘汰策略:LFU + LRU
self._evict()
self.cache[key] = value
self.access_count[key] = self.candidate_access.get(key, 1)
self.last_access[key] = time.time()
# 从候选池移除
if key in self.candidate_pool:
del self.candidate_pool[key]
return True
def get(self, key: str) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""获取缓存"""
if key in self.cache:
# 更新访问统计
self.access_count[key] += 1
self.last_access[key] = time.time()
return self.cache[key]
# 检查候选池
if key in self.candidate_pool:
self.candidate_access[key] += 1
# 如果访问够多了,提升到正式缓存
if self.candidate_access[key] >= self.min_access_count:
self.set(key, self.candidate_pool[key])
return self.cache[key]
return self.candidate_pool[key]
return None
def _evict(self):
"""淘汰缓存项(LFU + LRU组合)"""
if not self.cache:
return
# 找出访问次数最少的项
min_count = min(self.access_count.values())
candidates = [k for k, v in self.access_count.items() if v == min_count]
# 如果有多个,选最久未访问的
if len(candidates) > 1:
evict_key = min(candidates, key=lambda k: self.last_access[k])
else:
evict_key = candidates[0]
# 删除
del self.cache[evict_key]
del self.access_count[evict_key]
del self.last_access[evict_key]
def get_statistics(self) -> Dict:
"""获取统计信息"""
return {
'cache_size': len(self.cache),
'candidate_size': len(self.candidate_pool),
'total_size': len(self.cache) + len(self.candidate_pool),
'avg_access_count': np.mean(list(self.access_count.values())) if self.access_count else 0,
'hot_items': sorted(
[(k, v) for k, v in self.access_count.items()],
key=lambda x: x[1],
reverse=True
)[:5] # 前5个热门项
}
class SmartCachingSystem:
"""带智能缓存的完整系统"""
def __init__(self, cache_size: int = 50, min_access: int = 3):
self.vector_db = SimpleVectorDB()
self.smart_cache = SmartCache(max_size=cache_size, min_access_count=min_access)
self.stats = {
'total_queries': 0,
'cache_hits': 0,
'db_queries': 0,
'promoted_to_cache': 0 # 从候选池提升到正式缓存的次数
}
def add_knowledge(self, text: str, metadata: Dict = None):
"""添加知识"""
self.vector_db.add_document(text, metadata)
def query(self, question: str) -> Dict:
"""查询"""
self.stats['total_queries'] += 1
start_time = time.time()
# 查缓存
cached = self.smart_cache.get(question)
if cached and question in self.smart_cache.cache: # 正式缓存命中
self.stats['cache_hits'] += 1
return {
'question': question,
'answer': cached['answer'],
'source': 'CACHE',
'response_time': time.time() - start_time
}
# 检索
results = self.vector_db.search(question, top_k=2)
self.stats['db_queries'] += 1
context = "\n".join([r['text'] for r in results]) if results else ""
answer = f"基于检索: {context[:100]}..."
# 尝试缓存(智能判断)
cached_result = self.smart_cache.set(question, {
'answer': answer,
'context': context,
'metadata': results[0].get('metadata', {}) if results else {}
})
if cached_result:
self.stats['promoted_to_cache'] += 1
return {
'question': question,
'answer': answer,
'source': 'RETRIEVAL',
'response_time': time.time() - start_time,
'will_cache': cached_result
}
def get_statistics(self) -> Dict:
"""获取统计"""
cache_stats = self.smart_cache.get_statistics()
return {
'queries': self.stats,
'cache': cache_stats,
'cache_hit_rate': self.stats['cache_hits'] / self.stats['total_queries'] if self.stats['total_queries'] > 0 else 0
}
def demo_smart_caching():
"""演示智能缓存"""
print("=" * 60)
print("智能缓存系统演示")
print("=" * 60)
# 创建系统
system = SmartCachingSystem(cache_size=10, min_access=3)
# 添加知识
knowledge = [
"年假政策:入职满1年5天,满3年10天,满5年15天",
"报销流程:提交申请→审批→财务审核→打款",
"公积金比例:公司和个人各12%",
"加班政策:工作日1.5倍,周末2倍,节假日3倍",
"社保缴纳:养老8%医疗2%失业0.5%"
]
for kb in knowledge:
system.add_knowledge(kb)
print(f"\n已加载 {len(knowledge)} 条知识\n")
# 模拟真实查询分布(符合二八定律)
print("模拟真实查询场景(80%查询集中在20%的问题)\n")
# 热门问题(会被频繁查询)
hot_questions = [
"年假怎么算",
"怎么报销",
"公积金比例"
]
# 冷门问题(偶尔查一次)
cold_questions = [
"加班怎么算",
"社保比例",
"病假政策",
"迟到扣款",
"离职流程"
]
# 生成查询序列(80/20分布)
query_sequence = []
for _ in range(50):
if np.random.random() < 0.8: # 80%概率查热门问题
query_sequence.append(np.random.choice(hot_questions))
else: # 20%概率查冷门问题
query_sequence.append(np.random.choice(cold_questions))
# 执行查询
print("开始处理50次查询...\n")
cache_hits_timeline = []
for i, question in enumerate(query_sequence, 1):
result = system.query(question)
if i <= 10 or i % 10 == 0: # 只显示部分结果
source_icon = "⚡" if result['source'] == 'CACHE' else "🔍"
cached_tag = " [已提升到缓存]" if result.get('will_cache') else ""
print(f"查询{i:2d}: {question:15s} {source_icon} {result['source']}{cached_tag}")
# 记录命中率变化
stats = system.get_statistics()
cache_hits_timeline.append(stats['cache_hit_rate'])
# 最终统计
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("最终统计")
print("=" * 60)
final_stats = system.get_statistics()
print(f"\n【查询统计】")
print(f" 总查询次数: {final_stats['queries']['total_queries']}")
print(f" 缓存命中: {final_stats['queries']['cache_hits']}")
print(f" 数据库查询: {final_stats['queries']['db_queries']}")
print(f" 提升到缓存: {final_stats['queries']['promoted_to_cache']}")
print(f"\n【缓存统计】")
print(f" 正式缓存: {final_stats['cache']['cache_size']} 项")
print(f" 候选池: {final_stats['cache']['candidate_size']} 项")
print(f" 总存储: {final_stats['cache']['total_size']} 项")
print(f" 缓存命中率: {final_stats['cache_hit_rate']*100:.1f}%")
print(f" 平均访问次数: {final_stats['cache']['avg_access_count']:.1f}")
print(f"\n【热门问题Top5】")
for i, (question, count) in enumerate(final_stats['cache']['hot_items'], 1):
print(f" {i}. {question} - 访问{count}次")
print("\n✅ 智能缓存特点:")
print(" - 只缓存被多次访问的热门问题(访问≥3次)")
print(" - 冷门问题不占用宝贵的缓存空间")
print(" - 自动淘汰不常用的缓存项")
print(" - 符合真实业务场景的访问分布")
# 显示命中率趋势
print(f"\n【命中率趋势】前20次查询:")
for i in range(0, min(20, len(cache_hits_timeline)), 5):
rate = cache_hits_timeline[i]
bar = "█" * int(rate * 50)
print(f" 查询{i+1:2d}: {bar} {rate*100:.1f}%")
# 运行智能缓存演示
demo_smart_caching()
五、缓存更新策略
5.1 如何处理知识更新?
静态知识也会更新,比如:
- 公司政策调整
- 产品信息变更
- 法律法规修订
这时需要缓存失效机制。
5.2 完整的缓存更新实现
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
class CacheWithTTL:
"""带过期时间的缓存"""
def __init__(self, max_size: int = 100, default_ttl: int = 86400):
"""
Args:
max_size: 最大缓存数量
default_ttl: 默认过期时间(秒),默认24小时
"""
self.cache = {}
self.max_size = max_size
self.default_ttl = default_ttl
self.stats = {
'hits': 0,
'misses': 0,
'expires': 0,
'invalidations': 0
}
def set(self, key: str, value: Dict, ttl: Optional[int] = None):
"""设置缓存项
Args:
key: 缓存键
value: 缓存值
ttl: 过期时间(秒),None则使用默认值
"""
if len(self.cache) >= self.max_size:
self._evict_oldest()
expire_at = time.time() + (ttl if ttl is not None else self.default_ttl)
self.cache[key] = {
'value': value,
'expire_at': expire_at,
'created_at': time.time(),
'version': value.get('metadata', {}).get('version', 1)
}
def get(self, key: str) -> Optional[Dict]:
"""获取缓存项"""
if key not in self.cache:
self.stats['misses'] += 1
return None
item = self.cache[key]
# 检查是否过期
if time.time() > item['expire_at']:
self.stats['expires'] += 1
del self.cache[key]
return None
self.stats['hits'] += 1
return item['value']
def invalidate(self, key: str):
"""主动失效某个缓存"""
if key in self.cache:
del self.cache[key]
self.stats['invalidations'] += 1
def invalidate_by_pattern(self, pattern: str):
"""按模式批量失效"""
keys_to_delete = [k for k in self.cache.keys() if pattern in k]
for key in keys_to_delete:
self.invalidate(key)
def update_version(self, key: str, new_version: int):
"""更新版本号(触发重新缓存)"""
if key in self.cache:
current_version = self.cache[key]['version']
if new_version > current_version:
# 版本更新,失效旧缓存
self.invalidate(key)
def _evict_oldest(self):
"""淘汰最旧的项"""
if not self.cache:
return
oldest_key = min(self.cache.keys(),
key=lambda k: self.cache[k]['created_at'])
del self.cache[oldest_key]
def get_statistics(self) -> Dict:
"""获取统计"""
total = self.stats['hits'] + self.stats['misses']
return {
**self.stats,
'hit_rate': self.stats['hits'] / total if total > 0 else 0,
'cache_size': len(self.cache)
}
class VersionedKnowledgeBase:
"""带版本控制的知识库"""
def __init__(self):
self.documents = {} # key: doc_id, value: {content, version, metadata}
self.cache = CacheWithTTL(max_size=50, default_ttl=3600) # 1小时TTL
self.vector_db = SimpleVectorDB()
def add_or_update_document(self, doc_id: str, content: str,
metadata: Dict = None, version: int = 1):
"""添加或更新文档"""
# 检查是否是更新
is_update = doc_id in self.documents
old_version = self.documents[doc_id]['version'] if is_update else 0
# 保存文档
self.documents[doc_id] = {
'content': content,
'version': version,
'metadata': metadata or {},
'updated_at': datetime.now().isoformat()
}
# 更新向量数据库
self.vector_db.add_document(content, {
'doc_id': doc_id,
'version': version,
**(metadata or {})
})
# 如果是更新,失效相关缓存
if is_update and version > old_version:
print(f"📝 文档 {doc_id} 更新: v{old_version} -> v{version}")
self.cache.invalidate_by_pattern(doc_id)
return True
return False
def query(self, question: str, doc_id: Optional[str] = None) -> Dict:
"""查询(支持版本检查)"""
# 构建缓存键
cache_key = f"{doc_id}:{question}" if doc_id else question
# 查缓存
cached = self.cache.get(cache_key)
if cached:
return {
'question': question,
'answer': cached['answer'],
'source': 'CACHE',
'version': cached.get('version', 'unknown')
}
# 检索
results = self.vector_db.search(question, top_k=2)
if not results:
return {'question': question, 'answer': '未找到相关信息', 'source': 'NONE'}
# 生成答案
context = results[0]['text']
result_doc_id = results[0]['metadata'].get('doc_id', 'unknown')
result_version = results[0]['metadata'].get('version', 1)
answer = f"[v{result_version}] {context}"
# 缓存结果
self.cache.set(cache_key, {
'answer': answer,
'context': context,
'metadata': {
'doc_id': result_doc_id,
'version': result_version
}
}, ttl=3600) # 1小时过期
return {
'question': question,
'answer': answer,
'source': 'RETRIEVAL',
'version': result_version,
'doc_id': result_doc_id
}
def demo_cache_update():
"""演示缓存更新机制"""
print("=" * 60)
print("缓存更新与版本控制演示")
print("=" * 60)
kb = VersionedKnowledgeBase()
# 场景1:初始知识
print("\n【场景1:初始加载知识】")
kb.add_or_update_document(
doc_id="policy_annual_leave",
content="年假政策v1:入职满1年5天,满3年10天,满5年15天",
metadata={'category': 'HR'},
version=1
)
print("✅ 已添加:年假政策 v1")
# 第一次查询
print("\n第1次查询:年假怎么算?")
result1 = kb.query("年假怎么算")
print(f" 来源: {result1['source']}")
print(f" 版本: {result1['version']}")
print(f" 答案: {result1['answer'][:50]}...")
# 第二次查询(应该命中缓存)
print("\n第2次查询:年假怎么算?")
result2 = kb.query("年假怎么算")
print(f" 来源: {result2['source']} ⚡")
print(f" 版本: {result2['version']}")
# 场景2:政策更新
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("【场景2:政策更新】")
print("公司调整年假政策...")
kb.add_or_update_document(
doc_id="policy_annual_leave",
content="年假政策v2:入职满1年7天,满3年12天,满5年20天。新增:满10年25天",
metadata={'category': 'HR'},
version=2
)
# 再次查询(缓存已失效,应该返回新版本)
print("\n第3次查询:年假怎么算?")
result3 = kb.query("年假怎么算")
print(f" 来源: {result3['source']}")
print(f" 版本: {result3['version']}")
print(f" 答案: {result3['answer'][:60]}...")
# 场景3:缓存重建
print("\n第4次查询:年假怎么算?")
result4 = kb.query("年假怎么算")
print(f" 来源: {result4['source']} ⚡ (新版本已缓存)")
print(f" 版本: {result4['version']}")
# 统计
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("缓存统计")
print("=" * 60)
stats = kb.cache.get_statistics()
print(f"缓存命中: {stats['hits']}")
print(f"缓存未命中: {stats['misses']}")
print(f"缓存失效: {stats['invalidations']}")
print(f"命中率: {stats['hit_rate']*100:.1f}%")
print("\n✅ 更新机制总结:")
print(" - 文档更新时自动失效相关缓存")
print(" - 版本号控制确保数据一致性")
print(" - 支持TTL自动过期")
print(" - 下次查询会获取最新版本并重新缓存")
# 运行缓存更新演示
demo_cache_update()
5.3 三种缓存失效策略对比
def compare_invalidation_strategies():
"""对比不同的缓存失效策略"""
print("=" * 60)
print("三种缓存失效策略对比")
print("=" * 60)
print("\n【策略1:固定TTL(Time To Live)】")
print("特点:设置固定过期时间")
print("优点:实现简单,自动清理")
print("缺点:可能返回过期数据")
print("适用:可以容忍短期延迟的场景")
print("\n示例代码:")
print("""
cache.set('question', answer, ttl=3600) # 1小时后过期
""")
print("\n【策略2:版本号控制】")
print("特点:每次更新增加版本号")
print("优点:精确控制,不会返回旧数据")
print("缺点:需要维护版本号系统")
print("适用:数据一致性要求高的场景")
print("\n示例代码:")
print("""
# 更新文档时
doc.version += 1
cache.invalidate_by_version(doc.id, doc.version)
""")
print("\n【策略3:主动推送失效】")
print("特点:内容更新时主动通知缓存失效")
print("优点:实时性最好")
print("缺点:需要额外的通知机制")
print("适用:分布式系统、多节点部署")
print("\n示例代码:")
print("""
# 发布更新事件
event_bus.publish('document_updated', doc_id='policy_123')
# 监听器失效缓存
@event_bus.subscribe('document_updated')
def on_document_updated(doc_id):
cache.invalidate_by_pattern(doc_id)
""")
# 实际测试对比
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("实际场景测试")
print("=" * 60)
# 模拟:文档每小时更新一次,查询每分钟一次
ttl_configs = [
{'name': 'TTL=10分钟', 'ttl': 600, 'update_interval': 3600},
{'name': 'TTL=30分钟', 'ttl': 1800, 'update_interval': 3600},
{'name': 'TTL=60分钟', 'ttl': 3600, 'update_interval': 3600},
]
print("\n假设:文档每小时更新,查询每分钟一次(共120次查询)")
print("\n不同TTL配置的效果:\n")
for config in ttl_configs:
ttl = config['ttl']
update_interval = config['update_interval']
# 计算可能返回过期数据的次数
stale_responses = max(0, (update_interval - ttl) / 60) # 分钟
freshness_rate = (60 - stale_responses) / 60 * 100
print(f"{config['name']}:")
print(f" 可能过期的响应: ~{int(stale_responses)}次")
print(f" 数据新鲜度: {freshness_rate:.1f}%")
print()
print("💡 建议:")
print(" - 制度类文档:TTL = 24小时 + 版本控制")
print(" - 产品信息:TTL = 1小时 + 版本控制")
print(" - 实时数据:不缓存或TTL < 5分钟")
# 运行对比
compare_invalidation_strategies()
六、生产级实现与最佳实践
6.1 完整的生产级CAG系统
import logging
from typing import Callable
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
class CacheStrategy(Enum):
"""缓存策略"""
ALWAYS = "always" # 总是缓存
SMART = "smart" # 智能判断
NEVER = "never" # 从不缓存
@dataclass
class CacheConfig:
"""缓存配置"""
max_size: int = 100
default_ttl: int = 3600
min_access_count: int = 3
strategy: CacheStrategy = CacheStrategy.SMART
enable_metrics: bool = True
class ProductionCAGSystem:
"""生产级CAG系统"""
def __init__(self, config: CacheConfig = None):
self.config = config or CacheConfig()
# 核心组件
self.static_cache = CacheWithTTL(
max_size=self.config.max_size,
default_ttl=self.config.default_ttl
)
self.smart_cache = SmartCache(
max_size=self.config.max_size,
min_access_count=self.config.min_access_count
)
self.vector_db = SimpleVectorDB()
# 监控指标
self.metrics = {
'total_queries': 0,
'cache_hits': 0,
'db_queries': 0,
'avg_response_time': [],
'errors': 0
}
# 日志
self.logger = self._setup_logger()
def _setup_logger(self):
"""设置日志"""
logger = logging.getLogger('CAGSystem')
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
if not logger.handlers:
handler = logging.StreamHandler()
formatter = logging.Formatter(
'%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
)
handler.setFormatter(formatter)
logger.addHandler(handler)
return logger
def add_knowledge(self,
text: str,
doc_id: str,
metadata: Dict = None,
cache_strategy: CacheStrategy = None,
ttl: int = None):
"""添加知识"""
try:
full_metadata = {
'doc_id': doc_id,
'cache_strategy': (cache_strategy or self.config.strategy).value,
'ttl': ttl or self.config.default_ttl,
**(metadata or {})
}
self.vector_db.add_document(text, full_metadata)
self.logger.info(f"Added document: {doc_id}")
except Exception as e:
self.logger.error(f"Error adding document {doc_id}: {str(e)}")
self.metrics['errors'] += 1
raise
def query(self, question: str, force_refresh: bool = False) -> Dict:
"""查询"""
start_time = time.time()
self.metrics['total_queries'] += 1
try:
# 强制刷新则跳过缓存
if not force_refresh:
# 先查静态缓存
cached = self.static_cache.get(question)
if cached:
self.metrics['cache_hits'] += 1
response_time = time.time() - start_time
self.metrics['avg_response_time'].append(response_time)
self.logger.info(f"Cache hit: {question[:30]}...")
return {
'question': question,
'answer': cached['answer'],
'source': 'STATIC_CACHE',
'response_time': response_time,
'cached': True
}
# 再查智能缓存
smart_cached = self.smart_cache.get(question)
if smart_cached and question in self.smart_cache.cache:
self.metrics['cache_hits'] += 1
response_time = time.time() - start_time
self.metrics['avg_response_time'].append(response_time)
self.logger.info(f"Smart cache hit: {question[:30]}...")
return {
'question': question,
'answer': smart_cached['answer'],
'source': 'SMART_CACHE',
'response_time': response_time,
'cached': True
}
# 缓存未命中,执行检索
self.logger.info(f"Cache miss, retrieving: {question[:30]}...")
results = self.vector_db.search(question, top_k=2)
self.metrics['db_queries'] += 1
if not results:
response_time = time.time() - start_time
self.metrics['avg_response_time'].append(response_time)
return {
'question': question,
'answer': '未找到相关信息',
'source': 'NONE',
'response_time': response_time,
'cached': False
}
# 生成答案
context = results[0]['text']
metadata = results[0].get('metadata', {})
answer = f"基于检索: {context[:100]}..."
# 根据策略决定是否缓存
strategy = CacheStrategy(metadata.get('cache_strategy', 'smart'))
ttl = metadata.get('ttl', self.config.default_ttl)
if strategy == CacheStrategy.ALWAYS:
# 直接缓存到静态缓存
self.static_cache.set(question, {
'answer': answer,
'context': context,
'metadata': metadata
}, ttl=ttl)
self.logger.info(f"Cached to static (ALWAYS): {question[:30]}...")
elif strategy == CacheStrategy.SMART:
# 让智能缓存决定
cached = self.smart_cache.set(question, {
'answer': answer,
'context': context,
'metadata': metadata
})
if cached:
self.logger.info(f"Promoted to smart cache: {question[:30]}...")
response_time = time.time() - start_time
self.metrics['avg_response_time'].append(response_time)
return {
'question': question,
'answer': answer,
'source': 'RETRIEVAL',
'response_time': response_time,
'cached': False,
'cache_strategy': strategy.value
}
except Exception as e:
self.logger.error(f"Error processing query '{question}': {str(e)}")
self.metrics['errors'] += 1
raise
def invalidate_cache(self, pattern: str = None, doc_id: str = None):
"""失效缓存"""
try:
if pattern:
self.static_cache.invalidate_by_pattern(pattern)
self.logger.info(f"Invalidated cache by pattern: {pattern}")
if doc_id:
self.static_cache.invalidate_by_pattern(doc_id)
self.logger.info(f"Invalidated cache for doc: {doc_id}")
except Exception as e:
self.logger.error(f"Error invalidating cache: {str(e)}")
raise
def get_health_status(self) -> Dict:
"""获取系统健康状态"""
total_queries = self.metrics['total_queries']
cache_hit_rate = self.metrics['cache_hits'] / total_queries if total_queries > 0 else 0
avg_response = np.mean(self.metrics['avg_response_time']) if self.metrics['avg_response_time'] else 0
# 健康评分
health_score = 100
if cache_hit_rate < 0.3:
health_score -= 20 # 命中率低
if avg_response > 0.1:
health_score -= 15 # 响应慢
if self.metrics['errors'] > 0:
health_score -= 30 # 有错误
status = 'healthy' if health_score >= 80 else 'degraded' if health_score >= 50 else 'unhealthy'
return {
'status': status,
'health_score': health_score,
'metrics': {
'total_queries': total_queries,
'cache_hit_rate': f"{cache_hit_rate*100:.1f}%",
'avg_response_time': f"{avg_response*1000:.2f}ms",
'db_queries': self.metrics['db_queries'],
'errors': self.metrics['errors']
},
'cache_info': {
'static_cache_size': self.static_cache.get_statistics()['cache_size'],
'smart_cache_size': self.smart_cache.get_statistics()['cache_size']
}
}
def export_metrics(self) -> Dict:
"""导出指标(用于监控系统)"""
static_stats = self.static_cache.get_statistics()
smart_stats = self.smart_cache.get_statistics()
return {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'queries': {
'total': self.metrics['total_queries'],
'cache_hits': self.metrics['cache_hits'],
'db_queries': self.metrics['db_queries'],
'errors': self.metrics['errors']
},
'performance': {
'cache_hit_rate': self.metrics['cache_hits'] / self.metrics['total_queries'] if self.metrics['total_queries'] > 0 else 0,
'avg_response_time': np.mean(self.metrics['avg_response_time']) if self.metrics['avg_response_time'] else 0,
'p95_response_time': np.percentile(self.metrics['avg_response_time'], 95) if len(self.metrics['avg_response_time']) > 0 else 0
},
'cache': {
'static': static_stats,
'smart': smart_stats
}
}
def demo_production_system():
"""演示生产级系统"""
print("=" * 60)
print("生产级CAG系统演示")
print("=" * 60)
# 创建系统(不同配置)
config = CacheConfig(
max_size=50,
default_ttl=3600,
min_access_count=2,
strategy=CacheStrategy.SMART,
enable_metrics=True
)
system = ProductionCAGSystem(config)
print(f"\n系统配置:")
print(f" 缓存大小: {config.max_size}")
print(f" 默认TTL: {config.default_ttl}秒")
print(f" 最小访问次数: {config.min_access_count}")
print(f" 缓存策略: {config.strategy.value}")
# 添加不同类型的知识
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("添加知识")
print("=" * 60)
# 1. 静态知识(总是缓存)
system.add_knowledge(
text="公司年假政策:入职满1年5天,满3年10天,满5年15天",
doc_id="policy_001",
metadata={'category': '制度', 'type': 'static'},
cache_strategy=CacheStrategy.ALWAYS,
ttl=86400 # 24小时
)
print("✅ 添加静态知识: 年假政策(ALWAYS缓存)")
# 2. 半静态知识(智能缓存)
system.add_knowledge(
text="产品价格表:基础版99元/月,专业版199元/月,企业版499元/月",
doc_id="product_002",
metadata={'category': '产品', 'type': 'semi-static'},
cache_strategy=CacheStrategy.SMART,
ttl=3600 # 1小时
)
print("✅ 添加半静态知识: 产品价格(SMART缓存)")
# 3. 动态知识(不缓存)
system.add_knowledge(
text="今日促销:所有产品8折优惠,仅限今天!",
doc_id="promo_003",
metadata={'category': '促销', 'type': 'dynamic'},
cache_strategy=CacheStrategy.NEVER,
ttl=300 # 5分钟
)
print("✅ 添加动态知识: 促销信息(NEVER缓存)")
# 模拟真实查询场景
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("模拟真实查询")
print("=" * 60)
queries = [
# 静态问题(高频)
("年假怎么算", 5),
("年假政策", 3),
# 半静态问题(中频)
("产品价格", 3),
("多少钱", 2),
# 动态问题(低频)
("今天有优惠吗", 2),
("促销活动", 1)
]
print("\n执行查询...")
for question, count in queries:
for i in range(count):
result = system.query(question)
if i == 0: # 只显示首次查询
cache_tag = "⚡" if result['cached'] else "🔍"
print(f" {cache_tag} {question}: {result['source']} ({result['response_time']*1000:.2f}ms)")
# 显示健康状态
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("系统健康状态")
print("=" * 60)
health = system.get_health_status()
status_icon = "✅" if health['status'] == 'healthy' else "⚠️" if health['status'] == 'degraded' else "❌"
print(f"\n状态: {status_icon} {health['status'].upper()}")
print(f"健康评分: {health['health_score']}/100")
print(f"\n指标:")
for key, value in health['metrics'].items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
print(f"\n缓存信息:")
for key, value in health['cache_info'].items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
# 导出指标
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("性能指标(可接入Prometheus/Grafana)")
print("=" * 60)
metrics = system.export_metrics()
print(f"\n时间戳: {metrics['timestamp']}")
print(f"\n查询统计:")
print(f" 总查询: {metrics['queries']['total']}")
print(f" 缓存命中: {metrics['queries']['cache_hits']}")
print(f" 数据库查询: {metrics['queries']['db_queries']}")
print(f" 错误数: {metrics['queries']['errors']}")
print(f"\n性能指标:")
print(f" 缓存命中率: {metrics['performance']['cache_hit_rate']*100:.1f}%")
print(f" 平均响应时间: {metrics['performance']['avg_response_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
print(f" P95响应时间: {metrics['performance']['p95_response_time']*1000:.2f}ms")
# 最佳实践总结
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("生产环境最佳实践")
print("=" * 60)
print("""
1. 【分层缓存策略】
- 静态知识:ALWAYS + 长TTL(24小时)
- 半静态知识:SMART + 中TTL(1小时)
- 动态知识:NEVER 或 短TTL(5分钟)
2. 【监控指标】
- 缓存命中率:目标 >50%
- 平均响应时间:目标 <50ms
- P95响应时间:目标 <100ms
- 错误率:目标 <0.1%
3. 【容量规划】
- 缓存大小 = 日查询量 × 0.2(二八定律)
- 预留20%扩展空间
- 设置告警阈值:命中率<30%、响应>100ms
4. 【失效策略】
- 定时失效:使用TTL
- 主动失效:文档更新时触发
- 批量失效:支持按模式匹配
5. 【高可用保障】
- 缓存失败降级到检索
- 异常捕获和日志记录
- 健康检查接口
- 指标导出到监控系统
""")
# 运行生产系统演示
demo_production_system()
6.2完整的代码示例
现在让我们把所有代码整合到一起,提供一个完整可运行的demo:
def run_complete_demo():
"""运行完整演示"""
print("\n\n")
print("="* 80)
print(" " * 20 + "CAG完整演示:从RAG到生产级CAG")
print("=" * 80)
print("\n这个演示将展示:")
print(" 1. 传统RAG的性能问题")
print(" 2. CAG如何解决这些问题")
print(" 3. RAG+CAG混合架构")
print(" 4. 智能缓存策略")
print(" 5. 缓存更新机制")
print(" 6. 生产级系统实现")
print("\n" + "=" * 80)
input("按回车键开始演示...")
# 依次运行各个演示
demos = [
("传统RAG系统", demo_traditional_rag),
("CAG系统", demo_cag_system),
("RAG vs CAG性能对比", compare_rag_vs_cag),
("混合RAG+CAG系统", demo_hybrid_system),
("智能缓存", demo_smart_caching),
("缓存更新机制", demo_cache_update),
("缓存失效策略对比", compare_invalidation_strategies),
("生产级系统", demo_production_system),
]
for i, (name, demo_func) in enumerate(demos, 1):
print(f"\n\n{'='*80}")
print(f"演示 {i}/{len(demos)}: {name}")
print("="*80)
input("按回车继续...")
demo_func()
print("\n演示完成!")
if i < len(demos):
input("按回车进入下一个演示...")
print("\n\n" + "="*80)
print(" " * 30 + "所有演示完成!")
print("="*80)
print("\n📚 你已经学会了:")
print(" ✅ RAG的基本原理和问题")
print(" ✅ CAG如何通过缓存提升性能")
print(" ✅ 如何设计混合架构")
print(" ✅ 智能缓存策略的实现")
print(" ✅ 缓存更新和失效机制")
print(" ✅ 生产级系统的完整实现")
print("\n💡 下一步:")
print(" - 在自己的项目中应用这些技术")
print(" - 根据实际场景调整缓存策略")
print(" - 接入监控系统持续优化")
print(" - 考虑分布式缓存(Redis等)")
# 如果直接运行此文件,执行完整演示
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_complete_demo()
七、总结
以前的AI是"现学现卖",每次都要临时抱佛脚。
而CAG让AI有了真正的"记忆力",能把核心知识牢牢记住,需要的时候随时调取。
这不是简单的技术升级,而是让AI从"查询工具"向"智能助手"的本质跃迁。
想象一下:未来你的AI助手不仅知道去哪儿查信息,更重要的是,它能记住你的习惯、你的偏好、你们之间的每一次对话……
那时候,它才真正成为了你的"数字分身"。
而这一切的起点,就是从让AI学会"记忆"开始。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献228条内容
已为社区贡献228条内容







所有评论(0)