Android Build系列专题【篇五:构建系统build.prop生成机制】
Android Build系列专题【篇一:开发环境搭建】![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/118227738Android Build系列专题【篇二:AOSP编译流程】
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/118227738Android Build系列专题【篇二:AOSP编译流程】![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/113767664Android Build系列专题【篇三:平台编译流程】
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/113767664Android Build系列专题【篇三:平台编译流程】![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/153254875Android Build系列专题【篇四:编译文件相关语法】
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/153254875Android Build系列专题【篇四:编译文件相关语法】![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/153255058Android Build系列专题【篇五:构建系统主入口文件build/core/makefile】
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/153255058Android Build系列专题【篇五:构建系统主入口文件build/core/makefile】![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/154239576
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27672101/article/details/154239576
这里我们主要介绍一下android构建系统的主入口文件build/core/makefile,它承担着整个编译的启动和调度工作。该文件作为构建系统的起点,负责初始化编译环境并包含所有必要的子模块文件。具体功能包括:
- 版本检查:确保使用的 make 版本符合要求(通常需要 3.81 或更高)
- 环境设置:定义 BUILD_SYSTEM 等关键环境变量
- 核心配置:包含 config.mk、definitions.mk 等基础定义文件
- 目标管理:根据 MAKECMDGOALS 和 TARGET_BUILD_VARIANT 设置不同的编译目标
- 模块调度:协调整个构建系统的执行流程
Android构建系统采用模块化设计,位于build/core/目录下,由makefile和多个mk文件组成。makefile作为启动入口,main.mk作为核心流程文件,通过包含关系组织起整个构建框架。由于整个流程过于复杂,这里只记录我跟读过的一些模块。
再阅读本篇之前,建议先看看Android Build系列专题【篇四:编译文件相关语法】
android编译构建中,需要生成默认的系统属性的配置,即init进程的系统属性服务线程,解析的bu众多xxx/build.prop文件,并读取解析这些文件中的键值对,并加载到系统属性服务,这个时候,我们才可以通过getprop进行属性获取。那么xxx/build.prop是如何生成的呢?这里就来探究一下这套机制。
一、Kati构建方式之sysprop.mk
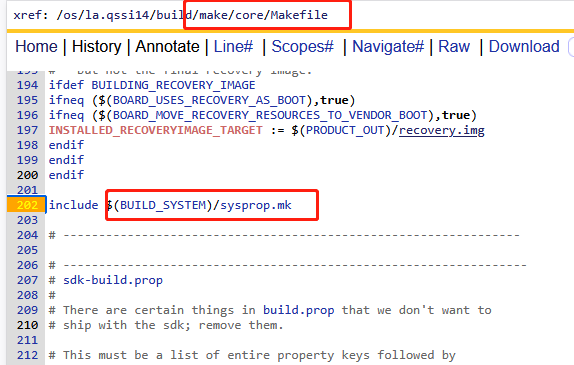
sysprop.mk文件在build/make/core/Makefile文件中直接include包含编译进去。sysprop.mk的主要目的就是为各个分区创建默认的build.prop文件,build.prop文件在init进程中的属性服务线程里面有去读取build.prop文件并把该文件中的键值对加载到内存中。由此系统属性才能被正式使用。
1、build-properties函数
build-properties函数主要目的是用来为各个分区创建build.prop文件,其定义如下:
# la.qssi16/build/core/sysprop.mk
# 函数功能:为各个分区partition创建etc/build.prop文件 Rule for generating <partition>/[etc/]build.prop file
# $(1): 分区名称,通常参数为system/product/vendor/odm
# $(2): 输出路径,通常为product/etc/build.prop
# $(3): 输入属性文件路径,此文件的内容通常为键值对直接输出到$(2)中, path to the input *.prop files. The contents of the files are directly emitted to the output
# $(4): 包含键值对格式属性的变量名列表,这些键值对直接输出到$(2)中, list of variable names each of which contains name=value pairs
# $(5): 可选的要强制移除的属性名列表,可以移除$3和$4的一些键值对,optional list of prop names to force remove from the output. Properties from both $(3) and (4) are affected
# $(6): 可选的要追加到文件末尾的文件列表,optional list of files to append at the end. The content of each file is emitted to the output
# $(7): 可选的跳过公共属性生成的标志,optional flag to skip common properties generation
# 函数名称:build-properties
define build-properties
# 流程1:把输出文件安装到系统中,即product/etc/build.prop安装到系统中生效能过被init进程解读
ALL_DEFAULT_INSTALLED_MODULES += $(2)
# 流程2:$4指定的键值对直接输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中
$(eval # Properties can be assigned using `prop ?= value` or `prop = value` syntax.)
$(eval # Eliminate spaces around the ?= and = separators.)
$(foreach name,$(strip $(4)),\
$(eval _temp := $$(call collapse-pairs,$$($(name)),?=))\
$(eval _resolved_$(name) := $$(call collapse-pairs,$$(_temp),=))\
)
$(eval # Implement the legacy behavior when BUILD_BROKEN_DUP_SYSPROP is on.)
$(eval # Optional assignments are all converted to normal assignments and)
$(eval # when their duplicates the first one wins)
$(if $(filter true,$(BUILD_BROKEN_DUP_SYSPROP)),\
$(foreach name,$(strip $(4)),\
$(eval _temp := $$(subst ?=,=,$$(_resolved_$(name))))\
$(eval _resolved_$(name) := $$(call uniq-pairs-by-first-component,$$(_resolved_$(name)),=))\
)\
$(eval _option := --allow-dup)\
)
# 流程3:清空或者创建输出文件,即通过touch指令创建product/etc/build.prop文件
$(2): $(POST_PROCESS_PROPS) $(INTERNAL_BUILD_ID_MAKEFILE) $(3) $(6) $(BUILT_KERNEL_VERSION_FILE_FOR_UFFD_GC)
$(hide) echo Building $$@
$(hide) mkdir -p $$(dir $$@)
$(hide) rm -f $$@ && touch $$@
# 流程4:如果$7不是true,调用generate-common-build-props函数,生成通用键值对到product/etc/build.prop文件中
ifneq ($(strip $(7)), true)
$(hide) $$(call generate-common-build-props,$(call to-lower,$(strip $(1))),$$@)
endif
# 流程5:遍历所有输入属性文件,添加分隔符和注释并输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中
# Make and Soong use different intermediate files to build vendor/build.prop.
# Although the sysprop contents are same, the absolute paths of android-info.prop are different.
# Print the filename for the intermediate files (files in OUT_DIR).
# This helps with validating mk->soong migration of android partitions.
$(hide) $(foreach file,$(strip $(3)),\
if [ -f "$(file)" ]; then\
echo "" >> $$@;\
echo "####################################" >> $$@;\
$(if $(filter $(OUT_DIR)/%,$(file)), \
echo "# from $(notdir $(file))" >> $$@;\
,\
echo "# from $(file)" >> $$@;\
)\
echo "####################################" >> $$@;\
cat $(file) >> $$@;\
fi;)
$(hide) $(foreach name,$(strip $(4)),\
echo "" >> $$@;\
echo "####################################" >> $$@;\
echo "# from variable $(name)" >> $$@;\
echo "####################################" >> $$@;\
$$(foreach line,$$(_resolved_$(name)),\
echo "$$(line)" >> $$@;\
)\
)
# 流程6:追加SDK版本等信息和文件结束符
$(hide) $(POST_PROCESS_PROPS) $$(_option) \
--sdk-version $(PLATFORM_SDK_VERSION) \
--kernel-version-file-for-uffd-gc "$(BUILT_KERNEL_VERSION_FILE_FOR_UFFD_GC)" \
$$@ $(5)
$(hide) $(foreach file,$(strip $(6)),\
if [ -f "$(file)" ]; then\
cat $(file) >> $$@;\
fi;)
$(hide) echo "# end of file" >> $$@
$(call declare-1p-target,$(2))
endef函数功能:为各个分区partition创建etc/build.prop文件
- $(1): 分区名称,通常参数为system/product/vendor/odm
- $(2): 输出路径,通常为product/etc/build.prop
- $(3): 输入属性文件路径,此文件的内容通常为键值对直接输出到$(2)中, path to the input *.prop files. The contents of the files are directly emitted to the output
- $(4): 包含键值对格式属性的变量名列表,这些键值对直接输出到$(2)中, list of variable names each of which contains name=value pairs
- $(5): 可选的要强制移除的属性名列表,可以移除$3和$4的一些键值对,optional list of prop names to force remove from the output. Properties from both $(3) and (4) are affected
- $(6): 可选的要追加到文件末尾的文件列表,optional list of files to append at the end. The content of each file is emitted to the output
- $(7): 可选的跳过公共属性生成的标志,optional flag to skip common properties generation
函数名称:build-properties
- 流程1:把输出文件安装到系统中,即product/etc/build.prop安装到系统中生效能过被init进程解读
- 流程2:$4指定的键值对直接输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中
- 流程3:清空或者创建输出文件,即通过touch指令创建product/etc/build.prop文件
- 流程4:如果$7不是true,调用generate-common-build-props函数,生成通用键值对到product/etc/build.prop文件中
- 流程5:遍历所有输入属性文件,添加分隔符和注释并输出到product/etc/build.prop文件中
- 流程6:追加SDK版本等信息和文件结束符
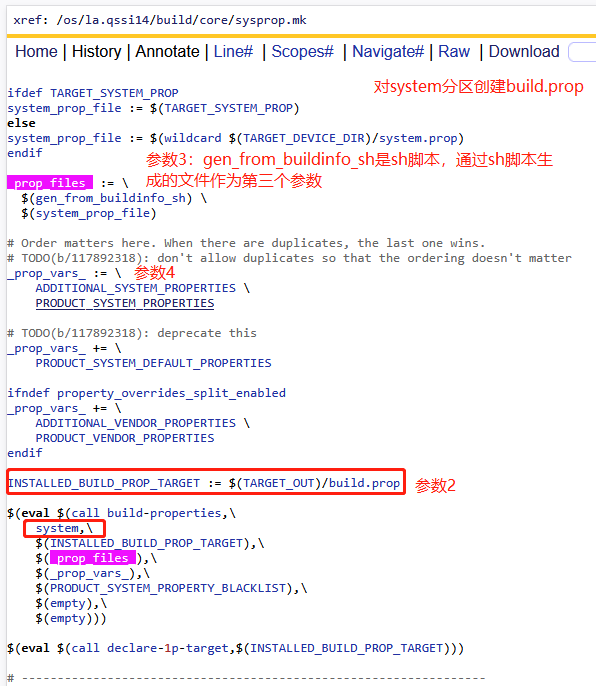
2、A14如何通过build-properties创建etc/build.prop默认文件?
1)system分区
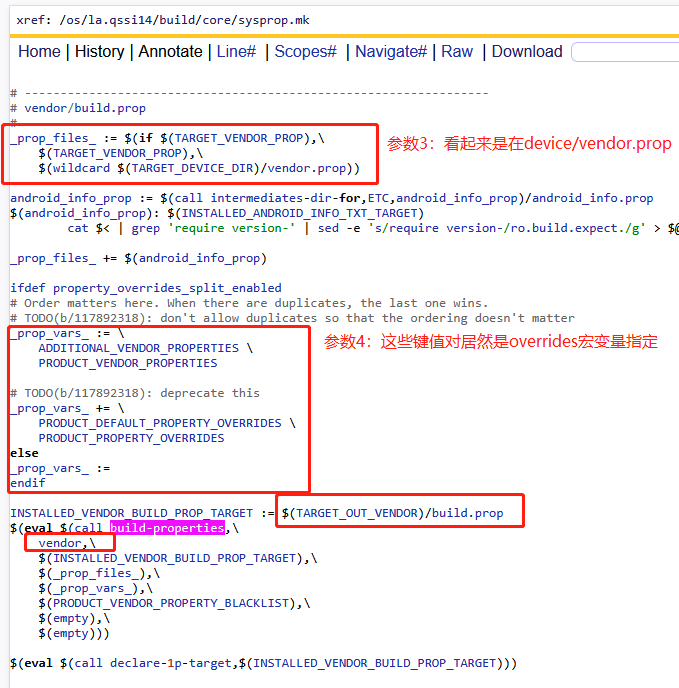
2)vendor分区
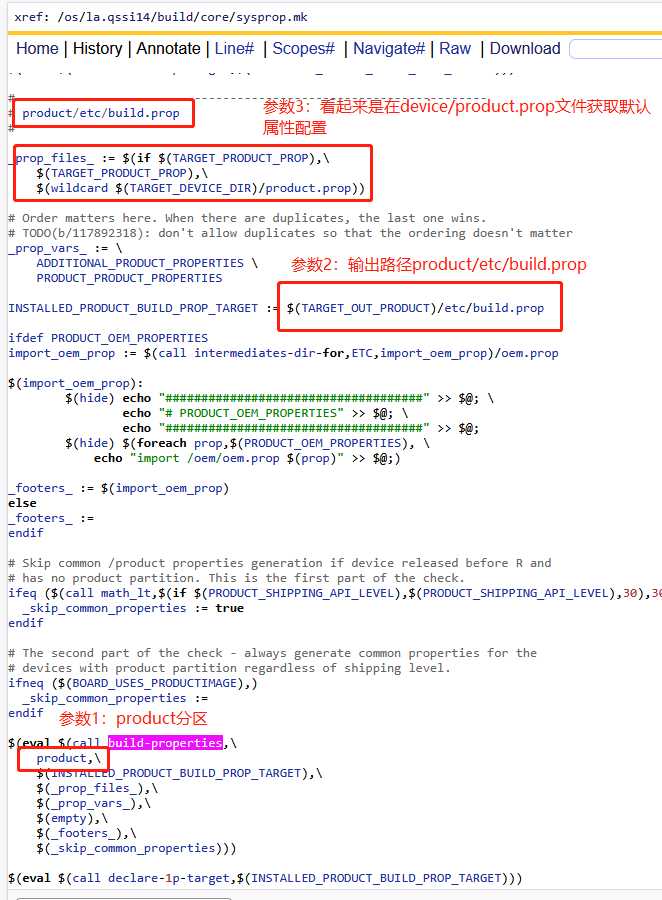
3)product分区
4)odm和其他分区
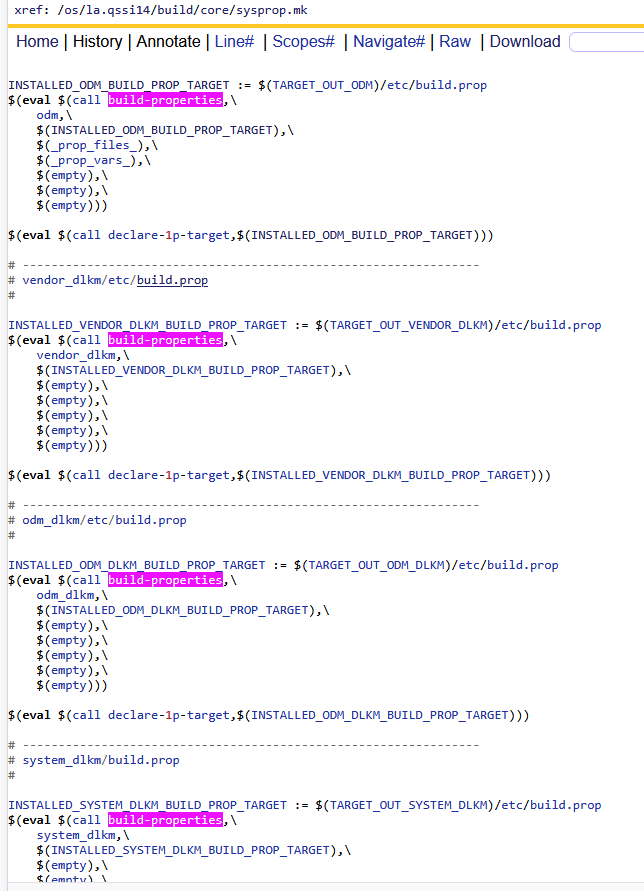
3、Kati构建方式总结
如上清一色的代码,这里发现有几个共同点,build-properties函数的目的是,根据一些(输入参数)规则来进行构建build.prop文件作为输出。这里分别介绍几个:
1)TARGET_XXX_PROP
TARGET_SYSTEM_PROP、TARGET_VENDOR_PROP、TARGET_PRODUCT_PROP、TARGET_ODM_PROP这几个值,如果他们存在,就作为第三个参数传递进去,我们来看看这些变量的值都是些撒?

原来如此,高通项目中这里在device目录下进行了指定,即可以把需要配置的属性写到device/xxx/system.prop文件内,编译后就默认生效。
PS:这个需要注意一下,其他几个变量TARGET_PRODUCT_PROP我没有看到有哪里进行指定,具体项目具体分析,具体平台具体分析,具体基线具体分析,只要锁定这个变量准没错
2)$(TARGET_DEVICE_DIR)/xxx.prop
$(TARGET_DEVICE_DIR)/system|vendor|product|odm.prop,如果他们存在,就作为第三个参数传递键,这里的TARGET_DEVICE_DIR目录是什么呢?
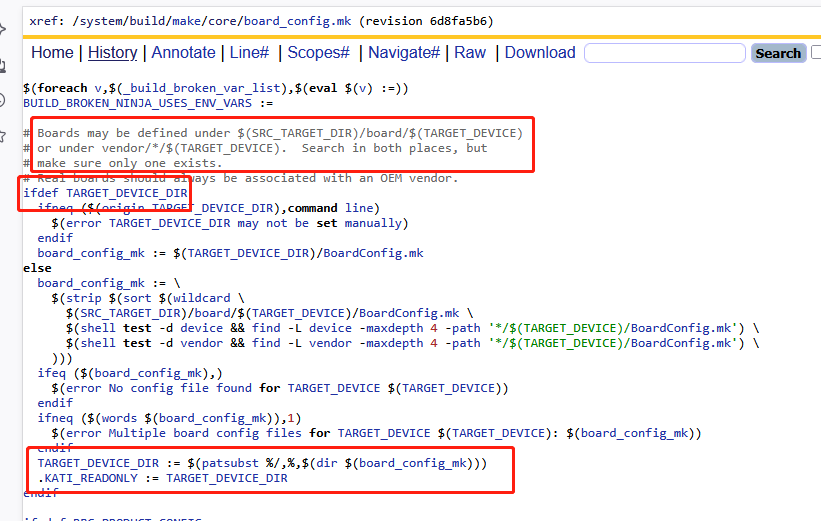
从这段逻辑中,TARGET_DEVICE_DIR 会被设置为 找到的 BoardConfig.mk 文件所在目录的路径,即如果找到的是 vendor/samsung/universal9820/BoardConfig.mk,那么 TARGET_DEVICE_DIR 就是 vendor/samsung/universal982
PS:因为比较深,用的比较少,我基本上没见过,同样具体平台具体分析
3)ADDITIONAL_XXX_PROPERTIES
ADDITIONAL_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES、ADDITIONAL_VENDOR_PROPERTIES、ADDITIONAL_PRODUCT_PROPERTIES、ADDITIONAL_ODM_PROPERTIES如果他们存在,就作为第四个参数传递键对,作为输入参数,即会被kati构建系统编译进去。
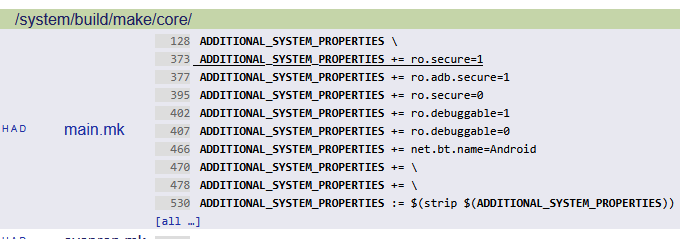
PS:这几个变量其实在A16上面已经被废弃了,如果有定义会直接编译报错
4)PRODUCT_XXX_PROPERTIES
PRODUCT_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES、PRODUCT_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES、PRODUCT_VENDOR_PROPERTIES、PRODUCT_ODM_PROPERTIES、PRODUCT_PRODUCT_PROPERTIES、PRODUCT_SYSTEM_EXT_PROPERTIES如果他们的值存在,就作为第四个参数传递键值对,即会被kati构建系统编译进去。
PS:这就是我们常用的那些宏变量,即在mk中进行配置属性的常用手段,这里的逻辑还进行了vendor/system分区隔离
5)XXX_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES
这里只找到了PRODUCT_DEFAULT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES和PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES,如果他们的值存在,就作为第四个参数传递键值对,即会被kati构建系统编译进去。
PS:这就是我们常用的那些宏变量,即在mk中进行覆盖配置属性的手段
6)gen_from_buildinfo_sh
自定义sh脚本来作为输出参数,通常手段就是通过echo语法来输入键值对,这种方式可读性不是很高,作为第四个参数传递进去,在A14 system就有一个很好的例子:
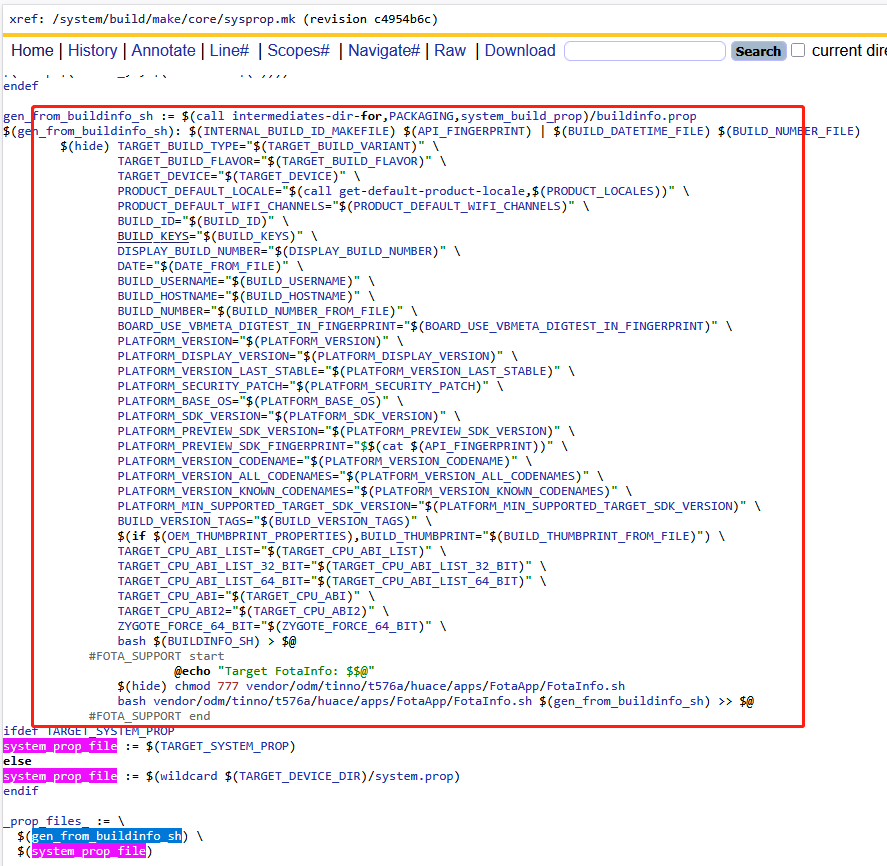
PS:这种方式可读性太低了,看的一脸懵逼,好在A16中默认删掉了这段代码
7)INSTALLED_XXX_BUILD_PROP_TARGET := $(TARGET_OUT_XXX)/etc/build.prop
这里就是build-properties函数的输出参数,即根据前文中A-F的输入参数,最终整理输出到xxx/out/etc/buid.prop文件,我们可以在编译out目录下进行查看,也可以在手机的xxx/etc.build.prop文件中进行查看。
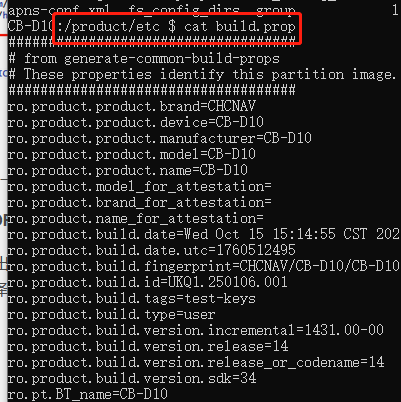
4、sysprop.mk日志打印
为了更好的解读sysprop.mk的编译流程,我添加日志如下:
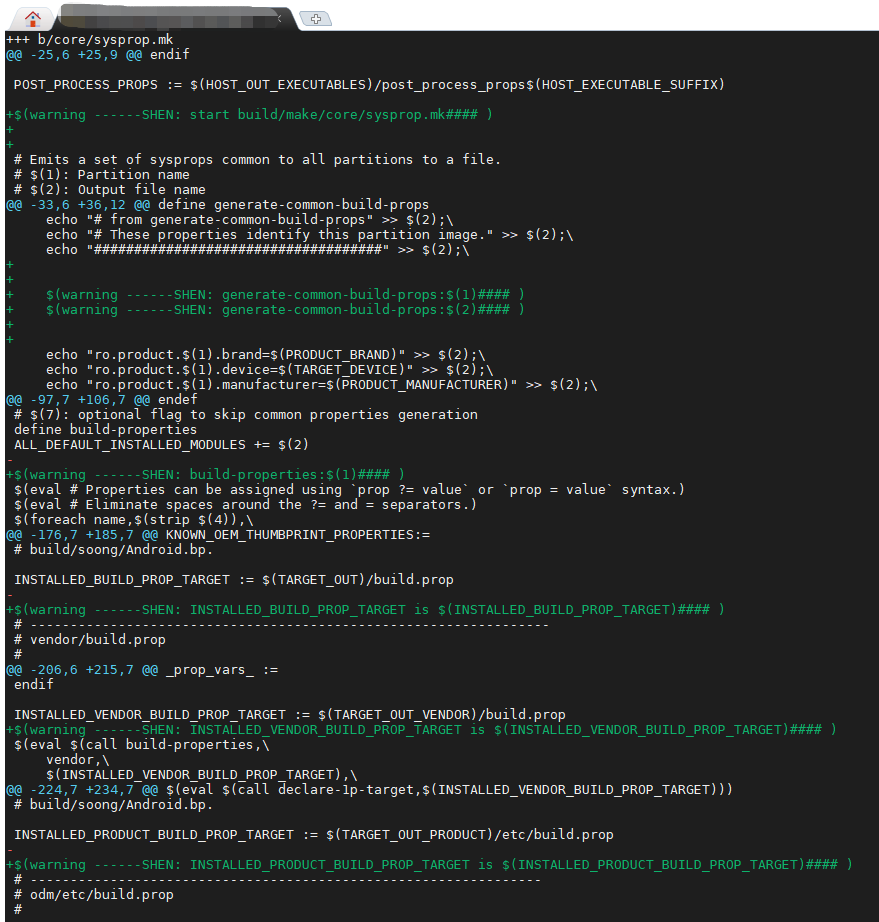
日志输出如下:
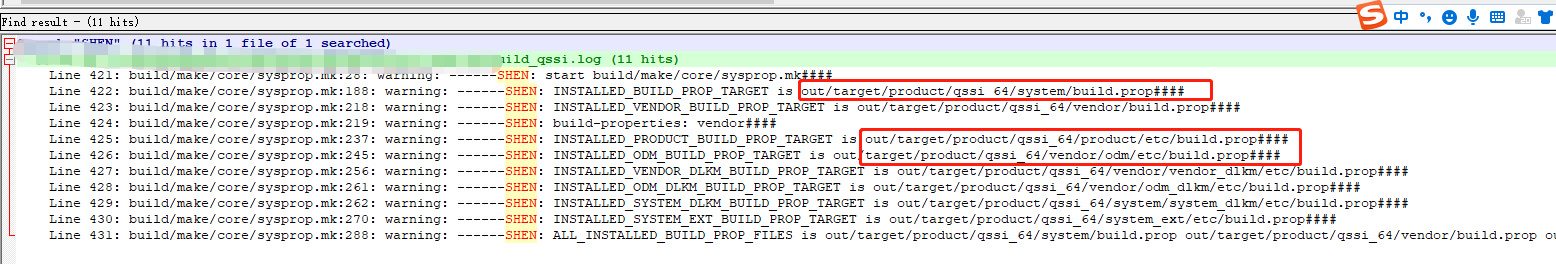
打开out/target/product/qssi_64/product/etc/build.prop文件:
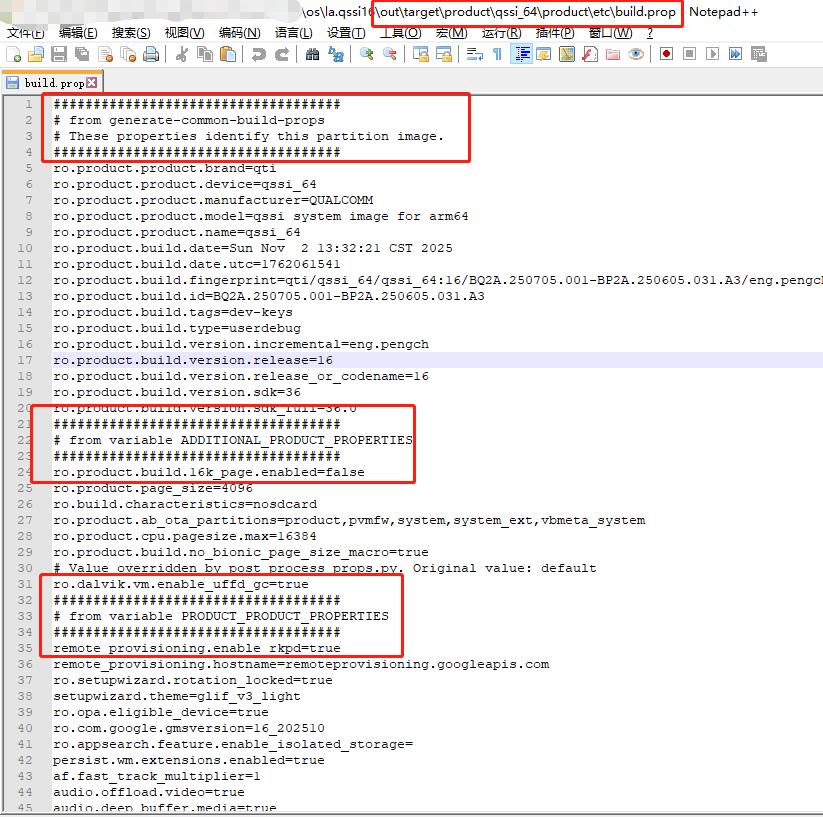
里面的内容输出和本章介绍的build-properties函数逻辑基本一致
二、Soong构建方式之build_prop
这里先下个结论,在A16的代码中,system|product|odm/etc/build.prop等生成方式存在了一些变化。到底什么变化?我们先看看A16的sysprop.mk文件
1、A16如何通过build-properties创建etc/build.prop默认文件?
A16对这块内容有所变更,主要是针对system/product/odm等分区的build.prop创建方式有变化,从代码来看vendor分区还是按照之前
1)vendor分区
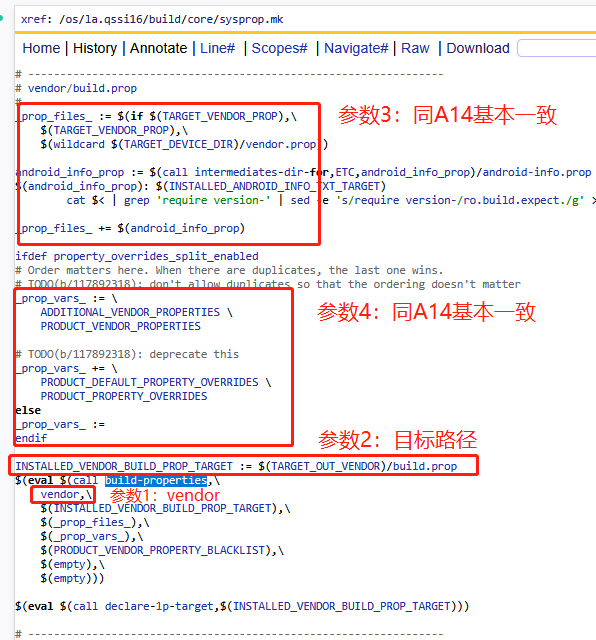
2)system & product & odm分区
# la.qssi16/build/core/sysprop.mk
# -----------------------------------------------------------------
# system/build.prop
#
# system/build.prop is built by Soong. See system-build.prop module in
# build/soong/Android.bp.
INSTALLED_BUILD_PROP_TARGET := $(TARGET_OUT)/build.prop
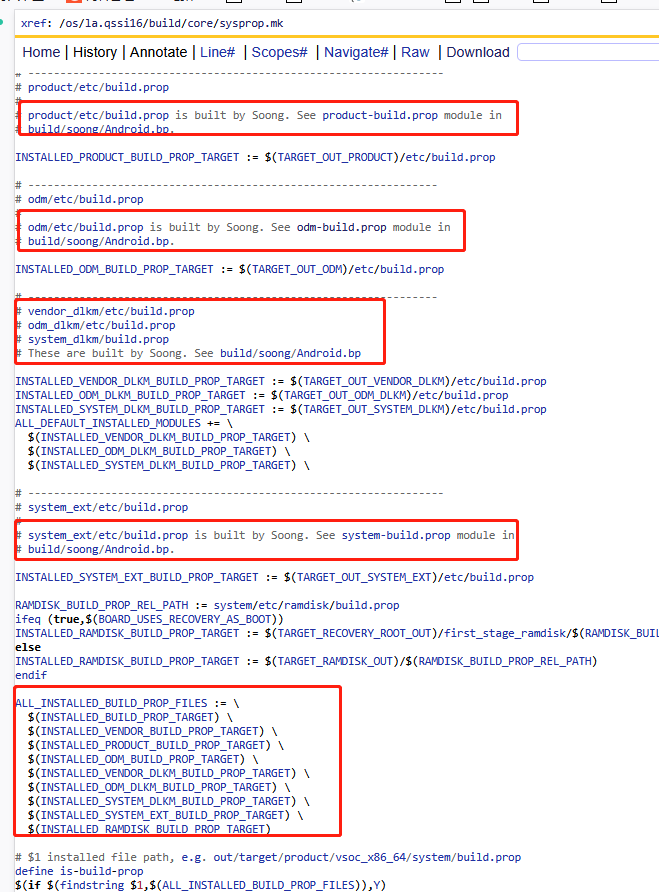
如上system/product/odm分区并没有在mk文件中调用build-properties函数进行创建build.prop文件,而是定义了输出路径,然后备注See system-build.prop module in build/soong/Android.bp.
Android 16 在构建系统上继续强化了 Soong 的作用。10 在您之前分析的 Android 14 中,我们看到了详细的 Makefile 规则来生成 build.prop 文件,但在这里,我们看到的是对 Soong 构建系统的引用,这表明:
Soong 主导:system/build.prop 的生成已从传统的 Makefile 规则迁移到 Soong 构建系统。
模块化定义:具体的生成规则现在定义在 build/soong/Android.bp 文件中的 system-build.prop 模块。
2、build_prop模块
1)build_prop模块定义
根据sysprop.mk的注释找到soong的线索,让我们参考build/soong/Android.bp文件:
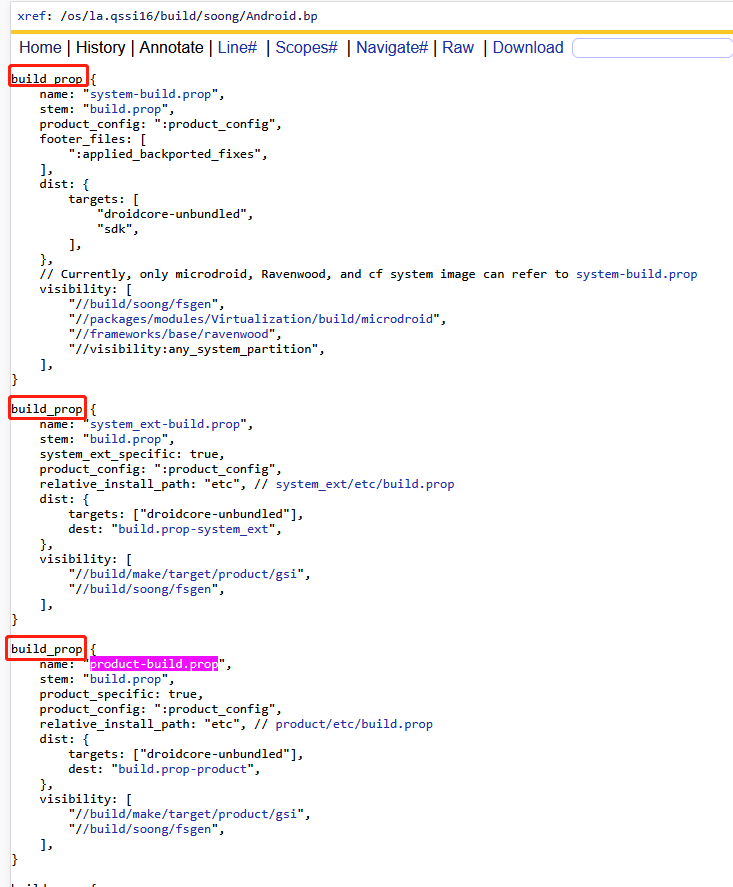
原来在这里通过android.bp定义了一些 build_prop模块,模块名称分别是:system-build.prop、system_ext-build.prop、product-build.prop、odm-build.prop等,难怪在sysprop.mk中就定义了一个输出文件,没有找到build-properties函数调用的地方。
build_prop作为android.bp文件中的关键字,用于生成 Android系统属性build.prop文件,这里介绍一下各个bp中的各个参数表示什么意思:
-
name: "product-build.prop" 模块名称,用于在构建系统中唯一标识该模块,其他模块可通过此名称引用
-
stem: "build.prop" 输出文件名,最终生成的文件名为 build.prop,即使模块名为 product-build.prop,输出文件仍为 build.prop
-
product_specific: true 标记为 product 分区特定,决定安装位置和属性来源(从 product 分区配置读取属性,安装输出位置product/xxx/build.prop)。PS:除了它还有xxx_specific
-
product_config: ":product_config" 指向产品配置 JSON 文件,:product_config 是同一 Android.bp 中名为 product_config 的模块引用,该文件包含产品相关的构建属性配置。PS:除了它还有xxx_config
-
relative_install_path: "etc" 安装路径,结合上面的product_specific为true,那么输出路径就是product/etc/build.prop
-
dist 配置: 分发配置?targets为droidcore-unbundled将文件复制到分发目录,dest为build.prop-product目标文件,不是很理解这有什么用?
-
visibility 配置:可见性规则,仅以下包可引用此模块,//build/make/target/product/gsi表示GSI(Generic System Image)相关,//build/soong/fsgen表示文件系统生成工具
2)build_prop工作原理
build_prop模块会在build_prop.go中实现具体做的事情,其工作原理如下:
- 输入参数:从 product_config JSON 读取产品配置,从 product 分区的属性文件读取属性,合并通用构建属性(版本号、指纹等)
- 输出参数:使用 gen_build_prop 工具生成初始 build.prop,使用 post_process_props 进行验证和处理,追加 footer_files
- 安装到product/etc/build.prop
总结:Soong工具中build_prop模块做的事情和Kati工具中的build-properties函数做的事情基本一模一样,通过一些输入参数,来生成文件out/target/product/<product>/system|product|odm/etc/build.prop,这个文件中包含了产品相关的系统属性,在系统启动的时候init属性服务线程读取加载这些属性,作为默认值。
这里先附上一个AI流程图:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ GenerateAndroidBuildActions (build_prop.go) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. 确定分区 (partition) │
│ 2. 收集属性文件 (propFiles) │
└───────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ 调用 gen_build_prop 工具 │
└───────────────────────────────┘
┌───────────────┴───────────────┐
▼ ▼
┌──────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐
│ 生成通用分区属性 │ │ 生成全局构建信息 │
│ (仅 system 分区) │ │ (所有分区) │
└──────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘
└───────────────┬───────────────┘
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ 读取属性文件内容 │
│ (device/xxx/system.prop) │
└───────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ 从产品配置读取变量属性 │
│ (PRODUCT_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES) │
└───────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ 调用 post_process_props │
│ - 验证格式 │
│ - 检查重复 │
│ - 排除 Block_list │
└───────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ 追加 Footer 文件 │
│ (applied_backported_fixes) │
└───────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ 安装到目标位置 │
│ (system/etc/build.prop) │
└───────────────────────────────┘
// GenerateAndroidBuildActions 生成 build.prop 文件的构建规则
// 调用时机:此函数由 Soong 构建系统在构建阶段自动调用,即soong的入口函数,
// 函数作用:为 build_prop 模块生成 Ninja 构建规则,用于生成指定分区的 build.prop 文件
func (p *buildPropModule) GenerateAndroidBuildActions(ctx ModuleContext) {
// 步骤 1: 确定输出文件路径:输出文件将生成在模块的输出目录中,文件名为 "build.prop"
outputFilePath := PathForModuleOut(ctx, "build.prop")
// 步骤 2:执行gen_build_prop命令,并设置了一系列参数
partition := p.partition(ctx.DeviceConfig())
rule := NewRuleBuilder(pctx, ctx)
config := ctx.Config()
cmd := rule.Command().BuiltTool("gen_build_prop")
// 传入构建主机名文件(包含构建机器的 hostname)
cmd.FlagWithInput("--build-hostname-file=", config.BuildHostnameFile(ctx))
// 传入构建编号文件(包含 BUILD_NUMBER)
cmd.FlagWithInput("--build-number-file=", config.BuildNumberFile(ctx))
// 传入构建指纹文件路径(使用 FlagWithArg 而非 FlagWithInput 以避免每次增量构建都重建),构建指纹用于唯一标识一个构建版本
cmd.FlagWithArg("--build-fingerprint-file=", config.BuildFingerprintFile(ctx).String())
// 仅在产品配置了 OEM 指纹属性时才导出构建缩略图(thumbprint)
if shouldAddBuildThumbprint(config) {
// 在之前的 Make 实现中,没有添加对 thumbprint 文件的依赖
cmd.FlagWithArg("--build-thumbprint-file=", config.BuildThumbprintFile(ctx).String())
}
// 传入构建用户名(BUILD_USERNAME 环境变量)
cmd.FlagWithArg("--build-username=", config.Getenv("BUILD_USERNAME"))
// 传入构建日期时间文件路径(使用 FlagWithArg 以避免每次增量构建都重建)
cmd.FlagWithArg("--date-file=", ctx.Config().Getenv("BUILD_DATETIME_FILE"))
// 传入平台预览版 SDK 指纹文件
cmd.FlagWithInput("--platform-preview-sdk-fingerprint-file=", ApiFingerprintPath(ctx))
// 传入产品配置 JSON 文件路径(包含产品相关的所有配置信息)
cmd.FlagWithInput("--product-config=", PathForModuleSrc(ctx, proptools.String(p.properties.Product_config)))
// 传入目标分区名称(system/vendor/product 等)
cmd.FlagWithArg("--partition=", partition)
// 传入属性文件列表(如 device/xxx/system.prop,这些文件会被合并到 build.prop 中)
cmd.FlagForEachInput("--prop-files=", p.propFiles(ctx))
// 指定输出文件路径
cmd.FlagWithOutput("--out=", outputFilePath)
//步骤 3:构建 post_process_props 工具的命令行,用于验证和处理生成的 build.prop 文件
postProcessCmd := rule.Command().BuiltTool("post_process_props")
// 如果启用了 BUILD_BROKEN_DUP_SYSPROP,则允许重复属性
if ctx.DeviceConfig().BuildBrokenDupSysprop() {
postProcessCmd.Flag("--allow-dup")
}
// 传入平台 SDK 版本号
postProcessCmd.FlagWithArg("--sdk-version ", config.PlatformSdkVersion().String())
// 处理 UFFD GC(Userfaultfd Garbage Collection)相关的内核版本文件
if ctx.Config().EnableUffdGc() == "default" {
// 如果启用 UFFD GC,传入内核版本文件
postProcessCmd.FlagWithInput("--kernel-version-file-for-uffd-gc ", PathForOutput(ctx, "dexpreopt/kernel_version_for_uffd_gc.txt"))
} else {
// 否则传入空字符串(仍需要传递参数以保持命令行格式一致)
postProcessCmd.FlagWithArg("--kernel-version-file-for-uffd-gc ", `""`)
}
// 指定要处理的 build.prop 文件(即 gen_build_prop 生成的输出文件)
postProcessCmd.Text(outputFilePath.String())
// 传入要排除的属性列表(Block_list 中指定的属性将被移除)
postProcessCmd.Flags(p.properties.Block_list)
// 步骤 4: 追加 Footer 文件内容(如果有),Footer 文件会在 post_process_props 处理完成后直接追加到文件末尾,不进行任何验证
for _, footer := range p.properties.Footer_files {
path := PathForModuleSrc(ctx, footer)
rule.appendText(outputFilePath, "####################################")
rule.appendTextf(outputFilePath, "# Adding footer from %v", footer)
rule.appendTextf(outputFilePath, "# with path %v", path)
rule.appendText(outputFilePath, "####################################")
// 使用 cat 命令将 footer 文件内容追加到 build.prop 末尾
rule.Command().Text("cat").FlagWithInput("", path).FlagWithArg(">> ", outputFilePath.String())
}
// 添加文件结束标记
rule.appendText(outputFilePath, "# end of file")
// 构建 Ninja 规则,这将生成实际的 Ninja 构建规则,用于在构建时执行上述命令
rule.Build(ctx.ModuleName(), "generating build.prop")
// 步骤 5: 安装build.prop,relative_install_path属性确定安装目录(如 "etc" 表示安装到分区根目录的 etc 子目录)
p.installPath = PathForModuleInstall(ctx, proptools.String(p.properties.Relative_install_path))
// 安装文件到目标位置(如 system/etc/build.prop)
ctx.InstallFile(p.installPath, p.stem(), outputFilePath)
// 设置模块的输出文件信息,这允许其他模块或工具查询此模块的输出文件
ctx.SetOutputFiles(Paths{outputFilePath}, "")
p.outputFilePath = outputFilePath
}build_prop.go中实现了build_prop模块的主要逻辑,GenerateAndroidBuildActions是它的入口函数,从命名来看翻译为通用安卓编译动作,在收到编译动作的时候被Soong构建系统自动调用。
3)build_prop如何读取json?
在build_prop.go中的GenerateAndroidBuildActions函数中,我发现了一系列的c.productVariables代码,他们是干嘛的?原来是读取json数据的。
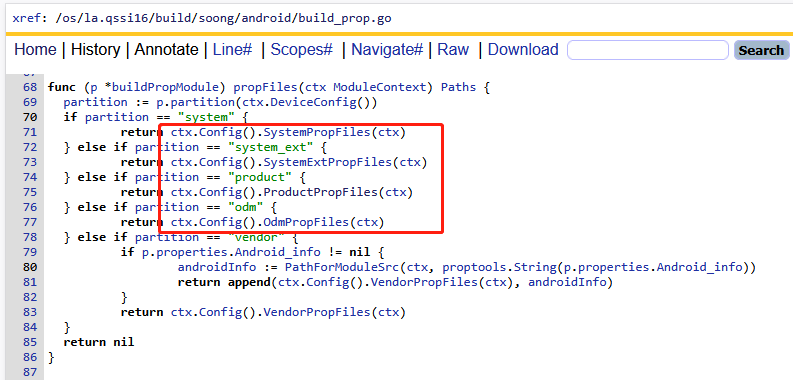
如上代码,如果是system分区,就调用Config.go的SystemPropFiles方法,如果是odm分区调用OdmPropFiles方法,如果是vendor分区处理逻辑比较负责,因为目前A16的vendor/etc/build.prop还是通过Kati的方式生成。build/soong/android/config.go代码如下:
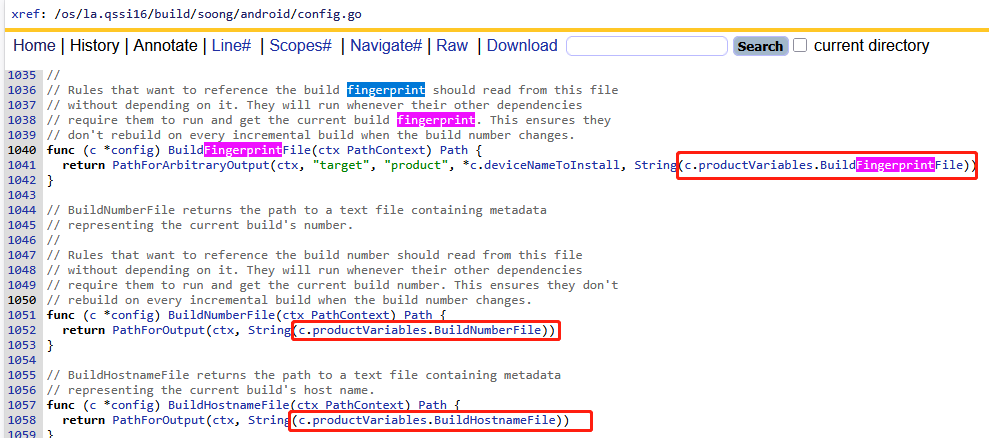
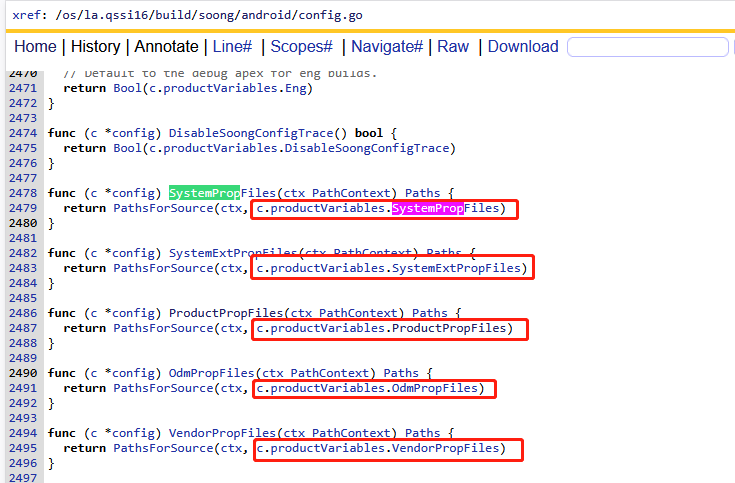
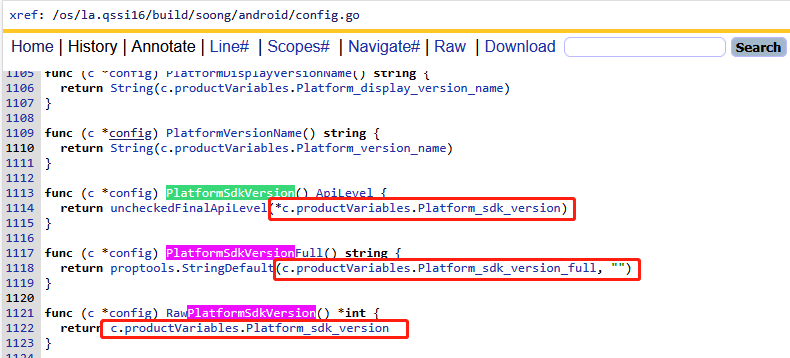
结合AI了解到c其实就是Soong构建系统从所有Android.bp解析出来的json数据的句柄,因此c.productVariables.XXX其实就是我们比较熟悉的Android.bp中的配置。例如:
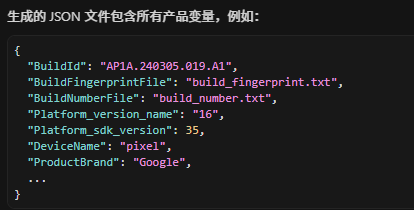
3、核心流程gen_build_prop
从前小节的工作流程可以看到,在创建确定输出路径后,其实并没有有效的做什么直到第三步进行安装的时候才有用。所以第一个核心步骤,就是通过gen_build_prop工具,来生成build.prop。如下代码:
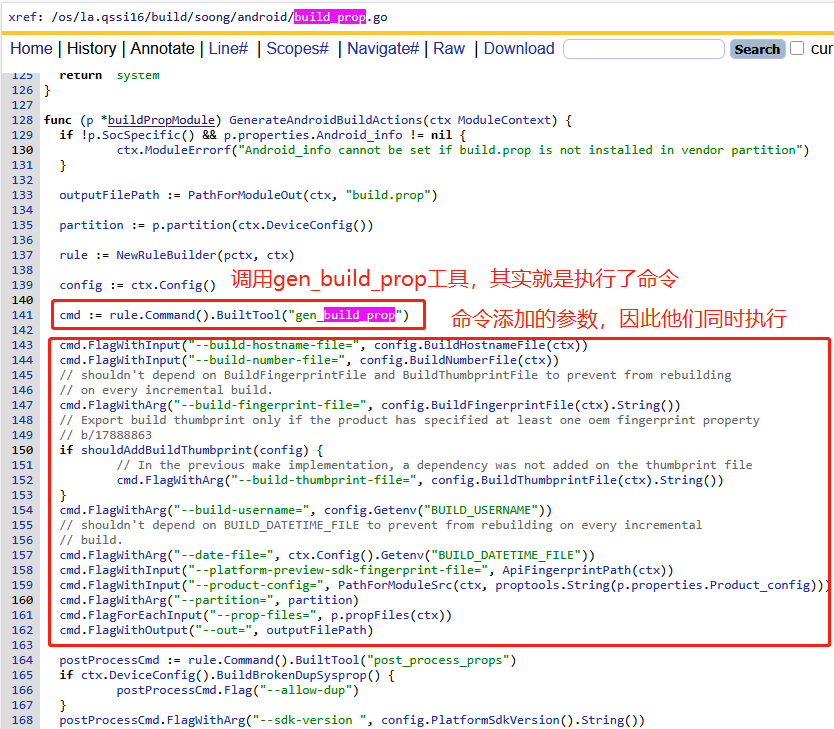
这里的gen_build_prop其实就是一个py脚本,如下代码,主函数就是根据传递进来的分区参数进行不同的prop构建:
# build/soong/scripts/gen_build_prop.py
# py的入口函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
def main():
args = parse_args()
with contextlib.redirect_stdout(args.out):
match args.partition:
case "system":
build_system_prop(args)
case "system_ext":
build_system_ext_prop(args)
case "odm":
build_odm_prop(args)
case "product":
build_product_prop(args)
case "vendor":
build_vendor_prop(args)
case "system_dlkm" | "vendor_dlkm" | "odm_dlkm" | "bootimage":
build_prop(args, gen_build_info=False, gen_common_build_props=True, variables=[])
case _:
sys.exit(f"not supported partition {args.partition}")
# 构建system分区的属性
def build_system_prop(args):
config = args.config
variables = [ # 这些配置其实和sysprop.mk基本一致
"ADDITIONAL_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES",
"PRODUCT_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES",
"PRODUCT_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES",
]
if not config["PropertySplitEnabled"]:
variables += [
"ADDITIONAL_VENDOR_PROPERTIES",
"PRODUCT_VENDOR_PROPERTIES",
]
build_prop(args, gen_build_info=True, gen_common_build_props=True, variables=variables)
# 构建system_ext分区的属性
def build_system_ext_prop(args):
config = args.config
variables = ["PRODUCT_SYSTEM_EXT_PROPERTIES"]
build_prop(args, gen_build_info=False, gen_common_build_props=True, variables=variables)
# 构建vendor分区的属性,其实在A16没有用这套机制
def build_vendor_prop(args):
config = args.config
variables = []
if config["PropertySplitEnabled"]:
variables += [
"ADDITIONAL_VENDOR_PROPERTIES",
"PRODUCT_VENDOR_PROPERTIES",
"PRODUCT_DEFAULT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES",
"PRODUCT_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES",
]
build_prop(args, gen_build_info=False, gen_common_build_props=True, variables=variables)
# 构建product分区的属性 这些配置其实和sysprop.mk基本一致
def build_product_prop(args):
config = args.config
variables = [
"ADDITIONAL_PRODUCT_PROPERTIES",
"PRODUCT_PRODUCT_PROPERTIES",
]
gen_common_build_props = True
if config["Shipping_api_level"] and int(config["Shipping_api_level"]) < 30:
gen_common_build_props = False
if config["UsesProductImage"]:
gen_common_build_props = True
build_prop(args, gen_build_info=False, gen_common_build_props=True, variables=variables)
if config["OemProperties"]:
print("####################################")
print("# PRODUCT_OEM_PROPERTIES")
print("####################################")
for prop in config["OemProperties"]:
print(f"import /oem/oem.prop {prop}")
# 构建odm分区的属性
def build_odm_prop(args):
variables = ["ADDITIONAL_ODM_PROPERTIES", "PRODUCT_ODM_PROPERTIES"]
build_prop(args, gen_build_info=False, gen_common_build_props=True, variables=variables)如上代码无论构建哪个分区,都是要了build_prop,此函数完美的刻画了四部曲
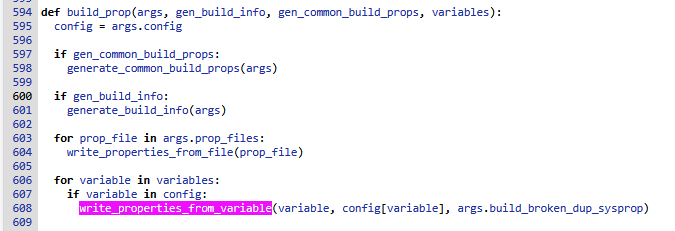
1)生成分区通用属性generate_common_build_props
通过generate_common_build_props生成通用属性,这些通用属性都是来自args,即来自build_prop中cmd添加的参数,他们又是来自android.bp的json配置。
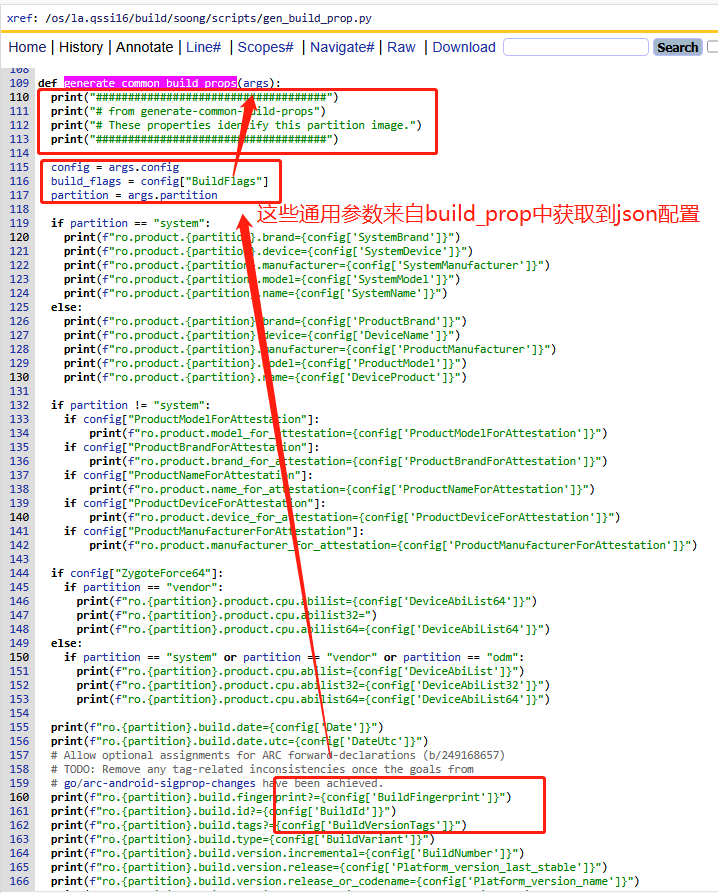
2)生成全局构建信息generate_build_info
同上,这些属性的参数来源于args,值得注意的是,仅仅只有system才会调用这个函数
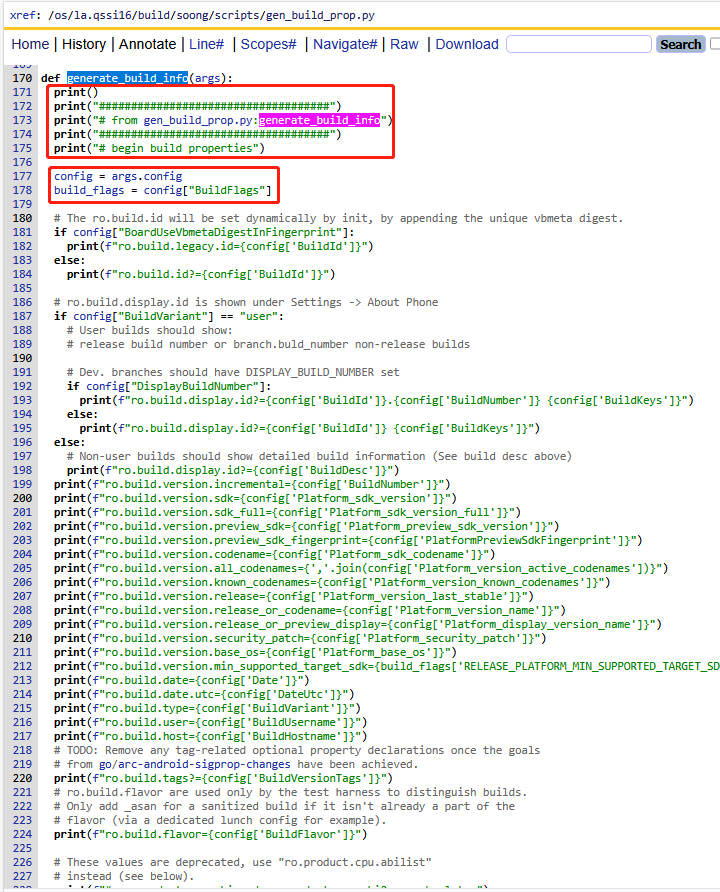
3)从属性文件生成内容write_properties_from_file
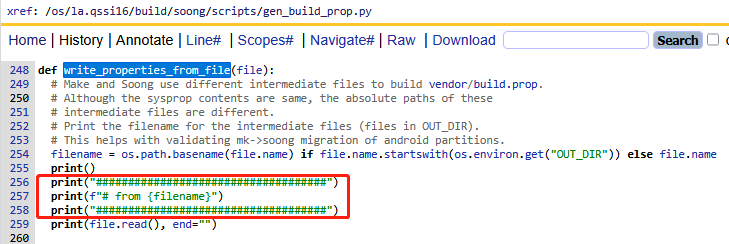
这段逻辑比较简单,先打印来自某文件,然后直接从文件中的内容读取出来进行输出。
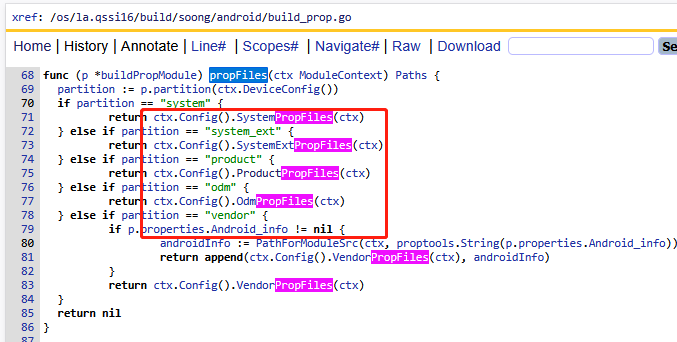
注意这里的参数file,其实就来自json中配置的SystemPropFiles、ProductPropFiles等的值,那么他们如何来的?
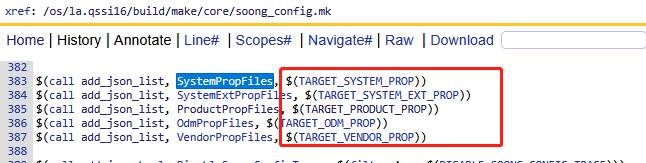
这段代码的意思如下:
- 编译宏TARGET_SYSTEM_PROP的值添加到json中SystemPropFiles字段里面
- 编译宏TARGET_PRODUCT_PROP的值添加到json中ProductPropFiles字段里面
- 编译宏TARGET_ODM_PROP的值添加到json中OdmPropFiles字段里面
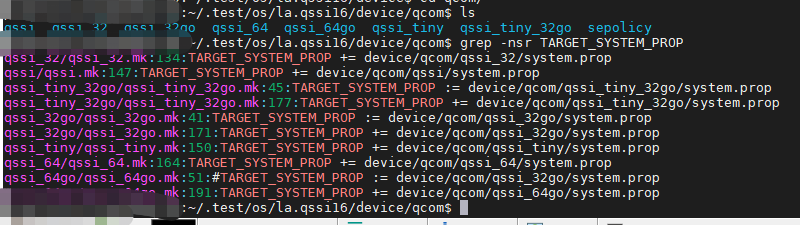
PS:在第一章讲解的Kati构建工具中的sysprop.mk的build-properties函数也是直接使用的这些宏变量。
4)从属性宏控生成内容write_properties_from_variable
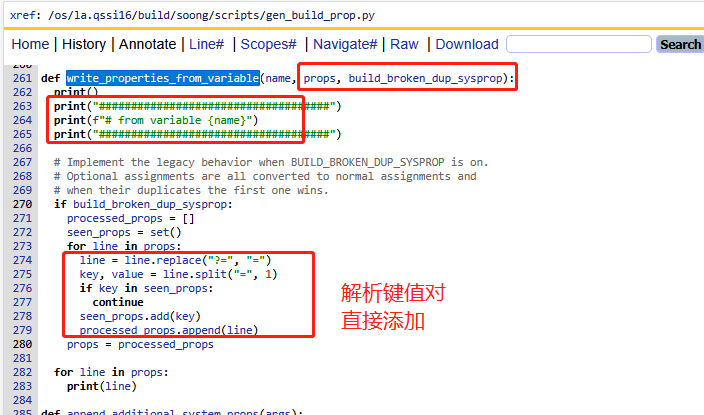
那么这些键值对是怎么来的?我们来看看他们的参数
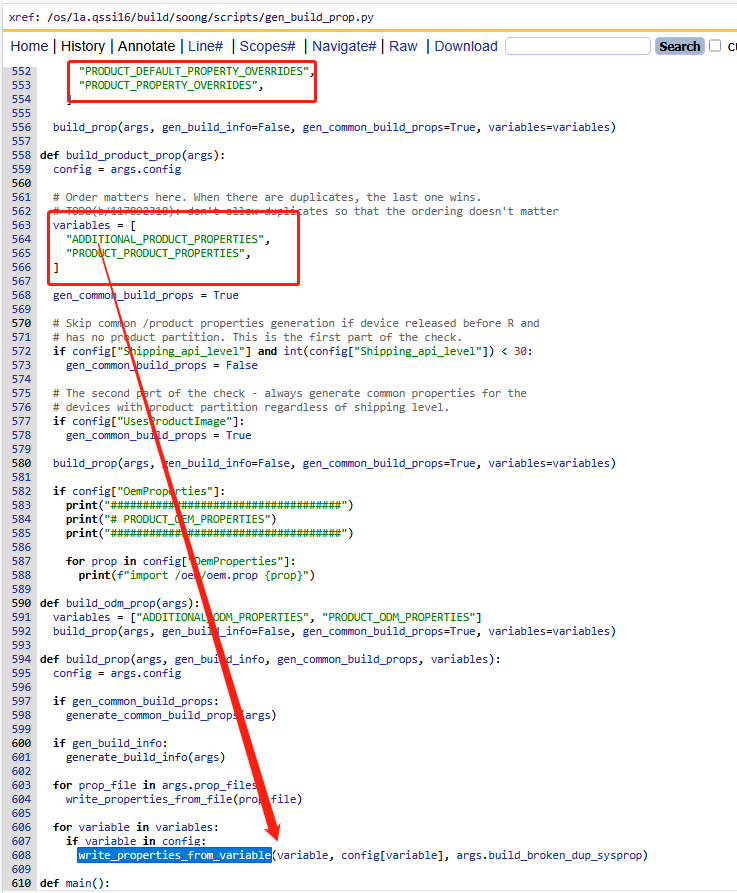
PS:原来是从ADDITIONAL_XXX_PROPERTIES和PRODUCT_XXX_PROPERTIES和XXX_PROPERTY_OVERRIDES等中获取的键值对,即我们在mk文件中常规使用的方式,在第一章讲解的Kati构建工具中的sysprop.mk的build-properties函数也是直接使用的这些宏变量。
4、输出文件system/build.prop
这里以system/build.prop输出文件举个例子,来看看soong build_prop模块都生成了那些默认的属性:
#la.qssi16\out\target\product\qssi_64\system\build.prop
####################################
# from generate-common-build-props
# These properties identify this partition image.
####################################
ro.product.system.brand=qti
ro.product.system.device=qssi_64
ro.product.system.manufacturer=QUALCOMM
ro.product.system.model=qssi system image for arm64
ro.product.system.name=qssi_64
ro.system.product.cpu.abilist=arm64-v8a
ro.system.product.cpu.abilist32=
ro.system.product.cpu.abilist64=arm64-v8a
ro.system.build.date=Tue Nov 25 01:03:55 CST 2025
ro.system.build.date.utc=1764003835
ro.system.build.fingerprint=qti/qssi_64/qssi_64:16/BQ2A.250831.001-BP2A.250605.031.A3/eng.pengch:userdebug/test-keys
ro.system.build.id=BQ2A.250831.001-BP2A.250605.031.A3
ro.system.build.tags=test-keys
ro.system.build.type=userdebug
ro.system.build.version.incremental=eng.pengch
ro.system.build.version.release=16
ro.system.build.version.release_or_codename=16
ro.system.build.version.sdk=36
ro.system.build.version.sdk_full=36.0
####################################
# from gen_build_prop.py:generate_build_info
####################################
# begin build properties
ro.build.id=BQ2A.250831.001-BP2A.250605.031.A3
ro.build.display.id=qssi_64-userdebug 16 BQ2A.250831.001-BP2A.250605.031.A3 eng.pengch test-keys
ro.build.version.incremental=eng.pengch
ro.build.version.sdk=36
ro.build.version.sdk_full=36.0
ro.build.version.preview_sdk=0
ro.build.version.preview_sdk_fingerprint=REL
ro.build.version.codename=REL
ro.build.version.all_codenames=REL
ro.build.version.known_codenames=Base,Base11,Cupcake,Donut,Eclair,Eclair01,EclairMr1,Froyo,Gingerbread,GingerbreadMr1,Honeycomb,HoneycombMr1,HoneycombMr2,IceCreamSandwich,IceCreamSandwichMr1,JellyBean,JellyBeanMr1,JellyBeanMr2,Kitkat,KitkatWatch,Lollipop,LollipopMr1,M,N,NMr1,O,OMr1,P,Q,R,S,Sv2,Tiramisu,UpsideDownCake,VanillaIceCream,Baklava
ro.build.version.release=16
ro.build.version.release_or_codename=16
ro.build.version.release_or_preview_display=16
ro.build.version.security_patch=2025-06-05
ro.build.version.base_os=
ro.build.version.min_supported_target_sdk=28
ro.build.date=Tue Nov 25 01:03:55 CST 2025
ro.build.date.utc=1764003835
ro.build.type=userdebug
ro.build.user=pengcheng.ding
ro.build.host=cdby110
ro.build.tags=test-keys
ro.build.flavor=qssi_64-userdebug
# ro.product.cpu.abi and ro.product.cpu.abi2 are obsolete,
# use ro.product.cpu.abilist instead.
ro.product.cpu.abi=arm64-v8a
ro.product.locale=en-US
ro.wifi.channels=
# ro.build.product is obsolete; use ro.product.device
ro.build.product=qssi_64
# Do not try to parse description or thumbprint
ro.build.description=qssi_64-userdebug 16 BQ2A.250831.001-BP2A.250605.031.A3 eng.pengch test-keys
# end build properties
####################################
# from device/qcom/qssi_64/system.prop
####################################
#
# system.prop for qssi
#
rild.libpath=/vendor/lib64/libril-qc-hal-qmi.so
#rild.libargs=-d /dev/smd0
persist.rild.nitz_plmn=
persist.rild.nitz_long_ons_0=
persist.rild.nitz_long_ons_1=
persist.rild.nitz_long_ons_2=
persist.rild.nitz_long_ons_3=
persist.rild.nitz_short_ons_0=
persist.rild.nitz_short_ons_1=
persist.rild.nitz_short_ons_2=
persist.rild.nitz_short_ons_3=
ril.subscription.types=NV,RUIM
#.......省略
####################################
# from variable ADDITIONAL_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES
####################################
ro.treble.enabled=true
ro.llndk.api_level=202504
ro.actionable_compatible_property.enabled=true
persist.debug.dalvik.vm.core_platform_api_policy=just-warn
ro.postinstall.fstab.prefix=/system
ro.secure=1
security.perf_harden=1
ro.allow.mock.location=0
dalvik.vm.lockprof.threshold=500
ro.debuggable=1
net.bt.name=Android
ro.force.debuggable=0
####################################
# from variable PRODUCT_SYSTEM_PROPERTIES
####################################
debug.atrace.tags.enableflags=0
persist.traced.enable=1
ro.surface_flinger.game_default_frame_rate_override=60
dalvik.vm.image-dex2oat-Xms=64m
dalvik.vm.image-dex2oat-Xmx=64m
dalvik.vm.dex2oat-Xms=64m
dalvik.vm.dex2oat-Xmx=512m
dalvik.vm.usejit=true
dalvik.vm.dexopt.secondary=true
dalvik.vm.dexopt.thermal-cutoff=2
dalvik.vm.appimageformat=lz4
ro.dalvik.vm.native.bridge=0
pm.dexopt.post-boot=verify
pm.dexopt.first-boot=verify
pm.dexopt.boot-after-ota=verify
pm.dexopt.boot-after-mainline-update=verify
pm.dexopt.install=speed-profile
pm.dexopt.install-fast=skip
pm.dexopt.install-bulk=speed-profile
pm.dexopt.install-bulk-secondary=verify
pm.dexopt.install-bulk-downgraded=verify
pm.dexopt.install-bulk-secondary-downgraded=verify
pm.dexopt.bg-dexopt=speed-profile
pm.dexopt.ab-ota=speed-profile
pm.dexopt.inactive=verify
pm.dexopt.cmdline=verify
pm.dexopt.shared=speed
dalvik.vm.dex2oat-resolve-startup-strings=true
dalvik.vm.dex2oat-max-image-block-size=524288
dalvik.vm.minidebuginfo=true
dalvik.vm.dex2oat-minidebuginfo=true
dalvik.vm.madvise.vdexfile.size=104857600
dalvik.vm.madvise.odexfile.size=104857600
dalvik.vm.usap_pool_enabled=false
dalvik.vm.usap_refill_threshold=1
dalvik.vm.usap_pool_size_max=3
dalvik.vm.usap_pool_size_min=1
dalvik.vm.usap_pool_refill_delay_ms=3000
dalvik.vm.useartservice=true
dalvik.vm.enable_pr_dexopt=true
ro.cp_system_other_odex=1
ro.apex.updatable=true
persist.device_config.runtime_native_boot.iorap_perfetto_enable=true
####################################
# from variable PRODUCT_SYSTEM_DEFAULT_PROPERTIES
####################################
ro.custom.build.version=SH4_ASCOM_A14_001.00
ro.tcustom.build.version=SH4_ASCOM_A14_001.00
ro.internal.build.version=P810AE_MP_14.0_ASCOM_CFC_001
ro.tn.performance=1
ro.feature.liftwrist=true
ro.feature.setupwizard_shutdown=true
# Auto-added by post_process_props.py
persist.sys.usb.config=adb
####################################
# Adding footer from :applied_backported_fixes
# with path out/soong/.intermediates/build/make/backported_fixes/applied_backported_fixes/gen/applied_backported_fixes.prop
####################################
# The following backported fixes have been applied
# https://issuetracker.google.com/issues/350037023 with alias 1
# https://issuetracker.google.com/issues/385124056 with alias 4
ro.build.backported_fixes.alias_bitset.long_list=18
# end of file
三、案例汇总
1、案例之生成OEM定制化build.prop文件
问题背景:这是某个项目的OneImage实现方案,即在product和odm分区创建多个build_xxx.prop文件,然后根据kernel传递过来的sku属性值,init动态加载不同的build_xxx.prop属性文件
1)A14之前的方案
该需求总体思路可以被拆分为两个步骤,创建多个不同的build_xxx.prop属性文件,在默认被加载的product/etc/build.prop中写入import指令即可
- 步骤一:创建不同的build_xxx.prop文件
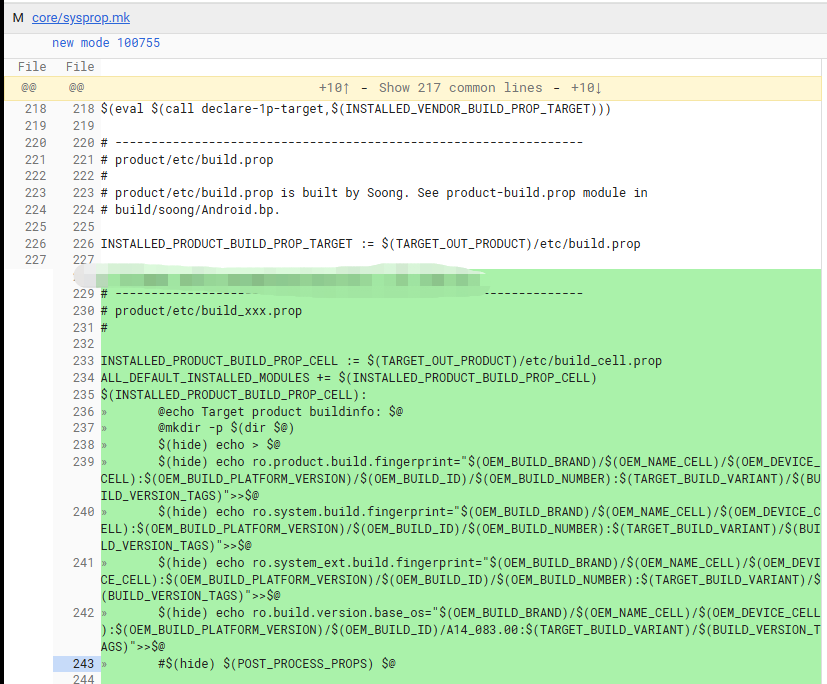
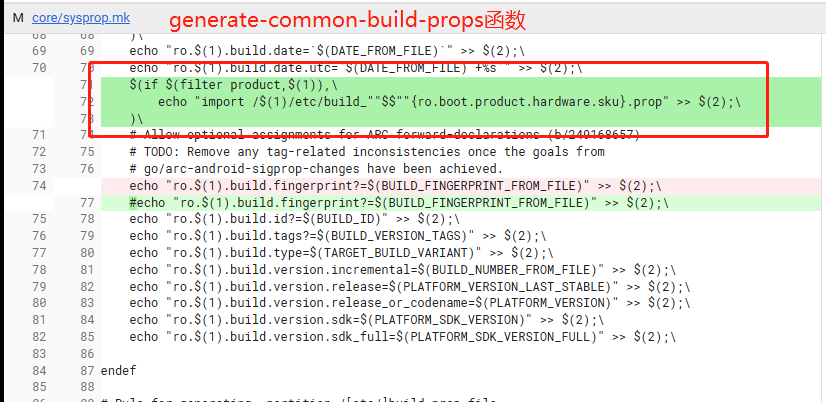
- 步骤二:在默认product/etc/build.prop中集成imprort指令
- 步骤三:init解析import product/etc/build_${ro.boot.product.hardware.sku}.prop指令
init进程在开机启动过程中,动态加载默认product/etc/build.prop文件的时候,解析到import product/etc/build_${ro.boot.product.hardware.sku}.prop语句的时候,能够直接拿到${ro.boot.product.hardware.sku}属性的值,因为他是从kernel侧传递进来,如果该值被配置为cell,那么init进程会继续加载product/etc/build_cell.prop里面的属性。
2)android通用方案
上述的方案只是针对A14和之前,那么在A16上面的步骤二需要换成Soong的机制,可以参考如下
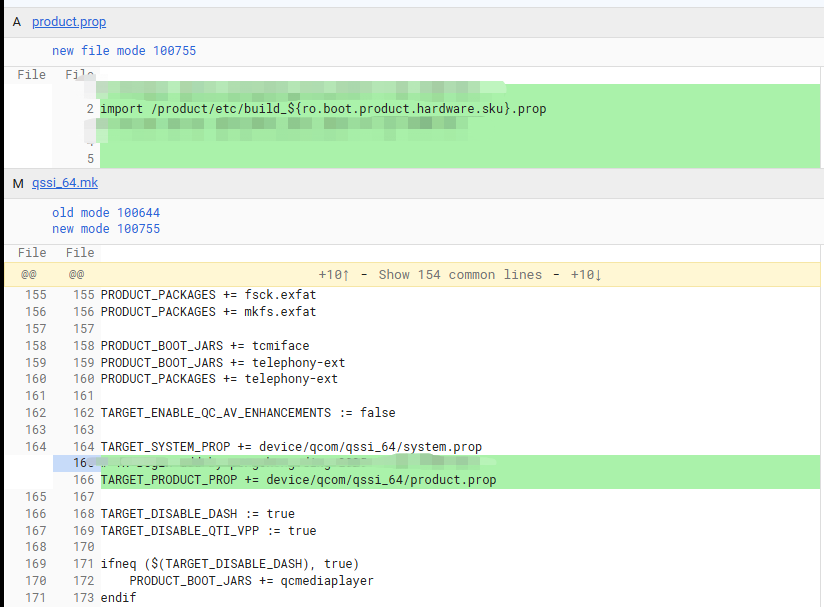
PS:其实TARGET_PRODUCT_PROP宏变量,根据第一章和第二章的论证,无论是在Soong机制下,还是在Kati机制下,都生效。
2、案例之Kati和Soong同时生成product/etc/build.prop导致编译报错
问题背景:同OEM定制化需求,这次是在A16上面实现,A16针对product/etc/build.prop的生成机制由Kati机制过渡到了Soong,当时对Soong这块还不是很了解,强行对A16的sysprop.mk做了如下修改:
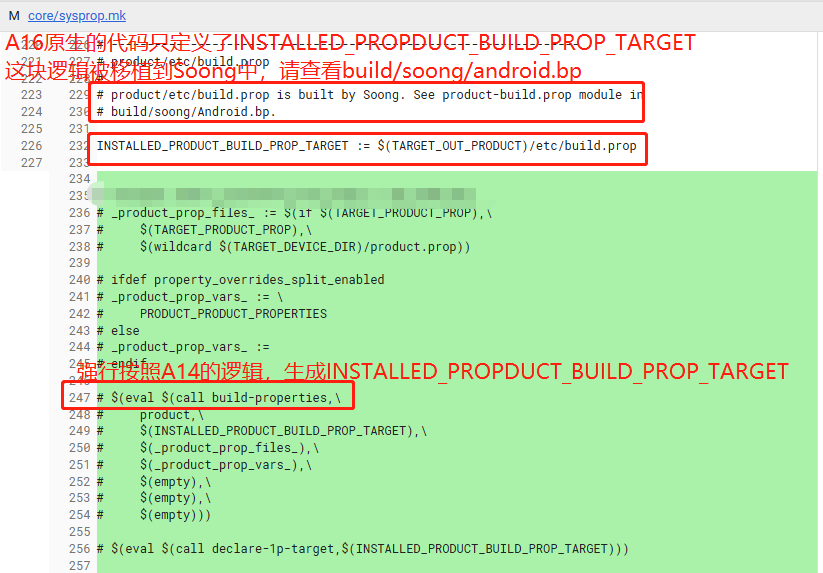
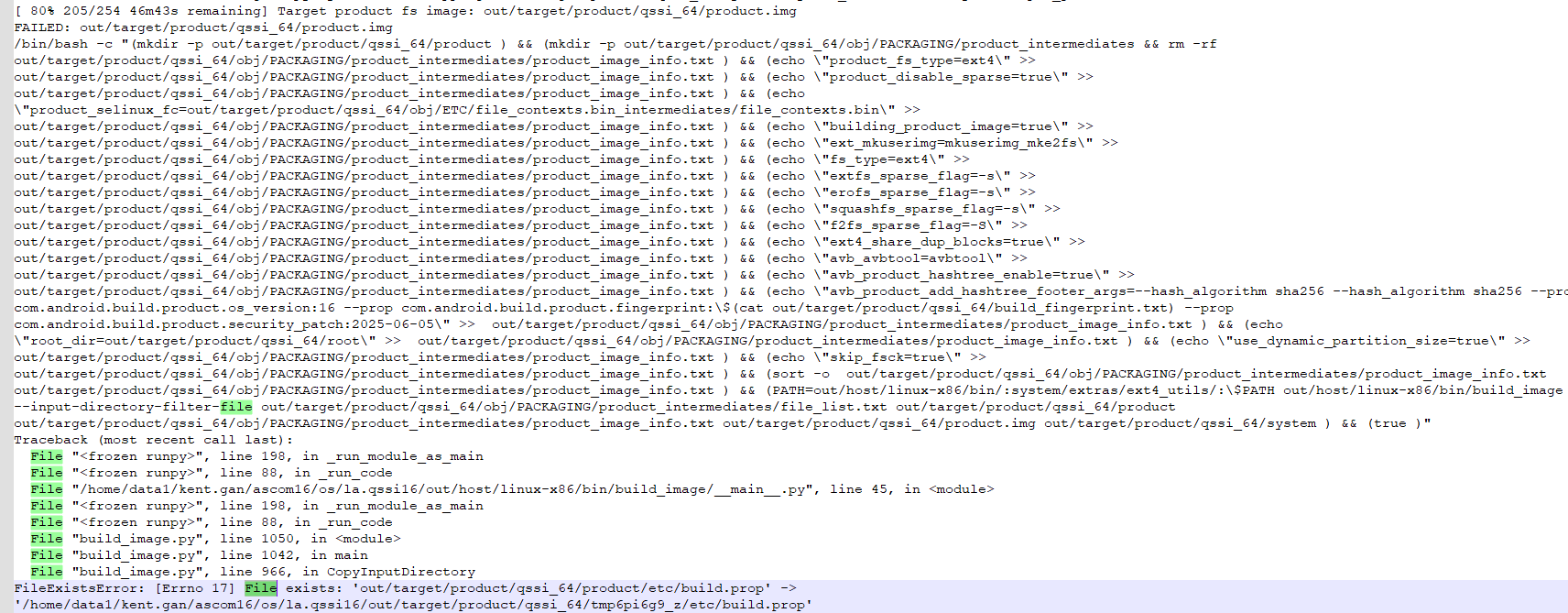
因为Soong生成了一份product/etc/build.prop,如上代码会让Kati在生成一份product/etc/build.prop,导致冲突,报如下异常:
解决方案:这种情况,要么干掉Soong的生成机制,要么干掉Kati的生成机制,如下两种
- 删除Soong机制:此方案没有验证过,理论上是可行的
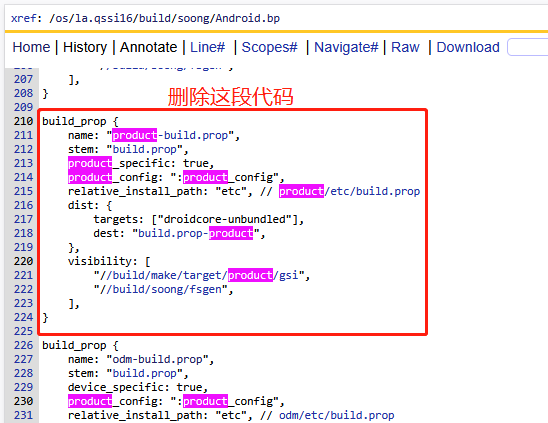
- 删除Kati机制:回退sysprop.mk文件里面的对build-properties函数的调用修改
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容







所有评论(0)