[论文阅读]ODDR: Outlier Detection & Dimension Reduction Based Defense Against Adversarial Patches
No.4、后门防御
摘要
英文:Adversarial attacks present a significant challenge to the dependable deployment of machine learning models, with patch-based attacks being particularly potent. These attacks introduce adversarial perturbations in localized regions of an image, deceiving even well-trained models. In this paper, we propose Outlier Detection and Dimension Reduction (ODDR), a comprehensive defense strategy engineered to counteract patch-based adversarial attacks through advanced statistical methodologies. Our approach is based on the observation that input features corresponding to adversarial patches—whether naturalistic or synthetic—deviate from the intrinsic distribution of the remaining image data and can thus be identified as outliers. ODDR operates through a robust three-stage pipeline: Fragmentation, Segregation, and Neutralization. This model-agnostic framework is versatile, offering protection across various tasks, including image classification, object detection, and depth estimation, and is proved effective in both CNN-based and Transformer-based architectures. In the Fragmentation stage, image samples are divided into smaller segments, preparing them for the Segregation stage, where advanced outlier detection techniques isolate anomalous features linked to adversarial perturbations. The Neutralization stage then applies dimension reduction techniques to these outliers, effectively neutralizing the adversarial impact while preserving critical information for the machine learning task. Extensive evaluation on benchmark datasets against state-of-the-art adversarial patches underscores the efficacy of ODDR. Our method enhances model accuracy from 39.26% to 79.1% under the GoogleAp attack, outperforming leading defenses such as LGS (53.86%), Jujutsu (60%), and Jedi (64.34%).
中文:对抗性攻击对机器学习模型的可靠部署提出了重大挑战,其中基于补丁的攻击特别强大。这些攻击在图像的局部区域引入对抗性扰动,甚至欺骗训练有素的模型。在本文中,我们提出了离群点检测和降维(ODDR),这是一种全面的防御策略,旨在通过先进的统计方法来对抗基于补丁的对抗性攻击。我们的方法是基于这样的观察,即对应于对抗补丁的输入特征-无论是自然的还是合成的-偏离剩余图像数据的内在分布,因此可以被识别为离群值。ODR通过强大的三阶段管道运行:碎片化、隔离和中和。这个模型不可知的框架是通用的,可以为各种任务(包括图像分类、对象检测和深度估计)提供保护,并且在基于CNN和基于Transformer的架构中被证明有效。在碎片阶段,图像样本被分成更小的部分,为隔离阶段做好准备,在该阶段,先进的异常值检测技术可以隔离与对抗性扰动相关的异常特征。然后,中和阶段对这些异常值应用维度缩减技术,有效地中和对抗影响,同时保留机器学习任务的关键信息。针对最先进的对抗补丁对基准数据集进行广泛评估强调了ODR的功效。在GoogleAp攻击下,我们的方法将模型准确性从39.26%提高到79.1%,优于LGS(53.86%)、Emotsu(60%)和Jedi(64.34%)等领先防御。
论文方法
ODDR(Outlier Detection & Dimension Reduction)是一种模型无关的防御策略,基于 “对抗性补丁对应的输入特征偏离图像其余数据的固有分布,可被识别为异常值” 的核心观察,通过三阶段 pipeline 实现防御,流程如图所示。碎片化、隔离和中和
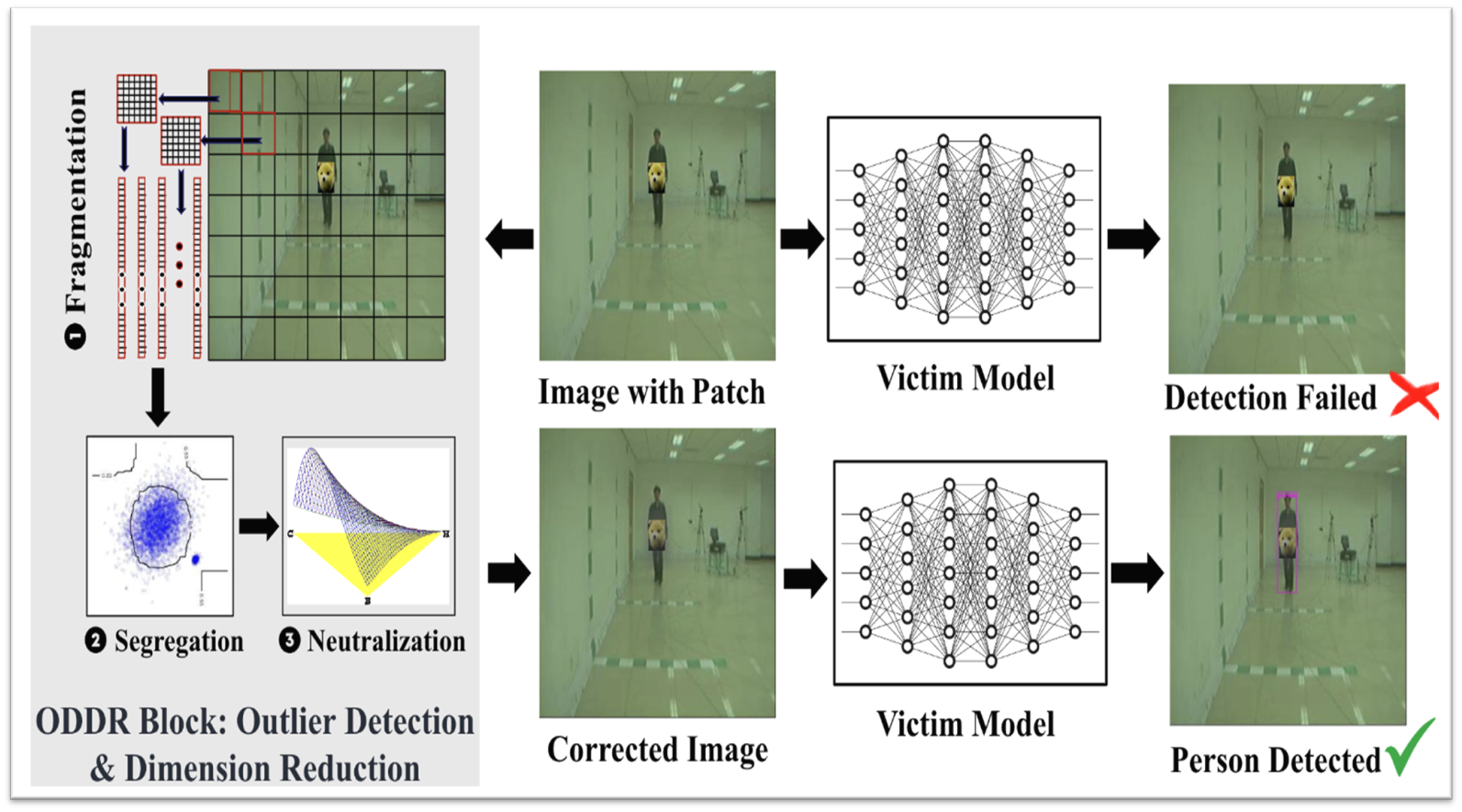
阶段 1:碎片化(Fragmentation)
- 操作:使用可调节的方形滑动核(核大小k、步长str为超参数,论文中str为 k/2 )将输入图像分割为部分重叠的片段,每个片段(含 3 个颜色通道)被展平为向量,为后续异常检测做准备。
- 目的:将图像拆解为细粒度单元,便于定位局部的对抗性补丁特征。
阶段 2:分离(Segregation)
- 核心技术:基于孤立森林(Isolation Forest) 的无监督异常检测。
- 原理:假设异常值(对抗性片段)在数据中占比少、特征与正常数据差异大,在孤立树中路径更短;通过集成多棵孤立树计算每个片段的异常分数。
- 操作:设定异常置信度c(超参数,0.8-0.95),筛选出 Top\((1-c)*n\)的异常片段,并通过聚类(要求聚类大小≥minPts)定位对抗性补丁所在区域。
阶段 3:中和(Neutralization)(降维)
- 核心技术:截断奇异值分解(Truncated SVD) 。
- 原理:对异常聚类中心周围的方形掩码区域(大小d为超参数)进行 SVD 分解,保留指定比例的信息(信息保留参数inf,70%-85%),在中和对抗性扰动的同时,避免丢失周围关键任务信息。
- 优势:相比神经网络修复(如 Jedi 的图像修复),计算复杂度更低(\(O(d^3)\),d为掩码维度),适合边缘设备部署。
- 补丁后效果:减弱触发器的识别
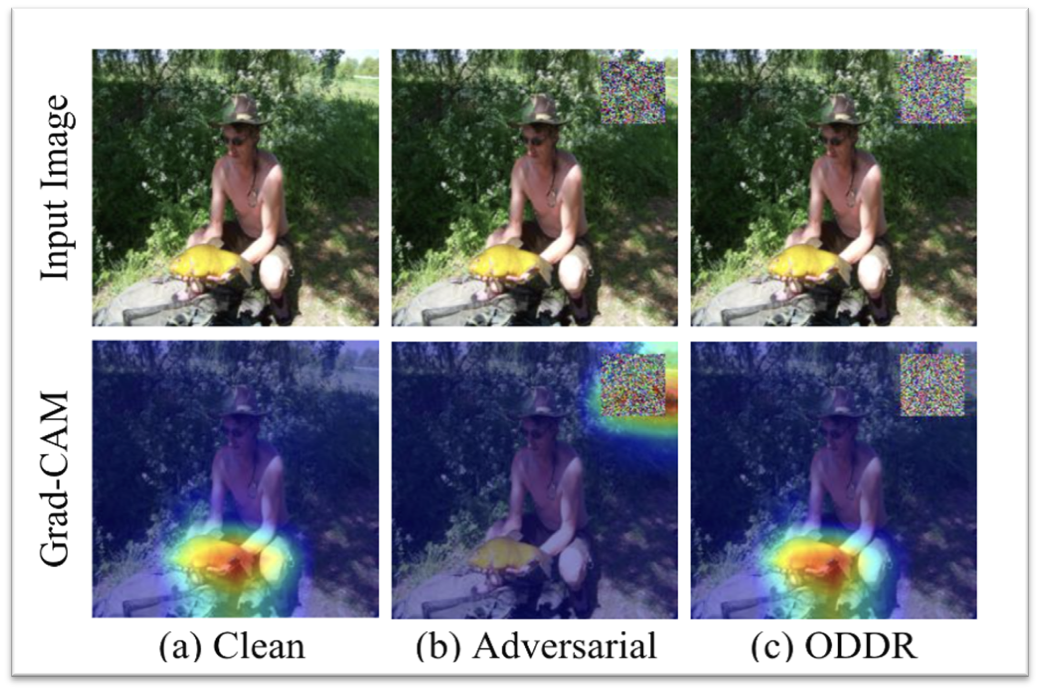

局限性
- 采用机器学习进行防御。
- 人为考了的超参数过多:异常置信度c(0.8-0.95)、掩码大小d(5-50 像素)、信息保留inf(70%-85%)、核大小k(20-40 像素)、步长\(str=k/2\)、孤立树数量\(T=100\)、聚类最小片段数(20-30)
小结
- 组件有效性:
- 异常检测:孤立森林比 DBSCAN 聚类的异常区域重叠率高 20%(ImageNet)。
- 中和方法:SVD 降维比 “掩码像素替换为均值 / 最值” 的下游任务准确率高 15%,且能处理上游误报。
- 核心结论:
- ODDR 通过 “异常检测定位补丁 + 降维中和扰动” 的组合策略,在多任务、多模型、多攻击场景下均实现最优防御性能。
- 相比现有方法,ODDR 在鲁棒性、计算效率、模型无关性上实现平衡,且对干净样本性能影响极小。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)