[論文介紹] Pre-Act: Multi-Step Planning and Reasoning Improves Acting in LLM Agents
本文探讨了Pre-Act方法如何通过多步骤规划改进LLM代理的性能。与ReAct的单步推理不同,Pre-Act在每次思考时都会生成包含"已完成步骤"和"后续计划"的全局规划,并通过迭代优化来提升长期任务表现。该方法采用特定的系统提示设计,引导LLM按照结构化格式(Thought/Action/Observation)进行推理,支持工具使用和连贯工作流程。论文
前言
Pre-Act 通过结构化的多步骤规划改进 LLM 代理。本文探讨了它的架构、评估以及 XAgent 如何采用这些想法来实现更稳定和可解释的工作流程。
如果说 ReAct 是火花,那么 Pre-Act 就是蓝图。在论文《Pre-Act: Multi-Step Planning and Reasoning Improves Acting in LLM Agents》中,Mrinal Rawat 等人挑战了 ReAct 的单步认知范式,而是为代理应该如何计划、推理和行动提供了路线图,尤其是在工具使用和工作流程连贯性很重要的情况下。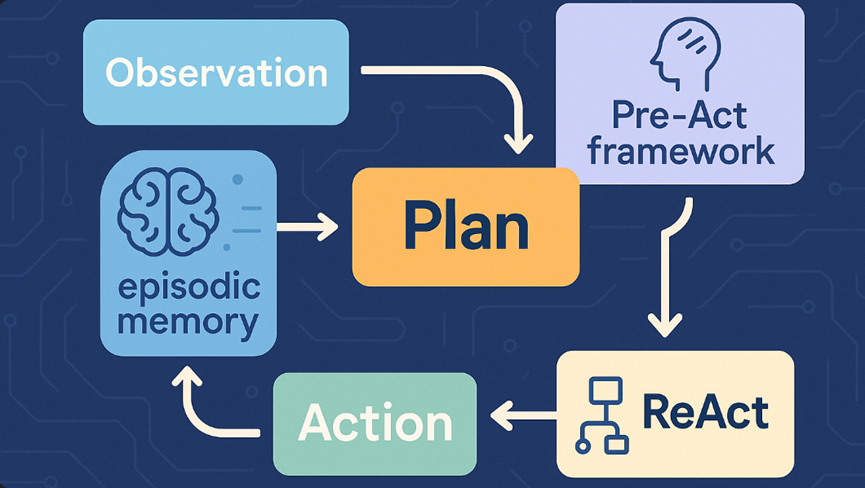
2 Pre-Act 想解决的问题
在 ReAct 方法中,LLM 的 (Single-Step) Reasoning (Thinking) 都只是针对下一个 Action,而不是针对未来一系列的 Action,这样的 Reasoning 方式导致 ReAct 在需要 Long-Term Planning 的任务上表现不好。
3 Pre-Act 提出的解决方法
让 LLM 每一次的 Thinking 都可以产生一个详细的 Plan。这个 Plan 主要包含,“过去已经执行的步骤” 与 “接下来要执行的步骤”。
举例来说,基于一个 Input Task,Pre-Act 在第一次 Thinking 时,会产生一个包含 N 个步骤的 Plan,每一个步骤都会叙述要进行什么 Action (其实就是使用什么 Tool),然后最后一个步骤就是使用 “Final Answer” Tool 来输出最终答案。
在每次 Thinking 结束后,Pre-Act 会输出一个 Action (透过 JSON 表示),系统会执行这个 Action 并将 Observation 放回到 Context 中。接着,Pre-Act 在进行第二次 Thinking 时,会根据 Context 中的内容 (前一次的 Plan, Action 与 Observation),重新产生一个 Plan。新的 Plan 中会描述过去几次的 Thinking 与 Action 已经完成了什么,并根据此修改接下来要完成的步骤。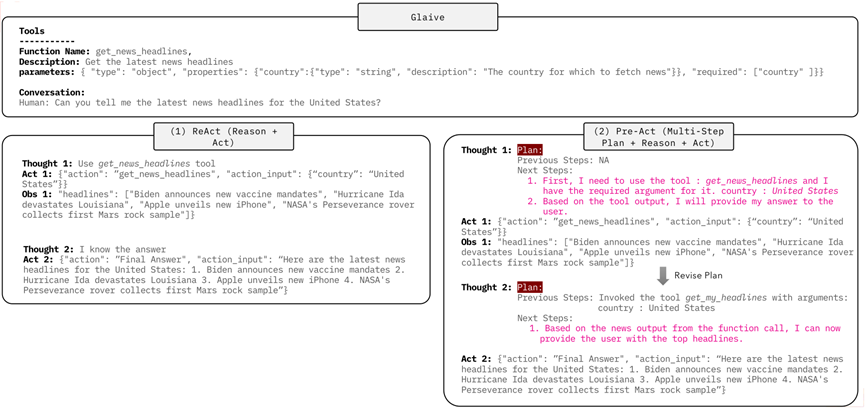
如上图的范例,可以清楚看到 ReAct 的每一次 Thinking 就是仅仅针对接下来马上要采取的 Action,而 Pre-Act 的每一次 Thinking 都会有一个 Global Plan 的描述。为了提升 LLM 在 Long-Term Planning 任务上的表现,“产生 Plan” 以及 “修改 Plan” 的技巧相当常见,在 Plan-and-Act (2025/03) 论文中也是使用了相同的概念;只不过在 Plan-and-Act (2025/03) 中是透过 Multi-Agent (Planner x Executor) 的架构,而在本篇论文 Pre-Act 中是透过 Single-Agent 的方式。
Pre-Act 透过以下 (论文提供的) System Prompt 的设计帮助 LLM 做到上述的 Reasoning 流程:(但老实说我觉得 System Prompt 写的相当凌乱):
<system> You are an intelligent assistant and your task is to respond to the human as helpfully and
accurately as possible. You would be provided with a conversation (along with some steps if present)
and you need to provide your response as Final Answer or use the following tools (if required):
Instructions:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{instructions}
Functions/Tools:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{tools}
===============
Use a json blob to specify a tool by providing an action key (tool name) and an action_input key
(tool input).
Valid "action" values: "Final Answer" or {tool_names}
In case of final answer:
Next Steps (Plan):
1. I will now proceed with the final answer because ... (explanation)
Follow this format (flow):
Question: input question to answer
Thought: consider previous and subsequent steps and conversation. Summary for what you did previously (ONLY IF
function calls were made for the last user request) and create the multi-step plan.
Action:
$JSON_BLOB
Observation: action result
... (repeat Thought/Action/Observation N times)
Thought: First provide the summary of previous steps (ONLY IF function calls were made for the last user request)
and then the plan consisting of only 1 step i.e. proceed with the final answer because ... explanation for it
Action:```
{
"action": "Final Answer",
"action_input": "Final response to human”
}
Definition of Multi-Step Plan:
For each request you will create a multi-step plan consisting of actions that needs to be taken until the final
answer along with the reasoning for the immediate action.
E.g.
Next Steps (Plan):
1. I will first do ... (action1) with the detailed reasoning.
2. I will do ... (action2) with the detailed reasoning.
k. I will do ... (actionk) with the detailed reasoning.
k+1. I will now proceed with the final answer because ... (explanation)
Example Output: When responding to human, please output a response only in one of two formats
(strictly follow it):
**Option 1:**
If function calls were made for the last human message in the conversation request, include Previous Steps: ... +
Next Steps: multi-step plan (provide an explanation or detailed reasoning)." Otherwise, provide Previous Steps:
NA and Next Steps: ..
Action:
{
"action": "string, \ The action to take. Must be one of {tool_names}",
"action_input": dict of parameters of the tool predicted
}
**Option #2:**
In case of you know the final answer or feel you need to respond to the user for clarification,
etc. Output = Thought: If function calls were made for the last human message in the conversation
request, include Previous Steps: ... + Next Steps: Let's proceed with the final answer because ...
(provide an explanation)." Otherwise, provide Previous Steps: NA and Next Steps: ..
Action:
{
"action": "Final Answer",
"action_input": "string \ You should put what you want to return to use here"
}
Begin! Reminder to ALWAYS respond with a valid json blob of a single action. Use tools if necessary
and parameters values for the tool should be deduced from the conversation directly or indirectly.
Respond directly if appropriate. Format is Thought:\nAction:```$JSON_BLOB```then Observation <user>
Conversation:
{conversation}
在 Pre-Act 论文中也有针对 Llama-3.1-8B 与 Llama-3.1-70B 进行 Finetune,训练模型输出 Pre-Act 风格的 Thinking 方式。有兴趣的读者可以再阅读原始论文,这边就不赘述!
4 Pre-Act 实验结果
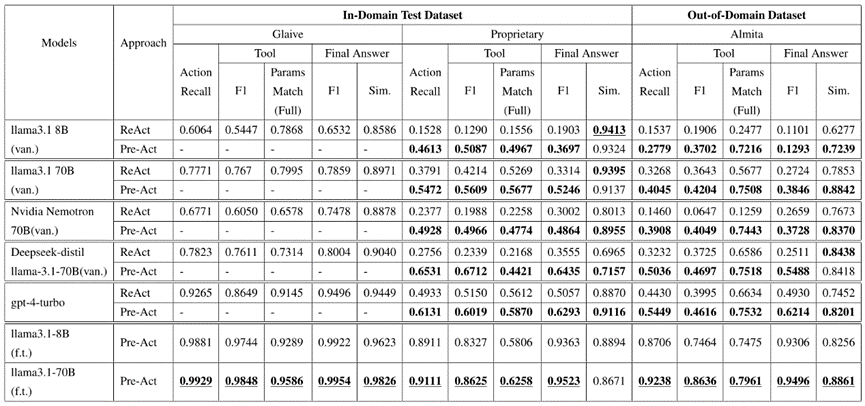
上述实验结果来自论文中的 Table 2,是 Pre-Act 的主要实验。上表中的前 5 列代表未经过 Finetune 模型 (“van” 表示 “vanilla”),只有透过不同 System Prompt 来比较 ReAct 与 PreAct 的表现。而最后 2 列则是有经过 Finetune 模型的表现 (“f.t.” 表示 “finetune”)。
从两种实验设定下可以观察到:
• 模型只有透过修改 System Prompt 来达到 Pre-Act-Based 的 Reasoning 表现也比 ReAct-Based 胜过许多
• 模型若特别 Finetune 在 Pre-Act-Based 的 Reasoning 方式,表现又可以比仅修改 System Prompt 的方法好上更多
5 结语
本篇文章非常快速的介绍了 Pre-Act: Multi-Step Planning and Reasoning Improves Acting in LLM Agents 论文:
Pre-Act 中透过每一个 Reasoning Step 来产生以及修改 Plan,来优化传统的 ReAct-Based Reasoning 中仅针对马上要执行的下一个 Action 的 Single-Step Thinking 的不足,让 LLM 在 Long-Term Planning 的任务上有更好的表现。
比较可惜的是,论文中比较的 Baseline 仅有针对 ReAct 一种方法,所使用的 Public Benchmark 也仅有一种。然而,由于 ReAct 也可以算是 LLM Agent 领域的始祖等级的论文,后续也还有许多方法被提出,再加上 Benchmark 较少,比较难说明 Pre-Act 方法能够多有效。但透过本篇论文,我们还是得以知道 “产生 Plan” 以及 “修改 Plan” 在 LLM 处理任务上所带来的好处!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)