c++:SLT容器之set、map详解
本文主要介绍了C++ STL中的关联式容器set和map。首先对比了序列式容器和关联式容器的区别,指出关联式容器具有非线性结构,元素之间存在紧密联系。然后详细分析了set容器的特性与常用操作,包括构造函数、插入、查找、删除等函数,并比较了set与multiset的区别。文章接着介绍了map容器,说明其与set的主要区别在于采用key-value结构,并介绍了pair类型的概念。最后,文章简要提及了
·

SLT容器之set、map详解
序列式容器和关联式容器
- 序列式容器:相互的两个值之间没有紧密的联系(线性结构),可以交换任意两个值。如string、vector、list、deque、array、forward_list
- 关联式容器:相互的两个位置有紧密的关联关系(通常为非线性结构),不能不是任意的两个值都能交换。如map/set,unordered_map/unordered_set系列。
一、set容器
set容器显然也是类模板,底层是一个平衡二叉搜索树
- 第一个参数是
key值,作为插入标准,不可被修改。 - 第二个参数是一个仿函数,默认参数的是一个
less类,因此默认是从小到大排序。 - 第三参数是空间配置器。

(一)函数分析
1、set的构造函数
一般来说,最常用的三种构造方式就是下面三种
- 直接构造,选择后续插入值
- 使用迭代器区间构造,它方便我们将其他的容器里的值引入进来
- 使用初始化列表构造,同样便捷。

void test01() {
set<int> s1;
set<int> s2({ 2,3,43,54,65,32,41,5,34 });
vector<int> v({ 23,43,65,76,24,48 });
set<int, greater<int>> s3(v.begin(), v.end());
for (auto x : s1) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto x : s2) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto x : s3) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}

2、set的插入
和上面的构造相似,插入对应三种方式。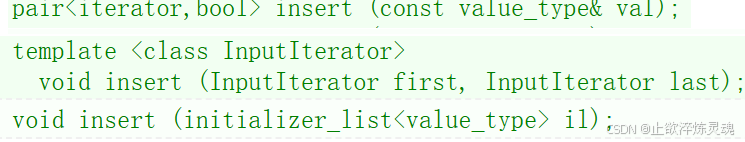
void test02() {
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(3);
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s1.insert({ 2,8,3,9 });
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
vector<int> v({ 23,43,65,76,24,48 });
s1.insert(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << endl;
for (auto e : s1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
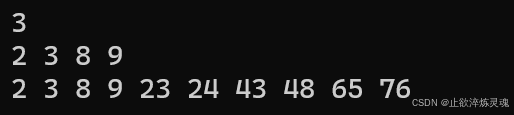
3、set的查找
在这里查找常用的有下面三种方式,其中第二种统计出现的次数,返回值为0(不存在)或者1(存在),加入这个接口是为了和multiset到达同时兼容。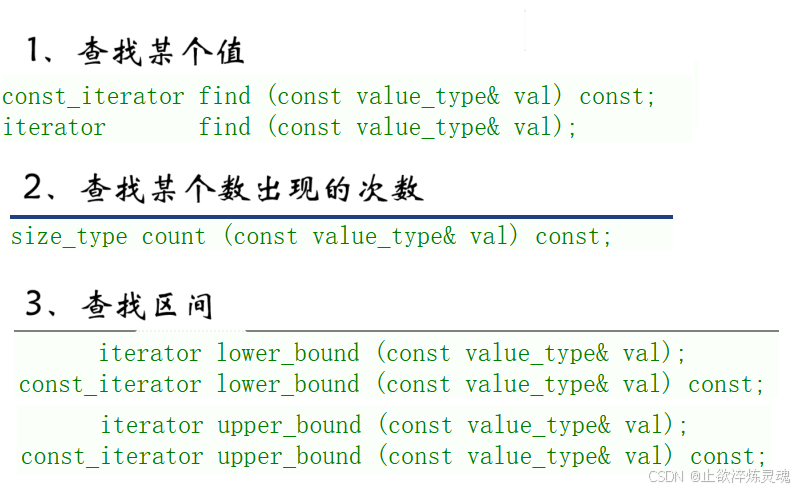
void test03() {
std::set<int> myset = { 10,20,35 ,40 ,50 ,65 ,70 ,80 ,90 };
for (auto e : myset)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
set<int>::iterator it = myset.find(10);
cout << *it << endl;
int n = myset.count(20);
cout << n << endl;
// 实现查找到的[itlow,itup)包含[30, 60]区间]
// 返回 >= 30
auto itlow = myset.lower_bound(30);
// 返回 > 60
auto itup = myset.upper_bound(60);
for (auto x = itlow; x != itup; x++) cout << *x << " ";
}

4、set的删除
删除主要是单个值的删除和迭代器区间的删除。
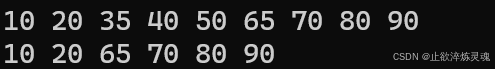
void test04() {
std::set<int> myset = { 10,20,35 ,40 ,50 ,65 ,70 ,80 ,90 };
for (auto e : myset)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 实现查找到的[itlow,itup)包含[30, 60]区间]
// 返回 >= 30
auto itlow = myset.lower_bound(30);
// 返回 > 60
auto itup = myset.upper_bound(60);
// 删除这段区间的值
myset.erase(itlow, itup);
for (auto e : myset)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
5、set和multiset的区别
我们通过下面的代码可以看出区别。
void test05() {
multiset<int> s = { 4,2,7,2,4,8,4,5,4,9 };
auto it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}

multiset和set的使⽤基本完全类似,区别在于multiset⽀持值冗余,insert/find/count/erase都围绕着⽀持值冗余有所差异
void test06() {
multiset<int> s = { 4,2,7,2,4,8,4,5,4,9,4 };
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//相比set不同的是,x可能会存在多个,find查找中序的第一个
auto pos = s.find(4);
while (pos != s.end() && *pos == 4)
{
cout << *pos << " ";
++pos;
}
cout << endl;
// 相比set不同的是,count会返回x的实际个数
cout << s.count(4) << endl;
//// 相比set不同的是,erase给值时会删除所有的x
s.erase(4);
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}

(二)set容器模拟实现
二、map容器
和上面的set唯一的区别就是map是key_value结构,因此就多了一个模板参数。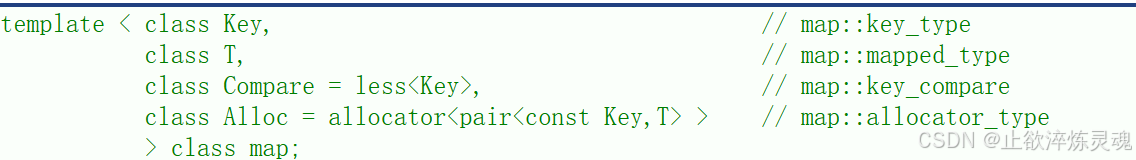
(一)函数分析
1、pair类型介绍
pair是一个类模板,可以将两种类型绑定起来,达到一一对应的效果。
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{
typedef T1 first_type;
typedef T2 second_type;
T1 first;
T2 second;
pair() : first(T1()), second(T2())
{}
pair(const T1& a, const T2& b) : first(a), second(b)
{}
template<class U, class V>
pair(const pair<U, V>& pr) : first(pr.first), second(pr.second)
{}
};
template <class T1, class T2>
inline pair<T1, T2> make_pair(T1 x, T2 y)
{
return (pair<T1, T2>(x, y));
}
void test07() {
pair<string, string> kv1("first", "第一个");
pair<string, string> kv2 = make_pair("sort", "排序");
cout << kv1.first << " " << kv1.second << endl;
cout << kv2.first << " " << kv2.second << endl;
}

2、map的构造函数
通常使用下面三种方式实现构造初始化
- 直接构造,选择后续插入值
- 使用迭代器区间构造,它方便我们将其他的容器里的值引入进来
- 使用初始化列表构造,同样便捷。

void test08() {
// initializer_list构造及迭代遍历
cout << "initializer_list构造及迭代遍历" << endl;
map<string, string> dict1 = { {"left", "左边"}, {"right", "右边"},{"insert", "插入"},{ "string", "字符串" } };
auto it = dict1.begin();
while (it != dict1.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
//迭代器区间构造
cout << endl;
cout << "迭代器区间构造" << endl;
vector<pair<string,string>> v = { {"left", "左边"}, {"right", "右边"},{"insert", "插入"},{ "string", "字符串" } };
map<string, string> dict2(v.begin(), v.end());
auto it2 = dict2.begin();
while (it2 != dict2.end())
{
cout << it2->first << ":" << it2->second << endl;
++it2;
}
cout << endl;
}

3、map的插入
插入主要也是三种方式,单值插入、迭代器区间插入以及initializer_list插入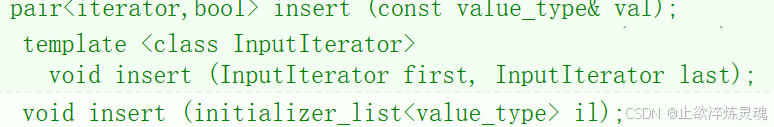
void test10() {
map<string, string> dict = { {"left", "左边"}, {"right", "右边"},{"insert", "插入"},{ "string", "字符串" } };
pair<string, string> kv1("first", "第一个");
dict.insert(kv1);
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("second", "第二个"));
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
dict.insert({ "auto", "自动的" });
for (const auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}

4、map的查找
// 查找k,返回k所在的迭代器,没有找到返回end()
iterator find (const key_type& k);
// 查找k,返回k的个数
size_type count (const key_type& k) const;
// 返回⼤于等k位置的迭代器
iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k);
// 返回⼤于k位置的迭代器
const_iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k) const;
4、map的删除
// 删除⼀个迭代器位置的值
iterator erase (const_iterator position);
// 删除k,k存在返回0,存在返回1
size_type erase (const key_type& k);
// 删除⼀段迭代器区间的值
iterator erase (const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
5、map的修改(value)
map支持修改value数据
- 迭代器,迭代器返回其value进行修改
- operator[],不仅仅支持修改,还支持插入数据和查找数据
operator[]
1、如果k不在map中,insert会插⼊k和mapped_type默认值,同时[]返回结点中存储
mapped_type值的引⽤,那么我们可以通过引⽤修改返映射值。所以[]具备了插⼊+修改功能
2、如果k在map中,insert会插⼊失败,但是insert返回pair对象的first是指向key结点的
迭代器,返回值同时[]返回结点中存储mapped_type值的引⽤,所以[]具备了查找+修改的功能
key_type -> The first template parameter (Key)
mapped_type -> The second template parameter (T)
value_type -> pair<const key_type,mapped_type>
mapped_type& operator[] (const key_type& k)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ k, mapped_type() });
iterator it = ret.first;
return it->second;
}
7、map和multimap的区别
和前面的multiset/set关系相同,就不再赘述。
8、结构化绑定遍历
在遍历map时,c++14可以使用下面的方式来遍历
void test09() {
map<string, string> dict1 = { {"left", "左边"}, {"right", "右边"},{"insert", "插入"},{ "string", "字符串" } };
// 结构化绑定 C++17
for (const auto& [k,v] : dict1)
{
cout << k << ":" << v << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)