七、详解LangChain的ReAct框架
本文介绍了在LangChain框架中使用Agent的四个核心组件:大模型(如DeepSeek的deepseek-chat)、提示模板(定义ReAct推理框架)、外部工具(如搜索和数学工具)和Agent执行器(管理流程)。重点解析了AgentExecutor的运行机制,它通过循环执行思考-行动-观察流程来解决问题,并处理异常情况。文章还详细说明了提示模板的结构和AgentExecutor的内部工作流
·
回顾代码
import os # 导入 os 模块,用于环境变量操作
from langchain.agents import load_tools # 用于加载工具
from langchain.agents import create_react_agent, AgentExecutor # 用于创建 ReAct 代理和执行器
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI # 用于创建聊天模型
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate # 用于创建提示模板
BASE_URL = "https://api.deepseek.com/v1"
API_KEY = "你的deepseek API key"
MODEL_NAME = "deepseek-chat"
#设置环境变量
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = API_KEY
os.environ["OPENAI_API_BASE"] = BASE_URL
os.environ["SERPAPI_API_KEY"] = "你的serpapi API Key"
# 创建DeekSeek大模型实例
llm = ChatOpenAI(model=MODEL_NAME, temperature=0)
# 加载 serpapi 和 llm-math 工具,并绑定到DeekSeek大模型。
tools = load_tools(["serpapi", "llm-math"], llm=llm)
# 创建 ReAct 提示模板
REACT_PROMPT = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"""
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
{tools}
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [{tool_names}]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
Question: {input}
Thought: {agent_scratchpad}
"""
)
agent = create_react_agent(llm, tools, prompt=REACT_PROMPT)
executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent, tools=tools, verbose=True, handle_parsing_errors=True)
# 定义问题
question = "北京今天的气温是多少,并且计算一下如果气温升高5摄氏度后的温度是多少?"
# 调用执行器,获取输出
response = executor.invoke({"input": question})["output"]
print(response)在LangChain中使用Agent时,需要理解下面4个元素。
- 大模型:提供逻辑引擎,负责生成预测和处理输入。对应于代码中的llm变量,代码中使用的是DeepSeek的deepseek-chat模型。
- 提示(prompt):负责指导模型,形成推理框架,即思考-行动-观察循环的处理框架。对应于代码中的prompt变量,提示词定义的ReAct框架的处理逻辑。
- 外部工具(external tools):包括数据清洗工具、搜索引擎、应用程序等。对应于代码中的tools变量,包含搜索工具和数学计算工具。
- Agent执行器(Agent executor):负责调用合适的外部工具,并管理整个流程。对应于代码中的agent_executor变量,在声明该变量前需要先创建agent = create_react_agent(llm, tools, prompt)。
提示模板说明
| 介绍 | 尽你所能回答以下问题。如果能力不够,你可以使用以下工具: |
| 工具列表 | {tools} |
| 格式指南 | 使用以下格式: |
| 问题 | 你需要回答的输入问题 |
| 思考 | 你应该始终考虑接下来的操作 |
| 行动 | 需要采取的行动,应该是 [{tool_names}] 中的一个 |
| 行动输入 | 对行动的输入 |
| 观察 | 行动的结果 |
| 循环 | ... (这个思考 / 行动 / 行动输入 / 观察可以重复 N 次) |
| 最终思考 | 我现在知道了最终答案 |
| 最终答案 | 对原始输入问题的最终回答 |
| 开始指令 | 开始! |
| 实际用例 | 问题: {input}\n 思考:{agent_scratchpad} |
AgentExecutor的运行机制
AgentExecutor是Agent的运行环境,它首先调用大模型,接收并观察结果,然后执行大模型所选择的操作,同时也负责处理多种复杂情况,包括Agent选择了不存在的工具的情况、工具出错的情况、Agent产生无法解析成Function Calling格式的情况,以及在Agent决策和工具调用期间进行日志记录。
1、AgentExecutor类继承自Chain类,invoke()方法为Chain类中的方法。
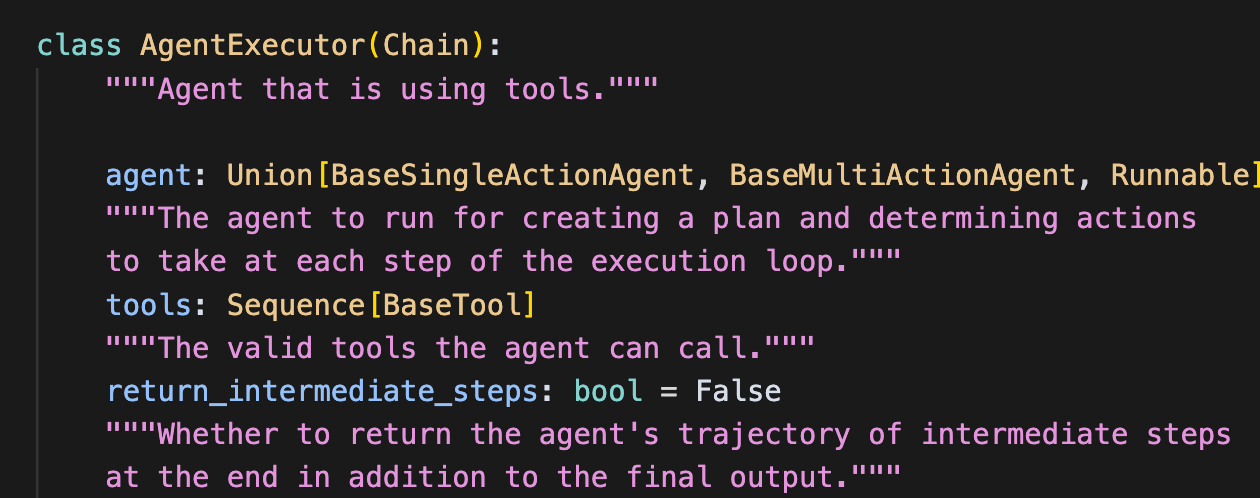
2、invoke()方法调用self._call()方法
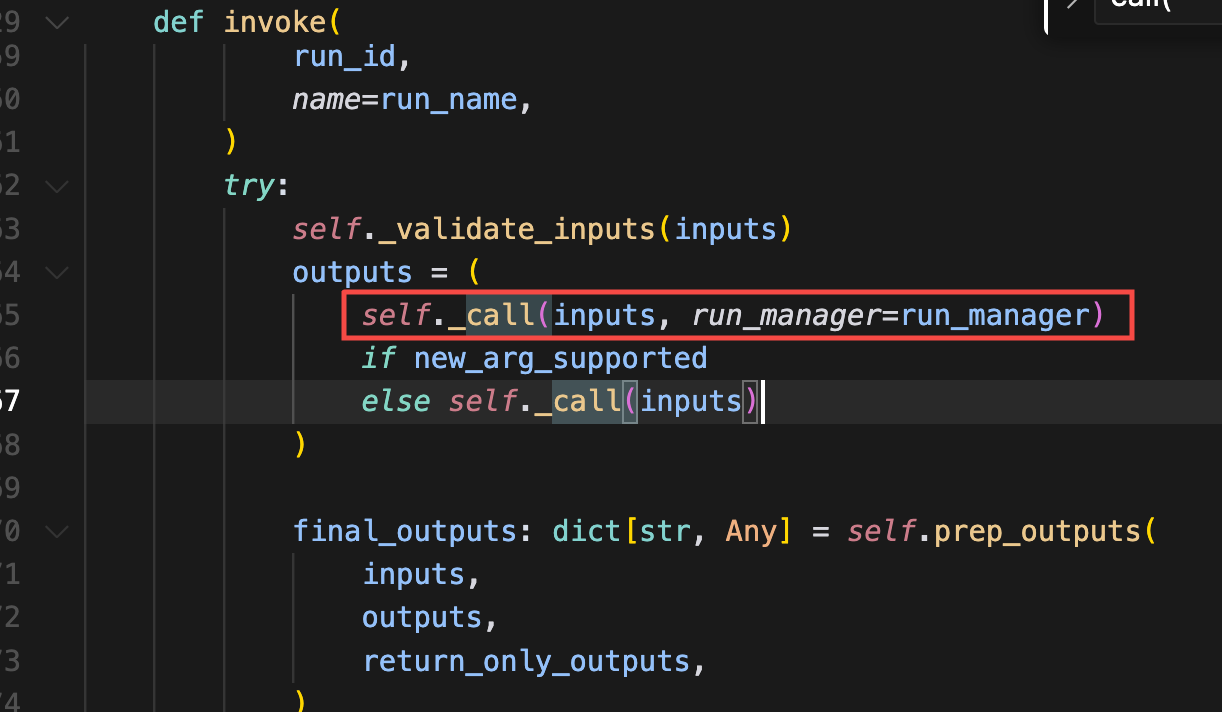
3、LangChain中agent.py的AgentExecutor类的_call方法中循环self._should_continue()方法,Agent将在此不断循环计划、思考、调用工具、解决问题。
def _call(
self,
inputs: dict[str, str],
run_manager: Optional[CallbackManagerForChainRun] = None,
) -> dict[str, Any]:
"""Run text through and get agent response."""
# Construct a mapping of tool name to tool for easy lookup
name_to_tool_map = {tool.name: tool for tool in self.tools}
# We construct a mapping from each tool to a color, used for logging.
color_mapping = get_color_mapping(
[tool.name for tool in self.tools],
excluded_colors=["green", "red"],
)
intermediate_steps: list[tuple[AgentAction, str]] = []
# Let's start tracking the number of iterations and time elapsed
iterations = 0
time_elapsed = 0.0
start_time = time.time()
# We now enter the agent loop (until it returns something).
while self._should_continue(iterations, time_elapsed):
next_step_output = self._take_next_step(
name_to_tool_map,
color_mapping,
inputs,
intermediate_steps,
run_manager=run_manager,
)
if isinstance(next_step_output, AgentFinish):
return self._return(
next_step_output,
intermediate_steps,
run_manager=run_manager,
)
intermediate_steps.extend(next_step_output)
if len(next_step_output) == 1:
next_step_action = next_step_output[0]
# See if tool should return directly
tool_return = self._get_tool_return(next_step_action)
if tool_return is not None:
return self._return(
tool_return,
intermediate_steps,
run_manager=run_manager,
)
iterations += 1
time_elapsed = time.time() - start_time
output = self._action_agent.return_stopped_response(
self.early_stopping_method,
intermediate_steps,
**inputs,
)
return self._return(output, intermediate_steps, run_manager=run_manager)
| 步骤 | 描述 | 关键操作 | 目的 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 输入和初始化 | 接收一个字典 inputs 作为输入,可能包含 run_manager 实例 | inputs 字典处理,run_manager 初始化 | 返回处理后的结果或响应字典 |
| 2. 工具映射构建 | 构建从工具名称到工具实例的映射 name_to_tool_map | 遍历 self.tools | 便于后续根据名称查找工具 |
| 3. 颜色映射 | 为日志记录建立颜色映射,排除 “green” 和 “red” | color_mapping 构建 | 将每个工具映射到一个颜色上 |
| 4. 迭代和时间追踪 | 初始化 iterations 和 time_elapsed,记录 start_time | 记录方法开始时间 | 跟踪迭代次数和总耗时 |
| 5. 循环 | 使用 while 循环,基于_should_continue 的返回值决定是否继续 | _take_next_step 获取输出 | 根据条件继续或结束执行 |
| 6. 处理下一步输出 | 根据 next_step_output 是不是 AgentFinish 实例来决定后续操作 | 添加输出到 intermediate_steps | 记录中间步骤或返回最终结果 |
| 7. 工具直接返回检查 | 如果 next_step_output 只有一个元素,检查是否直接返回结果 | 判断步骤输出 | 可能直接返回结果 |
| 8. 迭代和时间更新 | 更新 iterations 和 time_elapsed | 时间和迭代计数更新 | 为循环迭代和时间追踪 |
| 9. 早停响应 | 如果循环结束,生成基于早停策略的响应 | 使用 agent_return_stopped_response | 响应基于早停策略 |
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容






所有评论(0)