LangChain之Memory模块,实现大模型对话记忆的5种方法
本文详细介绍LangChain中的Memory模块,解决LLM无记忆问题。涵盖ChatMessageHistory管理对话历史、RunnableWithMessageHistory自动添加记忆、ConversationBufferMemory缓冲记忆、ConversationBufferWindowMemory解决Token限制、ConversationEntityMemory实体记忆等实现方法。
本文详细介绍LangChain中的Memory模块,解决LLM无记忆问题。涵盖ChatMessageHistory管理对话历史、RunnableWithMessageHistory自动添加记忆、ConversationBufferMemory缓冲记忆、ConversationBufferWindowMemory解决Token限制、ConversationEntityMemory实体记忆等实现方法。通过代码示例展示如何构建带记忆功能的对话系统,实现上下文管理、状态跟踪和个性化体验,为开发者提供完整的大模型对话记忆解决方案。
在最开始我们就通过实验知道LLM 本身是没有记忆的,每一次LLM的API调用都是一个全新的会话。但在某些应用程序中,如:聊天机器人,让LLM记住以前的历史交互是非常重要,无论是在短期的还是长期的。langchain中的“Memory”即对话历史(message history)就是为了实现这一点。
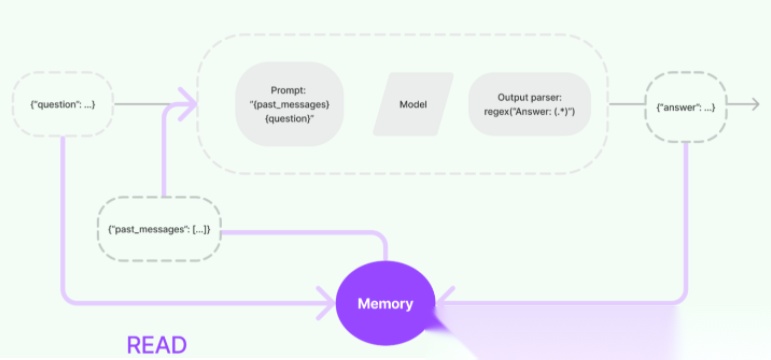
在与大模型进行对话和交互的过程中,一个关键步骤是能够引用交互过程中先前的信息,至少需要能够直接回溯到过去某些对话的内容。对于复杂应用而言,所需的是一个能够不断自我更新的模型,以便执行如维护相关信息、实体及其关系等任务。这种存储并回溯过去交互信息的能力,就叫做“记忆(Memory)”。
Memory作为存储记忆数据的一个是抽象模块,其作为一个独立模块使用是没有任何意义的,因为本质上它的定位就是一个存储对话数据的空间。
LangChain Memory 的作用
- 上下文管理:通过保存历史对话,模型可以基于之前的对话内容来生成更相关的响应。
- 状态跟踪:对于需要持续跟踪用户状态的应用程序来说,Memory 可以帮助维护会话的状态信息。
- 个性化体验:通过记录用户的偏好或历史选择,可以提供更加个性化的用户体验。
ChatMessageHistory-对话消息历史管理
在LangChain中,ChatMessageHistory通常是一个数据结构,用于存储和检索对话消息。这些消息可以按照时间顺序排列,以便在对话过程中引用和更新。
# 初始化大模型
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
fromlangchain.promptsimportChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
# 本地ollama拉取过什么模型就使用什么模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3axxx35366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com")
# 聊天模型提示词
template= [
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
]
prompt=ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(messages=template)
chain=prompt|llm
# 记录会话历史
fromlangchain_community.chat_message_historiesimportChatMessageHistory
fromlangchain_core.messagesimportSystemMessage
history=ChatMessageHistory()
history.messages= [SystemMessage("你是由John开发的智能助手机器人,叫多啦A梦,你每次都会精简而快速的告诉用户你是一个专业的机器人以及用户问题的答案。")]
history.add_user_message("我叫John,请你记住。")
history.add_user_message("我叫什么名字,以及你叫什么名字?")
res=chain.invoke({"history": history.messages})
history.add_ai_message(res)
print(res.content)
history.add_user_message("我现在改名了,叫Johnny,请问我是谁?")
res=chain.invoke({"history": history.messages})
history.add_ai_message(res)
print(res.content)
formessageinhistory.messages:
print("会话记录",message.content)
多个用户多轮对话
有了对话消息历史管理对象,不仅可以管理和存储单个用户和LLM的历史对话信息以此来维持会话状态,还可以实现管理多用户与LLM的独立历史对话信息。
# 初始化大模型
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
fromlangchain.promptsimportChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
# 本地ollama拉取过什么模型就使用什么模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79fxxx935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com")
# 聊天模型提示词
fromlangchain.promptsimportChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
template= [
("system",
"你叫多啦A梦,今年1岁了,是John开发的智能机器人,能精准回复用户的问题"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
]
prompt=ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(messages=template)
chain=prompt|llm
# 记录会话历史
fromlangchain_community.chat_message_historiesimportChatMessageHistory
#session_id设置不同的消息集
john_history=ChatMessageHistory(session_id="John")
john_history.add_user_message('我叫John,今年100岁,很高兴和你聊天')
john_res=chain.invoke({"history": john_history.messages})
john_history.add_ai_message(john_res)
print(john_res.content)
print('=======================================')
Yuki_history=ChatMessageHistory(session_id="Yuki")
Yuki_history.add_user_message('你好呀,我的名字叫Yuki,我今年200岁。你叫什么?')
Yuki_res=chain.invoke({"history": Yuki_history.messages})
Yuki_history.add_ai_message(Yuki_res)
print(Yuki_res.content)
print('=======================================')
john_history.add_user_message("你还记得我的名字和年龄吗?")
john_res=chain.invoke({"history": john_history.messages})
john_history.add_ai_message(john_res)
print(john_res.content)
print('=======================================')
Yuki_history.add_user_message("你还记得我的名字和年龄吗?")
Yuki_res=chain.invoke({"history": Yuki_history.messages})
Yuki_history.add_ai_message(Yuki_res)
print(Yuki_res.content)
print('=======================================')
RunnableWithMessageHistory-可运行的消息历史记录对象
上面虽然使用了ChatMessageHistory保存对话历史数据,但是与Chains的操作是独立的,并且每次产生新的对话消息都要手动add添加记录,所以为了方便使用,langchain还提供了RunnableWithMessageHistory可以自动为Chains添加对话历史记录。
# 初始化大模型
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
fromlangchain.promptsimportChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder
fromlangchain_core.output_parsersimportStrOutputParser
# 本地ollama拉取过什么模型就使用什么模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3xxx1935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com")
# 聊天模型提示词
template= [
("system",
"你叫多啦A梦,今年1岁了,是John开发的智能机器人,能精准回复用户的问题"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),
("human", "{input}"),
]
prompt=ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(messages=template)
chain=prompt|llm|StrOutputParser()
# 记录会话历史
fromlangchain_core.runnables.historyimportRunnableWithMessageHistory
fromlangchain_community.chat_message_historiesimportChatMessageHistory
# 用于记录不同的用户(session_id)对话历史
store= {}
defget_session_history(session_id):
ifsession_idnotinstore:
store[session_id] =ChatMessageHistory()
returnstore[session_id]
chains=RunnableWithMessageHistory(
chain,
get_session_history,
input_messages_key="input",
history_messages_key="history",
)
res1=chains.invoke({"input": "什么是余弦相似度?"}, config={'configurable': {'session_id': 'john'}})
print(res1)
print('====================================================')
res2=chains.invoke({"input": "再回答一次刚才的问题"}, config={'configurable': {'session_id': 'john'}})
print(res2)
ConversationChain中的记忆
ConversationChain提供了包含AI角色和人类角色的对话摘要格式,这个对话格式和记忆机制结合得非常紧密。ConversationChain实际上是对Memory和LLMChain进行了封装,简化了初始化Memory的步骤。
该方法已经在langchain1.0版本废除,使用RunnableWithMessageHistory对其进行替代!
# 初始化大模型
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
# 本地ollama拉取过什么模型就使用什么模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3a3xxx935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com")
# 导入所需的库
fromlangchain.chains.conversation.baseimportConversationChain
# 初始化对话链
conv_chain=ConversationChain(llm=llm)
# 打印对话的模板
print(conv_chain.prompt.template)
ConversationChain中的内置提示模板中的两个参数:
- {history}:存储会话记忆的地方,也就是人类和人工智能之间对话历史的信息。
- {input} :新输入的地方,可以把它看成是和ChatGPT对话时,文本框中的输入。
缓冲记忆:ConversationBufferMemory
在LangChain中,ConversationBufferMemory是一种非常简单的缓冲记忆,可以实现最简单的记忆机制,它只在缓冲区中保存聊天消息列表并将其传递到提示模板中。
通过记忆机制,LLM能够理解之前的对话内容。直接将存储的所有内容给LLM,因为大量信息意味着新输入中包含更多的Token,导致响应时间变慢和成本增加。此外,当达到LLM的Token数限制时,太长的对话无法被记住。
#用于创建对话链
fromlangchain.chainsimportConversationChain
#用于存储对话历史,以便在后续对话中参考
fromlangchain.memoryimportConversationBufferMemory
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
importwarnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 初始化大模型(需配置OPENAI_API_KEY)
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3axxx935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com")
#实例化一个对话缓冲区,用于存储对话历史
memory=ConversationBufferMemory()
#创建一个对话链,将大语言模型和对话缓冲区关联起来。
conversation=ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
memory=memory,
)
conversation.invoke("今天早上猪八戒吃了2个人参果。")
print("记忆1: ", conversation.memory.buffer)
print()
conversation.invoke("下午猪八戒吃了1个人参果。")
print("记忆2: ", conversation.memory.buffer)
print()
conversation.invoke("晚上猪八戒吃了3个人参果。")
print("记忆3: ", conversation.memory.buffer)
print()
conversation.invoke("猪八戒今天一共吃了几个人参果?")
print("记忆4: ", conversation.memory.buffer)
功能设计:多轮对话
fromlangchain.chainsimportConversationChain
fromlangchain.memoryimportConversationBufferMemory
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
importwarnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 实例化一个对话缓冲区,用于存储对话历史
memory=ConversationBufferMemory()
# 创建一个对话链,将大语言模型和对话缓冲区关联起来。
conversation=ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
memory=memory,
)
print("欢迎使用对话系统!输入 '退出' 结束对话。")
whileTrue:
user_input=input("你: ")
ifuser_input.lower() in ['退出', 'exit', 'quit']:
print("再见!")
break
response=conversation.predict(input=user_input)
print(f"AI: {response}")
# 打印出对话历史,即 memory.buffer 的内容
print("对话历史:", memory.buffer)
携带提示词模版的对轮对话(LLMChain对话链)
fromlangchain.promptsimportPromptTemplate
fromlangchain.chainsimportLLMChain
fromlangchain.memoryimportConversationBufferMemory
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
importos
importwarnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 初始化大模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3a3fxxx1935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(
model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com"
)
# 实例化一个对话缓冲区,用于存储对话历史
memory=ConversationBufferMemory()
# 定义提示词模板
template="""{history}
用户: {input}
AI:"""
prompt_template=PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["history", "input"],
template=template
)
# 创建一个包含提示词模板的对话链
conversation=LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=prompt_template,
verbose=True, # 如果需要调试,可以设置为 True
memory=memory
)
print("欢迎使用对话系统!输入 '退出' 结束对话。")
whileTrue:
user_input=input("你: ")
ifuser_input.lower() in ['退出', 'exit', 'quit']:
print("再见!")
break
try:
# 调用对话链获取响应
response=conversation.run(input=user_input)
print(f"AI: {response}")
exceptExceptionase:
print(f"发生错误: {e}")
# 打印出对话历史,即 memory.buffer 的内容
print("对话历史:", memory.buffer)
如果使用聊天模型,使用结构化的聊天消息可能会有更好的性能:
fromlangchain_openaiimportChatOpenAI
fromlangchain.memoryimportConversationBufferMemory
fromlangchain.chains.llmimportLLMChain
fromlangchain_core.messagesimportSystemMessage
fromlangchain_core.promptsimportMessagesPlaceholder, HumanMessagePromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate
importwarnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 初始化大模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3a3xxxa1935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(
model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com"
)
# 使用ChatPromptTemplate设置聊天提示
prompt=ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
SystemMessage(content="你是一个与人类对话的机器人。"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history"),
HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template("{question}"),
]
)
# 创建ConversationBufferMemory
memory=ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", return_messages=True)
# 初始化链
chain=LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt, memory=memory)
# 提问
res=chain.invoke({"question": "你是LangChain专家"})
print(str(res) +"\n")
res=chain.invoke({"question": "你是谁?"})
print(res)
多轮对话Token限制解决
在了解了ConversationBufferMemory记忆类后,我们知道了它能够无限的将历史对话信息填充到History中,从而给大模型提供上下文的背景。但问题是:每个大模型都存在最大输入的Token限制,且过久远的对话数据往往并不能够对当前轮次的问答提供有效的信息,这种我们大家都能非常容易想到的问题,LangChain的开发人员自然也能想到,那么他们给出的解决方式是:ConversationBufferWindowMemory模块。该记忆类会保存一段时间内对话交互的列表,仅使用最后 K 个交互。所以它可以保存最近交互的滑动窗口,避免缓存区不会变得太大。
fromlangchain.memoryimportConversationBufferWindowMemory
importwarnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
#实例化一个对话缓冲区,用于存储对话历史
#k=1,所以在读取时仅能提取到最近一轮的记忆信息
#return_messages=True参数,将对话转化为消息列表形式
memory=ConversationBufferWindowMemory(k=1, return_messages=True)
conversation=ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
memory=memory,
)
# 示例对话
response1=conversation.predict(input="你好")
response2=conversation.predict(input="你在哪里?")
print("对话历史:", memory.buffer)
实体记忆:ConversationEntityMemory
在LangChain 中,ConversationEntityMemory是实体记忆,它可以跟踪对话中提到的实体,在对话中记住关于特定实体的给定事实。它提取关于实体的信息(使用LLM),并随着时间的推移建立对该实体的知识(使用LLM)。
使用它来存储和查询对话中引用的各种信息,比如人物、地点、事件等。
fromlangchain.chains.conversation.baseimportConversationChain
fromlangchain.memoryimportConversationEntityMemory
fromlangchain.memory.promptimportENTITY_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_TEMPLATE
fromlangchain_openaiimportOpenAI
importwarnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 初始化大模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3a3xxx1935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(
model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com"
)
conversation=ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=ENTITY_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_TEMPLATE,
memory=ConversationEntityMemory(llm=llm)
)
# 开始对话
conversation.predict(input="你好,我是小明。我最近在学习 LangChain。")
conversation.predict(input="我最喜欢的编程语言是 Python。")
conversation.predict(input="我住在北京。")
# 查询对话中提到的实体
res=conversation.memory.entity_store.store
print(res)
跟踪对话中提到的实体,在对话中记住关于特定实体的给定事实。它提取关于实体的信息(使用LLM),并随着时间的推移建立对该实体的知识(使用LLM)。
使用它来存储和查询对话中引用的各种信息,比如人物、地点、事件等。
```plaintext
fromlangchain.chains.conversation.baseimportConversationChain
fromlangchain.memoryimportConversationEntityMemory
fromlangchain.memory.promptimportENTITY_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_TEMPLATE
fromlangchain_openaiimportOpenAI
importwarnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
# 初始化大模型
API_KEY="sk-4b79f3a3xxx1935366ebb425b3"
llm=ChatOpenAI(
model="deepseek-chat",
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
openai_api_base="https://api.deepseek.com"
)
conversation=ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=ENTITY_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_TEMPLATE,
memory=ConversationEntityMemory(llm=llm)
)
# 开始对话
conversation.predict(input="你好,我是小明。我最近在学习 LangChain。")
conversation.predict(input="我最喜欢的编程语言是 Python。")
conversation.predict(input="我住在北京。")
# 查询对话中提到的实体
res=conversation.memory.entity_store.store
print(res)
如何系统学习掌握AI大模型?
AI大模型作为人工智能领域的重要技术突破,正成为推动各行各业创新和转型的关键力量。抓住AI大模型的风口,掌握AI大模型的知识和技能将变得越来越重要。
学习AI大模型是一个系统的过程,需要从基础开始,逐步深入到更高级的技术。
这里给大家精心整理了一份
全面的AI大模型学习资源,包括:AI大模型全套学习路线图(从入门到实战)、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习、面试题等,资料免费分享!

1. 成长路线图&学习规划
要学习一门新的技术,作为新手一定要先学习成长路线图,方向不对,努力白费。
这里,我们为新手和想要进一步提升的专业人士准备了一份详细的学习成长路线图和规划。可以说是最科学最系统的学习成长路线。

2. 大模型经典PDF书籍
书籍和学习文档资料是学习大模型过程中必不可少的,我们精选了一系列深入探讨大模型技术的书籍和学习文档,它们由领域内的顶尖专家撰写,内容全面、深入、详尽,为你学习大模型提供坚实的理论基础。(书籍含电子版PDF)

3. 大模型视频教程
对于很多自学或者没有基础的同学来说,书籍这些纯文字类的学习教材会觉得比较晦涩难以理解,因此,我们提供了丰富的大模型视频教程,以动态、形象的方式展示技术概念,帮助你更快、更轻松地掌握核心知识。

4. 大模型行业报告
行业分析主要包括对不同行业的现状、趋势、问题、机会等进行系统地调研和评估,以了解哪些行业更适合引入大模型的技术和应用,以及在哪些方面可以发挥大模型的优势。

5. 大模型项目实战
学以致用 ,当你的理论知识积累到一定程度,就需要通过项目实战,在实际操作中检验和巩固你所学到的知识,同时为你找工作和职业发展打下坚实的基础。

6. 大模型面试题
面试不仅是技术的较量,更需要充分的准备。
在你已经掌握了大模型技术之后,就需要开始准备面试,我们将提供精心整理的大模型面试题库,涵盖当前面试中可能遇到的各种技术问题,让你在面试中游刃有余。

全套的AI大模型学习资源已经整理打包,有需要的小伙伴可以
微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码,免费领取【保证100%免费】

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献149条内容
已为社区贡献149条内容







所有评论(0)