Linux的线程池
本文介绍了Linux下日志系统和线程池的实现方案。日志系统采用策略模式,支持控制台和文件两种输出方式,提供DEBUG、INFO等5种日志级别,实现格式化输出和线程安全。线程池采用单例模式实现固定线程数量的管理,通过任务队列分配任务,支持线程同步和优雅退出。两种方案都运用了RAII思想管理资源,使用互斥锁保证线程安全,并提供了详细的代码实现和设计注意事项。日志系统可帮助开发者监控运行状态,线程池则优
·
基于前文Linux的多线程-CSDN博客。
基于前文Linux的生产者消费者模型-CSDN博客
目录
1、日志
1.1 日志的概念
- 日志是计算机系统、应用程序或服务在运行过程中生成的、按时间顺序记录的事件流文件或数据集合,主要作用是监控运行状态、记录异常信息,帮助快速定位问题并支持程序员进行问题修复。它是系统维护、故障排查和安全管理的重要工具。
1.2 日志的设计
- 要设计出下面的格式:
[可读性很好的时间] [日志等级] [进程PID] [打印对应日志的源文件名] [行号] - 消息内容(支持可
变参数,即多条不同的信息)
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [20] - hello world
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [21] - hello world
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [WARNING] [202938] [main.cc] [23] - hello world- 日志等级分为:DEBUG,INFO,WARNING,ERROR,FATAL。
- 采用策略模式,通过多态的方式,可以随时选择打印到显示器,还是文件。
- 重载 << 支持 C++ 风格的日志输入,使用模版,表示支持任意类型。
logger(LogLevel::DEBUG, "main.cc", 10) << "hello world," << 3.14
<< " " << 8899 << "aaaa";1.3 代码
1.3.1 Log.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <time.h>
#include <cstdio>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
#include <filesystem> // C++17,方便文件管理
#include <fstream> // 方便文件内容的操作
#include <sstream>
#include <memory>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
namespace LogModule
{
using namespace MutexModule;
std::string GetTime()
{
time_t curr = time(nullptr);
struct tm curr_tm;
localtime_r(&curr, &curr_tm);
char time_str[128];
snprintf(time_str, sizeof(time_str),
"%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
curr_tm.tm_year + 1900,
curr_tm.tm_mon + 1,
curr_tm.tm_mday,
curr_tm.tm_hour,
curr_tm.tm_min,
curr_tm.tm_sec);
return time_str;
}
enum class LogLevel
{
DEBUG,
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
std::string LogLeveltoString(LogLevel log_level)
{
if (log_level == LogLevel::DEBUG)
return "DEBUG";
else if (log_level == LogLevel::INFO)
return "INFO";
else if (log_level == LogLevel::WARNING)
return "WARNING";
else if (log_level == LogLevel::ERROR)
return "ERROR";
else if (log_level == LogLevel::FATAL)
return "FATAL";
else
return "UNKNOWN";
}
class LogStrategy
{
public:
// 纯虚函数,不需要实现,不能创建对象
virtual void SyncLog(const std::string &message) = 0;
};
class ConsoleLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
virtual void SyncLog(const std::string &message) override
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
std::cout << message << std::endl;
}
private:
Mutex _mutex;
};
const std::string default_path = "./log/";
const std::string default_name = "my.log";
const std::string gsep = "\r\n"; // 全局的分隔符
class FileLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
FileLogStrategy(const std::string &file_path = default_path,
const std::string &file_name = default_name)
: _file_path(file_path), _file_name(file_name)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
if (std::filesystem::exists(_file_path))
{
return;
}
try
{
std::filesystem::create_directories(_file_path);
}
catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error &e)
{
std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
}
}
virtual void SyncLog(const std::string &message) override
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
std::string file_path_name = _file_path +
(_file_path.back() == '/' ? "" : "/") + _file_name;
// 以追加写入的方式打开
std::ofstream out(file_path_name, std::ios::app);
if (!out.is_open())
{
return;
}
out << message << gsep;
}
public:
std::string _file_path;
std::string _file_name;
Mutex _mutex;
};
class Logger
{
public:
Logger()
{
EnableConsoleLogStrategy();
}
void EnableConsoleLogStrategy()
{
_fflush_strategy = std::make_unique<ConsoleLogStrategy>();
}
void EnableFileLogStrategy()
{
_fflush_strategy = std::make_unique<FileLogStrategy>();
}
class LogMessage
{
public:
LogMessage(LogLevel log_level, const std::string &file_name,
int line_number, const Logger *logger)
: _logger(logger)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "[" << GetTime() << "] "
<< "[" << LogLeveltoString(log_level) << "] "
<< "[" << getpid() << "] "
<< "[" << file_name << "] "
<< "[" << line_number << "] - ";
_message = ss.str();
}
template <typename T>
LogMessage& operator<<(const T &info)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << info;
_message += ss.str();
return *this;
}
~LogMessage()
{
if (_logger->_fflush_strategy)
{
_logger->_fflush_strategy->SyncLog(_message);
}
}
private:
std::string _message;
const Logger *_logger;
};
LogMessage operator()(LogLevel log_level,
const std::string &file_name, int line_number)
{
return LogMessage(log_level, file_name, line_number, this);
}
private:
std::unique_ptr<LogStrategy> _fflush_strategy = nullptr;
};
// 全局日志对象
Logger logger;
// 使用宏,简化用户操作,获取文件名和行号
#define LOG(level) logger(level, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#define Enable_Console_Log_Strategy() logger.EnableConsoleLogStrategy()
#define Enable_File_Log_Strategy() logger.EnableFileLogStrategy()
}1.3.2 Mutex.hpp
#pragma once
#include <pthread.h>
namespace MutexModule
{
class Mutex
{
public:
Mutex()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex, nullptr);
}
void Lock()
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
}
void Unlock()
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
pthread_mutex_t *Get()
{
return &_mutex;
}
~Mutex()
{
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t _mutex;
};
// RAII,资源的初始化与释放与对象的生命周期绑定
class LockGuard
{
public:
LockGuard(Mutex &mutex)
: _mutex(mutex)
{
_mutex.Lock();
}
~LockGuard()
{
_mutex.Unlock();
}
private:
Mutex &_mutex;
};
}1.4 注意事项
- 日志等级+日志写入的换行符:
- 为什么使用enum class,不用enum?因为enum class,不能隐式转换为整数,也不能与其他枚举类型的成员直接比较,提高了类型安全性;enum class的成员必须通过枚举名访问(如LogLevel::DEBUG),避免了命名污染。
- 为什么是/r/n?/r是回车(回到这一行的开头),/n是换行(换到下一行),有的操作系统,/n就有回车+换行的作用,有些操作系统不是。
- 一条日志信息的对象+多次<<:
- LogMessage,一条日志信息,RAII思想(利用类的构造(初始化)和析构(收尾))的日志格式化和刷新,作为内部类(独立于外部类,只是受外部类的访问限定符和外部类类域限制),外部类传this指针给内部类,内部类能访问外部类的私有和保护成员(内部类是外部类的"友元"),访问外部类的策略,而反过来,内部类传this指针给外部类,外部类无法访问内部类的私有或保护成员。
- Logger中的LogMessage operator()(),return LogMessage临时对象,而LogMessage中的LogMessage& operator<<(),也return *this,返回当前LogMessage的引用,所以,一个LogMessage临时对象可以多次<<,如:logger(LogLevel::DEBUG, "main.cc", 10) << "hello world," << 3.14 << " " << 8899 << "aaaa";。
2、线程池
2.1 线程池的概念
- 线程池是一种多线程处理模式,其核心思想是通过对线程资源的统一管理和复用,来优化程序性能,避免因线程过多而引发的各种问题。
2.2 线程池的设计
- 线程池分固定线程数量和浮动线程数量,本文选择固定线程个数的线程池。
- 采用单例模式,某些类,只应该具有⼀个对象(实例),就称之为单例。在很多服务器开发场景中,经常需要让服务器加载很多的数据(上百G)到内存中,此时往往要用一个单例的类来管理这些数据。
- 使用懒汉方式,核心是"延时加载",从而优化服务器的启动速度。
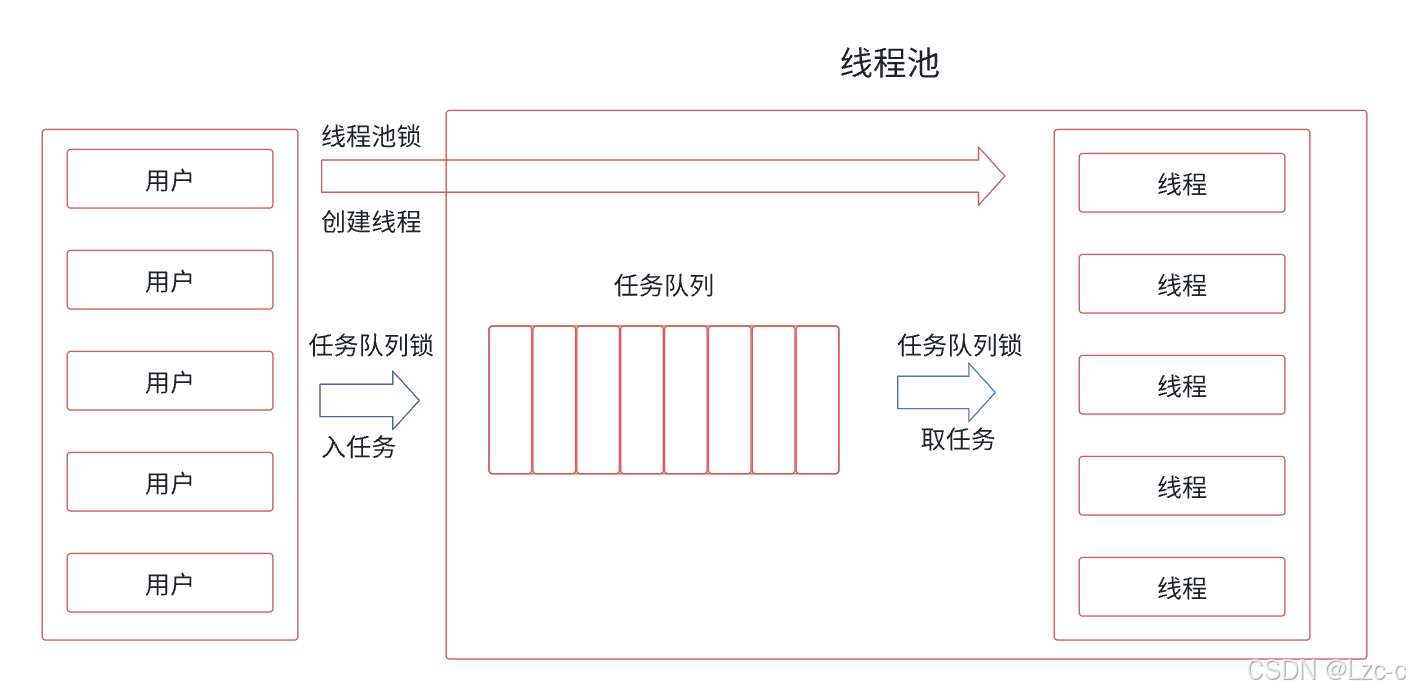
2.3 代码
2.3.1 Main.cc
#include <functional>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "ThreadPool.hpp"
using namespace LogModule;
using namespace ThreadPoolModule;
void Download()
{
std::cout << "下载一个任务" << std::endl;
sleep(3); // 假设任务的耗时。
}
using task_t = std::function<void()>;
int main()
{
Enable_Console_Log_Strategy();
int count = 10;
while (count)
{
sleep(1);
ThreadPool<task_t>::GetInstance()->Enqueue(Download);
count--;
}
ThreadPool<task_t>::GetInstance()->Stop();
ThreadPool<task_t>::GetInstance()->Join();
return 0;
}2.3.2 ThreadPool.hpp
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <thread>
#include <memory>
#include <atomic>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Cond.hpp"
#include "Mutex.hpp"
namespace ThreadPoolModule
{
using namespace MutexModule;
using namespace CondModule;
using namespace LogModule;
const int gnum = 5; // 线程个数
template <typename T>
class ThreadPool
{
private:
ThreadPool(int num = gnum)
: _num(num), _sleep_num(0), _running(true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < _num; ++i)
{
// 隐式使用了this,在成员函数内部默认是this->HandlerTask()
_threads.emplace_back([this]()
{ HandlerTask(); });
}
}
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool &) = delete;
ThreadPool &operator=(const ThreadPool &) = delete;
public:
static ThreadPool *GetInstance()
{
if (_inc == nullptr)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_inc_mutex);
if (_inc == nullptr)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "首次使用单例, 创建之....";
// _inc = std::make_unique<ThreadPool>();
// std::make_unique 是一个外部函数,无法访问 ThreadPool 类的私有构造函数
_inc.reset(new ThreadPool());
}
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "获取单例";
return _inc.get(); // 返回原始指针,不转移所有权
}
void HandlerTask()
{
while (true)
{
T task;
{
LockGuard lockguard(_tasks_mutex);
while (_tasks.empty() && _running)
{
++_sleep_num;
_tasks_cond.Wait(_tasks_mutex);
--_sleep_num;
}
if (_tasks.empty() && !_running)
break;
task = _tasks.front();
_tasks.pop();
}
task();
}
}
void Enqueue(const T &task)
{
if (_running)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_tasks_mutex);
if (_running)
{
_tasks.push(task);
if (_sleep_num == _num)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "唤醒一个休眠线程";
_tasks_cond.Signal();
}
}
}
}
void Stop()
{
if (!_running)
return;
_running = false;
if (_sleep_num)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "唤醒所有休眠线程";
_tasks_cond.Broadcast();
}
}
void Join()
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "join所有线程";
for (auto &thread : _threads)
{
if (thread.joinable())
thread.join();
}
}
private:
std::vector<std::thread> _threads;
int _num; // 线程个数
int _sleep_num; // 线程阻塞个数
std::queue<T> _tasks;
Mutex _tasks_mutex;
Cond _tasks_cond;
static std::unique_ptr<ThreadPool> _inc;
std::atomic<bool> _running; // 线程池是否启动。
static Mutex _inc_mutex;
};
template <typename T>
std::unique_ptr<ThreadPool<T>> ThreadPool<T>::_inc = nullptr;
template <typename T>
Mutex ThreadPool<T>::_inc_mutex;
}2.3.3 Cond.hpp
#pragma once
#include <pthread.h>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
namespace CondModule
{
class Cond
{
public:
// RAII,资源的初始化与释放与对象的生命周期绑定
Cond()
{
pthread_cond_init(&_cond,nullptr);
}
void Wait(MutexModule::Mutex& mutex)
{
pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,mutex.Get());
}
void Signal()
{
pthread_cond_signal(&_cond);
}
void Broadcast()
{
pthread_cond_broadcast(&_cond);
}
~Cond()
{
pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);
}
private:
pthread_cond_t _cond;
};
}2.4 注意事项
- 线程池的固定线程个数:
- static const int gnum = 5;?这是一个在头文件(.hpp)中定义的全局常量。static 在这里表示内部链接,即该变量仅在当前编译单元(包含此头文件的 .cpp 文件)中可见。若不使用 static,当多个 .cpp 文件包含此头文件时,gnum 会被多次定义,导致链接错误(重定义)。static 确保每个包含该头文件的编译单元都有一份独立的 gnum 实例,避免冲突。但是在命名空间里面直接const int gnum = 5;,也可以,比较推荐。
- 单例模式+懒汉模式:
- 构造函数私有,为什么还要delete拷贝构造和赋值重载?私有拷贝构造函数只能防止类外部的代码进行拷贝。但是,类的友元和成员函数内部仍然可以调用它,所以要=delete;。
- 第一个类(仅有的一个)类怎么来的?现在外部创建不了(不能创建),内部不能再拷贝和赋值,那么就要在没有对象的时候,在类内部创建,嗯?就是static?调用GetInstance()函数的时候再创建,不就是懒汉模式,延迟加载吗?所以是static(静态成员函数,不依赖于类的对象)。
- 为什么 _inc 和 _mutex 必须被 static 修饰?因为静态成员函数GetInstance() 只能访问静态成员。
- 为什么类内部不用一个static标记,标记类的对象个数,使只有一个?可以,可能会更复杂。
- 我其实也可以在类内部创建多个ThreadPool对象吧,单例模式就是自己规定只有一个?是的,通过代码约束。
- 线程池需要加锁保证线程安全。双层判断_inc,当不为nullptr时,就不用获取锁再判断了。
- GetInstance() 不能返回unique_ptr,因为不能拷贝,那么返回原始指针,是否有问题?没有,GetInstance() 返回 _inc.get()(原始指针),仅提供 “访问权” 而非 “所有权”,对象的生命周期仍由 unique_ptr 负责。
- 线程的处理:
- 线程获取任务后,任务已经是线程私有的了,线程处理任务不在临界区,支持并发。如果在临界区,就要等任务处理完,才轮到下一个线程。
- 规定:队列为空 && _running == true,线程需要等待;队列为空 && _running == false,线程退出。
- std::atomic<>是保证单个变量的读写操作原子化、可见性,仅针对单个变量。
- mutex是保护一段代码(临界区)的互斥执行,针对一段逻辑。
- 任务队列需要加锁保证线程安全。双层判断_running,当为false时,就不用获取锁再判断了。
- 线程池的线程的回收操作:
- 规定:stop()后,不允许再push数据,使线程退出。因为线程一直在运行,需要将线程池的运行状态置为false;,再唤醒所有线程对象,判断为false,使所有线程退出,才能join()成功。
- 如果底层的线程执行完了函数,"线程对象"还是活跃的吗?还要join吗?底层的线程结束了,资源回收了,但是"线程对象"仍然“关联”着那个已经结束的线程,还需要同步和清理。所以,无论底层线程是正在运行,还是已经结束,在 std::thread 对象析构之前,必须确保 joinable()从 true -> false(默认构造的(没有关联线程)或 被 move(线程所有权已转移)或 调用 join() 或 调用 detach())。如果joinable() == false,就不能再move()或join()或detach()。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容








所有评论(0)