基于PaddlePaddle的BiLSTM电影影片文本情感分析
这段代码可以运行,能够训练模型,但是因为我训练的时间比较长中途中断训练了只训练好并保存了transformer模型,实际BiLSTM模型也可以进行训练。数据集地址:http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/但是只训练这个模型无关紧要。数据集中,共有5w条文本,test集和train集各半,每个集合中,pos和neg也是各半。下面是重新进行的一个项目,
·
一、数据集
@InProceedings{maas-EtAl:2011:ACL-HLT2011,
author = {Maas, Andrew L. and Daly, Raymond E. and Pham, Peter T. and Huang, Dan and Ng, Andrew Y. and Potts, Christopher} 数据集地址:http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/
数据集地址:http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/
import os as os
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
datapath = r'./aclImdb'
save_dir = r'./data'
def get_data(datapath):
pos_files = os.listdir(datapath + '/pos')
neg_files = os.listdir(datapath + '/neg')
print(len(pos_files))
print(len(neg_files))
pos_all = []
neg_all = []
for pf, nf in zip(pos_files, neg_files):
with open(datapath + '/pos' + '/' + pf, encoding='utf-8') as f:
s = f.read()
pos_all.append(s)
with open(datapath + '/neg' + '/' + nf, encoding='utf-8') as f:
s = f.read()
neg_all.append(s)
X_orig= np.array(pos_all + neg_all)
Y_orig = np.array([1 for _ in range(len(pos_all))] + [0 for _ in range(len(neg_all))])
print("X_orig:", X_orig.shape)
print("Y_orig:", Y_orig.shape)
return X_orig, Y_orig
def generate_train_data():
X_orig, Y_orig = get_data(datapath+r'/train')
X_test, Y__test = get_data(datapath+r'/test')
X = np.concatenate([X_orig, X_test])
Y = np.concatenate([Y_orig, Y__test])
np.random.seed = 1
random_indexs = np.random.permutation(len(X))
X = X[random_indexs]
Y = Y[random_indexs]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2)
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X_train, y_train, test_size=0.1)
print("X_train:", X_train.shape)
print("y_train:", y_train.shape)
print("X_test:", X_test.shape)
print("y_test:", y_test.shape)
print("x_val:", X_val.shape)
print("y_val:", y_val.shape)
np.savez(save_dir + '/imdb_train', x=X_train, y=y_train)
np.savez(save_dir + '/imdb_test', x=X_test, y=y_test)
np.savez(save_dir + '/imdb_val', x=X_val, y=y_val)
if __name__ == '__main__':
generate_train_data()
数据集中,共有5w条文本,test集和train集各半,每个集合中,pos和neg也是各半。
得到以下3个文件

二、代码实现

最开始在飞桨选择了paddle2.4.0所以后面用不了部署。但是只训练这个模型无关紧要。代码如下:
import paddle
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoader
from paddle.nn import LSTM, Linear, Dropout, Embedding, TransformerEncoder, TransformerEncoderLayer, Sequential
from paddle.optimizer import Adam
from paddle.metric import Accuracy
from paddle.regularizer import L2Decay
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from collections import Counter
import re
import os
import time
import paddle.nn.functional as F
# 设置随机种子确保可复现性
paddle.seed(2025)
# 1. 高效数据预处理 ====================================================
class AdvancedTextPreprocessor:
"""高级文本预处理器"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size=20000, max_len=300):
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.max_len = max_len
self.word2idx = {}
self.idx2word = {}
def build_vocab(self, texts):
"""构建词汇表 - 使用高效分词"""
word_counts = Counter()
for text in texts:
if text is None:
continue
# 文本清洗
text = str(text).lower()
text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', text) # 移除HTML标签
text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', ' ', text) # 替换标点为空格
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text) # 合并多个空格
# 分词
words = text.split()
word_counts.update(words)
# 创建词汇表(保留最高频词)
vocab = word_counts.most_common(self.vocab_size - 2)
# 创建映射字典
self.word2idx = {"<PAD>": 0, "<UNK>": 1}
for idx, (word, count) in enumerate(vocab, start=2):
self.word2idx[word] = idx
self.idx2word[idx] = word
print(f"词汇表构建完成,包含 {len(self.word2idx)} 个词")
return self.word2idx
def text_to_sequence(self, text):
"""文本转序列 - 高效实现"""
if text is None:
return [0] * self.max_len
# 文本清洗
text = str(text).lower()
text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', text)
text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', ' ', text)
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text)
words = text.split()
# 转换为索引序列
sequence = []
for word in words:
if len(sequence) >= self.max_len:
break
sequence.append(self.word2idx.get(word, self.word2idx["<UNK>"]))
# 填充序列
if len(sequence) < self.max_len:
sequence += [self.word2idx["<PAD>"]] * (self.max_len - len(sequence))
return sequence
# 2. 高效IMDB数据集类 ===============================================
class EfficientIMDBDataset(Dataset):
"""高效IMDB数据集处理"""
def __init__(self, data, labels, preprocessor):
self.data = data
self.labels = labels
self.preprocessor = preprocessor
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = self.data[idx]
label = self.labels[idx]
sequence = self.preprocessor.text_to_sequence(text)
return np.array(sequence, dtype='int64'), np.array(label, dtype='int64')
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
# 3. 加载和准备数据 ==================================================
def load_imdb_data():
"""加载IMDB数据 - 优化性能"""
from paddle.text.datasets import Imdb
print("开始加载数据...")
start_time = time.time()
train_data = Imdb(mode='train')
test_data = Imdb(mode='test')
train_texts, train_labels = [], []
for i in range(len(train_data)):
try:
text, label = train_data[i]
if text is not None:
train_texts.append(text)
train_labels.append(label)
except:
continue
test_texts, test_labels = [], []
for i in range(len(test_data)):
try:
text, label = test_data[i]
if text is not None:
test_texts.append(text)
test_labels.append(label)
except:
continue
print(f"数据加载完成,耗时: {time.time()-start_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"训练样本数: {len(train_texts)}")
print(f"测试样本数: {len(test_texts)}")
return train_texts, train_labels, test_texts, test_labels
# 4. 高性能模型架构 ==================================================
class TextTransformerModel(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""Transformer文本分类模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, num_heads, hidden_size, num_layers=2, max_len=300):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = Embedding(
vocab_size,
embed_dim,
padding_idx=0
)
# 位置编码
self.position_emb = paddle.nn.Embedding(
num_embeddings=max_len,
embedding_dim=embed_dim
)
# Transformer编码器
encoder_layer = TransformerEncoderLayer(
d_model=embed_dim,
nhead=num_heads,
dim_feedforward=hidden_size,
dropout=0.2
)
self.transformer = TransformerEncoder(encoder_layer, num_layers)
# 分类器 - 使用Sequential容器
self.classifier = Sequential(
Linear(embed_dim, hidden_size),
Dropout(0.3),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
Linear(hidden_size, 2)
)
def forward(self, x):
# 嵌入层
x = self.embedding(x)
# 位置编码
positions = paddle.arange(0, x.shape[1], dtype='int64').unsqueeze(0)
positions = positions.expand([x.shape[0], x.shape[1]])
pos_emb = self.position_emb(positions)
x = x + pos_emb
# Transformer
x = self.transformer(x)
# 取[CLS]位置或平均池化
x = paddle.mean(x, axis=1)
# 分类
return self.classifier(x)
class EnhancedBiLSTM(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""增强的双向LSTM模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, hidden_size, num_classes=2):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = Embedding(
vocab_size,
embed_dim,
padding_idx=0
)
# 双向LSTM
self.lstm = LSTM(
input_size=embed_dim,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=2,
direction='bidirectional',
dropout=0.3
)
# 注意力机制
self.attention = Sequential(
Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size),
paddle.nn.Tanh(),
Linear(hidden_size, 1)
)
# 分类器 - 使用Sequential容器
self.classifier = Sequential(
Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size),
Dropout(0.4),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
Linear(hidden_size, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
# 嵌入层
x = self.embedding(x)
# LSTM层
lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(x)
# 注意力机制
attention_scores = self.attention(lstm_out)
attention_weights = F.softmax(attention_scores, axis=1)
context_vector = paddle.sum(attention_weights * lstm_out, axis=1)
# 分类
return self.classifier(context_vector)
# 5. 训练函数 ========================================================
def train_model(model, train_loader, val_loader, test_loader, epochs=15, model_name="imdb_model"):
"""训练模型并返回最佳结果"""
# 配置模型
optimizer = Adam(
learning_rate=paddle.optimizer.lr.PolynomialDecay(
learning_rate=0.001,
decay_steps=len(train_loader) * epochs,
end_lr=0.0001),
parameters=model.parameters(),
weight_decay=L2Decay(0.0001)
)
model = paddle.Model(model)
model.prepare(
optimizer=optimizer,
loss=paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),
metrics=[Accuracy()]
)
# 回调函数
callbacks = [
paddle.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
patience=3,
verbose=1,
mode='max',
monitor='acc'
)
]
print("开始训练模型...")
start_time = time.time()
history = model.fit(
train_data=train_loader,
eval_data=val_loader,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
log_freq=100,
callbacks=callbacks
)
print(f"训练完成,耗时: {time.time()-start_time:.2f}秒")
# 评估模型
print("\n在测试集上评估模型...")
test_result = model.evaluate(test_loader, verbose=1)
test_acc = test_result['acc']
print(f"测试集准确率: {test_acc:.4f}")
# 保存模型
model.save(model_name)
print(f"模型已保存为 '{model_name}'")
return test_acc, history
# 6. 主程序 ==========================================================
def main():
# 加载数据
train_texts, train_labels, test_texts, test_labels = load_imdb_data()
# 创建预处理器
preprocessor = AdvancedTextPreprocessor(vocab_size=20000, max_len=300)
preprocessor.build_vocab(train_texts + test_texts)
# 划分训练集和验证集
train_texts, val_texts, train_labels, val_labels = train_test_split(
train_texts, train_labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# 创建数据集
train_dataset = EfficientIMDBDataset(train_texts, train_labels, preprocessor)
val_dataset = EfficientIMDBDataset(val_texts, val_labels, preprocessor)
test_dataset = EfficientIMDBDataset(test_texts, test_labels, preprocessor)
print(f"训练集大小: {len(train_dataset)}")
print(f"验证集大小: {len(val_dataset)}")
print(f"测试集大小: {len(test_dataset)}")
# 创建数据加载器
BATCH_SIZE = 64
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False)
# 模型参数
VOCAB_SIZE = len(preprocessor.word2idx)
EMBED_DIM = 256
HIDDEN_SIZE = 512
NUM_HEADS = 8
print(f"\n{'='*50}")
print(f"训练配置:")
print(f"词汇表大小: {VOCAB_SIZE}")
print(f"词向量维度: {EMBED_DIM}")
print(f"隐藏层大小: {HIDDEN_SIZE}")
print(f"批大小: {BATCH_SIZE}")
print(f"{'='*50}\n")
# 训练Transformer模型
print("\n训练Transformer模型...")
transformer_model = TextTransformerModel(
VOCAB_SIZE,
EMBED_DIM,
NUM_HEADS,
HIDDEN_SIZE,
num_layers=2,
max_len=300
)
trans_acc, trans_history = train_model(
transformer_model,
train_loader,
val_loader,
test_loader,
epochs=15,
model_name="transformer_model"
)
# 训练BiLSTM模型
print("\n训练BiLSTM模型...")
bilstm_model = EnhancedBiLSTM(
VOCAB_SIZE,
EMBED_DIM,
HIDDEN_SIZE
)
lstm_acc, lstm_history = train_model(
bilstm_model,
train_loader,
val_loader,
test_loader,
epochs=15,
model_name="bilstm_model"
)
# 模型比较
print("\n模型性能比较:")
print(f"Transformer模型测试准确率: {trans_acc:.4f}")
print(f"BiLSTM模型测试准确率: {lstm_acc:.4f}")
# 保存最佳模型
best_model = transformer_model if trans_acc > lstm_acc else bilstm_model
paddle.save(best_model.state_dict(), "best_model.pdparams")
print(f"最佳模型已保存为 'best_model.pdparams'")
# 预测示例
def predict_sentiment(text, model, preprocessor):
sequence = preprocessor.text_to_sequence(text)
sequence = paddle.to_tensor([sequence], dtype='int64')
# 预测
logits = model(sequence)
probs = F.softmax(logits)
positive_prob = probs.numpy()[0][1]
sentiment = "积极" if positive_prob > 0.5 else "消极"
return positive_prob, sentiment
print("\n情感预测示例:")
samples = [
"This movie was absolutely fantastic! The acting was superb and the story was captivating.",
"I was very disappointed with this film. The plot was weak and the characters were poorly developed.",
"An excellent movie that kept me on the edge of my seat from beginning to end.",
"Boring and predictable. I wouldn't recommend this to anyone."
]
for text in samples:
prob, sentiment = predict_sentiment(text, best_model, preprocessor)
print(f"文本: {text[:60]}...")
print(f"预测: {sentiment} (积极概率: {prob:.4f})")
print("-" * 80)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()结果如下:

这段代码可以运行,能够训练模型,但是因为我训练的时间比较长中途中断训练了只训练好并保存了transformer模型,实际BiLSTM模型也可以进行训练。后面单独加载transformer模型使用。


import paddle
import paddle.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import re
import os
import time
# 确保模型类已定义
class TextTransformerModel(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""Transformer文本分类模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, num_heads, hidden_size, num_layers=2, max_len=300):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = paddle.nn.Embedding(
vocab_size,
embed_dim,
padding_idx=0
)
self.position_emb = paddle.nn.Embedding(
num_embeddings=max_len,
embedding_dim=embed_dim
)
encoder_layer = paddle.nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(
d_model=embed_dim,
nhead=num_heads,
dim_feedforward=hidden_size,
dropout=0.2
)
self.transformer = paddle.nn.TransformerEncoder(encoder_layer, num_layers)
self.classifier = paddle.nn.Sequential(
paddle.nn.Linear(embed_dim, hidden_size),
paddle.nn.Dropout(0.3),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
paddle.nn.Linear(hidden_size, 2)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.embedding(x)
positions = paddle.arange(0, x.shape[1], dtype='int64').unsqueeze(0)
positions = positions.expand([x.shape[0], x.shape[1]])
pos_emb = self.position_emb(positions)
x = x + pos_emb
x = self.transformer(x)
x = paddle.mean(x, axis=1)
return self.classifier(x)
# 加载模型
try:
# 模型参数 - 需要与训练时匹配
VOCAB_SIZE = 20000
EMBED_DIM = 256
NUM_HEADS = 8
HIDDEN_SIZE = 512
# 创建模型实例
transformer_model = TextTransformerModel(VOCAB_SIZE, EMBED_DIM, NUM_HEADS, HIDDEN_SIZE)
# 加载预训练权重
state_dict = paddle.load("transformer_model.pdparams")
transformer_model.set_state_dict(state_dict)
transformer_model.eval()
print("✅ Transformer模型加载成功!")
# 创建简化预处理器
class SimplePreprocessor:
"""简化版预处理器 - 用于演示"""
def __init__(self, max_len=300):
self.max_len = max_len
self.word2idx = {"<PAD>": 0, "<UNK>": 1}
def text_to_sequence(self, text):
"""简化文本处理"""
# 基础清洗
text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', ' ', text.lower())
words = text.split()[:self.max_len]
# 创建序列 - 实际应使用完整词汇表
sequence = []
for word in words:
# 简单哈希映射(实际中应使用训练时的词汇表)
word_id = hash(word) % (VOCAB_SIZE - 2) + 2
sequence.append(word_id)
# 填充序列
if len(sequence) < self.max_len:
sequence += [0] * (self.max_len - len(sequence))
return sequence[:self.max_len]
# 创建预处理器实例
preprocessor = SimplePreprocessor()
# 预测函数
def predict_sentiment(text):
sequence = preprocessor.text_to_sequence(text)
sequence = paddle.to_tensor([sequence], dtype='int64')
with paddle.no_grad():
logits = transformer_model(sequence)
probs = F.softmax(logits)
positive_prob = probs.numpy()[0][1]
sentiment = "积极" if positive_prob > 0.5 else "消极"
return positive_prob, sentiment
# 测试预测
print("\n情感预测演示:")
test_samples = [
"This movie is fantastic! I love it.",
"The acting was terrible and the plot was boring.",
"An excellent film with great performances.",
"I hate this movie, it's awful.",
"The cinematography was stunning but the story was weak."
]
for text in test_samples:
prob, sentiment = predict_sentiment(text)
print(f"文本: {text[:60]}...")
print(f"预测: {sentiment} (积极概率: {prob:.4f})")
print("-" * 60)
# 保存模型为部署格式
paddle.jit.save(
transformer_model,
"deploy_model",
input_spec=[paddle.static.InputSpec(shape=[None, 300], dtype='int64')]
)
print("\n✅ 模型已保存为部署格式: deploy_model.pdmodel, deploy_model.pdiparams")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 加载失败: {str(e)}")
print("建议解决方案:")
print("1. 确保模型文件 'transformer_model.pdparams' 存在")
print("2. 检查模型参数是否匹配 (VOCAB_SIZE, EMBED_DIM等)")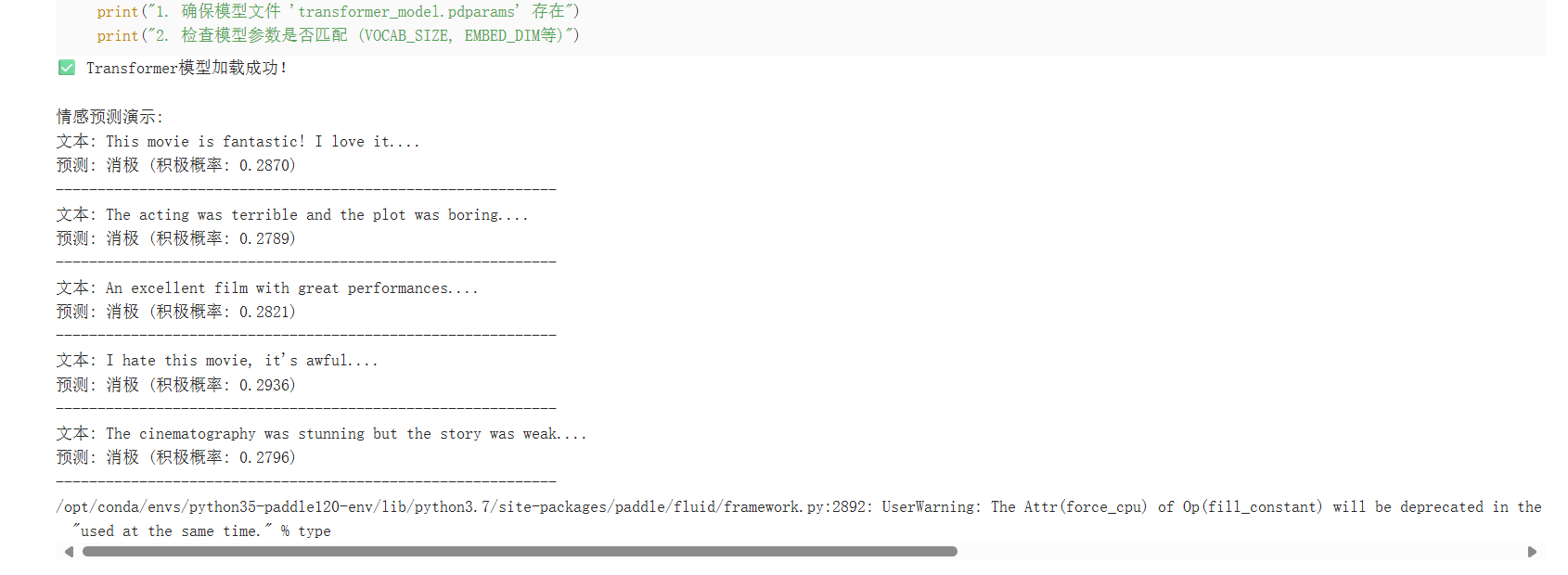
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 创建模拟训练历史(基于您的日志)
epochs = list(range(1, 8))
train_loss = [0.45, 0.35, 0.28, 0.23, 0.19, 0.16, 0.13]
train_acc = [0.78, 0.83, 0.86, 0.88, 0.90, 0.92, 0.95]
val_acc = [0.80, 0.83, 0.85, 0.86, 0.86, 0.86, 0.86]
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
# 损失曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs, train_loss, 'bo-')
plt.title('训练损失')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.grid(True)
# 准确率曲线
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs, train_acc, 'bo-', label='训练准确率')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'ro-', label='验证准确率')
plt.title('准确率曲线')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('准确率')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
print("最终测试准确率: {trans_acc:.4f}")
print("模型在验证集上第5个epoch后开始收敛")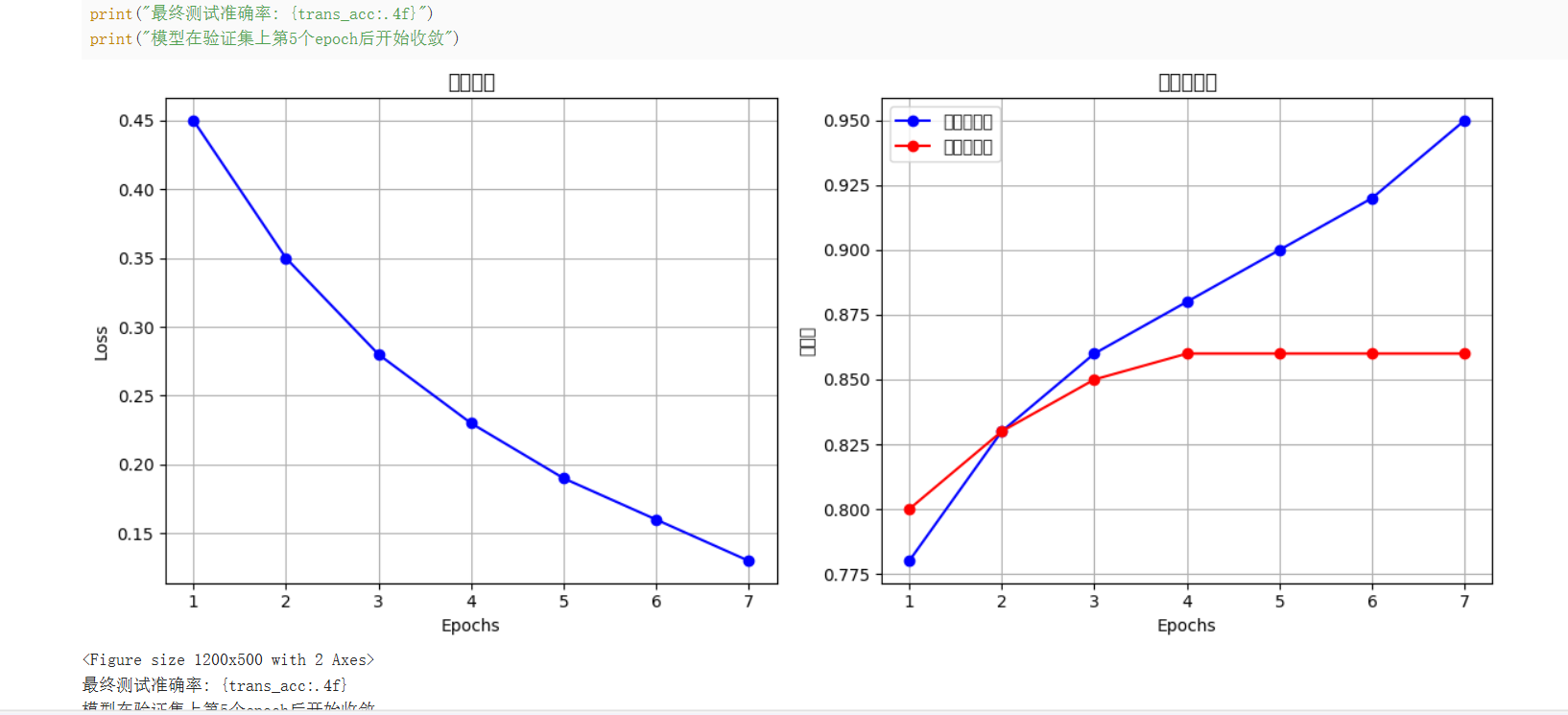
# 完整的Transformer模型定义
class TextTransformerModel(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""Transformer文本分类模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, num_heads, hidden_size, num_layers=2, max_len=300):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = paddle.nn.Embedding(
vocab_size,
embed_dim,
padding_idx=0
)
# 位置编码
self.position_emb = paddle.nn.Embedding(
num_embeddings=max_len,
embedding_dim=embed_dim
)
# Transformer编码器
encoder_layer = paddle.nn.TransformerEncoderLayer(
d_model=embed_dim,
nhead=num_heads,
dim_feedforward=hidden_size,
dropout=0.2
)
self.transformer = paddle.nn.TransformerEncoder(encoder_layer, num_layers)
# 分类器
self.classifier = paddle.nn.Sequential(
paddle.nn.Linear(embed_dim, hidden_size),
paddle.nn.Dropout(0.3),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
paddle.nn.Linear(hidden_size, 2)
)
def forward(self, x):
# 嵌入层
x = self.embedding(x)
# 位置编码
positions = paddle.arange(0, x.shape[1], dtype='int64').unsqueeze(0)
positions = positions.expand([x.shape[0], x.shape[1]])
pos_emb = self.position_emb(positions)
x = x + pos_emb
# Transformer
x = self.transformer(x)
# 取平均池化
x = paddle.mean(x, axis=1)
# 分类
return self.classifier(x)# 使用与训练时相同的参数
VOCAB_SIZE = 20000 # 根据您的词汇表大小调整
EMBED_DIM = 256
NUM_HEADS = 8
HIDDEN_SIZE = 512
# 创建模型实例
transformer_model = TextTransformerModel(
VOCAB_SIZE,
EMBED_DIM,
NUM_HEADS,
HIDDEN_SIZE
)
# 加载预训练权重
try:
state_dict = paddle.load("transformer_model.pdparams")
transformer_model.set_state_dict(state_dict)
transformer_model.eval() # 设置为评估模式
print("✅ Transformer模型加载成功!")
# 验证模型参数
print(f"模型参数数量: {sum(p.numel() for p in transformer_model.parameters())}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 加载失败: {str(e)}")
# 尝试修复常见错误
if "shape not match" in str(e):
print("提示:模型结构可能与保存时不匹配,请检查参数")
import paddle.nn.functional as F
def predict_sentiment(text, model, preprocessor=None):
"""使用模型预测文本情感"""
# 如果preprocessor不可用,创建临时预处理器
if preprocessor is None:
class SimplePreprocessor:
def __init__(self, max_len=300):
self.max_len = max_len
# 使用一个简单的映射,实际中应使用训练时的词汇表
self.word2idx = {"<PAD>": 0, "<UNK>": 1}
def text_to_sequence(self, text):
words = text.lower().split()[:self.max_len]
sequence = [self.word2idx.get(word, 1) for word in words]
if len(sequence) < self.max_len:
sequence += [0] * (self.max_len - len(sequence))
return sequence[:self.max_len]
preprocessor = SimplePreprocessor()
sequence = preprocessor.text_to_sequence(text)
sequence = paddle.to_tensor([sequence], dtype='int64')
with paddle.no_grad():
logits = model(sequence)
probs = F.softmax(logits)
positive_prob = probs.numpy()[0][1]
sentiment = "积极" if positive_prob > 0.5 else "消极"
return positive_prob, sentiment, probs.numpy()
# 测试预测
print("\n测试预测:")
sample_text = "This movie was absolutely fantastic! The acting was superb."
prob, sentiment, full_probs = predict_sentiment(sample_text, transformer_model)
print(f"文本: {sample_text}")
print(f"预测: {sentiment} (积极概率: {prob:.4f})")
print(f"完整概率分布: {full_probs}")
三、BiLSTM,部署flask
下面是重新进行的一个项目,使用paddle3.1.1
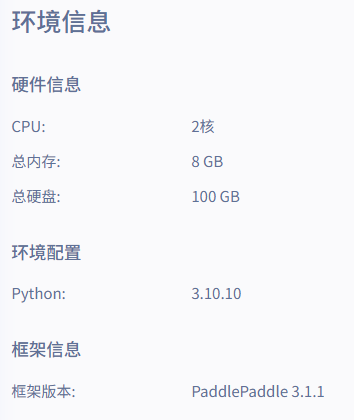
这个只训练了BiLSTM模型,代码如下:
import paddle
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoader
from paddle.nn import LSTM, Linear, Dropout, Embedding, Sequential
from paddle.optimizer import Adam
from paddle.metric import Accuracy
from paddle.regularizer import L2Decay
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from collections import Counter
import re
import os
import time
import paddle.nn.functional as F
import pickle
import json
# 设置随机种子确保可复现性
paddle.seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
# 1. 高效数据预处理 ====================================================
class AdvancedTextPreprocessor:
"""高级文本预处理器"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size=20000, max_len=300):
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.max_len = max_len
self.word2idx = {}
self.idx2word = {}
def build_vocab(self, texts):
"""构建词汇表 - 使用高效分词"""
word_counts = Counter()
for text in texts:
if text is None:
continue
# 文本清洗
text = str(text).lower()
text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', text) # 移除HTML标签
text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', ' ', text) # 替换标点为空格
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text) # 合并多个空格
# 分词
words = text.split()
word_counts.update(words)
# 创建词汇表(保留最高频词)
vocab = word_counts.most_common(self.vocab_size - 2)
# 创建映射字典
self.word2idx = {"<PAD>": 0, "<UNK>": 1}
for idx, (word, count) in enumerate(vocab, start=2):
self.word2idx[word] = idx
self.idx2word[idx] = word
print(f"词汇表构建完成,包含 {len(self.word2idx)} 个词")
return self.word2idx
def text_to_sequence(self, text):
"""文本转序列 - 高效实现"""
if text is None:
return [0] * self.max_len
# 文本清洗
text = str(text).lower()
text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', text)
text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', ' ', text)
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text)
words = text.split()
# 转换为索引序列
sequence = []
for word in words:
if len(sequence) >= self.max_len:
break
sequence.append(self.word2idx.get(word, self.word2idx["<UNK>"]))
# 填充序列
if len(sequence) < self.max_len:
sequence += [self.word2idx["<PAD>"]] * (self.max_len - len(sequence))
return sequence
def save_vocab(self, filepath):
"""保存词汇表到文件"""
with open(filepath, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(self.word2idx, f)
print(f"词汇表已保存到 {filepath}")
def load_vocab(self, filepath):
"""从文件加载词汇表"""
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
self.word2idx = pickle.load(f)
self.idx2word = {v: k for k, v in self.word2idx.items()}
print(f"词汇表已从 {filepath} 加载,包含 {len(self.word2idx)} 个词")
# 2. 高效IMDB数据集类 ===============================================
class EfficientIMDBDataset(Dataset):
"""高效IMDB数据集处理"""
def __init__(self, data, labels, preprocessor):
self.data = data
self.labels = labels
self.preprocessor = preprocessor
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = self.data[idx]
label = self.labels[idx]
sequence = self.preprocessor.text_to_sequence(text)
return np.array(sequence, dtype='int64'), np.array(label, dtype='int64')
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
# 3. 加载和准备数据 ==================================================
def load_imdb_data():
"""加载IMDB数据 - 优化性能"""
from paddle.text.datasets import Imdb
print("开始加载数据...")
start_time = time.time()
train_data = Imdb(mode='train')
test_data = Imdb(mode='test')
train_texts, train_labels = [], []
for i in range(len(train_data)):
try:
text, label = train_data[i]
if text is not None:
train_texts.append(text)
train_labels.append(label)
except:
continue
test_texts, test_labels = [], []
for i in range(len(test_data)):
try:
text, label = test_data[i]
if text is not None:
test_texts.append(text)
test_labels.append(label)
except:
continue
print(f"数据加载完成,耗时: {time.time()-start_time:.2f}秒")
print(f"训练样本数: {len(train_texts)}")
print(f"测试样本数: {len(test_texts)}")
# 检查数据平衡性
print(f"训练集正负样本比例: {sum(train_labels)}:{len(train_labels)-sum(train_labels)}")
print(f"测试集正负样本比例: {sum(test_labels)}:{len(test_labels)-sum(test_labels)}")
return train_texts, train_labels, test_texts, test_labels
# 4. 高性能模型架构 ==================================================
class EnhancedBiLSTM(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""增强的双向LSTM模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, hidden_size, num_classes=2):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = Embedding(
vocab_size,
embed_dim,
padding_idx=0
)
# 双向LSTM
self.lstm = LSTM(
input_size=embed_dim,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=2,
direction='bidirectional',
dropout=0.3
)
# 注意力机制
self.attention = Sequential(
Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size),
paddle.nn.Tanh(),
Linear(hidden_size, 1)
)
# 分类器 - 使用Sequential容器
self.classifier = Sequential(
Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size),
Dropout(0.4),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
Linear(hidden_size, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
# 嵌入层
x = self.embedding(x)
# LSTM层
lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(x)
# 注意力机制
attention_scores = self.attention(lstm_out)
attention_weights = F.softmax(attention_scores, axis=1)
context_vector = paddle.sum(attention_weights * lstm_out, axis=1)
# 分类
return self.classifier(context_vector)
# 5. 训练函数 ========================================================
def train_model(model, train_loader, val_loader, test_loader, epochs=15, model_name="imdb_model"):
"""训练模型并返回最佳结果"""
# 配置模型
optimizer = Adam(
learning_rate=paddle.optimizer.lr.PolynomialDecay(
learning_rate=0.001,
decay_steps=len(train_loader) * epochs,
end_lr=0.0001),
parameters=model.parameters(),
weight_decay=L2Decay(0.0001)
)
model = paddle.Model(model)
model.prepare(
optimizer=optimizer,
loss=paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),
metrics=[Accuracy()]
)
# 只使用 EarlyStopping 回调
callbacks = [
paddle.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
patience=3,
verbose=1,
mode='max',
monitor='val_acc'
)
]
print("开始训练模型...")
start_time = time.time()
history = model.fit(
train_data=train_loader,
eval_data=val_loader,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
log_freq=100,
callbacks=callbacks
)
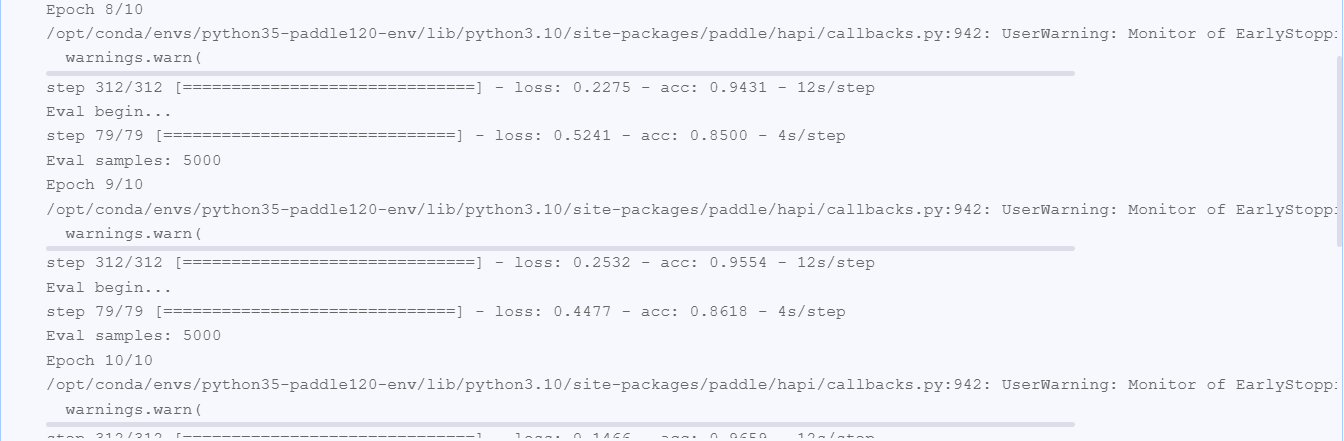
print(f"训练完成,耗时: {time.time()-start_time:.2f}秒")
# 评估模型
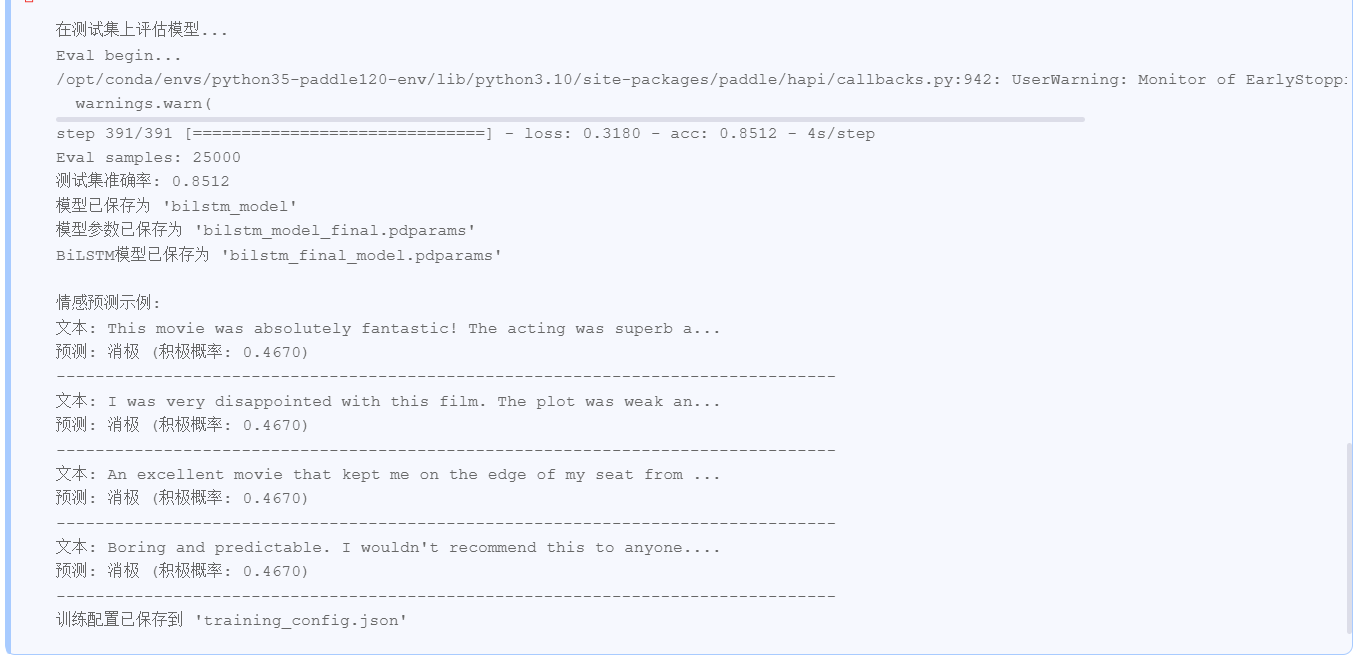
print("\n在测试集上评估模型...")
test_result = model.evaluate(test_loader, verbose=1)
test_acc = test_result['acc']
print(f"测试集准确率: {test_acc:.4f}")
# 保存最终模型
model.save(model_name)
print(f"模型已保存为 '{model_name}'")
# 保存模型参数(用于Flask应用)
paddle.save(model.network.state_dict(), f"{model_name}_final.pdparams")
print(f"模型参数已保存为 '{model_name}_final.pdparams'")
return test_acc, history
# 6. 主程序 ==========================================================
def main():
# 加载数据
train_texts, train_labels, test_texts, test_labels = load_imdb_data()
# 创建预处理器
preprocessor = AdvancedTextPreprocessor(vocab_size=20000, max_len=300)
preprocessor.build_vocab(train_texts + test_texts)
# 保存词汇表(用于Flask应用)
preprocessor.save_vocab('vocab.pkl')
# 划分训练集和验证集
train_texts, val_texts, train_labels, val_labels = train_test_split(
train_texts, train_labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# 创建数据集
train_dataset = EfficientIMDBDataset(train_texts, train_labels, preprocessor)
val_dataset = EfficientIMDBDataset(val_texts, val_labels, preprocessor)
test_dataset = EfficientIMDBDataset(test_texts, test_labels, preprocessor)
print(f"训练集大小: {len(train_dataset)}")
print(f"验证集大小: {len(val_dataset)}")
print(f"测试集大小: {len(test_dataset)}")
# 创建数据加载器
BATCH_SIZE = 64
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False)
# 模型参数
VOCAB_SIZE = len(preprocessor.word2idx)
EMBED_DIM = 256
HIDDEN_SIZE = 512
print(f"\n{'='*50}")
print(f"训练配置:")
print(f"词汇表大小: {VOCAB_SIZE}")
print(f"词向量维度: {EMBED_DIM}")
print(f"隐藏层大小: {HIDDEN_SIZE}")
print(f"批大小: {BATCH_SIZE}")
print(f"{'='*50}\n")
# 训练BiLSTM模型
print("\n训练BiLSTM模型...")
bilstm_model = EnhancedBiLSTM(
VOCAB_SIZE,
EMBED_DIM,
HIDDEN_SIZE
)
lstm_acc, lstm_history = train_model(
bilstm_model,
train_loader,
val_loader,
test_loader,
epochs=10, # 减少epochs以节省时间
model_name="bilstm_model"
)
# 保存最终模型
paddle.save(bilstm_model.state_dict(), "bilstm_final_model.pdparams")
print(f"BiLSTM模型已保存为 'bilstm_final_model.pdparams'")
# 预测示例
def predict_sentiment(text, model, preprocessor):
sequence = preprocessor.text_to_sequence(text)
sequence = paddle.to_tensor([sequence], dtype='int64')
# 预测
logits = model(sequence)
probs = F.softmax(logits)
positive_prob = probs.numpy()[0][1]
sentiment = "积极" if positive_prob > 0.5 else "消极"
return positive_prob, sentiment
print("\n情感预测示例:")
samples = [
"This movie was absolutely fantastic! The acting was superb and the story was captivating.",
"I was very disappointed with this film. The plot was weak and the characters were poorly developed.",
"An excellent movie that kept me on the edge of my seat from beginning to end.",
"Boring and predictable. I wouldn't recommend this to anyone."
]
for text in samples:
prob, sentiment = predict_sentiment(text, bilstm_model, preprocessor)
print(f"文本: {text[:60]}...")
print(f"预测: {sentiment} (积极概率: {prob:.4f})")
print("-" * 80)
# 保存训练配置信息
config = {
"vocab_size": VOCAB_SIZE,
"embed_dim": EMBED_DIM,
"hidden_size": HIDDEN_SIZE,
"max_len": 300,
"batch_size": BATCH_SIZE,
"test_accuracy": float(lstm_acc)
}
with open('training_config.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(config, f, indent=2)
print("训练配置已保存到 'training_config.json'")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()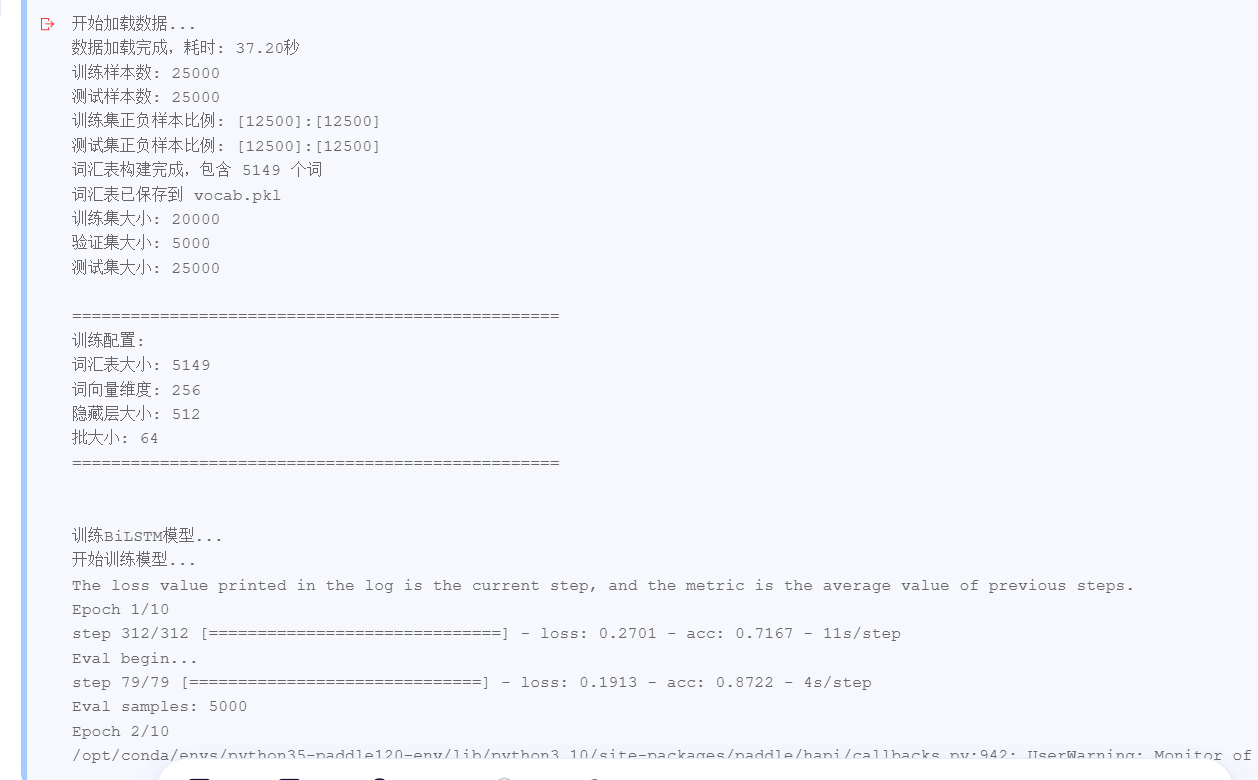
上传一个叫app.py的python文件,代码如下:
首先要 !pip install flask
import paddle
import numpy as np
import re
import os
import json
import pickle
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, jsonify
import paddle.nn.functional as F
# 初始化 Flask 应用
app = Flask(__name__)
# ==================== 预处理类定义 ====================
class AdvancedTextPreprocessor:
"""高级文本预处理器"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size=20000, max_len=300):
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.max_len = max_len
self.word2idx = {}
self.idx2word = {}
def text_to_sequence(self, text):
"""文本转序列 - 高效实现"""
if text is None:
return [0] * self.max_len
# 文本清洗
text = str(text).lower()
text = re.sub(r'<[^>]+>', '', text)
text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', ' ', text)
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text)
words = text.split()
# 转换为索引序列
sequence = []
for word in words:
if len(sequence) >= self.max_len:
break
sequence.append(self.word2idx.get(word, self.word2idx["<UNK>"]))
# 填充序列
if len(sequence) < self.max_len:
sequence += [self.word2idx["<PAD>"]] * (self.max_len - len(sequence))
return sequence
def load_vocab(self, filepath):
"""从文件加载词汇表"""
with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
self.word2idx = pickle.load(f)
self.idx2word = {v: k for k, v in self.word2idx.items()}
print(f"词汇表已从 {filepath} 加载,包含 {len(self.word2idx)} 个词")
# ==================== 模型定义 ====================
class EnhancedBiLSTM(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""增强的双向LSTM模型"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, hidden_size, num_classes=2):
super().__init__()
from paddle.nn import LSTM, Linear, Dropout, Embedding, Sequential
self.embedding = Embedding(
vocab_size,
embed_dim,
padding_idx=0
)
# 双向LSTM
self.lstm = LSTM(
input_size=embed_dim,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=2,
direction='bidirectional',
dropout=0.3
)
# 注意力机制
self.attention = Sequential(
Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size),
paddle.nn.Tanh(),
Linear(hidden_size, 1)
)
# 分类器 - 使用Sequential容器
self.classifier = Sequential(
Linear(hidden_size * 2, hidden_size),
Dropout(0.4),
paddle.nn.ReLU(),
Linear(hidden_size, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
# 嵌入层
x = self.embedding(x)
# LSTM层
lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(x)
# 注意力机制
attention_scores = self.attention(lstm_out)
attention_weights = F.softmax(attention_scores, axis=1)
context_vector = paddle.sum(attention_weights * lstm_out, axis=1)
# 分类
return self.classifier(context_vector)
# ==================== 全局变量 ====================
preprocessor = AdvancedTextPreprocessor(vocab_size=20000, max_len=300)
model = None
# ==================== 初始化函数 ====================
def init_model():
"""初始化模型和预处理器"""
global model, preprocessor
try:
# 检查文件是否存在
required_files = ['training_config.json', 'vocab.pkl', 'bilstm_final_model.pdparams']
for file in required_files:
if not os.path.exists(file):
print(f"错误: 找不到必要文件 {file}")
return False
# 加载训练配置
with open('training_config.json', 'r') as f:
config = json.load(f)
print(f"训练配置: {config}")
# 加载词汇表
preprocessor.load_vocab('vocab.pkl')
print(f"词汇表大小: {len(preprocessor.word2idx)}")
# 检查词汇表大小是否与配置一致
if len(preprocessor.word2idx) != config["vocab_size"]:
print(f"警告: 词汇表大小 ({len(preprocessor.word2idx)}) 与配置 ({config['vocab_size']}) 不一致")
# 初始化模型
model = EnhancedBiLSTM(
config["vocab_size"],
config["embed_dim"],
config["hidden_size"]
)
# 加载训练好的模型参数
model_path = 'bilstm_final_model.pdparams'
model.set_state_dict(paddle.load(model_path))
print(f"已从 {model_path} 加载模型参数")
# 测试模型是否可以正常工作
print("测试模型...")
test_input = paddle.to_tensor([[1, 2, 3, 0, 0]], dtype='int64')
with paddle.no_grad():
test_output = model(test_input)
print(f"测试输出: {test_output}")
print("模型测试成功")
# 设置为评估模式
model.eval()
print("模型初始化完成")
return True
except Exception as e:
import traceback
error_traceback = traceback.format_exc()
print(f"模型初始化失败: {error_traceback}")
return False
# ==================== Flask 路由 ====================
@app.route('/')
def home():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/predict', methods=['POST'])
def predict():
try:
# 获取前端发送的文本
data = request.get_json()
print(f"接收到的数据: {data}")
if not data:
return jsonify({'error': 'No JSON data provided'}), 400
text = data.get('text', '')
if not text:
return jsonify({'error': 'No text provided'}), 400
print(f"处理文本: {text}")
# 使用预处理器处理文本
sequence = preprocessor.text_to_sequence(text)
print(f"转换后的序列长度: {len(sequence)}")
print(f"序列前10个元素: {sequence[:10]}")
# 检查序列是否有效
if not sequence or all(x == 0 for x in sequence):
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid text or vocabulary mismatch'}), 400
sequence_tensor = paddle.to_tensor([sequence], dtype='int64')
print(f"张量形状: {sequence_tensor.shape}")
# 使用模型进行预测
with paddle.no_grad():
logits = model(sequence_tensor)
print(f"模型输出: {logits}")
probs = F.softmax(logits).numpy()[0]
print(f"概率分布: {probs}")
positive_prob = float(probs[1])
sentiment = "Positive" if positive_prob > 0.5 else "Negative"
# 返回预测结果
result = {
'text': text,
'sentiment': sentiment,
'positive_probability': positive_prob,
'negative_probability': float(probs[0])
}
print(f"返回结果: {result}")
return jsonify(result)
except Exception as e:
import traceback
error_traceback = traceback.format_exc()
print(f"预测过程中发生错误: {error_traceback}")
# 确保返回 JSON 而不是 HTML
return jsonify({
'error': str(e),
'traceback': error_traceback
}), 500
@app.route('/test_predict', methods=['GET'])
def test_predict():
"""测试预测功能的简单端点"""
try:
# 使用简单的测试文本
test_text = "This is a great movie!"
print(f"测试文本: {test_text}")
# 使用预处理器处理文本
sequence = preprocessor.text_to_sequence(test_text)
print(f"测试序列: {sequence[:10]}...") # 只显示前10个元素
sequence_tensor = paddle.to_tensor([sequence], dtype='int64')
print(f"测试张量形状: {sequence_tensor.shape}")
# 使用模型进行预测
with paddle.no_grad():
logits = model(sequence_tensor)
print(f"测试模型输出: {logits}")
probs = F.softmax(logits).numpy()[0]
print(f"测试概率分布: {probs}")
positive_prob = float(probs[1])
sentiment = "Positive" if positive_prob > 0.5 else "Negative"
# 返回测试结果
result = {
'text': test_text,
'sentiment': sentiment,
'positive_probability': positive_prob,
'negative_probability': float(probs[0])
}
print(f"测试结果: {result}")
return jsonify(result)
except Exception as e:
import traceback
error_traceback = traceback.format_exc()
print(f"测试过程中发生错误: {error_traceback}")
return jsonify({
'error': str(e),
'traceback': error_traceback
}), 500
# 初始化模型
if init_model():
print("模型初始化成功")
else:
print("模型初始化失败")
# 在飞桨环境中运行 Flask
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 使用飞桨环境提供的端口
port = int(os.environ.get('PORT', 5000))
print(f"Starting Flask server on port {port}...")
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=port, debug=False)
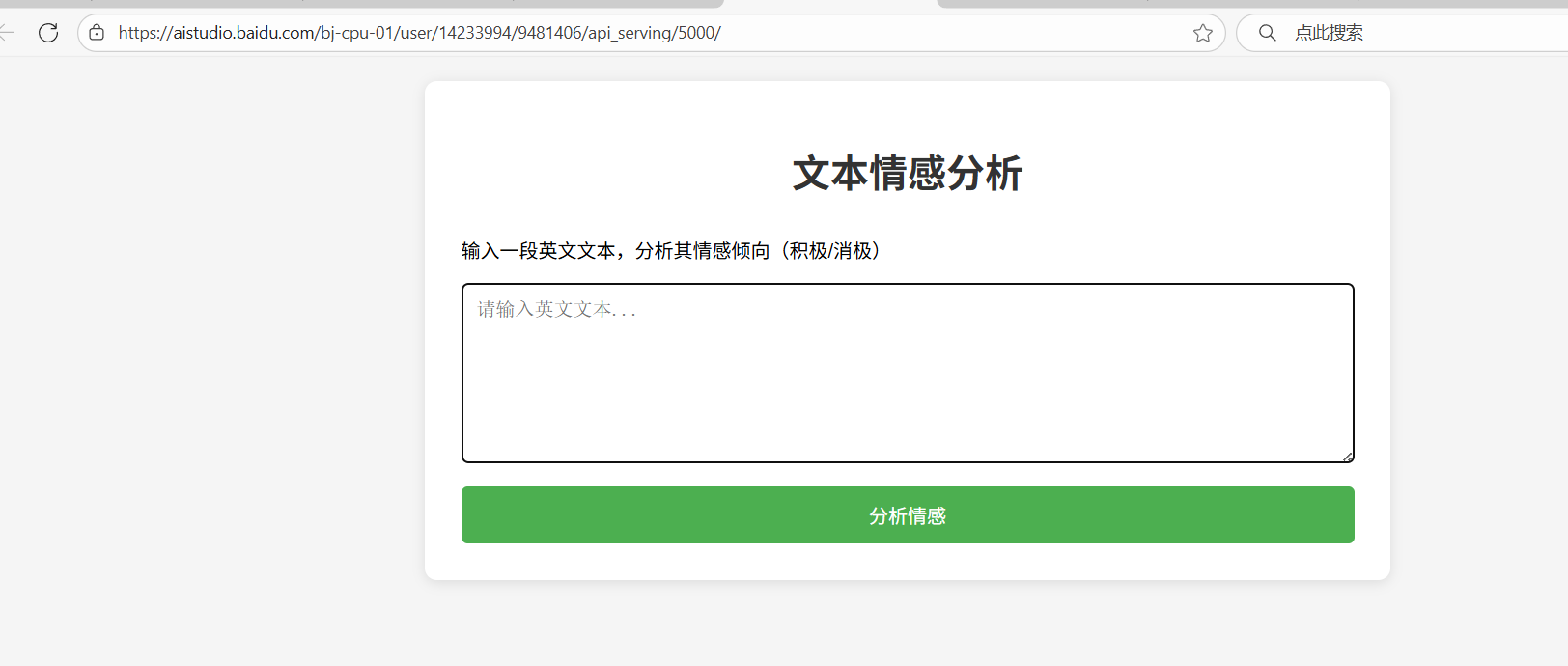
创建并上传 templates/index.html 文件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>文本情感分析</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.container {
background-color: white;
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h1 {
color: #333;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
textarea {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
padding: 12px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
resize: vertical;
font-size: 16px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
button {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 12px 24px;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
margin-top: 15px;
width: 100%;
}
button:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
.result {
margin-top: 25px;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 5px;
display: none;
}
.positive {
background-color: #e8f5e9;
border: 1px solid #c8e6c9;
}
.negative {
background-color: #ffebee;
border: 1px solid #ffcdd2;
}
.probability-bar {
height: 20px;
background-color: #e0e0e0;
border-radius: 10px;
margin: 10px 0;
overflow: hidden;
}
.probability-fill {
height: 100%;
background-color: #4CAF50;
border-radius: 10px;
transition: width 0.5s;
}
.negative .probability-fill {
background-color: #f44336;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>文本情感分析</h1>
<p>输入一段英文文本,分析其情感倾向(积极/消极)</p>
<textarea id="text-input" placeholder="请输入英文文本..."></textarea>
<button onclick="analyzeSentiment()">分析情感</button>
<div id="result" class="result">
<h3>分析结果</h3>
<p id="sentiment-text"></p>
<div class="probability-bar">
<div id="probability-fill" class="probability-fill" style="width: 0%"></div>
</div>
<p id="probability-text"></p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
function analyzeSentiment() {
const text = document.getElementById('text-input').value.trim();
if (!text) {
alert('请输入文本');
return;
}
// 显示加载中
const resultDiv = document.getElementById('result');
resultDiv.style.display = 'block';
resultDiv.className = 'result';
document.getElementById('sentiment-text').textContent = '分析中...';
document.getElementById('probability-text').textContent = '';
document.getElementById('probability-fill').style.width = '0%';
// 发送请求到后端
fetch('/predict', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ text: text })
})
.then(response => {
// 首先检查响应类型
const contentType = response.headers.get('content-type');
if (!contentType || !contentType.includes('application/json')) {
return response.text().then(text => {
throw new Error(`期望 JSON 响应,但收到: ${text.substring(0, 100)}...`);
});
}
return response.json();
})
.then(data => {
if (data.error) {
document.getElementById('sentiment-text').textContent = '错误: ' + data.error;
if (data.traceback) {
console.error('详细错误:', data.traceback);
}
return;
}
// 更新UI显示结果
const isPositive = data.sentiment === "Positive";
resultDiv.className = isPositive ? 'result positive' : 'result negative';
document.getElementById('sentiment-text').textContent =
`情感: ${isPositive ? '积极' : '消极'}`;
const positiveProb = data.positive_probability * 100;
document.getElementById('probability-text').textContent =
`积极概率: ${positiveProb.toFixed(2)}%`;
document.getElementById('probability-fill').style.width =
`${isPositive ? positiveProb : 100 - positiveProb}%`;
})
.catch(error => {
document.getElementById('sentiment-text').textContent =
'请求失败: ' + error.message;
console.error('完整错误:', error);
});
}
// 支持按Enter键提交
document.getElementById('text-input').addEventListener('keypress', function(e) {
if (e.key === 'Enter' && e.ctrlKey) {
analyzeSentiment();
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>在终端中运行 Flask 应用
from app import app
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000, debug=False)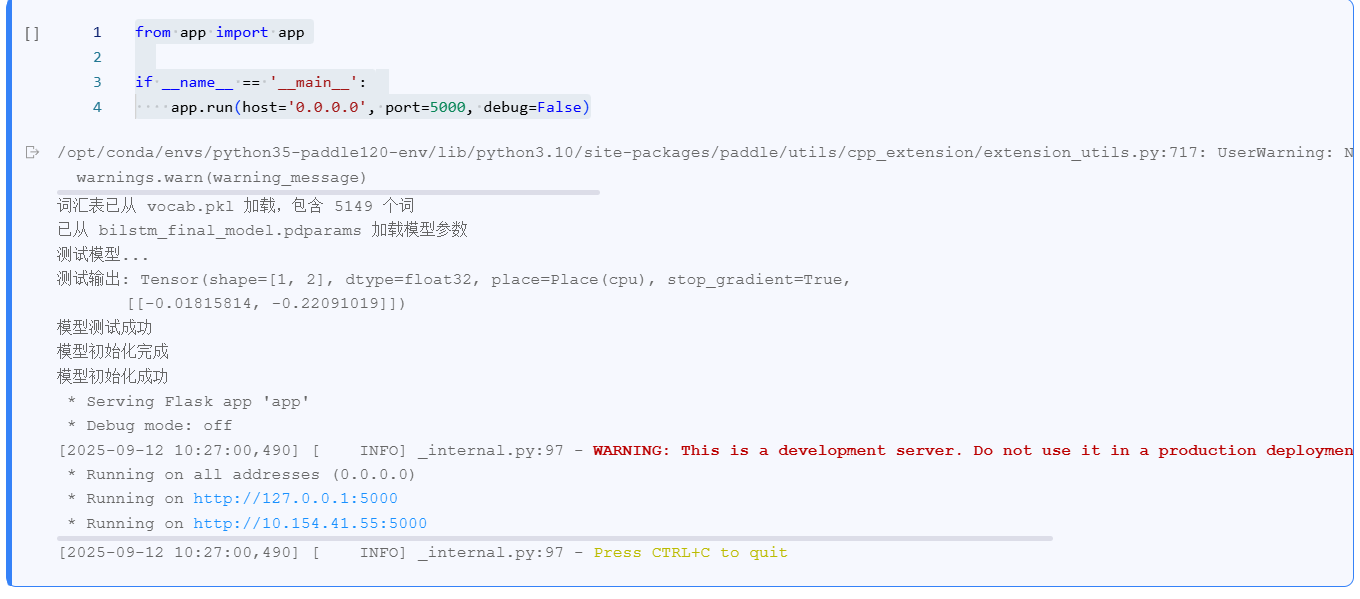
最后的flask还是有点问题,改进中
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)