Failover 故障转移
辅助系统是可行的:作为一般经验法则,无状态服务更容易复制,但当涉及到有状态服务(如数据库)时,设置辅助系统更加复杂和昂贵。有时,由于手头的要求或技术,辅助系统不可行:例如,由于 GDPR,数据不允许离开欧盟边界,但唯一可用的选项是在美国或中国。如果我们的依赖项在爱尔兰也可用,那就太理想了,但我们无法控制该系统的故障转移机制,对于负责我们依赖项的团队来说,成本也不合理。就用户而言,系统只是照常工作,
Failover and fallback are sometimes confused with each other. It is easy to see why:
故障转移和回退有时会相互混淆。原因很容易理解:
-
They are both F-words! 😄 The words “fail” and “fall” are conceptually related.
它们都是 F 字!😄 “失败”和“跌倒”这两个词在概念上是相关的。 -
They both rely on some predefined backup plan
它们都依赖于一些预定义的备份计划 -
They are both strategies to reduce the risk of failures
它们都是降低故障风险的策略 -
They both increase the system complexity and cost
它们都增加了系统的复杂性和成本 -
You may use one or both in a given system architecture
您可以在给定的系统架构中使用一个或两个
We need to distinguish between relevant terms because what you think may not be what you say and what you say may not be what is heard and what is heard may not be what is implemented!
我们需要区分相关术语,因为你认为的可能不是你说的, 你说的可能不是听到的, 听到的可能不是实施的 !
There are more terms like roll back/fix forward and blue-green/canary but they have to wait for other articles in this series. If you want to receive those articles when they’re out, you know what to do Subscribe
This article digs into different types of failover mechanisms, how they work, and some examples. In a follow-up article we will discuss fallback.
本文深入探讨了不同类型的故障转移机制、它们的工作原理以及一些示例。在后续文章中,我们将讨论回退。
What is Failover? 什么是故障转移?
Failover is a risk mitigation strategy to improve service continuity and reduce downtime.
故障转移是一种风险缓解策略,用于提高服务连续性并减少停机时间 。
How does failover work? 故障转移如何工作?
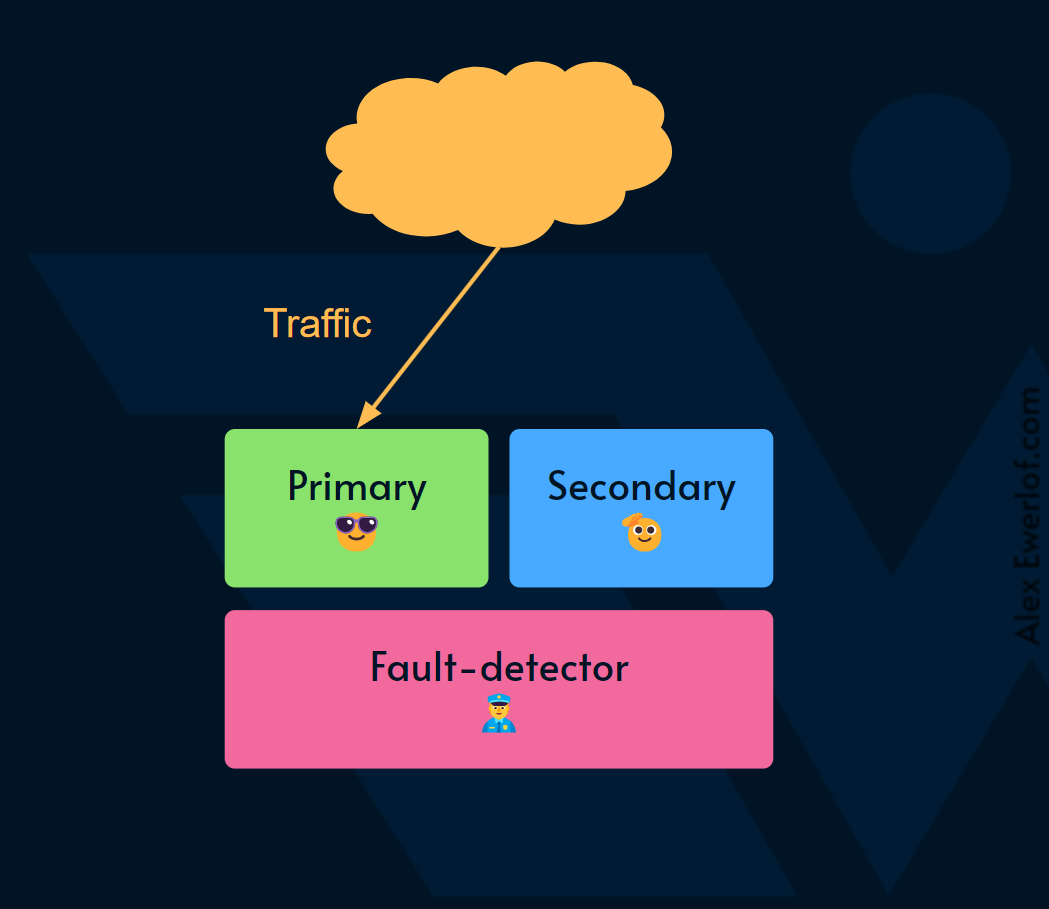
In a nutshell here’s how failover works:
简而言之,故障转移的工作原理如下:
-
The primary system is responsible for handling the load while one or more secondary systems are on stand-by. The secondary systems are of the same type as the primary and sometimes are called replicas.
主系统负责处理负载,而一个或多个辅助系统处于待机状态。辅助系统与主系统类型相同,有时称为副本 。 -
A fault-detection system continuously observes the behavior of the primary system
故障检测系统持续观察主系统的行为 -
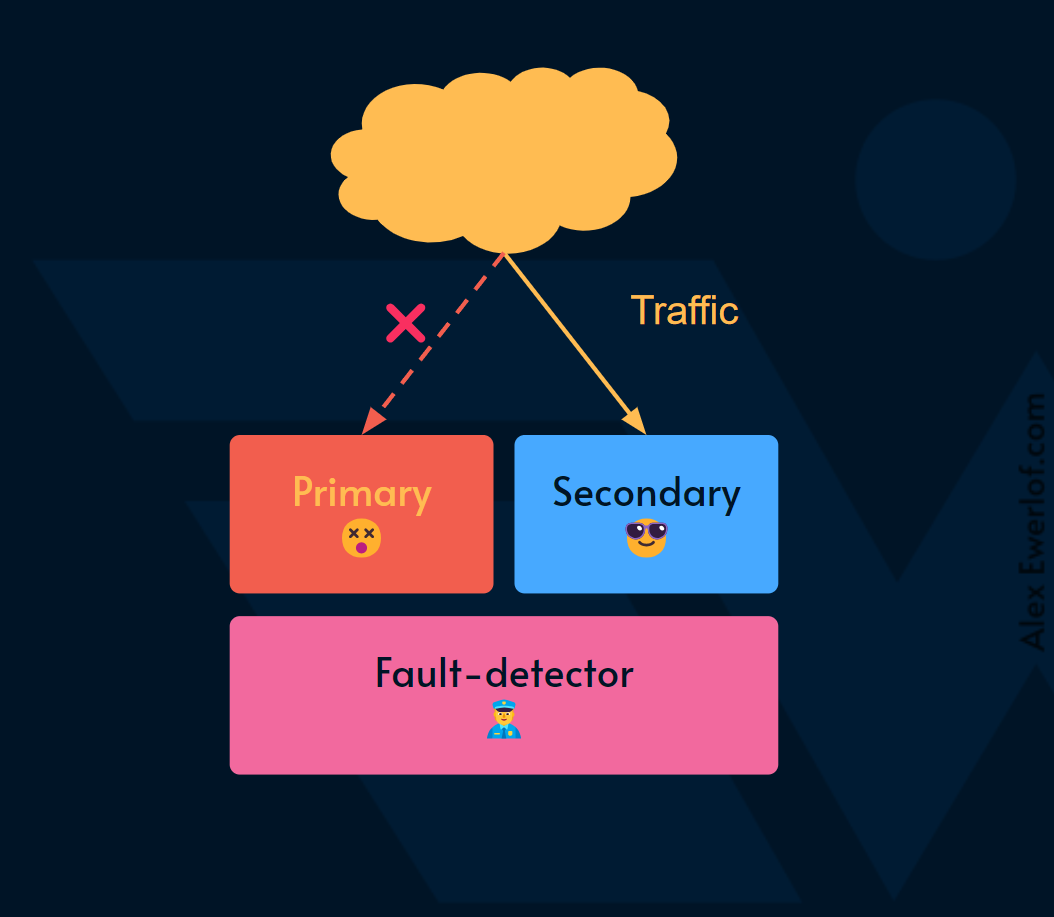
If a failure is detected in the primary system, the load is automatically shifted to the secondary systems
如果在主系统中检测到故障,则负载会自动转移到辅助系统 -
This buys time for the engineers or automation to fix the issue with the primary system
这为工程师或自动化人员争取了时间来解决主系统的问题 -
Once the issue is resolved, the primary system takes over
问题解决后,主系统将接管
Key characteristics of Failover
故障转移的主要特征
-
Service Continuity: The goal of failover is to minimize or eliminate the impact of failures from the consumer by switching to the secondary system. As far as the users are concerned the system is just working as usual without perceivable degradation.
服务连续性: 故障转移的目标是通过切换到辅助系统来最大程度地减少或消除使用者故障的影响。就用户而言,系统只是照常工作,没有明显的退化。 -
Redundancy: Failover relies on redundant systems (also called “backup” as in backup plan). The redundant systems are the same type and sometimes are called replicas. This redundancy ensures that if the primary system fails, the secondary system can take over seamlessly.
冗余: 故障转移依赖于冗余系统(也称为备份计划中的“备份”)。冗余系统是同一类型 ,有时称为副本。这种冗余确保如果主系统发生故障,辅助系统可以无缝接管。 -
Automation: Redundancy alone cannot guarantee high availability. Since humans are slow, automation is often used.
自动化: 仅靠冗余并不能保证高可用性。由于人类速度很慢,因此经常使用自动化。-
Automatic Detection: An automatic fault-detection mechanism observes the primary system to detect failures.
自动检测: 自动故障检测机制观察主系统以检测故障。 -
Automatic Switch: When a failure is detected, the failover mechanism kicks in and redirects load or workload to the secondary system. Also switching the load back to the primary when it recovers.
自动切换: 当检测到故障时,故障转移机制会启动并将负载或工作负载重定向到辅助系统。还会在负载恢复时将负载切换回主服务器。 -
Automated Recovery: Sometimes an automated process is used to recover the primary system using simple techniques. For example: resetting cache, restarting, starting a fresh instance, etc.
自动恢复: 有时使用自动化过程使用简单的技术来恢复主系统。例如:重置缓存、重启、启动新实例等。
-
-
Higher Cost: Redundancy and automation increase the resource cost and system complexity (compared to the happy land of 🌈 rainbows and 🦄 unicorns where nothing ever fails). The cost depends on the available technology, type of service, traffic volume and most importantly how the consumers perceive reliability.
成本更高: 冗余和自动化增加了资源成本和系统复杂性(与彩虹和🦄独角兽的🌈快乐之地相比,没有任何故障)。成本取决于可用技术、服务类型、流量,最重要的是消费者对可靠性的看法。
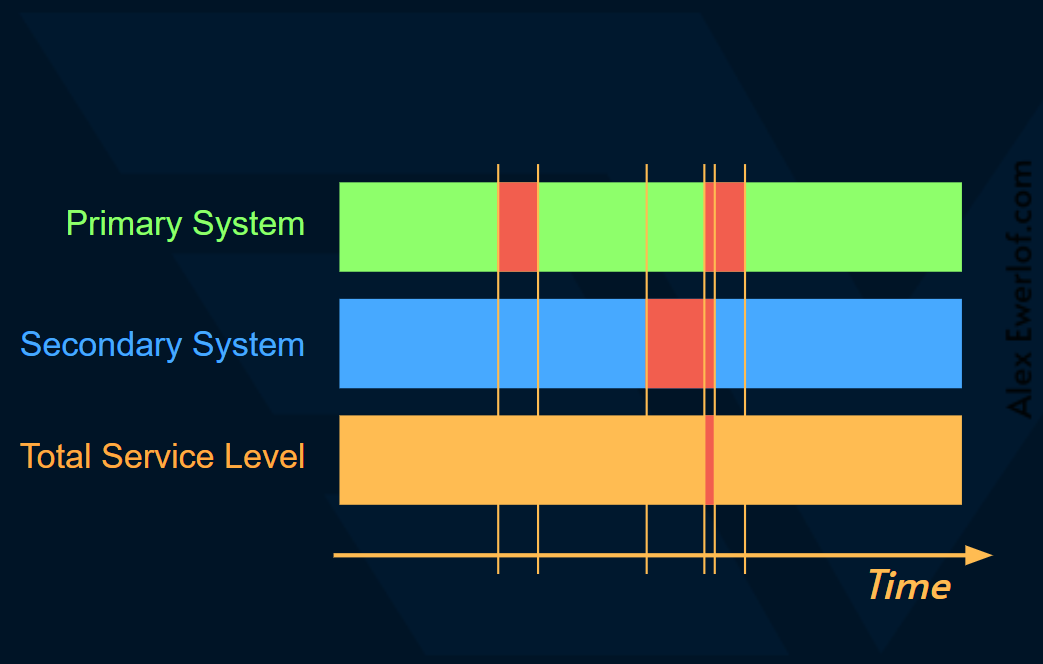
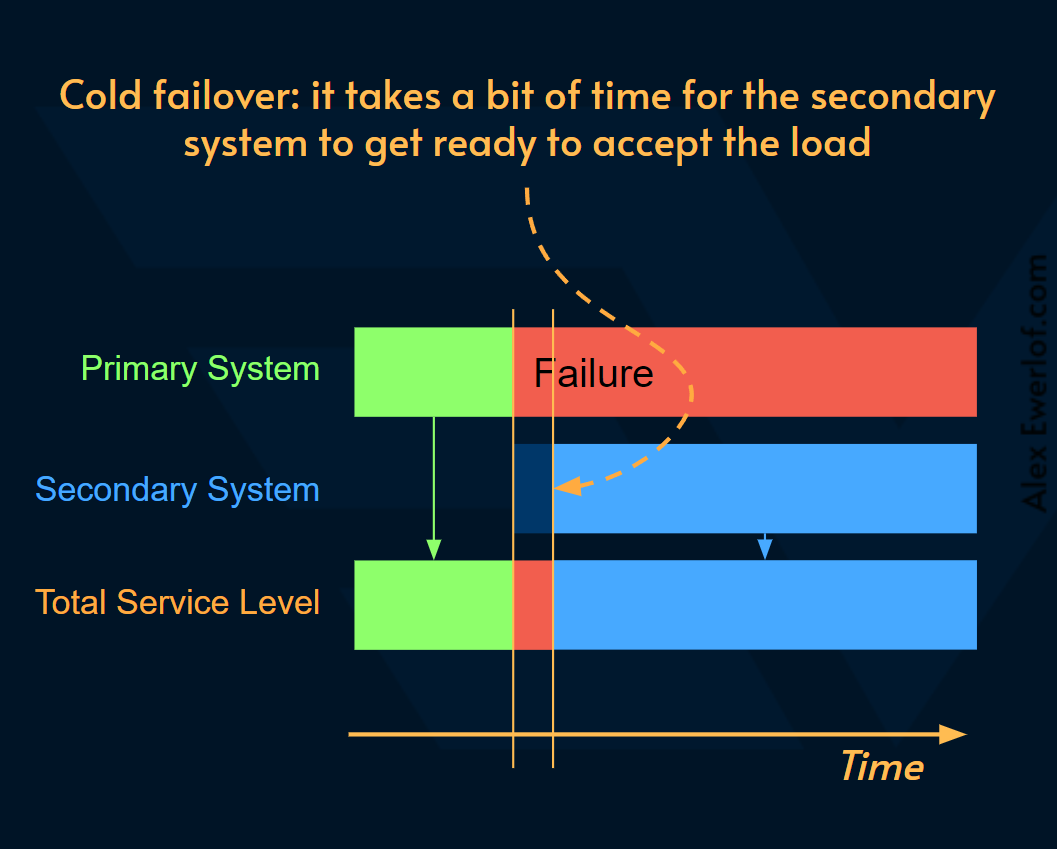
Below is a timeline for how the failures in primary and secondary systems cancel each out to achieve a higher total service level (e.g., Availability).
下面是主系统和辅助系统中的故障如何抵消每个故障以实现更高的总服务级别(例如可用性)的时间表。
Types of failover mechanisms
故障转移机制的类型
Active-Active/Passive 主动-主动/被动
There are two types of failover mechanisms based on how the primary and secondary systems handle the load:
根据主系统和辅助系统处理负载的方式,有两种类型的故障转移机制:
-
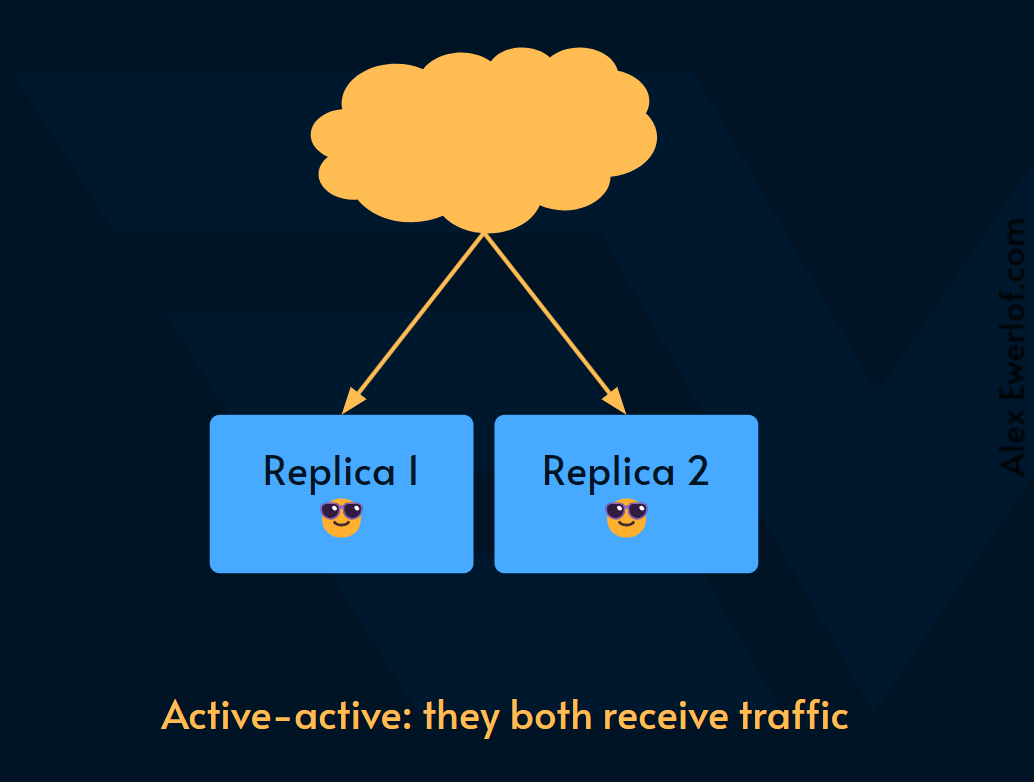
Active-active failover: both primary and secondary handle the load. This way one of them doesn’t get overloaded while the others are just standing by. This is how most load-balancers work: they distribute the load among similar systems.
主动-主动故障转移: 主和辅助都处理负载。这样,其中一个就不会在其他人袖手旁观时超载。这就是大多数负载均衡器的工作方式:它们在类似的系统之间分配负载。
-
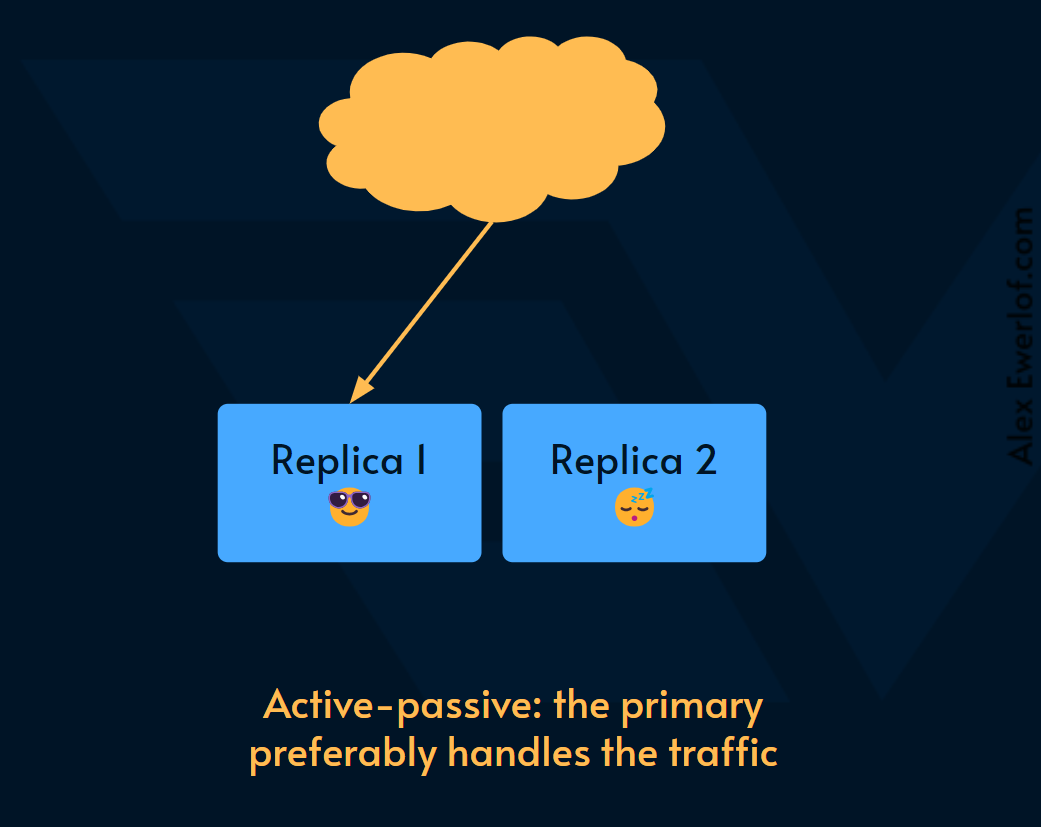
Active-passive failover: while the primary is handling the load, the failover system is on standby. This setup is also called Active-standby.
主动-被动故障转移: 当主节点处理负载时,故障转移系统处于待机状态。此设置也称为主动-备用 。
Which one you choose depends on the cost. We’re not just talking about the cost of extra resources. The cost can be anything from complexity to user-facing service levels like higher latency (see the examples below for multi-region failover).
您选择哪一个取决于成本。我们谈论的不仅仅是额外资源的成本。成本可以是从复杂性到面向用户的服务级别(例如更高的延迟)的任何内容(请参阅下面的多区域故障转移示例)。
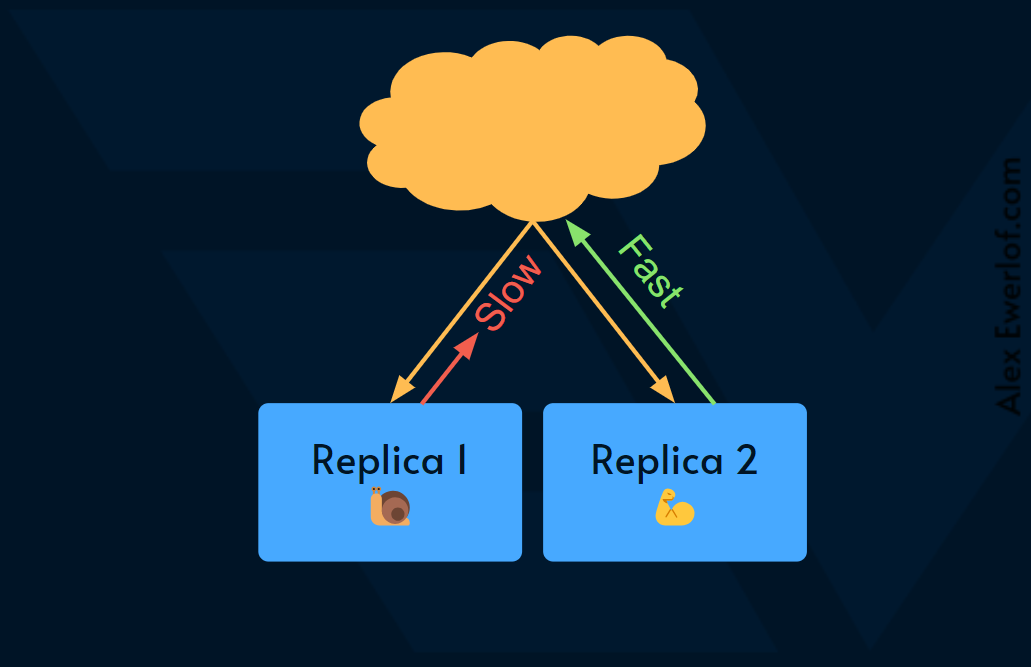
Having an active-active setup also enables cool trickery like improving the latency Service Level objective. For example, you can send the same requests to multiple systems and return the quickest response to the user.
拥有主动-主动设置还可以实现很酷的技巧,例如提高延迟服务级别目标。例如,您可以向多个系统发送相同的请求,并将最快的响应返回给用户。
This way the latency of the system as a whole is as fast as the quickest replica.
这样,整个系统的延迟与最快的副本一样快。
Hot/Cold 热/冷
When it is time to switch the load to the secondary system, there are two types of failover mechanisms:
当需要将负载切换到辅助系统时,有两种类型的故障转移机制:
-
Hot failover: the secondary system is ready to handle the load immediately. The active-active setup is always hot, but you may have a multi-cloud setup where Google Cloud can take over in case AWS fails. OK bad example! Who does that? 😄A better example is when the secondary system does not get any load to reduce the cost, but it has a couple of nodes running just in case. When the load shifts to the secondary, it’ll automatically scale to handle the demand.
热故障转移: 辅助系统已准备好立即处理负载。主动-主动设置始终是热的,但您可能有一个多云设置,如果 AWS 发生故障,Google Cloud 可以接管该设置。好吧,坏例子!谁会这样做?😄一个更好的例子是,当辅助系统没有获得任何负载以降低成本时,但它有几个节点在运行以防万一。当负载转移到辅助时,它将自动缩放以处理需求。 -
Cold failover: the secondary system is in standby, or hibernation mode and some work is needed to make it ready to accept the load. For example, new EC2 instances need to spin up or data needs to be synchronized prior to the secondary system being able to handle the load.
冷故障转移: 辅助系统处于待机或休眠模式,需要进行一些工作才能使其准备好接受负载。例如,新的 EC2 实例需要启动或需要同步数据,然后辅助系统才能处理负载。
The main difference between the two is the time it takes till the secondary system can take over the load and how much it impacts the perceived reliability from the consumer point of view:
两者之间的主要区别在于辅助系统接管负载所需的时间,以及从 消费者的角度来看 ,它对感知可靠性的影响有多大:
Cold failover hurts the service continuity, but it is often cheaper to implement. Sometimes a small increase in reliability can have a high cost in engineering but it is worth it as demonstrated by Project Nimble at Netflix.
冷故障转移会损害服务连续性,但实现起来通常更便宜。有时,可靠性的小幅提高可能会带来很高的工程成本,但正如 Netflix 的 Project Nimble 所证明的那样,这是值得的 。
Hard/Soft 硬/软
And when it comes to what happens to the primary system upon failure, there are two types of failover mechanisms:
当谈到主系统发生故障时会发生什么时,有两种类型的故障转移机制:
-
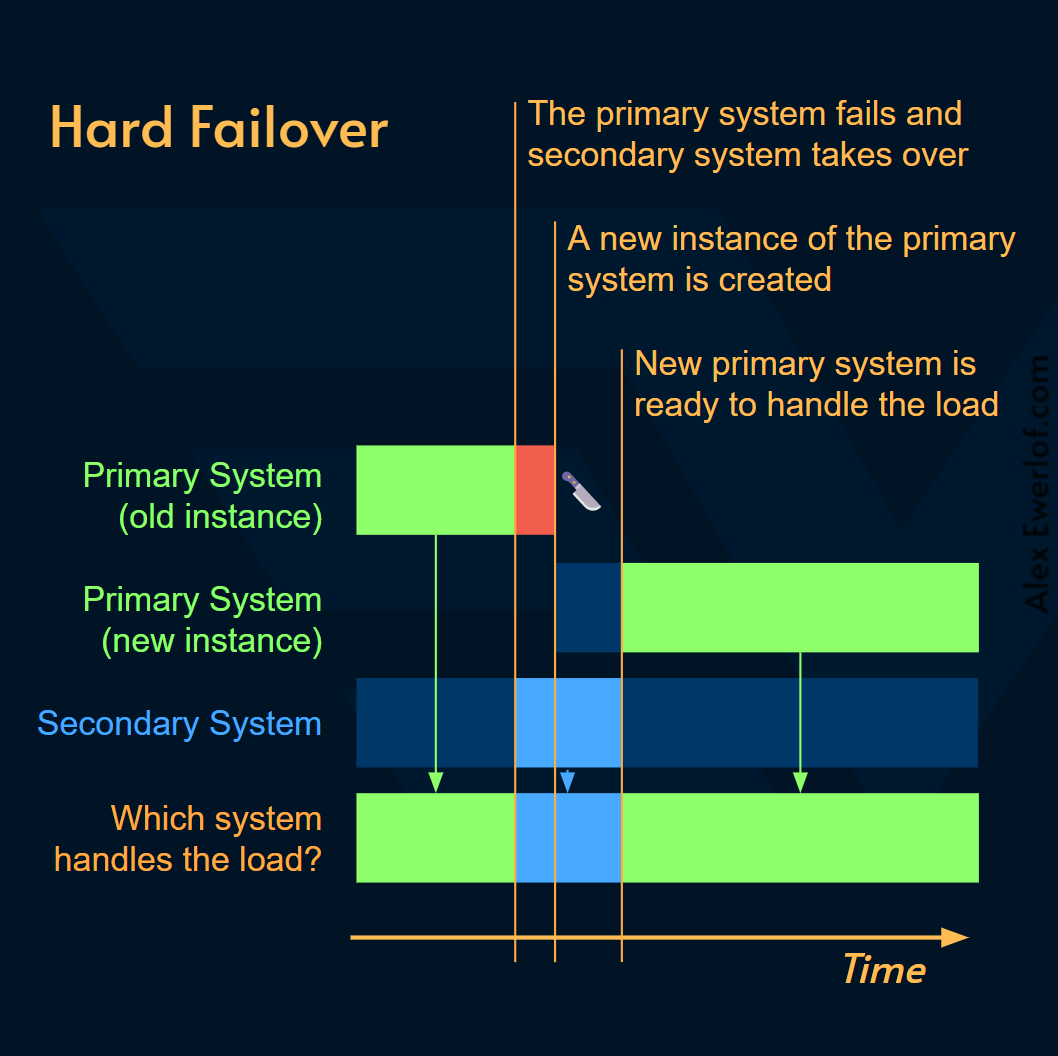
Hard failover: kills the primary system. This is a rather extreme measure that should be weighed against the cost of recreating the primary system. Sometimes the best option is the good old IT solution to all problems: “have you tried turning it off and on again”? 😄This solution is less suitable for stateful systems like databases or message queues.
硬故障转移: 终止主系统。这是一个相当极端的措施,应该与重建主系统的成本进行权衡。有时最好的选择是解决所有问题的旧 IT 解决方案:“您是否尝试过将其关闭并重新打开”?😄此解决方案不太适合数据库或消息队列等有状态系统。 -
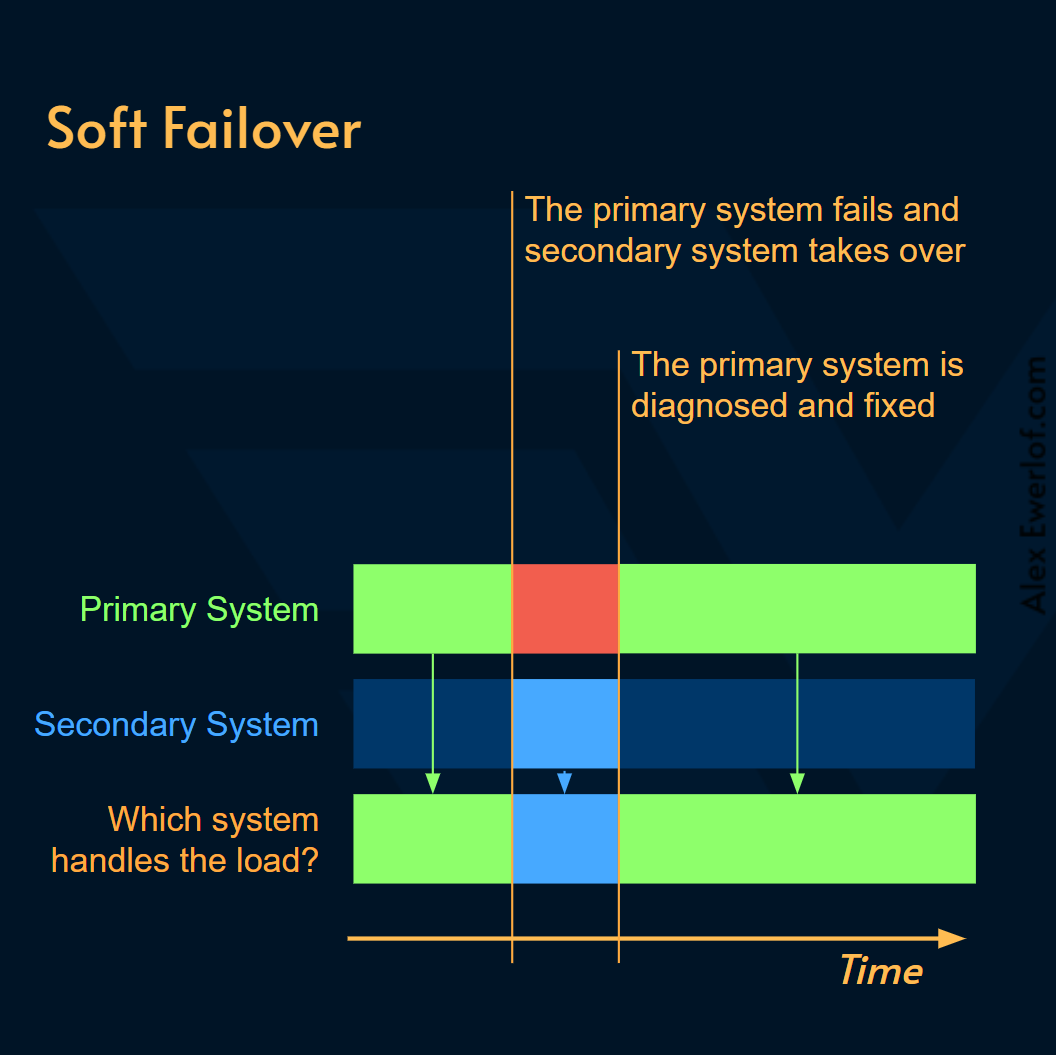
Soft failover: leaves the primary system alone so you can diagnose and fix the problem. This is also called graceful failover and can be done proactively before it is too late to save the system from permanent failure. (src: Couchbase)
软故障转移: 不让主系统处于不理状态,以便您可以诊断和修复问题。这也称为正常故障转移 ,可以在为时已晚之前主动完成,无法将系统从永久性故障中拯救出来。(来源: 沙发基地 )
Failover Examples 故障转移示例
A few years ago, I was working with a service running on AWS that had a high availability SLO (Service Level Objective).
几年前,我正在使用 AWS 上运行的一项服务,该服务具有高可用性 SLO( 服务级别目标 )。
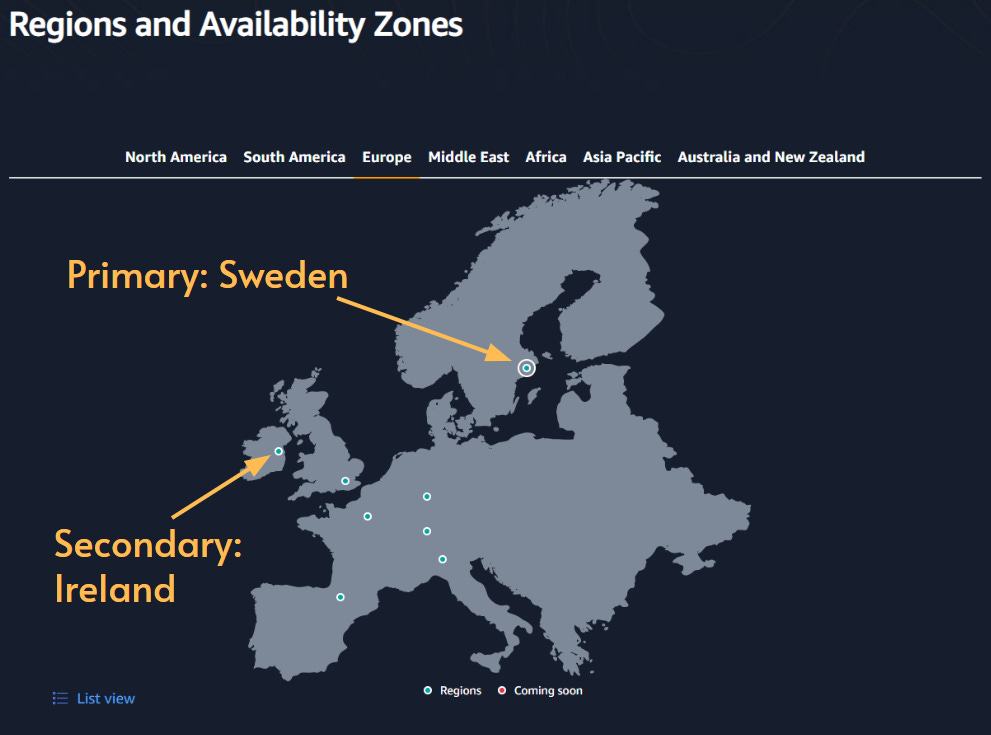
Most of the customers were in Scandinavia, so we served the bulk of the traffic from eu-north-1 region based in Stockholm, Sweden.
大多数客户都在斯堪的纳维亚半岛,因此我们为 来自瑞典斯德哥尔摩的 eu-north-1 地区的大部分流量提供服务。
But we also ran the same setup in Ireland in case our services failed in Stockholm. This was a hot failover. The Irish servers were ready to take over, but we had configured our AWS Route 53 to prefer Stockholm. When our service failed in Stockholm, we would shift the load to Ireland to guarantee a high availability towards the end users.
但我们也在爱尔兰运行了相同的设置,以防我们在斯德哥尔摩的服务出现故障。这是一个热故障转移。 爱尔兰服务器已准备好接管,但我们已将 AWS Route 53 配置为首选斯德哥尔摩。当我们在斯德哥尔摩的服务出现故障时,我们会将负载转移到爱尔兰,以保证最终用户的高可用性。
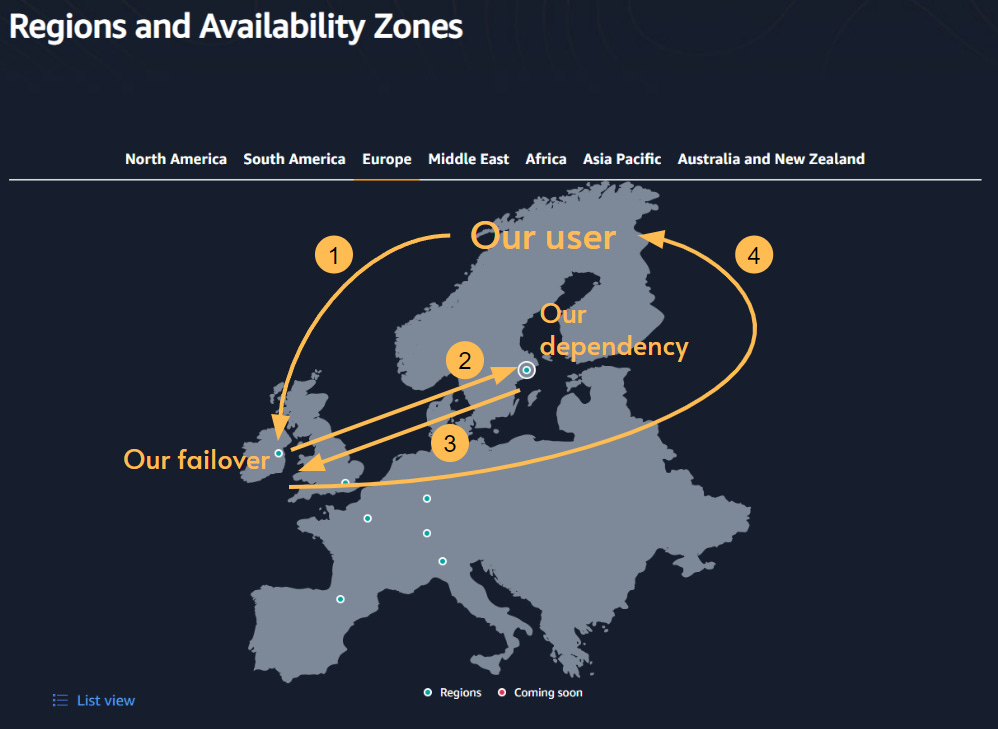
Using Ireland, however, wasn’t ideal because it would increase the latency. That is because our service had a dependency that could still run in Stockholm. In that case, the user requests would go to Ireland, Ireland would fetch data from Stockholm and then returned the result.
然而,使用爱尔兰并不理想,因为它会增加延迟。这是因为我们的服务有一个依赖项,仍然可以在斯德哥尔摩运行。在这种情况下,用户请求将转到爱尔兰,爱尔兰将从斯德哥尔摩获取数据,然后返回结果。
Since our dependency was still running in Stockholm, our failover system from Ireland had extra delay
由于我们的依赖项仍在斯德哥尔摩运行,我们来自爱尔兰的故障转移系统有额外的延迟
It would be ideal if our dependency were also available in Ireland, but we didn’t have control over the failover mechanism of that system, neither was the cost justified for the team responsible for our dependency. Our dependency was a stateful service and having a multi-region strategy would imply database replication. Our service didn’t justify the cost of resources and complexity.
如果我们的依赖项在爱尔兰也可用,那就太理想了,但我们无法控制该系统的故障转移机制,对于负责我们依赖项的团队来说,成本也不合理。我们的依赖项是有状态服务,拥有多区域策略意味着数据库复制。我们的服务并不能证明资源成本和复杂性的合理性。
The higher latency was an accepted cost in our case, but we preferred to serve the traffic from Stockholm. Hence the active-passive setup.
在我们的例子中,较高的延迟是可接受的成本,但我们更愿意为来自斯德哥尔摩的流量提供服务。因此采用主动-被动设置。
Other examples 其他例子
A good example of the active-active setup is Amazon Simple Queue Service. It stores all message queues and messages within a single region but with multiple redundant Availability Zones (AZs). That way if a single availability zone goes down (for example in case of natural disasters), another availability zone takes over.
主动-主动设置的一个很好的例子 是 Amazon Simple Queue Service。 它将所有消息队列和消息存储在单个区域中,但具有多个冗余可用区 (AZ)。这样,如果单个可用性区域出现故障(例如,在发生自然灾害时),另一个可用性区域将接管。
The multi-AZ failover strategy is a relatively cheap way to increase service levels. AWS EC2 Auto Scaling groups for example allow a load balancer to distribute the traffic among the instances running across different availability zones in one region with some configuration.
多可用区故障转移策略是提高服务级别的一种相对便宜的方法。 例如,AWS EC2 Auto Scaling 组允许负载均衡器通过某些配置在一个区域中跨不同可用区运行的实例之间分配流量。
When to use Failover? 何时使用故障转移?
-
High availability is critical: If the system requires minimal to no downtime and demands continuous availability, failover is a good risk mitigation strategy to consider.
高可用性至关重要:如果系统需要最少的停机时间甚至没有停机时间,并且需要持续可用性,那么故障转移是一个很好的风险缓解策略。 -
Secondary system is feasible: As a general rule of thumb, stateless services are easier to duplicate but when it comes to stateful services (like databases), it is more complex and costly to set up a secondary system. Sometimes a secondary system is not feasible due to requirements or technology at hand: for example, due to GDPR the data is not allowed to leave EU borders, but the only available options are in the US or China.
辅助系统是可行的:作为一般经验法则,无状态服务更容易复制,但当涉及到有状态服务(如数据库)时,设置辅助系统更加复杂和昂贵。有时,由于手头的要求或技术,辅助系统不可行:例如,由于 GDPR,数据不允许离开欧盟边界,但唯一可用的选项是在美国或中国。 -
The cost of mitigation is reasonable: This should be obvious based on what we discussed so far, but it’s important to avoid over-engineering the service when the requirement or the profit don’t justify a failover mechanism. Sometimes, a risk can be accepted because the mitigation is not worth it.
缓解成本是合理的:根据我们到目前为止讨论的内容,这应该是显而易见的,但当需求或利润不能证明故障转移机制的合理性时,避免过度设计服务非常重要。有时,可以接受风险,因为缓解措施不值得。
Conclusion 结论
Failover is a risk mitigation strategy that aims to improve service continuity through redundancy and automation.
故障转移是一种风险缓解策略,旨在通过冗余和自动化提高服务连续性。
Failover is usually more expensive than the other alternatives. This follow up article digs into fallbacks as a more affordable alternative.
故障转移通常比其他替代方案更昂贵。 这篇后续文章深入探讨了后备方案作为一种更实惠的替代方案。
This article took about 10 hours to research, draft, edit and illustrate. If you enjoy it, you could support my work by sparing a few bucks on a paid subscription. You get 20% off via this link. Thanks in advance. 🙌
本文花了大约 10 个小时进行研究、起草、编辑和说明。如果您喜欢它,您可以通过节省几美元付费订阅来支持我的工作。您可以通过此链接获得 20% 的折扣 。提前感谢。🙌
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)