Drools
Working Memory (insert a fact)Rule BaseInference EngineInsert a JavaBean into the Working Memory as a Fact.All rules in the Rule Base are matched against facts in the Working Memory through the Patter
核心元素
Working Memory (insert a fact)
Rule Base
Inference Engine
Pattern Matcher
Agenda
Execution Engine
元素
- Rule Base(规则库)
- Inference Engine(推理引擎)其中Inference Engine(推理引擎)又包括:
- Pattern Matcher(匹配器) 具体匹配哪一个规则,由这个完成
- Agenda(议程)
- Execution Engine(执行引擎)
流程
- Insert a JavaBean into the Working Memory as a Fact.
- All rules in the Rule Base are matched against facts in the Working Memory through the Pattern Matcher, and the matching rules are added to the Agenda.
- The Execution Engine will fire the Agenda activated by the Pattern Matcher.
基础组件
The Drools engine operates using the following basic components:
- Rules: Business rules or DMN decisions that you define. All rules must contain at a minimum the conditions that trigger the rule and the actions that the rule dictates.
- Facts: Data that enters or changes in the Drools engine that the Drools engine matches to rule conditions to execute applicable rules.
- Production memory: Location where rules are stored in the Drools engine.
- Working memory: Location where facts are stored in the Drools engine.
- Agenda: Location where activated rules are registered and sorted (if applicable) in preparation for execution.


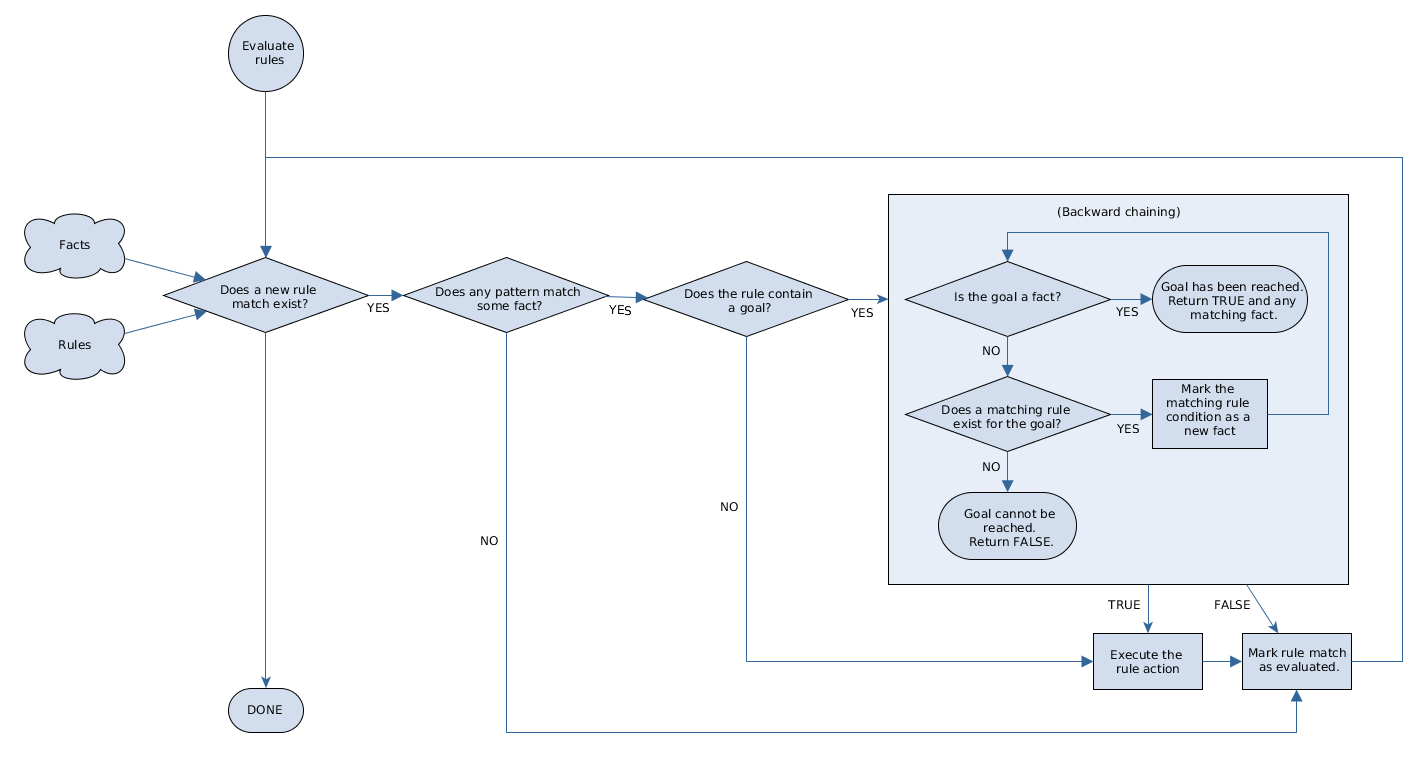
The following diagram illustrates how the Drools engine evaluates rules using forward chaining overall with a backward-chaining segment in the logic flow:
规则文件
关键字
package 包名,只限于逻辑上的管理,同一个包名下的查询或者函数可以直接调用
import 用于导入类或者静态方法
global 全局变量
function 自定义函数
query 查询
rule end 规则体
规则文件构成
在使用Drools时非常重要的一个工作就是编写规则文件,通常规则文件的后缀为.drl。
drl是Drools Rule Language的缩写。在规则文件中编写具体的规则内容。
一套完整的规则文件内容构成如下:
rule "ruleName"
attributes // 规则属性,是rule与when之间的参数,为可选项。
when
LHS // (Left Hand Side):是规则的条件部分的通用名称。它由零个或多个条件元素组成。如果LHS为空,则它将被视为始终为true的条件元素。
then
RHS // (Right Hand Side):是规则的后果或行动部分的通用名称。 (右手边)
end
LHS 部分由一个或者多个条件组成,条件又称为 pattern。
pattern 的语法结构为:绑定变量名:Object(Field约束)
其中绑定变量名可以省略,通常绑定变量名的命名一般建议以 $ 开始。如果定义了绑定变量名,就可以在规则体的RHS部分使用此绑定变量名来操作相应的Fact对象。Field约束部分是需要返回 true 或者 false 的0个或多个表达式。
//规则二:100元 - 500元 加100分
rule "order_rule_2"
when
$order:Order(amout >= 100 && amout < 500)
then
$order.setScore(100);
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则二:100元 - 500元 加100分");
end
通过上面的例子我们可以知道,匹配的条件为:
- 工作内存中必须存在Order这种类型的Fact对象-----类型约束
- Fact对象的amout属性值必须大于等于100------属性约束
- Fact对象的amout属性值必须小于500------属性约束
以上条件必须同时满足当前规则才有可能被激活。
比较操作符
Drools提供的比较操作符,如下表:
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
< |
小于 |
> |
大于 |
>= |
大于等于 |
<= |
小于等于 |
== |
等于 |
!= |
不等于 |
contains |
检查一个Fact对象的某个属性值是否包含一个指定的对象值 |
not contains |
检查一个Fact对象的某个属性值是否不包含一个指定的对象值 |
memberOf |
判断一个Fact对象的某个属性是否在一个或多个集合中 |
not memberOf |
判断一个Fact对象的某个属性是否不在一个或多个集合中 |
matches |
判断一个Fact对象的属性是否与提供的标准的Java正则表达式进行匹配 |
not matches |
判断一个Fact对象的属性是否不与提供的标准的Java正则表达式进行匹配 |
前6个比较操作符和Java中的完全相同。
Drools内置方法
规则文件的RHS部分的主要作用是通过插入,删除或修改工作内存中的Fact数据,来达到控制规则引擎执行的目的。
Drools提供了一些方法可以用来操作工作内存中的数据,操作完成后规则引擎会重新进行相关规则的匹配,原来没有匹配成功的规则在我们修改数据完成后有可能就会匹配成功了。
update方法
update方法的作用是更新工作内存中的数据,并让相关的规则重新匹配。 (要避免死循环)
//Fact对象,事实对象
Order order = new Order();
order.setAmout(30);
------------
//规则一:100元以下 不加分
rule "order_rule_1"
when
$order:Order(amout < 100)
then
$order.setAmout(150);
update($order) // update 方法用于更新Fact对象,会导致相关规则重新匹配
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则一:100元以下 不加分");
end
//规则二:100元 - 500元 加100分
rule "order_rule_2"
when
$order:Order(amout >= 100 && amout < 500)
then
$order.setScore(100);
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则二:100元 - 500元 加100分");
end
insert方法
insert方法的作用是向工作内存中插入数据,并让相关的规则重新匹配。
//规则一:100元以下 不加分
rule "order_rule_1"
when
$order:Order(amout < 100)
then
Order order = new Order();
order.setAmout(130);
insert(order); //insert方法的作用是向工作内存中插入Fact对象,会导致相关规则重新匹配
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则一:100元以下 不加分");
end
//规则二:100元 - 500元 加100分
rule "order_rule_2"
when
$order:Order(amout >= 100 && amout < 500)
then
$order.setScore(100);
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则二:100元 - 500元 加100分");
end
retract方法
retract方法的作用是删除工作内存中的数据,并让相关的规则重新匹配。
//规则一:100元以下 不加分
rule "order_rule_1"
when
$order:Order(amout < 100)
then
retract($order) //retract方法的作用是删除工作内存中的Fact对象,会导致相关规则重新匹配
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则一:100元以下 不加分");
end
规则属性 attributes
salience属性
salience属性用于指定规则的执行优先级,取值类型为Integer。数值越大越优先执行。 每个规则都有一个默认的执行顺序,如果不设置salience属性,规则体的执行顺序为由上到下
package com.order
rule "rule_1"
salience 9
when
eval(true)
then
System.out.println("规则rule_1触发");
end
rule "rule_2"
salience 10 // 最突出
when
eval(true)
then
System.out.println("规则rule_2触发");
end
rule "rule_3"
salience 8
when
eval(true)
then
System.out.println("规则rule_3触发");
end
no-loop属性
no-loop属性用于防止死循环,当规则通过update之类的函数修改了Fact对象时,可能使当前规则再次被激活从而导致死循环。取值类型为Boolean,默认值为false,测试步骤如下:
//订单积分规则
package com.order
import com.example.droolsdemo.model.Order
//规则一:100元以下 不加分
rule "order_rule_1"
no-loop true //防止陷入死循环
when
$order:Order(amout < 100)
then
$order.setScore(0);
update($order)
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则一:100元以下 不加分");
end
global 全局变量
global关键字用于在规则文件中定义全局变量,它可以让应用程序的对象在规则文件中能够被访问。可以用来为规则文件提供数据或服务。
语法结构为:global 对象类型 对象名称
在使用global定义的全局变量时有两点需要注意:
1、如果对象类型为包装类型时,在一个规则中改变了global的值,那么只针对当前规则有效,对其他规则中的global不会有影响。可以理解为它是当前规则代码中的global副本,规则内部修改不会影响全局的使用。
2、如果对象类型为集合类型或JavaBean时,在一个规则中改变了global的值,对java代码和所有规则都有效。
package com.example.drools.model;
public class Order {
private double amout;
public double getAmout() {
return amout;
}
public void setAmout(double amout) {
this.amout = amout;
}
}
package com.example.drools.model;
public class Integral {
private double score;
public double getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
}
//订单积分规则
package com.order
import com.example.droolsdemo.model.Order
global com.example.drools.model.Points points;
//规则一:100元以下 不加分
rule "order_rule_1"
no-loop true //防止陷入死循环
when
$order:Order(amout < 100)
then
points.setScore(10);
update($order)
System.out.println("成功匹配到规则一:100元以下 不加分");
end
@Test
public void test1(){
//从Kie容器对象中获取会话对象
KieSession session = kieContainer.newKieSession();
//Fact对象,事实对象
Order order = new Order();
order.setAmout(30);
//全局变量
Points points = new Points();
session.setGlobal("Points", points); // look here.
//将Order对象插入到工作内存中
session.insert(order);
//激活规则,由Drools框架自动进行规则匹配,如果规则匹配成功,则执行当前规则
session.fireAllRules();
//关闭会话
session.dispose();
System.out.println("订单金额:" + order.getAmout());
System.out.println("添加积分:" + integral.getScore());
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献8条内容
已为社区贡献8条内容







所有评论(0)