MySQL执行计划深度解析:从EXPLAIN输出到慢查询优化实战
MySQL执行计划深度解析与优化实战 本文系统性地讲解了MySQL执行计划分析技术,从基础EXPLAIN字段解析到高级JSON格式分析,结合实际案例展示优化方法。核心内容包括: 执行计划关键字段解读,重点分析type访问类型和Extra信息的性能含义 高级分析技术:EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON和EXPLAIN ANALYZE的使用与指标解析 三大典型优化案例: 索引失效导致全表扫描的优化
·
MySQL执行计划深度解析:从EXPLAIN输出到慢查询优化实战
本文结合MySQL优化器原理,深度解读EXPLAIN输出,并通过真实案例展示如何通过执行计划定位性能瓶颈。
一、执行计划基础:EXPLAIN字段全解析
1. 核心字段详解(基于MySQL 8.0)
| 字段 | 类型 | 说明 | 优化意义 | 最佳值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | int | 查询序列号 | 识别简单/复杂查询层级 | 数字越小优先级越高 |
| select_type | enum | 查询类型 | 判断查询复杂度 | SIMPLE, PRIMARY |
| table | varchar | 访问的表 | 表访问顺序 | - |
| partitions | text | 匹配的分区 | 分区查询效率 | NULL(未分区) |
| type | enum | 访问类型 | 核心性能指标 | const, eq_ref, ref |
| possible_keys | text | 可能使用的索引 | 索引选择范围 | - |
| key | text | 实际使用的索引 | 索引有效性验证 | 实际索引名 |
| key_len | int | 使用索引的长度 | 索引利用率 | 越短越好 |
| ref | text | 索引比较的列 | 连接条件分析 | const, 列名 |
| rows | bigint | 预估扫描行数 | 规模评估 | 接近实际值 |
| filtered | float | 过滤后剩余百分比 | 存储引擎过滤效率 | 100% |
| Extra | text | 额外信息 | 关键性能提示 | Using index |
2. 重点字段深度解析
(1) type访问类型(性能核心指标)
性能对比示例:
-- 案例1: const (最优)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1;
-- 案例2: ref (良好)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM orders WHERE user_id = 100;
-- 案例3: range (中等)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM logs WHERE create_time > '2023-01-01';
-- 案例4: index (警告)
EXPLAIN SELECT COUNT(*) FROM products;
-- 案例5: ALL (紧急优化)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM comments WHERE content LIKE '%mysql%';
(2) Extra字段(执行细节)
| 值 | 含义 | 优化建议 |
|---|---|---|
| Using index | 覆盖索引 | 理想状态,无需优化 |
| Using where | 服务层过滤 | 检查索引有效性 |
| Using temporary | 使用临时表 | 优化GROUP BY/ORDER BY |
| Using filesort | 文件排序 | 添加排序索引 |
| Using join buffer | 使用连接缓存 | 调大join_buffer_size |
| Select tables optimized away | 优化掉表访问 | 最佳优化结果 |
二、高级执行计划分析技术
1. EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON(MySQL 5.6+)
{
"query_block": {
"select_id": 1,
"cost_info": {
"query_cost": "1.20" // 整个查询预估成本
},
"nested_loop": [
{
"table": {
"table_name": "orders",
"access_type": "ref",
"possible_keys": ["idx_user"],
"key": "idx_user",
"key_length": "5",
"rows_examined_per_scan": 1,
"rows_produced_per_join": 1,
"filtered": "100.00",
"cost_info": {
"read_cost": "1.00",
"eval_cost": "0.20",
"prefix_cost": "1.20", // 当前表累计成本
"data_read_per_join": "256"
},
"used_columns": ["id","user_id","amount"],
"attached_condition": "orders.user_id = 1"
}
}
]
}
}
JSON核心字段解析:
cost_info.query_cost:整个查询预估成本rows_examined_per_scan:单次扫描行数rows_produced_per_join:参与连接的行数prefix_cost:当前步骤累计成本attached_condition:实际应用的条件
2. EXPLAIN ANALYZE(MySQL 8.0.18+)
-- 实际执行测量
EXPLAIN ANALYZE
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE user_id IN (SELECT id FROM users WHERE age > 30);
输出示例:
-> Nested loop inner join (cost=1.20 rows=5) (actual time=0.024..0.126 rows=5 loops=1)
-> Index lookup on orders using idx_user (user_id=users.id)
(actual time=0.020..0.022 rows=5 loops=3)
-> Single-row index lookup on users using PRIMARY (id=orders.user_id)
(actual time=0.002..0.002 rows=1 loops=5)
关键指标:
actual time:实际执行时间(启动时间…总时间)rows:实际返回行数loops:循环次数
三、执行计划优化实战案例
案例1:索引失效导致全表扫描
原始SQL:
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE YEAR(create_time) = 2023;
EXPLAIN输出:
id select_type table type key rows Extra
1 SIMPLE orders ALL NULL 100000 Using where
问题分析:
type=ALL全表扫描rows=100000扫描10万行Extra=Using where服务层过滤- 对
create_time使用YEAR()函数导致索引失效
优化方案:
-- 改为范围查询
SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE create_time BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-12-31';
优化后EXPLAIN:
id select_type table type key rows Extra
1 SIMPLE orders range idx_creatime 1000 Using index condition
案例2:临时表导致性能瓶颈
原始SQL:
SELECT user_id, COUNT(*)
FROM orders
GROUP BY user_id
ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;
EXPLAIN输出:
id select_type table type key rows Extra
1 SIMPLE orders index NULL 10000 Using temporary; Using filesort
问题分析:
Using temporary创建临时表Using filesort额外排序- 缺少支持聚合排序的索引
优化方案:
-- 添加覆盖索引
ALTER TABLE orders ADD INDEX idx_user_count(user_id, amount);
优化后EXPLAIN:
id select_type table type key rows Extra
1 SIMPLE orders index idx_user_count 10000 Using index
案例3:错误索引选择
原始SQL:
SELECT * FROM products
WHERE category_id = 5
AND price > 100
AND status = 1;
EXPLAIN输出:
id select_type table type key rows Extra
1 SIMPLE products ref idx_category 5000 Using where
问题分析:
- 优化器选择
idx_category索引 rows=5000预估扫描5000行- 实际
price > 100 AND status=1可能过滤更多行
优化方案:
-- 强制使用更优索引
SELECT * FROM products
FORCE INDEX(idx_price_status)
WHERE category_id = 5
AND price > 100
AND status = 1;
优化后EXPLAIN ANALYZE:
-> Index range scan on products using idx_price_status
(actual time=0.05..1.2 rows=100 loops=1)
四、执行计划分析工作流
五、进阶优化技巧
1. 索引优化策略
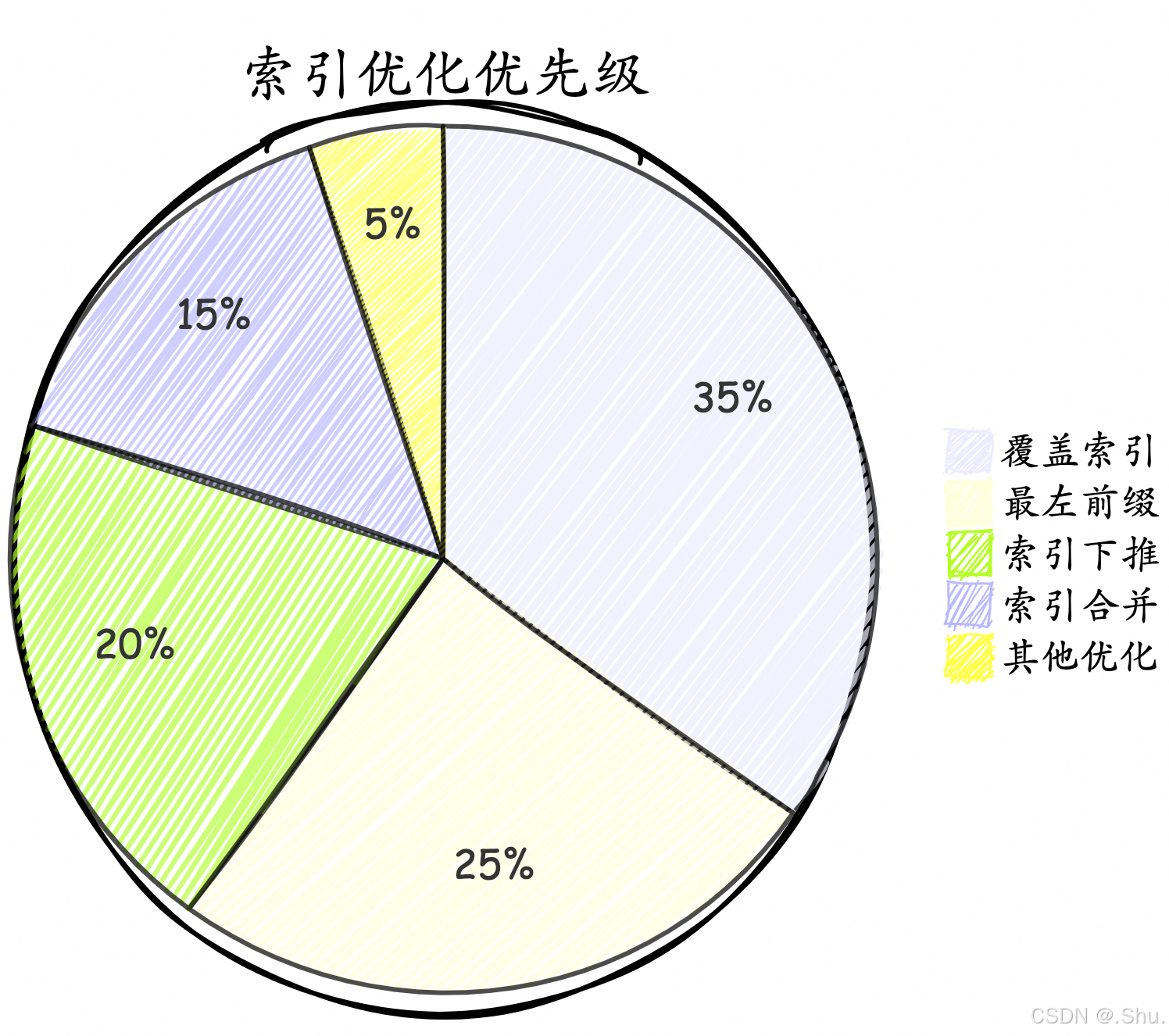
2. 优化器提示(Hints)
/*+ INDEX(products idx_price) */
SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > 100;
/*+ JOIN_ORDER(orders, customers) */
SELECT * FROM orders JOIN customers ON ...;
3. 执行计划可视化工具
- MySQL Workbench Visual Explain
- Percona PMM Query Analytics
- VividCortex
结论
通过深度解析EXPLAIN输出:
type和Extra是性能诊断的核心rows的准确性依赖统计信息- JSON格式提供成本模型细节
- EXPLAIN ANALYZE展示真实执行数据
- 结合优化器原理理解执行计划
优化黄金法则:先看type,再看Extra,结合rows,验证key,最后用ANALYZE确认实际效果。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献22条内容
已为社区贡献22条内容






所有评论(0)