每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 6 - JSON-RPC通信协议在MCP中的应用机制(一)
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP(适合小白):Day 6 - JSON-RPC通信协议在MCP中的应用机制(一):如果文章对你有帮助,还请给个三连好评,感谢感谢!
·
每天10分钟轻松掌握MCP 40 天学习计划的第6天
JSON-RPC通信协议在MCP中的应用机制(一)
🎯 今天我们要搞定什么?
想象一下,你要和朋友聊天,但你们说着不同的语言。这时候你需要一个翻译官,对吧?在MCP的世界里,JSON-RPC就是这个超级翻译官,让不同的程序能够愉快地"聊天"。今天我们就来揭秘这个翻译官是怎么工作的!
📖 第一部分:JSON-RPC基础与MCP消息格式
JSON-RPC 2.0就像是程序界的普通话,无论你的程序是用Python写的,还是用JavaScript写的,大家都能用这套标准来交流。它有个简单粗暴的原则:一问一答,清清楚楚。
1. JSON-RPC 2.0基础概念
JSON-RPC 2.0是一种轻量级的远程过程调用协议,在MCP中扮演着"通信桥梁"的关键角色。
基本消息类型对比表
| 消息类型 | 用途 | 是否需要响应 | 示例场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 请求(Request) | 客户端向服务端发起调用 | 是 | 调用工具、获取资源 |
| 响应(Response) | 服务端返回结果 | 否 | 返回工具执行结果 |
| 通知(Notification) | 单向消息 | 否 | 日志记录、状态更新 |
2. MCP中的标准消息格式
2.1 请求消息结构
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "请求的唯一标识符",
"method": "方法名称",
"params": {
"参数名": "参数值"
}
}
2.2 响应消息结构
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "对应请求的ID",
"result": {
"返回的结果数据"
}
}
2.3 错误响应结构
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "对应请求的ID",
"error": {
"code": -32601,
"message": "Method not found",
"data": "可选的额外错误信息"
}
}
3. 实际代码示例:简单的MCP客户端
import json
import uuid
import asyncio
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional
class MCPClient:
"""简单的MCP客户端实现"""
def __init__(self):
self.pending_requests: Dict[str, asyncio.Future] = {}
def create_request(self, method: str, params: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""创建标准的JSON-RPC请求"""
request_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
request = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"method": method
}
if params:
request["params"] = params
return request
def create_notification(self, method: str, params: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""创建通知消息(不需要响应)"""
notification = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": method
}
if params:
notification["params"] = params
return notification
def handle_response(self, response: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
"""处理服务端响应"""
request_id = response.get("id")
if request_id and request_id in self.pending_requests:
future = self.pending_requests.pop(request_id)
if "error" in response:
# 处理错误响应
error = response["error"]
future.set_exception(Exception(f"RPC Error {error['code']}: {error['message']}"))
else:
# 处理成功响应
future.set_result(response.get("result"))
# 使用示例
async def demo_mcp_communication():
"""演示MCP通信流程"""
client = MCPClient()
# 创建工具调用请求
tool_request = client.create_request(
method="tools/call",
params={
"name": "calculator",
"arguments": {
"operation": "add",
"a": 10,
"b": 5
}
}
)
print("发送的工具调用请求:")
print(json.dumps(tool_request, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
# 模拟服务端响应
mock_response = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": tool_request["id"],
"result": {
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "计算结果: 10 + 5 = 15"
}
],
"isError": False
}
}
print("\n收到的响应:")
print(json.dumps(mock_response, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
# 运行演示
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(demo_mcp_communication())
4. 请求ID管理策略
4.1 ID生成方法对比
| 方法 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| UUID4 | 唯一性强,无冲突 | 长度较长 | 生产环境推荐 |
| 时间戳 | 简单,有序 | 高并发可能重复 | 低并发场景 |
| 递增数字 | 简短,易读 | 需要状态维护 | 调试环境 |
4.2 ID管理实现
class RequestIDManager:
"""请求ID管理器"""
def __init__(self, strategy="uuid"):
self.strategy = strategy
self.counter = 0
def generate_id(self) -> str:
"""根据策略生成请求ID"""
if self.strategy == "uuid":
return str(uuid.uuid4())
elif self.strategy == "timestamp":
return str(int(time.time() * 1000000)) # 微秒时间戳
elif self.strategy == "counter":
self.counter += 1
return str(self.counter)
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的ID策略: {self.strategy}")
# 使用示例
id_manager = RequestIDManager(strategy="uuid")
request_id = id_manager.generate_id()
print(f"生成的请求ID: {request_id}")
5. 方法名规范与参数传递
5.1 MCP标准方法命名规范
| 方法类别 | 命名格式 | 示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工具相关 | tools/* | tools/call, tools/list | 工具操作 |
| 资源相关 | resources/* | resources/read, resources/list | 资源管理 |
| 提示相关 | prompts/* | prompts/get, prompts/list | 提示模板 |
| 系统相关 | initialize, ping | initialize, ping | 系统级操作 |
5.2 参数传递最佳实践
def create_tool_call_request(tool_name: str, arguments: Dict[str, Any]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""创建工具调用请求的标准格式"""
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": str(uuid.uuid4()),
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": tool_name,
"arguments": arguments
}
}
def create_resource_read_request(uri: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""创建资源读取请求"""
return {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": str(uuid.uuid4()),
"method": "resources/read",
"params": {
"uri": uri
}
}
# 使用示例
tool_request = create_tool_call_request(
tool_name="file_reader",
arguments={"path": "/home/user/data.txt"}
)
resource_request = create_resource_read_request(
uri="file:///home/user/config.json"
)
6. 基础错误处理机制
6.1 标准错误代码
| 错误代码 | 含义 | 处理建议 |
|---|---|---|
| -32700 | 解析错误 | 检查JSON格式 |
| -32600 | 无效请求 | 检查请求结构 |
| -32601 | 方法未找到 | 确认方法名称 |
| -32602 | 无效参数 | 检查参数格式 |
| -32603 | 内部错误 | 联系服务端 |
6.2 错误处理实现
class MCPError(Exception):
"""MCP协议错误类"""
def __init__(self, code: int, message: str, data: Any = None):
self.code = code
self.message = message
self.data = data
super().__init__(f"MCP Error {code}: {message}")
def create_error_response(request_id: str, error_code: int, error_message: str, error_data: Any = None) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""创建错误响应"""
error_response = {
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": request_id,
"error": {
"code": error_code,
"message": error_message
}
}
if error_data:
error_response["error"]["data"] = error_data
return error_response
# 使用示例
error_response = create_error_response(
request_id="123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174000",
error_code=-32601,
error_message="Method not found",
error_data="The method 'unknown_method' is not supported"
)
print(json.dumps(error_response, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
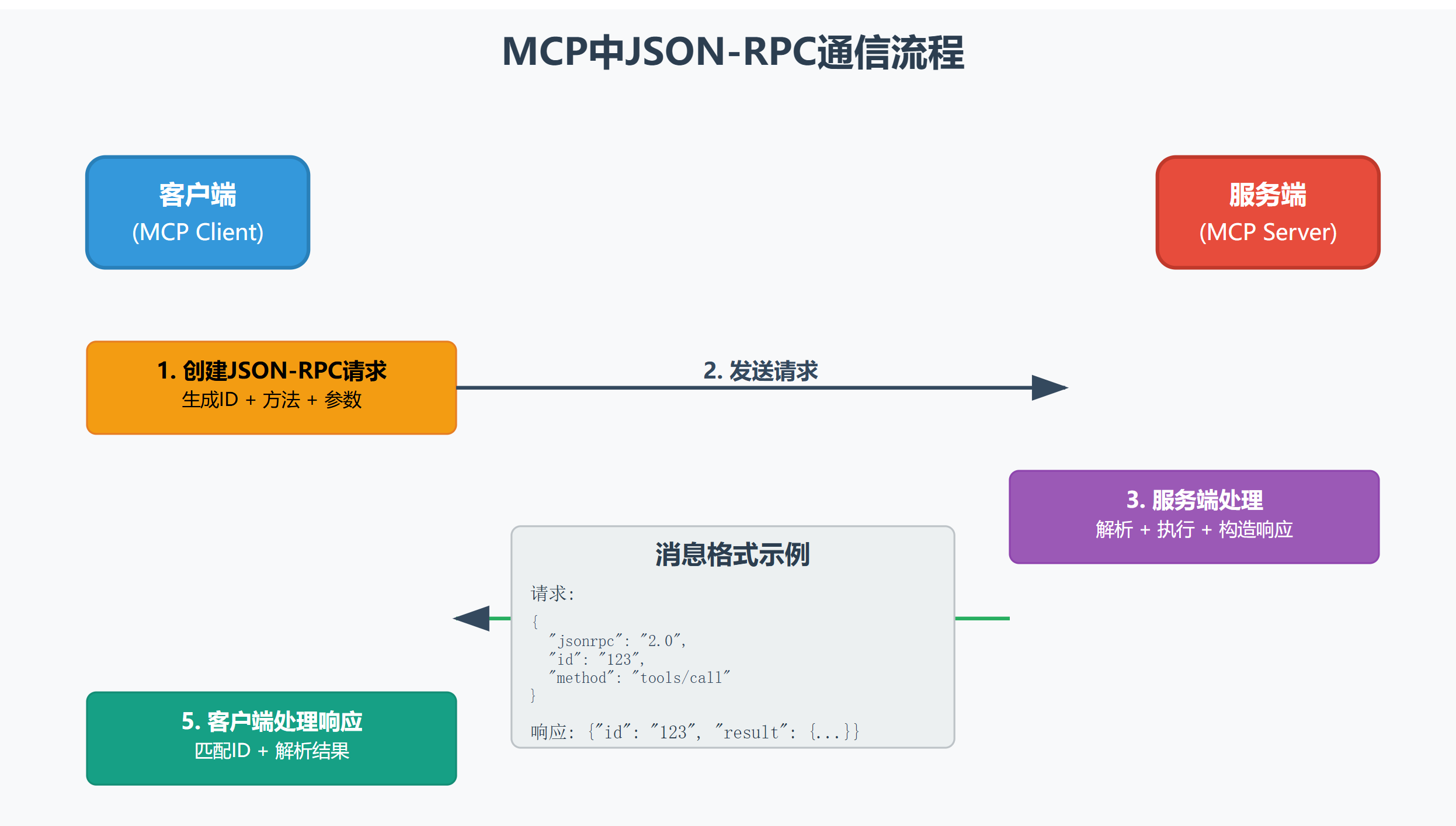
📚 第一部分要点回顾
这一部分我们重点学习了:
- JSON-RPC 2.0基础 - 理解了它就像程序界的"普通话"
- 标准消息格式 - 掌握了请求、响应、错误三种基本消息结构
- 实用代码示例 - 提供了可运行的Python MCP客户端实现
- ID管理策略 - 学会了UUID、时间戳、递增数字三种ID生成方法
- 方法名规范 - 了解了MCP中tools/*、resources/*等标准命名
- 错误处理机制 - 掌握了标准错误代码和处理方式
欢迎大家关注同名公众号《凡人的工具箱》:关注就送学习大礼包

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献53条内容
已为社区贡献53条内容









所有评论(0)