手写MyBatis第50弹:责任链模式在Executor包装中的精妙设计
摘要:本文深入解析MyBatis责任链插件机制,重点剖析其对Executor、StatementHandler等四大核心组件的智能包装过程。文章从Configuration配置中心出发,详细讲解InterceptorChain.pluginAll()方法实现的多层代理构建逻辑,揭示插件生效时机与执行顺序的底层原理。通过SQL执行监控、自动分页等实战案例,展示该机制在功能扩展中的应用价值,并提供性能
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我
🔥🔥🔥 文末有往期免费源码,直接领取获取(无删减,无套路)
目录
三、InterceptorChain.pluginAll():责任链包装的核心
-
"MyBatis核心机制解密:责任链插件如何智能包装SQL执行器"
-
"手写MyBatis源码:深度剖析责任链模式在Executor包装中的精妙设计"
-
"高性能MyBatis插件架构:责任链模式下的SQL执行器优化策略"
-
"从源码到实战:MyBatis四大组件责任链包装机制完全解析"
正文
在MyBatis框架的核心架构中,责任链插件机制是实现功能扩展和拦截的关键技术。今天我们将深入探讨MyBatis如何在SQL执行器创建过程中集成责任链模式,实现对Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler和ResultSetHandler四大核心组件的智能包装。
一、MyBatis四大核心组件概述
在深入责任链包装机制之前,我们需要先了解MyBatis的四大核心组件:
-
Executor:SQL执行的调度者,负责缓存管理、事务管理和SQL语句执行
-
StatementHandler:数据库语句处理器,负责PreparedStatement的创建和参数设置
-
ParameterHandler:参数处理器,负责将Java对象转换为JDBC参数
-
ResultSetHandler:结果集处理器,负责将JDBC结果集转换为Java对象
这四大组件构成了MyBatisSQL执行的核心流水线,而责任链插件机制正是在这个流水线的关键节点上插入扩展功能。
二、Configuration:插件管理的核心枢纽
Configuration类是MyBatis配置信息的总容器,也是插件管理的核心枢纽:
public class Configuration {
// 拦截器链,管理所有注册的插件
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
// 注册插件的方法
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
// 创建Executor实例的核心方法
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 启用二级缓存
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 关键步骤:通过拦截器链包装Executor
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
// 创建StatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement,
parameterObject, rowBounds,
resultHandler, boundSql);
// 通过拦截器链包装StatementHandler
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
// 创建ParameterHandler
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = new DefaultParameterHandler(mappedStatement,
parameterObject, boundSql);
// 通过拦截器链包装ParameterHandler
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
// 创建ResultSetHandler
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement,
RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement,
rowBounds, parameterHandler,
resultHandler, boundSql);
// 通过拦截器链包装ResultSetHandler
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
}三、InterceptorChain.pluginAll():责任链包装的核心
pluginAll()方法是责任链模式实现的关键,它负责将原始对象通过所有拦截器进行层层包装:
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
// 按照拦截器的注册顺序依次包装目标对象
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
}四、插件生效时机与包装过程
1. 对象创建时机
插件包装发生在四大组件的创建过程中,这是一个非常关键的设计选择:
-
初始化时创建:在Configuration初始化阶段创建基础组件
-
运行时包装:在每次创建组件实例时都会重新应用插件包装
-
动态性保证:支持运行期间动态添加或移除插件
2. 多层代理的构建过程
假设我们注册了三个拦截器:A、B、C,包装过程如下:
// 原始Executor
SimpleExecutor rawExecutor = new SimpleExecutor();
// 第一层包装:拦截器A
Executor executorA = interceptorA.plugin(rawExecutor);
// 第二层包装:拦截器B
Executor executorB = interceptorB.plugin(executorA);
// 第三层包装:拦截器C
Executor executorC = interceptorC.plugin(executorB);
// 最终返回多层代理的Executor
return executorC;3. 执行时的调用顺序
当调用被包装的Executor的方法时,执行顺序为:
-
拦截器C的前置处理
-
拦截器B的前置处理
-
拦截器A的前置处理
-
执行原始SimpleExecutor的方法
-
拦截器A的后置处理
-
拦截器B的后置处理
-
拦截器C的后置处理
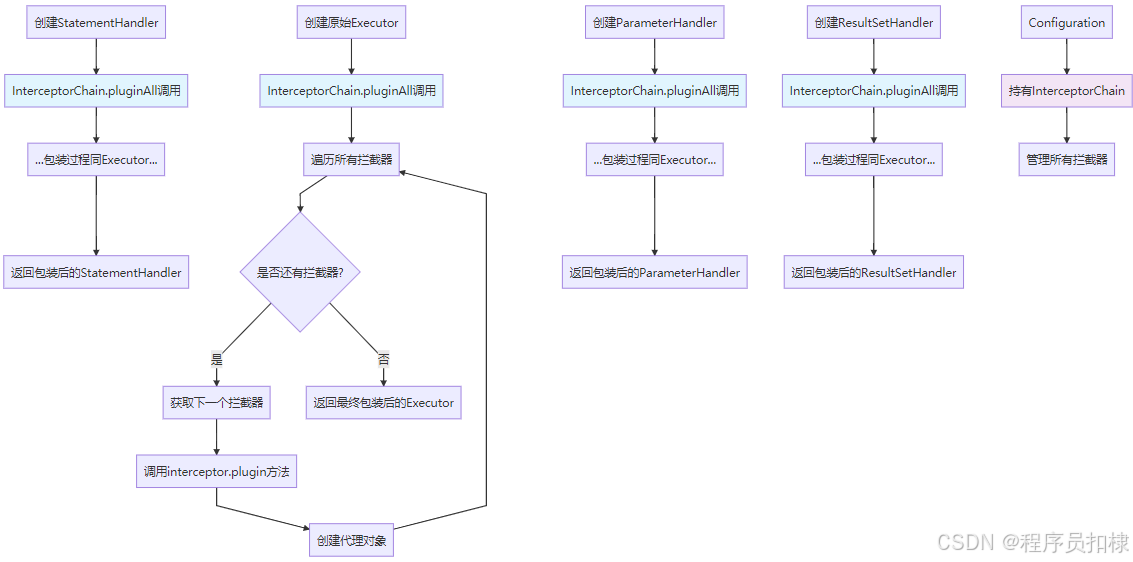
五、设计优势与精妙之处
1. 解耦设计
-
组件创建与插件管理分离:Configuration负责组件创建,InterceptorChain负责插件管理
-
插件间相互独立:每个插件只需要关注自己的功能,不需要知道其他插件的存在
2. 灵活扩展
-
动态插件管理:可以在运行时动态添加、移除或禁用插件
-
顺序可控:插件执行顺序由添加顺序决定,可以根据需要调整
3. 性能优化
-
按需包装:只有在真正需要时才创建代理对象
-
最小化影响:没有插件时直接返回原始对象,无额外开销
六、实战应用场景
1. SQL执行时间监控
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class SqlExecuteTimeInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return invocation.proceed();
} finally {
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("SQL执行时间: " + (end - start) + "ms");
}
}
}2. 自动分页处理
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})
})
public class PaginationInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
// 解析分页参数并重写SQL
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String originalSql = boundSql.getSql();
// 添加分页逻辑
String pagedSql = addPagination(originalSql);
// 通过反射修改SQL
Field field = boundSql.getClass().getDeclaredField("sql");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(boundSql, pagedSql);
return invocation.proceed();
}
}七、性能优化策略
1. 懒加载代理
对于不常用的插件,可以采用懒加载策略:
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
if (interceptor.isEnabled()) { // 添加启用状态检查
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
}
return target;
}2. 代理对象缓存
避免重复创建代理对象:
private final Map<Object, Object> proxyCache = new WeakHashMap<>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
if (proxyCache.containsKey(target)) {
return proxyCache.get(target);
}
Object result = target;
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
result = interceptor.plugin(result);
}
proxyCache.put(target, result);
return result;
}八、常见问题与解决方案
1. 插件执行顺序问题
问题:多个插件之间的执行顺序可能影响功能 解决方案:提供插件优先级配置机制
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor, int order) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
interceptors.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(Interceptor::getOrder));
}2. 循环代理问题
问题:插件可能错误地多次代理同一个对象 解决方案:添加代理检查机制
public Object plugin(Object target) {
if (isAlreadyProxied(target)) {
return target; // 避免重复代理
}
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}九、最佳实践建议
-
精确拦截:使用准确的@Signature定义,避免过度拦截
-
性能意识:在插件中避免昂贵的操作,特别是频繁调用的方法
-
异常处理:确保插件中的异常不会影响主要业务流程
-
状态管理:避免在插件中维护可变状态,保证线程安全
-
文档完善:为自定义插件提供详细的使用文档和示例
十、总结
MyBatis的责任链插件包装机制是其架构设计中的精华所在。通过在四大核心组件的创建过程中集成InterceptorChain.pluginAll()调用,MyBatis实现了高度灵活和可扩展的拦截机制。这种设计不仅保证了功能的强大性,还确保了系统的性能和稳定性。
理解这一机制的实现原理和设计思想,对于深入掌握MyBatis框架、开发高质量插件以及在其他项目中应用责任链模式都具有重要的指导意义。在实际开发中,我们应该充分利用这一机制的优势,同时注意避免其潜在的风险,从而构建出既灵活又稳定的系统架构。
往期免费源码 (无删减,无套路):🔥🔥🔥
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1sjAr08PU9Xe7MQf1gjGM5w?pwd=6666
「在线考试系统源码(含搭建教程)」 (无删减,无套路):🔥🔥🔥
链接:https://pan.quark.cn/s/96c4f00fdb43 提取码:WR6M
往期免费源码对应视频:
免费获取--SpringBoot+Vue宠物商城网站系统
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献17条内容
已为社区贡献17条内容








所有评论(0)