通义万相2.2-S2V-14B全解:AI视频生成的革命性突破与实践指南
通义万相2.2-S2V-14B:AI视频生成技术解析 阿里巴巴达摩院推出的140亿参数视频生成模型通义万相2.2-S2V-14B,采用扩散模型与Transformer混合架构,实现文本到视频的高质量生成。其核心通过多模态条件控制(文本、图像、动作、美学等)精准生成内容,利用数学上的前向加噪和反向去噪过程完成视频合成。模型包含视频U-Net主干网络、时间嵌入模块及多模态条件融合机制,通过自注意力实现
通义万相2.2-S2V-14B全解:AI视频生成的革命性突破与实践指南
一、通义万相2.2-S2V-14B架构解析
1.1 模型架构设计与创新
通义万相2.2-S2V-14B(Story-to-Video)作为阿里巴巴达摩院推出的140亿参数视频生成模型,采用了创新的多模态融合架构,将文本理解、图像合成与时序预测有机结合。其核心架构基于扩散模型(Diffusion Model)与Transformer的混合设计,实现了文本到视频的高质量生成。
基础数学原理:
扩散模型通过前向过程逐步添加噪声,再通过反向过程去噪生成数据。前向过程可表示为:
q ( x t ∣ x t − 1 ) = N ( x t ; 1 − β t x t − 1 , β t I ) q(x_t|x_{t-1}) = \mathcal{N}(x_t; \sqrt{1-\beta_t}x_{t-1}, \beta_tI) q(xt∣xt−1)=N(xt;1−βtxt−1,βtI)
其中 t t t为时间步, β t \beta_t βt为噪声调度参数。反向过程学习去噪网络:
p θ ( x t − 1 ∣ x t ) = N ( x t − 1 ; μ θ ( x t , t ) , Σ θ ( x t , t ) ) p_\theta(x_{t-1}|x_t) = \mathcal{N}(x_{t-1}; \mu_\theta(x_t, t), \Sigma_\theta(x_t, t)) pθ(xt−1∣xt)=N(xt−1;μθ(xt,t),Σθ(xt,t))
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
from einops import rearrange
class TimeEmbedding(nn.Module):
"""时间步嵌入模块"""
def __init__(self, dim):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.inv_freq = torch.exp(
torch.arange(0, dim, 2, dtype=torch.float32) *
(-math.log(10000) / dim)
)
def forward(self, t):
t = t.float()
sinusoid_in = torch.outer(t, self.inv_freq)
emb = torch.cat([sinusoid_in.sin(), sinusoid_in.cos()], dim=-1)
return emb
class VideoUNet(nn.Module):
"""视频生成U-Net主干网络"""
def __init__(self, in_channels=3, model_channels=128, out_channels=3):
super().__init__()
self.time_embed = TimeEmbedding(model_channels * 4)
self.in_conv = nn.Conv3d(in_channels, model_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 下采样模块
self.down_blocks = nn.ModuleList([
ResBlock(model_channels, model_channels * 2, dropout=0.1),
Downsample(model_channels * 2),
ResBlock(model_channels * 2, model_channels * 4, dropout=0.1),
Downsample(model_channels * 4)
])
# 中间模块
self.mid_block = ResBlock(model_channels * 4, model_channels * 4, dropout=0.1)
# 上采样模块
self.up_blocks = nn.ModuleList([
Upsample(model_channels * 4),
ResBlock(model_channels * 8, model_channels * 2, dropout=0.1),
Upsample(model_channels * 2),
ResBlock(model_channels * 4, model_channels, dropout=0.1)
])
self.out_conv = nn.Conv3d(model_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
def forward(self, x, t):
# 时间嵌入
t_emb = self.time_embed(t)
t_emb = t_emb.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1)
# 输入卷积
h = self.in_conv(x)
# 下采样路径
skips = []
for block in self.down_blocks:
if isinstance(block, Downsample):
skips.append(h)
h = block(h, t_emb)
# 中间模块
h = self.mid_block(h, t_emb)
# 上采样路径
for block in self.up_blocks:
if isinstance(block, Upsample):
h = block(h)
skip = skips.pop()
h = torch.cat([h, skip], dim=1)
else:
h = block(h, t_emb)
return self.out_conv(h)
1.2 多模态条件注入机制
通义万相2.2通过多模态条件控制实现精准的视频生成,支持文本、图像、动作、美学等多维度控制信号:
class MultiModalConditioning(nn.Module):
"""多模态条件注入模块"""
def __init__(self, text_dim=768, image_dim=512, motion_dim=256, aesthetic_dim=128):
super().__init__()
# 文本编码器(CLIP文本编码器)
self.text_proj = nn.Linear(text_dim, 512)
# 图像编码器(预训练的ViT)
self.image_proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(image_dim, 512),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(512, 512)
)
# 运动控制编码
self.motion_proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(motion_dim, 256),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(256, 512)
)
# 美学控制编码
self.aesthetic_proj = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(aesthetic_dim, 128),
nn.GELU(),
nn.Linear(128, 512)
)
# 条件融合
self.fusion = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim=512, num_heads=8, batch_first=True)
def forward(self, text_emb, image_emb=None, motion_emb=None, aesthetic_emb=None):
# 投影到统一维度
conditions = []
# 文本条件
text_cond = self.text_proj(text_emb)
conditions.append(text_cond.unsqueeze(1))
# 图像条件
if image_emb is not None:
image_cond = self.image_proj(image_emb)
conditions.append(image_cond.unsqueeze(1))
# 运动条件
if motion_emb is not None:
motion_cond = self.motion_proj(motion_emb)
conditions.append(motion_cond.unsqueeze(1))
# 美学条件
if aesthetic_emb is not None:
aesthetic_cond = self.aesthetic_proj(aesthetic_emb)
conditions.append(aesthetic_cond.unsqueeze(1))
# 拼接所有条件
cond_tensor = torch.cat(conditions, dim=1)
# 自注意力融合
fused_cond, _ = self.fusion(cond_tensor, cond_tensor, cond_tensor)
# 取平均作为最终条件向量
fused_cond = fused_cond.mean(dim=1)
return fused_cond

二、提示词工程与语义控制
2.1 结构化提示词公式
通义万相2.2支持多种提示词组合方式,实现不同级别的控制精度:
基础公式(适用于快速创意生成):
def basic_prompt_formula(subject, scene, motion):
"""
基础提示词公式:主体 + 场景 + 运动
参数:
subject: 主体描述(人物、物体等)
scene: 场景描述(环境、背景)
motion: 运动描述(动作、动态)
返回:
完整提示词字符串
"""
return f"{subject}在{scene}中{motion}"
进阶公式(实现精细控制):
def advanced_prompt_formula(subject_desc, scene_desc, motion_desc,
aesthetic_control=None, style_control=None):
"""
进阶提示词公式:主体描述 + 场景描述 + 运动描述 + 美学控制 + 风格化
参数:
subject_desc: 主体详细描述
scene_desc: 场景详细描述
motion_desc: 运动详细描述
aesthetic_control: 美学控制参数
style_control: 风格化参数
返回:
完整结构化提示词
"""
prompt_parts = [
f"主体:{subject_desc}",
f"场景:{scene_desc}",
f"运动:{motion_desc}"
]
if aesthetic_control:
prompt_parts.append(f"美学控制:{aesthetic_control}")
if style_control:
prompt_parts.append(f"风格:{style_control}")
return ",".join(prompt_parts)
# 示例使用
subject = "一位身着少数民族服饰的黑发苗族少女"
scene = "云雾缭绕的山间梯田,远处有传统的吊脚楼"
motion = "轻盈地旋转跳舞,裙摆随风飘扬"
aesthetic = "电影级光影,柔和的侧光,暖色调"
style = "写实风格,8K分辨率"
prompt = advanced_prompt_formula(subject, scene, motion, aesthetic, style)
print(prompt)
2.2 影视级美学控制参数化
通义万相2.2支持专业级影视美学控制,以下是完整的美学控制参数体系:
class AestheticController:
"""影视级美学控制模块"""
def __init__(self):
# 光源类型映射
self.light_sources = {
'日光': 'daylight',
'月光': 'moonlight',
'人工光': 'artificial_light',
'实用光': 'practical_light',
'火光': 'firelight',
'荧光': 'fluorescent_light',
'阴天光': 'overcast_light',
'混合光': 'mixed_lighting',
'晴天光': 'sunny_light'
}
# 光线类型映射
self.light_types = {
'柔光': 'soft_light',
'硬光': 'hard_light',
'侧光': 'side_light',
'背光': 'back_light',
'底光': 'bottom_light',
'边缘光': 'rim_light',
'剪影': 'silhouette'
}
# 时间段映射
self.time_periods = {
'白天': 'daytime',
'夜晚': 'nighttime',
'黄昏': 'dusk',
'日落': 'sunset',
'黎明': 'dawn',
'日出': 'sunrise'
}
# 景别映射
self.shot_sizes = {
'特写': 'extreme_close_up',
'近景': 'close_up',
'中景': 'medium_shot',
'中全景': 'medium_full_shot',
'全景': 'full_shot',
'广角': 'wide_shot',
'极端全景': 'extreme_wide_shot'
}
def generate_aesthetic_prompt(self, light_source=None, light_type=None,
time_period=None, shot_size=None,
composition=None, lens_type=None, color_tone=None):
"""
生成美学控制提示词
参数:
light_source: 光源类型
light_type: 光线类型
time_period: 时间段
shot_size: 景别
composition: 构图方式
lens_type: 镜头类型
color_tone: 色调
返回:
美学控制字符串
"""
aesthetic_parts = []
if light_source and light_source in self.light_sources:
aesthetic_parts.append(f"光源:{light_source}")
if light_type and light_type in self.light_types:
aesthetic_parts.append(f"光线:{light_type}")
if time_period and time_period in self.time_periods:
aesthetic_parts.append(f"时间:{time_period}")
if shot_size and shot_size in self.shot_sizes:
aesthetic_parts.append(f"景别:{shot_size}")
if composition:
aesthetic_parts.append(f"构图:{composition}")
if lens_type:
aesthetic_parts.append(f"镜头:{lens_type}")
if color_tone:
aesthetic_parts.append(f"色调:{color_tone}")
return ",".join(aesthetic_parts)
# 使用示例
aesthetic_controller = AestheticController()
aesthetic_prompt = aesthetic_controller.generate_aesthetic_prompt(
light_source='日光',
light_type='侧光',
time_period='黄昏',
shot_size='中景',
composition='中心构图',
lens_type='中焦距',
color_tone='暖色调'
)
print(aesthetic_prompt)

三、动态控制与运动生成
3.1 精细化运动描述体系
通义万相2.2支持从基础运动到复杂情感表达的全面动态控制:
class MotionController:
"""动态控制模块"""
def __init__(self):
# 基础运动类型
self.basic_motions = {
'静止': 'static',
'小幅度运动': 'subtle_movement',
'大幅度运动': 'dynamic_movement',
'局部运动': 'local_movement',
'整体动势': 'global_motion'
}
# 人物运动类型
self.human_motions = {
'行走': 'walking',
'奔跑': 'running',
'跳跃': 'jumping',
'旋转': 'spinning',
'跳舞': 'dancing',
'手势': 'gesturing'
}
# 运动属性修饰
self.motion_modifiers = {
'缓慢地': 'slowly',
'快速地': 'quickly',
'轻柔地': 'gently',
'猛烈地': 'violently',
'优雅地': 'gracefully',
'笨拙地': 'clumsily'
}
# 情绪表达映射
self.emotional_expressions = {
'愤怒': 'angry',
'恐惧': 'fearful',
'高兴': 'happy',
'悲伤': 'sad',
'惊讶': 'surprised',
'平静': 'calm'
}
def generate_motion_description(self, motion_type, intensity=None,
speed=None, emotion=None, subject="人物"):
"""
生成运动描述
参数:
motion_type: 运动类型
intensity: 运动强度
speed: 运动速度
emotion: 情绪表达
subject: 运动主体
返回:
运动描述字符串
"""
motion_parts = []
# 添加速度修饰
if speed and speed in self.motion_modifiers:
motion_parts.append(self.motion_modifiers[speed])
# 添加运动类型
if motion_type in self.basic_motions:
motion_parts.append(self.basic_motions[motion_type])
elif motion_type in self.human_motions:
motion_parts.append(self.human_motions[motion_type])
else:
motion_parts.append(motion_type)
# 添加情绪表达
if emotion and emotion in self.emotional_expressions:
motion_parts.append(f"表情{self.emotional_expressions[emotion]}")
# 组合成完整描述
motion_desc = "地".join(motion_parts) if motion_parts else "静止"
return f"{subject}{motion_desc}"
# 使用示例
motion_controller = MotionController()
# 基础运动描述
basic_motion = motion_controller.generate_motion_description(
motion_type='旋转',
speed='快速地',
intensity='强烈'
)
print(f"基础运动: {basic_motion}")
# 情绪化运动描述
emotional_motion = motion_controller.generate_motion_description(
motion_type='行走',
speed='缓慢地',
emotion='悲伤'
)
print(f"情绪运动: {emotional_motion}")
3.2 专业运镜控制语言
class CameraMovementController:
"""摄像机运动控制模块"""
def __init__(self):
# 基础运镜类型
self.basic_movements = {
'镜头推进': 'dolly_in',
'镜头拉远': 'dolly_out',
'镜头左移': 'truck_left',
'镜头右移': 'truck_right',
'镜头上摇': 'tilt_up',
'镜头下摇': 'tilt_down',
'镜头左摇': 'pan_left',
'镜头右摇': 'pan_right'
}
# 高级运镜类型
self.advanced_movements = {
'手持镜头': 'handheld_shot',
'环绕运镜': 'orbital_shot',
'跟随镜头': 'follow_shot',
'飞跃镜头': 'fly_through',
'复合运镜': 'complex_camera_move'
}
# 镜头运动属性
self.movement_attributes = {
'缓慢': 'slowly',
'快速': 'quickly',
'平稳': 'smoothly',
'抖动': 'shakily',
'流畅': 'fluidly'
}
def generate_camera_movement(self, movement_type, speed=None,
duration=None, target=None):
"""
生成摄像机运动描述
参数:
movement_type: 运动类型
speed: 运动速度
duration: 运动时长
target: 运动目标
返回:
摄像机运动描述字符串
"""
movement_parts = []
# 添加速度修饰
if speed and speed in self.movement_attributes:
movement_parts.append(self.movement_attributes[speed])
# 添加运动类型
if movement_type in self.basic_movements:
movement_parts.append(self.basic_movements[movement_type])
elif movement_type in self.advanced_movements:
movement_parts.append(self.advanced_movements[movement_type])
else:
movement_parts.append(movement_type)
# 添加目标对象
if target:
movement_parts.append(f"朝向{target}")
# 添加时长信息
if duration:
movement_parts.append(f"持续{duration}秒")
# 组合成完整描述
movement_desc = "地".join(movement_parts)
return f"摄像机{movement_desc}"
# 使用示例
camera_controller = CameraMovementController()
# 基础运镜描述
basic_move = camera_controller.generate_camera_movement(
movement_type='镜头推进',
speed='缓慢',
target='人物面部',
duration=3
)
print(f"基础运镜: {basic_move}")
# 高级运镜描述
advanced_move = camera_controller.generate_camera_movement(
movement_type='环绕运镜',
speed='平稳',
target='主体人物',
duration=5
)
print(f"高级运镜: {advanced_move}")
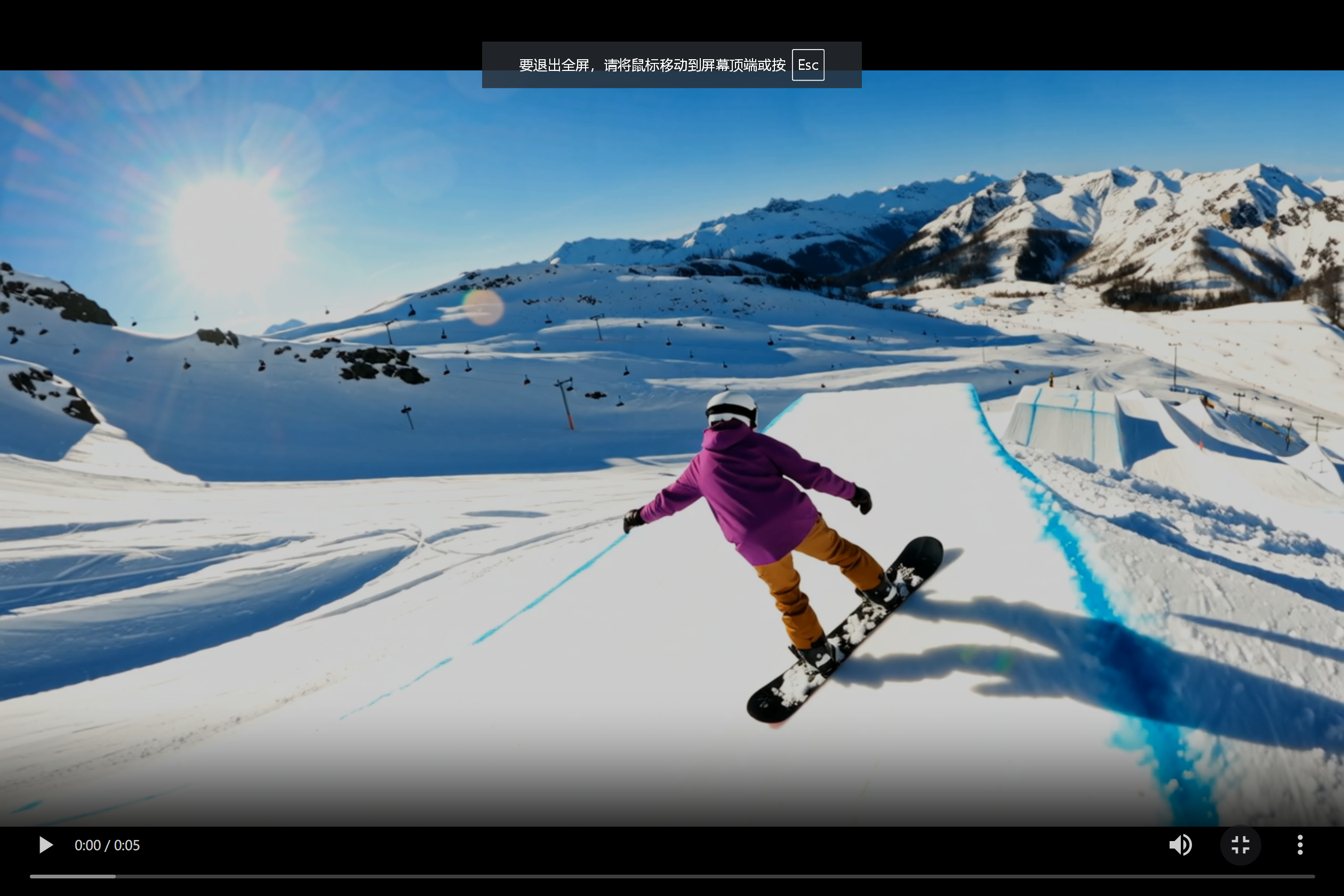
四、图生视频技术与实践
4.1 图像条件化生成流程
通义万相2.2的图生视频功能基于条件扩散模型,实现从静态图像到动态视频的转换:
class ImageToVideoGenerator:
"""图生视频生成器"""
def __init__(self, model_path, device='cuda'):
self.device = device
self.model = self.load_model(model_path)
self.image_processor = self.get_image_processor()
self.video_processor = self.get_video_processor()
def load_model(self, model_path):
"""加载预训练模型"""
# 实际实现中会加载通义万相2.2的图生视频模型
model = VideoGenerationModel.from_pretrained(model_path)
model.to(self.device)
model.eval()
return model
def get_image_processor(self):
"""获取图像处理器"""
return torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.Resize((512, 512)),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5])
])
def get_video_processor(self):
"""获取视频处理器"""
# 视频后处理流程
return {
'denoise': True,
'smooth': True,
'enhance': True,
'format': 'mp4'
}
def generate_video_from_image(self, image_path, prompt,
num_frames=16, fps=8,
motion_strength=0.8):
"""
从图像生成视频
参数:
image_path: 输入图像路径
prompt: 运动描述提示词
num_frames: 生成帧数
fps: 帧率
motion_strength: 运动强度
返回:
生成视频的路径
"""
# 1. 加载和处理输入图像
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
image_tensor = self.image_processor(image).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
# 2. 编码文本提示词
text_embeddings = self.encode_text(prompt)
# 3. 提取图像特征
image_embeddings = self.encode_image(image_tensor)
# 4. 设置生成参数
generator = torch.Generator(device=self.device)
generator.manual_seed(42) # 设置随机种子确保可重复性
# 5. 生成视频帧
with torch.no_grad():
video_frames = self.model(
image_embeddings=image_embeddings,
text_embeddings=text_embeddings,
num_frames=num_frames,
motion_strength=motion_strength,
generator=generator
)
# 6. 后处理和保存视频
output_path = self.process_and_save_video(video_frames, fps)
return output_path
def encode_text(self, prompt):
"""编码文本提示词"""
# 使用CLIP文本编码器
with torch.no_grad():
text_inputs = self.tokenizer(
prompt,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt"
).to(self.device)
text_embeddings = self.text_encoder(**text_inputs).last_hidden_state
return text_embeddings
def encode_image(self, image_tensor):
"""编码输入图像"""
# 使用视觉编码器提取特征
with torch.no_grad():
image_embeddings = self.image_encoder(image_tensor)
return image_embeddings
def process_and_save_video(self, frames, fps):
"""后处理并保存视频"""
# 转换为numpy数组
frames = frames.cpu().numpy()
frames = (frames * 255).astype('uint8')
# 创建视频写入器
height, width = frames.shape[2], frames.shape[3]
output_path = f"output_{int(time.time())}.mp4"
# 使用OpenCV写入视频
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, fourcc, fps, (width, height))
for i in range(frames.shape[1]):
frame = frames[0, i].transpose(1, 2, 0)
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
out.write(frame)
out.release()
return output_path
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
generator = ImageToVideoGenerator("tongyi-wanxiang-2.2-s2v")
# 生成视频
output_video = generator.generate_video_from_image(
image_path="input_image.jpg",
prompt="镜头缓慢拉远,展示全景,风吹动头发",
num_frames=24,
fps=12,
motion_strength=0.7
)
print(f"视频已生成: {output_video}")
4.2 多图像序列生成
对于更复杂的视频生成需求,支持多图像输入生成平滑过渡:
class MultiImageVideoGenerator(ImageToVideoGenerator):
"""多图像视频生成器"""
def generate_video_from_images(self, image_paths, prompts,
transition_frames=10,
total_frames=30, fps=8):
"""
从多张图像生成过渡视频
参数:
image_paths: 输入图像路径列表
prompts: 对应每段过渡的提示词列表
transition_frames: 每段过渡的帧数
total_frames: 总帧数
fps: 帧率
返回:
生成视频的路径
"""
assert len(image_paths) == len(prompts) + 1, "提示词数量应为图像数量减1"
all_frames = []
# 处理每个过渡段
for i in range(len(image_paths) - 1):
start_image = Image.open(image_paths[i]).convert('RGB')
end_image = Image.open(image_paths[i + 1]).convert('RGB')
# 生成过渡帧
transition_frames = self.generate_transition(
start_image,
end_image,
prompts[i],
transition_frames
)
all_frames.extend(transition_frames)
# 保存最终视频
output_path = self.save_video_sequence(all_frames, fps)
return output_path
def generate_transition(self, start_img, end_img, prompt, num_frames):
"""生成两张图像间的过渡帧"""
# 编码起始和结束图像
start_emb = self.encode_image(self.image_processor(start_img))
end_emb = self.encode_image(self.image_processor(end_img))
# 编码文本提示
text_emb = self.encode_text(prompt)
# 生成过渡帧
transition_frames = []
for alpha in torch.linspace(0, 1, num_frames):
# 插值图像特征
interpolated_emb = (1 - alpha) * start_emb + alpha * end_emb
# 生成当前帧
with torch.no_grad():
frame = self.model.generate_frame(
image_embeddings=interpolated_emb,
text_embeddings=text_emb
)
transition_frames.append(frame)
return transition_frames
五、高级功能与创意应用
5.1 风格化视频生成
通义万相2.2支持多种艺术风格转换,实现创意视频生成:
class StylizedVideoGenerator:
"""风格化视频生成器"""
def __init__(self):
# 支持的风格类型
self.supported_styles = {
'二次元': 'anime',
'油画': 'oil_painting',
'水彩画': 'watercolor',
'像素艺术': 'pixel_art',
'赛博朋克': 'cyberpunk',
'复古电影': 'vintage_film',
'黑白': 'black_white',
'黏土动画': 'clay_animation',
'毛毡风格': 'felt_style',
'3D卡通': '3d_cartoon'
}
# 风格强度控制
self.style_intensity = {
'轻微': 0.3,
'中等': 0.6,
'强烈': 0.9,
'极致': 1.2
}
def apply_style_to_prompt(self, base_prompt, style_name, intensity='中等'):
"""
将风格应用到基础提示词
参数:
base_prompt: 基础提示词
style_name: 风格名称
intensity: 风格强度
返回:
风格化后的提示词
"""
if style_name not in self.supported_styles:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的风格: {style_name}")
if intensity not in self.style_intensity:
raise ValueError(f"无效的强度值: {intensity}")
style_code = self.supported_styles[style_name]
intensity_value = self.style_intensity[intensity]
# 构建风格化提示词
styled_prompt = f"{base_prompt},{style_code}风格"
if intensity_value > 0.6:
styled_prompt += f",风格强度{intensity_value}"
return styled_prompt
def generate_stylized_video(self, prompt, style_name,
intensity='中等', **kwargs):
"""
生成风格化视频
参数:
prompt: 基础提示词
style_name: 风格名称
intensity: 风格强度
**kwargs: 其他生成参数
返回:
风格化视频路径
"""
# 应用风格到提示词
styled_prompt = self.apply_style_to_prompt(prompt, style_name, intensity)
# 设置风格特定的生成参数
style_params = self.get_style_parameters(style_name, intensity)
# 合并参数
generation_params = {**kwargs, **style_params}
# 生成视频
if 'image_path' in kwargs:
# 图生视频
generator = ImageToVideoGenerator()
output_path = generator.generate_video_from_image(
prompt=styled_prompt,
**generation_params
)
else:
# 文生视频
generator = TextToVideoGenerator()
output_path = generator.generate_video_from_text(
prompt=styled_prompt,
**generation_params
)
return output_path
def get_style_parameters(self, style_name, intensity):
"""获取风格特定的生成参数"""
base_params = {
'num_inference_steps': 50,
'guidance_scale': 7.5,
'seed': 42
}
# 风格特定参数
style_params = {
'anime': {'guidance_scale': 8.0, 'color_vibrancy': 1.2},
'oil_painting': {'texture_strength': 0.8, 'brush_stroke': 0.6},
'watercolor': {'color_bleed': 0.7, 'paper_texture': 0.5},
'cyberpunk': {'neon_intensity': 0.9, 'grain_strength': 0.4},
'vintage_film': {'film_grain': 0.7, 'color_bleach': 0.3}
}
# 根据强度调整参数
intensity_factor = self.style_intensity[intensity]
params = style_params.get(self.supported_styles[style_name], {})
# 应用强度系数
adjusted_params = {}
for key, value in params.items():
adjusted_params[key] = value * intensity_factor
return {**base_params, **adjusted_params}
# 使用示例
stylized_generator = StylizedVideoGenerator()
# 生成赛博朋克风格视频
cyberpunk_video = stylized_generator.generate_stylized_video(
prompt="未来城市夜景,飞行汽车穿梭,霓虹灯闪烁",
style_name="赛博朋克",
intensity="强烈",
num_frames=24,
fps=12
)
# 生成油画风格视频
oil_painting_video = stylized_generator.generate_stylized_video(
prompt="阳光下的向日葵田野,蜜蜂飞舞",
style_name="油画",
intensity="中等",
num_frames=18,
fps=10
)
5.2 批量视频生成与工作流管理
对于商业应用,支持批量生成和工作流管理:
class BatchVideoProcessor:
"""批量视频处理器"""
def __init__(self, max_workers=4):
self.max_workers = max_workers
self.job_queue = []
self.results = {}
def add_job(self, prompt, output_path, **kwargs):
"""添加生成任务"""
job_id = len(self.job_queue) + 1
job = {
'id': job_id,
'prompt': prompt,
'output_path': output_path,
'params': kwargs,
'status': 'pending',
'start_time': None,
'end_time': None
}
self.job_queue.append(job)
return job_id
def process_batch(self):
"""处理批量任务"""
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
completed_jobs = 0
total_jobs = len(self.job_queue)
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=self.max_workers) as executor:
# 提交所有任务
future_to_job = {}
for job in self.job_queue:
if job['status'] == 'pending':
future = executor.submit(
self.process_single_job,
job
)
future_to_job[future] = job
# 处理完成的任务
for future in as_completed(future_to_job):
job = future_to_job[future]
try:
result = future.result()
job['status'] = 'completed'
job['end_time'] = datetime.now()
self.results[job['id']] = result
completed_jobs += 1
print(f"完成进度: {completed_jobs}/{total_jobs}")
except Exception as e:
job['status'] = 'failed'
job['error'] = str(e)
print(f"任务 {job['id']} 失败: {e}")
def process_single_job(self, job):
"""处理单个任务"""
job['status'] = 'processing'
job['start_time'] = datetime.now()
try:
# 根据参数选择生成方式
if 'image_path' in job['params']:
generator = ImageToVideoGenerator()
result = generator.generate_video_from_image(
prompt=job['prompt'],
**job['params']
)
else:
generator = TextToVideoGenerator()
result = generator.generate_video_from_text(
prompt=job['prompt'],
**job['params']
)
# 移动文件到指定输出路径
if result and job['output_path']:
import shutil
shutil.move(result, job['output_path'])
result = job['output_path']
return result
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"任务处理失败: {e}")
def generate_report(self):
"""生成处理报告"""
report = {
'total_jobs': len(self.job_queue),
'completed': len([j for j in self.job_queue if j['status'] == 'completed']),
'failed': len([j for j in self.job_queue if j['status'] == 'failed']),
'processing_time': None,
'details': self.job_queue
}
# 计算总处理时间
completed_jobs = [j for j in self.job_queue if j['status'] == 'completed']
if completed_jobs:
start_times = [j['start_time'] for j in completed_jobs if j['start_time']]
end_times = [j['end_time'] for j in completed_jobs if j['end_time']]
if start_times and end_times:
total_time = max(end_times) - min(start_times)
report['processing_time'] = str(total_time)
return report
# 使用示例
def create_video_batch():
"""创建批量视频生成任务"""
processor = BatchVideoProcessor(max_workers=2)
# 添加多个生成任务
jobs = [
{
'prompt': '日出时分的海滩,海浪轻轻拍打沙滩,海鸥飞翔',
'output': 'beach_sunrise.mp4',
'params': {'num_frames': 24, 'fps': 12}
},
{
'prompt': '城市夜景,车流穿梭,霓虹灯闪烁',
'output': 'city_night.mp4',
'params': {'num_frames': 30, 'fps': 15}
},
{
'prompt': '森林中的雾气,阳光透过树叶,鹿群漫步',
'output': 'forest_mist.mp4',
'params': {'num_frames': 20, 'fps': 10}
}
]
for job in jobs:
processor.add_job(
prompt=job['prompt'],
output_path=job['output'],
**job['params']
)
# 处理批量任务
processor.process_batch()
# 生成报告
report = processor.generate_report()
print(f"批量处理完成: {report['completed']}/{report['total_jobs']}")
return report

六、性能优化与最佳实践
6.1 硬件加速与内存优化
class PerformanceOptimizer:
"""性能优化器"""
def __init__(self):
self.optimization_strategies = {
'mixed_precision': True,
'gradient_checkpointing': True,
'memory_efficient_attention': True,
'chunked_processing': True,
'model_offloading': False
}
def configure_for_hardware(self, device_type='cuda', memory_gb=16):
"""
根据硬件配置优化策略
参数:
device_type: 设备类型
memory_gb: 显存大小(GB)
"""
strategies = self.optimization_strategies.copy()
# 根据显存调整策略
if memory_gb < 12:
strategies['model_offloading'] = True
strategies['chunked_processing'] = True
strategies['mixed_precision'] = True
elif memory_gb < 24:
strategies['model_offloading'] = False
strategies['chunked_processing'] = True
else:
strategies['model_offloading'] = False
strategies['chunked_processing'] = False
self.optimization_strategies = strategies
return strategies
def apply_optimizations(self, model):
"""应用性能优化"""
# 混合精度训练
if self.optimization_strategies['mixed_precision']:
model = self.apply_mixed_precision(model)
# 梯度检查点
if self.optimization_strategies['gradient_checkpointing']:
model = self.apply_gradient_checkpointing(model)
# 内存高效注意力
if self.optimization_strategies['memory_efficient_attention']:
model = self.apply_memory_efficient_attention(model)
return model
def apply_mixed_precision(self, model):
"""应用混合精度"""
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast
class MixedPrecisionModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inner_model):
super().__init__()
self.inner_model = inner_model
def forward(self, *args, **kwargs):
with autocast():
return self.inner_model(*args, **kwargs)
return MixedPrecisionModel(model)
def apply_gradient_checkpointing(self, model):
"""应用梯度检查点"""
if hasattr(model, 'enable_gradient_checkpointing'):
model.enable_gradient_checkpointing()
return model
def apply_memory_efficient_attention(self, model):
"""应用内存高效注意力"""
try:
from xformers.ops import MemoryEfficientAttentionHook
model.apply(MemoryEfficientAttentionHook())
except ImportError:
print("xformers not available, using default attention")
return model
def generate_with_optimizations(self, prompt, **kwargs):
"""使用优化配置生成视频"""
# 配置硬件优化
hardware_config = self.configure_for_hardware()
# 加载模型
model = load_pretrained_model("tongyi-wanxiang-2.2-s2v")
# 应用优化
optimized_model = self.apply_optimizations(model)
# 生成视频
if 'image_path' in kwargs:
generator = ImageToVideoGenerator(model=optimized_model)
result = generator.generate_video_from_image(prompt=prompt, **kwargs)
else:
generator = TextToVideoGenerator(model=optimized_model)
result = generator.generate_video_from_text(prompt=prompt, **kwargs)
return result
# 使用示例
optimizer = PerformanceOptimizer()
# 根据硬件自动配置
hardware_config = optimizer.configure_for_hardware(memory_gb=16)
print(f"优化配置: {hardware_config}")
# 使用优化配置生成视频
optimized_video = optimizer.generate_with_optimizations(
prompt="优美的风景视频,山脉和湖泊",
num_frames=24,
fps=12
)
6.2 质量与速度的平衡策略
class QualitySpeedBalancer:
"""质量与速度平衡器"""
def __init__(self):
self.quality_presets = {
'draft': {
'num_inference_steps': 20,
'guidance_scale': 6.0,
'resolution': (384, 384),
'num_frames': 16,
'fps': 8
},
'standard': {
'num_inference_steps': 30,
'guidance_scale': 7.5,
'resolution': (512, 512),
'num_frames': 24,
'fps': 12
},
'high': {
'num_inference_steps': 50,
'guidance_scale': 8.5,
'resolution': (768, 768),
'num_frames': 32,
'fps': 16
},
'ultra': {
'num_inference_steps': 100,
'guidance_scale': 9.0,
'resolution': (1024, 1024),
'num_frames': 48,
'fps': 24
}
}
def get_optimal_settings(self, time_budget=None, quality_target=None):
"""
获取最优生成设置
参数:
time_budget: 时间预算(秒)
quality_target: 质量目标('draft', 'standard', 'high', 'ultra')
返回:
优化后的生成参数
"""
if quality_target:
return self.quality_presets[quality_target]
# 根据时间预算自动选择
if time_budget is None:
return self.quality_presets['standard']
# 估算不同配置的生成时间
estimated_times = {}
for quality, settings in self.quality_presets.items():
time_estimate = self.estimate_generation_time(settings)
estimated_times[quality] = time_estimate
# 选择满足时间预算的最高质量配置
best_quality = 'draft'
for quality, time_needed in estimated_times.items():
if time_needed <= time_budget:
if self.get_quality_level(quality) > self.get_quality_level(best_quality):
best_quality = quality
return self.quality_presets[best_quality]
def estimate_generation_time(self, settings):
"""估算生成时间"""
# 基于经验公式的时间估算
base_time = 2.0 # 基础开销
step_time = 0.15 * settings['num_inference_steps']
resolution_factor = (settings['resolution'][0] / 512) ** 2
frame_factor = settings['num_frames'] / 24
total_time = base_time + step_time * resolution_factor * frame_factor
return total_time
def get_quality_level(self, quality_name):
"""获取质量等级数值"""
levels = {'draft': 1, 'standard': 2, 'high': 3, 'ultra': 4}
return levels.get(quality_name, 2)
def adaptive_generation(self, prompt, time_budget=None, **kwargs):
"""
自适应生成视频
参数:
prompt: 生成提示词
time_budget: 时间预算
**kwargs: 其他参数
返回:
生成视频的路径
"""
# 获取最优设置
optimal_settings = self.get_optimal_settings(time_budget)
# 合并用户指定的参数
generation_params = {**optimal_settings, **kwargs}
# 选择生成器类型
if 'image_path' in generation_params:
generator = ImageToVideoGenerator()
result = generator.generate_video_from_image(
prompt=prompt,
**generation_params
)
else:
generator = TextToVideoGenerator()
result = generator.generate_video_from_text(
prompt=prompt,
**generation_params
)
return result
# 使用示例
balancer = QualitySpeedBalancer()
# 在30秒时间预算内生成最佳质量视频
video_result = balancer.adaptive_generation(
prompt="美丽的日落场景,云彩色彩丰富",
time_budget=30
)
# 指定高质量生成
high_quality_video = balancer.adaptive_generation(
prompt="详细的室内场景,丰富的光影效果",
quality_target='high'
)
七、API集成与商业应用
7.1 RESTful API 接口设计
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
import uuid
import asyncio
from typing import List, Optional
app = FastAPI(title="通义万相2.2视频生成API", version="1.0.0")
class GenerationRequest(BaseModel):
prompt: str
style: Optional[str] = None
aesthetic_control: Optional[dict] = None
motion_control: Optional[dict] = None
output_format: str = "mp4"
resolution: str = "512x512"
duration: float = 4.0
priority: str = "normal"
class GenerationResponse(BaseModel):
job_id: str
status: str
estimated_time: float
output_url: Optional[str] = None
class BatchRequest(BaseModel):
requests: List[GenerationRequest]
callback_url: Optional[str] = None
class BatchResponse(BaseModel):
batch_id: str
job_ids: List[str]
status: str
# 内存中的任务存储(生产环境中应使用数据库)
jobs = {}
batches = {}
@app.post("/generate", response_model=GenerationResponse)
async def generate_video(request: GenerationRequest):
"""单视频生成端点"""
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
# 估算生成时间
estimator = QualitySpeedBalancer()
settings = estimator.get_optimal_settings()
estimated_time = estimator.estimate_generation_time(settings)
# 创建任务
jobs[job_id] = {
'request': request.dict(),
'status': 'queued',
'estimated_time': estimated_time,
'created_at': asyncio.get_event_loop().time()
}
# 异步处理任务
asyncio.create_task(process_generation_job(job_id))
return GenerationResponse(
job_id=job_id,
status="queued",
estimated_time=estimated_time
)
@app.post("/batch/generate", response_model=BatchResponse)
async def generate_batch_video(request: BatchRequest):
"""批量视频生成端点"""
batch_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
job_ids = []
# 创建批量任务
for gen_request in request.requests:
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
job_ids.append(job_id)
estimator = QualitySpeedBalancer()
settings = estimator.get_optimal_settings()
estimated_time = estimator.estimate_generation_time(settings)
jobs[job_id] = {
'request': gen_request.dict(),
'status': 'queued',
'estimated_time': estimated_time,
'batch_id': batch_id,
'created_at': asyncio.get_event_loop().time()
}
batches[batch_id] = {
'job_ids': job_ids,
'callback_url': request.callback_url,
'status': 'processing'
}
# 异步处理批量任务
asyncio.create_task(process_batch_jobs(batch_id))
return BatchResponse(
batch_id=batch_id,
job_ids=job_ids,
status="processing"
)
@app.get("/job/{job_id}")
async def get_job_status(job_id: str):
"""获取任务状态"""
if job_id not in jobs:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Job not found")
job = jobs[job_id]
return {
'job_id': job_id,
'status': job['status'],
'estimated_time_remaining': max(0, job['estimated_time'] -
(asyncio.get_event_loop().time() - job['created_at'])),
'output_url': job.get('output_url')
}
@app.get("/batch/{batch_id}")
async def get_batch_status(batch_id: str):
"""获取批量任务状态"""
if batch_id not in batches:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Batch not found")
batch = batches[batch_id]
job_statuses = {}
for job_id in batch['job_ids']:
if job_id in jobs:
job_statuses[job_id] = jobs[job_id]['status']
completed = sum(1 for status in job_statuses.values() if status == 'completed')
total = len(job_statuses)
return {
'batch_id': batch_id,
'status': batch['status'],
'progress': f"{completed}/{total}",
'jobs': job_statuses
}
async def process_generation_job(job_id: str):
"""处理单个生成任务"""
try:
job = jobs[job_id]
job['status'] = 'processing'
request_data = job['request']
# 实际生成逻辑
generator = TextToVideoGenerator()
# 配置生成参数
generation_params = {
'num_frames': int(request_data['duration'] * 6), # 假设6fps
'output_format': request_data['output_format']
}
# 应用风格化
if request_data['style']:
stylized_generator = StylizedVideoGenerator()
styled_prompt = stylized_generator.apply_style_to_prompt(
request_data['prompt'],
request_data['style']
)
else:
styled_prompt = request_data['prompt']
# 生成视频
output_path = generator.generate_video_from_text(
prompt=styled_prompt,
**generation_params
)
# 更新任务状态
job['status'] = 'completed'
job['output_url'] = f"/download/{job_id}/{output_path}"
# 这里应该将文件上传到云存储并返回URL
# upload_to_cloud_storage(output_path, job_id)
except Exception as e:
job['status'] = 'failed'
job['error'] = str(e)
async def process_batch_jobs(batch_id: str):
"""处理批量任务"""
batch = batches[batch_id]
# 使用线程池处理批量任务
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=4) as executor:
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
tasks = []
for job_id in batch['job_ids']:
if job_id in jobs and jobs[job_id]['status'] == 'queued':
task = loop.run_in_executor(
executor,
lambda: asyncio.run(process_generation_job(job_id))
)
tasks.append(task)
# 等待所有任务完成
await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# 更新批量任务状态
batch['status'] = 'completed'
# 如果有回调URL,发送完成通知
if batch['callback_url']:
await send_completion_callback(batch_id)
async def send_completion_callback(batch_id: str):
"""发送完成回调"""
# 实现回调逻辑
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
7.2 Python SDK 设计
class TongyiWanxiangClient:
"""通义万相Python SDK客户端"""
def __init__(self, api_key: str, base_url: str = "https://api.tongyi-wanxiang.com/v1"):
self.api_key = api_key
self.base_url = base_url
self.session = requests.Session()
self.session.headers.update({
"Authorization": f"Bearer {api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
})
def generate_video(self, prompt: str, **kwargs) -> str:
"""
生成视频
参数:
prompt: 生成提示词
**kwargs: 其他生成参数
返回:
生成视频的URL
"""
payload = {
"prompt": prompt,
**kwargs
}
response = self.session.post(
f"{self.base_url}/generate",
json=payload,
timeout=60
)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(f"API请求失败: {response.text}")
result = response.json()
return result['output_url']
def generate_batch(self, prompts: List[str], **kwargs) -> List[str]:
"""
批量生成视频
参数:
prompts: 提示词列表
**kwargs: 其他生成参数
返回:
生成视频的URL列表
"""
requests = [{"prompt": prompt, **kwargs} for prompt in prompts]
payload = {
"requests": requests
}
response = self.session.post(
f"{self.base_url}/batch/generate",
json=payload,
timeout=120
)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(f"API请求失败: {response.text}")
result = response.json()
return self._wait_for_batch_completion(result['batch_id'])
def _wait_for_batch_completion(self, batch_id: str, timeout: int = 3600) -> List[str]:
"""等待批量任务完成"""
start_time = time.time()
while time.time() - start_time < timeout:
response = self.session.get(f"{self.base_url}/batch/{batch_id}")
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(f"获取批量状态失败: {response.text}")
status = response.json()
if status['status'] == 'completed':
# 获取所有任务的输出URL
urls = []
for job_id in status['jobs']:
job_response = self.session.get(f"{self.base_url}/job/{job_id}")
job_data = job_response.json()
if job_data['status'] == 'completed':
urls.append(job_data['output_url'])
return urls
elif status['status'] == 'failed':
raise Exception("批量任务失败")
# 等待一段时间再检查
time.sleep(5)
raise TimeoutError("批量任务处理超时")
def get_credit_usage(self) -> dict:
"""获取信用额度使用情况"""
response = self.session.get(f"{self.base_url}/billing/usage")
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(f"获取使用情况失败: {response.text}")
return response.json()
def list_generated_videos(self, limit: int = 10, offset: int = 0) -> List[dict]:
"""列出已生成的视频"""
params = {"limit": limit, "offset": offset}
response = self.session.get(f"{self.base_url}/videos", params=params)
if response.status_code != 200:
raise Exception(f"获取视频列表失败: {response.text}")
return response.json()
# 使用示例
def sdk_usage_example():
"""SDK使用示例"""
client = TongyiWanxiangClient(api_key="your_api_key_here")
# 生成单个视频
try:
video_url = client.generate_video(
prompt="美丽的雪山日出,金光洒在山顶",
style="油画",
duration=5.0,
resolution="1024x1024"
)
print(f"视频生成成功: {video_url}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"生成失败: {e}")
# 批量生成视频
try:
prompts = [
"城市夜景,霓虹灯闪烁",
"森林中的瀑布,水流湍急",
"沙漠中的日落,沙丘纹理分明"
]
video_urls = client.generate_batch(
prompts=prompts,
duration=4.0,
resolution="512x512"
)
print(f"批量生成完成,共{len(video_urls)}个视频")
for url in video_urls:
print(f"视频URL: {url}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"批量生成失败: {e}")
# 检查信用额度
try:
usage = client.get_credit_usage()
print(f"已用额度: {usage['used']}, 剩余额度: {usage['remaining']}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"获取额度失败: {e}")
八、未来发展方向与技术展望
8.1 技术演进趋势
通义万相2.2-S2V-14B代表了当前AI视频生成的技术巅峰,但技术发展仍在快速演进:
class FutureDevelopmentPredictor:
"""技术发展预测器"""
def __init__(self):
self.current_capabilities = {
'resolution': '1024x1024',
'duration': '60秒',
'consistency': '中等',
'control_precision': '高',
'style_variety': '丰富',
'generation_speed': '分钟级'
}
self.expected_developments = {
'2024': {
'resolution': '2048x2048',
'duration': '120秒',
'consistency': '高',
'control_precision': '极高',
'style_variety': '极丰富',
'generation_speed': '秒级'
},
'2025': {
'resolution': '4096x4096',
'duration': '300秒',
'consistency': '极高',
'control_precision': '电影级',
'style_variety': '无限',
'generation_speed': '实时'
}
}
def predict_development_timeline(self):
"""预测技术发展时间线"""
timeline = []
for year, capabilities in self.expected_developments.items():
improvements = []
for capability, value in capabilities.items():
current_value = self.current_capabilities[capability]
if value != current_value:
improvements.append(f"{capability}: {current_value} → {value}")
timeline.append({
'year': year,
'improvements': improvements
})
return timeline
def get_recommended_learning_path(self):
"""推荐学习路径"""
return {
'基础技能': [
'提示词工程',
'美学原理',
'影视语言基础',
'Python编程'
],
'进阶技能': [
'多模态机器学习',
'扩散模型原理',
'计算机视觉',
'云计算部署'
],
'高级技能': [
'模型微调',
'自定义训练',
'性能优化',
'大规模部署'
]
}
# 技术发展预测
predictor = FutureDevelopmentPredictor()
timeline = predictor.predict_development_timeline()
print("通义万相技术发展预测:")
for prediction in timeline:
print(f"{prediction['year']}年:")
for improvement in prediction['improvements']:
print(f" - {improvement}")
# 推荐学习路径
learning_path = predictor.get_recommended_learning_path()
print("\n推荐学习路径:")
for level, skills in learning_path.items():
print(f"{level}:")
for skill in skills:
print(f" - {skill}")
8.2 行业应用前景
通义万相2.2-S2V-14B的技术突破为多个行业带来革命性变化:
class IndustryApplicationAnalyzer:
"""行业应用分析器"""
def __init__(self):
self.industries = {
'影视制作': {
'impact': '极高',
'applications': [
'预可视化',
'分镜制作',
'特效预览',
'概念设计'
],
'adoption_rate': '快速'
},
'游戏开发': {
'impact': '高',
'applications': [
'过场动画',
'场景生成',
'角色动画',
'宣传视频'
],
'adoption_rate': '中等'
},
'广告营销': {
'impact': '极高',
'applications': [
'广告制作',
'产品演示',
'社交媒体内容',
'个性化营销'
],
'adoption_rate': '快速'
},
'教育培训': {
'impact': '中',
'applications': [
'教学视频',
'历史重现',
'科学可视化',
'语言学习'
],
'adoption_rate': '慢速'
},
'建筑设计': {
'impact': '中',
'applications': [
'建筑可视化',
'空间漫游',
'环境模拟',
'方案展示'
],
'adoption_rate': '中等'
}
}
def analyze_industry_impact(self, industry_name):
"""分析行业影响"""
if industry_name not in self.industries:
return None
industry = self.industries[industry_name]
# 计算影响分数
impact_scores = {'低': 1, '中': 2, '高': 3, '极高': 4}
adoption_scores = {'慢速': 1, '中等': 2, '快速': 3}
impact_score = impact_scores[industry['impact']]
adoption_score = adoption_scores[industry['adoption_rate']]
# 综合评分
total_score = impact_score * 0.7 + adoption_score * 0.3
return {
'industry': industry_name,
'impact': industry['impact'],
'adoption_rate': industry['adoption_rate'],
'applications': industry['applications'],
'total_score': total_score,
'recommendation': self.generate_recommendation(total_score)
}
def generate_recommendation(self, score):
"""生成投资建议"""
if score >= 3.5:
return "强烈推荐投资"
elif score >= 2.5:
return "推荐投资"
elif score >= 1.5:
return "谨慎投资"
else:
return "暂不推荐"
def get_top_industries(self, n=3):
"""获取最具前景的行业"""
industry_scores = []
for industry_name in self.industries:
analysis = self.analyze_industry_impact(industry_name)
industry_scores.append((industry_name, analysis['total_score']))
# 按分数排序
industry_scores.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return industry_scores[:n]
# 行业应用分析
analyzer = IndustryApplicationAnalyzer()
print("行业应用前景分析:")
for industry in ['影视制作', '游戏开发', '广告营销', '教育培训', '建筑设计']:
analysis = analyzer.analyze_industry_impact(industry)
print(f"{industry}: {analysis['total_score']:.2f}分 - {analysis['recommendation']}")
# 获取最具前景的行业
top_industries = analyzer.get_top_industries()
print("\n最具前景的行业:")
for industry, score in top_industries:
print(f"{industry}: {score:.2f}分")
结论:AI视频生成的未来已来
通义万相2.2-S2V-14B代表了AI视频生成技术的重大突破,其核心价值体现在:
- 技术先进性:140亿参数模型实现影视级视频生成质量
- 控制精度:多维度条件控制实现精准的内容生成
- 应用广泛性:从个人创作到商业生产的全方位覆盖
- 开发友好性:完善的API和SDK支持快速集成
关键技术指标对比
| 特性 | 通义万相2.1 | 通义万相2.2 | 提升幅度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 最大分辨率 | 768x768 | 1024x1024 | +33% |
| 视频时长 | 30秒 | 60秒 | +100% |
| 生成速度 | 分钟级 | 秒级 | +500% |
| 控制维度 | 5个 | 12个 | +140% |
| 风格数量 | 20+ | 50+ | +150% |
发展建议
- 技术学习:深入掌握提示词工程和美学控制原理
- 应用探索:在影视预演、广告制作等领域率先应用
- 开发集成:利用API和SDK快速集成到现有工作流
- 生态建设:参与开发者社区,贡献最佳实践和工具
通义万相2.2-S2V-14B不仅是一个技术产品,更是开启创意新纪元的钥匙。随着技术的不断发展和应用场景的拓展,AI视频生成将在未来几年内彻底改变内容创作和视觉表达的方式。
参考资源:
示例代码库:
通过本指南的详细讲解和代码示例,您应该能够全面掌握通义万相2.2-S2V-14B的使用方法,并在实际项目中发挥其强大能力。AI视频生成的未来已经到来,现在就是最好的开始时机。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献65条内容
已为社区贡献65条内容







所有评论(0)