【LangChain RAG从零学】Routing
【LangChain RAG从零学】Routing
·
前言
- 该篇为【LangChain RAG从零学】的第三章,旨在记录学习RAG的过程
Routing
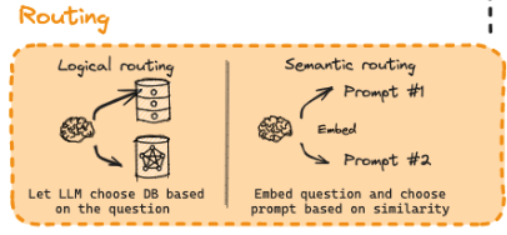
- 在检索增强生成系统中,Routing(路由)扮演着至关重要的“智能导航员”的功能
- 它是一个决策过程,负责分析用户的输入问题,并将其导向最合适的数据源、处理路径或LLM模型
- 当RAG系统需要从多个选项中做出选择时,路由机制便会介入,确保用户的请求得到最高效、最准确的处理
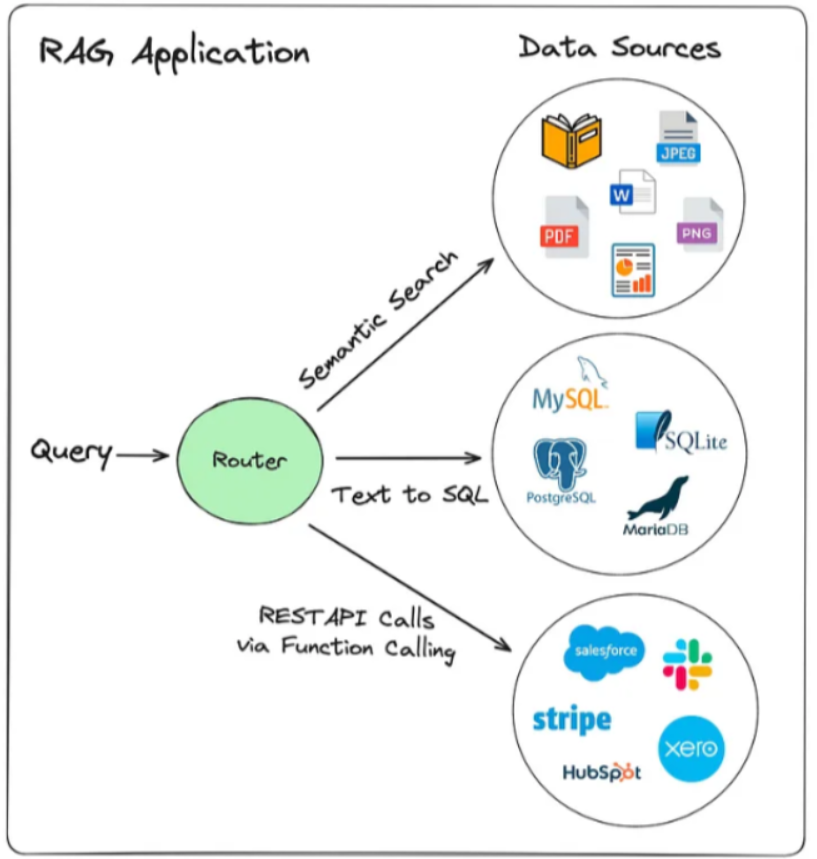
- 一个基础的RAG系统通常只有一个知识库和语言模型,这不仅会导致使用强大语言模型的成本浪费同时准确度也会下降
- 复杂真实的场景中:信息可能分布在不同的数据库、文档库或者API或知识图谱中;多样化的问题需要不同的检索方式
Logic routing
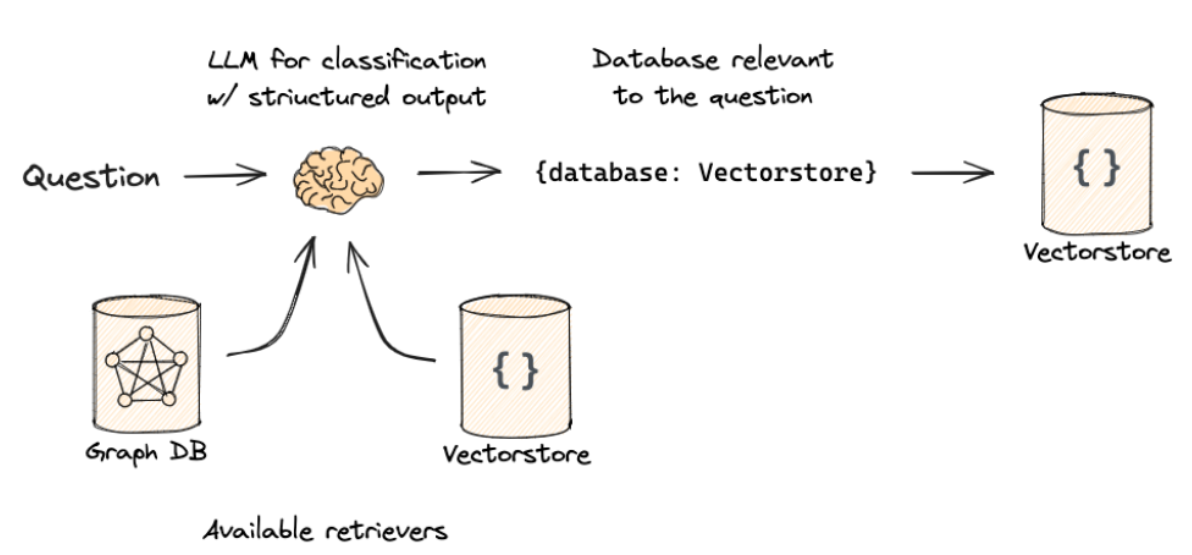
- 函数式调用路由将Routing这个任务转换为模型的函数调用,让LLM根据用户的提问选择调用哪个函数
- 核心机制为:LLM的受控推理和结构化输出能力
代码实现
from typing import Literal
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
# Data Model
class RouteQuery(BaseModel):
# 定义查询类型
datasource: Literal["python_docs","js_docs","golang_docs"]=Field(
...,
description="Given a user question choose which datasource would be most relevant for answering their question",
)
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-1.5-flash", temperature=0)
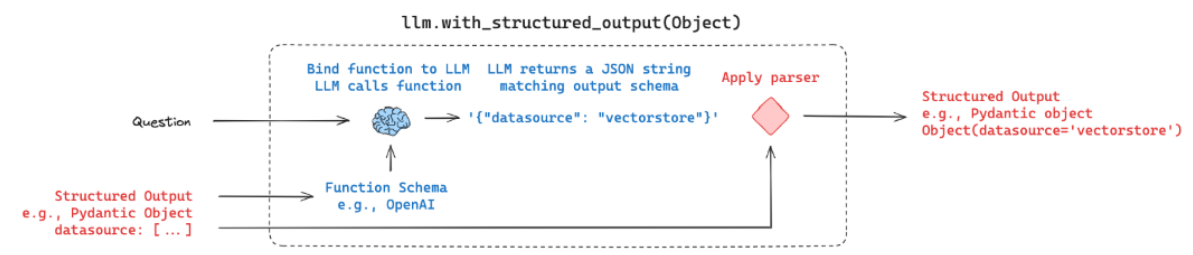
# 结构化调用
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(RouteQuery)
# 提示词
system = """You are an expert at routing a user question to the appropriate data source.
Based on the programming language the question is referring to, route it to the relevant data source."""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system),
("human", "{question}"),
])
router = prompt | structured_llm
- 展示路由
question = """Why doesn't the following code work:
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(["human", "speak in {language}"])
prompt.invoke("french")
"""
result = router.invoke({"question": question})
输出:RouteQuery(datasource='python_docs')
- 模拟后续工具调用
# 模拟Tool Calling
def choose_route(result):
if "python_docs" in result.datasource.lower():
### Logic here
return "chain for python_docs"
elif "js_docs" in result.datasource.lower():
### Logic here
return "chain for js_docs"
else:
### Logic here
return "golang_docs"
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda
# 延长chain
full_chain = router | RunnableLambda(choose_route)
full_chain.invoke({"question": question})
输出:chain for python_docs
Semantic Routing
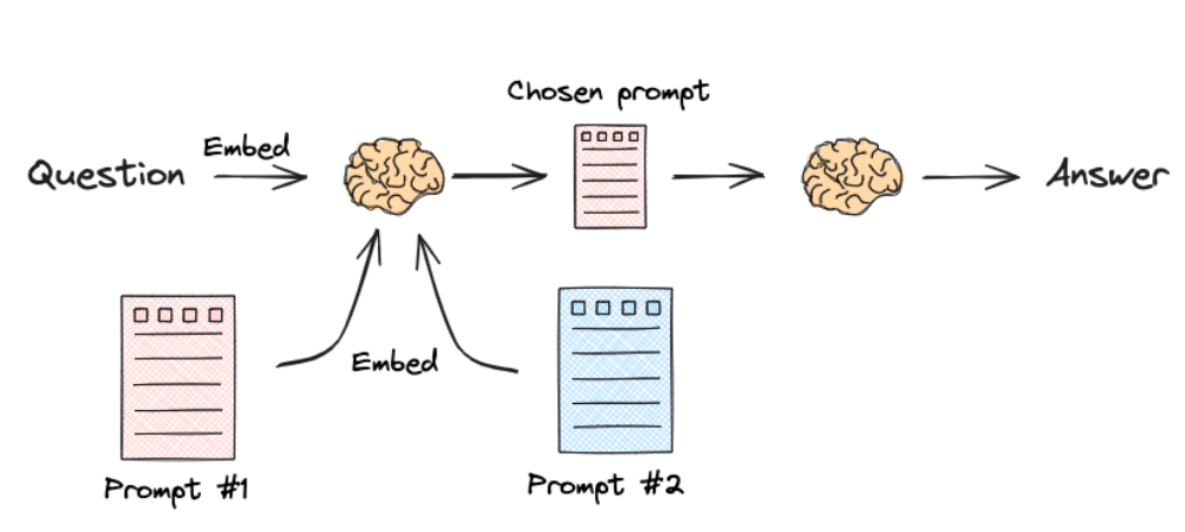
- 这种路由方式将问题转换为一个数学上的距离问题:不依赖于LLM进行实时决策而是通过比较文本向量在嵌入空间中的接近程度来判断相关性
- 核心机制:嵌入模型和向量相似度
- 嵌入模型的调用比大模型便宜但对语义描述的丰富度有要求
代码实现
from langchain.utils.math import cosine_similarity
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda, RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI, GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings
# Two prompts
physics_template = """You are a very smart physics professor. \
You are great at answering questions about physics in a concise and easy to understand manner. \
When you don't know the answer to a question you admit that you don't know.
Here is a question:
{query}"""
math_template = """You are a very good mathematician. You are great at answering math questions. \
You are so good because you are able to break down hard problems into their component parts, \
answer the component parts, and then put them together to answer the broader question.
Here is a question:
{query}"""
# Embed prompts
embeddings = GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings(model="models/text-embedding-004")
prompt_templates = [physics_template, math_template]
prompt_embeddings = embeddings.embed_documents(prompt_templates)
# Route question to prompt
def prompt_router(input):
# Embed question
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query(input["query"])
# Compute similarity
similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], prompt_embeddings)[0]
most_similar = prompt_templates[similarity.argmax()]
# Chosen prompt
print("Using MATH" if most_similar == math_template else "Using PHYSICS")
return PromptTemplate.from_template(most_similar)
chain = (
{"query": RunnablePassthrough()}
| RunnableLambda(prompt_router)
| ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-1.5-flash", temperature=0)
| StrOutputParser()
)
print(chain.invoke("What's a black hole"))
输出:Using PHYSICS
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. It's formed when a massive star collapses at the end of its life, its matter compressed into an incredibly dense point called a singularity. The boundary beyond which escape is impossible is called the event horizon.
参考文献
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容






所有评论(0)