基于通义千问的智能体构建
Qwen-Agent是基于通义千问模型的开发框架,支持构建具备指令遵循、工具使用和规划能力的Agent应用。该框架提供浏览器助手、代码解释器等示例,支持通过源码或PyPI安装,可配置DashScope或OpenAI兼容的LLM服务。开发者能自定义工具(如图像生成),并通过chat接口实现流式交互。框架内置RAG、代码解释器等扩展功能,支持多模态任务处理。典型使用流程包括:配置LLM参数、注册工具、
Qwen-Agent
• https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen-Agent
• Qwen-Agent是一个开发框架。可基于本框架开发Agent应用,充分利用
基于通义千问模型(Qwen)的指令遵循、工具使用、规划、记忆能力。
它提供了浏览器助手、代码解释器、自定义助手等示例应用。
• Qwen>=2.0
从源代码安装最小依赖
git clone https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen-Agent.git
cd Qwen-Agent
pip install -e .
从 PyPI 安装稳定版本
pip install -U "qwen-agent[rag,code_interpreter,python_executor,gui]"
# 或者,使用 `pip install -U qwen-agent` 来安装最小依赖。
# 可使用双括号指定如下的可选依赖:
# [gui] 用于提供基于 Gradio 的 GUI 支持;
# [rag] 用于支持 RAG;
# [code_interpreter] 用于提供代码解释器相关支持;
# [python_executor] 用于支持 Qwen2.5-Math 基于工具的推理。
• # 步骤 1:配置您所使用的 LLM
• llm
_
cfg = {
•
# 使用 DashScope 提供的模型服务:
• 'model': 'qwen-max',
• 'model
_
server': 'dashscope',
•
# 'api_key': 'YOUR_DASHSCOPE_API_KEY',
• # 如果这里没有设置 'api_key',它将读取 `DASHSCOPE_API_KEY` 环境变量。
• # 使用与 OpenAI API 兼容的模型服务,例如 vLLM 或 Ollama:
• # 'model': 'Qwen2-7B-Chat',
• # 'model
_
server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # base_url,也称为 api_base
•
# 'api_key': 'EMPTY',
• # (可选) LLM 的超参数:
• 'generate_cfg': {
• 'top_p': 0.8
• }
• }
• # 步骤2(可选):添加一个名为 `my_image_gen` 的自定义工具
• @register_tool('my_image_gen')
• class MyImageGen(BaseTool):
• # `description` 用于告诉智能体该工具的功能。
• description = 'AI 绘画(图像生成)服务,输入文本描述,返回基于文本信息绘制的图像 URL。'
• # `parameters` 告诉智能体该工具有哪些输入参数。
• parameters = [{
• 'name': 'prompt',
• 'type': 'string',
• 'description': '期望的图像内容的详细描述',
• 'required': True
• }]
• def call(self, params: str, **kwargs) -> str:
• # `params` 是由 LLM 智能体生成的参数。
• prompt = json5.loads(params)['prompt']
• prompt = urllib.parse.quote(prompt)
• return json5.dumps(
• {'image_url': f'https://image.pollinations.ai/prompt/{prompt}'},
• ensure_ascii=False)
• # 步骤 3:创建一个智能体。这里以 `Assistant` 智能体为例,它能够使用工具并读取文件。
• system_instruction = '''你是一个乐于助人的AI助手。
• 在收到用户的请求后,你应该:
• - 首先绘制一幅图像,得到图像的url,
• - 然后运行代码`request.get`以下载该图像的url,
• - 最后从给定的文档中选择一个图像操作进行图像处理。
• 用 `plt.show()` 展示图像。
• 你总是用中文回复用户。'''
• tools = ['my_image_gen', 'code_interpreter'] # `code_interpreter` 是框架自带的工具,用于执行代码。
• files = ['./examples/resource/doc.pdf'] # 给智能体一个 PDF 文件阅读。
• bot = Assistant(llm=llm_cfg,
• system_message=system_instruction,
• function
_
list=tools,
•
files=files)
• # 步骤 4:作为聊天机器人运行智能体
• messages = [] # 这里储存聊天历史。
• while True:
• # 例如,输入请求 "绘制一只狗并将其旋转 90 度"。
• query = input('用户请求: ')
• # 将用户请求添加到聊天历史。
• messages.append({'role': 'user', 'content': query})
• response = []
• for response in bot.run(messages=messages):
• # 流式输出。
• print('机器人回应:')
• pprint.pprint(response, indent=2)
• # 将机器人的回应添加到聊天历史。
• messages.extend(response)
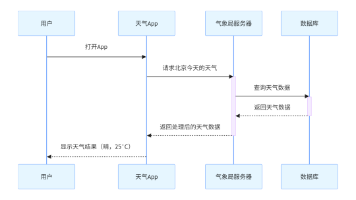
LLM使用
• Qwen-Agent提供了Qwen的DashScope API和OpenAI API访问接口;Qwen-VL的DashScope API访
问接口。均已经支持流式Function Calling。
• 外部直接调用:LLM统一使用get_chat_model(cfg: Optional[Dict] = None) -> BaseChatModel 接口
来调用,参数传入LLM的配置文件, 配置文件格式如下:
• model_type: 对应某个具体的llm类,是llm类注册的名字,即唯一ID。使用内置的dashscope和OpenAI
API时,可以省略这个参数。外部注册的LLM类,需要传入这个参数来指定。
• model:具体的模型名称
• model_server:模型服务地址
• generate_cfg:模型生成时候的参数
• LLM类统一使用llm.chat(...) 接口生成回复,支持输入消息列表、函数等参数,具体参数列表详见
BaseChatModel。 LLM完整使用样例见Function Calling。
LLM使用
from qwen_agent.llm import get_chat_model
llm
_
cfg = {
# Use the model service provided by DashScope:
# 'model_type': 'qwen_dashscope',
'model': 'qwen-max',
'model
_
server': 'dashscope',
# Use your own model service compatible with OpenAI API:
# 'model': 'Qwen',
# 'model
_
server': 'http://127.0.0.1:7905/v1',
# (Optional) LLM hyper-paramters:
'generate_cfg': {
'top_p': 0.8
}
}
llm = get_chat_model(llm_cfg)
messages = [{
'role': 'user',
'content': "What's the weather like in San Francisco?"
}]
functions = [{
'name': 'get_current_weather',
'description': 'Get the current weather in a given location',
'parameters': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'location': {
'type': 'string',
'description':
'The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA',
},
'unit': {
'type': 'string',
'enum': ['celsius', 'fahrenheit']
},
},
'required': ['location'],
},
}]
# 此处演示流式输出效果
responses = []
for responses in llm.chat(messages=messages,
functions=functions,
stream=True):
print(responses)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献21条内容
已为社区贡献21条内容







所有评论(0)