《嵌入式数据结构笔记(四):栈结构与队结构链表》
本文摘要: 文章系统讲解了三种核心数据结构实现原理:1.内核链表采用双向循环设计,通过list_head嵌入业务数据实现解耦,配合offset_of/container_of宏实现高效访问;2.栈(FILO)和队列(FIFO)分别给出链式实现方案,包含完整操作接口(push/pop等)及安全校验逻辑;3.深入剖析二级指针的三种核心应用场景:跨函数修改指针、处理指针数组及作为函数参数。特别强调内核链
1.内核链表设计精要
内核链表:双向循环链表
不再将数据存储在链表节点中,而是将结点嵌入到存储的数据中。
- 传统链表缺陷
struct Node { int data; // 数据与节点耦合 struct Node *next; }; - 内核链表方案
struct list_head { // 纯链表节点 struct list_head *prev, *next; }; struct task_struct { // 业务数据结构 int pid; struct list_head tasks; // 节点嵌入业务数据 };
关键宏操作
| 宏 | 功能 | 实现原理 |
|---|---|---|
offset_of |
计算成员在结构体中的偏移量 | (size_t)&((type*)0)->member |
container_of |
通过成员地址获取结构体首地址 | (type*)((char*)ptr - offset) |
2.栈与队列实现机制
栈结构(FILO)
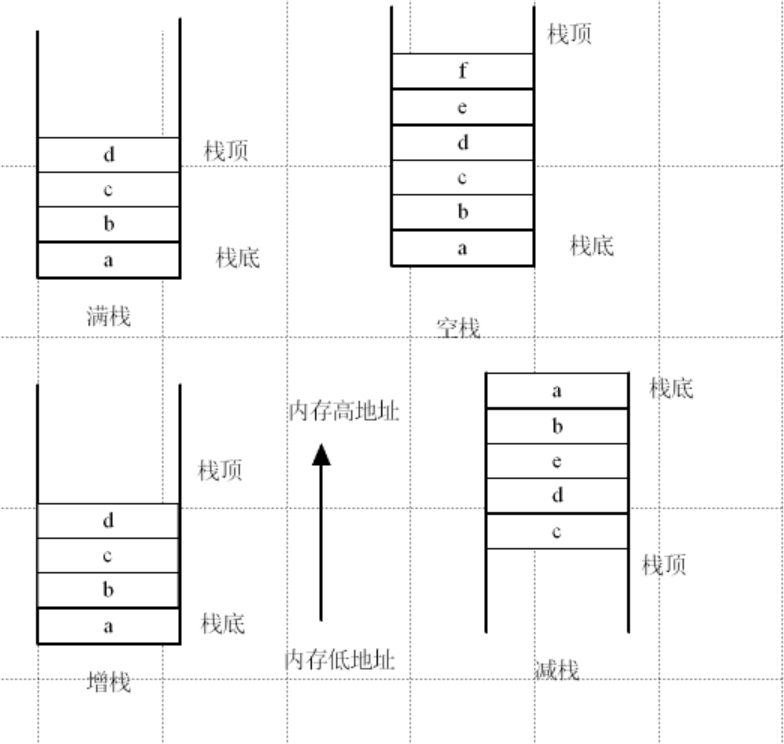
栈:只允许从一端进行数据的插入和删除的线性存储结构,称之为栈结构
特点:先进后出: FILO
顺序栈(数组),满增栈、满减栈、空增栈、空减栈
满栈、空栈:栈顶所在位置是否存在数据
增栈、减栈:按照栈的生长方向区分
链式栈
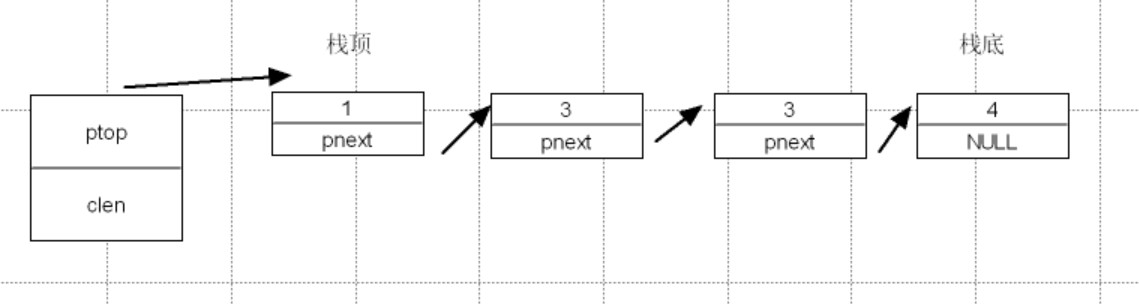
1.创建链式栈
2. 入栈(头插)
3. 出栈(头删)
4. 判断是否为空栈
5. 获取栈顶元素
6. 销毁栈
//.h
#ifndef _SATCK_H_
#define _STACK_H_
typedef int Data_type_t;
typedef struct stnode
{
Data_type_t data;
struct stnode *pnext;
}STNode_t;
typedef struct stack
{
STNode_t *ptop;
int clen;
}Stack_t;
extern Stack_t *create_stack();
extern int is_empty_stack(Stack_t *pstack);
extern void stack_for_each(Stack_t *pstack);
extern int push_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t mydata);
extern int pop_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata);
extern int get_top_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata);
extern void destroy_stack(Stack_t **pstack);
#endif//fun.c
#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
Stack_t *create_stack()
{
Stack_t *pstack = malloc(sizeof(Stack_t));
if(NULL == pstack)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
}
pstack -> ptop = NULL;
pstack -> clen = 0;
return pstack;
}
int is_empty_stack(Stack_t *pstack)
{
return NULL == pstack -> ptop;
}
void stack_for_each(Stack_t *pstack)
{
if(is_empty_stack(pstack))
{
return;
}
STNode_t *ptmp = pstack -> ptop;
while(NULL != ptmp)
{
printf("%d\n", ptmp -> data);
ptmp = ptmp -> pnext;
}
}
//入栈(toucha)
int push_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t mydata)
{
STNode_t *pstnode = malloc(sizeof(STNode_t));
if(NULL == pstnode)
{
printf("malloc errror\n");
}
pstnode -> data = mydata;
pstnode -> pnext = NULL;
if(is_empty_stack(pstack))
{
pstack -> ptop = pstnode;
}
else
{
pstnode -> pnext = pstack -> ptop;
pstack -> ptop = pstnode;
}
pstack -> clen--;
return 0;
}
//出栈(toushan)
int pop_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata)
{
if(is_empty_stack(pstack))
{
return -1;
}
else
{
STNode_t *ptmp = pstack -> ptop;
pstack -> ptop = ptmp -> pnext;
if(pdata != NULL)
{
*pdata = ptmp -> data;
}
free(ptmp);
pstack -> clen--;
return 0;
}
}
//取栈顶元素
int get_top_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata)
{
if(is_empty_stack(pstack))
{
return -1;
}
else
{
STNode_t *ptmp = pstack -> ptop;
*pdata = ptmp -> data;
return *pdata;
}
}
//销毁栈链表
void destroy_stack(Stack_t **ppstack)
{
while (!is_empty_stack(*ppstack))
{
pop_stack(*ppstack, NULL);
}
free(*ppstack);
*ppstack = NULL;
}//main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stack.h"
int main(void)
{
Stack_t *pstack = create_stack();
if(NULL == pstack)
{
return -1;
}
push_stack(pstack, 6);
push_stack(pstack, 5);
push_stack(pstack, 4);
push_stack(pstack, 3);
push_stack(pstack, 2);
push_stack(pstack, 1);
stack_for_each(pstack);
int pdata;
printf("%d\n", get_top_stack(pstack, &pdata));
destroy_stack(&pstack);
return 0;
}//makefile
OBJ=a.out
SRC=main.c
SRC+=stack.c
INC=./
CC=gcc
$(OBJ):$(SRC)
$(CC) $^ -o $@ -I$(INC)
clean:
rm $(OBJ)
队列结构(FIFO)
队列:允许从一端进行数据的插入,另一端进行数据删除的线性存储结构,称为队列结构
插入操作,叫入队操作,插入的这端称为队列的队尾;
删除操作,叫出队操作,删除的这端称为队列的队头。
顺序队列(数组):[head, tail)
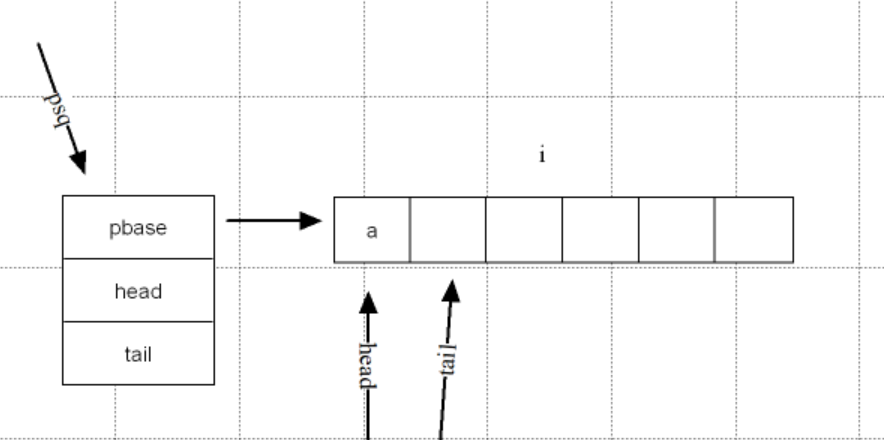
假溢出问题:循环队列为了区分队空和队满,将来少存储一个数据。
循环队列如何判空?队头和队尾处于同一位置,此时认为队列为空
循环队列如何判满?当队尾+1跟上队头时,任务认为队列为满
1. 创建循环队列
2. 入队操作
3. 出队操作
4. 判空
5. 获取队头元素
6. 销毁队列
7. 遍历队列
//.h
#ifndef __SEQQUE_H__
#define __SEQQUE_H__
#define SEQQUE_MAX_LEN 10
typedef int Data_type_t;
typedef struct seqque
{
Data_type_t *pbase;
int head;
int tail;
}Seqque_t;
extern Seqque_t *create_seqque();
extern int is_full_seqque(Seqque_t *psq);
extern int is_empty_seqque(Seqque_t *psq);
extern int push_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t data);
extern void seqque_for_each(Seqque_t *psq);
extern void destroy_seqque(Seqque_t **pppsq);
extern int get_top_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *pdata);
extern int pop_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *data);
#endif//fun.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"seqque.h"
Seqque_t *create_seqque()
{
Seqque_t *psq = malloc(sizeof(Seqque_t));
if (NULL == psq)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
psq->head = 0;
psq->tail = 0;
psq->pbase = malloc(sizeof(Data_type_t) * SEQQUE_MAX_LEN);
if (NULL == psq->pbase)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
return psq;
}
int is_full_seqque(Seqque_t *psq)
{
if ((psq->tail+1)%SEQQUE_MAX_LEN == psq->head)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int is_empty_seqque(Seqque_t *psq)
{
if (psq->head == psq->tail)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int push_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t data)
{
if (is_full_seqque(psq))
{
printf("seqque is full\n");
return -1;
}
psq->pbase[psq->tail] = data;
psq->tail = (psq->tail+1) % SEQQUE_MAX_LEN;
return 0;
}
void seqque_for_each(Seqque_t *psq)
{
for (int i = psq->head; i != psq->tail; i = (i+1)%SEQQUE_MAX_LEN)
{
printf("%d ", psq->pbase[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int pop_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *data)
{
if(is_empty_seqque(psq))
{
printf("seqque is NUKK\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
Data_type_t *pdel = psq -> pbase;
if(NULL != data)
{
*data = psq -> pbase[psq -> head];
}
psq -> head = (psq -> head + 1) % SEQQUE_MAX_LEN;
return 1;
}
}
int get_top_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *pdata)
{
if(is_empty_seqque(psq))
{
printf("seqque is NUKK\n");
return -1;
}
if (NULL == pdata)
{
return -1;
}
*pdata = psq -> pbase[psq -> head];
return 0;
}
void destroy_seqque(Seqque_t **pppsq)
{
free((*pppsq) -> pbase);
free(*pppsq);
*pppsq = NULL;
}
//main.c
#ifndef __SEQQUE_H__
#define __SEQQUE_H__
#define SEQQUE_MAX_LEN 10
typedef int Data_type_t;
typedef struct seqque
{
Data_type_t *pbase;
int head;
int tail;
}Seqque_t;
extern Seqque_t *create_seqque();
extern int is_full_seqque(Seqque_t *psq);
extern int is_empty_seqque(Seqque_t *psq);
extern int push_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t data);
extern void seqque_for_each(Seqque_t *psq);
extern void destroy_seqque(Seqque_t **pppsq);
extern int get_top_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *pdata);
extern int pop_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *data);
#endif链式队列
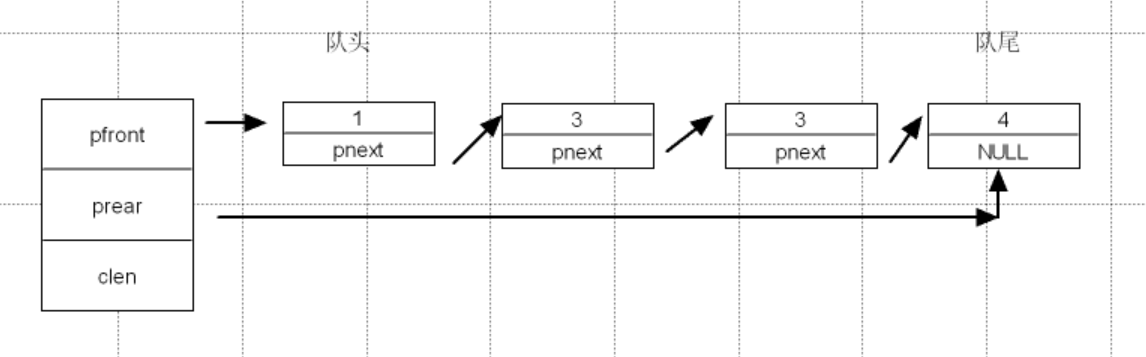
1. 创建链式队列
2. 入队操作(尾插)
3. 出队操作(头删)
4. 判空
5. 获取队头元素
6. 销毁队列
7. 遍历队列
//.h
#ifndef __LQUEUE_H__
#define __LQUEUE_H__
typedef int Data_type_t;
typedef struct lqnode
{
Data_type_t data;
struct lqnode *pnext;
}LQNode_t;
typedef struct lqueue
{
LQNode_t *phead;
LQNode_t *ptail;
int clen;
}LQueue_t;
extern LQueue_t *creat_lqueue();
extern int is_empty_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue);
extern void queue_for_each(LQueue_t *pqueue);
extern int push_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue, Data_type_t mydata);
extern int pop_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue, Data_type_t *pdata);
extern int get_top_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue, Data_type_t *pdata);
extern void destroy_queue(LQueue_t **ppqueue);
#endif//fun.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "lqueue.h"
LQueue_t *creat_lqueue()
{
LQueue_t *pqueue = malloc(sizeof(LQueue_t));
if(NULL == pqueue)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
}
pqueue -> phead = NULL;
pqueue -> ptail = NULL;
pqueue -> clen = 0;
return pqueue;
}
int is_empty_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue)
{
return NULL == pqueue -> phead && NULL == pqueue -> ptail;
}
void queue_for_each(LQueue_t *pqueue)
{
if(is_empty_queue(pqueue))
{
return;
}
LQNode_t *ptmp = pqueue -> phead;
while(NULL != ptmp)
{
printf("%d\n", ptmp -> data);
ptmp = ptmp -> pnext;
}
}
int push_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue, Data_type_t mydata)
{
LQNode_t *plqnode = malloc(sizeof(LQNode_t));
if(NULL == pqueue)
{
printf("malloc errror\n");
}
plqnode -> data = mydata;
plqnode -> pnext = NULL;
if(is_empty_queue(pqueue))
{
pqueue -> phead = plqnode;
pqueue -> ptail = plqnode;
}
else
{
LQNode_t *ptmp = pqueue -> phead;
while(NULL != ptmp -> pnext)
{
ptmp = ptmp -> pnext;
}
ptmp -> pnext = plqnode;
pqueue -> ptail = plqnode;
}
pqueue -> clen++;
return 0;
}
int pop_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue, Data_type_t *pdata)
{
if(is_empty_queue(pqueue))
{
return -1;
}
else
{
LQNode_t *ptmp = pqueue -> phead;
pqueue -> phead = ptmp -> pnext;
if(pdata != NULL)
{
*pdata = ptmp -> data;
}
if(pqueue -> clen == 1)
{
pqueue -> ptail = NULL;
}
free(ptmp);
pqueue -> clen--;
return 0;
}
}
int get_top_queue(LQueue_t *pqueue, Data_type_t *pdata)
{
if(is_empty_queue(pqueue))
{
return -1;
}
else
{
LQNode_t *ptmp = pqueue -> phead;
*pdata = ptmp -> data;
return *pdata;
}
}
void destroy_queue(LQueue_t **ppqueue)
{
while(!is_empty_queue(*ppqueue))
{
pop_queue(*ppqueue, NULL);
}
free(*ppqueue);
*ppqueue = NULL;
}
//main.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include"lqueue.h"
int main(void)
{
LQueue_t *pqueue = creat_lqueue();
if(NULL == pqueue)
{
return -1;
}
push_queue(pqueue, 1);
push_queue(pqueue, 2);
push_queue(pqueue, 3);
push_queue(pqueue, 4);
push_queue(pqueue, 5);
queue_for_each(pqueue);
puts("");
puts("");
Data_type_t i;
pop_queue(pqueue, &i);
queue_for_each(pqueue);
printf("delete number: %d\n", i);
Data_type_t j;
get_top_queue(pqueue, &j);
printf("%d\n", j);
destroy_queue(&pqueue);
return 0;
}//makefile
OBJ=a.out
SRC=main.c
SRC+=lqueue.c
INC=./
CC=gcc
$(OBJ):$(SRC)
$(CC) $^ -o $@ -I$(INC)
clean:
rm $(OBJ)3.二级指针核心原理
二级指针本质
- 应用场景
- 修改主调函数中的一级指针(传递指针的地址)
- 接收指针数组作为参数(
char* arr[10]→char**)
- 操作模型
void modify_ptr(int **pptr) { *pptr = malloc(sizeof(int)); // 修改外部指针指向 }
指针数组解析
| 类型 | 声明 | 内存模型 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符指针数组 | char *a[10] |
连续存储10个char*地址 |
| 整型指针数组 | int *a[10] |
连续存储10个int*地址 |
- 数组名本质:首元素地址(
a≡&a[0],类型为char**)
4.关键技巧总结
-
二级指针安全操作
- 解引用前校验空指针:
if (!pptr) return; - 类型匹配检查:
int**不能操作char**
- 解引用前校验空指针:
-
内核链表工程优势
- 通用性:同一链表操作复用所有数据结构
- 零拷贝:数据移动只需修改指针
// 任务迁移示例 list_move(&task1->tasks, &new_queue); -
循环队列设计规范
- 容量定义为
2^n(位运算优化模计算:index & (size-1)) - 内存屏障保证多线程安全
- 容量定义为
5.总结
-
二级指针本质
- 指针的指针 → 跨函数修改指针的终极工具
- 指针数组枢纽 → 字符串表/命令参数处理核心
-
内核链表哲学
- 解耦数据与结构(Linux内核基石)
container_of宏 → C语言"面向对象"实现
-
栈与队列本质差异
结构 操作端 应用场景 栈 单端操作(TOP) 函数调用/表达式求值 队列 双端操作 消息缓冲/任务调度 -
嵌入式场景适配
- 静态分配循环队列(无动态内存需求)
- 链式栈实现深度递归(避免栈溢出)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容






所有评论(0)