C++ 多线程(三)
dwCreationFlags 控制线程的标准,0为一开始就执行,#define CREATE_SUSPENDED0x00000004 为开始挂起。WaitForSingleObject 是类似lock一样的上锁,后面的参数为等待的时间。为了更方便的使用多线程,UE中有Runnable,仿造UE的实现,实现一个简易版本的。我们创建的子线程名称是系统自动生成的,如果我们需要自己修改创建的名称该如何处
一、Windows创建线程
我们先来看一下创建windows线程的API
WINBASEAPI
_Ret_maybenull_
HANDLE
WINAPI
CreateThread(
_In_opt_ LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes,
_In_ SIZE_T dwStackSize,
_In_ LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress,
_In_opt_ __drv_aliasesMem LPVOID lpParameter,
_In_ DWORD dwCreationFlags,
_Out_opt_ LPDWORD lpThreadId
);
以下是形参的具体用途
lpThreadAttributes 线程安全有关,一般传入null
dwStackSize 分配的空间大小,0为自动分配
lpStartAddress 需要在线程中执行的函数
lpParameter 传入的参数
dwCreationFlags 控制线程的标准,0为一开始就执行,#define CREATE_SUSPENDED 0x00000004 为开始挂起
lpThreadId 线程的id
定义在window线程中执行的函数
DWORD WINAPI FuncThread(LPVOID lpParam)
{
Sleep(1000);
std::cout << "Hello World" << std::endl;
return 0l;
}
创建windows线程,注意使用完毕后要CloseHandle。
windows的一些操作都要使用CloseHandle
HANDLE h = CreateThread(nullptr, 0, FuncThread, nullptr, 0, nullptr);
Sleep(2000);
CloseHandle(h);
二、Windows互斥锁
WINBASEAPI
_Ret_maybenull_
HANDLE
WINAPI
CreateMutexW(
_In_opt_ LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpMutexAttributes,
_In_ BOOL bInitialOwner,
_In_opt_ LPCWSTR lpName
);
lpMutexAttributes 线程安全有关,一般传入null
bInitialOwner 有没有该锁的控制权
lpName 锁的名称
WaitForSingleObject 是类似lock一样的上锁,后面的参数为等待的时间
ReleaseMutex(WindowMu) 是类似unlock的功能,释放这个锁
DWORD WINAPI Func01(LPVOID Params)
{
WaitForSingleObject(WindowMu, INFINITE);
std::cout << "Hello World" << std::endl;
ReleaseMutex(WindowMu);
return 0;
}
下面是使用案例
WindowMu = CreateMutex(nullptr, false, L"TestLock");
WaitForSingleObject(WindowMu, INFINITE);
HANDLE h = CreateThread(nullptr, 0, Func01, nullptr, 0, nullptr);
Sleep(5000);
ReleaseMutex(WindowMu);
Sleep(2000);
三、windows挂起和唤醒线程
和之前的std的线程一样都是使用一样的api
这个是挂起线程
SuspendThread(h);
这个是唤醒线程
ResumeThread(h);
四、简单架构Runnable
为了更方便的使用多线程,UE中有Runnable,仿造UE的实现,实现一个简易版本的
主要文件有三个Runnable、RunnableThread、Platform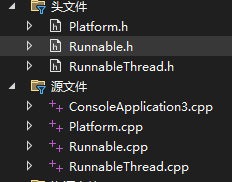
Runnable.h
#pragma once
class RunnableThread;
class Runnable
{
public:
Runnable();
virtual bool Init();
virtual int Run();
virtual int Stop();
virtual bool Exit();
protected:
virtual int Run_Func() = 0;
bool bStop = false;
RunnableThread* Thread;
};
Runnable.cpp
#include "Runnable.h"
#include "Platform.h"
Runnable::Runnable()
{
Thread = Platform::Create(this);
}
bool Runnable::Init()
{
return true;
}
int Runnable::Run()
{
for(;;)
{
while (!bStop)
{
Run_Func();
Platform::Sleep(100);
}
Exit();
break;
}
return 0;
}
int Runnable::Stop()
{
if (!bStop)
{
bStop = true;
}
return 0;
}
bool Runnable::Exit()
{
return true;
}
RunnableThread.h
#pragma once
#include "Runnable.h"
class RunnableThread
{
public:
RunnableThread();
virtual bool Create(Runnable* Runnable) = 0;
};
RunnableThread.cpp
#include "RunnableThread.h"
RunnableThread::RunnableThread()
{
}
Platform.h
#pragma once
class Runnable;
class RunnableThread;
typedef unsigned long SLEEP_TIME;
class Platform
{
public:
static RunnableThread* Create(Runnable* Runnable);
static void Sleep(SLEEP_TIME SpTime);
};
Platform.cpp
class WindowsRunnableThread : public RunnableThread
{
protected:
HANDLE ThreadHandle;
public:
bool Create(Runnable* InRunnable) override
{
auto ThreadFunc = [](LPVOID Params) -> DWORD
{
Runnable* runnable = (Runnable*)Params;
if (runnable)
{
DWORD ReturnValue = runnable->Run();
return ReturnValue;
}
return 0;
};
ThreadHandle = CreateThread(nullptr, 0, ThreadFunc, InRunnable, 0, nullptr);
return true;
}
~WindowsRunnableThread()
{
CloseHandle(ThreadHandle);
delete ThreadHandle;
}
};
class LinuxRunnableThread : public RunnableThread
{
bool Create(Runnable* Runnable) override
{
return false;
}
};
RunnableThread* Platform::Create(Runnable* Runnable)
{
RunnableThread* Thread = nullptr;
if (Runnable)
{
if (Runnable->Init())
{
#if _WIN32
Thread = new WindowsRunnableThread();
#elif __linux__
Thread = new LinuxRunnableThread();
#endif
if (Thread->Create(Runnable)) {
return Thread;
}
else {
delete Thread;
return nullptr;
}
}
}
return Thread;
}
void Platform::Sleep(SLEEP_TIME SpTime)
{
#if _WIN32
::Sleep(SpTime);
#elif __linux__
#endif
}
- RunnableThread:对线程进行封装的接口,具体平台的线程需要继承此接口进行具体的线程创建。
- Runnable:有关具体需要在线程中执行的函数的声明周期。
- Platform:创建具体平台对应的线程,类似工厂。
五、线程命名修改
我们创建的子线程名称是系统自动生成的,如果我们需要自己修改创建的名称该如何处理?
一种老式的固定写法(调试器可见)
struct FThreadInfo
{
DWORD dwType;
LPCSTR szName;
DWORD dwThreadID;
DWORD dwFlags;
};
FThreadInfo ThreadInfo;
ThreadInfo.dwType = 0x1000;
ThreadInfo.szName = runnable->GetThread()->GetThreadName();
ThreadInfo.dwThreadID = GetCurrentThreadId();
ThreadInfo.dwFlags = 0;
__try
{
RaiseException(0x406D1388, 0, sizeof(ThreadInfo) / sizeof(DWORD), (ULONG_PTR*)(&ThreadInfo));
}
__except(EXCEPTION_EXECUTE_HANDLER)
{
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容






所有评论(0)