基于最小外接矩形及霍夫变换的图像倾斜矫正
文章目录一、基于图像内容最小外接矩形边框矫正二、基于霍夫变换的图像倾斜矫正一、基于图像内容最小外接矩形边框矫正前提: 图像有明显的轮廓,需要对图像进行降噪处理特点: 对于表格矫正效果很好缺点: 当图片边缘存在文字时,外接矩形的边框会将整张图片框住,导致计算出的旋转角为0而无法有效矫正图像,如下图。代码:# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @Author: ChenXin# @Time
·
一、基于图像内容最小外接矩形的图像倾斜矫正
前提: 图像有明显的轮廓,需要对图像进行降噪处理
特点: 对于表格矫正效果很好
缺点: 当图片边缘存在文字时,外接矩形的边框会将整张图片框住,导致计算出的旋转角为0而无法有效矫正图像,如下图。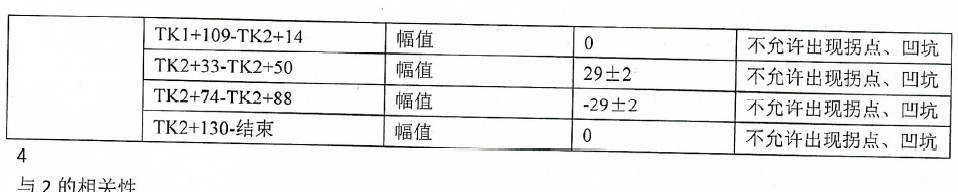
代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Author : ChenXin
# @Time : 2021/8/6 12:50
# @Function: 图像倾斜矫正
import cv2 as cv # opencv-python==4.2.0.34
import numpy as np
import os
import os.path as osp
import time
import math
# 转为灰度图,并二值化
def binary(img):
'''
:param img: 原始图像
:return: 二值化后的图像
'''
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # cvtColor用于转换色彩空间,将图像转换为GRAY灰度图像
# gray = cv.medianBlur(gray,5) # 中值滤波
gray = cv.GaussianBlur(gray, (9, 9), 9) # 高斯滤波
ret, binary = cv.threshold(gray, 0, 255,
cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv.THRESH_OTSU) # 由于文本是黑底白字的,需要让背景是黑色的,所以在传入参数时需要使用cv.THRESH_BINARY_INV 加上_INV使二值图反转
return binary
def Transformation(img, src, result, h, w):
'''
:param img: 二值化后的图像
:param src: 原始图像
:param result: 矫正图像保存路径
:param h: 原始图像的高
:param w: 原始图像的宽
:return: 外接矩形的顶点
'''
coords = np.column_stack(np.where(img > 0))
# print(coords)
# print(coords.shape)
angle = cv.minAreaRect(coords)[-1] # 最小外接矩形旋转角
pts = cv.boxPoints(cv.minAreaRect(coords)) # 外接矩形的顶点
a, b, c = cv.minAreaRect(coords)
print("矩形中心点:", (round(a[0], 2), round(a[1], 2)), "矩形长:{} 宽:{}".format(round(b[0], 2), round(b[1], 2)))
print("原始矩形旋转角度:", angle)
if -45 < angle < 45:
angle = -angle
else:
angle = 0
# if angle < -45:
# angle = -(90 + angle)
# else:
# angle = -angle
center = (w // 2, h // 2)
M = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0) # 传入中心和角度,得到旋转矩形
rotated = cv.warpAffine(src, M, (w, h), flags=cv.INTER_CUBIC, borderMode=cv.BORDER_REPLICATE)
# cv.putText(rotated,'Angle:{:.2f} degrees'.format(angle),(10,30),cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.7,(0,0,255),2) # 绘制文字
# pts = pts.reshape((-1, 1, 2)) # 顶点个数:4,矩阵变成4*1*2维
cv.imwrite(result, rotated)
return pts
def is_img(ext):
ext = ext.lower()
if ext in ['.jpg', '.png', '.jpeg', '.bmp']:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
filepath = 'image/'
result_path = 'result/'
start = time.time()
for file in os.listdir(filepath):
if is_img(osp.splitext(file)[1]):
print(file)
src = cv.imread(filepath + file)
src = cv.copyMakeBorder(src, 50, 50, 50, 50, cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=[255, 255, 255])
(h, w) = src.shape[:2]
binary_ = binary(src) # 二值化、滤波处理
Transformation(binary_, src, result_path + file, h, w) # 矩形矫正
print("耗时:", time.time() - start)
二、基于霍夫变换的图像倾斜矫正
- 原理:
- 检测图片中的直线
- 将图片中所有横向直线的旋转角求平均值。
- 根据旋转角进行倾斜矫正。
相比之前的方法适用范围更广,对表格图像预处理基本没有要求,并且对于整张文档图片也可进行矫正。
- 效果:
画出图像中所有的直线: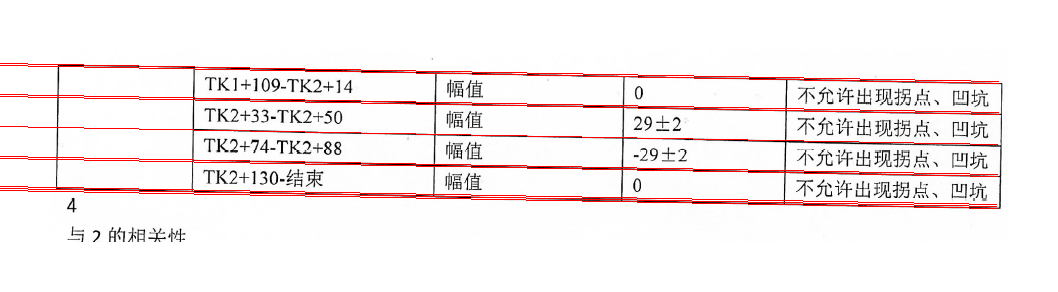
矫正结果: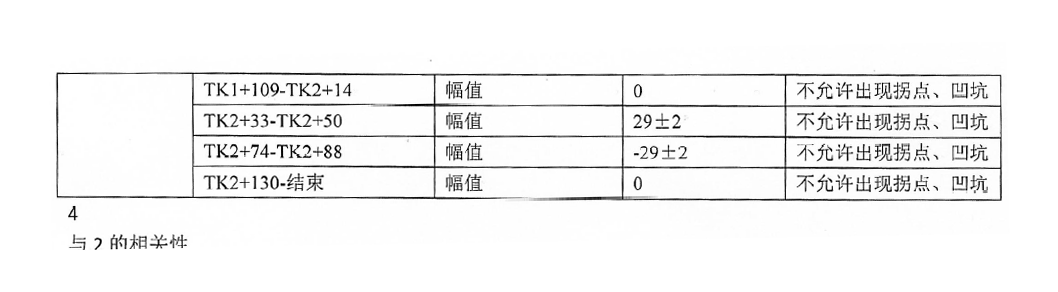
代码:
arg = 300
arg初始值设为300,数值越大,检测出的直线越少、越精确,代码中进行了arg值的自调节,如果检测不出直线,arg会以40递减,直到检测出直线。
其他用到的函数见一、中代码
def HoughTrans(img, src, result, h, w):
'''
:param img: 二值化后的图像
:param src: 原始图像
:param result: 矫正图像保存路径
:param h: 原始图像的高
:param w: 原始图像的宽
:return: 霍夫变换的阈值、旋转角度
'''
edges = cv.Canny(img, 50, 200, apertureSize=3) # 边缘检测
arg = 300
lines = cv.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi / 180, arg) # 霍夫变换检测直线,返回数组:(rho,theta)。rho以像素为单位测量,theta以弧度为单位测量。
while not isinstance(lines, np.ndarray):
if arg <= 200:
break
arg -= 40
lines = cv.HoughLines(edges, 1, np.pi / 180, arg)
sum_theta = 0
sum_0 = 0
for line in lines:
rho, theta = line[0]
real_angel = -(theta * 180 / math.pi - 90)
# 只计算真实角度在-45°到45°之间的直线,目的是为了去除竖向直线的影响
if -45 < real_angel < 45:
sum_theta += theta
else:
sum_0 += 1
a = np.cos(theta)
b = np.sin(theta)
x0 = a * rho
y0 = b * rho
x1 = int(x0 + 1000 * (-b))
y1 = int(y0 + 1000 * (a))
x2 = int(x0 - 1000 * (-b))
y2 = int(y0 - 1000 * (a))
cv.line(src, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 0, 255), 1)
# 将所有直线画出
cv.imshow('table/23_1.jpg', src)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
average_theta = sum_theta / len(lines)
angle = average_theta * 180 / math.pi - 90
if -45 < angle < 45:
angle = -angle
else:
angle = 0
center = (w // 2, h // 2) # 矩形中心
M = cv.getRotationMatrix2D(center, -angle, 1.0) # 传入中心和角度,得到旋转矩形
rotated = cv.warpAffine(src, M, (w, h), flags=cv.INTER_CUBIC, borderMode=cv.BORDER_REPLICATE) # 最后要换成原图
cv.imwrite(result, rotated)
return arg, angle
if __name__ == '__main__':
filepath = 'image/'
result_path = 'result/'
start = time.time()
for file in os.listdir(filepath):
if is_img(osp.splitext(file)[1]):
print(file)
src = cv.imread(filepath + file)
src = cv.copyMakeBorder(src, 50, 50, 50, 50, cv.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=[255, 255, 255])
(h, w) = src.shape[:2]
binary_ = binary(src) # 二值化、滤波处理
HoughTrans(binary_, src, result_path + file, h, w) # 霍夫变换矫正
print("耗时:", time.time() - start)
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)