阿里AI天池大赛-新闻文本分类-TF-IDF特征+LightGBM模型
1:报名地址https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/531810/rankingList/12:排名分数3:模型源码废话不多说,直接上源码import pandas as pdimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport sklearnfrom sklearn.model_se
1:报名地址
https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/531810/rankingList/1
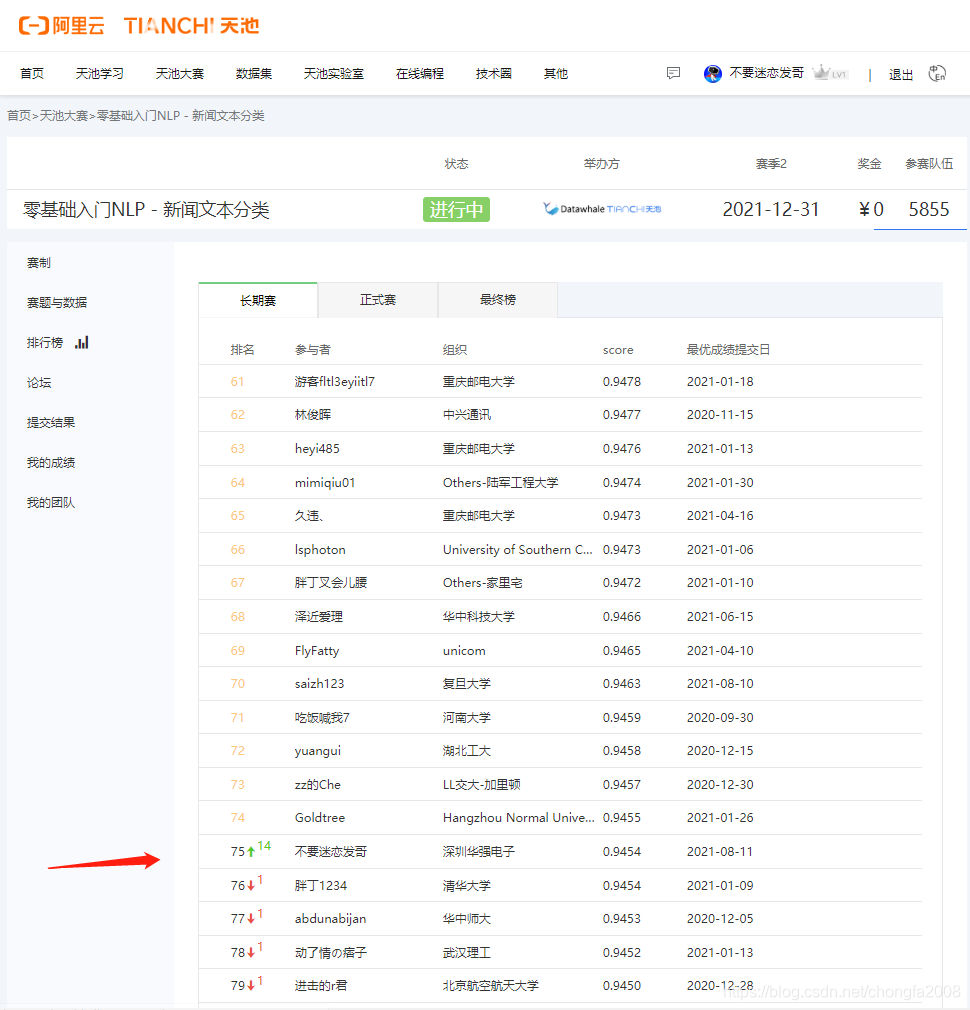
2:排名分数
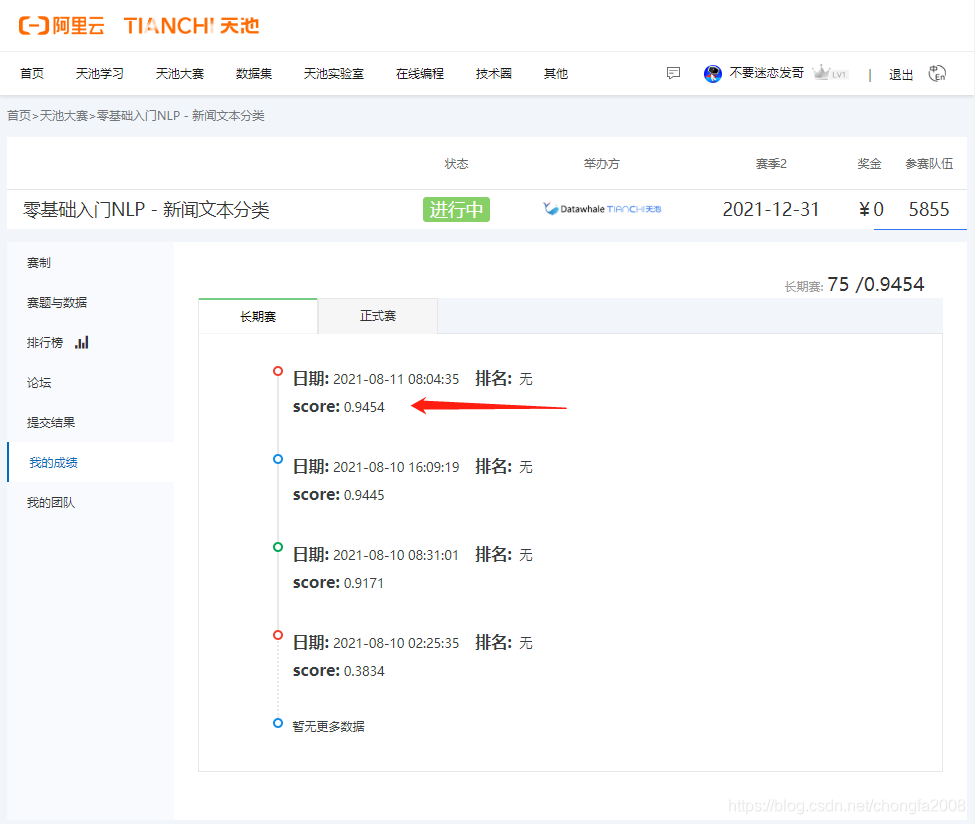
3:模型源码
废话不多说,直接上源码
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
#数据加载
train = pd.read_csv('./train_set.csv',sep='\t')
test = pd.read_csv('./test_a.csv',sep='\t')
train['text_split'] = train['text'].apply(lambda x: str(x.split()))
test['text_split'] = test['text'].apply(lambda x: str(x.split()))
# tfidf
word_vec = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word',
ngram_range=(1,2),
min_df=3,
max_df=0.9,
use_idf=True,
max_features = 3000,
smooth_idf=True,
sublinear_tf=True)
train_term_doc = word_vec.fit_transform(train['text_split'])
test_term_doc = word_vec.transform(test['text_split'])
#计算宏平均
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
def cal_macro_f1(y_true,y_pred):
score = f1_score(y_true,y_pred,average='macro')
return score
#拆分训练集
X_train, X_eval, y_train, y_eval = train_test_split(train_term_doc,train['label'],test_size=0.2,shuffle=True,random_state=2021)
# 十折交叉校验
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
kf = KFold(n_splits=10, shuffle=True, random_state=2021)
#记录验证集的概率
train_matrix = np.zeros((train.shape[0],14))
#将每轮的测试概率分别保存起来
test_pre_matrix = np.zeros((10,test.shape[0],14))
#记录每一轮的成绩
cv_scores=[]
#lgb模型
import lightgbm as lgb
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
for i,(train_index,eval_index) in enumerate(kf.split(train_term_doc)):
print(len(train_index),len(eval_index))
#训练集
X_train = train_term_doc[train_index]
y_train = train['label'][train_index]
#验证集
X_eval = train_term_doc[eval_index]
y_eval = train['label'][eval_index]
model =lgb.LGBMClassifier(boosting_type='gbdt',
num_leaves=2**5,
max_depth=-1,
learning_rate= 0.1,
n_estimators=2000,
objective='multiclass',
subsample=0.7,
colsample_bytree=0.5,
reg_lambda=12,
n_jobs=16,
num_class=19,
silent=True,
random_state=2021,
colsample_bylevel=0.5,
min_child_weight=1.5,
metric='multi_logloss'
)
model.fit(X_train,y_train,eval_set=(X_eval,y_eval), early_stopping_rounds=100)
#对验证集进行预测
eval_prob = model.predict_proba(X_eval)
train_matrix[eval_index] = eval_prob.reshape((X_eval.shape[0], 14))
eval_pred = np.argmax(eval_prob,axis=1)
score = cal_macro_f1(y_eval,eval_pred)
cv_scores.append(score)
print("The score this time is ",score)
#对于测试集进行预测
test_prob = model.predict_proba(test_term_doc)
test_pre_matrix[i,:,:] = test_prob.reshape((test_term_doc.shape[0], 14))
all_pred = np.argmax(train_matrix,axis=1)
score = cal_macro_f1(train['label'],all_pred)
print("The average score is ",score)
test_pred = test_pre_matrix.mean(axis=0)
test_pred = np.argmax(test_pred,axis=1)
test['label'] = test_pred
test['label'].to_csv("./baseline.0.9454.csv",index=False)
4:提分要领
1:LGBMClassifier函数的调参技巧
①lightGBM适合较大数据集的样本
而对于较小的数据集(<10000条记录),lightGBM可能不是最佳选择。所以,如果进行调优lightgbm参数,这可能没有帮助。
②建议使用更小的learning_rate和更大的num_iteration
此外,如果您想要更高的num_iteration,那么您应该使用early_stopping_rounds,以便在无法学习任何有用的内容时停止训练。
③样本不平衡调参技巧
lightgbm中,可以设置两个参数is_unbalance和scale_pos_weight。
is_unbalace:当其为True时,算法将尝试自动平衡占主导地位的标签的权重(使用列集中的pos/neg分数)
scale_pos_weight:默认1,即假设正负标签都是相等的。在不平衡数据集的情况下,建议使用以下公式:
sample_pos_weight = number of negative samples / number of positive samples
④调参时,可将参数字典分为两大类
调优参数
search_params = {'learning_rate': 0.4,
'max_depth': 15,
'num_leaves': 20,
'feature_fraction': 0.8,
'subsample': 0.2}
固定参数
fixed_params={'objective': 'binary',
'metric': 'auc',
'is_unbalance':True,
'boosting':'gbdt',
'num_boost_round':300,
'early_stopping_rounds':30}
2:十折校验
相比五折运算分数会提高0.09,如果想尽快得到结果,可以采用五折校验
3:tfidf
调整tfidf祖传参数以达到模型的最优
例如将参数 ngram_range 更改为 (1,3)
min_df更改为4,5
max_df更改为0.95,1
5:相关知识
1:机器学习中的F1-score
函数原型:
sklearn.metrics.f1_score(y_true, y_pred, labels=None, pos_label=1, average=’binary’, sample_weight=None)
参数:
y_true : 1d array-like, or label indicator array / sparse matrix.
目标的真实类别
y_pred : 1d array-like, or label indicator array / sparse matrix.
分类器预测得到的类别
average : string,[None, ‘binary’(default), ‘micro’, ‘macro’, ‘samples’, ‘weighted’]
如果是二分类问题则选择参数‘binary’
如果考虑类别的不平衡性,需要计算类别的加权平均,则使用‘weighted’
如果不考虑类别的不平衡性,计算宏平均,则使用‘macro’
2:LGBMClassifier参数扩展
boosting_type=‘gbdt’# 提升树的类型 gbdt,dart,goss,rf
num_leavel=32#树的最大叶子数,对比xgboost一般为2^(max_depth)
max_depth=-1#最大树的深度
learning_rate#学习率
n_estimators=10: 拟合的树的棵树,相当于训练轮数
subsample=1.0: 训练样本采样率 行
colsample_bytree=1.0: 训练特征采样率 列
subsample_freq=1: 子样本频率
reg_alpha=0.0: L1正则化系数
reg_lambda=0.0: L2正则化系数
random_state=None: 随机种子数
n_jobs=-1: 并行运行多线程核心数
silent=True: 训练过程是否打印日志信息
min_split_gain=0.0: 最小分割增益
min_child_weight=0.001: 分支结点的最小权重
3:TF-IDF原理
TF-IDF其中"TF"代表词频(term frequency, TF),"IDF"代表逆向文件频率 (inverse document frequency, IDF)。
TF:是指某一个字词在某一个分类中出现的频率。这里为避免长文章中某一个字词出现的次数自然会比较多的问题,对其进行归一化,即让其除上总个分类中的总词数。这里又要做一个小处理,是因为对于长文章中某一个词可能很少出现,或只出现一次的,这样得到的TF值可能就会为0,所以这里我让某一个字词出现的次数去除以分类中出现次数最多的那个词。
IDF:是训练文档中所有文件数去除以包含了这个关键字词的文件数(为了让除数不可能为0,这里进行+1处理)。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容






所有评论(0)