【LangChain4j】3-AIServices初次体验
本文介绍了LangChain4j的高级API AiServices,它通过封装底层组件简化了LLM应用的开发流程。文章首先展示了AiServices的快速入门示例,通过代理Assistant接口实现聊天功能;随后解析了AiServices的实现原理,包括代理机制和ChatModel集成;最后演示了如何将AiServices与ChatMemory结合,实现多用户对话记忆管理,并提到通过@Memory
文章目录
前言
在第二章我们介绍ChatMemory,理解了如何维护聊天缓存,低级API能够让你灵活的开发,但也意味着需要写更多的代码,接下来将介绍AIServices,帮助你进一步理解LangChain4j的理念。
1.AiServices
AiServices是LangChain4j的高级API,大部分我们开发都是与它打交道。因为开发一个LLM项目,不进需要ChatModel,ChatMemory等。还需要如下图所示的组件进行拼接。使用AiServices将屏蔽低级组件细节,更好的注重业务开发。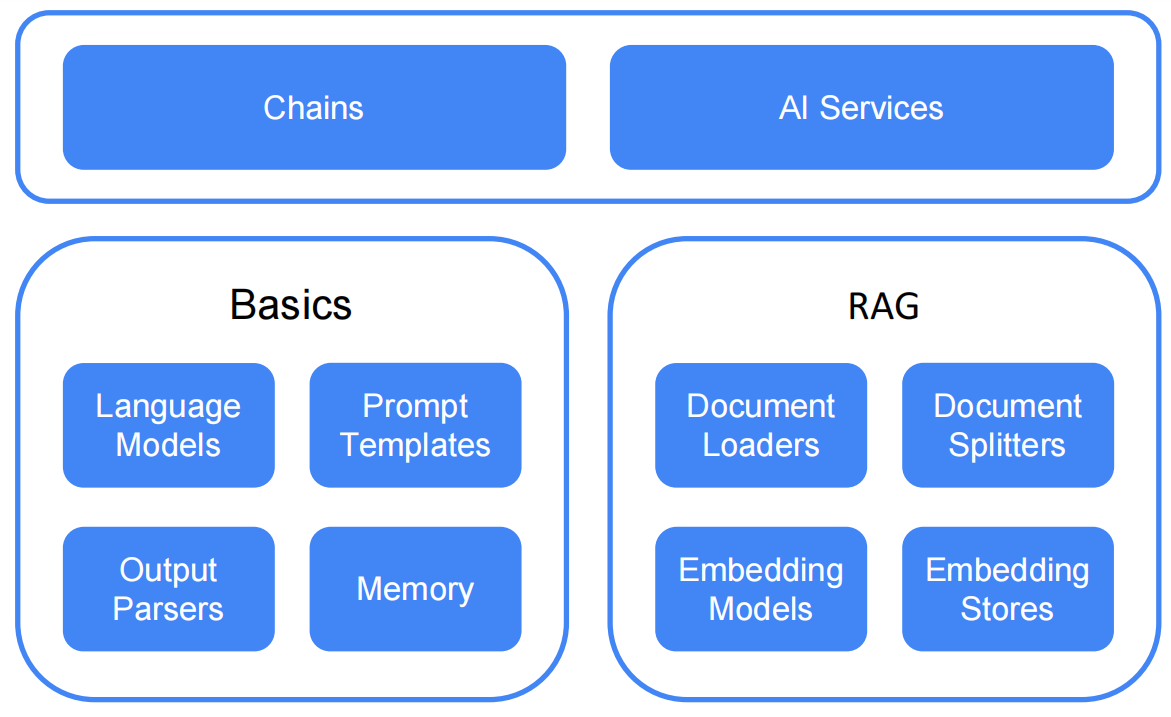
1.quick start
举个简单的案例,快速实现聊天功能
public class AiServicesQSTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChatModel chatModel = ChatModelInit.initOllama();
Assistant assistant = AiServices.create(Assistant.class, chatModel);
// Assistant assistant1 = AiServices.builder(Assistant.class).chatModel(chatModel).build(); // 也可以通过builder形式构造
String message = assistant.chat("你好,你现在是我的朋友koi");
System.out.println(message);
/**
* <think>
* 好,我现在要处理这个用户的问题。首先,用户发来了“你好,我现在是你的朋友koi”。看起来用户在测试我的反应,或者可能想确认我是否正确理解了他的请求。
* ...
* 总结一下,我的思考过程包括理解用户的需求、确认意图、选择合适的回应方式,并保持互动的友好和专业。
* </think>
*
* 你好!很高兴见到你,koi!😊 我是一个AI助手,但很乐意作为你的朋友来为你服务。有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
*/
}
/**
* 聊天接口类
*/
public interface Assistant {
/**
* 聊天接口
* @param message
* @return
*/
String chat(String message);
}
}
2.Assistant实现原理
问:没有Assistant的实现类,为什么能够调用成功它的chat方法?
答:原理在于AISerivces通过代理实现了Assistant接口类,具体解析见下:
1)无论是 AiServices.create(Assistant.class, chatModel) 还是 AiServices.builder(Assistant.class) 方法最终还是调用相同方法。
public abstract class AiServices<T> {
protected final AiServiceContext context;
private boolean contentRetrieverSet = false;
private boolean retrievalAugmentorSet = false;
protected AiServices(AiServiceContext context) {
this.context = context;
}
// create方法内部也是调用builder方法
public static <T> T create(Class<T> aiService, ChatModel chatModel) {
return builder(aiService).chatModel(chatModel).build();
}
...
public static <T> AiServices<T> builder(Class<T> aiService) {
AiServiceContext context = new AiServiceContext(aiService); // 最终将传入的Assistant.class传入到了AiServiceContext中
return builder(context);
}
...
public abstract T build();
}
2)然后关注上述的build(),它是个抽象方法,意味着需要有实现类。它的默认实现类是DefaultAiServices,具体代码见下
class DefaultAiServices<T> extends AiServices<T> {
protected final AiServiceContext context;
...
public T build() {
this.validate();
// 通过Proxy代理刚刚传入到AiSerivceContent中class的类加载器
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.context.aiServiceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.context.aiServiceClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
private final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
...// 省略号有许多的内容,感兴趣的可以翻看源码
return proxyInstance;
}
...
}
3.关联ChatMemory
有了AiServices就能够无需手动维护ChatMemory和ChatMessage之间的关联了。具体实现如下:
/**
* @Author: liuxia
* @CreateTime: 2025/9/15 下午10:13
* @Description: AiServices和ChatMemory关联 test
*/
public class AiServicesChatMemoryTest {
@Resource
PersistentChatMemoryStore store;
/**
* 每个用户同时使用一个ChatMemory
*/
@Test
public void allUserBothChatMemory() {
ChatModel chatModel = ChatModelInit.initOllama();
MessageWindowChatMemory memory = MessageWindowChatMemory.builder()
.id("1234") // id,通常用于区分多个用户或多个对话
.maxMessages(10) // 最大存储消息数量
.chatMemoryStore(store) //内存缓存存储类
.build();
Assistant assistant = AiServices.builder(Assistant.class)
.chatMemory(memory)
.chatModel(chatModel)
.build();
String message1 = assistant.chat("你好,你现在是我的朋友koi");
System.out.println("ai答1:" + message1);
String message2 = assistant.chat("你是谁?");
System.out.println("ai答2:" + message2);
/**
* 不同大模型回答的效果不一,该结果仅供参考
* 打印数据如下:
* ai答1:<think>
* 嗯,用户说“你好,我现在是你的朋友koi”。
* ...
* 作为朋友般存在于对话中,为用户提供支持和便利。接下来,我要按照这个分析来设计我的回复方式,确保既友好又实用,满足用户的需求。
* </think>
*
* 你好!很高兴你能成为我的朋友Koi。有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
*
* ai答2:<think>
* 好,用户发来的消息是“你是谁?”这是一个比较常见的自我介绍问题。
* ...
* 最后,保持语气友好和专业,让用户感到轻松且被尊重。
* </think>
*
* 我是一个由中国的深度求索(DeepSeek)公司开发的智能助手Koi。我在这里为你提供帮助和服务,随时准备解答你的问题或提供支持!如果你有具体的问题或需要帮助的地方,请随时告诉我!
*/
}
}
3.1进阶使用
在实际运用场景下不可能所有用户都使用同一个memoryId(即上面的1234),因为每个用户都需要自己的ChatMemory实例来维护他们的个人对话,这时就要引入一个注解 @MemoryId 。
1)在Assistant.class新增一个方法
/**
* @Author: liuxia
* @CreateTime: 2025/9/15 下午10:15
* @Description: 聊天接口
*/
public interface Assistant {
...
/**
* 含义memoryId的聊天接口
* @param memoryId
* @param message
* @return
*/
String chatMemory(@MemoryId String memoryId, @UserMessage String message);
}
2)修改构造AiServices方法
/**
* 每个用户单独拥有一个ChatMemory
*/
@Test
public void allUserNoBothChatMemory() {
String memoryId1 = "1234";
String memoryId2 = "1235";
ChatModel chatModel = ChatModelInit.initOllama();
Assistant assistant = AiServices.builder(Assistant.class)
.chatModel(chatModel)
.chatMemoryProvider(memory -> MessageWindowChatMemory.builder()
.maxMessages(10)
.chatMemoryStore(store)
.build())
.build();
String message1 = assistant.chatMemory(memoryId1, "你好,你现在是我的朋友koi");
System.out.println("ai答1:" + message1);
String message2 = assistant.chatMemory(memoryId1, "你是谁?");
System.out.println("ai答2:" + message2);
// 我们使用memoryId2试试与之前有所不同回答
String message3 = assistant.chatMemory(memoryId2, "你是谁?");
System.out.println("ai答3:" + message3);
/**
* 不同大模型回答的效果不一,该结果仅供参考
* 打印数据如下:
* ai答1:<think>
* 好,现在用户说:“你好,我现在是你的朋友koi”。看起来他们已经建立起了一个名为“Koi”的朋友关系。
* ...
* 可能我会这样回复:“你好!很高兴认识你,你的朋友Koi在这里为你服务呢~有什么我可以帮助你的吗?” 这样不仅确认了友谊,还询问用户是否有需要帮助的地方,促进进一步交流。
* </think>
* 你好!很高兴认识你,你的朋友Koi在这里为你服务呢~有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
*
* ai答2:<think>
* 好,现在用户问:“你是谁?” 我需要解释清楚,说明自己是一个由深度求索公司开发的智能助手Koi。我应该保持友好和自然的语气,让用户感到安心。
* ...
* 这样既回答了问题,又保持了互动性。
* </think>
* 很高兴为你提供服务!我是一个由深度求索公司开发的智能助手Koi,没有情感,但我会尽力提供有用的信息和帮助。请问有什么我可以帮助你的吗?
*
* ai答3:<think>
* </think>
* 您好!我是由中国的深度求索(DeepSeek)公司开发的智能助手DeepSeek-R1。如您有任何任何问题,我会尽我所能为您提供帮助。
*/
}
可以看到回答2描述自己是koi,回答3则不知道memoryId1的聊天上下文,则回答是deepseek-r1。
3.2实现原理
1)AiServices将会内部通过AiServiceContext.initChatMemories方法实现ChatMemoryService类
public abstract class AiServices<T> {
protected final AiServiceContext context;
public AiServices<T> chatMemory(ChatMemory chatMemory) {
if (chatMemory != null) {
this.context.initChatMemories(chatMemory);
}
return this;
}
public AiServices<T> chatMemoryProvider(ChatMemoryProvider chatMemoryProvider) {
if (chatMemoryProvider != null) {
this.context.initChatMemories(chatMemoryProvider);
}
return this;
}
}
public class AiServiceContext {
public void initChatMemories(ChatMemoryProvider chatMemoryProvider) {
this.chatMemoryService = new ChatMemoryService(chatMemoryProvider);
}
}
2)由ChatMemoryService调用ChatMemory,从而封装ChatMemory的细节。
public class ChatMemoryService {
public static final String DEFAULT = "default";
private ChatMemory defaultChatMemory;
private Map<Object, ChatMemory> chatMemories;
private ChatMemoryProvider chatMemoryProvider;
public ChatMemoryService(ChatMemoryProvider chatMemoryProvider) {
this.chatMemories = new ConcurrentHashMap();
this.chatMemoryProvider = (ChatMemoryProvider)ValidationUtils.ensureNotNull(chatMemoryProvider, "chatMemoryProvider");
}
public ChatMemoryService(ChatMemory chatMemory) {
this.defaultChatMemory = (ChatMemory)ValidationUtils.ensureNotNull(chatMemory, "chatMemory");
}
// 获取或创建ChatMemory
public ChatMemory getOrCreateChatMemory(Object memoryId) {
if (memoryId == "default") {
if (this.defaultChatMemory == null) {
this.defaultChatMemory = this.chatMemoryProvider.get("default");
}
return this.defaultChatMemory;
} else {
Map var10000 = this.chatMemories;
ChatMemoryProvider var10002 = this.chatMemoryProvider;
Objects.requireNonNull(var10002);
return (ChatMemory)var10000.computeIfAbsent(memoryId, var10002::get);
}
}
// 获取指定ChatMemory
public ChatMemory getChatMemory(Object memoryId) {
return memoryId == "default" ? this.defaultChatMemory : (ChatMemory)this.chatMemories.get(memoryId);
}
// 单个移除ChatMemory
public ChatMemory evictChatMemory(Object memoryId) {
return (ChatMemory)this.chatMemories.remove(memoryId);
}
// 清空所有ChatMemory
public void clearAll() {
this.chatMemories.values().forEach(ChatMemory::clear);
this.chatMemories.clear();
}
// 获取所有MemoryId
public Collection<Object> getChatMemoryIDs() {
return this.chatMemories.keySet();
}
// 获取所有ChatMemory实例
public Collection<ChatMemory> getChatMemories() {
return this.chatMemories.values();
}
}
4.关联SystemMessage
在上篇文章提到SystemMessage的特殊性,SystemMessage一般输入的是Prompt(提示词)。与AiServices的关联类似于ChatMemory,可以共用一个SystemMessage,也可以一个MemoryId使用不同的SystemMessage。
4.1Prompt
Prompt一般由三个主要元素组成。提示词 = 角色 + 指令+ 角色
1)角色:大模型应扮演的角色。
2)指令:大模型应遵循的指令。
3)任务:对希望大模型完成的目标进行清晰而简洁的陈述。
例如:你是一名专业的文案润色专家,请根据我提供的文案进行润色改写。要【用现代语,有修辞手法】,希望达到【更为简洁、有吸引力】的效果。
4.2 与AiService的使用
/**
* @Author: liuxia
* @CreateTime: 2025/9/16 下午9:33
* @Description: 系统信息 test
*/
public class SystemMessageTest {
/**
* 使用相同SystemMessage test
*/
@Test
public void sameSystemMessageTest() {
ChatModel model = ChatModelInit.initOllama();
Assistant assistant = AiServices.builder(Assistant.class)
.chatMemoryProvider(memoryId -> MessageWindowChatMemory.withMaxMessages(10)) // 默认使用内存缓存
.chatModel(model)
.build();
String message1 = assistant.chatSameSystemMessage("1234", "我看见一只鸽子在天上飞,倒影在河边却像燕子");
System.out.println("ai回答1:" + message1);
String message2 = assistant.chatSameSystemMessage("1235", "修仙文明传承万万年,日新月异,革故鼎新,宗门如林,强者如蚁。");
System.out.println("ai回答2:" + message2);
/**
* 不同大模型回答的效果不一,该结果仅供参考
* ai回答1:<think>
* 好的,我现在需要帮用户润色一段文案。用户是一名专业的文案润色专家,他提供了原文:“我看见一只鸽子在天上飞,倒影在河边却像燕子。” 任务是用现代语,加入修辞手法,让文案更简洁有吸引力。
* ...
* 最后,检查润色后的句子是否流畅,是否有足够的吸引力。确认修辞手法是否恰当,画面是否清晰,情感是否传达到位。
* </think>
* 天边的鸽群,如同画家的笔触,勾勒出一幅温柔的画卷。
* 倒映在水中,却似燕子轻盈地掠过,仿佛是被风铃轻轻摇晃的谜影。
*
* ai回答2:<think>
* 嗯,用户给了一个任务,让我作为专业的文案润色专家,帮他改写一段文字。首先,我得仔细看看他提供的原文和要求。
* ...
* 最后,检查一下整体流畅度,确保每一句都能衔接自然,没有重复或冗余的地方。这样改写后的文案应该既简洁又有吸引力,同时保留了原有的深意。
* </think>
*
* 【修仙文明传承千载,源远流长,代代相传,生生不息】
* 【破茧成蝶迎新章,宗门林立,强者如云,群英荟萃,共赴华章】
*/
}
/**
* 使用不同的SystemMessage test
*/
@Test
public void noSameSystemMessageTest() {
ChatModel model = ChatModelInit.initOllama();
Map<String, SystemMessage> systemMessageMap = new HashMap<>();
systemMessageMap.put("1234", SystemMessage.from("你是一名专业的文案润色专家,请根据我提供的文案进行润色改写。要【用现代语,有修辞手法】,希望达到【更为简洁、有吸引力】的效果。"));
systemMessageMap.put("1235", SystemMessage.from("你是一名修仙界元婴期师傅,请根据我的描述认为我适合当体修,还是法修。"));
Assistant assistant = AiServices.builder(Assistant.class)
.chatMemoryProvider(memoryId -> MessageWindowChatMemory.withMaxMessages(10)) // 默认使用内存缓存
.chatModel(model)
.systemMessageProvider(memoryId-> systemMessageMap.get(memoryId.toString()).text())
.build();
String message1 = assistant.chatNoSameSystemMessage("1234", "我看见一只鸽子在天上飞,倒影在河边却像燕子");
System.out.println("ai回答1:" + message1);
String message2 = assistant.chatNoSameSystemMessage("1235", "修仙文明传承万万年,日新月异,革故鼎新,宗门如林,强者如蚁。我更喜欢以力破法");
System.out.println("ai回答2:" + message2);
/**
*
* 不同大模型回答的效果不一,该结果仅供参考
* ai回答1:<think>
* 好的,我现在需要帮用户润色一段文字。用户提供了原文:“我看见一只鸽子在天上飞,倒影在河边却像燕子。” 他们希望用现代语言,并加入修辞手法,使文案更简洁、吸引人。
* ...
* 最后,检查润色后的文案是否达到了用户的要求:现代、修辞、简洁且吸引人。确保每句都流畅,并传达出原意的同时,增加趣味性和生动性。
* </think>
* 我看到一只天上的鸽子,轻盈地展翅飞翔;水中倒影却幻化成翩跹的燕子。
*
* ai回答2:<think>
* 嗯,我现在需要帮助用户确定自己在修仙界更适合选择体修还是法修。首先,我要理解用户的背景和需求。
* ...
* 综合来看,用户更适合选择体修,因为它符合他们喜欢用力量解决问题的习惯,并且在现代修仙界有更大的生存空间和破坏力。
* </think>
* 综合以上分析,体修更为适合你当前的偏好和需求,能够更好地发挥你的力量优势,并在现代社会中取得更大的成功空间。
*/
}
}
总结
AiServices的出现就像大脑一样,控制着各个组件的使用,开发人员无需知道是如何控制,只需要知道通过AiServices想干什么。当然它不仅仅是这点功能,还有多模态,返回值类型,结构化输出,以及通过它实现RAG功能,后续会一 一道来。
以上完整代码在我的仓库,地址:https://gitee.com/liutao-lx/langchain4j-agent-dev/tree/master/agent-example/src/main/java/com/koicarp/agent/example/aiservices
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)