【数据结构】树-哈夫曼树(动态图解、c++、java、优先队列实现哈夫曼树)
URLeisure的哈夫曼树“完美”复习资料。
文章目录
GitHub同步更新(已分类):Data_Structure_And_Algorithm-Review
公众号:URLeisure 的复习仓库
公众号二维码见文末
以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考。
什么是哈夫曼树?
-
给定N个权值作为N个叶子结点,构造一棵二叉树,若该树的带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。
-
哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值(可以理解为出现的概率)较大的结点离根较近。(百度百科)
哈夫曼树的概述
1). 哈夫曼树
举个例子,看看哈夫曼树都能解决什么问题。
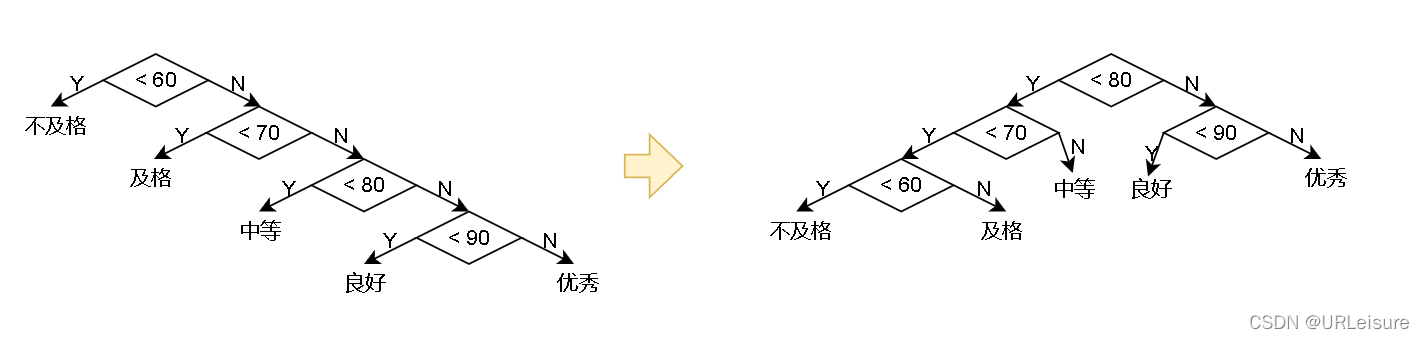
- 比如,将一个班级的成绩从百分制转为等级制(100人)。
可能有人这么写代码:
if(score < 60){
cout<<"不及格"<<endl;
}else if(score < 70){
cout<<"及格"<<endl;
}else if(score < 80){
cout<<"中等"<<endl;
}else if(score < 90){
cout<<"良好"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"优秀"<<endl;
}
-
这么写确实没问题,但是在判定次数就不一定了。
-
例如,这个班成绩服从正态分布,五个档的概率分别为
10 % , 20 % , 40 % , 20 % , 10 % 10\%,20\%,40\%,20\%,10\% 10%,20%,40%,20%,10% -
我们算一下,一共需要判断:
100 × 10 % × 1 + 100 × 20 % × 2 + 100 × 40 % × 3 + 100 × 20 % × 4 + 100 × 10 % × 5 = 300 次 100×10\%×1 + 100×20\%×2 + 100×40\%×3 + 100×20\%×4 +100×10\%×5 = 300 次 100×10%×1+100×20%×2+100×40%×3+100×20%×4+100×10%×5=300次
而当我们先判断概率最大的一组时:
if(score < 80){
if(score < 70){
if(score < 60){
cout<<"不及格"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"及格"<<endl;
}
}else{
cout<<"中等"<<endl;
}
}else if(score < 90){
cout<<"良好"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"优秀"<<endl;
}
- 我们算一下,一共需要判断:
100 × 40 % × 2 + 100 × 20 % × 2 + 100 × 10 % × 2 + 100 × 20 % × 3 + 100 × 10 % × 3 = 230 次 100×40\%×2 + 100×20\%×2 + 100×10\%×2 + 100×20\%×3 + 100×10\%×3 = 230 次 100×40%×2+100×20%×2+100×10%×2+100×20%×3+100×10%×3=230次
2). 哈夫曼编码
-
1952年,数学家 D.A.Huffman 提出了用字符在文件中出现的频率(0、1串)表示各字符的最佳编码方式,称为哈夫曼编码。
-
哈夫曼编码很好地解决了上述问题,被广泛地应用于数据压缩,尤其是远距离通信和大容量数据存储,常用的 JPEG 图片就是采用的哈夫曼编码压缩的。
-
哈夫曼编码的基本思想是以字符的使用频率作为权来构建一棵哈夫曼树,然后利用哈夫曼树对字符进行编码。
-
哈夫曼编码的核心思想是让权值大的叶子离根最近。
哈夫曼树的算法步骤
(可以直接看图解)
-
哈夫曼树是通过将索要编码的字符作为叶子节点,将该字符在文件中的使用频率作为叶子节点的权值,以自底向上的方式,做 n-1 次”合并“运算构建出来的。
-
哈夫曼算法采用的贪心策略是每次从树的集合中取出没有双亲且权值最小的两棵树作为左右子树,构建一棵新树,新树根节点的权值为其左右孩子节点权值之和,并将新树插入树的结合中。
- 确定合适的数据结构:编写程序先要考虑以下情况。
-
哈夫曼树中没有度为1的节点,即一棵有 n0 个叶子节点的哈夫曼树共有 2n0 - 1 个节点。
-
构成哈夫曼树后,为求哈夫曼编码需从叶子节点出发有一条从叶子到根的路径。
-
译码需要从根出发走一条从根到叶子的路径。那么对每个接待你而言,需要知道每个节点的权值、双亲、左孩子、右孩子和节点信息。
-
初始化:构建 n 棵节点为 n 个字符的单节点树集合 T = {t1,t2,… ,tn},每棵树只有一个带权的根节点,权值为该字符的使用频率。
-
如果 T 中只剩下一棵树,则哈夫曼树构建成功,跳到第 6 步。否则,从集合 T 中取出没有双亲且权值最小的两颗树 ti 和 tj ,将它们合并成一棵新树 zK,新树的左孩子为 ti,右孩子为 tj,zk 的权值为 ti 和 tj 的权值之和。
-
从集合 T 中删去 ti、tj,加入 zk。
-
重复第 3、4步。
-
约定左分支上的编码为 ”0“,右分支上的编码为 ”1“。
- 从叶子节点到根节点逆向求出每个字符的哈夫曼编码,那么从根节点到叶子节点路径上的字符组成的字符串为该叶子节点的哈夫曼编码,算法结束。
哈夫曼树的图解
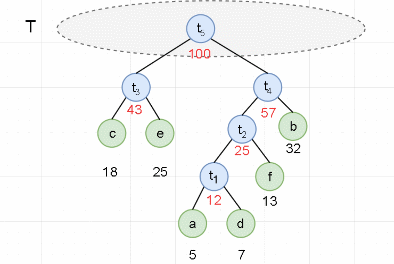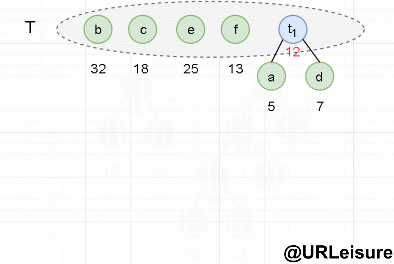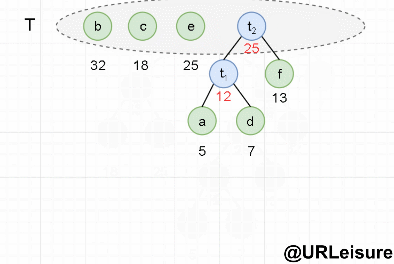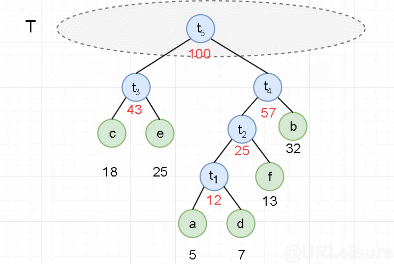
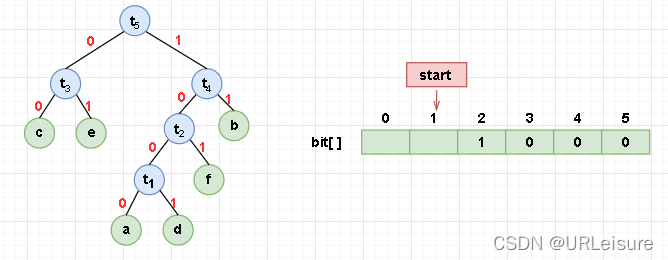
- 用以下字符和它们的频率,构建一个哈夫曼树,得到它们的哈夫曼编码。
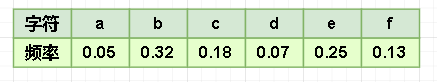
- 为了存储方便,我们将他们的频率都扩大 100 倍。
a : 5 、 b : 32 、 c : 18 、 d : 7 、 e : 25 、 f : 13 a:5 、b:32、c:18、d:7、e:25、f:13 a:5、b:32、c:18、d:7、e:25、f:13
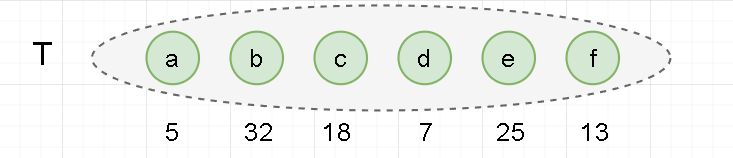
- 初始化:构建 n 棵节点为 n 个字符的单节点树集合 T = {a,b,c,d,e,f}。
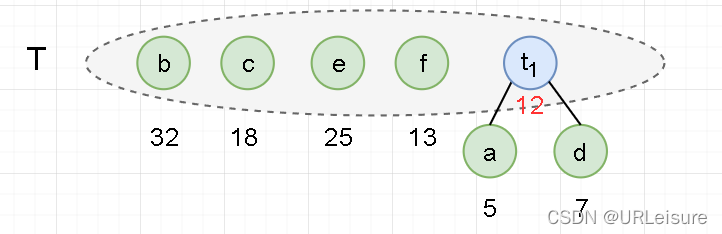
- 从集合 T 中取出没有双亲的且权值最小的两棵树 a 和 d,将它们合并成一棵新树 t1,新树的左孩子为 a,右孩子为 d,新树的权值为 a+b = 12。新树的根 t1 追加入集合 T,从集合 T 中删除 a 和 d。
…
- 约定左分支上的编码为“ 0 ”,右分支上的编码为“ 1 ”。
从叶子节点到根节点逆向求出每个字符的哈夫曼编码。那么从根节点到叶子节点路径上的字符组成的字符串为该叶子节点的哈夫曼编码。
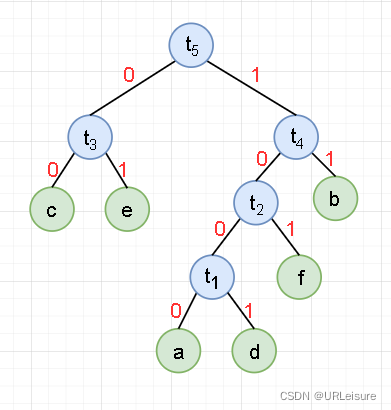
a : 1000 、 b : 11 、 c : 00 、 d : 1001 、 e : 01 、 f : 101 a:1000、b:11、c:00、d:1001、e:01、f:101 a:1000、b:11、c:00、d:1001、e:01、f:101
注意:
下图中,有 2 个 25 权值的节点,我们为了减少树的层数,优先选用层数少的节点。
哈夫曼树的代码实现
-
我们的代码都是用的最朴素的方法写的,优化代码在最后。
-
首先声明: HuffNode[ ] 存的是所有的节点信息,HuffCode[ ] 存的是所有节点的哈夫曼编码。
首先创建两个结构体(内部类)。
- 节点结构体:包含权值、双亲、左孩子、右孩子和节点字符信息 5 个域。
- 哈夫曼编码结构体:包含编码数组和记录编码开始下标
c++代码如下(示例):
typedef struct HNode{
double weight;//权值
int parent;//双亲
int lchild;//左孩子
int rchild;//右孩子
char value;//当前节点字符信息
}*HNodeType;
typedef struct HCode{
int bit[MAXBIT];//存储正序的编码数组
int start;//编码开始下标
}HCodeType;
java代码如下(示例):
public static class NodeType{
double weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
String value;
}
public static class CodeType{
int bit[] = new int[MAXBIT];
int start;
}
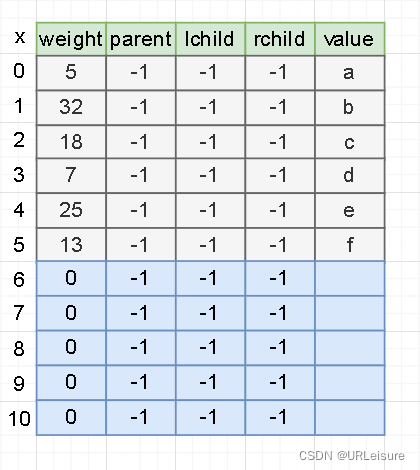
1).初始化
例如,我们的节点信息如下:
/*
a 5
b 32
c 18
d 7
e 25
f 13
*/
c++代码如下(示例):
void InitHuffmanTree(HNodeType HuffNode[],int n){
for(int i = 0;i<2*n-1;i++){//由公式推导出 一共有 2n-1 个节点
HuffNode[i].weight = 0;
HuffNode[i].parent = -1;
HuffNode[i].lchild = -1;
HuffNode[i].rchild = -1;
}
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
cin>>HuffNode[i].value>>HuffNode[i].weight;
}
}
java代码如下(示例):
public static NodeType[] initHuffmanTree(NodeType HuffNode[],int n){
for(int i = 0;i<2*n-1;i++){
HuffNode[i] = new NodeType();
HuffNode[i].weight = 0;
HuffNode[i].parent = -1;
HuffNode[i].lchild = -1;
HuffNode[i].rchild = -1;
}
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
HuffNode[i].value = sc.next();
HuffNode[i].weight = sc.nextDouble();
}
return HuffNode;
}
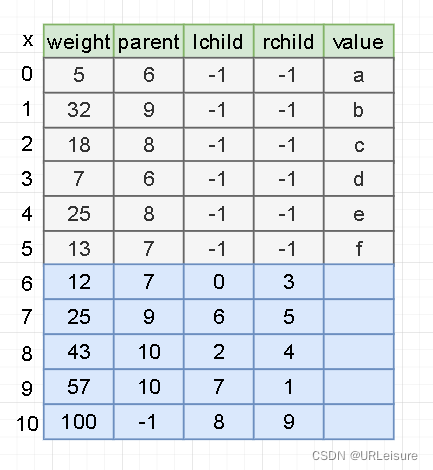
2). 循环建树
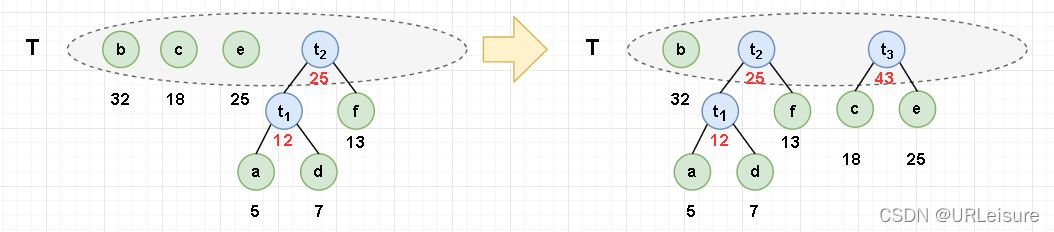
- 从集合 T 中取出双亲为 -1 的且权值最小的两棵树 ti 和 tj,将它们合并成一棵新树 zk,其左孩子为权值最小的节点 ti,右孩子为次小的节点 tj,zk 的权值为 ti 和 tj 的权值之和。
完成后如图:
优先队列在算法优化中
c++代码如下(示例):
void HuffmanTree(HNodeType HuffNode[],int n){
int x1,x2;//x1.最小序号 x2.次小序号
double m1,m2;//m1.最小权值 m2.次小权值
for(int i = 0;i<n-1;i++){//n 个节点 n-1 次合并
x1 = x2 = 0;
m1 = m2 = MAXVALUE;
for(int j = 0;j<n+i;j++){//找出没有双亲且最小权值的两个节点,合并成一棵二叉树(新生成的也要排,所以是 n+i)
double k = HuffNode[j].weight;
if(k<m1 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1){//次小最小替换
x2 = x1;
m2 = m1;
x1 = j;
m1 = k;
}else if(k<m2 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1){//次小替换
x2 = j;
m2 = k;
}
}
HuffNode[n+i].weight = m1 + m2;//新节点权值
HuffNode[n+i].lchild = x1;//新节点左孩子.最小
HuffNode[n+i].rchild = x2;//新节点右孩子.次小
HuffNode[x1].parent = n+i;//追加双亲
HuffNode[x2].parent = n+i;//追加双亲
}
}
java代码如下(示例):
public static NodeType[] huffmanTree(NodeType HuffNode[],int n){
int x1,x2;
double m1,m2;
for(int i = 0;i<n-1;i++){
x1 = x2 = 0;
m1 = m2 = MAXVALUE;
for(int j = 0;j<n+i;j++){
double k = HuffNode[j].weight;
if(k < m1 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1){
m2 = m1;
x2 = x1;
x1 = j;
m1 = k;
}else if(k < m2 && HuffNode[j].parent == -1){
m2 = k;
x2 = j;
}
}
HuffNode[n+i].weight = m1+m2;
HuffNode[n+i].lchild = x1;
HuffNode[n+i].rchild = x2;
HuffNode[x1].parent = n+i;
HuffNode[x2].parent = n+i;
}
return HuffNode;
}
3). 哈夫曼编码
-
我们的哈夫曼编码是从叶子找到根,而译码需要从根到叶子,是相反的过程。
-
所以为了方便,我们直接倒叙存数组。
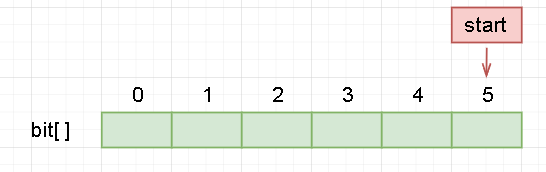
比如,我们存个 a 的哈夫曼编码:
-
我们的存储过程是先将 0 或 1 存储进数组,然后 start 向左移动一位。
-
这就造成 start 位于第一个有用存储空间的前面,所以最后我们让 start 后退一位。
c++代码如下(示例):
void HuffmanCode(HCodeType HuffCode[],HNodeType HuffNode[],int n) {
HCodeType temp;
int p,cur;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){//n 个叶子,存储 n 个
temp.start = n-1;// 数组从 n-1 开始存储
cur = i;//当前节点序号
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;//当前接i但双亲
while(p != -1){//有双亲
if(HuffNode[p].lchild == cur){//判断 cur 是否为左子
temp.bit[temp.start] = 0;
}else{//判断是否为右子
temp.bit[temp.start] = 1;
}
temp.start --;//左移
cur = p;//下一个节点序号
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;//下一个节点的双亲
}
HuffCode[i] = temp;//把编码信息复制出来
HuffCode[i].start += 1;//右移一位
}
}
java代码如下(示例):
public static CodeType[] huffmanCode(CodeType HuffCode[],NodeType HuffNode[],int n){
int cur,p;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
HuffCode[i] = new CodeType();
HuffCode[i].start = n-1;
cur = i;
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;
while(p!=-1){
if(HuffNode[p].lchild == cur){
HuffCode[i].bit[HuffCode[i].start] = 0;
}else{
HuffCode[i].bit[HuffCode[i].start] = 1;
}
HuffCode[i].start --;
cur = p;
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;
}
HuffCode[i].start += 1;
}
return HuffCode;
}
4). 完整代码
c++代码如下(示例):
#include<iostream>
#include<climits>
using namespace std;
#define MAXBIT 100 //编码个数
#define MAXVALUE INT_MAX
#define MAXLEAF 30 //叶子数
#define MAXNODE (MAXLEAF*2-1)//节点个数
typedef struct HNode{
double weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
char value;
}HNodeType;
typedef struct HCode{
int bit[MAXBIT];
int start;
}HCodeType;
void InitHuffmanTree(HNodeType HuffNode[],int n){
for(int i = 0;i<2*n-1;i++){
HuffNode[i].weight = 0;
HuffNode[i].parent = -1;
HuffNode[i].lchild = -1;
HuffNode[i].rchild = -1;
}
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
cin>>HuffNode[i].value>>HuffNode[i].weight;
}
}
void HuffmanTree(HNodeType HuffNode[],int n){
int x1,x2;
double m1,m2;
for(int i = 0;i<n-1;i++){
x1 = x2 = 0;
m1 = m2 = MAXVALUE;
for(int j = 0;j<n+i;j++){
double k = HuffNode[j].weight;
if(k<m1 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1){
x2 = x1;
m2 = m1;
x1 = j;
m1 = k;
}else if(k<m2 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1){
x2 = j;
m2 = k;
}
}
HuffNode[n+i].weight = m1 + m2;
HuffNode[n+i].lchild = x1;
HuffNode[n+i].rchild = x2;
HuffNode[x1].parent = n+i;
HuffNode[x2].parent = n+i;
}
}
void HuffmanCode(HCodeType HuffCode[],HNodeType HuffNode[],int n) {
HCodeType temp;
int p,cur;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
temp.start = n-1;
cur = i;
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;
while(p != -1){
if(HuffNode[p].lchild == cur){
temp.bit[temp.start] = 0;
}else{
temp.bit[temp.start] = 1;
}
temp.start --;
cur = p;
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;
}
HuffCode[i] = temp;
HuffCode[i].start += 1;
}
}
int main(){
int n=6;
HNodeType HuffNode[MAXNODE];
InitHuffmanTree(HuffNode,n);
HuffmanTree(HuffNode,n);
HCodeType HuffCode[MAXLEAF];
HuffmanCode(HuffCode,HuffNode,n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<HuffNode[i].value<<":哈夫曼编码是:";
for(int j=HuffCode[i].start;j<n;j++){
cout<<HuffCode[i].bit[j];
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
java代码如下(示例):
import java.util.Scanner;
public class A {
private static int MAXBIT = 100;
private static int MAXVALUE = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static int MAXLEAF = 30;
private static int MAXNODE = MAXLEAF*2-1;
private static NodeType HuffNode[];
private static CodeType HuffCode[];
private static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static class NodeType{
double weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
String value;
}
public static class CodeType{
int bit[] = new int[MAXBIT];
int start;
}
public static NodeType[] initHuffmanTree(NodeType HuffNode[],int n){
for(int i = 0;i<2*n-1;i++){
HuffNode[i] = new NodeType();
HuffNode[i].weight = 0;
HuffNode[i].parent = -1;
HuffNode[i].lchild = -1;
HuffNode[i].rchild = -1;
}
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
HuffNode[i].value = sc.next();
HuffNode[i].weight = sc.nextDouble();
}
return HuffNode;
}
public static NodeType[] huffmanTree(NodeType HuffNode[],int n){
int x1,x2;
double m1,m2;
for(int i = 0;i<n-1;i++){
x1 = x2 = 0;
m1 = m2 = MAXVALUE;
for(int j = 0;j<n+i;j++){
double k = HuffNode[j].weight;
if(k < m1 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1){
m2 = m1;
x2 = x1;
x1 = j;
m1 = k;
}else if(k < m2 && HuffNode[j].parent == -1){
m2 = k;
x2 = j;
}
}
HuffNode[n+i].weight = m1+m2;
HuffNode[n+i].lchild = x1;
HuffNode[n+i].rchild = x2;
HuffNode[x1].parent = n+i;
HuffNode[x2].parent = n+i;
}
return HuffNode;
}
public static CodeType[] huffmanCode(CodeType HuffCode[],NodeType HuffNode[],int n){
int cur,p;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
HuffCode[i] = new CodeType();
HuffCode[i].start = n-1;
cur = i;
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;
while(p!=-1){
if(HuffNode[p].lchild == cur){
HuffCode[i].bit[HuffCode[i].start] = 0;
}else{
HuffCode[i].bit[HuffCode[i].start] = 1;
}
HuffCode[i].start --;
cur = p;
p = HuffNode[cur].parent;
}
HuffCode[i].start += 1;
}
return HuffCode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n=6;
NodeType huffNode[]=new NodeType[MAXNODE];
initHuffmanTree(huffNode,n);
huffmanTree(huffNode,n);
CodeType codeType[]=new CodeType[MAXLEAF];
huffmanCode(codeType,huffNode,n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
System.out.print("哈夫曼编码是"+huffNode[i].value+" ");
for(int j=codeType[i].start;j<n;j++){
System.out.print(codeType[i].bit[j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
哈夫曼树的算法复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度
在 HuffmanTree() 中, if(k<m1 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1) 为基本语句,外层 i 与 j 构成双层循环。
- i = 0 时,该语句执行 n 次;
- i = 1 时,该语句执行 n+1 次;
- i = 2 时,该语句执行 n+2 次;
- …
- i = n-2 时,该语句执行 n+n-2 次;
因此,基本语句共执行:
n + ( n + 1 ) + ( n + 2 ) + . . . + ( n + n − 2 ) = ( n − 1 ) ( 3 n − 2 ) 2 n+(n+1)+(n+2)+ ... +(n+n-2) =\frac{(n-1)(3n-2)}{2} n+(n+1)+(n+2)+...+(n+n−2)=2(n−1)(3n−2)
- 在函数 HuffmanCode() 中,编码的时间复杂度接近 n2,则该算法时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)。
- 空间复杂度
- 所需存储空间为节点结构体数组与编码结构体数组,哈夫曼树数组 HuffmanNode[ ] 中的节点为 2n-1 个,其中 n 个节点包含 bit[ ] 和 start 两个域,则 该算法空间复杂度为 O ( n × M A X B I T ) O(n × MAXBIT) O(n×MAXBIT)。
哈夫曼树的算法优化
- 函数 HuffmanTree() 中,找两个权值最小的节点时使用优先队列,时间复杂度为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),执行 n-1 次,总时间复杂度为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)。
- 在比较时,要注意两个权值相等的节点,这时需要再比较其在 HuffNode[ ] 中的序号大小,越靠前的,层数越少,所以相等时,序号小的排到前面。
c++代码如下(示例):
bool operator<(const HNodeType &a, const HNodeType &b) {
return a.weight > b.weight;//升序排列
}
void HuffmanTree1(HNodeType HuffNode[],int n){
HNodeType temp,x1,x2;//x1.最小项 x2.次小项
priority_queue<HNodeType> q;
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
q.push(HuffNode[i]);//存入优先队列
}
int k = 0;
while(q.size()>1){//等于 1 是所有的都合并完了,就剩权值100了
x1 = q.top();//最小
q.pop();
x2 = q.top();//次小
q.pop();
//创建新节点
temp.parent = -1;
temp.lchild = x1.index;
temp.rchild = x2.index;
temp.weight = x1.weight + x2.weight;
temp.index = n + k;//节点结构体里加了一个索引位置变量,来确定左右子位置
HuffNode[x1.index].parent = n+k;//添加x1双亲
HuffNode[x2.index].parent = n+k;//添加x2双亲
HuffNode[n+k] = temp;//把新节点加到节点数组中
q.push(temp);//添加新节点
k++;
}
}
java代码如下(示例):
public static void huffmanTree1(NodeType HuffNode[],int n){
Queue<NodeType> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<NodeType>() {
@Override
public int compare(NodeType o1, NodeType o2) {
if(o1.weight > o2.weight ) {
return 1;
}else if(o1.weight == o2.weight && o1.index > o2.index){//为了使生成树的层数最小,当权值相等时,我们先选序号靠前的,层数少
return 1;
}
return -1;
}
});
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){
queue.add(HuffNode[i]);
}
NodeType x1,x2,temp;
int k = 0;
while(queue.size() > 1){
x1 = queue.poll();
x2 = queue.poll();
temp = new NodeType();
temp.parent = -1;
temp.lchild = x1.index;
temp.rchild = x2.index;
temp.index = n + k;
temp.weight = x1.weight + x2.weight;
HuffNode[n+k] = temp;
HuffNode[x1.index].parent = n+k;
HuffNode[x2.index].parent = n+k;
queue.add(temp);
k++;
}
}
- 函数 HuffmanCode() 中,哈夫曼编码数组 HuffNode[ ] 中可以定义一个动态分配空间的线性表来存储编码,每个线性表的长度为实际的编码长度,这样可以大大节省空间。
- 不打了,记着前后颠倒一下位置,或者逆序输出就好。
开图了,有好多东西。
关注公众号,感受不同的阅读体验

下期预告:图的基础理论
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容







所有评论(0)