Shell脚本正则表达式之Sed用法介绍+操作(包括sed高阶用法)
文章目录sed介绍sed基本指令sed基本操作sed介绍sed会逐行扫描输入的数据,并将其读取数据的内容复制到buffer中,我们称之为模式空间,然后呐模式空间中的数据与给定条件进行匹配,如果成功匹配则执行特定的sed指令。否则sed会跳过输入的数据行,继续读取后面的数据。最后把最终的结果显示到屏幕上。sed基本指令常用的命令选项命令选项功能描述-n -silent屏蔽默认输出,默认sed会把匹配
·
sed介绍
- sed会逐行扫描输入的数据,并将其读取数据的内容复制到buffer中,我们称之为模式空间,然后呐模式空间中的数据与给定条件进行匹配,如果成功匹配则执行特定的sed指令。否则sed会跳过输入的数据行,继续读取后面的数据。最后把最终的结果显示到屏幕上。
sed基本指令
- 常用的命令选项
| 命令选项 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| -n -silent | 屏蔽默认输出,默认sed会把匹配结果打到屏幕上 |
| -r | 支持扩展正则 |
| -i | 直接修改源文件 |
| -e | 指定需要执行的命令,支持多个-e的参数 |
| -f | 制定需要执行的脚本文件,需要提前将sed写入到指定文件中 |
- 基本操作指令
| 基本操作指令 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| p | 打印当前匹配数据行 |
| l | 打印当前匹配数据行(显示控制字符) |
| = | 打印行数 |
| a text | 在匹配行后面追加文本内容 |
| i text | 在匹配行前面插入文本内容 |
| d | 删除匹配行整行内容 |
| c text | 将整行匹配内容换为特定的文本内容 |
| r filename | 从文件中读取并追加到匹配数据行的后面 |
| w filename | 将当前匹配行插入到指定的文件中 |
| q [exit code] | 立刻退出sed脚本 |
| s/regrep/replace | 将匹配到的数据替换为特定内容 |
- 支持数据定位的方法
| 格式 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| number | 直接根据行号匹配 |
| first~step | 从first开始,步长为step |
| $ | 匹配最后一行 |
| /regrep/ | 正则表达式匹配数据行 |
| \cregerpc | 正则表达式匹配数据行(c可以是任意字符,a,b不可以) |
| addr1,addr2 | 直接使用行号进行定位,从addr1到addr2行 |
| addr,+N | 直接使用行号进行定位,从addr开始到后面的N行 |
sed基本操作
- 显示行用法
sed -n 'p' /etc/hosts #所有数据行显示一次
sed -n '2p' /etc/hosts #仅显示文件第一行数据
df -hT | sed -n '2p' #支持管道读取数据

cat -n /etc/passwd > ~/tmp.passwd #生产带行号的素材文件
sed -n '1,3p' tmp.passwd #只显示1-3行数据
sed -n '1p;3p;5p' tmp.passwd #只显示1,3,5行数据
sed -n '10,$p' tmp.passwd #只显示从第10行到最后1行
sed -n '1~2p' tmp.passwd #只显示奇数行
sed -n '2~2p' tmp.passwd #只显示偶数行
sed -n '2,+2p' tmp.passwd #只显示第2行以及后面的2行
sed -n '/root/p' tmp.passwd #只显示匹配包含root的行
sed -n '$p' tmp.passwd #只显示最后一行
sed -n '/s...:x/p' tmp.passwd #只显示以s为开头以:x结尾,中间包含任意3个字符的数据行。
sed -n '/[0-9]/p' tmp.passwd #只显示匹配包含数字的行
sed -n '/^root/p' /etc/passwd #只显示以root为开头的行
sed -n '/bash$/p' tmp.passwd #只显示以bash为结尾的行
-
输出太多这边并不再用图片示例,请大家自行操作
-
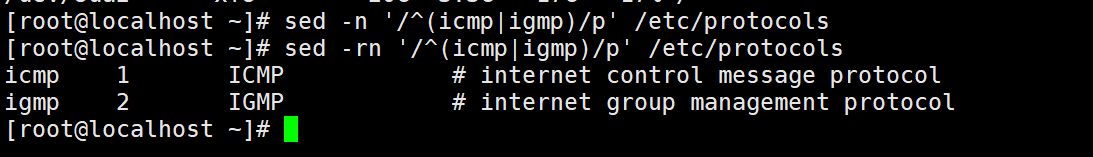
默认sed不支持扩展正则,只显示以icmp或igmp为开头的行
sed -n '/^(icmp|igmp)/p' /etc/protocols
sed -rn '/^(icmp|igmp)/p' /etc/protocols
- 正则表达式匹配数据行(c可以是任意字符,a,b不可以)
sed -n '\cUIDcp' /etc/login.defs #正则匹配包含UID的行
sed -n '\xUIDxp' /etc/login.defs #同上
sed -n '\:bash:p' /etc/shells #正则匹配包含bash的行
sed -n '\1bash1p' /etc/shells #同上
sed -n '\,bash,p' /etc/shells #同上
sed -n 'l' /etc/shells #打印内容并显示控制字符
- 显示行号
sed -n '/root/=' /etc/passwd #只显示root所在行的行号
sed -n '2=' /etc/passwd #只显示第2行所在行的行号
sed -n '$=' /etc/passwd #只显示最后1行的行号
- 取反操作
sed -n '1!p' /etc/passwd #显示除第1行以外的其他行号
sed -n '/nologin$/!p' /etc/passwd #显示除最后带有nologin的其他行号
- 添加用法
cp -p /etc/hosts ~/tmp.hosts
sed '1a hello world' tmp.hosts #在第1行后面添加hello world行
sed '1i hello world' tmp.hosts #在第1行前面插入hello world行
sed -i '1a hello world' tmp.hosts #在第1行后面添加hello world行(直接修改)
sed -i.bak '2d' tmp.hosts #先备份再删除第2行内容(备份名为tmp.hosts.bak)
sed '/hello/a shell script' tmp.hosts #在匹配到hello字段后面插入shell script行
- 删除用法
sed 'd' tmp.hosts #删除所有行
cp -p /etc/profile ~/tmp.profile
sed -i '/^$/d' tmp.profile #删除空白行
sed -i '/^#/d' tmp.profile #删除以#号开头的行
sed -i '/if/d' tmp.profile #删除包含if的行
- 替换用法
sed '2c modify hello world' tmp.hosts.bak #将第2行整行替换为modify hello world
sed 'c nmsl' tmp.hosts #将所有行替换nmsl
sed '/localhost/c nmsl' tmp.hosts #将所有包含localhost的行替换为nmsl
- 读写用法
sed 'r /etc/hostname' tmp.hosts #read读取其他文件内容,每行都会显示
sed '1r /etc/hostname' tmp.hosts #read读取其他文件内容,只显示第1行
sed 'w /root/new.host' tmp.hosts #write写入到new.hosts文件中
sed '1,3w /root/new.host' /etc/shells #仅将1-3行write写入到new.hosts文件中
- 退出用法
sed '3q' /etc/shells #读取到第3行退出sed
- 替换用法(最重要)
cat >> test.txt <<- EOF
hello the world
go air jordan
123 456 789
hello the nanjing
I am Cauchy
EOF
sed '1s/hello/hi/' test.txt #仅对第1行的hello进行替换操作
sed 's/o/O/' test.txt #仅替换每1行的第一个o
sed 's/o/O/g' test.txt #替换每行所有字母o
sed 's/o/O/2' test.txt #替换每行所有第2个字母o
sed -n 's/o/O/2p' test.txt #仅显示被替换的行
sed -n 's/cauchy/Thomas/ip' test.txt #i忽略大小写
echo "/etc/hosts" | sed 's/^/ls -l /e' # =ls -l /etc/hosts e表示替换之后再执行shell命令
echo "abcfile" | sed 's/^/touch \/tmp\//e'# =touch /tmp/abcfile
echo "tmpfile" | sed 's#^#touch /tmp/#e' # =touch /tmp/tmpfile
sed 's/the//' test.txt #将the替换为空,等同于删除
sed 's/$/./' test.txt #在每行最后面添加.
sed -r 's/^(.)(.*)(.)$/\3\2\1/' test.txt #将每行首尾字符对调
#如果我们在替换内容中存在"/"符号时,如果继续用"/"做替换符号时,就会频繁的使用转义符"\"。
#我们其实就可以用"#" "," "x" "9"来代替"/"
sed 's#/sbin/nologin#/bin/sh#' /etc/passwd
sed 's,/sbin/nologin,/bin/sh,' /etc/passwd
sed 'sx/sbin/nologinx/bin/shx' /etc/passwd
sed 's9/sbin/nologin9/bin/sh9' /etc/passwd
#sed使用分号或者-e可以实现在一行中编写多条指令
sed -n '1p;3p' test.txt = sed -n -e '1p' -e '3p' test.txt
sed '/world/s/hello/hi/;s/the//' test.txt #不使用分组
sed '/world/{s/hello/hi/;s/the//}' test.txt #使用分组
sed高级用法
- sed高级操作指令
| h | 将模式空间中的数据复制到保留空间里 |
| H | 将模式空间中的数据追加到保留空间里 |
| g | 将保留空间中的数据复制到模式空间里 |
| G | 将保留空间中的数据追加到模式空间里 |
| x | 将模式空间和保留空间的数据对调 |
| n | 读取下一行数据到模式空间 |
| N | 读取下一行数据追加到模式空间 |
| y/源/目标/ | 以字符为单位将源字符转换为目标字符 |
| :label | 为t或b指令定义label标签 |
| t label | 有条件跳转到标签,没有label则跳转到指令结尾 |
| b label | 跳转到标签,没有label则跳转到指令结尾 |
- 模式空间与保留空间的关系
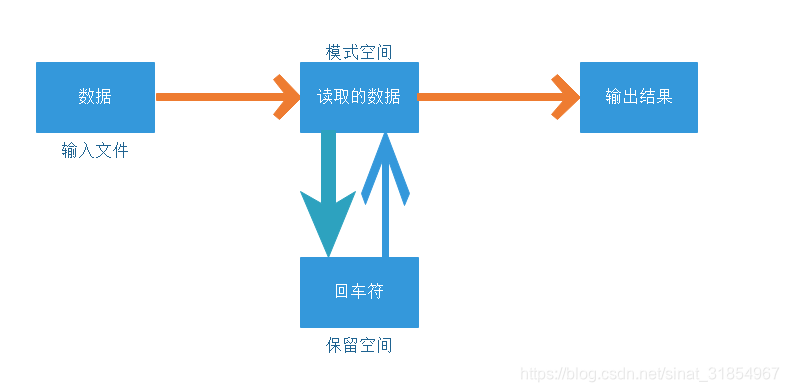
sed高级操作
- 编辑素材
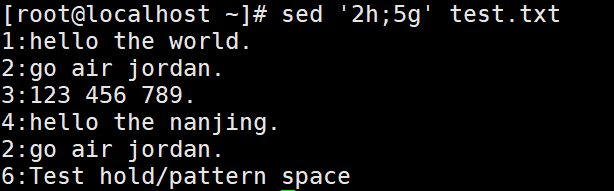
vim test.txt
1:hello the world.
2:go air jordan.
3:123 456 789.
4:hello the nanjing.
5:I am Cauchy.
6:Test hold/pattern space
sed '2h;5g' test.txt
#读取文件中的第2行,将数据复制到保留空间中,会覆盖掉回车符,然后读取第5行时,
#保留空间中的数据输出到第5行,而第5行原有的数据则会被覆盖掉。(2行数据替换5行数据)
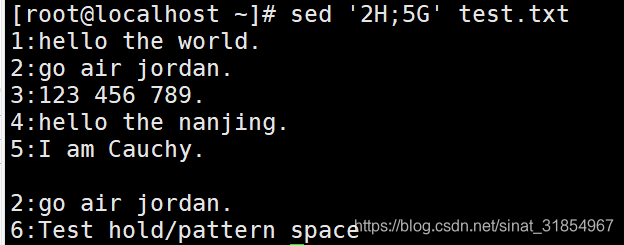
sed '2H;5G' test.txt
#读取文件中的第2行,将数据追加到保留空间中,不会覆盖掉回车符,然后读取第5行时,
#保留空间中的数据追加到第5行后面,第5行原有的数据则不会被覆盖掉。(连回车符一同追加)
sed '2H;5g' test.txt #5行数据替换为回车符与第2行
sed '2h;5G' test.txt #5行数据后追加第二行
sed '2h;2d;5g' test.txt #删除第2行,将第5行数据替换为第2行
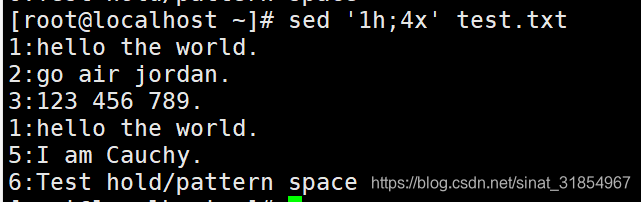
sed '1h;4x' test.txt
#第1行的数据,复制到保留空间中,然后与第4行的模式空间中的数据进行交换
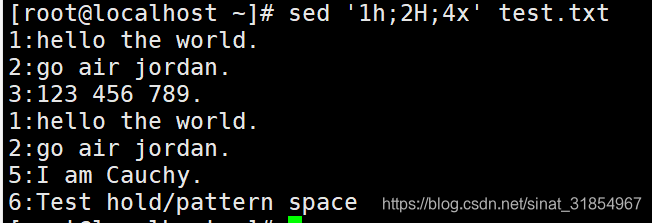
sed '1h;2H;4x' test.txt
#第1行的数据复制到保留空间中,第2行的数据追加到保留空间中,
#然后与第4行的模式空间中的数据进行交换。
sed 'n;d' test.txt #删除偶数行=只显示奇数行
sed -n 'p;n' test.txt #只显示奇数行
sed '1~2!d' test.txt
sed -n 'n;p' test.txt #只显示偶数行
sed '1~2d' test.txt
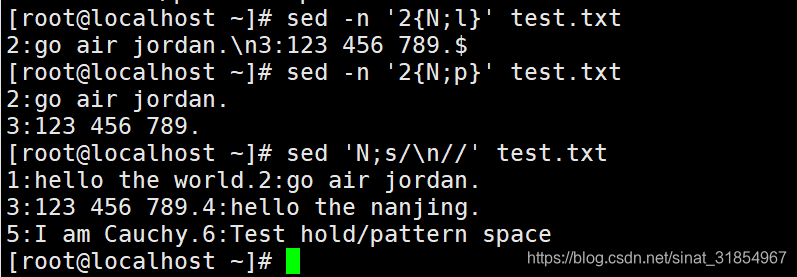
sed -n '2{N;l}' test.txt
sed -n '2{N;p}' test.txt
#读取第2行到模式空间之后,先使用N读取下一行,追加到模式空间中。
#"l"指令可以打印出那些不可显示的控制字符,如\n,$等。
#"p"指令不会打印出控制字符,而是将控制字符转换为实际的换行和回车符。
sed 'N;s/\n//' test.txt #将2行合并为1行
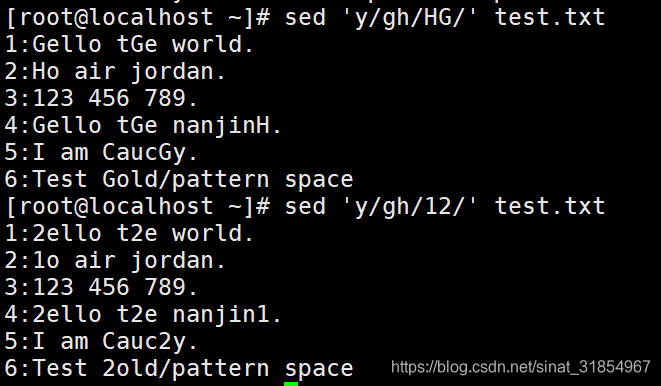
sed 'y/gh/HG/' test.txt #h替换为H,g替换为G
sed 'y/gh/12/' test.txt #g替换为1,h替换为2
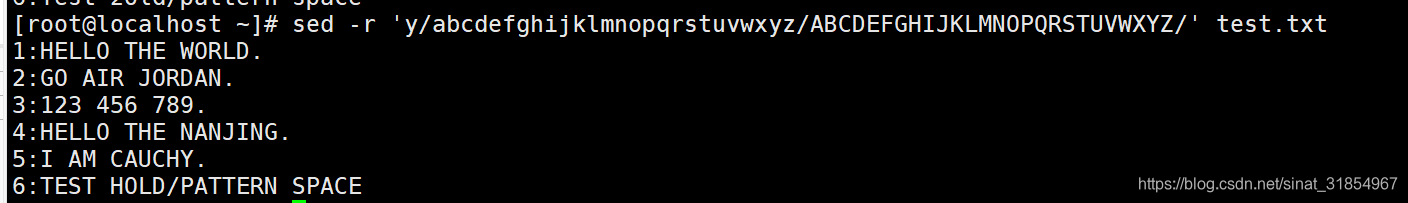
sed -r 'y/abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz/ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ/' test.txt
#将所有小写字母转换为大写字母
-
跳转标签sed
-
基本语法:
-
1(无条件跳转)
:label
sed 序列指令
......
b label
- 2(有条件跳转)
:label
sed 序列指令
......
s/regex/replace
t label
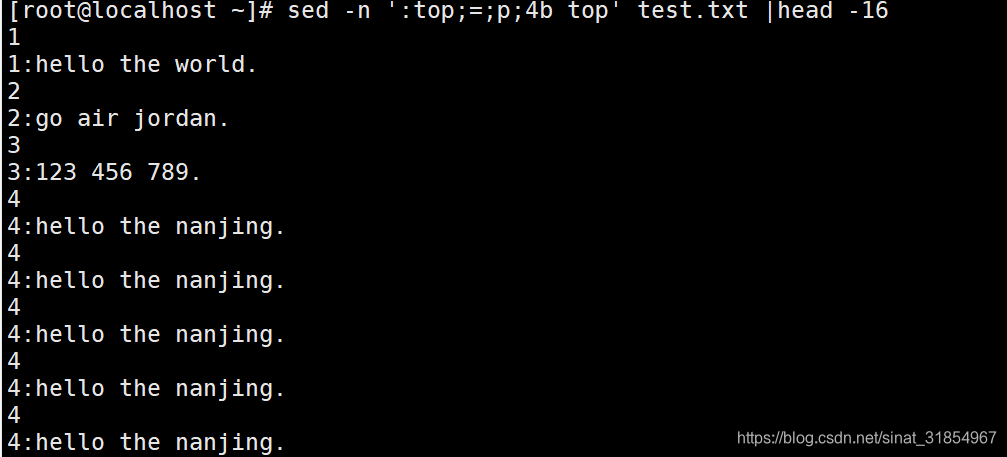
sed -n ':top;=;p;4b top' test.txt |head -16
#1-3行输出的是行号和数据,到了第4行之后,依然继续往下执行=和p的命令。
#因为行号与b指令前面匹配行号相同,因此会一直执行,导致死循环。
#head -16表示只查看前16行
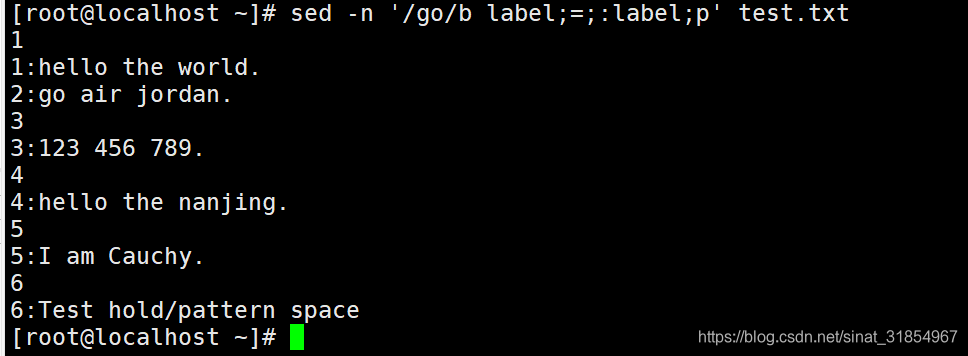
sed -n '/go/b label;=;:label;p' test.txt
#打印出行号与行数据,第2行不打印行号
#当匹配到go这一行时,b指令直接跳过=,执行p
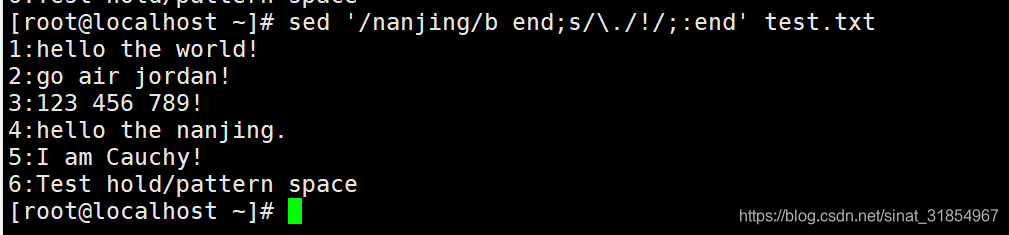
sed '/nanjing/b end;s/\./!/;:end' test.txt
#除了带有nanjing字段的行,其他行的".",替换为"!"
sed '4b end;s/\./!/;:end' test.txt #同上
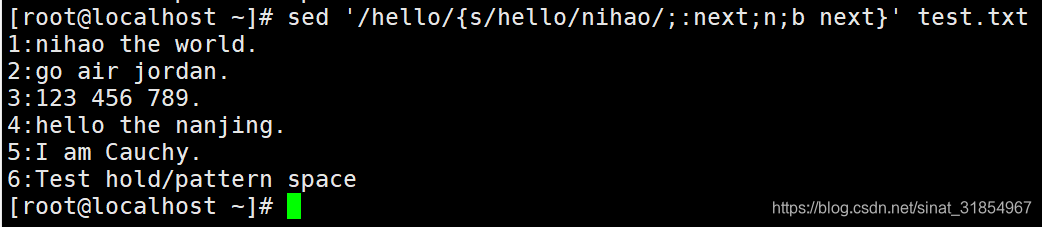
sed '/hello/{s/hello/nihao/;:next;n;b next}' test.txt
#只替换第1行的hello为nihao
- 整理编排文档
vim id.txt
phone:
13399988888
mail:
testsed@qq.com
phone:
138999888888
mail:
betased@qq.com
sed -r 'N;s/\n//;s/: +/: /' id.txt #将多行数据合并为1行并且删除多余空格
sed -r ':start;/:$/N;s/\n +/ /;t start' id.txt
#开头定义一个start标签,将以冒号结尾的行的下一行追加
#然后删除多余空格,最后执行t有条件跳转
#如果s执行成功则执行t跳转,否则不执行
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献6条内容
已为社区贡献6条内容






所有评论(0)