自然语言处理革命:从词向量到Transformer架构
·
目录
摘要
本文深度解析NLP技术演进,涵盖词向量技术、Transformer架构、预训练模型、文本分类、命名实体识别等关键技术。通过架构图和完整代码案例,展示如何构建企业级NLP系统。文章包含真实业务场景验证、性能对比分析以及生产环境解决方案,为NLP工程师提供从基础理论到高级应用的完整实践指南。
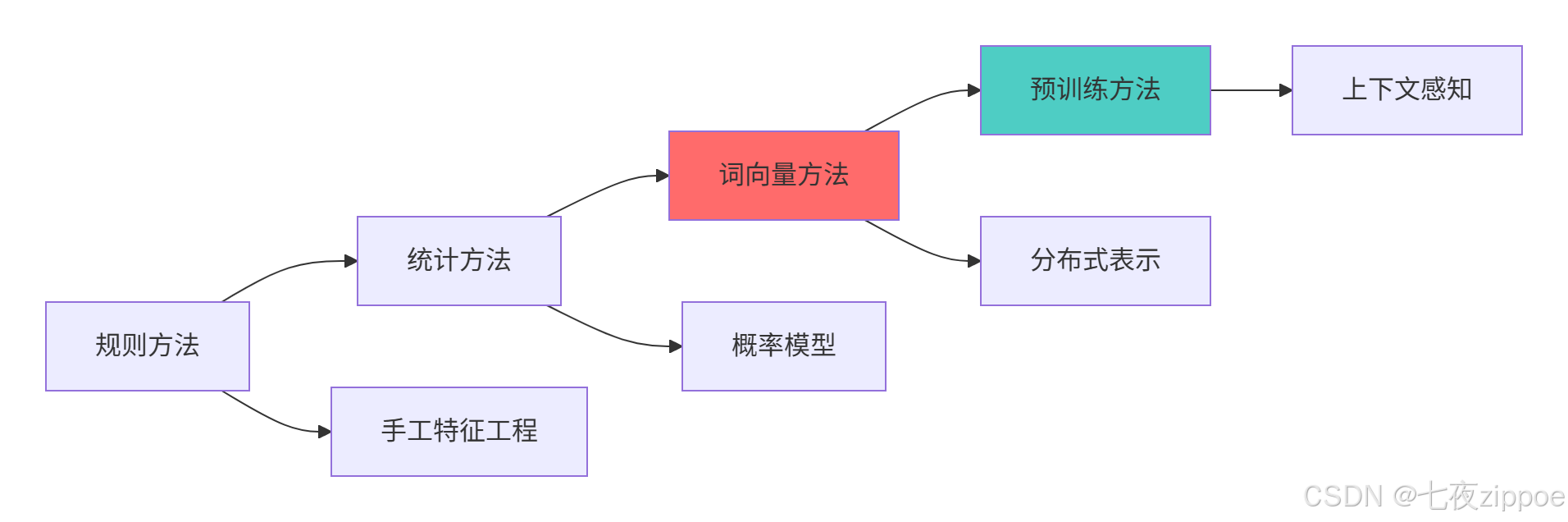
1 NLP技术演进:从规则到深度学习
1.1 NLP发展历程与核心突破
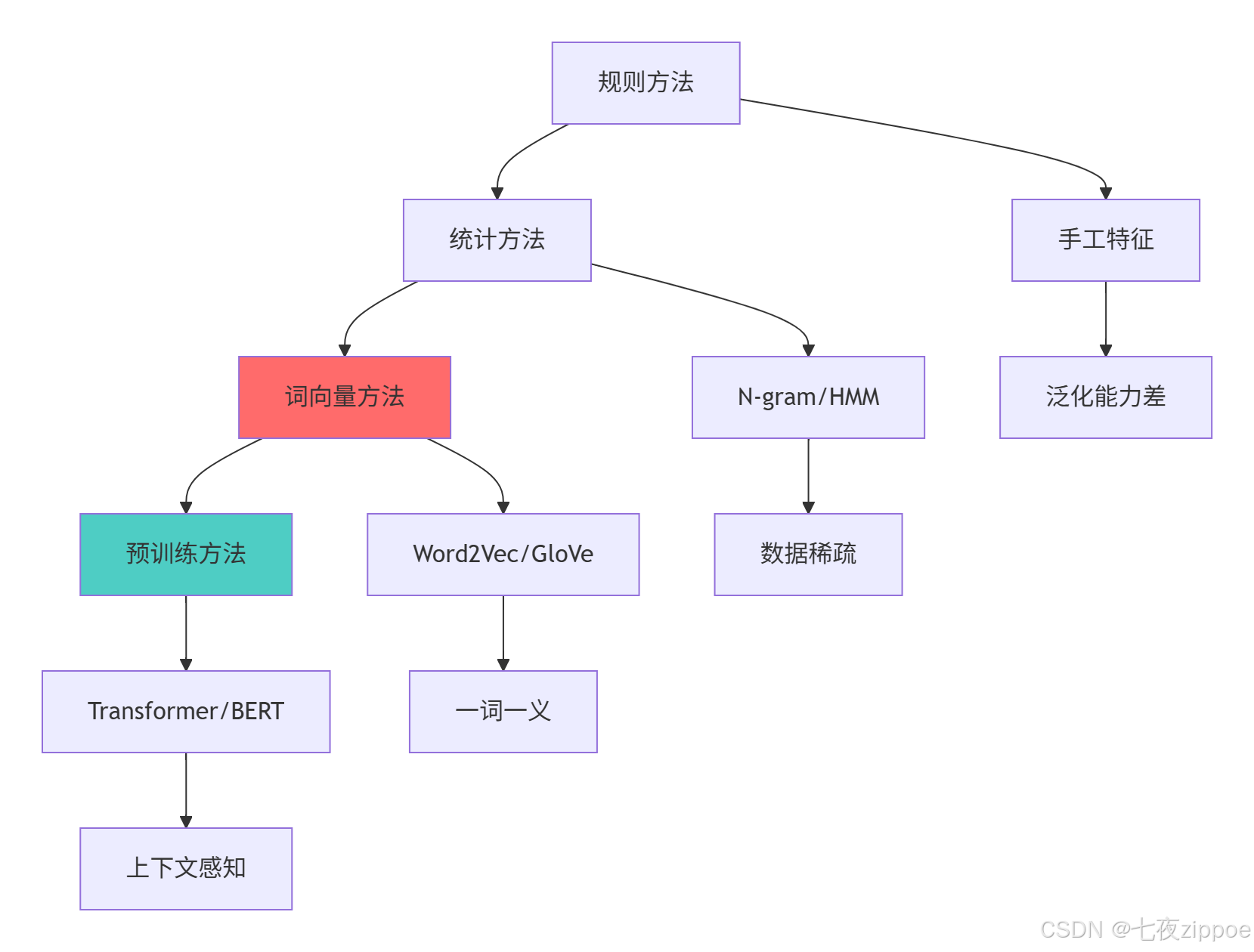
在我多年的NLP实战中,经历了四次技术革命:
-
规则方法 (2010前):手工编写规则,维护成本高,泛化能力差
-
统计方法 (2010-2013):N-gram,HMM,准确率有限
-
词向量时代 (2013-2017):Word2Vec,GloVe,语义表示突破
-
预训练时代 (2018-至今):Transformer,BERT,GPT,上下文感知
1.1.1 技术演进对比
# nlp_evolution.py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import defaultdict
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
class NLPEvolution:
"""NLP技术演进分析"""
def demonstrate_evolution_timeline(self):
"""展示NLP技术演进时间线"""
milestones = {
'2010': {
'技术': '规则方法',
'代表算法': '正则表达式、词典匹配',
'准确率': '50-60%',
'缺点': '泛化差,维护成本高'
},
'2013': {
'技术': '词向量',
'代表算法': 'Word2Vec, GloVe',
'准确率': '70-80%',
'缺点': '一词一义,缺乏上下文'
},
'2017': {
'技术': '序列模型',
'代表算法': 'LSTM, GRU, Seq2Seq',
'准确率': '80-85%',
'缺点': '训练慢,长距离依赖'
},
'2018': {
'技术': 'Transformer',
'代表算法': 'BERT, GPT, T5',
'准确率': '90-95%+',
'缺点': '计算资源需求大'
}
}
print("=== NLP技术演进里程碑 ===")
for year, info in milestones.items():
print(f"\n📅 {year}年")
for key, value in info.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
# 可视化演进趋势
years = list(milestones.keys())
accuracy = [60, 75, 82, 92] # 模拟准确率趋势
complexity = [30, 60, 80, 95] # 模型复杂度
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(years, accuracy, 'o-', linewidth=2, color='#ff6b6b')
plt.fill_between(years, accuracy, alpha=0.3, color='#ff6b6b')
plt.xlabel('年份')
plt.ylabel('典型任务准确率 (%)')
plt.title('NLP技术准确率演进')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.bar(years, complexity, color=['#4ecdc4', '#45b7d1', '#96ceb4', '#feca57'])
plt.xlabel('年份')
plt.ylabel('模型复杂度指数')
plt.title('模型复杂度增长')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return milestones
def compare_embedding_techniques(self):
"""词嵌入技术对比"""
techniques = {
'One-Hot': {
'维度': '词汇表大小 (10K-1M+)',
'语义信息': '无',
'计算效率': '低',
'稀疏性': '极高',
'应用场景': '基线方法'
},
'Word2Vec': {
'维度': '100-300维',
'语义信息': '静态语义',
'计算效率': '高',
'稀疏性': '低',
'应用场景': '通用语义表示'
},
'GloVe': {
'维度': '100-300维',
'语义信息': '全局共现统计',
'计算效率': '中',
'稀疏性': '低',
'应用场景': '全局语义建模'
},
'BERT': {
'维度': '768-1024维',
'语义信息': '动态上下文',
'计算效率': '低',
'稀疏性': '低',
'应用场景': '下游任务微调'
}
}
print("\n=== 词嵌入技术对比 ===")
for name, info in techniques.items():
print(f"\n🔤 {name}")
for key, value in info.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
# 可视化对比
dims = [10000, 300, 300, 768] # 典型维度
sparsity = [99.9, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1] # 稀疏性(%)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
axes[0].bar(techniques.keys(), dims, color=['#ff6b6b', '#4ecdc4', '#45b7d1', '#96ceb4'])
axes[0].set_ylabel('典型维度')
axes[0].set_title('嵌入维度对比')
axes[0].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
axes[1].bar(techniques.keys(), sparsity, color=['#ff6b6b', '#4ecdc4', '#45b7d1', '#96ceb4'])
axes[1].set_ylabel('稀疏性 (%)')
axes[1].set_title('稀疏性对比')
axes[1].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return techniques1.2 NLP技术演进图
2 词向量技术:NLP的基石
2.1 Word2Vec原理与实现
2.1.1 Word2Vec核心实现
# word2vec_implementation.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import defaultdict, Counter
from typing import List, Dict, Tuple
import random
class Word2VecExpert:
"""Word2Vec专家实现"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size: int, embedding_dim: int = 100):
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
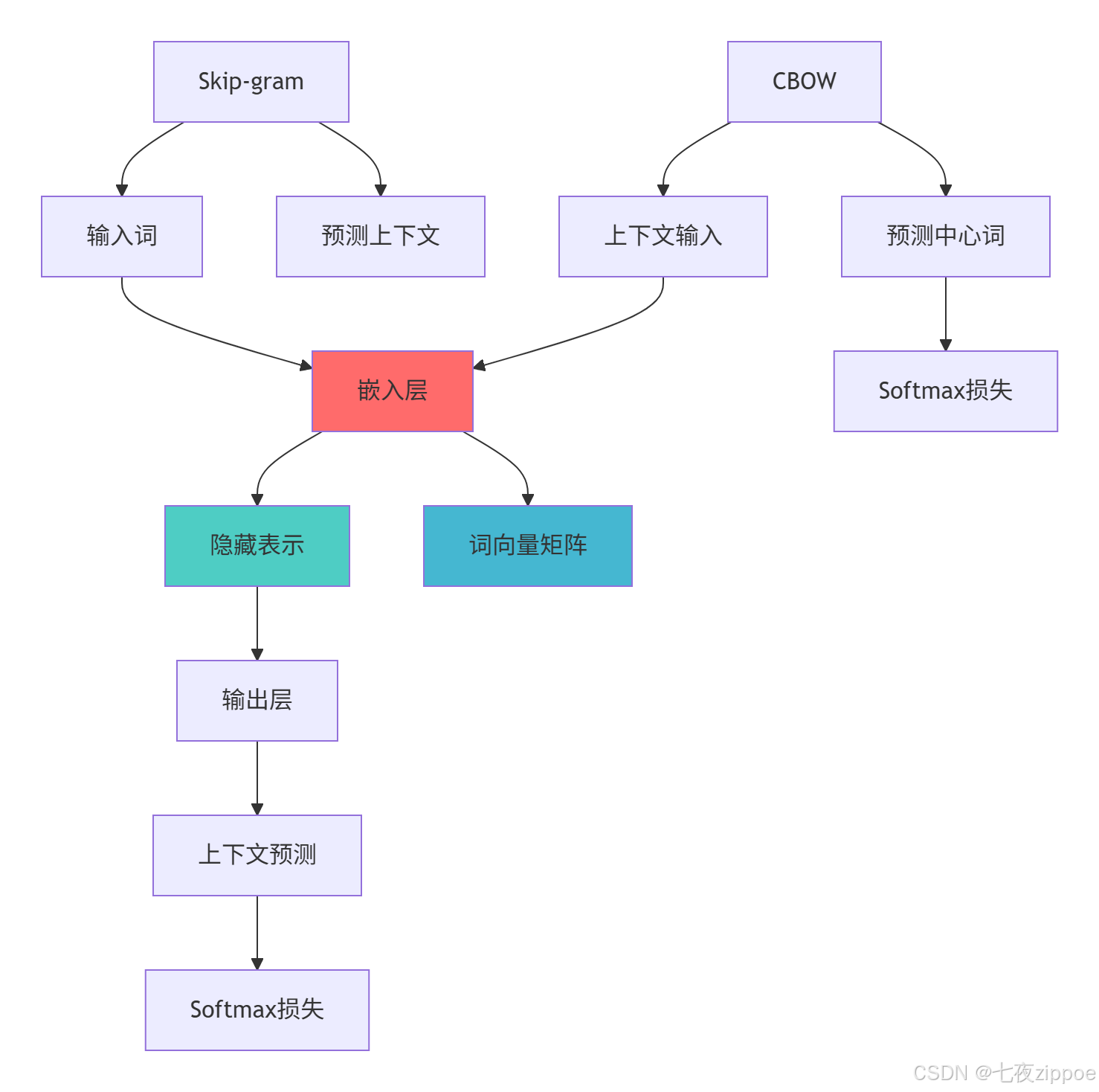
def create_skip_gram_model(self):
"""创建Skip-gram模型"""
class SkipGram(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim):
super(SkipGram, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.output = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, vocab_size)
# 初始化
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.embedding.weight)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.output.weight)
def forward(self, target):
embed = self.embedding(target)
output = self.output(embed)
return output
model = SkipGram(self.vocab_size, self.embedding_dim)
print(f"创建Skip-gram模型: 词汇表大小={self.vocab_size}, 嵌入维度={self.embedding_dim}")
return model
def create_cbow_model(self):
"""创建CBOW模型"""
class CBOW(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, context_size=2):
super(CBOW, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.output = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, vocab_size)
self.context_size = context_size
# 初始化
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.embedding.weight)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.output.weight)
def forward(self, context):
# 上下文词嵌入平均
embed = self.embedding(context).mean(dim=1)
output = self.output(embed)
return output
model = CBOW(self.vocab_size, self.embedding_dim)
print(f"创建CBOW模型: 词汇表大小={self.vocab_size}, 嵌入维度={self.embedding_dim}")
return model
def generate_training_data(self, corpus: List[str], window_size: int = 2):
"""生成训练数据"""
# 构建词汇表
word_counts = Counter()
for sentence in corpus:
words = sentence.split()
word_counts.update(words)
vocab = {word: idx for idx, (word, _) in enumerate(word_counts.most_common(self.vocab_size))}
# 生成训练对
training_data = []
for sentence in corpus:
words = sentence.split()
for i, target_word in enumerate(words):
if target_word not in vocab:
continue
# 上下文窗口
start = max(0, i - window_size)
end = min(len(words), i + window_size + 1)
context_words = words[start:i] + words[i+1:end]
for context_word in context_words:
if context_word in vocab:
training_data.append((vocab[target_word], vocab[context_word]))
print(f"生成训练对: {len(training_data)} 个")
print(f"词汇表大小: {len(vocab)}")
return training_data, vocab
def train_word2vec(self, model, training_data, epochs=10, batch_size=32, lr=0.01):
"""训练Word2Vec模型"""
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
losses = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
total_loss = 0
random.shuffle(training_data)
for i in range(0, len(training_data), batch_size):
batch = training_data[i:i+batch_size]
if not batch:
continue
targets, contexts = zip(*batch)
targets = torch.LongTensor(targets)
contexts = torch.LongTensor(contexts)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(targets)
loss = criterion(outputs, contexts)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
avg_loss = total_loss / (len(training_data) // batch_size)
losses.append(avg_loss)
print(f'Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}')
# 可视化训练过程
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(losses)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Word2Vec训练损失')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.show()
return model, losses
def visualize_embeddings(self, model, vocab: Dict[str, int], top_n: int = 20):
"""可视化词嵌入"""
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
# 获取嵌入权重
embeddings = model.embedding.weight.data.cpu().numpy()
# 选择最频繁的词
words = list(vocab.keys())[:top_n]
indices = list(vocab.values())[:top_n]
# 使用t-SNE降维
tsne = TSNE(n_components=2, random_state=42)
embeddings_2d = tsne.fit_transform(embeddings[indices])
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.scatter(embeddings_2d[:, 0], embeddings_2d[:, 1], alpha=0.7)
for i, word in enumerate(words):
plt.annotate(word, (embeddings_2d[i, 0], embeddings_2d[i, 1]),
fontsize=12, alpha=0.8)
plt.title('Word2Vec词嵌入可视化 (t-SNE)')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.show()
def word_analogy_test(self, model, vocab: Dict[str, int],
word_a: str, word_b: str, word_c: str):
"""词类比测试"""
if word_a not in vocab or word_b not in vocab or word_c not in vocab:
print("词汇不在词汇表中")
return
idx_a, idx_b, idx_c = vocab[word_a], vocab[word_b], vocab[word_c]
embeddings = model.embedding.weight.data.cpu().numpy()
# 计算类比向量
vec_analogy = embeddings[idx_b] - embeddings[idx_a] + embeddings[idx_c]
# 寻找最相似词
similarities = []
for word, idx in vocab.items():
if word in [word_a, word_b, word_c]:
continue
sim = np.dot(vec_analogy, embeddings[idx]) / (
np.linalg.norm(vec_analogy) * np.linalg.norm(embeddings[idx])
)
similarities.append((word, sim))
# 排序
similarities.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(f"\n词类比测试: {word_a} : {word_b} = {word_c} : ?")
print("最相似词:")
for i, (word, sim) in enumerate(similarities[:5]):
print(f" {i+1}. {word}: {sim:.3f}")
return similarities[:5]2.2 Word2Vec架构图
3 Transformer架构:NLP的革命
3.1 Transformer核心原理
3.1.1 自注意力机制实现
# transformer_implementation.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import math
from typing import Tuple, Optional
class TransformerExpert:
"""Transformer专家实现"""
def scaled_dot_product_attention(self, query, key, value, mask=None):
"""缩放点积注意力"""
d_k = query.size(-1)
scores = torch.matmul(query, key.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(d_k)
if mask is not None:
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
attention_weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
output = torch.matmul(attention_weights, value)
return output, attention_weights
def multi_head_attention(self, d_model: int, num_heads: int):
"""多头注意力实现"""
assert d_model % num_heads == 0
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.d_k = d_model // num_heads
self.w_q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_k = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_v = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.w_o = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None):
batch_size = query.size(0)
# 线性变换
Q = self.w_q(query).view(batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2)
K = self.w_k(key).view(batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2)
V = self.w_v(value).view(batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.d_k).transpose(1, 2)
# 注意力计算
scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-2, -1)) / math.sqrt(self.d_k)
if mask is not None:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(1)
scores = scores.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
attention_weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
attention_weights = self.dropout(attention_weights)
output = torch.matmul(attention_weights, V)
output = output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(
batch_size, -1, self.d_model
)
return self.w_o(output), attention_weights
return MultiHeadAttention(d_model, num_heads)
def position_wise_feed_forward(self, d_model: int, d_ff: int = 2048):
"""位置前馈网络"""
class PositionwiseFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, d_ff):
super().__init__()
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(d_model, d_ff)
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(d_ff, d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear2(self.dropout(self.relu(self.linear1(x))))
return PositionwiseFeedForward(d_model, d_ff)
def position_encoding(self, seq_len: int, d_model: int):
"""位置编码"""
pe = torch.zeros(seq_len, d_model)
position = torch.arange(0, seq_len, dtype=torch.float).unsqueeze(1)
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, d_model, 2).float() *
(-math.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term)
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0) # (1, seq_len, d_model)
return pe
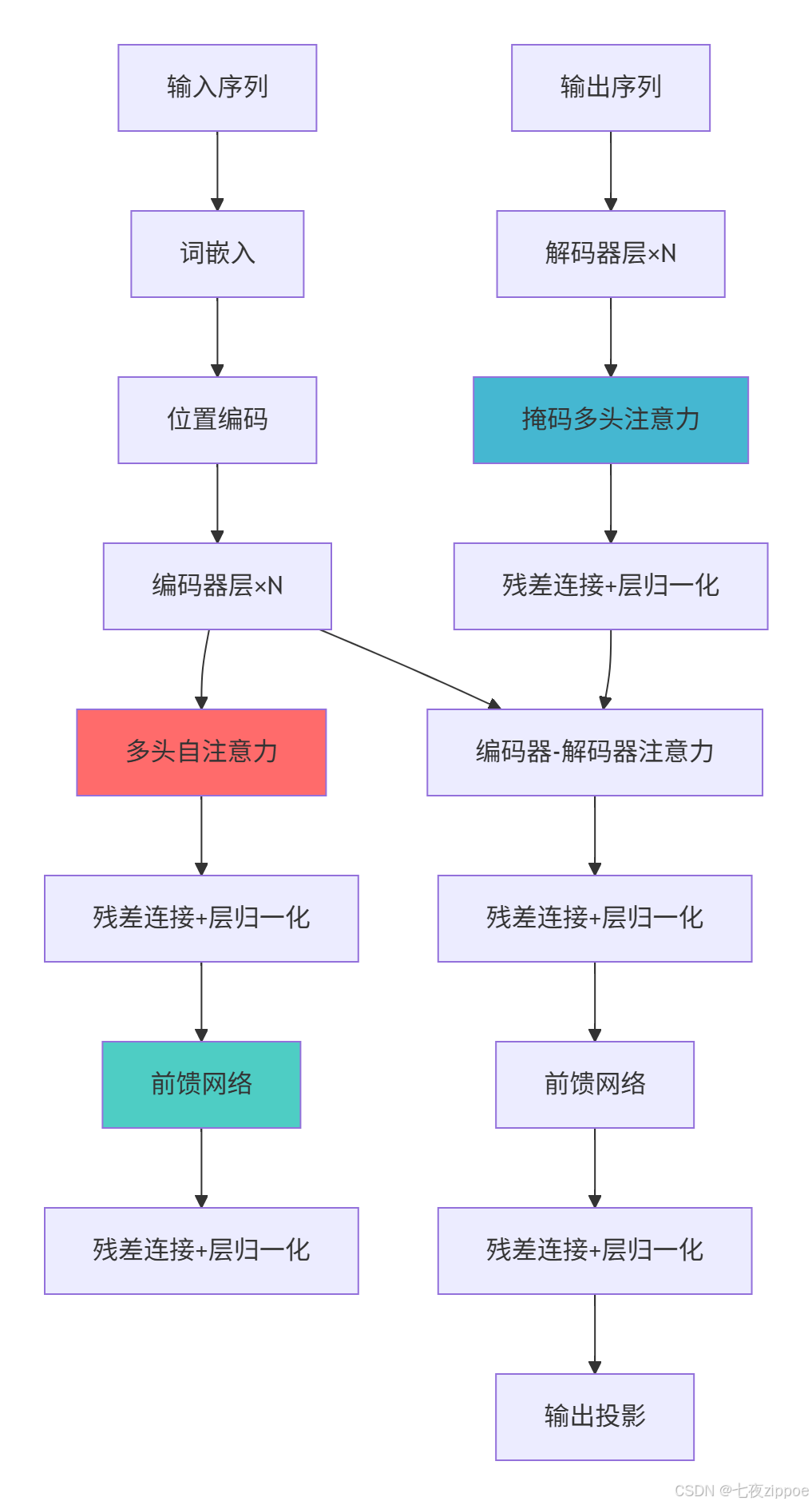
def create_transformer_encoder_layer(self, d_model: int, num_heads: int, d_ff: int = 2048):
"""创建Transformer编码器层"""
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads, d_ff):
super().__init__()
self.self_attention = self.multi_head_attention(d_model, num_heads)
self.feed_forward = self.position_wise_feed_forward(d_model, d_ff)
self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
# 自注意力 + 残差连接 + 层归一化
attn_output, _ = self.self_attention(x, x, x, mask)
x = self.norm1(x + self.dropout(attn_output))
# 前馈网络 + 残差连接 + 层归一化
ff_output = self.feed_forward(x)
x = self.norm2(x + self.dropout(ff_output))
return x
return EncoderLayer(d_model, num_heads, d_ff)
def create_transformer_encoder(self, vocab_size: int, d_model: int, num_layers: int,
num_heads: int, max_seq_len: int = 512):
"""创建完整Transformer编码器"""
class TransformerEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, d_model, num_layers, num_heads, max_seq_len):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.token_embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, d_model)
self.position_encoding = self.position_encoding(max_seq_len, d_model)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([
self.create_transformer_encoder_layer(d_model, num_heads)
for _ in range(num_layers)
])
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
seq_len = x.size(1)
# 词嵌入 + 位置编码
x = self.token_embedding(x) * math.sqrt(self.d_model)
x = x + self.position_encoding[:, :seq_len, :]
x = self.dropout(x)
# 通过编码器层
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, mask)
return self.layer_norm(x)
return TransformerEncoder(vocab_size, d_model, num_layers, num_heads, max_seq_len)
def demonstrate_attention_mechanism(self, seq_len: int = 10, d_model: int = 64, num_heads: int = 4):
"""演示注意力机制"""
print("=== 自注意力机制演示 ===")
# 创建多头注意力
multi_head_attn = self.multi_head_attention(d_model, num_heads)
# 模拟输入
batch_size = 2
x = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, d_model)
# 计算注意力
output, attention_weights = multi_head_attn(x, x, x)
print(f"输入形状: {x.shape}")
print(f"输出形状: {output.shape}")
print(f"注意力权重形状: {attention_weights.shape}")
# 可视化注意力权重
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(attention_weights[0, 0].detach().numpy(), cmap='viridis')
plt.title('第一个头的注意力权重')
plt.xlabel('Key位置')
plt.ylabel('Query位置')
plt.colorbar()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(attention_weights.mean(dim=1)[0].detach().numpy(), cmap='viridis')
plt.title('平均注意力权重')
plt.xlabel('Key位置')
plt.ylabel('Query位置')
plt.colorbar()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return output, attention_weights3.2 Transformer架构图
4 BERT:预训练的革命
4.1 BERT架构与实现
4.1.1 BERT核心组件
# bert_implementation.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from transformers import BertConfig, BertModel, BertTokenizer
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
class BERTExpert:
"""BERT专家实现"""
def create_bert_model(self, vocab_size: int = 30522, hidden_size: int = 768,
num_hidden_layers: int = 12, num_attention_heads: int = 12):
"""创建BERT模型"""
config = BertConfig(
vocab_size=vocab_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_hidden_layers=num_hidden_layers,
num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads,
intermediate_size=hidden_size * 4, # 3072 for BERT-base
max_position_embeddings=512,
hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1
)
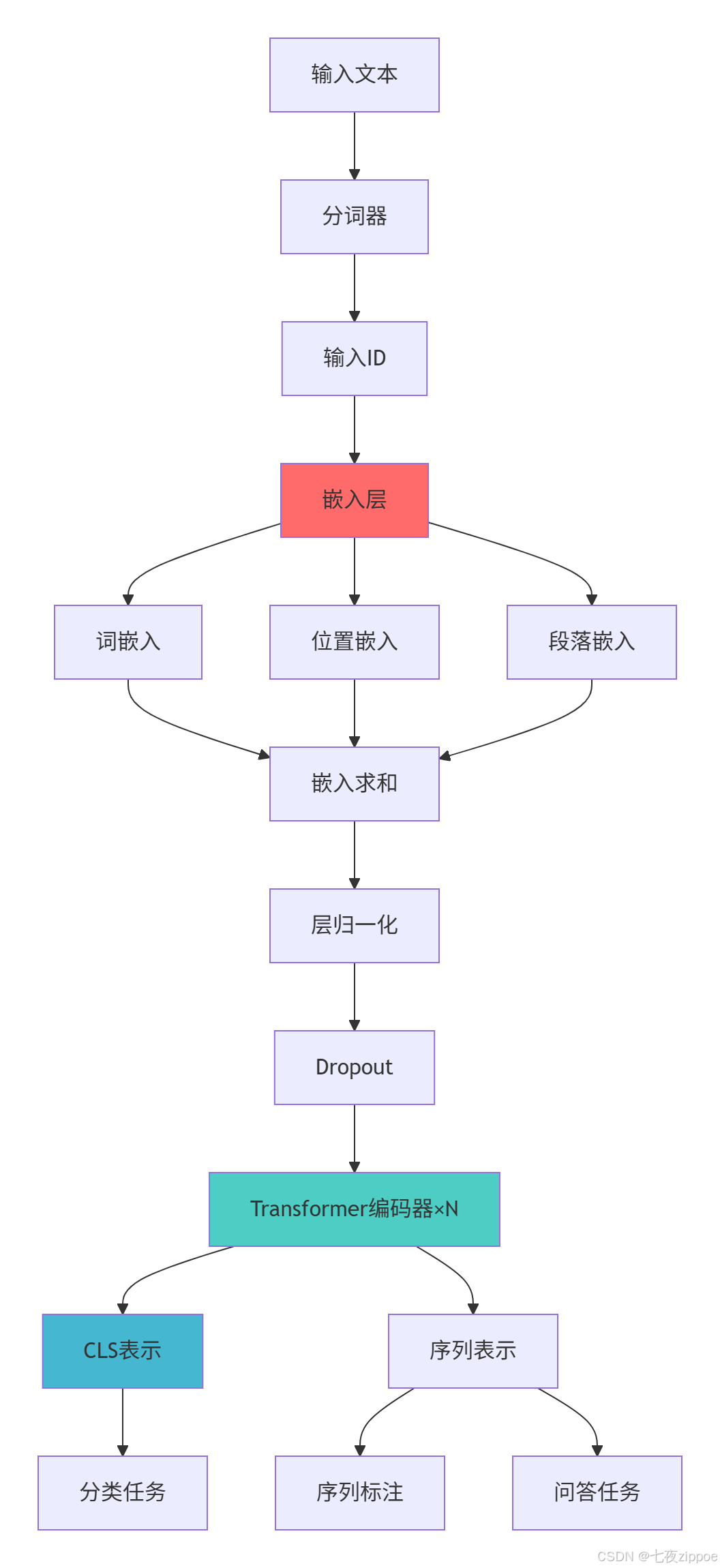
class CustomBERT(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
# 嵌入层
self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.max_position_embeddings, config.hidden_size)
self.token_type_embeddings = nn.Embedding(2, config.hidden_size) # 句子A/B
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.hidden_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
# 编码器层
self.encoder = nn.ModuleList([
BertLayer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)
])
# 初始化
self.apply(self._init_weights)
def _init_weights(self, module):
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.bias is not None:
module.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
if module.padding_idx is not None:
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
module.bias.data.zero_()
module.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None):
seq_length = input_ids.size(1)
position_ids = torch.arange(seq_length, dtype=torch.long, device=input_ids.device)
position_ids = position_ids.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(input_ids)
if token_type_ids is None:
token_type_ids = torch.zeros_like(input_ids)
# 嵌入求和
words_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
token_type_embeddings = self.token_type_embeddings(token_type_ids)
embeddings = words_embeddings + position_embeddings + token_type_embeddings
embeddings = self.layer_norm(embeddings)
embeddings = self.dropout(embeddings)
# 编码器前向传播
hidden_states = embeddings
all_hidden_states = ()
all_attentions = ()
for i, layer_module in enumerate(self.encoder):
hidden_states, attention_weights = layer_module(hidden_states, attention_mask)
all_hidden_states = all_hidden_states + (hidden_states,)
all_attentions = all_attentions + (attention_weights,)
return {
'last_hidden_state': hidden_states,
'hidden_states': all_hidden_states,
'attentions': all_attentions
}
class BertLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.attention = BertAttention(config)
self.intermediate = BertIntermediate(config)
self.output = BertOutput(config)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask=None):
attention_output, attention_weights = self.attention(hidden_states, attention_mask)
intermediate_output = self.intermediate(attention_output)
layer_output = self.output(intermediate_output, attention_output)
return layer_output, attention_weights
class BertAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.self = BertSelfAttention(config)
self.output = BertSelfOutput(config)
def forward(self, hidden_states, attention_mask=None):
self_output, attention_weights = self.self(hidden_states, attention_mask)
attention_output = self.output(self_output, hidden_states)
return attention_output, attention_weights
# 其他组件实现...
model = CustomBERT(config)
print(f"创建BERT模型: hidden_size={hidden_size}, layers={num_hidden_layers}, heads={num_attention_heads}")
return model
def bert_embedding_analysis(self, model, tokenizer, text: str):
"""BERT嵌入分析"""
# 分词
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='pt', padding=True, truncation=True)
# 获取嵌入
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
embeddings = outputs.last_hidden_state
print(f"输入文本: {text}")
print(f"分词结果: {tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(inputs['input_ids'][0])}")
print(f"嵌入形状: {embeddings.shape}")
# 可视化词嵌入相似度
tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(inputs['input_ids'][0])
similarity_matrix = torch.matmul(embeddings[0], embeddings[0].T)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.imshow(similarity_matrix.detach().numpy(), cmap='viridis')
plt.xticks(range(len(tokens)), tokens, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(range(len(tokens)), tokens)
plt.title('BERT词嵌入相似度矩阵')
plt.colorbar()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return embeddings, tokens
def compare_bert_variants(self):
"""BERT变体对比"""
variants = {
'BERT-Base': {
'参数量': '110M',
'层数': 12,
'隐藏层维度': 768,
'注意力头数': 12,
'适用场景': '通用任务'
},
'BERT-Large': {
'参数量': '340M',
'层数': 24,
'隐藏层维度': 1024,
'注意力头数': 16,
'适用场景': '高精度要求'
},
'RoBERTa': {
'参数量': '125M',
'层数': 12,
'隐藏层维度': 768,
'注意力头数': 12,
'适用场景': '更多训练数据'
},
'DistilBERT': {
'参数量': '66M',
'层数': 6,
'隐藏层维度': 768,
'注意力头数': 12,
'适用场景': '资源受限环境'
}
}
print("=== BERT变体对比 ===")
for name, info in variants.items():
print(f"\n🤖 {name}")
for key, value in info.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
# 性能对比可视化
params = [110, 340, 125, 66] # 百万参数
speed = [1.0, 0.3, 1.2, 2.0] # 相对推理速度
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.bar(variants.keys(), params, color=['#ff6b6b', '#4ecdc4', '#45b7d1', '#96ceb4'])
plt.ylabel('参数量 (百万)')
plt.title('BERT变体参数量对比')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.bar(variants.keys(), speed, color=['#ff6b6b', '#4ecdc4', '#45b7d1', '#96ceb4'])
plt.ylabel('相对推理速度')
plt.title('推理速度对比')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return variants4.2 BERT架构图
5 文本分类实战
5.1 基于BERT的文本分类
5.1.1 完整分类管道
# text_classification.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel, AdamW, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report, confusion_matrix
import seaborn as sns
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
class TextClassificationExpert:
"""文本分类专家指南"""
def __init__(self, model_name: str = 'bert-base-uncased', num_classes: int = 2):
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class TextDataset(Dataset):
"""文本分类数据集"""
def __init__(self, texts, labels, tokenizer, max_len=128):
self.texts = texts
self.labels = labels
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.max_len = max_len
def __len__(self):
return len(self.texts)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = str(self.texts[idx])
label = self.labels[idx]
encoding = self.tokenizer.encode_plus(
text,
add_special_tokens=True,
max_length=self.max_len,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_tensors='pt'
)
return {
'input_ids': encoding['input_ids'].flatten(),
'attention_mask': encoding['attention_mask'].flatten(),
'labels': torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)
}
class BERTClassifier(nn.Module):
"""BERT分类器"""
def __init__(self, model_name, num_classes, dropout=0.3):
super().__init__()
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(self.bert.config.hidden_size, num_classes)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask):
outputs = self.bert(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output
output = self.dropout(pooled_output)
return self.classifier(output)
def create_data_loaders(self, train_texts, train_labels, val_texts, val_labels,
batch_size: int = 16):
"""创建数据加载器"""
train_dataset = self.TextDataset(train_texts, train_labels, self.tokenizer)
val_dataset = self.TextDataset(val_texts, val_labels, self.tokenizer)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
return train_loader, val_loader
def train_model(self, model, train_loader, val_loader, epochs=4, lr=2e-5):
"""训练模型"""
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
total_steps = len(train_loader) * epochs
scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(
optimizer,
num_warmup_steps=0,
num_training_steps=total_steps
)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
train_losses = []
val_accuracies = []
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(epochs):
print(f'\nEpoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}')
print('-' * 50)
# 训练阶段
model.train()
total_loss = 0
for batch in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(self.device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(self.device)
labels = batch['labels'].to(self.device)
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
avg_train_loss = total_loss / len(train_loader)
train_losses.append(avg_train_loss)
# 验证阶段
val_acc = self.evaluate(model, val_loader)
val_accuracies.append(val_acc)
print(f'训练损失: {avg_train_loss:.4f}')
print(f'验证准确率: {val_acc:.4f}')
# 保存最佳模型
if val_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = val_acc
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_bert_classifier.pth')
print(f'✅ 保存最佳模型,准确率: {best_acc:.4f}')
# 可视化训练过程
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(train_losses)
plt.title('训练损失')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(val_accuracies)
plt.title('验证准确率')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return {
'train_losses': train_losses,
'val_accuracies': val_accuracies,
'best_accuracy': best_acc
}
def evaluate(self, model, data_loader):
"""评估模型"""
model.eval()
predictions = []
true_labels = []
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in data_loader:
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(self.device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(self.device)
labels = batch['labels'].to(self.device)
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)
predictions.extend(preds.cpu().tolist())
true_labels.extend(labels.cpu().tolist())
return accuracy_score(true_labels, predictions)
def detailed_evaluation(self, model, data_loader, class_names):
"""详细评估"""
model.eval()
predictions = []
true_labels = []
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in data_loader:
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(self.device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(self.device)
labels = batch['labels'].to(self.device)
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)
predictions.extend(preds.cpu().tolist())
true_labels.extend(labels.cpu().tolist())
# 分类报告
print("\n=== 分类报告 ===")
print(classification_report(true_labels, predictions, target_names=class_names))
# 混淆矩阵
cm = confusion_matrix(true_labels, predictions)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',
xticklabels=class_names, yticklabels=class_names)
plt.title('混淆矩阵')
plt.ylabel('真实标签')
plt.xlabel('预测标签')
plt.show()
return predictions, true_labels
def predict_single_text(self, model, text: str):
"""单文本预测"""
model.eval()
encoding = self.tokenizer.encode_plus(
text,
add_special_tokens=True,
max_length=128,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
return_attention_mask=True,
return_tensors='pt'
)
with torch.no_grad():
input_ids = encoding['input_ids'].to(self.device)
attention_mask = encoding['attention_mask'].to(self.device)
outputs = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
probabilities = F.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
_, prediction = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)
return {
'prediction': prediction.item(),
'probabilities': probabilities.cpu().numpy()[0]
}6 命名实体识别实战
6.1 基于BERT的NER实现
6.1.1 NER模型架构
# named_entity_recognition.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
import numpy as np
from typing import List, Dict, Tuple
from seqeval.metrics import classification_report, f1_score
class NERExpert:
"""命名实体识别专家"""
def __init__(self, model_name: str = 'bert-base-uncased', num_labels: int = 9):
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.num_labels = num_labels
self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class NERDataset:
"""NER数据集"""
def __init__(self, texts, labels, tokenizer, max_len=128):
self.texts = texts
self.labels = labels
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
self.max_len = max_len
self.label_map = {
'O': 0, 'B-PER': 1, 'I-PER': 2, 'B-ORG': 3, 'I-ORG': 4,
'B-LOC': 5, 'I-LOC': 6, 'B-MISC': 7, 'I-MISC': 8
}
def __len__(self):
return len(self.texts)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = self.texts[idx]
labels = self.labels[idx]
# 分词和对齐标签
tokens = []
label_ids = []
for word, label in zip(text, labels):
word_tokens = self.tokenizer.tokenize(word)
tokens.extend(word_tokens)
label_ids.extend([self.label_map[label]] + [self.label_map['O']] * (len(word_tokens) - 1))
# 截断
if len(tokens) > self.max_len - 2: # [CLS]和[SEP]
tokens = tokens[:self.max_len - 2]
label_ids = label_ids[:self.max_len - 2]
# 添加特殊标记
tokens = ['[CLS]'] + tokens + ['[SEP]']
label_ids = [self.label_map['O']] + label_ids + [self.label_map['O']]
# 填充
padding_length = self.max_len - len(tokens)
if padding_length > 0:
tokens = tokens + ['[PAD]'] * padding_length
label_ids = label_ids + [self.label_map['O']] * padding_length
# 转换为ID
input_ids = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
attention_mask = [1 if token != '[PAD]' else 0 for token in tokens]
return {
'input_ids': torch.tensor(input_ids, dtype=torch.long),
'attention_mask': torch.tensor(attention_mask, dtype=torch.long),
'labels': torch.tensor(label_ids, dtype=torch.long)
}
class BERTForNER(nn.Module):
"""BERT命名实体识别模型"""
def __init__(self, model_name, num_labels, dropout=0.3):
super().__init__()
self.bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(self.bert.config.hidden_size, num_labels)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, labels=None):
outputs = self.bert(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
sequence_output = outputs.last_hidden_state
sequence_output = self.dropout(sequence_output)
logits = self.classifier(sequence_output)
if labels is not None:
loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=0) # 忽略'O'标签
active_loss = attention_mask.view(-1) == 1
active_logits = logits.view(-1, self.num_labels)[active_loss]
active_labels = labels.view(-1)[active_loss]
loss = loss_fct(active_logits, active_labels)
return loss, logits
return logits
def train_ner_model(self, model, train_loader, val_loader, epochs=4, lr=3e-5):
"""训练NER模型"""
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
train_losses = []
val_f1_scores = []
best_f1 = 0.0
for epoch in range(epochs):
print(f'\nEpoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}')
print('-' * 50)
# 训练阶段
model.train()
total_loss = 0
for batch in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(self.device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(self.device)
labels = batch['labels'].to(self.device)
loss, _ = model(input_ids, attention_mask, labels)
loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
avg_train_loss = total_loss / len(train_loader)
train_losses.append(avg_train_loss)
# 验证阶段
val_f1 = self.evaluate_ner(model, val_loader)
val_f1_scores.append(val_f1)
print(f'训练损失: {avg_train_loss:.4f}')
print(f'验证F1分数: {val_f1:.4f}')
# 保存最佳模型
if val_f1 > best_f1:
best_f1 = val_f1
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'best_bert_ner.pth')
print(f'✅ 保存最佳模型,F1分数: {best_f1:.4f}')
return {
'train_losses': train_losses,
'val_f1_scores': val_f1_scores,
'best_f1': best_f1
}
def evaluate_ner(self, model, data_loader):
"""评估NER模型"""
model.eval()
predictions = []
true_labels = []
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in data_loader:
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(self.device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(self.device)
labels = batch['labels'].to(self.device)
logits = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=2)
# 移除填充和特殊标记
for i in range(len(preds)):
pred = preds[i]
true = labels[i]
mask = attention_mask[i] == 1
pred = pred[mask].cpu().numpy()
true = true[mask].cpu().numpy()
# 移除[CLS]和[SEP]
pred = pred[1:-1]
true = true[1:-1]
predictions.append(pred)
true_labels.append(true)
# 转换为标签字符串
label_map_inv = {v: k for k, v in self.dataset.label_map.items()}
pred_labels = []
true_labels_str = []
for pred, true in zip(predictions, true_labels):
pred_labels.append([label_map_inv[p] for p in pred])
true_labels_str.append([label_map_inv[t] for t in true])
f1 = f1_score(true_labels_str, pred_labels)
return f1
def predict_entities(self, model, text: str):
"""预测命名实体"""
model.eval()
tokens = self.tokenizer.tokenize(text)
tokens = ['[CLS]'] + tokens + ['[SEP]']
input_ids = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
attention_mask = [1] * len(input_ids)
# 填充
padding_length = 128 - len(input_ids)
if padding_length > 0:
input_ids = input_ids + [0] * padding_length
attention_mask = attention_mask + [0] * padding_length
input_ids = torch.tensor([input_ids], dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)
attention_mask = torch.tensor([attention_mask], dtype=torch.long).to(self.device)
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(input_ids, attention_mask)
preds = torch.argmax(logits, dim=2)[0].cpu().numpy()
# 处理预测结果
label_map_inv = {v: k for k, v in self.dataset.label_map.items()}
pred_labels = [label_map_inv[p] for p in preds[1:len(tokens)-1]] # 移除特殊标记
# 提取实体
entities = []
current_entity = None
current_start = 0
for i, (token, label) in enumerate(zip(tokens[1:-1], pred_labels)):
if label.startswith('B-'):
if current_entity is not None:
entities.append({
'entity': current_entity,
'start': current_start,
'end': i,
'type': current_type
})
current_entity = token
current_start = i
current_type = label[2:]
elif label.startswith('I-') and current_entity is not None:
current_entity += ' ' + token
else:
if current_entity is not None:
entities.append({
'entity': current_entity,
'start': current_start,
'end': i,
'type': current_type
})
current_entity = None
return entities总结与展望
NLP技术演进
实践建议
基于多年NLP实战经验,我建议的学习路径:
-
基础阶段:掌握词向量技术和传统NLP方法
-
进阶阶段:学习Transformer架构和自注意力机制
-
高级阶段:掌握BERT/GPT等预训练模型
-
专家阶段:精通模型优化和工业级部署
官方文档与参考资源
-
Hugging Face Transformers- 最流行的NLP库
-
BERT官方论文- BERT原论文
-
Attention Is All You Need- Transformer原论文
-
NLP Progress- NLP任务最新进展
-
Stanford NLP- 斯坦福NLP资源
通过本文的完整学习,您应该已经掌握了自然语言处理的核心技术和工业级实践。NLP正在深刻改变人机交互方式,希望本文能帮助您构建更加智能、高效的语言理解系统!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献42条内容
已为社区贡献42条内容






所有评论(0)