Claude 3.5 +LlamaIndex+Milvus,六步教你搭建Agentic RAG
OpenAI 的 ChatGPT为代表的基础模型的出现显著加速了 LLM 应用的发展,但是如果只使用 LLM 依赖其“自有”知识来回答问题,往往会出现大模型幻觉,或者知识更新不及时等问题。

过去三年中, OpenAI 的 ChatGPT为代表的基础模型的出现显著加速了 LLM 应用的发展,但是如果只使用 LLM 依赖其“自有”知识来回答问题,往往会出现大模型幻觉,或者知识更新不及时等问题。基于这一背景,使用多个 LLM,每个 LLM 针对不同类型的问题进行优化的解决思路应运而生。但这也会出现一定的局限,那就是让整体系统变得复杂且难以扩展
过去三年中, OpenAI 的 ChatGPT为代表的基础模型的出现显著加速了 LLM 应用的发展,但是如果只使用 LLM 依赖其“自有”知识来回答问题,往往会出现大模型幻觉,或者知识更新不及时等问题。基于这一背景,使用多个 LLM,每个 LLM 针对不同类型的问题进行优化的解决思路应运而生。
但过多的模型拼合,又会导致整体系统变得复杂且难以扩展。那么,要如何解决这个问题呢?
答案是复合人工智能系统(CAIS)。接下来,我们将重点解读CAIS的历史演变以及搭建流程。
01.
CAIS的历史演变,从RAG到Agent
这一概念最早是2024年初加州大学伯克利分校的AI研究实验室网站上的一篇题为《从模型到复合人工智能系统的转变》的博客中被提及,它强调通过集成多种AI技术和模块来实现更高效、更可靠、更可解释的智能系统。
比如,我们可以通过在 LLM pipeline 中添加额外组件,进而提升系统性能。一个常见的代表是 RAG,RAG 通过将“知识库”或“上下文”存储在向量数据库(如 Milvus 或 Zilliz Cloud)中,并将其作为上下文与LLM结合,可以生成更准确、相关性更高的回答。
通常来说,构建 RAG 系统的基本步骤如下:
-
Chunking:将文档拆分为较小的部分,以提高在向量数据库中用语义搜索内容的相关性,这是 Zilliz Cloud 和 Milvus 等向量数据库的核心特性。
-
Embedding:将分块向量化(创建向量数值表示)并存入向量数据库。
-
Prompt:向 LLM 提供指令,基于查询在向量数据库中检索以获取答案。
-
Query:向 LLM 提出的问题。
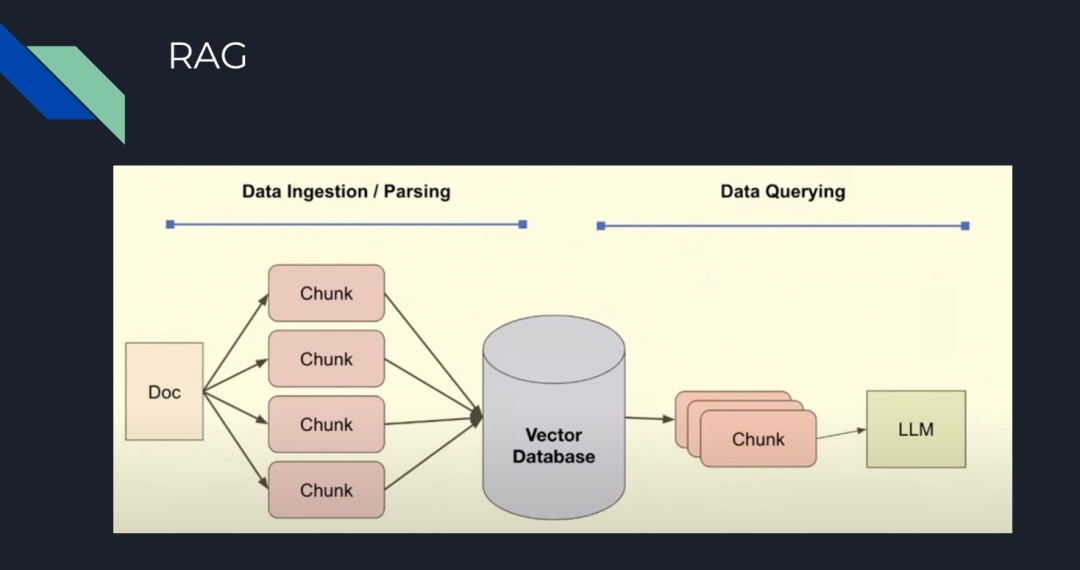
图 1:RAG 的基本步骤
不难发现,以上各个环节,主要基于向量相似性进来完成检索以及内容生成,可一旦分块不够精准,或者分块后的内容与答案相关性不高,就会导致最终生成的答案也会不尽如人意。
与此同时,RAG的另一大局限性在于,对特定模型的过分依赖。比如,我们做一个比较任务,但模型可能是为归纳任务训练的。
在此基础上,Agent应运而生。
LLM Agent 是复杂的系统,它们通过在 pipeline 中添加了“类人”步骤,如推理、工具使用或规划,可以完成各种复杂操作。
比如,在下图中,LLM Agent 包含多个组件,它们可以在迭代过程中互动,不仅可以做相似性检索,还能完成包括规划、推理、工具使用和记忆等多种功能。
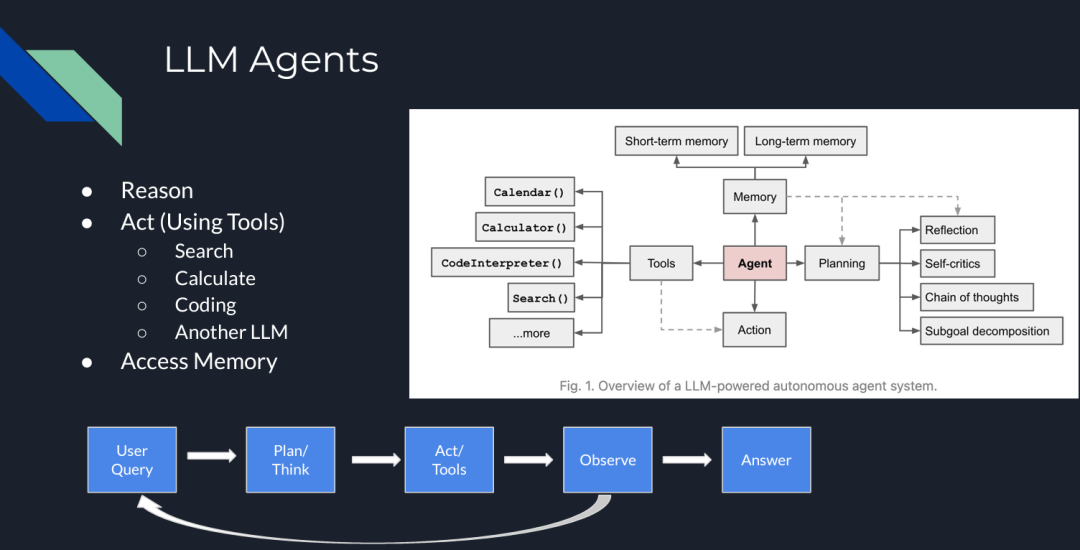
图 2:LLM Agents
目前各种 Agent 架构和框架中,最流行的是 ReAct(推理/行动)。其概念最早出自论文《ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models》。
在ReAct中,主要包括四个步骤:规划/推理(Plan/Think)、行动(act/tools)、评估(observe)和答案生成(answer)。
比较值得一提的是评估环节,在这一环节中,如果模型没有找到答案,它会返回推理步骤或要求用户给出更多额外提示来继续生成答案。
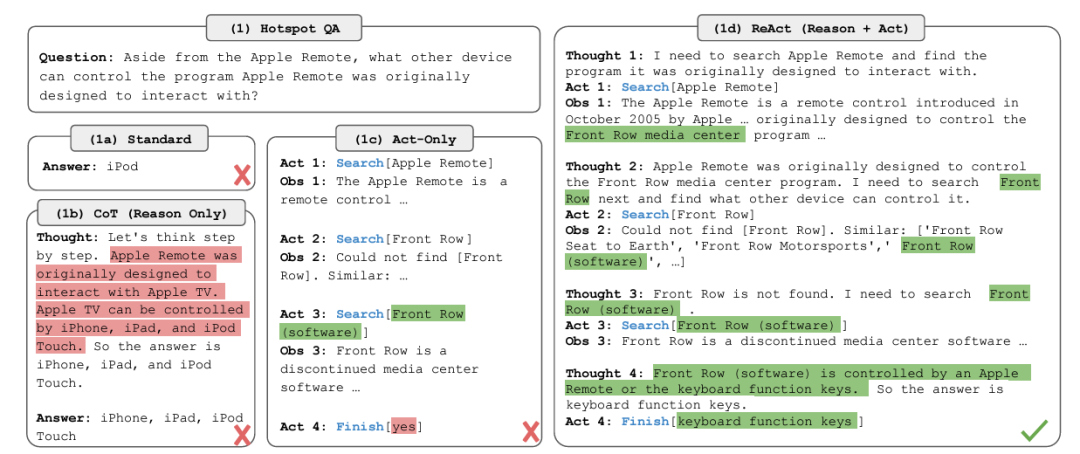
图 3:ReAct 框架
那么,我们如何在 RAG pipeline 中使用这些 Agent 呢?以下是在 RAG pipeline 中五种常见的智能体构建方式:
-
Routing(路由):将用户查询重定向到与查询相关的特定知识库。
-
示例:如果用户询问特定类型书籍的推荐,查询可以被路由到包含这些类型书籍信息的知识库。
-
Query Planning(查询规划):将查询拆分为子查询,每个子查询定向到相关的 RAG pipeline。
-
示例:如果您想知道一家公司过去三年的财务结果,Agent 会为每一年创建子查询,并将每个子查询定向到适当的知识库。
-
Tool Use(工具使用):LLM 与外部 API 或工具交互,确定交互所需的参数。
-
示例:如果用户请求天气预报,LLM 调用天气 API,确定位置和日期等参数,并处理 API 的响应以提供答案。
-
ReAct:一个迭代过程,结合推理和行动,包括规划、工具使用和观察步骤。
-
示例:为了生成详细的旅行行程,系统推理用户需求,使用 API 收集景点、餐饮和住宿信息,观察结果的准确性和相关性,然后提供全面的旅行计划。
-
Dynamic Query Planning(动态查询规划):Agent 并行执行多个任务或子查询,而不是顺序执行,并聚合结果。
-
示例:如果您想比较两家公司的财务结果并计算特定指标的差异,Agent 会并行处理两家公司的数据,然后合并结果以提供比较。LLMCompiler 是一个示例框架,支持高效且有效地编排并行函数调用。
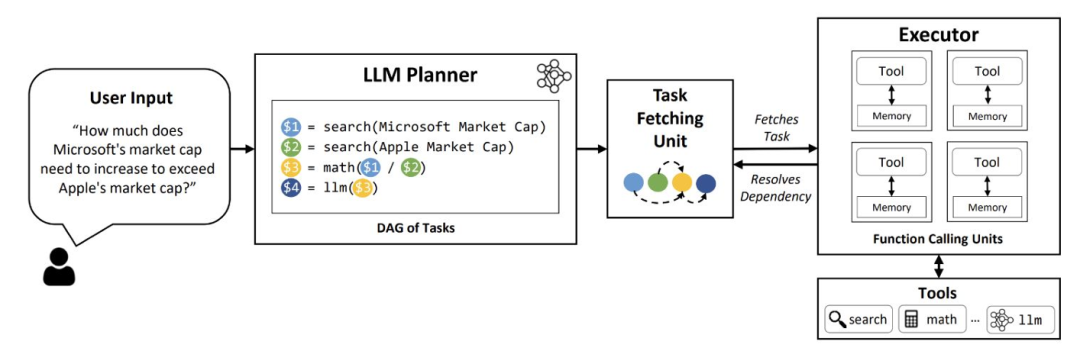
图 4:LLM 编译器
现在,让我们搭建一个使用 Milvus 向量数据库的简单 Agentic pipeline。
02.
使用 Claude 3.5 Sonnet、LlamaIndex 和 Milvus 构建 Agentic RAG
以下内容是一个使用 LlamaIndex 作为 Agent 框架、Milvus 作为向量数据库、Claude 3.5 Sonnet 作为 LLM 的 Agentic RAG peipeline示例,我们将用其构建一个 Agentic RAG。
步骤 1:数据加载
我们使用 Milvus documentation 2.4.x 的 FAQ 页面作为 RAG 的私有知识库。
!pip install -qq llama-index pymilvus llama-index-vector-stores-milvus llama-index-llms-anthropic
!wget https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/releases/download/v2.4.6-preview/milvus_docs_2.4.x_en.zip
!unzip -q /content/milvus_docs_2.4.x_en.zip -d /content/milvus_docs
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader
# load documents
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(
input_files=["/content/milvus_docs/en/faq/operational_faq.md"]
).load_data()
print("Document ID:", documents[0].doc_id)
步骤 2:环境变量
我们需要导入两个 API 密钥:Anthropic 和 OpenAI。
import os
from google.colab import userdata
os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"] = userdata.get('ANTHROPIC_API_KEY')
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')
步骤 3:数据索引
使用 Milvus 向量数据库创建文档索引,作为我们的知识库。由于 OpenAI 是 LlamaIndex 中的默认 embedding 模型(可以更改),我们需要在 MilvusVectorStore 中定义相同的维度(dim = 1536)。运行以下代码后,将创建一个本地数据库,其中包含我们的知识库。
from llama\_index.core import VectorStoreIndex, StorageContext
from llama\_index.vector\_stores.milvus import MilvusVectorStore
vector\_store = MilvusVectorStore(dim=1536)
storage\_context = StorageContext.from\_defaults(vector\_store=vector\_store)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from\_documents(documents, storage\_context=storage\_context)
步骤 4:简单查询引擎
首先测试没有 Agent 的查询引擎。它由 Claude 3.5 Sonnet 提供支持,并在我们的索引中搜索相关内容。
llm = Anthropic(model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620")
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5, llm=llm)
res = query_engine.query("What is the maximum vector dimension supported in Milvus?")
print(res)
"""
Output:
Milvus supports vectors with up to 32,768 dimensions by default. However, if you need to work with vectors of even higher dimensionality, you have the option to increase the value of the 'Proxy.maxDimension' parameter. This allows Milvus to accommodate vectors with dimensions exceeding the default limit.
"""
步骤 5:Agent 查询引擎
现在,我们添加 QueryEngineTool,它将作为查询引擎的包装工具,供 Agent 使用。
from llama_index.core import VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.core.tools import QueryEngineTool, ToolMetadata
from llama_index.llms.anthropic import Anthropic
llm = Anthropic(model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620")
query_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5, llm=llm)
query_engine_tool = QueryEngineTool(
query_engine=query_engine,
metadata=ToolMetadata(
name="knowledge_base",
description=("Provides information about Milvus FAQ.""Use a detailed plain text question as input to the tool."
),
),
)
步骤 6:AI Agent 创建
本例中使用的 Agent 是 LlamaIndex 的 FunctionCallingAgentWorker,它在查询回复上部署 critic reflection,利用查询引擎工具生成改进的答案。
from llama_index.core.agent import FunctionCallingAgentWorker
agent_worker = FunctionCallingAgentWorker.from_tools(
[query_engine_tool], llm=llm, verbose=True
)
agent = agent_worker.as_agent()
response = agent.chat("What is the maximum vector dimension supported in Milvus?")
print(str(response))
"""
Output:
Added user message to memory: What is the maximum vector dimension supported in Milvus?
=== LLM Response ===
To answer your question about the maximum vector dimension supported in Milvus, I'll need to consult the Milvus FAQ knowledge base. Let me do that for you.
=== Calling Function ===
Calling function: knowledge_base with args: {"input": "What is the maximum vector dimension supported in Milvus?"}
=== Function Output ===
Milvus supports vectors with up to 32,768 dimensions by default. However, if you need to work with vectors of even higher dimensionality, you have the option to increase the value of the 'Proxy.maxDimension' parameter. This allows Milvus to accommodate vectors with dimensions exceeding the default limit.
=== LLM Response ===
Based on the information from the Milvus FAQ knowledge base, I can provide you with the following answer:
The maximum vector dimension supported in Milvus is 32,768 by default. This means that out of the box, Milvus can handle vectors with up to 32,768 dimensions, which is suitable for most applications.
However, it's important to note that Milvus offers flexibility for cases where you might need to work with even higher-dimensional vectors. If your use case requires vectors with dimensions exceeding 32,768, you have the option to increase this limit. This can be done by adjusting the 'Proxy.maxDimension' parameter in Milvus configuration.
So, to summarize:
1. Default maximum dimension: 32,768
2. Can be increased: Yes, by modifying the 'Proxy.maxDimension' parameter
This flexibility allows Milvus to accommodate a wide range of use cases, from typical machine learning and AI applications to more specialized scenarios that might require extremely high-dimensional vectors.
Based on the information from the Milvus FAQ knowledge base, I can provide you with the following answer:
The maximum vector dimension supported in Milvus is 32,768 by default. This means that out of the box, Milvus can handle vectors with up to 32,768 dimensions, which is suitable for most applications.
However, it's important to note that Milvus offers flexibility for cases where you might need to work with even higher-dimensional vectors. If your use case requires vectors with dimensions exceeding 32,768, you have the option to increase this limit. This can be done by adjusting the 'Proxy.maxDimension' parameter in Milvus configuration.
So, to summarize:
1. Default maximum dimension: 32,768
2. Can be increased: Yes, by modifying the 'Proxy.maxDimension' parameter
This flexibility allows Milvus to accommodate a wide range of use cases, from typical machine learning and AI applications to more specialized scenarios that might require extremely high-dimensional vectors.
"""
Agent 的输出提供了更详细的答案,包括信息来源、答案背后的推理过程以及一些与话题相关的额外建议。这帮助我们更好地理解 LLM 模型给出的答案。
03.
Agentic RAG 架构
我们刚刚构建的 Agentic RAG 的完整架构如下所示。
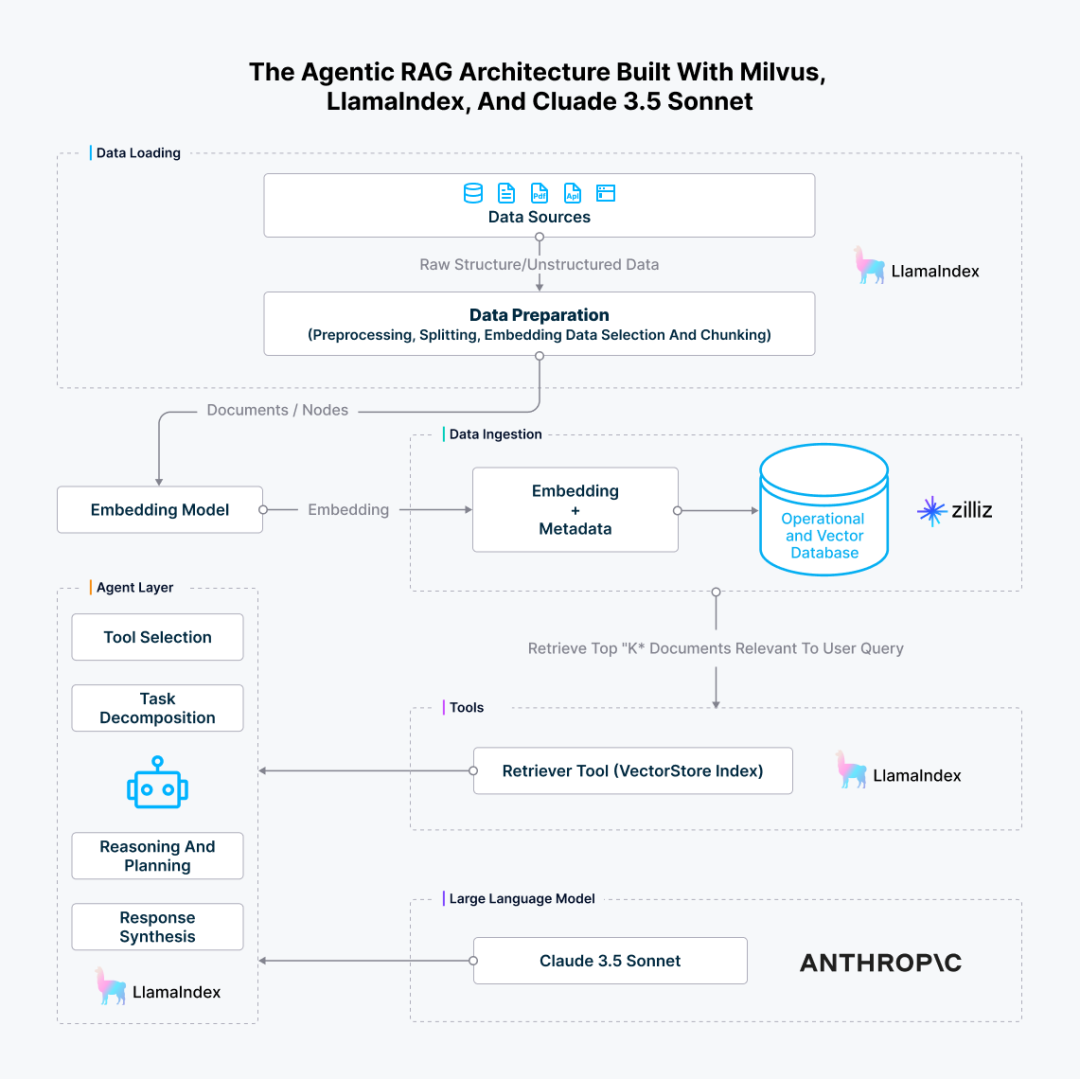
图 5:使用 Milvus、LlamaIndex 和 Claude 3.5 Sonnet 构建的 Agentic RAG 架构
04.
结论
Compund AI 的概念将复杂的人工智能系统分解为多个独立的模块,进而带来了更多的灵活性、可扩展性、可复用性,并降低了系统耦合度,极大提升了 pipeline 的整体效率。沿着这一理念, LLM 系统的演变,经历了从独立模型到结合 RAG 和 Agent 的更复杂架构的转变。
而在此过程中,Milvus为代表的向量数据库技术通过提供强大的数据管理、检索和融合能力,显著提升了系统的效率、准确性和可靠性。它不仅优化了 RAG 和 Agent 等模块的性能,还为多模态数据处理和实时决策提供了支持,并极大提升了系统的灵活性和可扩展性。
如何系统的去学习大模型LLM ?
大模型时代,火爆出圈的LLM大模型让程序员们开始重新评估自己的本领。 “AI会取代那些行业?”“谁的饭碗又将不保了?”等问题热议不断。
事实上,抢你饭碗的不是AI,而是会利用AI的人。
继科大讯飞、阿里、华为等巨头公司发布AI产品后,很多中小企业也陆续进场!超高年薪,挖掘AI大模型人才! 如今大厂老板们,也更倾向于会AI的人,普通程序员,还有应对的机会吗?
与其焦虑……
不如成为「掌握AI工具的技术人」,毕竟AI时代,谁先尝试,谁就能占得先机!
但是LLM相关的内容很多,现在网上的老课程老教材关于LLM又太少。所以现在小白入门就只能靠自学,学习成本和门槛很高。
针对所有自学遇到困难的同学们,我帮大家系统梳理大模型学习脉络,将这份 LLM大模型资料 分享出来:包括LLM大模型书籍、640套大模型行业报告、LLM大模型学习视频、LLM大模型学习路线、开源大模型学习教程等, 😝有需要的小伙伴,可以 扫描下方二维码领取🆓↓↓↓

一、LLM大模型经典书籍
AI大模型已经成为了当今科技领域的一大热点,那以下这些大模型书籍就是非常不错的学习资源。

二、640套LLM大模型报告合集
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。(几乎涵盖所有行业)

三、LLM大模型系列视频教程

四、LLM大模型开源教程(LLaLA/Meta/chatglm/chatgpt)

LLM大模型学习路线 ↓
阶段1:AI大模型时代的基础理解
-
目标:了解AI大模型的基本概念、发展历程和核心原理。
-
内容:
- L1.1 人工智能简述与大模型起源
- L1.2 大模型与通用人工智能
- L1.3 GPT模型的发展历程
- L1.4 模型工程
- L1.4.1 知识大模型
- L1.4.2 生产大模型
- L1.4.3 模型工程方法论
- L1.4.4 模型工程实践
- L1.5 GPT应用案例
阶段2:AI大模型API应用开发工程
-
目标:掌握AI大模型API的使用和开发,以及相关的编程技能。
-
内容:
- L2.1 API接口
- L2.1.1 OpenAI API接口
- L2.1.2 Python接口接入
- L2.1.3 BOT工具类框架
- L2.1.4 代码示例
- L2.2 Prompt框架
- L2.3 流水线工程
- L2.4 总结与展望
阶段3:AI大模型应用架构实践
-
目标:深入理解AI大模型的应用架构,并能够进行私有化部署。
-
内容:
- L3.1 Agent模型框架
- L3.2 MetaGPT
- L3.3 ChatGLM
- L3.4 LLAMA
- L3.5 其他大模型介绍
阶段4:AI大模型私有化部署
-
目标:掌握多种AI大模型的私有化部署,包括多模态和特定领域模型。
-
内容:
- L4.1 模型私有化部署概述
- L4.2 模型私有化部署的关键技术
- L4.3 模型私有化部署的实施步骤
- L4.4 模型私有化部署的应用场景
这份 LLM大模型资料 包括LLM大模型书籍、640套大模型行业报告、LLM大模型学习视频、LLM大模型学习路线、开源大模型学习教程等, 😝有需要的小伙伴,可以 扫描下方二维码领取🆓↓↓↓

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献646条内容
已为社区贡献646条内容







所有评论(0)