【MySQL】SQL 调优
本文摘要: 文章系统介绍了SQL调优方法,重点讲解了MySQL执行计划(Explain)的关键参数分析。主要内容包括:1)压测工具mysqlslap的使用;2)Explain结果中各列含义详解,特别是type列的性能等级划分;3)关键参数如select_type、key_len、ref、rows、filtered的解读;4)不同查询场景下的索引使用情况分析。文章通过具体SQL示例,展示了如何通过执
文章目录
文章讲解思路:先讲解 SQL 调优依靠的字段和 sql 指令,然后 MySQL 优化文章讲解 MySQL 怎么完成的优化、自己如何利用这些完成自己的 sql 优化和表优化索引优化
SQL 调优
压测工具
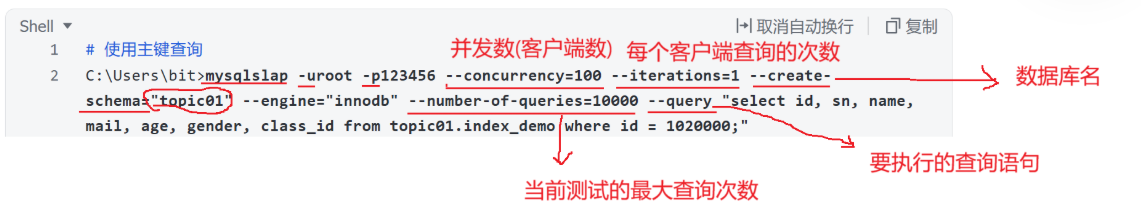
mysqlslap -uroot -p123 --concurrency=100 --iterations=1 --create-schema="topic01" --engine="innodb" --number-of-queries=10000 --query "select id from topic01 where id = 1";
执行计划 Explain
对于 select delete replace update 的 sql 语句查看执行情况。(并不会执行 sql,只是分析并返回结果)
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| id | select 标识符(SELECT 的执行顺序编号,一个 sql 可能多个 select) |
| select_type | select 类型(表示这个 select 是子查询还是最外层还是最简单的 select,主要是为了标注 select 在 sql 的位置) |
| table | 表名字(如果是中间结果表会有 deriverdN 或 unionM,N 标明) |
| partitions | 查询的分区(只对分区表有效) |
| type | 查询的方式(主要优化的字段) |
| possible_keys | where 筛选时可能用到的索引 |
| key | 实际选择的索引 |
| key_len | 索引长度,判断复合索引使用了前多少列 |
| ref | 与索引比较的列的属性 |
| rows | 估算要检查的行数 |
| filtered | 按条件筛选行的百分比,有多少比例行能满足 where 条件,越大说明过滤的效果越好 |
| Extra | 附加信息 |
关键参数讲解
select_type
key_len
查询中使用的索引字节数长度,可以用来判断复合索引使用了前几列。
key_len 越小越说明在索引树上查找导致的 IO 操作越少,索引效率越高。不过前提是保障你对于磁盘数据不变,
ref
查询中与索引比较的列或常量。
| **值 ** | 含义 |
|---|---|
| const | 使用常量(直接写的值,如 = ‘test@example’) |
| NULL | 没有引用任何列(可能是函数计算或全索引扫描) |
| 表名.列名 | 使用另一张表的列(JOIN 操作) |
| func | 使用了函数/表达式的结果 |
-- 场景1:使用常量
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = 'test@example.com';
| key | ref |
|-----|-----|
| idx_email | const |
-- 场景2:使用函数(索引失效)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM users WHERE UPPER(email) = 'TEST@EXAMPLE.COM';
| key | ref |
|-----|-----|
| NULL | NULL | -- 函数导致索引无法使用
-- 场景3:JOIN 操作
EXPLAIN SELECT u.* FROM users u JOIN orders o ON u.id = o.user_id;
| table | key | ref |
|-------|-----|-----|
| u | PRIMARY | NULL | -- 主键扫描
| o | idx_user_id | u.id | -- 使用了 users 表的 id 列
rows
MySQL 优化器预估要检查的物理行数。rows 越小越好
filtered
预估符合条件的行数占扫描行数的百分比。
比如:
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM orders WHERE status = 1;
- 优化器知道 status=1 有 6000 行
- 因为 status 有索引,精准定位到 6000 行
- 所以 filtered = 100%(全部符合)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM orders WHERE user_id > 5000;
扫描 10000 行(没有索引),预计 50% 符合条件,那么 filtered 就是 50
- 代码如下:其中 status 是 index,别的都不是
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM orders
WHERE status = 1
AND user_id > 5000
AND created_at > '2024-01-01';
- 先用 idx_status 定位到 status=1 的 6000 行(rows=6000)
- 然后在 6000 行中过滤其他条件
- 预计只有 10% 满足所有条件
- 预计返回行数 = 6000 × 10% = 600 行
possible_keys 和 key 关系
:::info
会不会出现 possible_type = null,但是key不为空的情况?
:::
有的,比如:EXPLAIN SELECT id, name FROM orders;其中 name 是表的唯一键索引
因为没有使用 where,所以 possible_type 为 NULL ,但是 mysql 优化器发现全表扫描太慢,会选择遍历索引树、
还有其他情况,比如:使用索引的排序结果,其中因为没有 where 也会导师 possible_keys 为 NULL
Type 列详解
性能从好到坏:system const eq_ref ref fulltext ref_or_null index_merge unique_subquery index_subquery range index ALL
| type 列类型 | 场景 |
|---|---|
| system | MyIsam 引擎下,且表只有一行数据 |
| const | 使用常量对非空唯一键或主键进行筛选 |
| eq_ref | 用于多表连接,表关联条件是主键索引或者非空唯一键 |
| ref | 通过非唯一索引的 “等值匹配”(针对非 NULL 值)查找数据,返回所有匹配该值的行。 |
| ref_or_null | 优化器在一次索引扫描中,同时匹配 “等值条件的非 NULL 值” 和 “NULL 值”,避免分两次查询。 列 = 某个非NULL值OR列 IS NULL |
| index_merge | 使用多个索引,or 两边都是单独索引,然后对结果集合并。此时 key_len 返回最长索引长度 |
| unique_subquery | 子查询返回外层表的唯一索引或主键索引,比如<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);background-color:rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">value in (select primary_key from signal where expr)</font> |
| index_subquery | 子查询返回普通索引 |
| range | 使用比较运算符或者 is NULL is not NULL like in 对索引列进行范围查询,对于 NULL 相关,优化器会判断使用 range 和 ref 哪个效率更高做出抉择 |
| index | 遍历索引树查询,比如排序,或者 like %s,因为不知道 like 前缀就只能遍历索引树了 |
| ALL | 全表扫描,不用索引 |
对于 ref ref_or_null
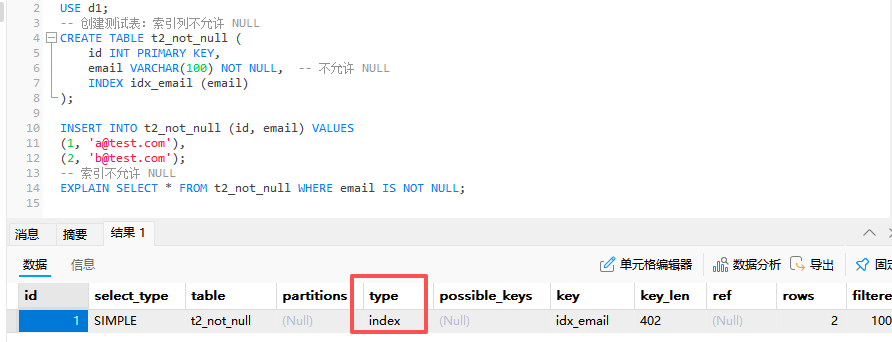
-- 创建测试表:索引列允许 NULL
CREATE TABLE t1_with_null (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
email VARCHAR(100), -- 允许 NULL
INDEX idx_email (email)
);
-- 创建测试表:索引列不允许 NULL
CREATE TABLE t2_not_null (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, -- 不允许 NULL
INDEX idx_email (email)
);
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO t1_with_null (id, email) VALUES
(1, 'a@test.com'),
(2, 'b@test.com'),
(3, NULL);
INSERT INTO t2_not_null (id, email) VALUES
(1, 'a@test.com'),
(2, 'b@test.com');
-- 测试 1:精确匹配
-- 索引允许 NULL
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1_with_null WHERE email = 'a@test.com';
-- 索引不允许 NULL
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t2_not_null WHERE email = 'a@test.com';
-- 测试 2:IS NULL 查询
-- 索引允许 NULL
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1_with_null WHERE email IS NULL;
-- 索引不允许 NULL where后面筛选恒不成立,相当于啥也没有
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t2_not_null WHERE email IS NULL;
-- 测试 3:IS NOT NULL 查询
-- 索引允许 NULL 范围查找
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1_with_null WHERE email IS NOT NULL;
-- 索引不允许 NULL
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t2_not_null WHERE email IS NOT NULL;
-- 测试 4:OR ... IS NULL
-- 索引允许 NULL
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1_with_null WHERE email = 'a@test.com' OR email IS NULL;
-- 索引不允许 NULL
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t2_not_null WHERE email = 'a@test.com' OR email IS NULL;
✓ (4 queries)
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|-------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|-------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1_with_null | [null] | ref | idx_email | idx_email | 303 | const | 1 | 100 | Using index |
|----|-------------|-------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|-------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|-------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|-------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2_not_null | [null] | ref | idx_email | idx_email | 302 | const | 1 | 100 | Using index |
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|--------------------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|--------------------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1_with_null | [null] | ref | idx_email | idx_email | 303 | const | 1 | 100 | Using where; Using index |
|----|-------------|--------|------------|--------|---------------|--------|---------|--------|--------|----------|------------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|--------|------------|--------|---------------|--------|---------|--------|--------|----------|------------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | [null] | [null] | [null] | [null] | [null] | [null] | [null] | [null] | [null] | Impossible WHERE |
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|-------|---------------|-----------|---------|--------|------|----------|--------------------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|-------|---------------|-----------|---------|--------|------|----------|--------------------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1_with_null | [null] | range | idx_email | idx_email | 303 | [null] | 2 | 100 | Using where; Using index |
|----|-------------|-------------|------------|-------|---------------|-----------|---------|--------|------|----------|-------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|-------------|------------|-------|---------------|-----------|---------|--------|------|----------|-------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2_not_null | [null] | index | [null] | idx_email | 302 | [null] | 2 | 100 | Using index |
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|-------------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|--------------------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|--------------|------------|-------------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|--------------------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | t1_with_null | [null] | ref_or_null | idx_email | idx_email | 303 | const | 2 | 100 | Using where; Using index |
|----|-------------|-------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|-------------|
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|----|-------------|-------------|------------|------|---------------|-----------|---------|-------|------|----------|-------------|
| 1 | SIMPLE | t2_not_null | [null] | ref | idx_email | idx_email | 302 | const | 1 | 100 | Using index |
其中,我原本不理解这个结果
:::info
where筛选条件恒为真,那么全表不应该更快么?
经过计算,认为扫描整个索引的成本更低,因为毕竟也不用回表。我们如果让复合索引不完全包含*就可以发现使用 ALL 了 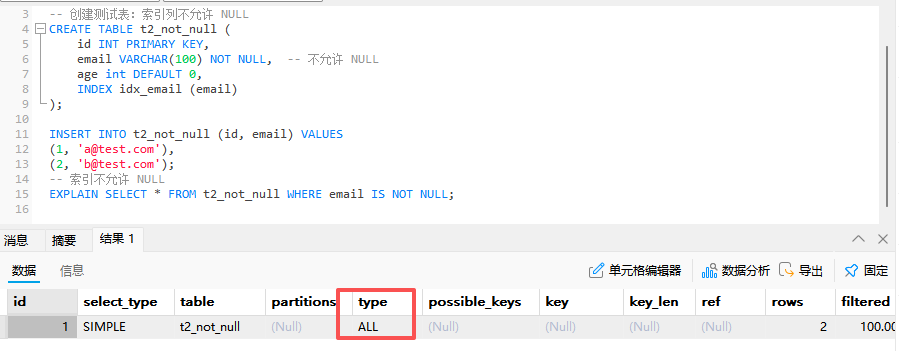
:::
const
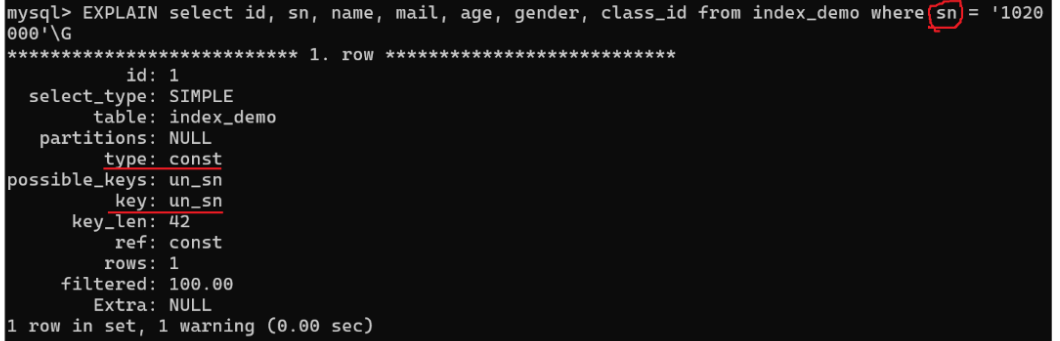
Extra 列
如果出现 Using filesort 和 Using temporary,将会严重影响效率,一个是使用文件排序,一个是把数据放入内存,使用临时表排序。当在内存排序发现空间不足时,就只能申请临时文件,此时临时表排序就会变成文件排序,IO 更多
| 属性 | 效果 |
|---|---|
| Using temporary | 使用非索引列进行分组,会用临时表下排序,优化时可以对分组的列加索引 |
| Using filesort | 对非索引列排序,优化时可以对排序的列加索引 |
| Using where | 使用非索引列检索数据 |
| Using index | 使用索引检索数据,发生索引覆盖,高效查询 |
| NULL | 发生回表查询 |
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容








所有评论(0)