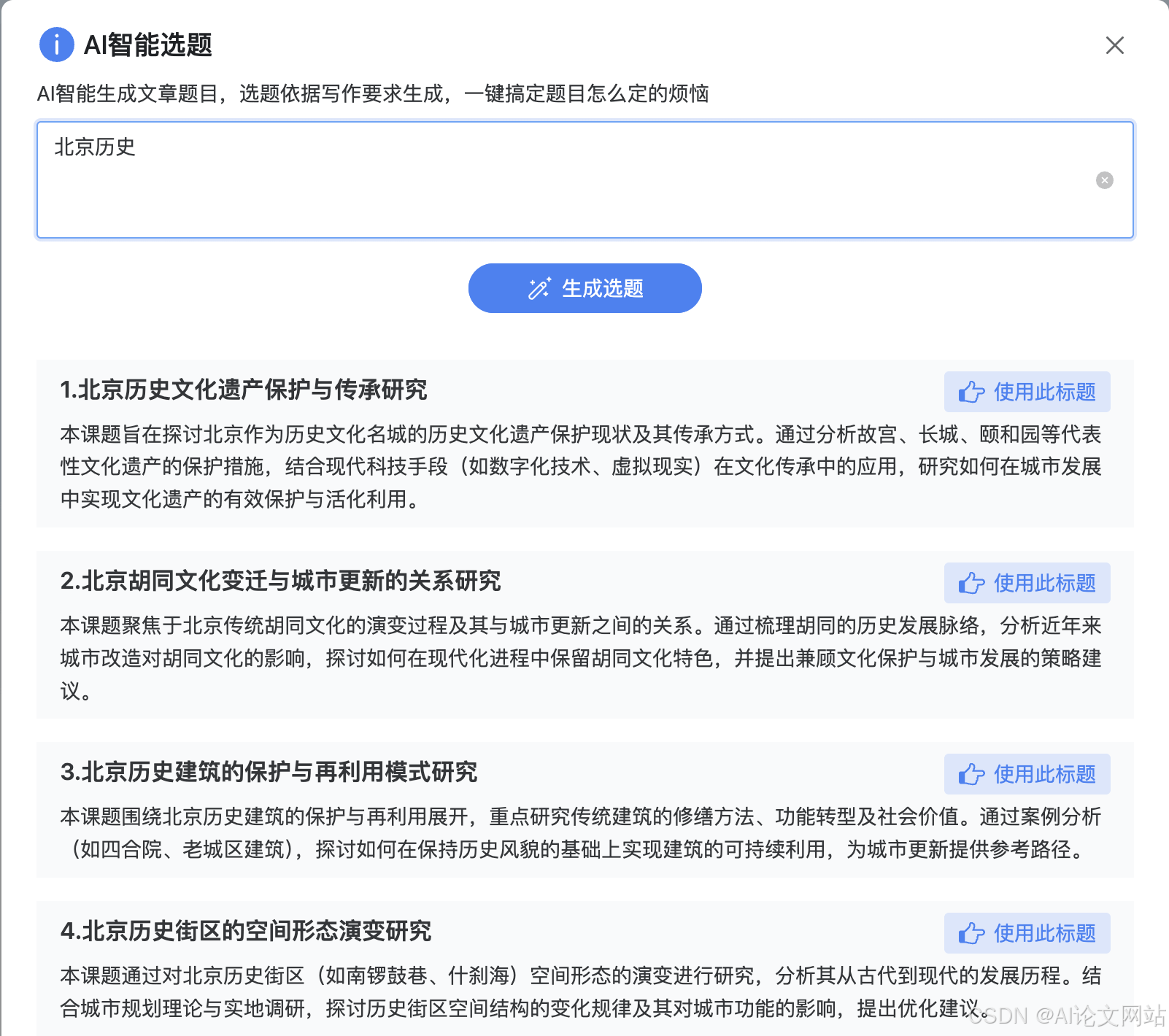
细胞多尺度仿真软件:PhysiCell_(2).PhysiCell软件介绍及安装
PhysiCell是一个开源的多尺度细胞仿真软件,基于C++开发,旨在模拟生物组织中的细胞行为和相互作用。它将单个细胞的生理过程(如增殖、代谢、迁移等)与宏观组织环境(如营养物质扩散、力学作用等)结合在一起,提供了一个高度可扩展的框架,适用于多种生物医学研究领域。PhysiCell的核心是基于多代理系统(Multi-Agent System, MAS)的思想,每个细胞都作为一个独立的代理,具有自己
PhysiCell软件介绍及安装
软件介绍
PhysiCell是一个开源的多尺度细胞仿真软件,基于C++开发,旨在模拟生物组织中的细胞行为和相互作用。它将单个细胞的生理过程(如增殖、代谢、迁移等)与宏观组织环境(如营养物质扩散、力学作用等)结合在一起,提供了一个高度可扩展的框架,适用于多种生物医学研究领域。PhysiCell的核心是基于多代理系统(Multi-Agent System, MAS)的思想,每个细胞都作为一个独立的代理,具有自己的状态和行为,通过与环境和其他细胞的相互作用来模拟复杂的生命过程。
软件特点
-
高度可扩展性:PhysiCell的设计允许用户轻松添加新的细胞类型、行为和环境因素。
-
多尺度建模:从细胞层面到组织层面,PhysiCell能够模拟多个尺度的生物过程。
-
生物物理建模:支持详细的生物物理过程建模,如代谢、力学、信号传导等。
-
可视化工具:提供强大的可视化工具,帮助用户更好地理解仿真结果。
-
高性能计算:支持并行计算,能够在高性能计算集群上运行大规模仿真。
应用领域
-
癌症研究:模拟肿瘤生长、浸润和治疗反应。
-
组织工程:研究细胞在不同环境中的生长和分化。
-
免疫学:模拟免疫细胞与病原体的相互作用。
-
发育生物学:研究细胞在组织发育过程中的行为。
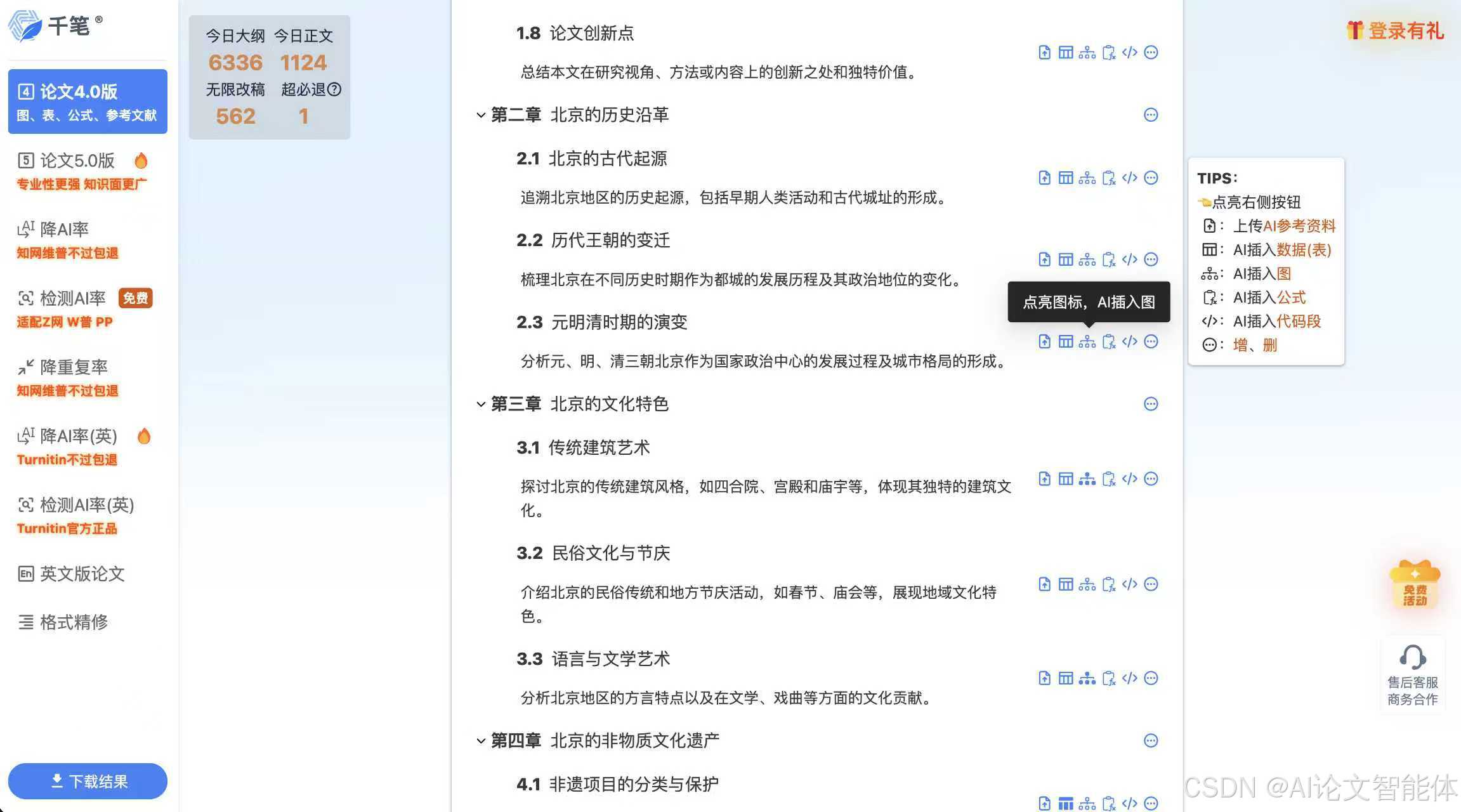
软件安装
系统要求
PhysiCell可以在多种操作系统上运行,包括Windows、Linux和macOS。以下是安装PhysiCell的基本系统要求:
-
操作系统:Windows 10/11, Ubuntu 18.04及以上版本, macOS 10.14及以上版本。
-
编译器:需要支持C++11标准的编译器,如GCC 4.8及以上版本、Clang 3.3及以上版本或Visual Studio 2015及以上版本。
-
依赖库:PhysiCell依赖于几个开源库,如BioFVM(用于模拟物质扩散)、pugixml(用于XML解析)、nanoflann(用于空间查询)等。
安装步骤
1. 安装依赖库
在开始安装PhysiCell之前,需要先安装其依赖库。以下是安装这些依赖库的步骤:
Ubuntu
# 更新软件包列表
sudo apt-get update
# 安装必要的依赖库
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt-get install cmake
sudo apt-get install libxml2-dev
sudo apt-get install libxerces-c-dev
sudo apt-get install libhdf5-dev
sudo apt-get install libvtk7-dev
sudo apt-get install libgsl-dev
sudo apt-get install libboost-all-dev
sudo apt-get install libEigen3-dev
Windows
在Windows上,建议使用vcpkg来管理依赖库。首先安装vcpkg:
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/vcpkg.git
cd vcpkg
.\bootstrap-vcpkg.bat
然后安装PhysiCell所需的依赖库:
vcpkg install eigen3
vcpkg install boost-all
vcpkg install xerces-c
vcpkg install hdf5
vcpkg install vtk
macOS
在macOS上,可以使用Homebrew来安装依赖库:
# 安装Homebrew
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
# 安装依赖库
brew install cmake
brew install eigen
brew install boost
brew install xerces-c
brew install hdf5
brew install vtk
2. 下载PhysiCell
PhysiCell的源代码托管在GitHub上,可以通过以下命令克隆仓库:
git clone https://github.com/PhysiCell/PhysiCell.git
cd PhysiCell
3. 编译PhysiCell
Ubuntu和macOS
在Linux和macOS上,编译PhysiCell的步骤如下:
# 创建构建目录
mkdir build
cd build
# 生成Makefile
cmake ..
# 编译PhysiCell
make -j4
Windows
在Windows上,可以使用Visual Studio来编译PhysiCell。首先,生成Visual Studio项目文件:
# 创建构建目录
mkdir build
cd build
# 生成Visual Studio项目文件
cmake .. -G "Visual Studio 16 2019"
然后,打开生成的项目文件(通常是PhysiCell.sln),选择适当的配置(如Release或Debug),并编译项目。
4. 验证安装
安装完成后,可以通过运行一个简单的示例来验证PhysiCell是否安装成功。PhysiCell仓库中包含多个示例项目,可以使用以下命令编译并运行其中一个示例:
# 编译示例项目
cd ../examples
make -j4
# 运行示例项目
./PhysiCell_multicell_2D
如果一切正常,示例项目将运行并生成仿真结果文件。
示例项目:2D多细胞仿真
为了更好地理解PhysiCell的安装和运行,我们来看一个具体的示例项目:2D多细胞仿真。
项目结构
示例项目的结构如下:
PhysiCell/
├── examples/
│ ├── PhysiCell_multicell_2D/
│ │ ├── PhysiCell_settings.xml
│ │ ├── PhysiCell_multicell_2D.cpp
│ │ ├── PhysiCell_multicell_2D.h
│ │ ├── Makefile
│ │ └── README.md
配置文件
PhysiCell_settings.xml文件用于配置仿真参数。以下是一个简单的配置文件示例:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<PhysiCell_settings>
<microenvironment_setup>
<initial_condition>
<variable units="mmHg" ID="0" name="oxygen">
<value type="constant">38.0</value>
</variable>
</initial_condition>
<diffusion>
<variable units="mmHg" ID="0" name="oxygen">
<diffusion coefficient type="constant">6.72e-7</diffusion coefficient>
<decay rate type="constant">0.1</decay rate>
</variable>
</diffusion>
</microenvironment_setup>
<user_parameters>
<max_time units="min" value="1000.0" />
<output_interval units="min" value="100.0" />
</user_parameters>
</PhysiCell_settings>
代码示例
PhysiCell_multicell_2D.cpp文件包含仿真的主要代码。以下是一个简化的代码示例,展示了如何设置和运行一个2D多细胞仿真:
#include <iostream>
#include "PhysiCell.h"
#include "PhysiCell_PhysiCell.h"
#include "PhysiCell_settings.h"
// 定义细胞类型
void create_custom_cell_types( void )
{
PhysiCell::custom_cell_definitions.push_back( make_custom_cell_definition<PhysiCell::oxygen_based_phenotype_cell>() );
}
// 初始化仿真环境
void initialize_simulation( void )
{
// 设置仿真时间
PhysiCell_settings.total_simulation_time = 1000.0;
PhysiCell_settings.output_time_interval = 100.0;
// 初始化微环境
PhysiCell::initialize_microenvironment();
PhysiCell::setup_physi_cell_microenvironment();
}
// 设置细胞初始位置
void set_initial_conditions( void )
{
// 添加一个细胞
PhysiCell::Cell* pC = create_cell( custom_cell_definitions[0] );
pC->position = PhysiCell::setPhysiCellPhysicellPosition( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 );
pC->initialize_cell_state();
add_cell( pC );
}
// 主函数
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
// 设置细胞类型
create_custom_cell_types();
// 初始化仿真环境
initialize_simulation();
// 设置初始条件
set_initial_conditions();
// 运行仿真
while( current_simulation_time() < total_simulation_time() )
{
update_cell_states();
update_microenvironment();
output_vtk_and_cells();
}
return 0;
}
运行仿真
编译并运行上述示例项目后,PhysiCell将生成一系列的VTK文件和细胞状态文件。这些文件可以使用VTK viewers(如ParaView)进行可视化,帮助用户更好地理解仿真结果。
可视化结果
-
安装ParaView:
-
Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install paraview -
Windows:
从ParaView官网下载并安装。
-
macOS:
从ParaView官网下载并安装。
-
-
打开VTK文件:
-
启动ParaView。
-
选择
File->Open,选择生成的VTK文件(通常在output目录下)。 -
点击
Apply按钮,查看仿真结果。
-
代码解析
create_custom_cell_types函数
该函数用于定义和创建自定义的细胞类型。在示例中,我们使用了oxygen_based_phenotype_cell,这是一种基于氧气浓度的细胞类型。
void create_custom_cell_types( void )
{
PhysiCell::custom_cell_definitions.push_back( make_custom_cell_definition<PhysiCell::oxygen_based_phenotype_cell>() );
}
initialize_simulation函数
该函数用于初始化仿真环境,包括设置仿真时间、初始化微环境等。
void initialize_simulation( void )
{
// 设置仿真时间
PhysiCell_settings.total_simulation_time = 1000.0;
PhysiCell_settings.output_time_interval = 100.0;
// 初始化微环境
PhysiCell::initialize_microenvironment();
PhysiCell::setup_physi_cell_microenvironment();
}
set_initial_conditions函数
该函数用于设置初始条件,例如添加细胞到仿真环境中。
void set_initial_conditions( void )
{
// 添加一个细胞
PhysiCell::Cell* pC = create_cell( custom_cell_definitions[0] );
pC->position = PhysiCell::setPhysiCellPhysicellPosition( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 );
pC->initialize_cell_state();
add_cell( pC );
}
main函数
main函数是程序的入口点,负责调用上述函数并运行仿真。
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
// 设置细胞类型
create_custom_cell_types();
// 初始化仿真环境
initialize_simulation();
// 设置初始条件
set_initial_conditions();
// 运行仿真
while( current_simulation_time() < total_simulation_time() )
{
update_cell_states();
update_microenvironment();
output_vtk_and_cells();
}
return 0;
}
常见问题
1. 编译错误
如果在编译过程中遇到错误,可以尝试以下步骤:
-
检查依赖库是否安装成功:确保所有依赖库都已正确安装。
-
检查CMake版本:确保CMake版本不低于3.10。
-
清理构建目录:删除
build目录并重新生成项目文件。
2. 运行错误
如果在运行过程中遇到错误,可以尝试以下步骤:
-
检查配置文件:确保
PhysiCell_settings.xml文件正确无误。 -
检查环境变量:确保所有必要的环境变量已正确设置。
-
查看日志文件:PhysiCell在运行时会生成日志文件,查看日志文件以获取更多信息。
进一步学习
PhysiCell的官方文档和示例项目提供了更多的学习资源。建议用户在安装和运行示例项目后,进一步阅读官方文档,了解如何添加新的细胞类型、行为和环境因素,以满足特定的研究需求。
-
官方文档:PhysiCell文档
-
示例项目:PhysiCell示例项目
通过这些资源,用户可以深入了解PhysiCell的内部机制,并掌握如何进行二次开发,以扩展其功能和应用范围。
结尾
通过上述步骤,您应该能够成功安装并运行PhysiCell。接下来,我们将深入探讨如何在PhysiCell中添加新的细胞类型和行为,以及如何利用其强大的多尺度建模能力进行更复杂的研究。希望您在使用PhysiCell的过程中,能够不断探索和发现新的科学问题。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献139条内容
已为社区贡献139条内容








所有评论(0)