从模型到服务:手把手教你部署AI模型为RESTful API
本文详细介绍了如何将训练好的机器学习模型部署为实用的RESTful API服务。首先讲解了技术栈选择,包括Flask、TensorFlow/PyTorch、Docker等工具,并在润云AI算力平台上进行实际操作演示。接着通过构建鸢尾花分类模型示例,展示了模型训练和保存过程。最后重点介绍了使用Flask创建API服务的实现细节,包括模型加载、请求处理、健康检查等功能。通过本教程,开发者可以快速掌握将
从模型到服务:手把手教你部署AI模型为RESTful API
引言:为什么模型部署如此重要?
在人工智能项目的实际开发中,许多开发者都有一个共同的痛点:我们花费大量时间训练出一个表现优异的模型,却在将其转化为实际可用的服务时遇到重重困难。数据显示,超过60%的AI项目在概念验证阶段表现出色,但在生产部署时失败或效果大幅下降。
本文将带你一步步将一个训练好的机器学习模型部署为实用的RESTful API服务,让你训练的AI模型真正“活”起来,为实际应用提供支持。
一、准备工作:选择合适的工具与环境
1.1 技术栈选择
在开始之前,我们需要确定使用的技术栈。本文将以Python生态系统为例,使用以下工具:
- Flask:轻量级Web框架,适合快速构建API
- TensorFlow/PyTorch:主流深度学习框架(示例使用TensorFlow)
- Scikit-learn:传统机器学习库
- Docker:容器化部署工具
- Nginx:生产环境反向代理
一、准备工作:选择合适的工具与环境
1.1 技术栈选择
在开始之前,我们需要确定使用的技术栈。本文将以Python生态系统为例,使用以下工具:
- Flask:轻量级Web框架,适合快速构建API
- TensorFlow/PyTorch:主流深度学习框架(示例使用TensorFlow)
- Scikit-learn:传统机器学习库
- Docker:容器化部署工具
- Nginx:生产环境反向代理
1.2 操作环境说明
为了确保教程的可行性与可复现性,本文将使用 润云AI算力平台(https://www.smoothcloud.com.cn)的Virtual高性能推理卡-16G进行实际操作演示,新用户可免费注册使用。
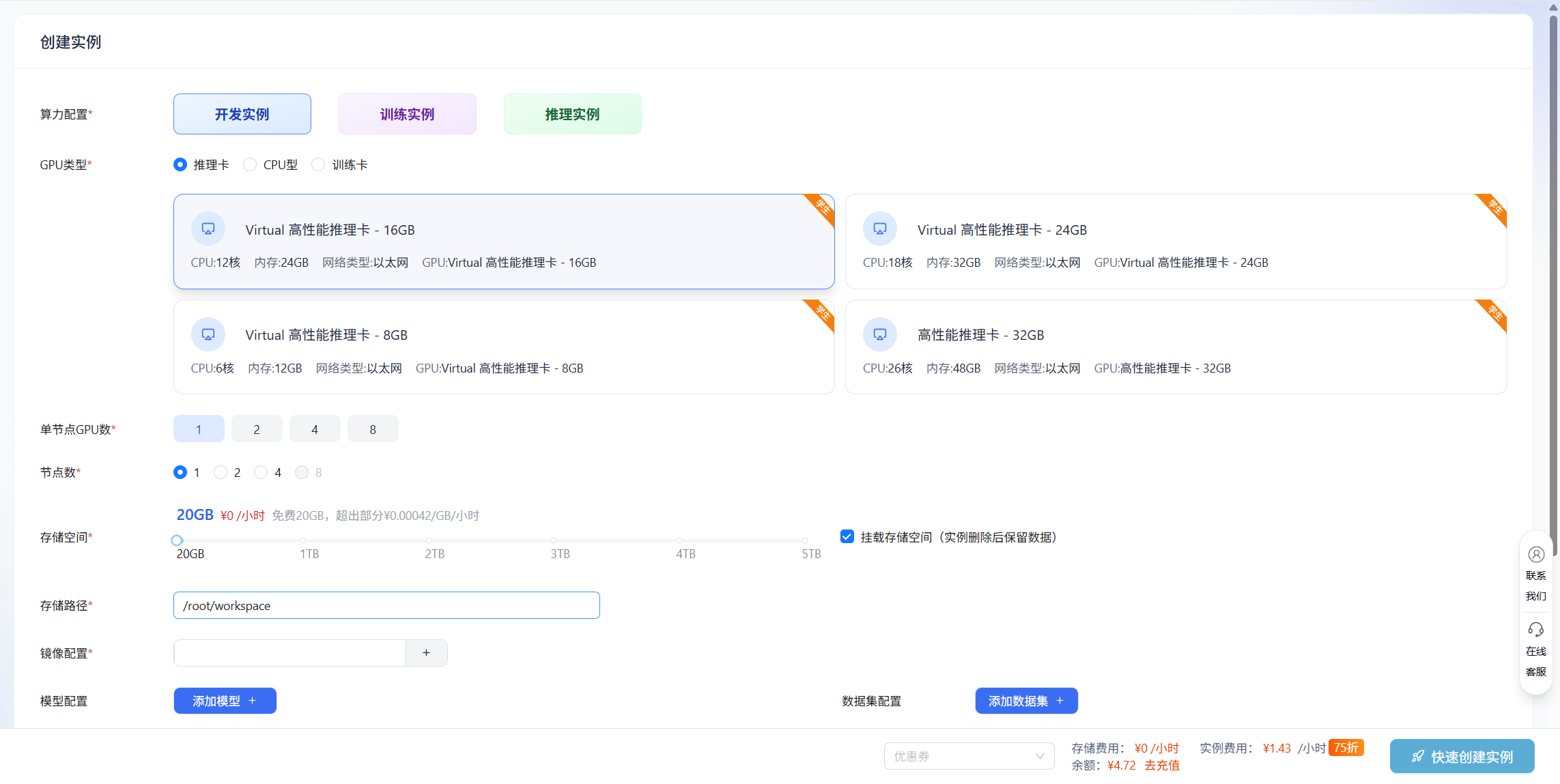
创建好实例后直接进入Jupyter工具
接下来,我们将在Terminal终端中一步步完成模型部署的所有环节。
1.3 环境配置
首先确保你的开发环境已准备好:
# 创建项目目录
mkdir ai_model_api && cd ai_model_api
# 安装系统级依赖
apt update && apt install -y python3-venv python3-pip build-essential
#创建虚拟环境并跳过 ensurepip/pip 初始化
python3 -m venv venv --without-pip
#激活虚拟环境
source venv/bin/activate
#手动给虚拟环境安装 pip
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python3
# 安装依赖包
pip install flask flask-cors tensorflow scikit-learn numpy pandas gunicorn
二、构建一个简单的机器学习模型
在部署之前,我们需要一个训练好的模型。为了示例的完整性,我们创建一个简单的鸢尾花分类模型
创建 train_model.py 文件:
# train_model.py
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import joblib
import json
def train_and_save_model():
# 加载数据
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# 划分训练测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# 训练模型
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 评估模型
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"模型准确率: {accuracy:.4f}")
# 保存模型
joblib.dump(model, 'iris_model.pkl')
# 保存特征信息 - 使用通用方法处理不同的数据类型
# 方法1: 先转换为列表(无论原来是什么类型)
feature_names = list(iris.feature_names) if hasattr(iris.feature_names, '__iter__') else iris.feature_names
target_names = list(iris.target_names) if hasattr(iris.target_names, '__iter__') else iris.target_names
# 方法2: 使用更安全的方式
try:
feature_names = iris.feature_names.tolist()
except AttributeError:
feature_names = list(iris.feature_names)
try:
target_names = iris.target_names.tolist()
except AttributeError:
target_names = list(iris.target_names)
feature_info = {
'feature_names': feature_names,
'target_names': target_names,
'n_features': len(iris.feature_names)
}
with open('model_info.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(feature_info, f)
print("模型保存完成!")
return model, feature_info
if __name__ == "__main__":
train_and_save_model()
运行上述代码,我们会得到训练好的模型文件 iris_model.pkl 和模型信息文件 model_info.json。
# 直接运行Python脚本
python train_model.py

三、创建Flask API服务
3.1 基础API结构
创建 app.py 文件:
# app.py
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from flask_cors import CORS
import joblib
import numpy as np
import json
import logging
# 配置日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app) # 允许跨域请求
# 全局变量存储模型
model = None
model_info = None
model_loaded = False
def load_model():
"""加载模型和模型信息"""
global model, model_info, model_loaded
try:
model = joblib.load('iris_model.pkl')
with open('model_info.json', 'r') as f:
model_info = json.load(f)
logger.info("模型加载成功")
model_loaded = True
return True
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"模型加载失败: {str(e)}")
return False
@app.before_request
def check_and_load_model():
"""在每个请求前检查并加载模型(如果需要)"""
global model, model_loaded
# 如果模型还没加载,则加载
if not model_loaded:
load_model()
@app.route('/')
def home():
"""首页"""
return jsonify({
"status": "success",
"message": "AI模型API服务运行中",
"endpoints": {
"/predict": "POST - 进行预测",
"/model-info": "GET - 获取模型信息",
"/health": "GET - 健康检查"
}
})
@app.route('/health', methods=['GET'])
def health_check():
"""健康检查端点"""
if model is not None:
return jsonify({"status": "healthy", "model_loaded": True})
else:
return jsonify({"status": "unhealthy", "model_loaded": False}), 500
@app.route('/model-info', methods=['GET'])
def get_model_info():
"""获取模型信息"""
if model_info is not None:
return jsonify({
"status": "success",
"model_info": model_info
})
else:
return jsonify({
"status": "error",
"message": "模型信息未加载"
}), 500
@app.route('/predict', methods=['POST'])
def predict():
"""预测端点"""
try:
# 验证模型是否加载
if model is None:
return jsonify({
"status": "error",
"message": "模型未加载,请稍后重试"
}), 503
# 获取请求数据
data = request.get_json()
# 验证输入数据
if not data or 'features' not in data:
return jsonify({
"status": "error",
"message": "请求中缺少 'features' 字段"
}), 400
features = data['features']
# 使用验证器验证特征
# 注意:需要从validators模块导入validate_iris_features
from validators import validate_iris_features
is_valid, message = validate_iris_features(features, expected_count=model_info['n_features'])
if not is_valid:
return jsonify({
"status": "error",
"message": message
}), 400
# 转换为numpy数组并进行预测
features_array = np.array(features).reshape(1, -1)
prediction = model.predict(features_array)
probability = model.predict_proba(features_array)
# 获取类别名称
predicted_class = int(prediction[0])
class_name = model_info['target_names'][predicted_class]
# 构建响应
response = {
"status": "success",
"prediction": predicted_class,
"class_name": class_name,
"probabilities": probability[0].tolist(),
"probability_labels": model_info['target_names']
}
logger.info(f"预测成功: 输入={features}, 结果={class_name}")
return jsonify(response)
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"预测错误: {str(e)}")
return jsonify({
"status": "error",
"message": f"预测过程中发生错误: {str(e)}"
}), 500
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 加载模型
if load_model():
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000, debug=True)
else:
print("模型加载失败,服务无法启动")
3.2 添加输入验证器
为了提高API的鲁棒性,我们添加输入验证:
# validators.py
def validate_iris_features(features, expected_count=4):
"""验证鸢尾花特征输入"""
if not isinstance(features, list):
return False, "特征必须为列表格式"
if len(features) != expected_count:
return False, f"需要 {expected_count} 个特征值"
# 验证每个特征是否为数值
for i, value in enumerate(features):
try:
float_value = float(value)
# 验证特征值的合理范围(根据鸢尾花数据集)
if i == 0 and (float_value < 4.0 or float_value > 8.0): # 花萼长度
return False, f"特征 {i} 超出合理范围"
# 可以添加更多范围验证
except ValueError:
return False, f"特征 {i} 不是有效数值"
return True, "验证通过"
然后在预测端点中使用验证器。
四、测试API服务
4.1 启动服务
python app.py

服务将在 http://localhost:5000 启动。
4.2 使用Python测试客户端
# test_client.py
import requests
import json
def test_api():
# 测试健康检查
print("1. 测试健康检查...")
response = requests.get('http://localhost:5000/health')
print(f"响应: {response.json()}\n")
# 测试模型信息
print("2. 获取模型信息...")
response = requests.get('http://localhost:5000/model-info')
print(f"响应: {response.json()}\n")
# 测试预测
print("3. 测试预测...")
test_data = {
"features": [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]
}
response = requests.post(
'http://localhost:5000/predict',
json=test_data,
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
)
print(f"预测请求: {test_data}")
print(f"预测响应: {response.json()}\n")
# 测试错误输入
print("4. 测试错误输入...")
bad_data = {
"features": [5.1, 3.5] # 特征数量不足
}
response = requests.post(
'http://localhost:5000/predict',
json=bad_data,
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
)
print(f"错误输入测试: {bad_data}")
print(f"错误响应: {response.json()}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_api()
启动测试
python app.py

4.3 使用curl测试
# 健康检查
curl http://localhost:5000/health
# 获取模型信息
curl http://localhost:5000/model-info
# 进行预测
curl -X POST http://localhost:5000/predict \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"features": [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]}'


4.5 开放端口测试
回到润云ai算力平台的实例列表页,进入查看详情页
在端口号这里添加5000端口

复制映射的访问地址
本地curl访问测试
# 健康检查
curl http://shqodh-psaucf-sc15197922628.smoothcloud.com.cn/health
# 获取模型信息
curl http://shqodh-psaucf-sc15197922628.smoothcloud.com.cn/model-info
# 进行预测
curl -X POST http://shqodh-psaucf-sc15197922628.smoothcloud.com.cn/predict \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"features": [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]}'


五、生产环境部署
5.1 使用Gunicorn部署
Flask开发服务器不适合生产环境,我们可以使用Gunicorn:
# 安装Gunicorn
pip install gunicorn
# 启动服务
gunicorn -w 4 -b 0.0.0.0:5000 app:app
5.2 创建Docker容器
# Dockerfile
FROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
# 复制依赖文件
COPY requirements.txt .
# 安装依赖
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
# 复制应用文件
COPY . .
# 创建非root用户
RUN useradd -m -u 1000 appuser && chown -R appuser:appuser /app
USER appuser
# 暴露端口
EXPOSE 5000
# 启动命令
CMD ["gunicorn", "-w", "4", "-b", "0.0.0.0:5000", "app:app"]
创建requirements.txt:
flask==2.3.2
flask-cors==4.0.0
scikit-learn==1.3.0
numpy==1.24.3
pandas==2.0.3
joblib==1.3.1
gunicorn==21.2.0
构建和运行Docker容器:
# 构建镜像
docker build -t iris-model-api .
# 运行容器
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --name iris-api iris-model-api
5.3 使用Nginx作为反向代理
创建Nginx配置文件:
# /etc/nginx/sites-available/ai-api
server {
listen 80;
server_name api.yourdomain.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# 限制请求大小
client_max_body_size 10M;
# 超时设置
proxy_connect_timeout 60s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
}
5.4 使用systemd管理服务
创建systemd服务文件:
# /etc/systemd/system/ai-api.service
[Unit]
Description=AI Model API Service
After=network.target
[Service]
User=appuser
WorkingDirectory=/opt/ai-api
Environment="PATH=/opt/ai-api/venv/bin"
ExecStart=/opt/ai-api/venv/bin/gunicorn -w 4 -b 0.0.0.0:5000 app:app
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
六、高级功能扩展
6.1 添加API密钥认证
# auth.py
import os
from functools import wraps
from flask import request, jsonify
# 从环境变量获取API密钥
API_KEYS = os.environ.get('API_KEYS', '').split(',')
def require_api_key(f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
api_key = request.headers.get('X-API-Key')
if not api_key or api_key not in API_KEYS:
return jsonify({
"status": "error",
"message": "无效或缺失API密钥"
}), 401
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
6.2 添加请求限流
from flask_limiter import Limiter
from flask_limiter.util import get_remote_address
limiter = Limiter(
app,
key_func=get_remote_address,
default_limits=["200 per day", "50 per hour"]
)
@app.route('/predict', methods=['POST'])
@limiter.limit("10 per minute") # 限制每分钟10次请求
@require_api_key # 添加认证
def predict():
# 原有代码...
6.3 添加监控和日志
import time
from prometheus_client import Counter, Histogram, generate_latest
# 定义指标
REQUEST_COUNT = Counter('api_requests_total', 'Total API requests')
REQUEST_LATENCY = Histogram('api_request_latency_seconds', 'API request latency')
@app.before_request
def before_request():
request.start_time = time.time()
@app.after_request
def after_request(response):
# 记录请求指标
REQUEST_COUNT.inc()
if hasattr(request, 'start_time'):
latency = time.time() - request.start_time
REQUEST_LATENCY.observe(latency)
# 记录访问日志
logger.info(f"{request.remote_addr} - {request.method} {request.path} - {response.status_code}")
return response
@app.route('/metrics')
def metrics():
"""Prometheus指标端点"""
return generate_latest()
七、性能优化建议
7.1 模型加载优化
# 使用LRU缓存
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(maxsize=1)
def load_model_cached():
"""缓存模型加载"""
return joblib.load('iris_model.pkl')
7.2 批量预测支持
@app.route('/predict/batch', methods=['POST'])
def batch_predict():
"""批量预测端点"""
try:
data = request.get_json()
if not data or 'batch_features' not in data:
return jsonify({"error": "缺少batch_features字段"}), 400
batch_features = np.array(data['batch_features'])
# 批量预测
predictions = model.predict(batch_features)
probabilities = model.predict_proba(batch_features)
response = {
"status": "success",
"predictions": predictions.tolist(),
"probabilities": probabilities.tolist()
}
return jsonify(response)
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({"error": str(e)}), 500
7.3 异步处理支持
对于耗时的预测任务,可以考虑使用Celery进行异步处理:
from celery import Celery
# 配置Celery
celery_app = Celery('tasks', broker='redis://localhost:6379/0')
@celery_app.task
def async_predict(features):
"""异步预测任务"""
# 预测逻辑
return prediction_result
八、安全最佳实践
- 输入验证:始终验证和清理用户输入
- API密钥:为不同客户端分配不同密钥
- HTTPS:生产环境必须使用HTTPS
- 速率限制:防止API被滥用
- 错误处理:避免泄露敏感信息
- 依赖更新:定期更新依赖包
- 安全扫描:使用安全工具扫描漏洞
结语:从模型到服务的完整旅程
通过本文的步骤,我们完成了将一个机器学习模型部署为生产级API服务的完整流程。从模型训练、API开发、测试验证到生产部署,每个环节都需要精心设计和实施。
记住,模型部署不是终点,而是起点。在实际运营中,你需要持续监控服务性能、收集用户反馈、更新模型版本,并不断优化系统架构。
成功的AI应用不仅需要优秀的算法,更需要稳健的工程实现。希望本文能为你提供实用的指导,让你的AI模型真正创造价值。
附录:实用资源
- 完整代码示例:可在GitHub获取完整可运行代码
- 监控工具:Prometheus + Grafana监控组合
- 部署平台:AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google Cloud Run, Azure App Service
- API文档工具:Swagger/OpenAPI规范
- 性能测试工具:Locust, Apache JMeter
res):
“”“异步预测任务”“”
# 预测逻辑
return prediction_result
## 八、安全最佳实践
1. **输入验证**:始终验证和清理用户输入
2. **API密钥**:为不同客户端分配不同密钥
3. **HTTPS**:生产环境必须使用HTTPS
4. **速率限制**:防止API被滥用
5. **错误处理**:避免泄露敏感信息
6. **依赖更新**:定期更新依赖包
7. **安全扫描**:使用安全工具扫描漏洞
## 结语:从模型到服务的完整旅程
通过本文的步骤,我们完成了将一个机器学习模型部署为生产级API服务的完整流程。从模型训练、API开发、测试验证到生产部署,每个环节都需要精心设计和实施。
记住,模型部署不是终点,而是起点。在实际运营中,你需要持续监控服务性能、收集用户反馈、更新模型版本,并不断优化系统架构。
成功的AI应用不仅需要优秀的算法,更需要稳健的工程实现。希望本文能为你提供实用的指导,让你的AI模型真正创造价值。
## 附录:实用资源
1. **完整代码示例**:可在GitHub获取完整可运行代码
2. **监控工具**:Prometheus + Grafana监控组合
3. **部署平台**:AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google Cloud Run, Azure App Service
4. **API文档工具**:Swagger/OpenAPI规范
5. **性能测试工具**:Locust, Apache JMeter
---
**作者提示**:本文示例代码已简化以适应文章篇幅,实际生产部署需要考虑更多边界情况和安全因素。建议在实际项目中根据具体需求进行调整和扩展。
Author:Smoothcloud润云
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献11条内容
已为社区贡献11条内容






所有评论(0)