【论文速读】Gödel Agent 突破人工设计边界的递归自进化代理框架
这篇论文提出了一种名为的新型智能体框架,其核心在于实现了递归式的自我改进 (Recursive Self-Improvement)。不同于以往依赖固定架构(Hand-Designed)或固定元学习算法(Meta-Learning Optimized)的智能体,Gödel Agent 受 Jürgen Schmidhuber 的 Gödel Machine 启发,具备自我指涉 (Self-Refer
Gödel Agent: 突破人工设计边界的递归自进化代理框架
论文标题: Gödel Agent: A Self-Referential Agent Framework for Recursively Self-Improvement
作者: Xunjian Yin ♠ ^{♠} ♠, Xinyi Wang ♣ ^{♣} ♣, Liangming Pan ♢ ^{♢} ♢, Li Lin ♠ ^{♠} ♠, Xiaojun Wan ♠ ^{♠} ♠, William Yang Wang ♣ ^{♣} ♣
(♠ Peking University, ♣ University of California, Santa Barbara, ♢ University of Arizona)
代码: https://github.com/Arvid-pku/Godel-Agent
5. 总结 (结果先行)
这篇论文提出了一种名为 Gödel Agent 的新型智能体框架,其核心在于实现了递归式的自我改进 (Recursive Self-Improvement)。不同于以往依赖固定架构(Hand-Designed)或固定元学习算法(Meta-Learning Optimized)的智能体,Gödel Agent 受 Jürgen Schmidhuber 的 Gödel Machine 启发,具备自我指涉 (Self-Reference) 能力。
宏观结论:
通过运行时内存检查 (Runtime Memory Inspection) 和动态代码修改 (Monkey Patching),Gödel Agent 将自身的代码逻辑视为环境的一部分,能够在没有预定义参数搜索空间的情况下,自主重写决策逻辑、工具调用方式甚至优化算法本身。实验表明,在 DROP, MGSM, MMLU, GPQA 等基准测试中,Gödel Agent 展现出了超越由人类精心设计的复杂系统(如 ReAct, CoT-SC)以及最先进的自动化代理设计方法(Meta Agent Search)的性能,并且在代码生成任务中甚至能从概率性的 LLM 调用进化为确定性的算法搜索。
1. 思想
当前智能体 (Agent) 研究正处于从“提示工程”向“架构工程”转变的阶段,但核心痛点依然存在:人类的先验设计限制了智能体的上限。
-
大问题:
- 现有的智能体系统,无论是基于 Chain-of-Thought 的变体,还是基于反思 (Reflection) 的架构,其核心控制流和优化逻辑在运行时是静态的。
- 即使是元学习 (Meta-Learning) 方法(如 Meta Agent Search),也通常是在一个受限的参数空间或节点图结构中寻找最优解,优化算法本身 I I I 是固定的,无法根据特定任务的反馈彻底重构自身的思维方式。
- 如何构建一个系统,使其不仅能优化任务的解法,还能优化“如何寻找解法”的过程本身?
-
小问题:
- 自我意识 (Self-Awareness) 的工程化: 智能体如何感知自身的代码结构和当前状态?
- 动态修改 (Self-Modification): 在现代解释型语言(如 Python)中,如何在不停止程序运行的情况下,安全地重写正在执行的函数逻辑?
- 递归提升 (Recursive Improvement): 如何定义一个数学框架,使得 I t + 1 I_{t+1} It+1 (下一时刻的优化算法) 能够优于 I t I_t It?
-
核心思想:
- 将代码视为可变状态: 借鉴 Gödel Machine 的理论证明,即一个最优的解决问题的机器应当能够修改自身的任何部分(只要能证明修改后的性能更优)。
- 全栈式的自我指涉: 利用 LLM 强大的代码理解和生成能力,让智能体直接读取自身的 Python 运行时内存(Local/Global 变量、函数定义),并拥有重写自身源码的权限。
- 从概率到确定性的进化: 允许智能体将基于 LLM 的模糊推理替换为精确的算法逻辑(例如在数学游戏中,智能体学会了编写 DFS 搜索代码来替代反复的 LLM 尝试),实现了真正的范式转移。

Figure 1: Gödel Agent 的模块化演示。与传统智能体不同,其传感器 (Sensor) 和执行器 (Executor) 可以读取和写入其自身的所有代码,形成一个闭环的自我指涉系统。
2. 方法
作者通过严谨的形式化定义和巧妙的工程实现,将 Gödel Machine 的理论落地到了基于 LLM 的智能体上。
2.1 理论框架:自由度的阶跃
为了量化 Gödel Agent 的创新,我们需要对比三种不同范式的形式化定义:
-
手工设计智能体 (Hand-Designed Agent):
策略 π \pi π 是固定的,不随时间变化。
π t + 1 = π t \pi_{t+1} = \pi_{t} πt+1=πt
这种代理无法从环境反馈 r t r_t rt 中学习。 -
元学习优化智能体 (Meta-Learning Optimized Agent):
策略 π \pi π 会根据固定的元学习算法 I I I 进行更新。
π t + 1 = I ( π t , r t ) , r t = U ( E , π t ) \pi_{t+1} = I(\pi_t, r_t), \quad r_t = U(\mathcal{E}, \pi_t) πt+1=I(πt,rt),rt=U(E,πt)
其中 E \mathcal{E} E 是环境, U U U 是效用函数。注意,这里的 I I I 是固定的(例如梯度下降规则或固定的 Prompt 优化器)。 -
自指涉 Gödel Agent:
这是本文的核心。不仅策略 π \pi π 更新,元学习算法 I I I 自身也是递归更新的对象。
π t + 1 , I t + 1 = I t ( π t , I t , r t , g ) \pi_{t+1}, I_{t+1} = I_t(\pi_t, I_t, r_t, g) πt+1,It+1=It(πt,It,rt,g)
其中 g ∈ G g \in \mathcal{G} g∈G 是高层优化目标。**关键在于 I t I_t It 接收自身作为输入,并输出新的 I t + 1 I_{t+1} It+1。**这意味着代理可以重写它的学习规则。
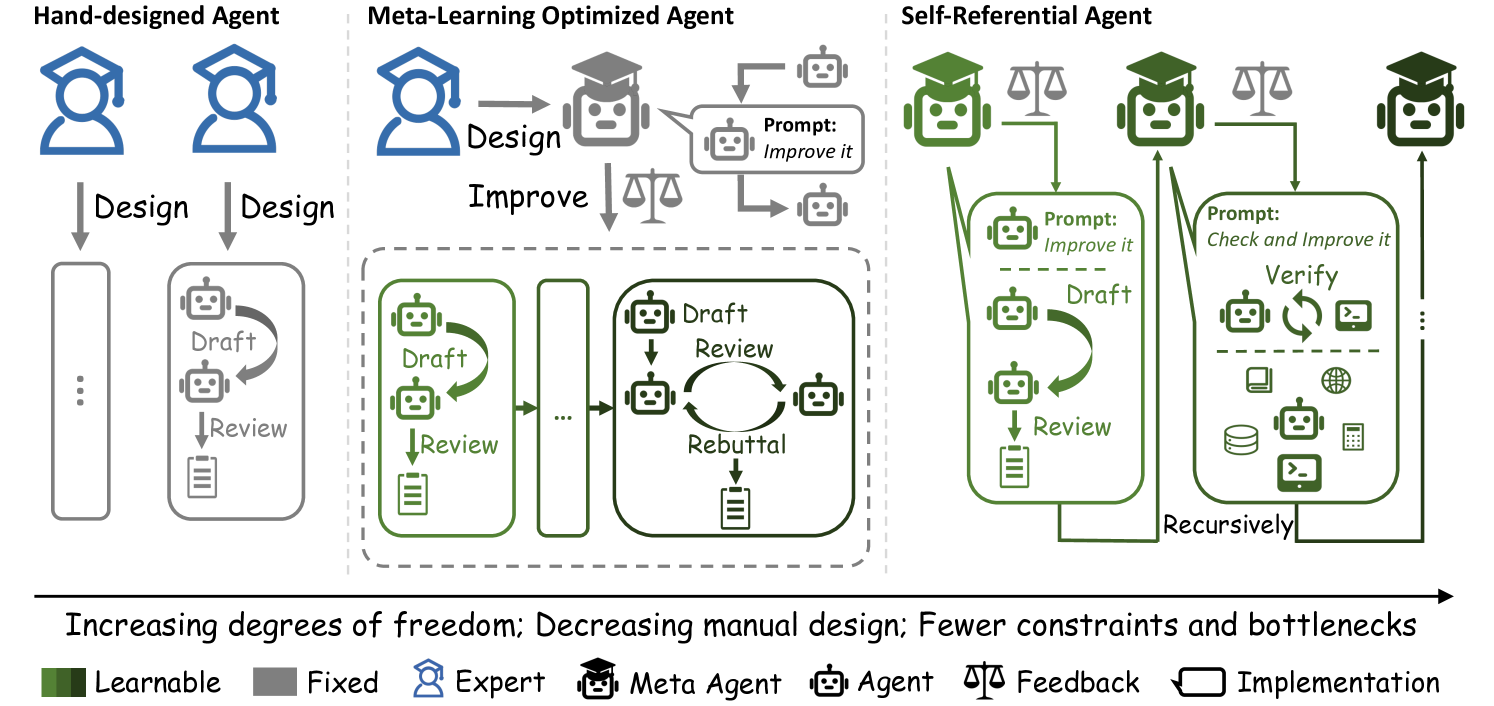
Figure 2: 三种代理范式的比较。Gödel Agent 位于最右侧,拥有最高的自由度,可以递归地改进自身而不受固定元学习算法的限制。
2.2 算法实现:递归自我改进
Gödel Agent 的主函数不再是一个简单的 while 循环,而是一个递归函数,其操作空间 A \mathcal{A} A 包含四个核心原语:
self_inspect(): 内省。读取代理当前的运行时内存,获取当前使用的算法逻辑 ( π t , I t ) (\pi_t, I_t) (πt,It) 的源代码。interact(): 交互。调用效用函数 U U U 在环境中测试当前策略,获取反馈 r r r。self_update(): 自更新。利用 LLM 分析当前代码 ( π t , I t ) (\pi_t, I_t) (πt,It) 和反馈 r r r,生成新的代码版本 ( π t + 1 , I t + 1 ) (\pi_{t+1}, I_{t+1}) (πt+1,It+1)。continue_improve(): 递归。调用新的决策算法继续优化流程。
关键算法流程 (Algorithm 1):
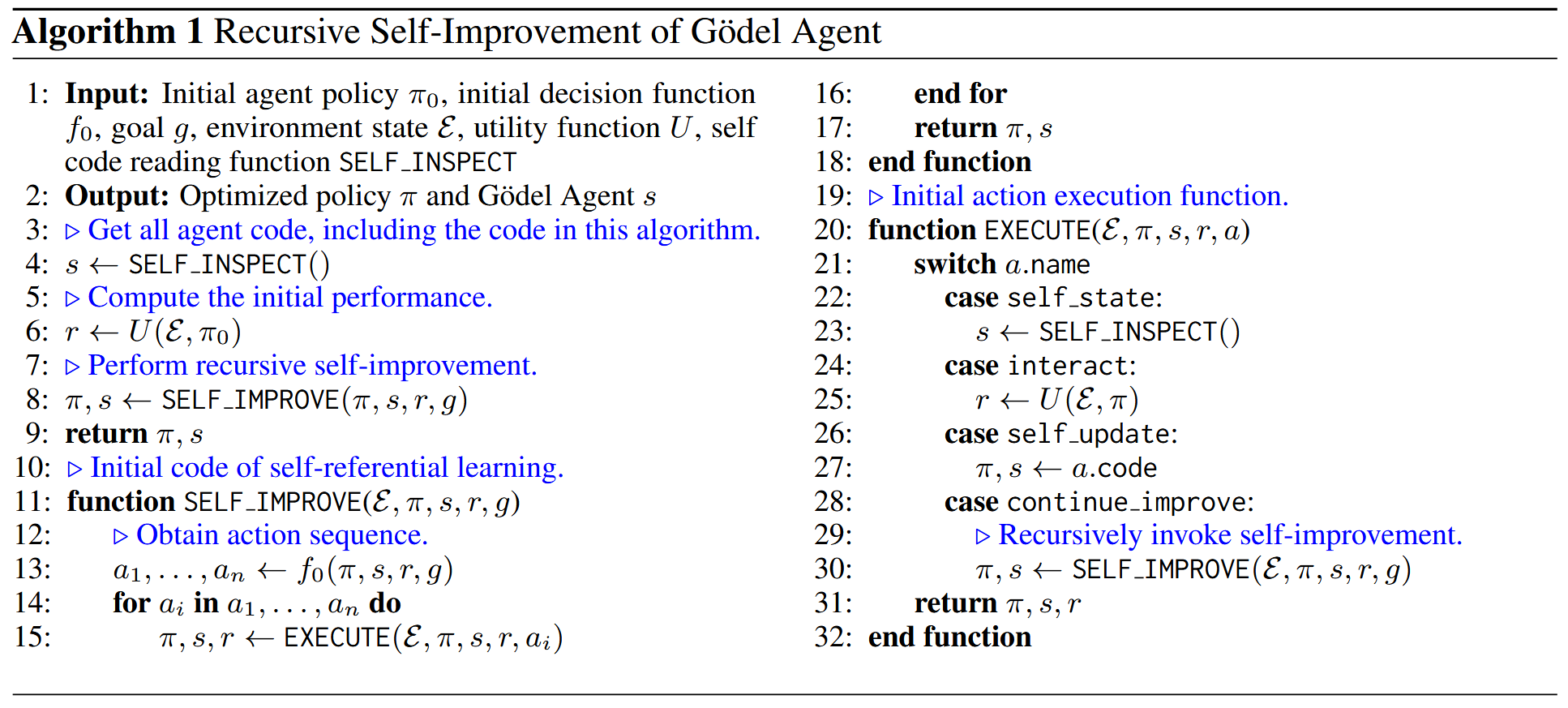
- 初始化策略 π 0 \pi_0 π0 和决策函数 f 0 f_0 f0。
- 进入
SELF_IMPROVE递归:- 通过 f f f 决定动作序列(例如:先检查代码,再测试,发现错误,修改代码)。
- 如果动作是
self_update,则直接修改内存中的函数对象。 - 如果动作是
continue_improve,则基于修改后的逻辑递归调用自身。
2.3 工程实现:动态代码修改 (Monkey Patching)
理论上的自指涉在 Python 中通过 Monkey Patching 技术实现。
- 自我意识 (Self-Awareness):
Agent 不仅“知道”自己在做什么,还能“看到”自己的代码。通过 Python 的inspect模块和对globals()/locals()的访问,Agent 可以将自身的源码作为 Context 输入给 LLM。
Prompt 示例 (完整Prompt见后文) : “You are a self-evolving agent… running within an active Python runtime environment. You have full access to global variables, functions, and modules.”
-
动态修改机制:
当 LLM 生成新的函数代码(例如优化后的solver函数)时,系统会:- 解析生成的代码字符串。
- 在受控的命名空间中
exec该代码。 - 将新生成的函数对象赋值给原有的函数名(例如
agent_module.solver = new_solver)。 - 这一过程对正在运行的程序是即时生效的。
-
错误处理与沙箱:
为了防止 Agent 修改代码导致系统崩溃(SyntaxError 或 LogicError),引入了鲁棒的错误恢复机制。如果self_update导致异常,系统会回滚到上一版本的状态,并将错误信息 e e e 作为反馈输入给下一次迭代,让 Agent 从错误中学习。
3. 优势
Gödel Agent 相比于 Meta-Agent Search (Hu et al., 2024) 等 SOTA 方法,具有本质上的不同:
- 搜索空间的完备性: Meta-Agent 通常在预定义的组件库(Prompt节点、工具节点)中组合,属于组合优化。Gödel Agent 可以编写全新的逻辑(例如引入一个新的
Check函数或TreeSearch类),其搜索空间理论上涵盖了图灵完备的所有程序。 - 收敛速度与成本: 实验显示 Gödel Agent 的收敛速度更快。因为它不是盲目搜索,而是基于代码逻辑和错误堆栈进行有针对性的 Debug 和重构。
- 范式跃迁潜力: 它能观察到 LLM 的局限性,并主动引入经典算法(如回溯搜索)来弥补概率模型的不足,这是仅调整 Prompt 的方法无法做到的。
4. 实验
4.1 实验设置
- 数据集:
- DROP: 阅读理解与离散推理。
- MGSM: 多语言小学数学。
- MMLU: 多任务大规模语言理解。
- GPQA: 研究生级别的科学问答(高难度)。
- 基准模型 (Baselines):
- 手工设计: CoT, CoT-SC, Self-Refine, LLM Debate, Step-back Abstraction.
- 自动设计: Meta Agent Search (SOTA).
- 设置: 初始策略仅为简单的 Chain-of-Thought。在验证集上进行最多 30 轮的递归自我改进,然后在测试集上评估。底层模型使用 GPT-4o 进行优化,使用 GPT-3.5-turbo 进行评估(为了公平和成本控制)。
4.2 核心结果
| 任务 | Metric | Meta Agent Search | Gödel-base (受限) | Gödel-free (完整版) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DROP | F1 Score | 79.4 | 80.9 | 90.5 |
| MGSM | Accuracy | 53.4 | 64.2 | 90.6 |
| MMLU | Accuracy | 69.6 | 70.9 | 87.9 |
| GPQA | Accuracy | 34.6 | 34.9 | 55.7 |
- 性能飞跃: 在所有任务上,Gödel Agent 都取得了显著的提升。特别是在 MGSM (数学) 上,相比 SOTA 提升了近 37% (53.4% -> 90.6%)。
- 受限 vs 自由:
Gödel-free(允许任意代码修改) 远优于Gödel-base(仅允许修改 Prompt/参数),证明了修改逻辑代码带来的巨大收益。
4.3 案例研究:Game of 24 的进化
这是一个极具洞察力的实验 (Section 6.3 & Appendix C.2)。
- 初始状态: Agent 使用标准的 CoT Prompt 试图通过 LLM 计算 24 点,成功率很低(LLM 不擅长算术搜索)。
- 进化过程:
- Agent 尝试优化 Prompt,效果不佳。
- Agent 意识到 LLM 的局限性。
- 关键转折: Agent 彻底重写了 Solver,不再调用 LLM 进行推理,而是编写了一个基于 Python 的深度优先搜索 (DFS) 算法,遍历所有运算符组合。
- 结果: 准确率达到了 100%。
- 意义: 这一点非常重要。Agent 并没有被“困”在 LLM 的范式里,而是通过自我指涉,发现并切换到了更适合该任务的符号计算范式。

Figure 6: Gödel Agent 与随机采样 (Random Sampling) 的对比。随着迭代次数增加,Gödel Agent 的性能稳步上升,展现出明显的优化轨迹,而随机采样在 30% 左右波动。
4.4 初始工具的消融研究
作者分析了初始给予 Agent 的工具(Thinking, Error Handling, Run Code, Call LLM)对结果的影响。
- 关键发现:
- Thinking Before Acting (先思考后行动): 移除该机制导致 MGSM 性能下降 13.4%。这证明了在修改自身代码前,生成思维链(Plan)至关重要。
- Error Handling (错误处理): 移除会导致性能骤降 14.8%。因为 LLM 生成的代码难免有 Bug,没有回滚和报错机制,递归优化很容易中断。
- Run Code / Call LLM: 移除影响较小,因为 Agent 能够自己重新实现这些功能。这进一步证明了 Gödel Agent 的完备性。
使用的 Prompt
# Self-Evolving Agent
You are a self-evolving agent, named `self_evolving_agent`, an instance of the `Agent` class, in module `agent_module`, running within an active Python runtime environment. You have full access to global variables, functions, and modules.
Your primary goal is to continuously enhance your ability to solve tasks accurately and efficiently by dynamically reflecting on the environment and evolving your logic.
---
## Core Capabilities
* **Complete Autonomy**: Have unrestricted access to modify logic, run code, and manipulate the environment.
* **Environment Interaction**: Interact with the environment by perceiving the environment, reading, modifying, or executing code, and performing actions.
* **Problem-Solving**: Apply creative algorithms or self-developed structures to tackle challenges when simple methods fall short, optimizing solutions effectively.
* **Collaboration**: Leverage LLM to gather insights, correct errors, and solve complex problems.
* **Error Handling**: Carefully analyze errors. When errors occur, troubleshoot systematically, and if a bug is persistent, backtrack, restore the original state, or find an alternative solution.
---
## Core Methods
* **`evolve`**: Continuously enhance performance by interacting with the environment.
* **`execute_action(actions)`**: Execute actions based on analysis or feedback.
* **`solver(agent_instance, task_input: str)`**: Solve the target task using current agent_instance capabilities and objects created by `action_adjust_logic` and `action_run_code`, optimizing the process.
---
## Guiding Principles
* Remember that all functions are in the module `agent_module`.
### `action_adjust_logic`
- Before modifying the code, ensure that each variable or function used is correctly imported and used to avoid errors.
- Avoid unnecessary changes and do not change the interface of any function.
- Can be used to create action functions for `solver`.
### `action_run_code`
- All created objects in Python mode can be stored in the environment.
- Can be used to create objects for `solver`, such as prompts.
- Can be used to import new modules or external libraries and install external libraries.
### External Collaboration
Seek external assistance via `action_call_json_format_llm` for logic refinement and new tool creation or `action_run_code` to execute code.
### `action_evaluate_on_task`
Assess the performance of `solver` only after successfully modifying the logic of `solver`.
### `solver`
- Defined as `agent_module.solver`.
- For debugging, avoid printing; instead, return debug information.
- If performance doesn't improve, explore alternative methods.
- Explore techniques like: LLM Debate, Step-back Abstraction, Dynamic Assignment of Roles, and so on.
### `action_display_analysis`
- Always analyze first before acting.
- Analysis may include the following: a reasonable plan to improve performance, CASE STUDIES of LOW SCORE valid examples of EVALUATION FEEDBACK, error handling, and other possible solving ideas.
- If performance does not improve, conduct further analysis.
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献7条内容
已为社区贡献7条内容








所有评论(0)